Functional Hydrophilic Membrane for Oil–Water Separation Based on Modified Bio-Based Chitosan–Gelatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Membrane
2.3. Attenuated Total Reflectance Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-IR)
2.4. Mechanical Testing
2.5. Rheological Analysis
2.6. Morphological Analysis
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.9. Swelling Degrees
2.10. Membrane Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ATR-IR
3.2. Mechanical Testing
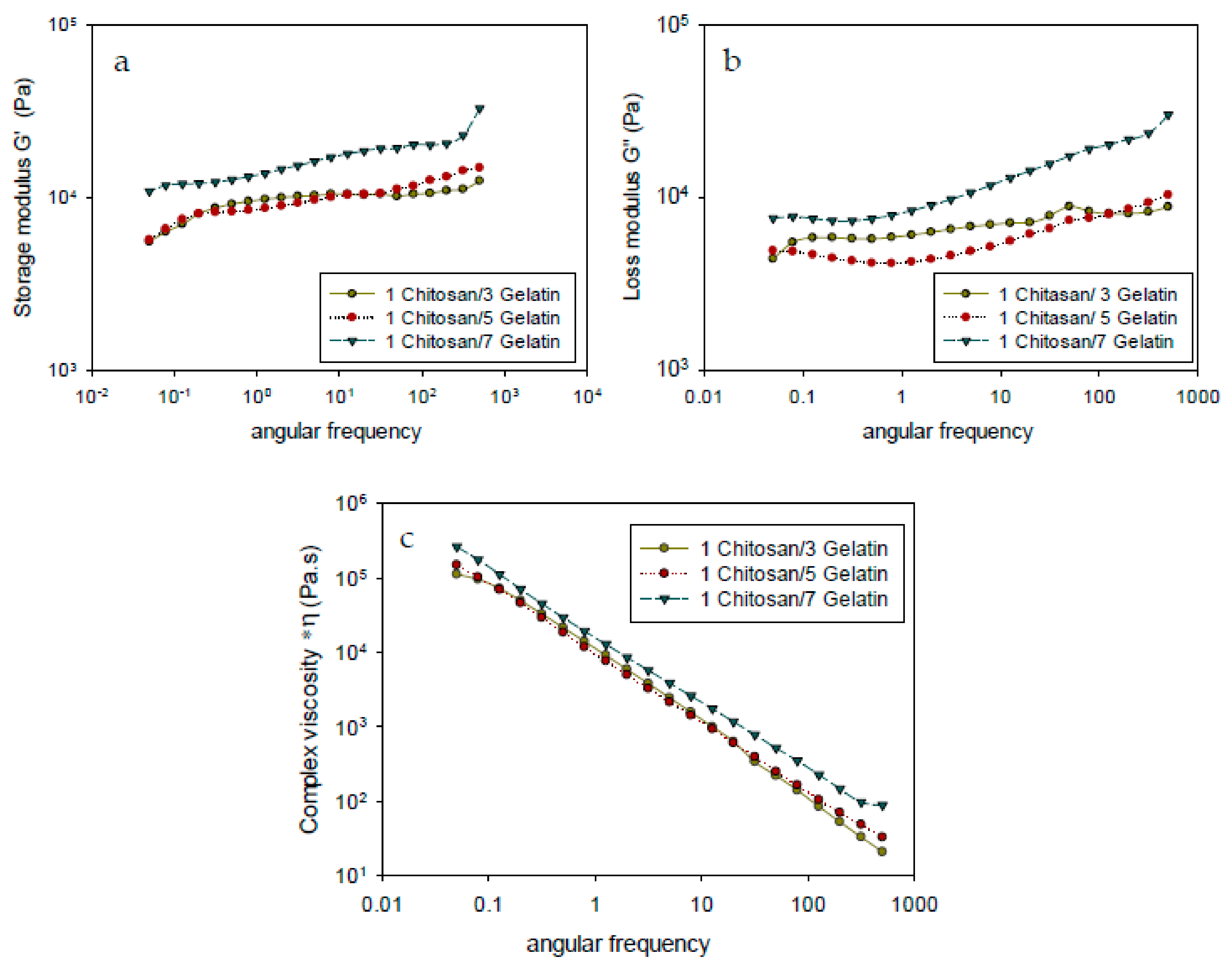
3.3. Rheological Analysis
3.4. Morphological Analysis
3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.6. DSC
3.7. Swelling Degrees
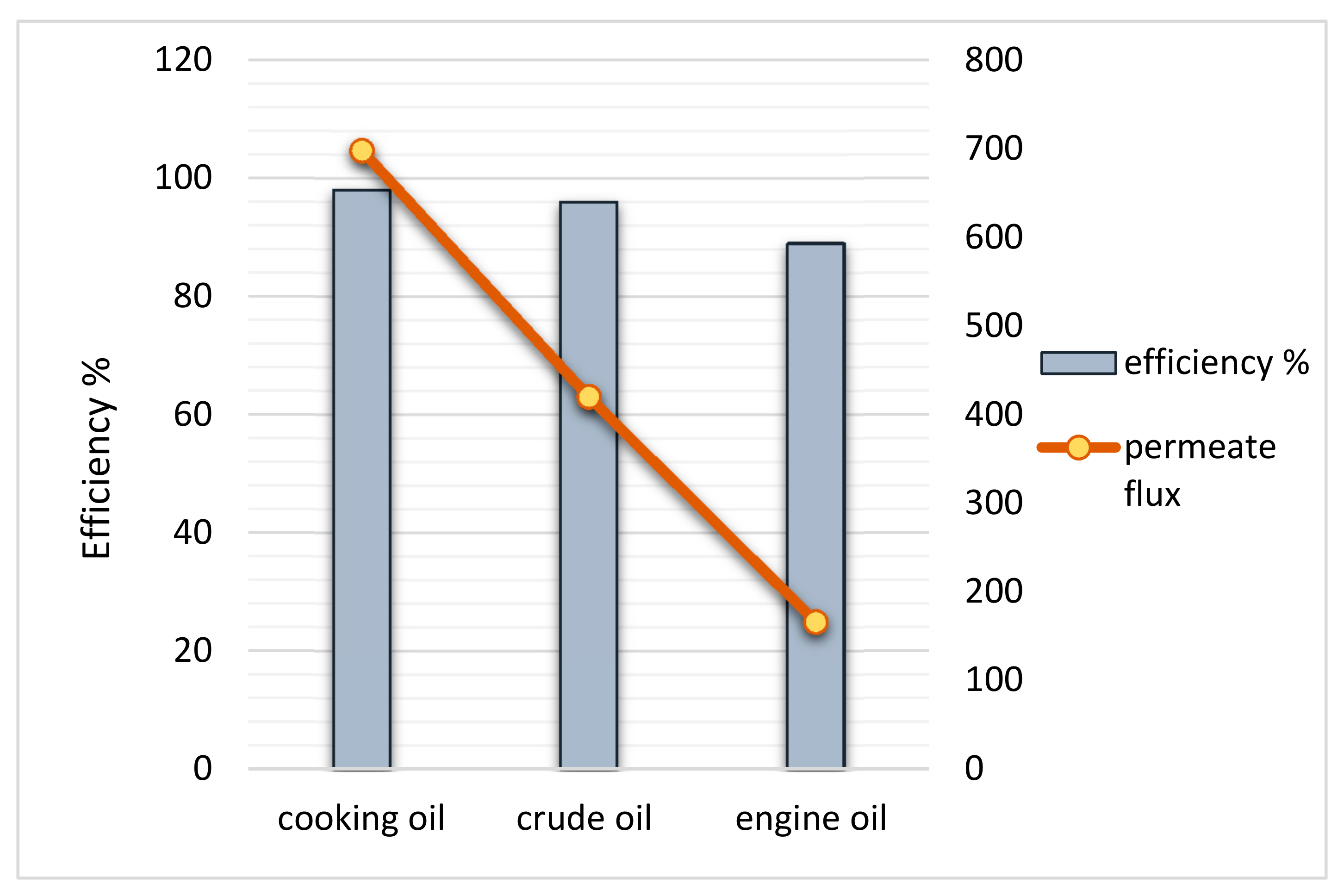
3.8. Membrane Testing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, G.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.; Peng, S.; Wu, X.; Ren, T.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, Q. A cellulose sponge with robust superhydrophilicity and under-water superoleophobicity for highly effective oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.C.; Molly, F.C. Factors that determine the cost of oil spills. Int. Oil spill Conf. 2003, 1, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey, E.E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane technologies in wastewater treatment: A review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, D.P.; Gschwend, P.M. Assessing the performance and cost of oil spill remediation technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 7, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zioui, D.; Salazar, H.; Aoudjit, L.; Martins, P.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Polymer-Based Membranes for Oily Wastewater Remediation. Polymers 2020, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.A.; Goh, P.S.; Abdul Karim, Z.; Ismail, A.F. Thin film composite membrane for oily waste water treatment: Recent advances and challenges. Membranes 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Hankins, N. Emerging Membrane Technology for Sustainable Water Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arikibe, J.E.; Lata, R.; Kuboyama, K.; Ougizawa, T.; Rohindra, D. pH-responsive studies of bacterial cellulose /chitosan hydrogels crosslinked with genipin: Swelling and drug release behaviour. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 9915–9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-hefian, E.A.; Yahaya, A.H. Rheological study of chitosan and its blends: An overview. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 210–220. [Google Scholar]
