Electrospun Biomaterials from Chitosan Blends Applied as Scaffold for Tissue Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Chitosan and PEC Nanofiber Stabilization
2.4. Casting and Stabilization of Chitosan and PEC Films
2.5. Electrospinning
2.6. Characterization of Nanofibers
2.6.1. Morphology of the Nanofiber Membranes
2.6.2. Determination of Swelling Capacity
2.6.3. Mechanicalharacterization
2.7. Cell Culture and Cell Development
2.7.1. Cell Culture
2.7.2. Cell Quantification
2.8. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Characterization
2.8.1. Substrate Fixing
2.8.2. AFM Measurements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pure Chitosan Nanofiber Electrospinning
3.1.1. Experimental Conditions
3.1.2. Characterization of Chitosan Nanofibers
3.2. Complex Chitosan/Hyaluronan Nanofibers
3.2.1. Experimental Conditions
3.2.2. Characterization
3.3. Application in Tissue Engineering
3.3.1. Interaction of Cells/Chitosan by AFM
3.3.2. Cell Development
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Chang, G.Y.; Chen, J.K. Electrospun collagen/chitosan nanofibrous membrane as wound dressing. Colloids Surf. A 2008, 313, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.G.; Wang, P.W.; Wei, B.; Mo, X.M.; Cui, F.Z. Electrospun collagen–chitosan nanofiber: A biomimetic extracellular matrix for endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Reddy, V.J.; Wong, S.Y.; Li, X.; Su, B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Enhanced biomineralization in osteoblasts on a novel electrospun biocomposite nanofibrous substrate of hydroxyapatite/collagen/chitosan. Tissue Eng. Part A 2010, 16, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.P.; Chen, S.H.; Lai, G.J. Preparation and characterization of biomimetic silk fibroin/chitosan composite nanofibers by electrospinning for osteoblasts culture. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Venugopal, J.R.; El-Turki, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Su, B.; Lim, C.T. Electrospun biomimetic nanocomposite nanofibers of hydroxyapatite/chitosan for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4314–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalaja, K.; Naskar, D.; Kundu, S.C.; James, N.R. Potential of electrospun core–shell structured gelatin-chitosan nanofibers for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Ocio, M.J.; Lagaron, J.M. Development of active Antimicrobial fiber-based chitosan polysaccharide nanostructures using electrospinning. Eng. Life Sci. 2008, 8, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Vu, D.; Larsen, G.F.; Lin, H.Y. Preparation and evaluation of the electrospun chitosan/PEO fibers for potential applications in cartilage tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2005, 16, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sapkota, S.; Chou, S.F. Electrospun Chitosan-based Fibers for Wound Healing Applications. J. Biomater. 