3-O-Ethyl-L-Ascorbic Acid Doped Enteric-Coated Gelatin Capsules towards the Advanced Oral Curcumin Delivery for Cancers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
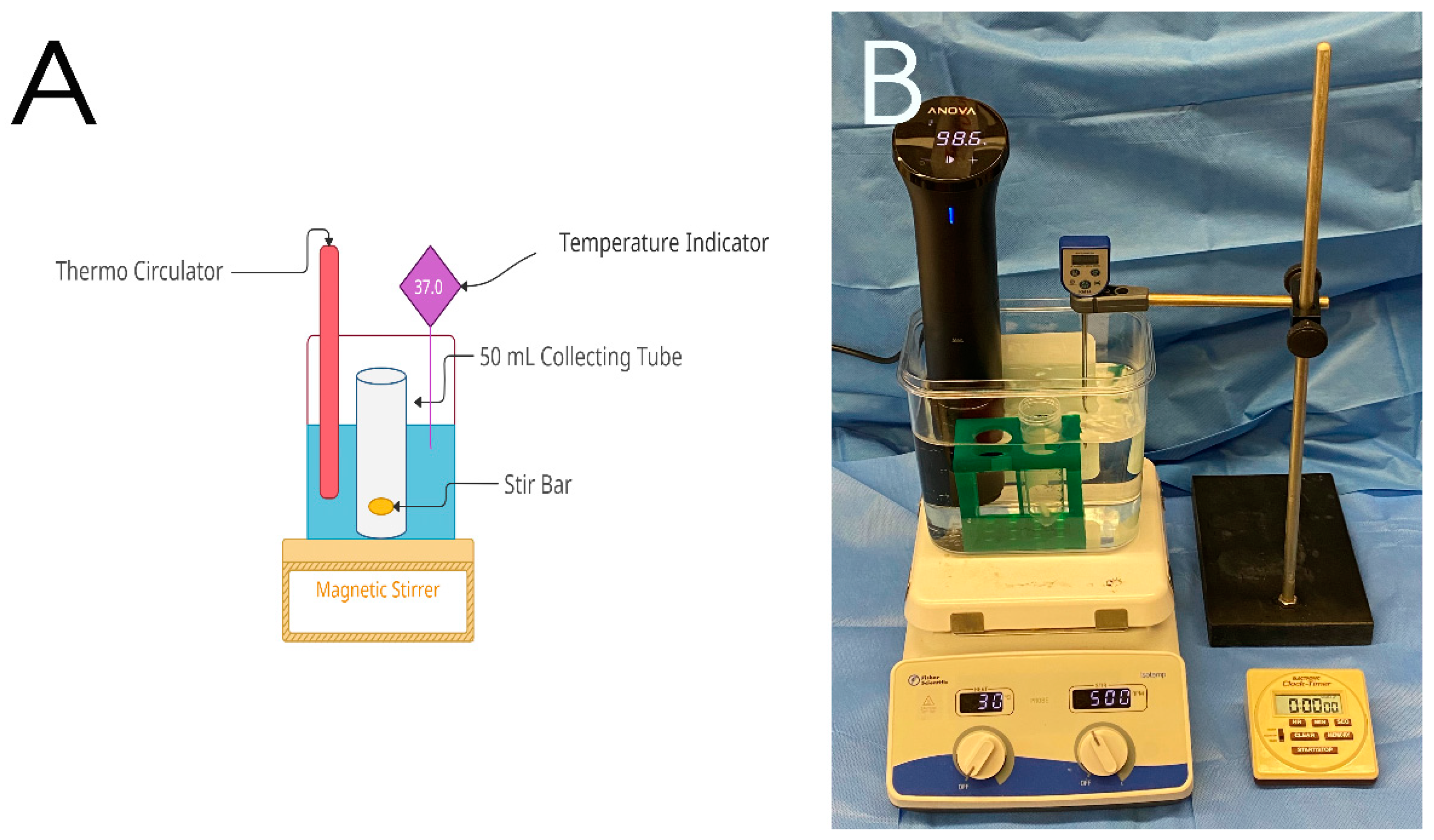
2.2. Coating Procedures
2.3. In-Vitro Release of Curcumin
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
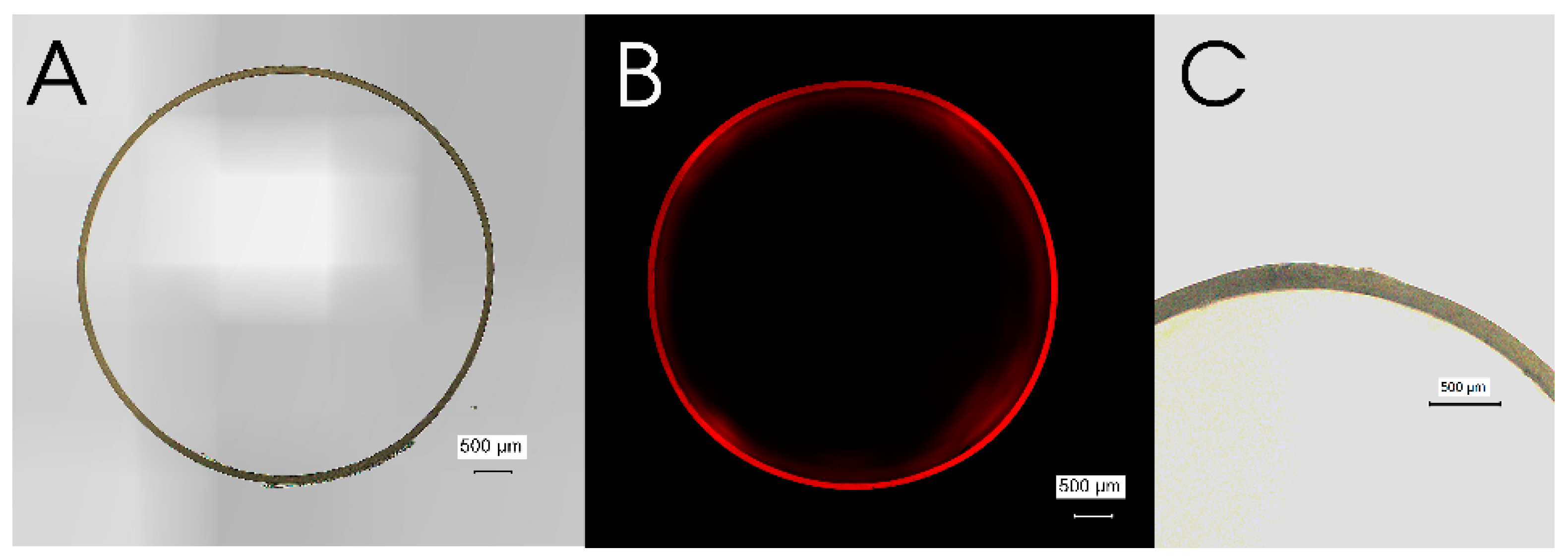
3.1. Microscopic Characterization of Pristine Gelatin Capsule
3.2. Microscopic Characterization of EA Doped Enteric-Coated Gelatin Capsule
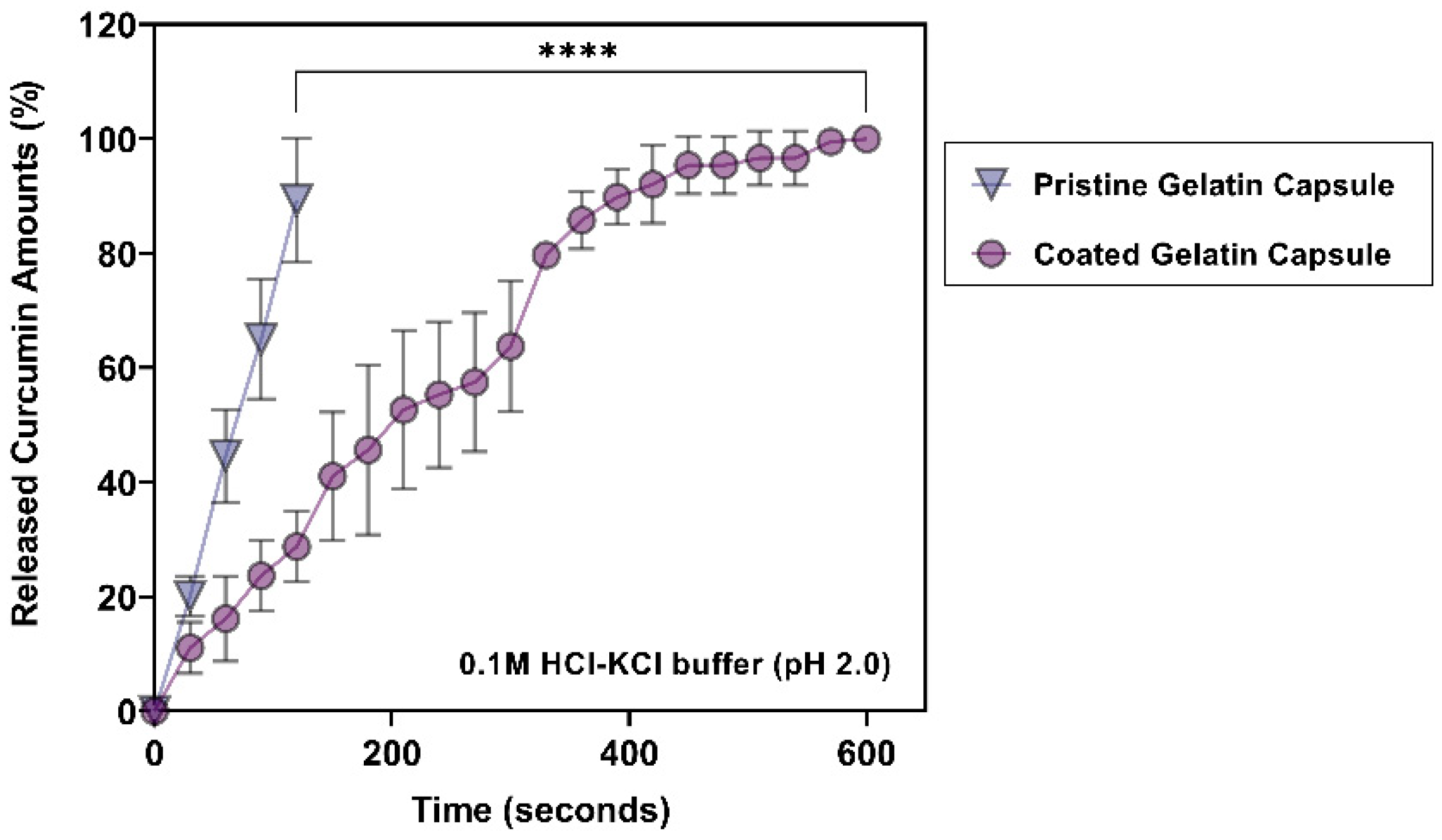
3.3. Release Profiles of Curcumin at Gastric pH (pH 2.0)
3.4. Release Profiles of Curcumin at pH 5.0
3.5. Release Profiles of Curcumin at pH 6.0
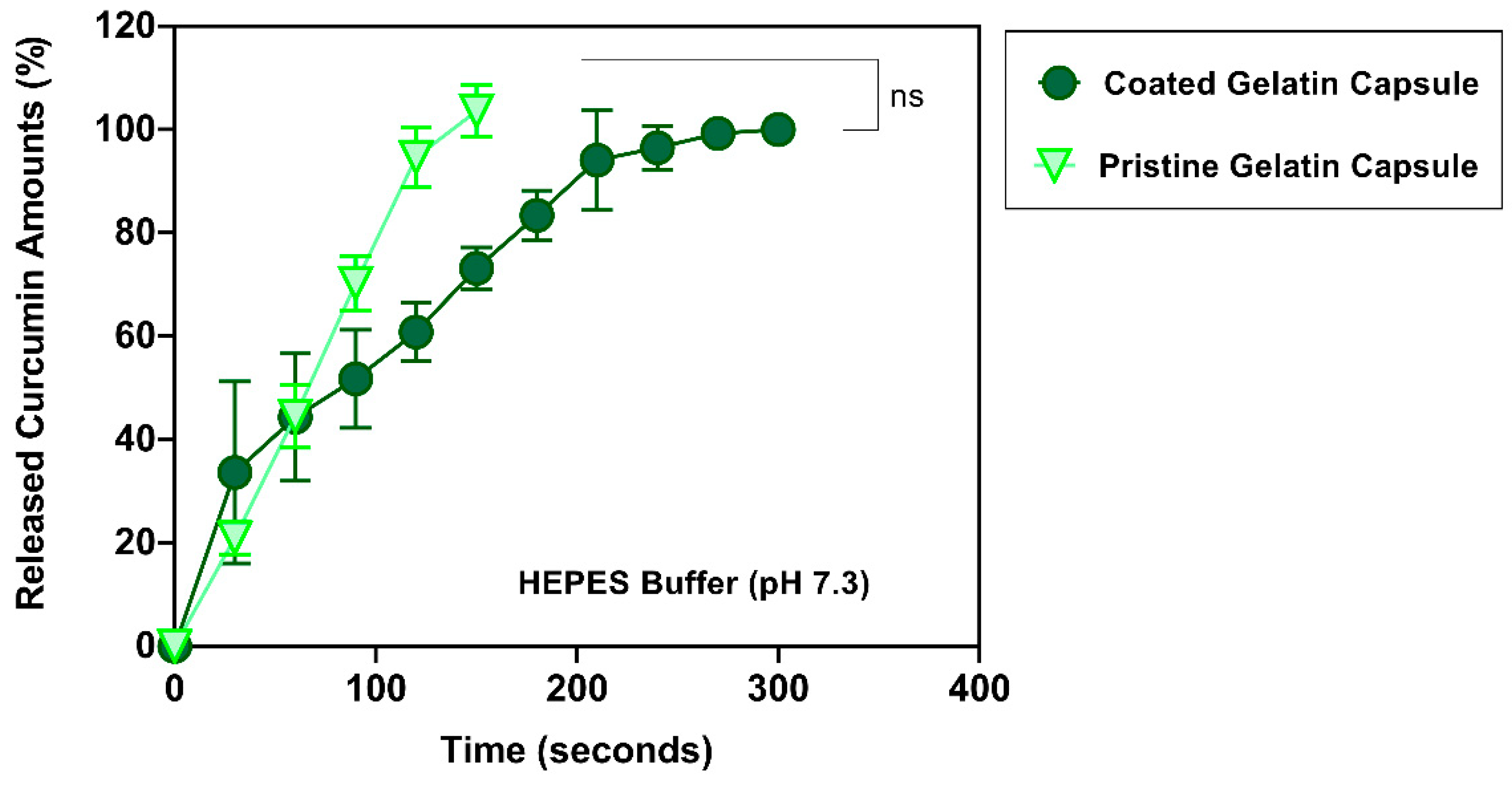
3.6. Release Profiles of Curcumin at pH 7.3
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sundaram, C.; Malani, N.; Ichikawa, H. Curcumin: The Indian solid gold. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 595, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindarajan, V.S. Turmeric—Chemistry, technology, and quality. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1980, 12, 199–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Huebbe, P.; Ernst, I.M.A.; Chin, D.; Wagner, A.E.; Rimbach, G. Curcumin—From Molecule to Biological Function. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5308–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yang, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, S.; Lee, O.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, M.J. Korean turmeric is effective for dyslipidemia in human intervention study. J. Ethn. Foods 2016, 3, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schraufstatter, E.; Bernt, H. Antibacterial action of curcumin and related compounds. Nature 1949, 164, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.; See, P.; Lee, S.T.; Chan, S.Y. Protective effects of curcumin against oxidative damage on skin cells in vitro: Its implication for wound healing. J. Trauma 2001, 51, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakrishnan, V.; Viswanathan, P.; Rajasekharan, K.N.; Menon, V.P. Neuroprotective role of curcumin from curcuma longa on ethanol-induced brain damage. Phytother. Res. PTR 1999, 13, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aziz, M.T.; El-Asmar, M.F.; El Nadi, E.G.; Wassef, M.A.; Ahmed, H.H.; Rashed, L.A.; Obaia, E.M.; Sabry, D.; Hassouna, A.A.; Abdel Aziz, A.T. The effect of curcumin on insulin release in rat-isolated pancreatic islets. Angiology 2010, 61, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, V.Y.; Foshaug, R.R.; MacFarlane, S.M.; Churchill, T.A.; Doyle, J.S.; Sydora, B.C.; Fedorak, R.N. Oral administration of curcumin emulsified in carboxymethyl cellulose has a potent anti-inflammatory effect in the IL-10 gene-deficient mouse model of IBD. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Beevers, C.S.; Huang, S. The targets of curcumin. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Tommonaro, G. Curcumin and Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: Globocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.J.; Mamtani, R.; Bange, E.M. Immunotherapy Adverse Effects. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahreddine, H.; Borden, K. Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenwell, M.; Rahman, P.K. Medicinal Plants: Their Use in Anticancer Treatment. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 6, 4103–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devassy, J.G.