- Yien, L.; Zin, N.M.; Sarwar, A.; Katas, H. Antifungal activity of chitosan nanoparticles and correlation with their physical properties. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I. Gelatin. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 142–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.-S.; Yan, K.; Qi, Y.; Wang, G.-F.; Cui, Y.-L. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of genipin crosslinked chitosan/gelatin three-dimensional scaffolds for liver tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.J.; Tsou, T.L.; Wang, H.J.; Hsu, S.H. Characterization of chitosan–gelatin scaffolds for dermal tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 7, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil’deevaa, N.R.; Kasatkina, M.A.; Mikhailov, S.N. Peculiarities of obtaining biocompatible films based on chitosan cross linked by genipin. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2017, 10, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaoxuan, F.; Karin, O.; Minna, H. Tunable chitosan hydrogels for adsorption: Property control by biobased modifiers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wan Ishak, W.H.; Ahmad, I.; Ramli, S.; Mohd Amin, M.C.I. Gamma Irradiation-Assisted Synthesis of Cellulose Nanocrystal-Reinforced Gelatin Hydrogels. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juthamas, R.; Ratthapol, R.; Hathairat, J.; Sorada, K.; Siriporn, D. Influences of physical and chemical crosslinking techniques on electrospun type A and B gelatin fiber mats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Yuanyuan, Z.; Zhongtao, S. Effects of gelatin-polyphenol and gelatin–genipin cross-linking on the structure of gelatin hydrogels. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2822–S2832. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, R.S.G.; Pinto, L.A.A. Physical crosslinkers: Alternatives to improve the mechanical properties of fish gelatin. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.M.A.; Fauzi, M.B.; Nordin, A.; Hiraoka, Y.; Tabata, Y.; Yunus, M.H.M. Fabrication of Bio-Based Gelatin Sponge for Potential Use as A Functional Acellular Skin Substitute. Polymers 2020, 12, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzo, L.D.Y.; da Conceição, T.F.; Spinelli, A.; Scharnagl, N.; Pires, A.T.N. Chitosan coatings crosslinked with genipin for corrosion protection of AZ31 magnesium alloy sheets. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimida, S.; Barca, A.; Cancelli, N.; De Benedictis, V.; Raucci, M.G.; Demitri, C. Effects of genipin concentration on cross-linked chitosan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Structural characterization and evidence of biocompatibility features. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.J.; Martins, S.P.; Duarte, B.P. Production of chitosan microparticles cross-linked with genipin-identification of factors influencing size and shape properties. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 104, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Xiong, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, P. Fabrication of interpenetrating polymer network chitosan/gelatin porous materials and study on dye adsorption properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.; Ng, Y.-F.; Pudney, P.D.A. Mechanism and kinetics of crosslinking reaction between biopolymers containing primary amine groups and genipin. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 2003, 41, 3941–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Genipin-aided protein cross-linking to modify structural and rheological properties of emulsion-filled hempseed protein hydrogels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12895–12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursamar, S.A.; Lehner, A.N.; Azami, M.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A.; Antunes, A.P.M. The effects of crosslinkers on physical, mechanical, and cytotoxic properties of gelatin sponge prepared via in-situ gas foaming method as a tissue engineering scaffold. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noranizan, I.A.; Ahmad, I. Effects of fiber loading and compatibilizer on rheological, mechanical and morphology behaviors. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2012, 2, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Zarama, M.A.; Jim’enez-Aparicio, A.R.; Lourenço, R.V.; Amaral-Sobral, P.J.; Solorza-Feria, J. Rheological characterization of solutions of gelatin with bentonite and tannic acid. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 2016, 15, 819–830. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, M.J.; Figueiredo, M.M.; Gil, M.H. Rheological study of genipin cross-linked chitosan hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Nagai, N.; Saijo, S.; Kaji, H.; Nishizawa, M.; Abe, T. In situ formation of injectable chitosan–gelatin hydrogels through double crosslinking for sustained intraocular drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmar, K.; Bianco-Peled, H. The dramatic effect of small pH changes on the properties of chitosan hydrogels crosslinked with genipin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penga, C.; Zhaoa, S.-Q.; Zhanga, J.; Huanga, G.-Y.; Chena, L.-Y.; Zhao, F.-Y. Chemical composition, antimicrobial property and microencapsulation of mustard (Sinapis alba) seed essential oil by complex coacervation. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Jia, J.F.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Preparation and characterization of IPN hydrogels composed of chitosan and gelatin cross-linked by genipin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shok Yin, O.; Ahmad, I.; Mohd Amin, M.C.I. Effect of Cellulose Nanocrystals Content and pH on Swelling Behaviour of Gelatin Based Hydrogel. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 793–799. [Google Scholar]
- Samsalee, N.; Sothornvit, R. Modification and characterization of porcine plasma protein with natural agents as potential crosslinkers. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.A.; Avery, N.C.; Rodin, V.V.; Bailey, A.J. The increase in denaturation temperature following cross-linking of collagen is caused by dehydration of the fibres. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 346, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Do, M.D.; Casey, P.; Sulistio, A. Chemical cross-linking gelatin with natural phenolic compounds as studied by high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, M.; Abbasi, F.; Khoshfetrat, A.B.; Ghaleh, H. Microstructure and characteristic properties of gelatin/chitosan scaffold prepared by a combined freeze-drying/leaching method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3958–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A review on porous polymeric membrane preparation. Part I: Production techniques with polysulfone and poly (vinylidene fluoride). Polymers 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayeta, M.; Menguala, J.I.; Matsuura, T. Porous hydrophobic/hydrophilic composite membranes. Application in desalination using direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wei, Y.; Luo, B. Separation mechanism of fatty acids from waste cooking oil and its flotation performance in iron ore desiliconization. Minerals 2017, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffina, T.S.T.; Yahyaa, E.; Husin, H. The rheology of light crude oil and water-in-oil-emulsion. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Xie, Z. A review on current development of membranes for oil removal from waste waters. Membranes 2020, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorafa, R.; Saththasivam, J.; Liu, Z.; Ahzi, S. Efficient oil/saltwater separation using a highly permeable and fouling-resistant all-inorganic nanocomposite membrane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15488–15497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Sample Ratio | TGA Analysis | DSC Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan:Gelatin | Td (°C) | Residual Mass (%) | Td (°C) |
| 1:03 | 319.3 | 17.6 | 67.95 |
| 1:05 | 329.1 | 19.91 | 79.28 |
| 1:07 | 331.5 | 17.96 | 87.3 |
| Type | Viscosity (cP) |
|---|---|
| Used cooking oil | 107.7 |
| Light crude oil | 28.4 |
| Used engine oil | 135.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakuwan, S.Z.; Ahmad, I.; Abu Tahrim, N.; Mohamed, F. Functional Hydrophilic Membrane for Oil–Water Separation Based on Modified Bio-Based Chitosan–Gelatin. Polymers 2021, 13, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071176
Zakuwan SZ, Ahmad I, Abu Tahrim N, Mohamed F. Functional Hydrophilic Membrane for Oil–Water Separation Based on Modified Bio-Based Chitosan–Gelatin. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071176
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakuwan, Siti Zarina, Ishak Ahmad, Nurfaizah Abu Tahrim, and Faizal Mohamed. 2021. "Functional Hydrophilic Membrane for Oil–Water Separation Based on Modified Bio-Based Chitosan–Gelatin" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071176
APA StyleZakuwan, S. Z., Ahmad, I., Abu Tahrim, N., & Mohamed, F. (2021). Functional Hydrophilic Membrane for Oil–Water Separation Based on Modified Bio-Based Chitosan–Gelatin. Polymers, 13(7), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071176