2020, 4, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Jacobs, V.; Luyt, A.S. A review on electrospun bio-based polymers for water treatment. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 839–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Naguib, H.F.; Morsi, R.E. Chitosan based nanofibers, review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Wang, T.; Zhu, M.-L.; Leach, M.K.; Naim, Y.I.; Corey, J.M.; Feng, Z.-Q.; Jiang, Q. Electrospun Fibers and Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribba, L.; Parisi, M.; D’Accorso, N.B.; Goyanes, S. Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats: From Vascular Repair to Osteointegration. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 3508–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, K.; Pandit, A.; Zeugolis, D.I. The Multifaceted Potential of Electro-spinning in Regenerative Medicine. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Paneva, D.; Rashkov, I. Preparation of chitosan-containing nanofibres by electrospinning of chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) blend solutions. e-Polymers 2004, 4, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Edmondson, D.; Veiseh, O.; Matsen, F.A.; Zhang, M. Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers and their cellular compatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6176–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M.; Perez, S. From Chitin to Chitosan. Available online: http://www.glycopedia.eu/e-chapters/chitin-chitosan (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohkawa, K.; Cha, D.; Kim, H.; Nishida, A.; Yamamoto, H. Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Li, Z.H. Preparations, properties and applications of chitosan-based nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Kwon, O.H.; Jang, J. Electrospinning of chitosan dissolved in concentrated acetic acid solution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, W.A.; Azzazy, H.M.E. High concentration honey chitosan electrospun nanofibers: Biocompatibility and antibacterial effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayoni, H.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Valizadeh, M. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: Processing optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Park, S.Y. Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibers and their applications to the adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. One-step electrospinning of cross-linked chitosan fibers. