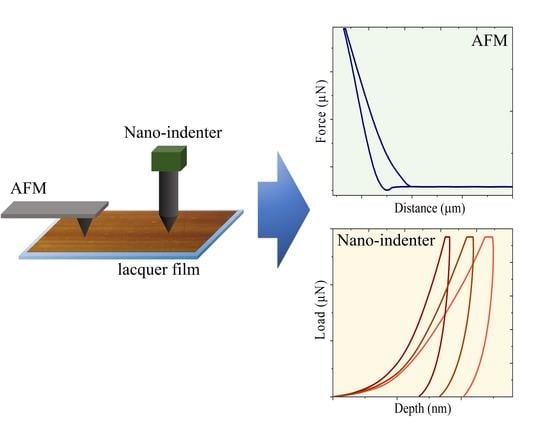
Improved Measurements of the Physical Properties of Oriental Lacquers Using Atomic Force Microscopy and a Nanoindenter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preperation of Lacquer Films
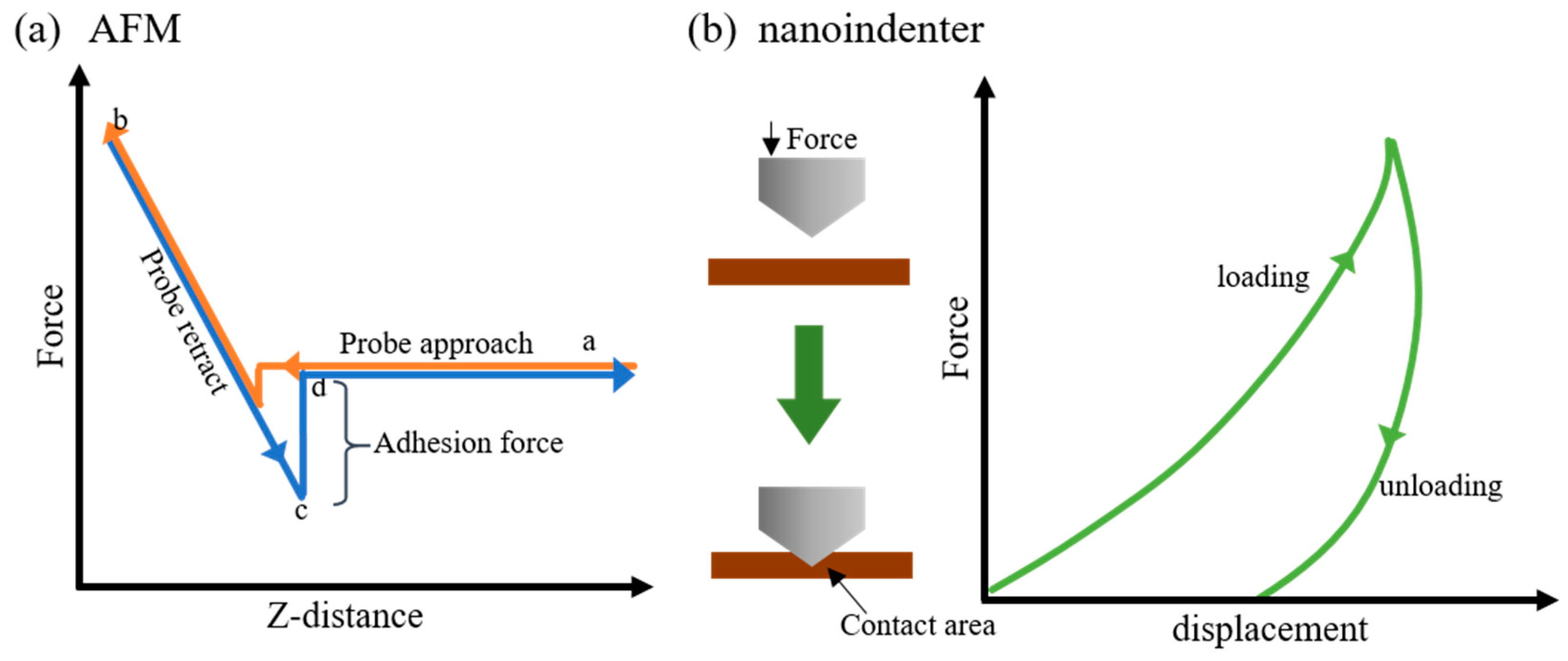
2.3. Instrumentation
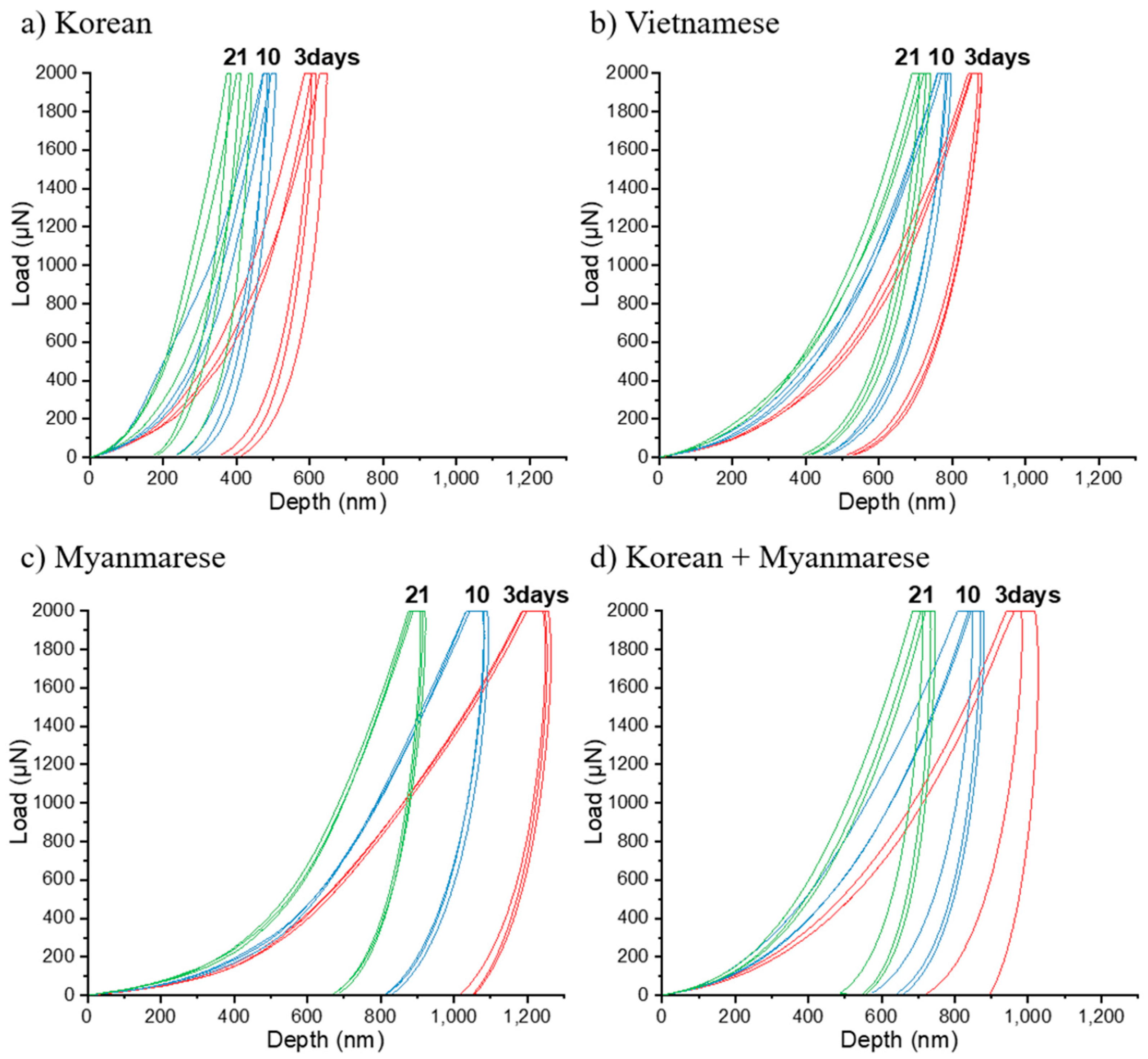
3. Results and Discussion
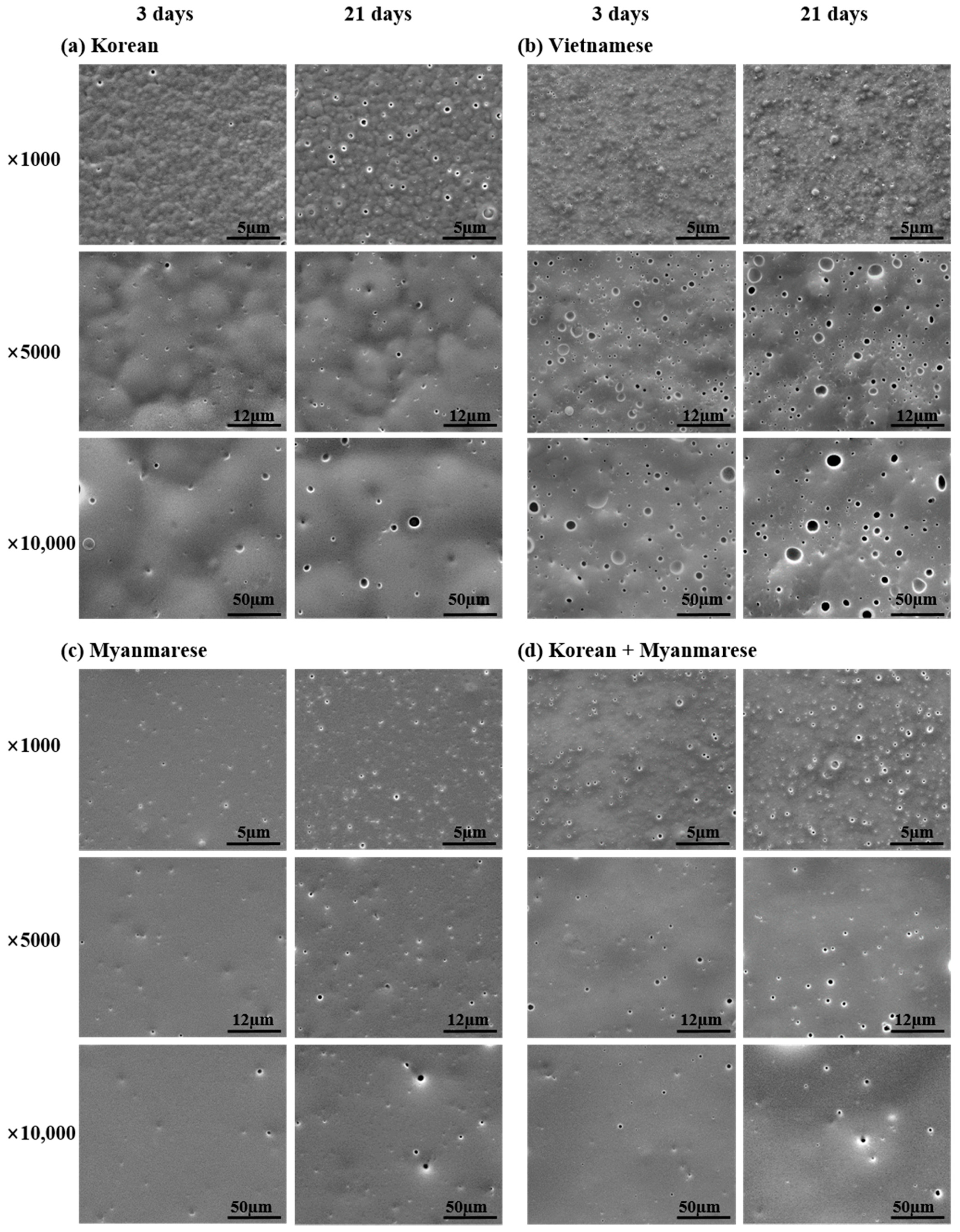
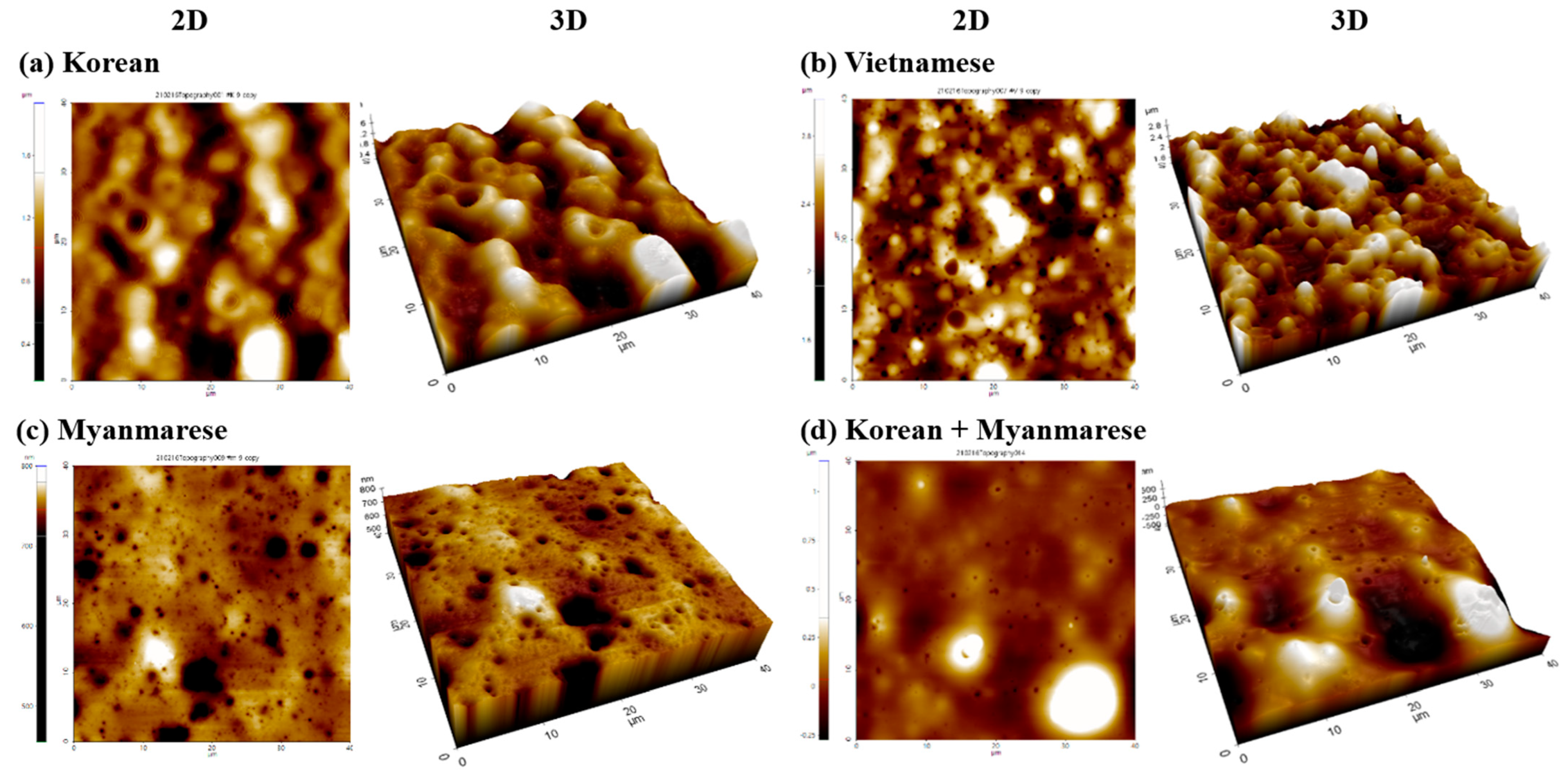
3.1. Surface Images
3.2. Traditional Methods for Physical Properties
3.3. Accurate Measurements of Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, R.; Miyakoshi, T. Lacquer Chemistry and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Yoshida, T.; Miyakoshi, T. Oriental lacquer: A natural polymer. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 153–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanotani, J. Urushi (Oriental lacquer)—A natural aesthetic durable and future-promising coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 1995, 26, 163–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimura, N.; Miyakoshi, T. Characterization of natural resin films and identification of ancient coating. J. Mass Spectrom. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 51, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.M. An overview of Oriental lacquer: Art and chemistry of the original high-tech coating. J. Chem. Educ. 1989, 66, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harigaya, S.; Honda, T.; Rong, L.; Miyakoshi, T.; Chen, C.-L. Enzymatic Dehydrogenative Polymerization of Urushiols in Fresh Exudates from the Lacquer Tree, Rhus Vernicifera DC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urushi Proceedings of the Urushi Study Group; Brommelle, N.S.; Smith, P. (Eds.) Getty Conservation Institute: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Vogl, O. Oriental lacquer, poison ivy, and drying oils. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2000, 38, 4327–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, K.T.; Baik, S.K.