Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P.; methodology, R.S.S. and A.P.; software, R.S.S.; validation, R.S.S.; formal analysis, R.S.S. and A.P.; investigation, R.S.S. and A.P.; resources, A.P. and R.S.S.; data curation, R.S.S.; writing—R.S.S.; writing—R.S.S. and A.P.; visualization, R.S.S. and A.P.; supervision, A.P.; project administration, A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
Typical ship deck composed of stiffened plates subjected to axial and out-of-plane load.
Figure 1.
Typical ship deck composed of stiffened plates subjected to axial and out-of-plane load.
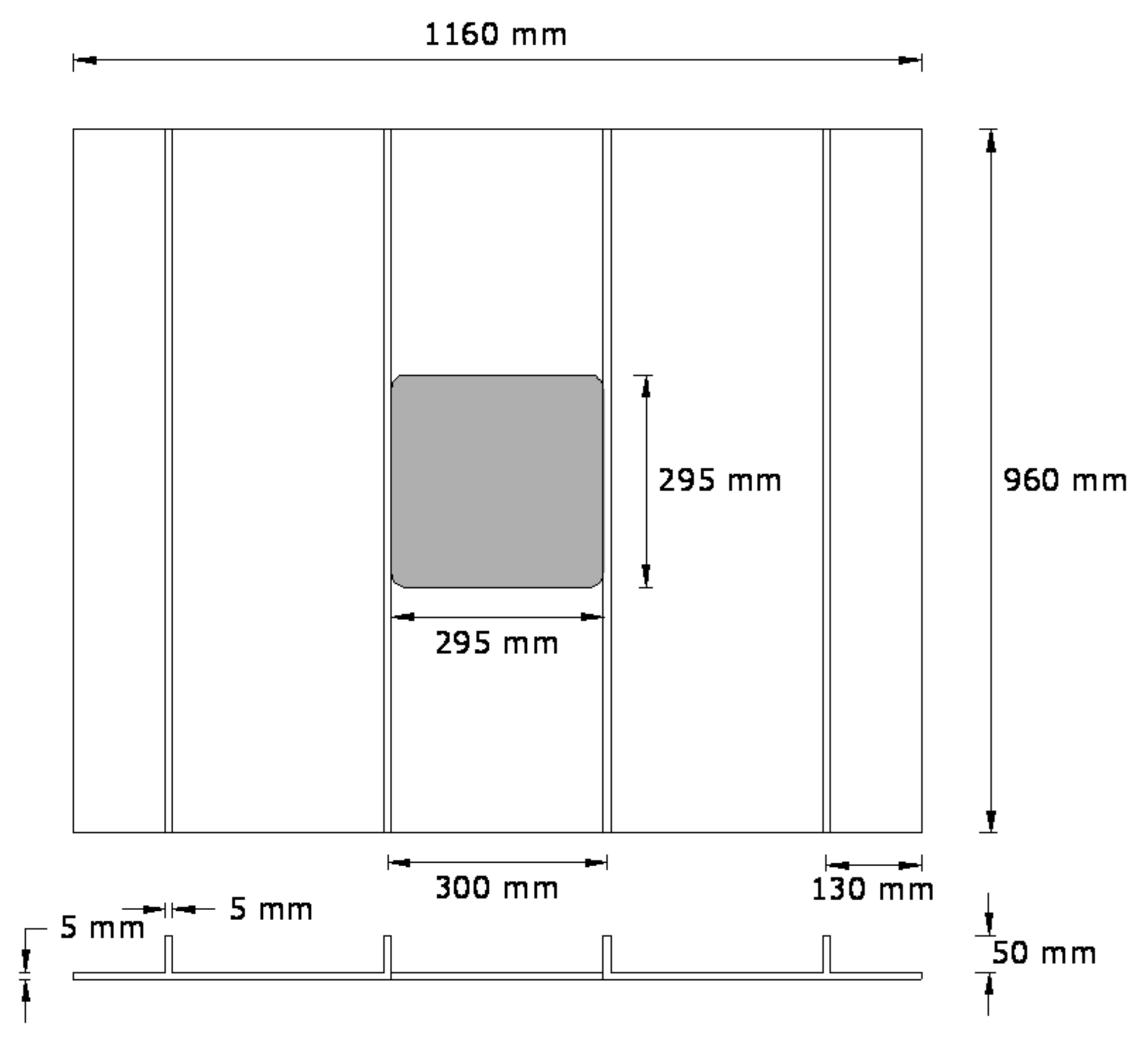
Figure 2.
Geometry of glass-fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP)-stiffened composite plate.
Figure 2.
Geometry of glass-fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP)-stiffened composite plate.
Figure 3.
Layup structure of GFRP-stiffened composite plate (not to scale).
Figure 3.
Layup structure of GFRP-stiffened composite plate (not to scale).
Figure 4.
Casting of GFRP-stiffened composite plates. (a) Laying of the first three layers (b) Laying of last three layers.
Figure 4.