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2665–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsanoh, P.; Supaphol, P. Stability improvement of electrospun chitosan nanofibrous membranes in neutral or weak basic aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2710–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.M.; Lee, S.W.; Lim, J.N.; You, Y.; Lee, T.S.; Kang, P.H.; Park, W.H. Chitin and chitosan nanofibers: Electrospinning of chitin and deacetylation of chitin nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 7137–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.T.; Gong, J.; Gu, X.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Dong, J.; Shen, X.Y. Fabrication and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blend nanofibers produced by electrospinning method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Duan, B.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Yuan, X. Preparation of electrospun chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2007, 285, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandayuthapani, B.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-gelatin blend nanofibers for skin tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Zandi, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Fabrication of gelatin/chitosan nanofibrous scaffold: Process optimization and empirical modeling. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, X.; He, C.; Wang, H. Intermolecular interactions in electrospun collagen–chitosan complex nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, X.; Qing, F. Electrospinning of collagen-chitosan complex. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3490–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.R.; Rodrigues, G.; Martins, G.G.; Roberto, M.A.; Mafra, M.; Henriques, C.M.R.; Silva, J.C. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of electrospun nanofibers of PCL, chitosan and gelatin: A comparative study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Chen, X.N.; Wang, H.J. Acceleration of osteogenic differentiation of preosteoblastic cells by chitosan containing nanofibrous scaffolds. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2772–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalumon, K.T.; Anulekha, K.H.; Girish, C.M.; Prasantha, R.; Naira, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Single step electrospinning of chitosan/poly(caprolactone) nanofibers using formic acid/acetone solvent mixture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Y.; Soleimani, M.; Fallahi-Sichani, M.; Gazme, A.