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.M.; Paeng, K.J.; Uh, Y.; Jang, I.H.; Cho, M.Y.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, M.J.; et al. Anti-bacterial effects of the urushiol component in the sap of the lacquer tree (Rhus verniciflua Stokes) on Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Heo, J.; Son, B.; Choi, D.; Park, T.H.; Chang, M.; Hong, J. Intrinsic hydrophobic cairnlike multilayer films for antibacterial effect with enhanced durability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26117–26123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niimura, N. Determination of the type of lacquer on East Asian lacquer ware. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 284, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Oda, K.; Oyabu, H.; Asami, T. Urushi—The Science and Practice; Rikou Publisher: Tokyo, Japan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Frade, J.C.; Ribeiro, M.I.; Graça, J.; Rodrigues, J. Applying pyrolysis–gas chromatography/mass spectrometry to the identification of Oriental lacquers: Study of two lacquered shields. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsukagoshi, M.; Kitahara, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Fujii, T. Pyrolysis analysis of Japanese lacquer films: Direct probe-Li+ ion attachment mass spectrometry versus pyrolysis/gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 95, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hô, A.L.; Regert, M.; Marescot, O.; Duhamel, C.; Langlois, J.; Miyakoshi, T.; Genty, C.; Sablier, M. Molecular criteria for discriminating museum Asian lacquerware from different vegetal origins by pyrolysis gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 710, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Jung, S.-B.; Terlier, T.; Lee, K.-B.; Lee, Y. Molecular identification of Asian lacquers from different trees using Py–GC/MS and ToF–SIMS. Surf. Interface Anal. 2018, 50, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Lim, J.