Casting of GFRP-stiffened composite plates. (a) Laying of the first three layers (b) Laying of last three layers.
Figure 5.
Fabricated GFRP-stiffened composite plate with cutout.
Figure 5.
Fabricated GFRP-stiffened composite plate with cutout.
Figure 6.
Initial imperfection measurement setup.
Figure 6.
Initial imperfection measurement setup.
Figure 7.
Imperfection profile of specimen LSTP1.
Figure 7.
Imperfection profile of specimen LSTP1.
Figure 9.
Position of dial and strain gauges. STF1, STF2, STF3, STF4—stiffeners. P1, P2…. P12—Position of strain gauges on flange plate. S1, S2, S3, S4—Position of strain gauges on stiffeners. D1, D2, D3, D4, D5—position of dial gauges.
Figure 9.
Position of dial and strain gauges. STF1, STF2, STF3, STF4—stiffeners. P1, P2…. P12—Position of strain gauges on flange plate. S1, S2, S3, S4—Position of strain gauges on stiffeners. D1, D2, D3, D4, D5—position of dial gauges.
Figure 10.
Load–strain behavior of LSTP1.
Figure 10.
Load–strain behavior of LSTP1.
Figure 11.
Buckling of LSTP1 (a) experiment (b) finite element analysis (FEA).
Figure 11.
Buckling of LSTP1 (a) experiment (b) finite element analysis (FEA).
Figure 12.
Buckling of LSTPO1 (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 12.
Buckling of LSTPO1 (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 13.
Failure of LSTP1 (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 13.
Failure of LSTP1 (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 14.
Load–strain behavior of LSTP4.
Figure 14.
Load–strain behavior of LSTP4.
Figure 15.
Failure of LSTP4. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 15.
Failure of LSTP4. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 16.
Failure of LSTPO4. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 16.
Failure of LSTPO4. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 17.
Failure of LSTP2. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 17.
Failure of LSTP2. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 18.
Failure of LSTPO2. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 18.
Failure of LSTPO2. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 19.
Failure of LSTP3. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 19.
Failure of LSTP3. (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 20.
Failure of LSTPO3 (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 20.
Failure of LSTPO3 (a) Experiment (b) FEA.
Figure 21.
Axial load vs. deformation curve for GFRP-stiffened composite plates. (a) LSTP1 (b) LSTPO1 (c) LSTP2 (d)LSTPO2 (e) LSTP3 (f) LSTPO3.
Figure 21.
Axial load vs. deformation curve for GFRP-stiffened composite plates. (a) LSTP1 (b) LSTPO1 (c) LSTP2 (d)LSTPO2 (e) LSTP3 (f) LSTPO3.
Figure 22.
Out-of-plane load vs. deflection curve for GFRP-stiffened composite plates. (a) LSTP4 (b) LSTPO4.
Figure 22.
Out-of-plane load vs. deflection curve for GFRP-stiffened composite plates. (a) LSTP4 (b) LSTPO4.
Table 1.
Properties of resin.
Table 1.
Properties of resin.
| Property | Value |
|---|
| Viscosity | 9825 centipoises |
| Gel time of resin | 36 min |
| Peak exothermic temperature | 154 °C |
| Specific gravity | 1.159 |
| Tensile strength | 42 MPa |
| Tensile modulus | 3147 MPa |
| Flexural strength | 95 MPa |
| Flexural modulus | 3015 MPa |
| Water absorption (7 days) | 0.2050% |
Table 2.
Properties of glass-fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP).
Table 2.
Properties of glass-fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP).
| Property | Value | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|
| Tensile strength—warp direction | 250 MPa | 3.06 |
| Tensile strength—weft direction | 211 MPa | 8.53 |
| Compressive strength | 138 MPa | 5.42 |
| Shear strength | 52 MPa | 4.17 |
| Flexural strength | 384 MPa | 9.91 |
| Longitudinal modulus, (E1) | 15,800 MPa | 10.89 |
| Transverse modulus, (E2) | 15,333 MPa | 9.96 |
| Shear modulus (G12) | 2806 MPa | 1.19 |
| Flexural modulus | 15,388 MPa | 5.07 |
| Major Poisson’s ratio (ν12) | 0.1386 | 3.28 |
| Minor Poisson’s ratio (ν21) | 0.1248 | 2.62 |
Table 3.
Initial geometric imperfections.
Table 3.
Initial geometric imperfections.
| Specimen | Measured Imperfections (mm) |
|---|
| Δx | Δsx | Δsy |
|---|
| LSTP1 | 1.10 | 0.671 | 1.27 |
| LSTP2 | 0.90 | 0.476 | 1.57 |
| LSTP3 | 1.70 | 0.820 | 2.00 |
| LSTP4 | 0.71 | 0.454 | 1.44 |
| LSTPO1 | 1.22 | 1.83 | 1.81 |
| LSTPO2 | 1.87 | 1.45 | 1.43 |
| LSTPO3 | 1.89 | 1.37 | 1.51 |
| LSTPO4 | 1.81 | 1.21 | 1.24 |
Table 4.