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Arefian, E.; Kiani, J.; Moradi, R.; Atashi, A.; Ahmadbeigi, N. Nanofibrous poly(ε-caprolactone)/poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2007, 30, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-H.; Huh, M.-W.; Meng, W.; Yuan, J.; Hyun, S.H.; Bae, J.-S.; Hudson, S.M.; Kang, I.-K. Preparation and antibacterial activity of PET/chitosan nanofibrous mats using an electrospinning technique. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 2816–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.C.; Ajji, A. A fundamental study of chitosan/PEO electrospinning. Polymer 2011, 52, 4813–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, K.A.; Birch, N.P.; Schiffman, J.D. Electrospinning chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) solutions with essential oils: Correlating solution rheology to nanofiber formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 139, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Dong, C.; Yuan, X.; Yao, K. Electrospinning of chitosan solutions in acetic acid with poly(ethylene oxide). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2004, 15, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.L.; Yuan, Z.H.; Zhong, L.B.; Liu, Q.; Wu, R.X.; Zheng, Y.M. Preparation of chitosan based electrospun nanofiber membrane and its adsorptive removal of arsenate from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Shape-memory behaviors of electrospun chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) composite nanofibrous membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsari, I.; Shariatinia, Z.; Pourmortazavi, S.M. Antibacterial electrospun chitosan–polyethylene oxide nanocomposite mats containing bioactive silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, S.S.; Stevens, D.R.; Hoffman, T.J.; Stano, K.; Klossner, R.; Scott, M.C.; Gorga, R.E. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun chitosan nanofibers formed via templating with polyethylene oxide. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.C.; Ajji, A. Core-shell structured PEO-chitosan nanofibers by coaxial electrospinning. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, D.A.; Keil, K.; Bruns, D.E. Oxidation of polyethylene glycols by alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1989, 38, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohbergh, M.E.; Katsman, A.; Botta, G.P.; Lazarovici, P.; Schauer, C.L.; Wegst, U.G.; Lelkes, P.I. Electrospun hydroxyapatite-containing chitosan nanofibers crosslinked with genipin for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9167–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mengistu Lemma, S.; Bossard, F.; Rinaudo, M. Preparation of Pure and Stable Chitosan Nanofibers by Electrospinning in the Presence of Poly(ethylene oxide). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, C.E.G.; Martínez, F.A.S.; Bossard, F.; Rinaudo, M. Biomaterials Based on Electrospun Chitosan. Relation between Processing Conditions and Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nirwan, V.P.; Al-Kattan, A.; Fahmi, A.; Kabashin, A.V. Fabrication of Stable Nanofiber Matrices for Tissue Engineering via Electrospinning of Bare Laser-Synthesized Au Nanoparticles in Solutions of High Molecular Weight Chitosan. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamane, S.; Iwasaki, N.; Majima, T.; Funakoshi, T.; Masuko, T.; Harada, K.; Nishimura, S.I. Feasibility of chitosan-based hyaluronic acid hybrid biomaterial for a novel scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, N.; Kasahara, Y.; Yamane, S.; Igarashi, T.; Minami, A.; Nisimura, S.I. Chitosan-based hyaluronic acid hybrid polymer fibers as a sca_old biomaterial for cartilage tissue engineering. Polymers 2011, 3, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahire, J.J.; Robertson, D.D.; van Reenen, A.J.; Dicks, L.M.T. Polyethylene oxide (PEO)-hyaluronic acid (HA) nanofibers with kanamycin inhibits the growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabjańczyk-Wlazło, E.; Krucińska, I.; Chrzanowski, M.; Szparaga, G.; Chaberska, A.; Kolesińska, B.; Komisarczyk, A.; Boguń, M. Fabrication of pure electrospun materials from hyaluronic acid. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2017, 3, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, E.K.; Schi_man, J.D.; Thompson, E.A.; Toth, L.J.; Schauer, C.L. Electrospinning of hyaluronic acid nanofibers from aqueous ammonium solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guo, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Preparation, characterization, and application of PEO/HA core-shell nanofibers based on electric field induced phase separation during electrospinning. Polymer 2016, 83, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ghosh, K.; Shu, X.Z.; Li, B.; Sokolov, J.C.; Prestwich, G.D.; Rafailovich, M.H. Electrospun three-dimensional hyaluronic acid nanofibrous scaffolds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3782–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatej, I.; Popa, M.; Rinaudo, M. Role of the pH on hyaluronan behavior in aqueous solution. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.I.; Krebs, M.D.; Bonino, C.A.; Samorezov, J.E.; Khan, S.A.; Alsberg, E. Electrospun chitosan–alginate nanofibers with in situ polyelectrolyte complexation for use as tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nista, S.V.G.; Bettini, J.; Mei, L.H.I. Coaxial nanofibers of chitosan–alginate–PEO polycomplex obtained by electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Liu, Y.; Fang, D.; Chen, J.; Peng, C.; Fei, X.; Nie, J. Hyaluronic acid/chitosan polyelectrolyte complexes nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, Y.; Iwasaki, N.; Yamane, S.; Igarashi, T.; Majima, T.; Nonaka, S.; Harada, K.; Nishimura, S.-I.; Minami, A. Development of mature cartilage constructs using novel three-dimensional porous scaffolds for enhanced repair of osteochondral defects. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2008, 86, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S.; Iwasaki, N.; Kasahara, Y.; Harada, K.; Majima, T.; Monde, K.; Minami, A. Effect of pore size on in vitro cartilage formation using chitosan-based hyaluronic acid hybrid polymer fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 81, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majima, T.; Irie, T.; Sawaguchi, N.; Funakoshi, T.; Iwasaki, N.; Harada, K.; Nishimura, S.I. Chitosan-based hyaluronan hybrid polymer fibre scaffold for ligament and tendon tissue engineering. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H 2007, 221, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M.; Pavlov, G.; Desbrieres, J. Influence of acetic acid concentration on the solubilization of chitosan. Polymer 1999, 40, 7029–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Garcia, C.E.; Soltero Martínez, F.A.; Bossard, F.; Rinaudo, M. Production of chitosan/hyaluronan complex nanofibers. Characterization and physical properties as a function of the composition. Polymers 2020, 12, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peniche, C.; Elvira, C.; San Roman, J. Interpolymer complexes of chitosan and polymethacrylic derivatives of salicylic acid: Preparation, characterization and modification by thermal treatment. Polymer 1998, 39, 6549–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peniche, C.; Argüelles-Monal, W.; Davidenko, N.; Sastre, R.; Gallardo, A.; San Román, J. Self-curing membranes of chitosan/PAA IPNs obtained by radical polymerization: Preparation, characterization and interpolymer complexation. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabé, P.; Peniche, C.; Argüelles-Monal, W. Swelling behavior of chitosan/pectin polyelectrolyte complex membranes. Effect of thermal cross-linking. Polym. Bull. 2005, 55, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.; Bhattarai, N.; Kievit, F.M.; Rossol, M.; Zhang, M. Electrospinning of chitosan derivative nanofibers with structural stability in an aqueous environment. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 9969–9972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotkin, M.A.; Vikhoreva, G.A.; Smotrina, T.V.; Derbenev, M.A. Thermal modification and study of the structure of chitosan films. Fibre Chem. 2004, 36, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B.; Birkhead, J.R.; Suen, L.F.; Yamin, R.; Mizuno, S.; Glowacki, J.; Arbiser, J.L.; Apperley, J.F. Interleukin-1,8-modulated Gene Expression in Immortalized Human Chondrocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, J.L.; Bechhoefer, J. Calibration of atomic-force microscope tips. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 64, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundar Rajan, V.; Laurent, V.M.; Verdier, C.; Duperray, A. Unraveling the Receptor-Ligand Interactions between Bladder Cancer Cells and the Endothelium Using AFM. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 1246–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurent, V.M.; Duperray, A.; Sundar Rajan, V.; Verdier, C. Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals a Role for Endothelial Cell ICAM-1 Expression in Bladder Cancer Cell Adherence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinca, R.B.; Westin, C.B.; da Silva, J.A.F.; Moraes, Â.M. Electrospun multilayer chitosan scaffolds as potential wound dressings for skin lesions. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Guo, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, B.; Peng, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. The ECM-cell interaction of cartilage extracellular matrix on chondrocytes. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 648459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurtis, M.S.; Tu, B.P.; Gaya, O.A.; Mollenhauer, J.; Knudson, W.; Loeser, R.F.; Knudson, C.B.; Sah, R.L. Mechanisms of chondrocyte adhesion to cartilage: Role of β1-integrins, CD44, and annexin V. J. Orthop. Res. 2001, 19, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtis, M.S.; Schmidt, T.A.; Bugbee, W.D.; Loeser, R.F.; Sah, R.L. Integrin-mediated adhesion of human articular chondrocytes to cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
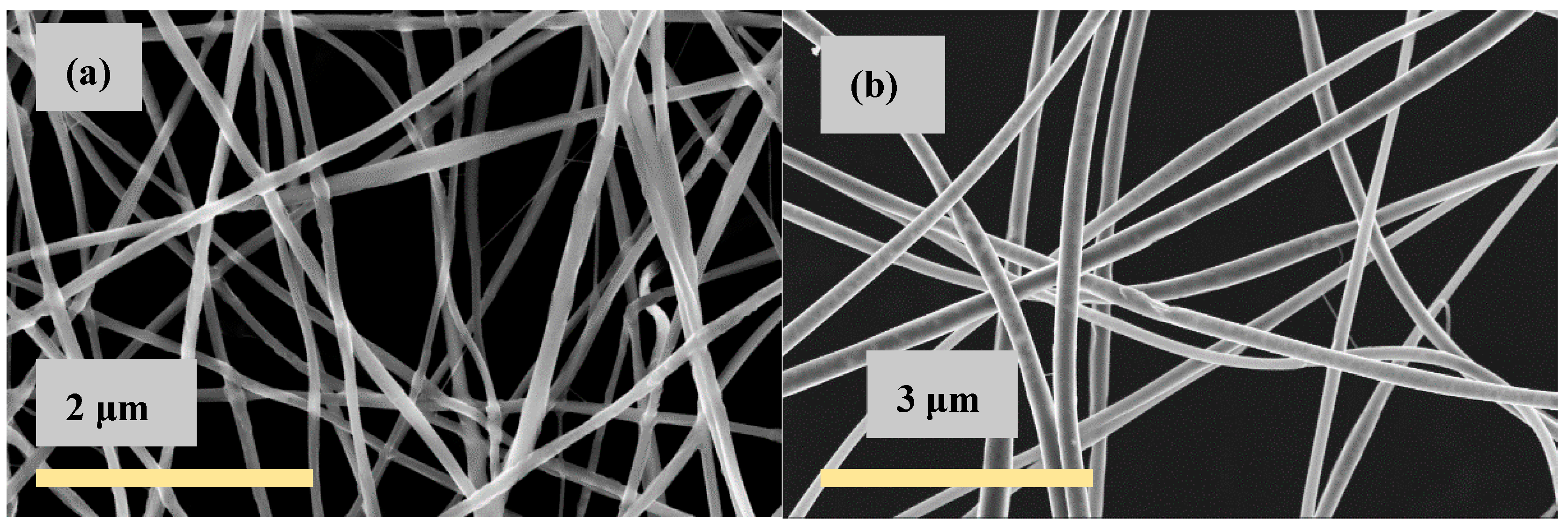
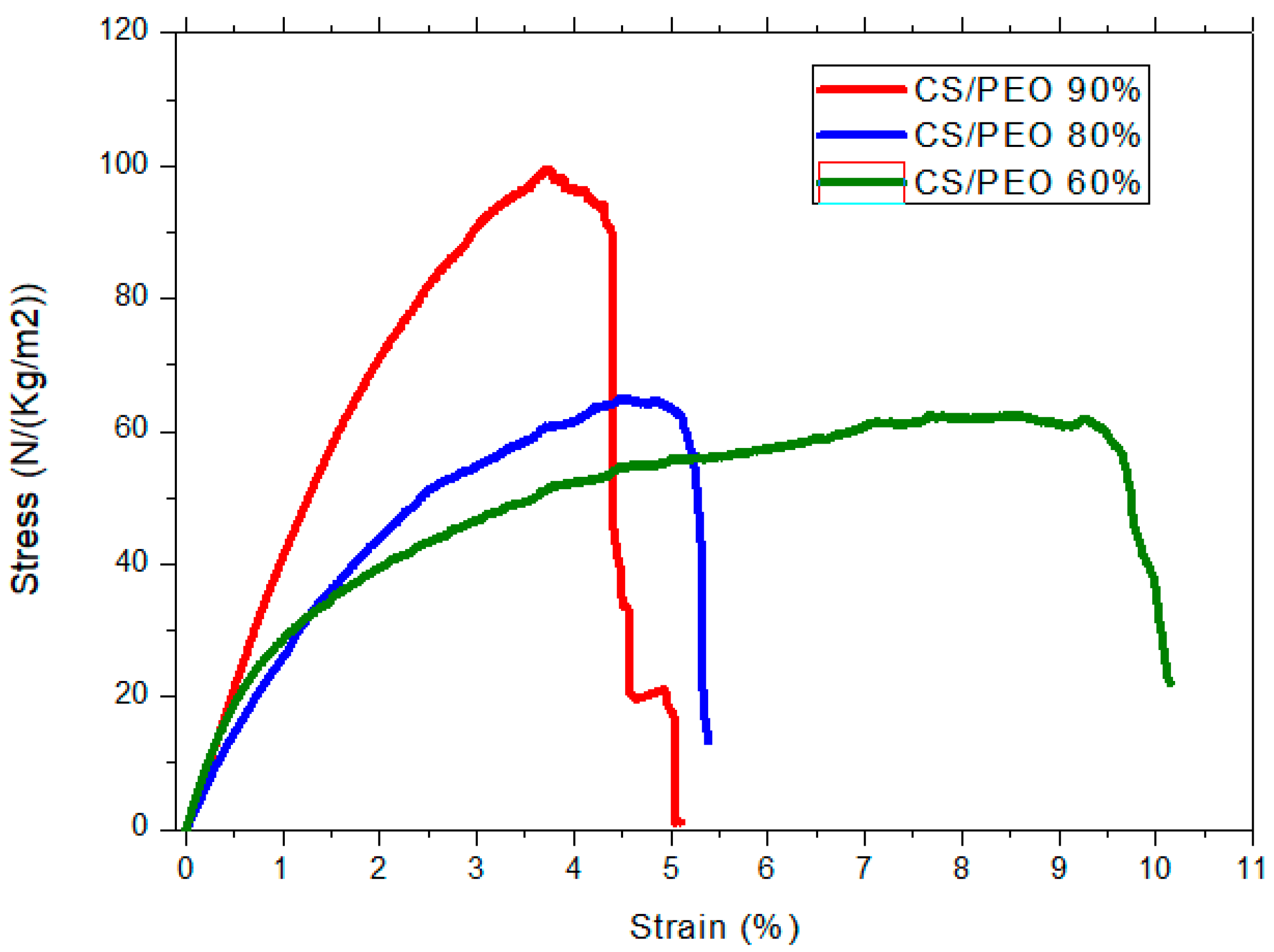
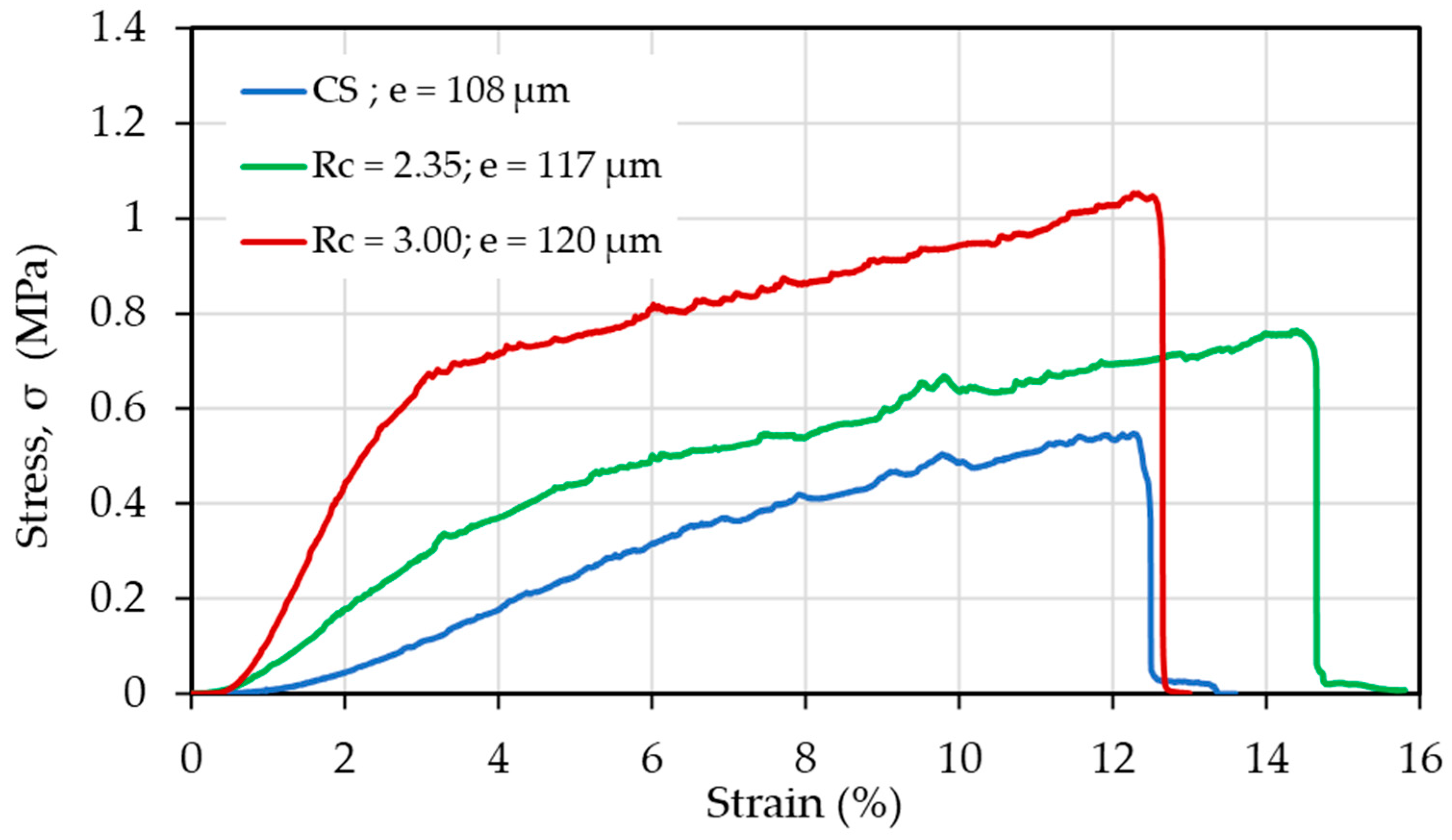
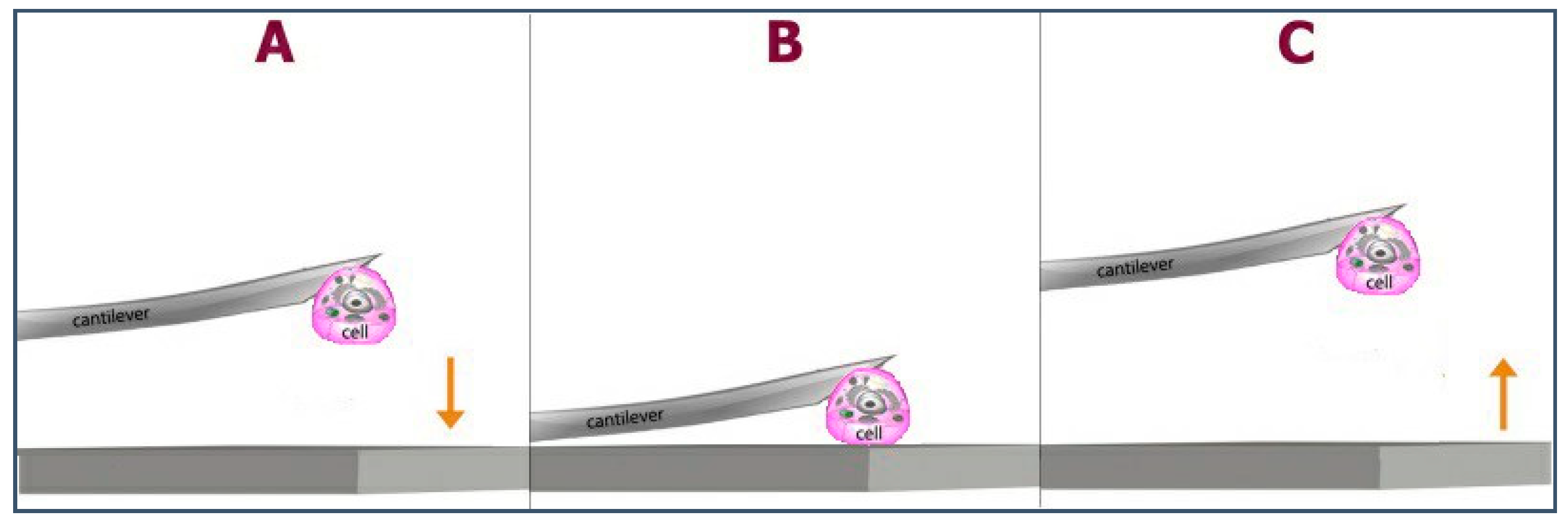
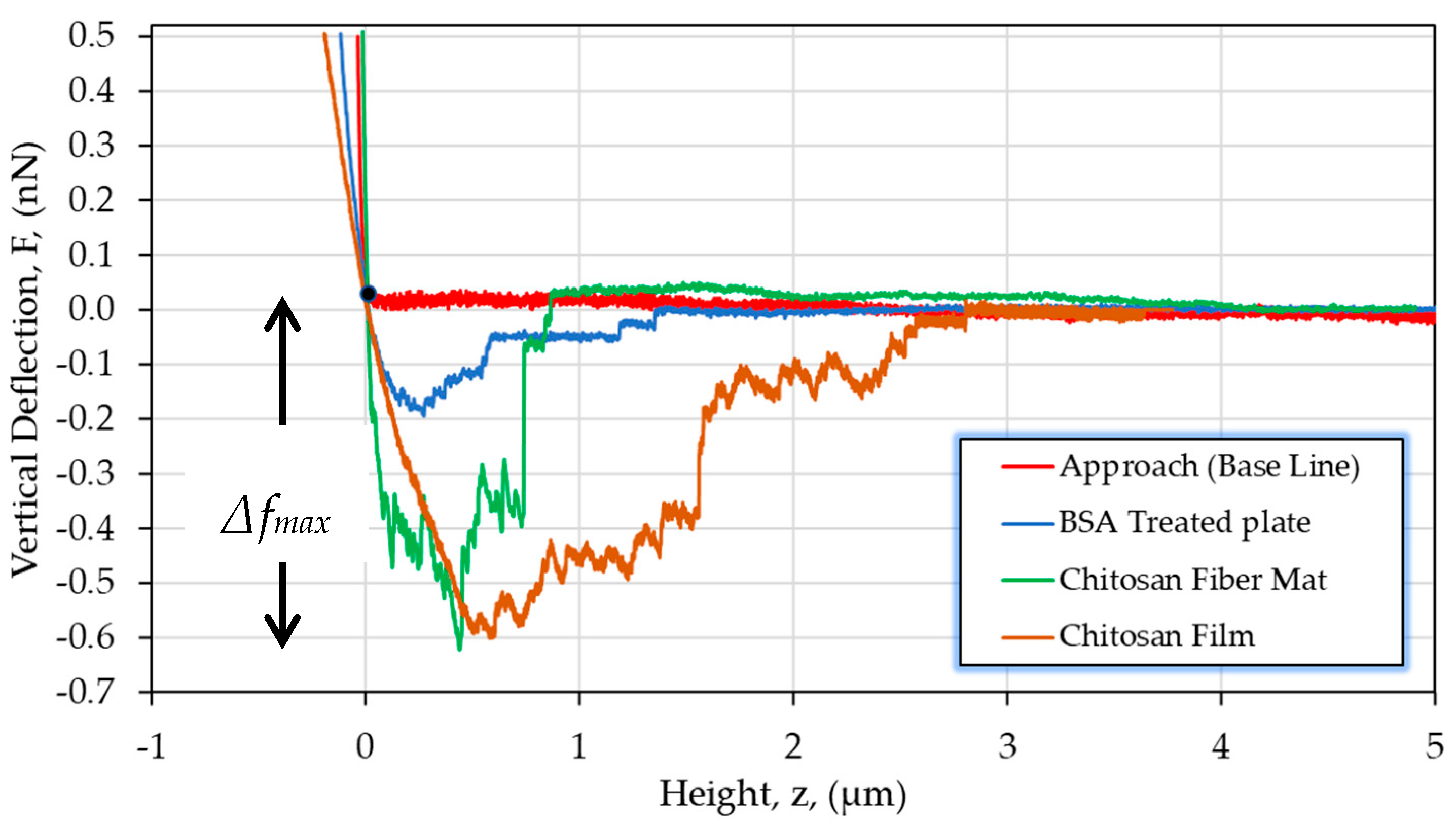
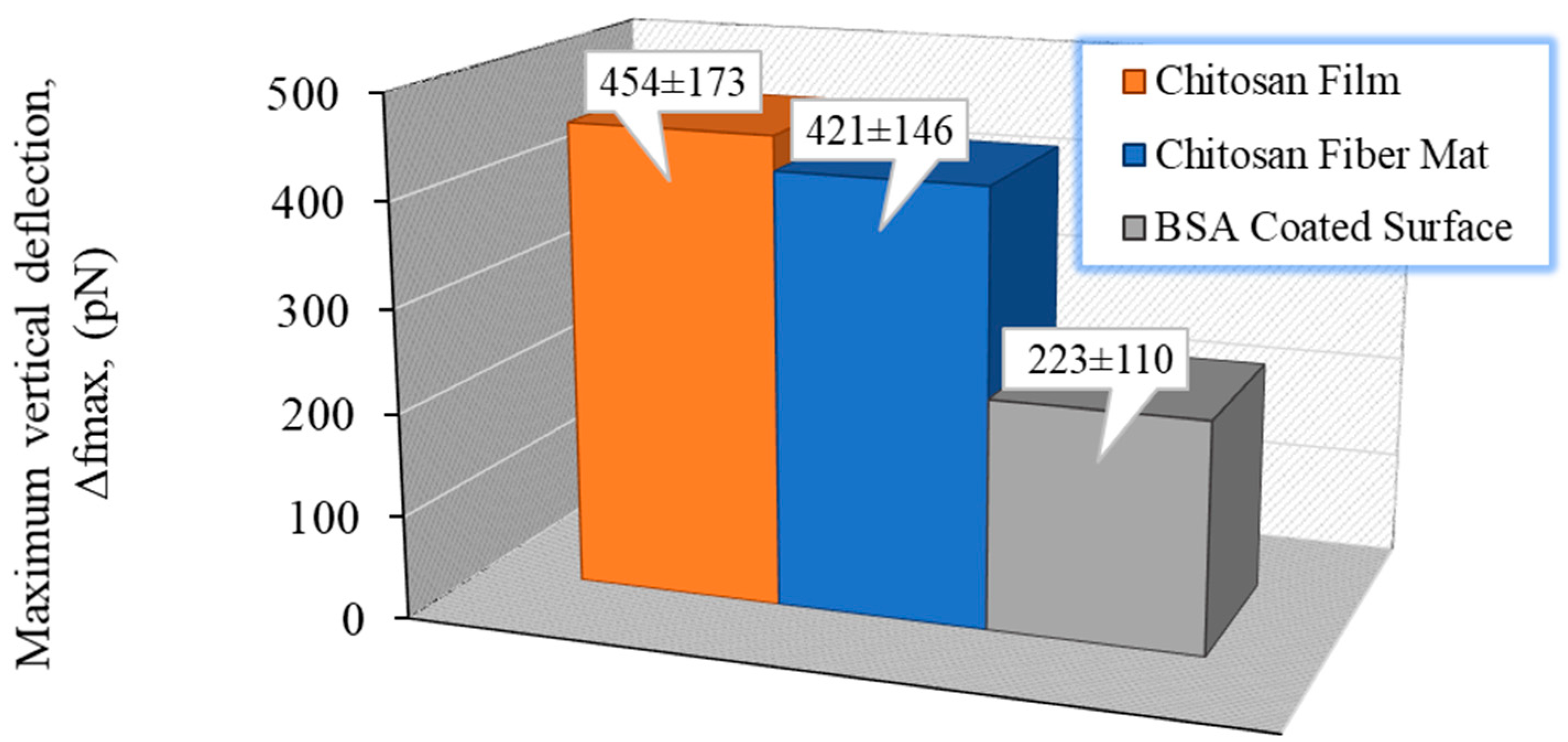
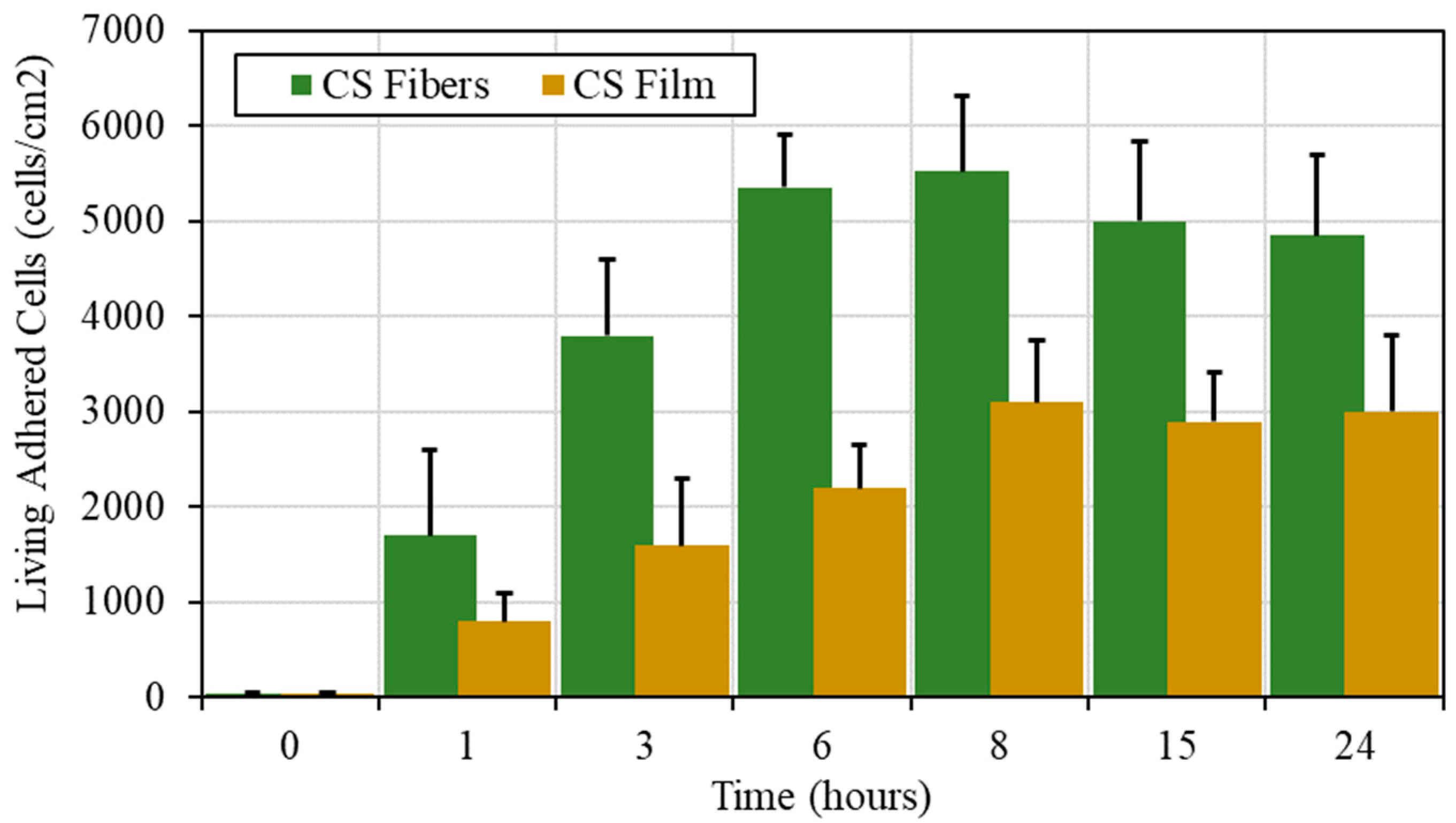

| CS (mg/mL) | PEO (mg/mL) | PEO MW (kg/mol) | CS/PEO (w/w) % | Electrospun Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 12.0 | 100 | 80/20 | Beads |
| 50 | 12.0 | 300 | 80/20 | Beads |
| 50 | 12.0 | 1000 | 80/20 | Fibers |
| 50 | 12.0 | 5000 | 80/20 | Fibers |
| 50 | 12.0 | 8000 | 80/20 | Fibers |
| 50 | 12.0 | 300 | 80/20 | Beads |
| 50 | 20.0 | 300 | 70/30 | Fibers |