-A.; Ham, S.W.; Lee, K.-B.; Lee, Y. Quantitative analysis of blended Asian lacquers using ToF–SIMS, Py–GC/MS and HPLC. Polymers 2021, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Hariygaya, S.; Ishimura, T.; Nagase, K.; Miyakoshi, T. Development of a fast drying lacquer based on raw lacquer sap. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 51, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Lu, L.; Phuc, B.T. Investigation and development on processing of Vietnamese lacquer. Adv. Biol. Chem. 2014, 4, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niimura, N. Structural study of a Japanese lacquer film with thermogravimetry-linked scan mass spectrometry. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2012, 17, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, N.; Zhu, J.; Cai, J.; Deng, J.; Pan, F.; Gao, L.; Jiang, Z.; Shen, F. Polymerization mechanism of natural lacquer sap with special phase structure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.; Lu, R.; Miyakoshi, T.; Jung, J. Thermal polymerization mechanism of thitsiol separated from Gluta usitata. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2017, 22, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimura, N.; Iijima, Y.; Miyakoshi, T. Hardening process and surface structure of lacquer films studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Surf. Interface Anal. 1996, 24, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.C. A study on application of enzyme additives to improve drying speed of Urushi lacquer. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 326–344. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-W.; Lee, J.-J.; Lu, K.