Loading pattern of GFRP-stiffened composite.
Table 4.
Loading pattern of GFRP-stiffened composite.
| Specimen | Specimen Type | Loading Pattern |
|---|
| LSTP1 | Without cutout | Axial load until failure |
| LSTPO1 | With cutout | Axial load until failure |
| LSTP2 | Without cutout | 1/3rd of ultimate out-of-plane load + Incremental axial load until failure |
| LSTPO2 | With cutout | 1/3rd of ultimate out-of-plane load + Incremental axial load until failure |
| LSTP3 | Without cutout | 2/3rd of ultimate out-of-plane load + Incremental axial load until failure |
| LSTPO3 | With cutout | 2/3rd of ultimate out-of-plane load + Incremental axial load until failure |
| LSTP4 | Without cutout | Uniform out-of-plane loading until failure |
| LSTPO4 | With cutout | Uniform out-of-plane loading until failure |
Table 5.
Axial ultimate loads were obtained from the experiment and FEA.
Table 5.
Axial ultimate loads were obtained from the experiment and FEA.
| S. No. | Specimen | Out-of-Plane Load (kN/m2) | Axial Ultimate Load (kN) | Maximum Axial Deformation (mm) | | | Mode of Failure |
|---|
| PEXPT | PFEA | ΔEXPT | ΔFEA | | | |
|---|
| 1 | LSTP1 | 0 | 249 | 226 | 5.58 | 5.24 | 0.907 | 0.939 | SC 1 |
| 2 | LSTP2 | 20 | 208 | 193 | 6.24 | 6.44 | 0.928 | 1.032 | ST 2 |
| 3 | LSTP3 | 40 | 180 | 171 | 6.44 | 6.18 | 0.950 | 0.960 | ST 2 |
| 4 | LSTPO1 | 0 | 211 | 204 | 6.20 | 6.67 | 0.967 | 1.075 | SC 1 |
| 5 | LSTPO2 | 20 | 176 | 169 | 5.82 | 6.08 | 0.960 | 1.045 | ST 2 |
| 6 | LSTPO3 | 40 | 121 | 112 | 9.11 | 9.03 | 0.926 | 0.991 | ST 2 |
| ) | 0.9397 | 1.007 | |
| Standard deviation (σ) | 0.0231 | 0.0525 | |
| Coefficient of variation (cv) | 0.0245 | 0.0521 | |
Table 6.
Out-of-plane ultimate loads obtained from experiment and finite element analysis.
Table 6.
Out-of-plane ultimate loads obtained from experiment and finite element analysis.
| S. No. | Specimen | Out-of-Plane Ultimate Load (kN/m2) | | Reduction in Strength (%) | Mode of Failure |
|---|
| QEXPT | QFEA |
|---|
| 1 | LSTP4 | 61 | 56 | 0.914 | - | ST 2 |
| 2 | LSTPO4 | 56 | 52 | 0.929 | 8 | ST 2 |
Table 7.
Influence of square cutout on the ultimate axial load.
Table 7.
Influence of square cutout on the ultimate axial load.
| S. No. | Constant Out-of-Plane Load (q) (kN/m2) | Stiffened Plate without Cutout | Stiffened Plate with Cutout | Reduction in Strength (%) |
|---|
| Specimen | Mode of Failure * | PEXPT (kN) | Specimen | Failure | PEXPT (kN) |
|---|
| 1 | 0 | LSPT1 | SC | 249 | LSTPO1 | SC | 211 | 15% |
| 2 | 20 | LSTP2 | ST | 208 | LSTPO2 | ST | 176 | 15% |
| 3 | 40 | LSTP3 | ST | 180 | LSTPO3 | ST | 121 | 32% |
Table 8.
Influence of out-of-plane load on the axial load of GFRP-stiffened composite plates.
Table 8.
Influence of out-of-plane load on the axial load of GFRP-stiffened composite plates.
| S. No. | Specimen | Constant Out-of-Plane Load (q) (kN/m2) | Axial Ultimate Load (PEXPT) (kN) | Reduction in Strength | Mode of Failure |
|---|
| 1 | LSPT1 | 0 | 249 | - | SC |
| 2 | LSTP2 | 20 | 208 | 16% | ST |
| 3 | LSTP3 | 40 | 180 | 28% | ST |
Table 9.
Influence of out-of-plane load on the axial load of GFRP-stiffened composite plates with cutout.
Table 9.
Influence of out-of-plane load on the axial load of GFRP-stiffened composite plates with cutout.
| S. No. | Specimen | Constant Out-of-Plane Load (q) (kN/m2) | Axial Ultimate Load (PEXPT) (kN) | Reduction in Strength | Mode of Failure |
|---|
| 1 | LSPTO1 | 0 | 211 | - | SC |
| 2 | LSTPO2 | 20 | 176 | 17% | ST |
| 3 | LSTPO3 | 40 | 121 | 43% | ST |