Phase Structure and Properties of Ternary Polylactide/Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Polysilsesquioxane Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analytic Methods
3. Results and Discussion
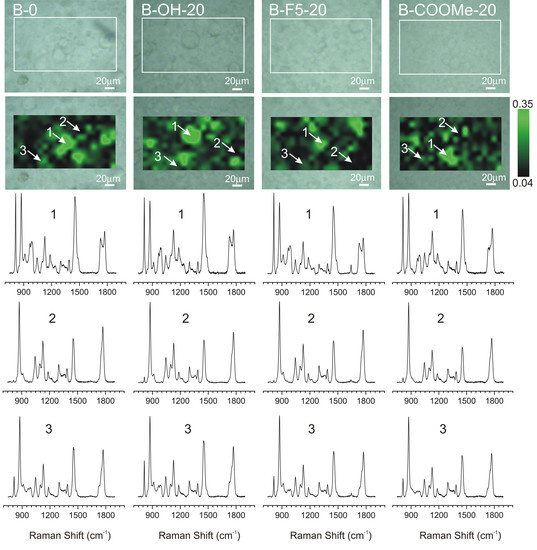
3.1. Phase Distribution in the PLA/PMMA Mixture and Ternary Blends Containing LPSQ-R
3.2. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of the Hybrid Blends
3.3. Mechanical Properties in Micro-Scale and Surface Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, S. Chain structure, phase morphology, and toughness relationships in polymers and blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grijpma, D.W.; Pennings, A. (Co)polymers of L-lactide, 2. Mechanical properties. J. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1994, 195, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Abe, S.; Ishikawa, M. The fracture mechanism of polylactic acid resin and the improving mechanism of its toughness by addition of acrylic modifier. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Research Progress in Toughening Modification of Poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1051–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Sacligil, D.; Carreau, P.J.; Kamal, M.R.; Marie-Claude Heuzey, M.-C. Poly (lactic acid) blends: Processing, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 307–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Super tough poly(lactic acid) blends: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13316–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalewska, A.; Nowacka, M. Supramolecular Interactions in Hybrid Polylactide Blends—The Structures, Mechanisms and Properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Shen, D. Miscibility and phase structure of binary blends of polylactide and poly(methyl methacrylate). J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossement, D.; Gouttebaron, R.; Cornet, V.; Viville, P.; Hecq, M.; Lazzaroni, R. PLAPMMA blends: A study by XPS and ToF-SIMS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 6636–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, C.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dubois, P. PLLA/PMMA blends: A shear-induced miscibility with tunable morphologies and properties? Polymer 2013, 54, 3931–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckelt, J.; Enders, S.; do Carmo Gonçalves, M.; Queiroz, D.P.; Wolf, B.A. Polydispersity effects on the phase diagram of the system chloroform/poly-L-lactic acid/polymethyl methacrylate. And morphology of PLA/PMMA films. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2000, 171, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-H.; Woo, E.M. Immiscibility-miscibility phase transitions in blends of poly(L-lactide) with poly(methyl methacrylate). Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canetti, M.; Cacciamani, A.; Bertini, F. Miscible Blends of Polylactide and Poly(methyl methacrylate): Morphology, Structure, and Thermal Behavior. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Woo, E.M. Effects of chain configuration on UCST behavior in blends of poly(L-lactic acid) with tactic poly(methyl methacrylate)s. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imre, B.; Renner, K.; Pukanszky, B. Interactions, structure and properties in poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic polymer blends. Express Polym. Lett 2014, 8, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, X.; Kaschta, J.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Schubert, D.W. Entanglement network formed in miscible PLA/PMMA blends and its role in rheological and thermo-mechanical properties of the blends. Polymer 2015, 80, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-H.; Kuo, M.C.; Chen, C.-W. Physical properties and crystallization behavior of poly(lactide)/poly(methyl methacrylate)/silica composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anakabe, J.; Zaldua Huici, A.M.; Eceiza, A.; Arbelaiz, A. Melt blending of polylactide and poly(methyl methacrylate): Thermal and mechanical properties and phase morphology characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, E.L.; Chow, W.S. Transparency, ultraviolet transmittance, and miscibility of poly(lactic acid)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blends. J. Elastom. Plast. 