-T. The effects of adding different HALS on the curing process, film properties and light-fastness of refined Oriental lacquer. Polymers 2020, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, C.; Okahisa, Y.; Yamada, K. Plasticizing effect of lignin on urushi in bio-composite films. Polymer 2019, 161, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royall, C.P.; Donald, A.M. Surface properties and structural collapse of silica in matte water-based lacquers. Langmuir 2002, 18, 9519–9526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Guo, K.; Bian, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Sun, J. Durable and room-temperature curable superhydrophobic composite coating on nitrocellulose lacquer. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 328, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Liang, M.; Chen, X.; Long, G. A fractal model for kozeny–carman constant and dimensionless permeability of fibrous porous media with toughened surfaces. Fractals 2019, 27, 1950116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Long, G. A fractal model for capillary flow through a single tortuous capillary with roughened surfaces in fibrous porous media. Fractals 2021, 29, 2150017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.; Lee, H.-L.; Lu, K.-T. Manufacture and characteristics of oil-modified refined lacquer for wood coatings. Coatings 2019, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, T.; Lu, R.; Sakai, R.; Ishimura, T.; Miyakoshi, T. Characterization and comparison of Asian lacquer saps. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 61, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, K.; Lu, R.; Phuc, B.T.; Miyakoshi, T. Development and characterization of laccol lacquer blended with urushiol lacquer. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Chem. 2014, 19, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domene-López, D.; García-Quesada, J.C.; Martín-Gullón, I. A correlation between the wolf-wilburn scale and atomic force microscopy for anti-scratch resistance determination. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 125, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H.; Kim, H.