| 50 | 30.0 | 300 | 60/40 | Fibers |
| 50 | 40.0 | 300 | 55/45 | Fibers |
| CS (mg/mL) | PEO (mg/mL) | CS-MW (kg/mol) | CS/PEO (w/w) % | Electrospun Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35.8 | 4.2 | 102 | 90/10 | Beads |
| 32.0 | 8.0 | 102 | 80/20 | Fibers + beads |
| 28.6 | 11.4 | 102 | 70/30 | Fibers |
| 13.5 | 1.6 | 500 | 90/10 | Fibers + beads |
| 12.8 | 3.4 | 500 | 80/20 | Fibers + beads |
| 12.3 | 4.9 | 500 | 70/30 | Fibers + beads |
| 11.2 | 7.8 | 500 | 60/40 | Beads |
| System | Fiber Mat Thickness (mm) | Chitosan Weight Concentration Ratio | Density (g/cm3) | Rehydration Degree (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blend of CS and PEO 5% Solutions | 0.128 | 95 | 0.173 | 3.58 |
| 0.122 | 90 | 0.163 | 3.71 | |
| 0.102 | 80 | 0.200 | 3.95 | |
| 0.115 | 70 | 0.164 | 4.19 |
| System | [CS] % | Initial State | Wet State after Rehydration | σBreak | εBreak | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPa | % | ||||||
| 5% CS/PEO solution | 70 | 939 | 421 | 2.23 | 0.42 | 18 | 44.9 |
| 80 | 1490 | 652 | 2.28 | 1.43 | 40 | 46.0 | |
| 90 | 1370 | 602 | 2.28 | 1.19 | 47 | 31.9 | |
| Charge Ratio NH2/COOH | Weight Ratio NH2/COOH | Electrospun Products |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.21 | Fibers, few beads |
| 1.0 | 0.42 | Fibers |
| 1.8 | 0.77 | Fibers |
| 2.35 | 1.0 | Fibers |
| 3.0 | 1.26 | Fibers |
| RC | Weight Loss (%) after TT | Remaining Polymer (%) after EtOH/H2O Washing | Swelling Degree (gH2O/g) at pH 7.4 | Solubility (%) at pH = 7.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.35 | 9.8 ± 2.5 | 69.8 ± 8.1 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 12.2 |
| 3.0 | 10.9 ± 0.4 | 73.79 ± 0.18 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 13.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia Garcia, C.E.; Bossard, F.; Rinaudo, M. Electrospun Biomaterials from Chitosan Blends Applied as Scaffold for Tissue Regeneration. Polymers 2021, 13, 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071037
Garcia Garcia CE, Bossard F, Rinaudo M. Electrospun Biomaterials from Chitosan Blends Applied as Scaffold for Tissue Regeneration. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071037
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia Garcia, Christian Enrique, Frédéric Bossard, and Marguerite Rinaudo. 2021. "Electrospun Biomaterials from Chitosan Blends Applied as Scaffold for Tissue Regeneration" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071037
APA StyleGarcia Garcia, C. E., Bossard, F., & Rinaudo, M. (2021). Electrospun Biomaterials from Chitosan Blends Applied as Scaffold for Tissue Regeneration. Polymers, 13(7), 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071037