2017, 50, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garzon, M.; Shahbikian, S.; Huneault, M.A. Properties and phase structure of melt-processed PLA/PMMA blend. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Shahbikian, S.; Marcos, B.; Huneault, M.A. Hydrolytic stability of polylactide and poly(methyl methacrylate) blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangin, R.; Vahabi, H.; Sonnier, R.; Chivas-Joly, C.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M.; Cochez, M. Improving the resistance to hydrothermal ageing of flame-retarded PLA by incorporating miscible PMMA. Polym. Degr. Stab. 2018, 155, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaoud, N.; Benali, S.; Mincheva, R.; Satha, H.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dubois, P. Hydrolytic degradation of poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blends. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choochottiros, C.; Chin, I.-J. Potential transparent PLA impact modifiers based on PMMA copolymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Nagarajan, V.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Supertoughened Renewable PLA Reactive Multiphase Blends System: Phase Morphology and Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12436–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuryev, Y.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Novel super-toughened bio-based blend from polycarbonate and poly(lactic acid) for durable applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 105094–105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anakabe, J.; Zaldua Huici, A.M.; Eceiza, A.; Arbelaiz, A. The effect of the addition of poly(styrene-co-glycidyl methacrylate) copolymer on the properties of polylactide/poly(methyl methacrylate) blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchwattana, N.; Naknaen, P.; Jakrabutr, W.; Sanetuntikul, J.; Narupai, B. Modification of poly(lactic acid) by blending with poly(methylmethacrylate-co-ethyl acrylate) for extrusion blow molding application). J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 12, 2766–2777. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzouita, A.; Notta-Cuvier, D.; Delille, R.; Lauro, F.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dubois, P. Design of toughened PLA based material for application in structures subjected to severe loading conditions. Part 2. Quasi-static tensile tests and dynamic mechanical analysis at ambient and moderately high temperature. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Yuan, D.; Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Liang, X. Bio-Based PLA/NR-PMMA/NR Ternary Thermoplastic Vulcanizates with Balanced Stiffness and Toughness: “Soft−Hard” Core−Shell Continuous Rubber Phase, In Situ Compatibilization, and Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6488–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anakabe, J.; Orue, A.; Zaldua Huici, A.M.; Eceiza, A.; Arbelaiz, A. Properties of PLA/PMMA blends with high polylactide content prepared by reactive mixing in presence of poly(styrene-co-glycidyl methacrylate) copolymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; He, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Chen, M.; Zhan, Z. A Facile Fabrication of High Toughness Poly(lactic Acid) via Reactive Extrusion with Poly(butylene Succinate) and Ethylene-Methyl Acrylate-Glycidyl Methacrylate. Polymers 2018, 10, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, Z.; Bu, J.; Pan, X.; Hu, X. Probing the nanomechanical properties of PLA/PC blends compatibilized with compatibilizer and nucleation agent by AFM. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, S.; Sun, S.; Li, Q. Highly-modified polylactide transparent blends with better heat-resistance, melt strength, toughness and stiffness balance due to the compatibilization and chain extender effects of methacrylate-co-glycidyl methacrylate copolymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, e50124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Kaschta, J.; Pan, X.; Liu, X.; Schubert, D.W. Intermolecular cooperativity and entanglement network in a miscible PLA/PMMA blend in the presence of nanosilica. Polymer 2016, 82, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Zhen, W.; Song, Z.; Wang, X. Synthesis, characterization of layered double hydroxidepoly(methylmethacrylate) graft copolymers via activators regenerated by electron transfer for atom transfer radical polymerization and its effect on the performance of poly(lactic acid). Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garzon, M.; Shahbikian, S.; Huneault, M.A. Properties of mineral filled poly(lactic acid)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 46927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Feng, C.-X.; Chen, H.-M.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y. Toughening effect of poly(methyl methacrylate) on an immiscible poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polylactide blend. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.M.; Berahman, R.; Edalat, A. Phase morphology, fracture toughness and failure mechanisms in supertoughened PLA/PB-g-SAN/PMMA ternary blends: A quantitative analysis of crack resistance. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.M.; Edalat, A.; Berahman, R.; Hosseini, F.S. Highly-Toughened Polylactide- (PLA-) Based Ternary Blends with Significantly Enhanced Glass Transition and Melt Strength: Tailoring the Interfacial Interactions, Phase Morphology, and Performance. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 4298–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zuo, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Yuan, G.; Satija, S.K.; Gersappe, D.; et al. Enhancing Impact Resistance of Polymer Blends via Self-Assembled Nanoscale Interfacial Structures. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3897–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, T.-D.; Wang, L.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Rafailovich, M.H.; Guo, Y. The use of low cost, abundant, homopolymers for engineering degradable polymer blends: Compatibilization of poly(lactic acid)/styrenics using poly(methyl methacrylate). Polymer 2020, 186, 122010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J.; Alagarsamy, A.; Pan, L.; Song, D.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y. Supertough Poly(lactic acid) and Sustainable Elastomer Blends Compatibilized by PLLA-b-PMMA Block Copolymers as Effective A-b-C-Type Compatibilizers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 13956–13968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herc, A.S.; Lewiński, P.; Kaźmierski, S.; Bojda, J.; Kowalewska, A. Hybrid SC-polylactide/poly(silsesquioxane) blends of improved thermal stability. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 687, 178592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herc, A.S.; Bojda, J.; Nowacka, M.; Lewiński, P.; Maniukiewicz, W.; Piorkowska, E.; Kowalewska, A. Crystallization, structure and properties of polylactide/ladder poly (silsesquioxane) blends. Polymer 2020, 201, 122563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewska, A.; Herc, A.S.; Bojda, J.; Palusiak, M.; Markiewicz, E.; Ławniczak, P.; Nowacka, M.; Sołtysiak, J.; Różański, A.; Piorkowska, E. Supramolecular interactions involving fluoroaryl groups in hybrid blends of laddder polysilsesquioxanes and polylactide. Polym. Test. 2021, 94, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svyntkivska, M.; Makowski, T.; Piorkowska, E.; Brzezinski, M.; Herc, A.; Kowalewska, A. Modification of Polylactide Nonwovens with Carbon Nanotubes and Ladder Poly(silsesquioxane). Molecules 2021, 26, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janaszewska, A.; Gradzinska, K.; Marcinkowska, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B.; Stanczyk, W.A. In Vitro Studies of Polyhedral Oligo Silsesquioxanes: Evidence for Their Low Cytotoxicity. Materials 2015, 8, 6062–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Chai, C.L.L. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 5th ed.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wu, T.; Wei, J.; Fan, Z.; Li, S. Morphological investigation on melt crystallized polylactide homo- and stereocopolymers by enzymatic degradation with proteinase K. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojda, J.; Piorkowska, E. Shear-induced nonisothermal crystallization of two grades of PLA. Polym. Test. 2014, 50, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reaction. Kolloid-Zu Z-Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, M.G. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bhushan, B. A review of nanoindentation continuous stiffness measurement technique and its applications. Mater. Charact. 2002, 48, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, H. Poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: Formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 569–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguiburu, J.L.; Iruin, J.J.; Fernandez-Berridia, M.J.; San Román, J. Blends of amorphous and crystalline polylactides with poly(methyl methacrylate) and poly(methyl acrylate): A miscibility study. Polymer 1998, 39, 6891–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auliawan, A.; Woo, E.M. Nanocomposites based on vermiculite clay and ternary blend of poly(L-lactic acid), poly(methyl methacrylate), and poly(ethylene oxide). Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auliawan, A.; Woo, E.M. Crystallization kinetics and degradation of nanocomposites based on ternary blend of poly(L-lactic acid), poly(methyl methacrylate), and poly(ethylene oxide) with two different organoclays. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, E444–E458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, M.; Piorkowska, E.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Sowinski, P. Toughening of polylactide by blending with a novel random aliphatic-aromatic copolyester. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 59, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudharshan Phani, P.; Oliver, W.C. A critical assessment of the effect of indentation spacing on themeasurement of hardness and modulus using instrumentedindentation testing. Mater. Des. 2019, 164, 107563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herc, A.S.; Włodarska, M.; Nowacka, M.; Bojda, J.; Szymański, W.; Kowalewska, A. Supramolecular interactions between polylactide and model cyclosiloxanes with hydrogen bonding-capable functional groups. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2020, 14, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ji, F.; Li, Z.; Tao, S. Preparation of Hydrophobic Surface on PLA and ABS by Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2020, 12, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







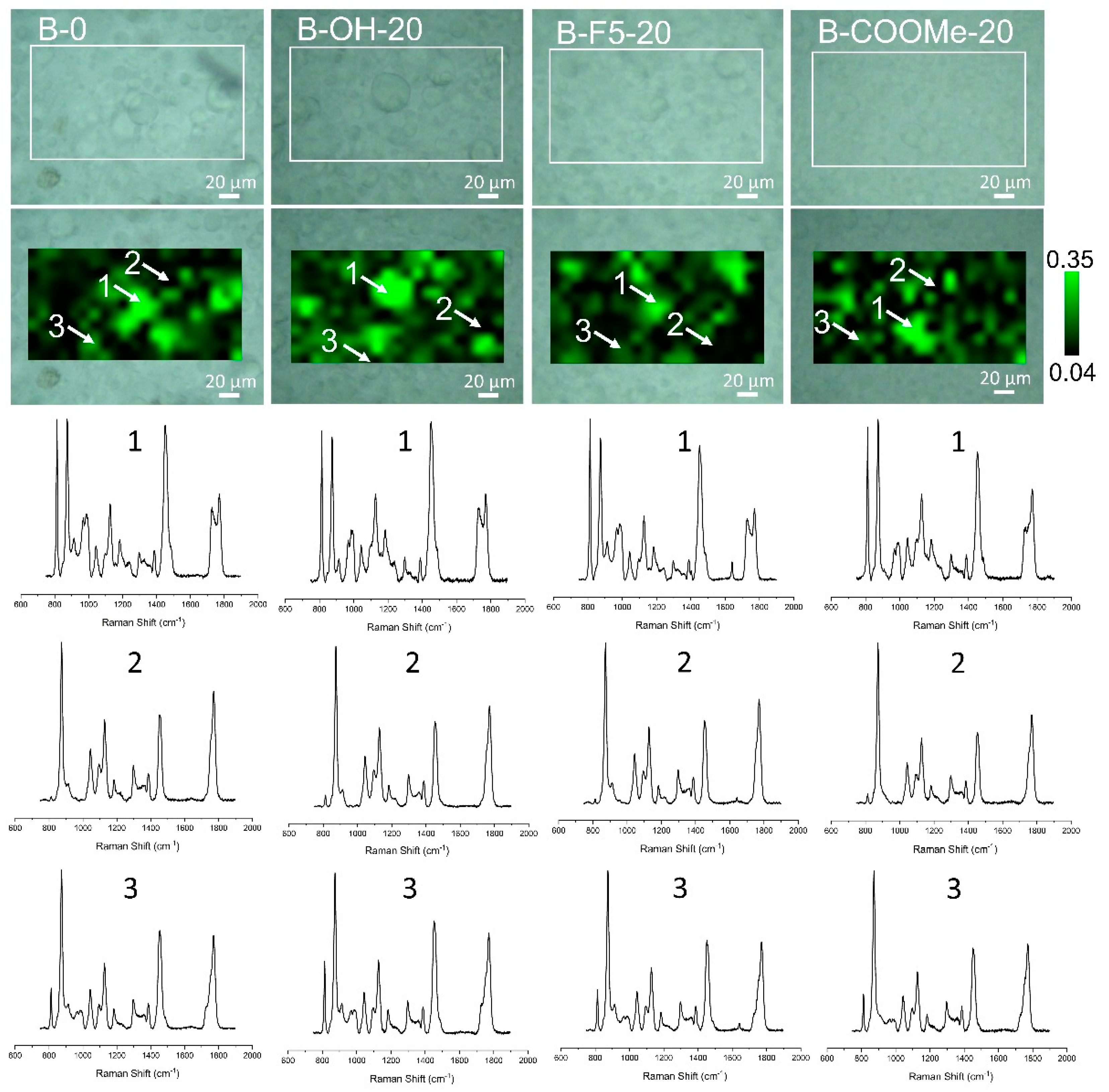





| Sample Code | Component Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA (wt.%) | PMMA (wt.%) | LPSQ-R (wt.%) | |
| B-0 | 90.0 | 10.0 | - |
| B-R-10 | 89.1 | 9.9 | 1.0 |
| B-R-20 | 88.2 | 9.8 | 2.0 |
| B-R-30 | 87.4 | 9.7 | 2.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalewska, A.; Herc, A.S.; Bojda, J.; Nowacka, M.; Svyntkivska, M.; Piorkowska, E.; Kaczorowski, W.; Szymański, W. Phase Structure and Properties of Ternary Polylactide/Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Polysilsesquioxane Blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071033
Kowalewska A, Herc AS, Bojda J, Nowacka M, Svyntkivska M, Piorkowska E, Kaczorowski W, Szymański W. Phase Structure and Properties of Ternary Polylactide/Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Polysilsesquioxane Blends. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071033
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalewska, Anna, Agata S. Herc, Joanna Bojda, Maria Nowacka, Mariia Svyntkivska, Ewa Piorkowska, Witold Kaczorowski, and Witold Szymański. 2021. "Phase Structure and Properties of Ternary Polylactide/Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Polysilsesquioxane Blends" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071033
APA StyleKowalewska, A., Herc, A. S., Bojda, J., Nowacka, M., Svyntkivska, M., Piorkowska, E., Kaczorowski, W., & Szymański, W. (2021). Phase Structure and Properties of Ternary Polylactide/Poly(methyl methacrylate)/Polysilsesquioxane Blends. Polymers, 13(7), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071033