-J. Curing behaviors of Korean Dendropanax lacquer determined by chemical and physical measures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Ishimura, T.; Tsutida, K.; Honda, T.; Miyakoshi, T. Development of a fast drying hybrid lacquer in a low-relative-humidity environment based on kurome lacquer sap. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 2409: 2020. Paints and Varnishes—Cross-Cut Test; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample (25 °C, 85% RH) | Drying Time (Days) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 21 | 28 | |||||
| Rrms (nm) | Ra (nm) | Rrms (nm) | Ra (nm) | Rrms (nm) | Ra (nm) | Rrms (nm) | Ra (nm) | |
| Korean (K) | 267.08 | 211.80 | 247.83 | 201.25 | 242.29 | 188.11 | 224.26 | 180.17 |
| Vietnamese | 331.37 | 262.31 | 254.14 | 206.00 | 197.46 | 155.52 | 262.84 | 200.86 |
| Myanmarese (M) | 13.12 | 7.51 | 16.10 | 9.24 | 17.32 | 9.98 | 17.40 | 10.56 |
| Mixed (K + M) 1 | 104.49 | 77.96 | 62.74 | 46.80 | 122.97 | 77.79 | 112.08 | 87.32 |
| Sample (25 °C, 85% RH) | Drying Time | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 h | 5 h | 8 h | 10 h | 16 h | 20 h | 24 h | 36 h | 48 h | 3 d | 7 d | 14 d | |
| Korean (K) | DF * | DF | DF | TF |  | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD |
| Vietnamese | DF | DF | DF | DF | DF | DF | DF | TF |  | HD | HD | HD |
| Myanmarese (M) | DF | DF | DF | DF | DF | TF |  | |||||
| Mixed (K + M) | DF | DF | TF |  | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | ||
| Sample (25 °C, 85% RH) | Drying Time (Days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 21 | 28 | |
| Pencil hardness | ||||
| Korean (K) | 3H | 3H | 4H | 3H |
| Vietnamese | 2B | F | 4H | 4H |
| Myanmarese (M) | 4B | B | 2B | 4B |
| Mixed (K + M) | B | 3H | H | 3H |
| Sample (25 °C, 85% RH) | Drying Time (Days) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 10 | |
| Cross-cut test/glass slide | |||
| Korean (K) | 1B | 0B | 0B |
| Myanmarese (M) | 0B | 0B | 0B |
| Mixed (K + M) | 0B | 0B | 0B |
| Cross-cut test/stainless steel | |||
| Korean (K) | 3B | 4B | 4B |
| Myanmarese (M) | 0B | 0B | 0B |
| Mixed (K + M) | 1B | 2B | 2B |
| Sample (25 °C, 85% RH) | Drying Time (Days) | |
|---|---|---|
| 28 | 60 | |
| Adhesion energy (N/m) | ||
| Korean (K) | 9.41 | 8.62 |
| Vietnamese | 5.19 | 4.70 |
| Myanmarese (M) | 6.96 | 2.74 |
| Sample (25 °C, 85% RH) | Drying Time (Days) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 21 | |
| Adhesion energy (J × 1015) (±SD) | |||
| Korean (K) | 14.7 (±6.9) | 8.2 (±3.6) | 5.2 (±1.1) |
| Vietnamese | 45.2 (±19.9) | 36.1 (±16.7) | 12.8 (±5.9) |
| Myanmarese (M) | 1662.1 (±225.4) | 531.8 (±73.6) | 17.0 (±5.8) |
| Mixed (K + M) | 29.9 (±8.0) | 24.3 (±7.3) | 1.9 (±0.4) |
| Young’s modulus (GPa) (±SD) | |||
| Korean (K) | 236.6 (±66.8) | 348.1 (±42.6) | 496.2 (±60.6) |
| Vietnamese | 141.6 (±38.2) | 187.9 (±43.4) | 336.2 (±55.3) |
| Myanmarese (M) | 16.3 (±1.0) | 27.0 (±3.0) | 283.0 (±56.7) |
| Mixed (K + M) | 198.7 (±28.8) | 175.9 (±39.0) | 679.3 (±79.5) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.H.; Lim, J.-A.; Lee, K.-B.; Lee, Y. Improved Measurements of the Physical Properties of Oriental Lacquers Using Atomic Force Microscopy and a Nanoindenter. Polymers 2021, 13, 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091395
Yu HH, Lim J-A, Lee K-B, Lee Y. Improved Measurements of the Physical Properties of Oriental Lacquers Using Atomic Force Microscopy and a Nanoindenter. Polymers. 2021; 13(9):1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091395
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hye Hyun, Jung-Ah Lim, Kang-Bong Lee, and Yeonhee Lee. 2021. "Improved Measurements of the Physical Properties of Oriental Lacquers Using Atomic Force Microscopy and a Nanoindenter" Polymers 13, no. 9: 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091395
APA StyleYu, H. H., Lim, J.-A., Lee, K.-B., & Lee, Y. (2021). Improved Measurements of the Physical Properties of Oriental Lacquers Using Atomic Force Microscopy and a Nanoindenter. Polymers, 13(9), 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091395