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Jones, P.J.H. Curcumin and cancer: Barriers to obtaining a health claim. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, N.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Newman, R.A.; Wolff, R.A.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Ng, C.S.; Badmaev, V.; Kurzrock, R. Phase II Trial of Curcumin in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lao, C.D.; Ruffin, M.T.; Normolle, D.; Heath, D.D.; Murray, S.I.; Bailey, J.M.; Boggs, M.E.; Crowell, J.; Rock, C.L.; Brenner, D.E. Dose escalation of a curcuminoid formulation. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2006, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, A.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, J.K.; Hsu, M.M.; Ho, Y.F.; Shen, T.S.; Ko, J.Y.; Lin, J.T.; Lin, B.R.; Ming-Shiang, W.; et al. Phase I clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer. Res. 2001, 21, 2895–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Sanidad, K.Z.; Sukamtoh, E.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J.; Zhang, G. Curcumin: Recent Advances in the Development of Strategies to Improve Oral Bioavailability. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Udeni Gunathilake, T.M.S.; Ching, Y.C.; Chuah, C.H. Enhancement of Curcumin Bioavailability Using Nanocellulose Reinforced Chitosan Hydrogel. Polymers 2017, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Senanayake, T.H.; Bohling, A.; Vinogradov, S.V. Targeted Nanogel Conjugate for Improved Stability and Cellular Permeability of Curcumin: Synthesis, Pharmacokinetics, and Tumor Growth Inhibition. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, M.; Guo, C.; Yu, A.; Cao, F.; Zhao, L.; Tan, Q.; Zhai, G. N-trimethyl chitosan chloride-coated liposomes for the oral delivery of curcumin. J. Liposome Res. 2012, 22, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuchapreeda, S.; Fukumori, Y.; Okonogi, S.; Ichikawa, H. Preparation of Lipid Nanoemulsions Incorporating Curcumin for Cancer Therapy. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2012, 270383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marefati, A.; Bertrand, M.; Sjöö, M.; Dejmek, P.; Rayner, M. Storage and digestion stability of encapsulated curcumin in emulsions based on starch granule Pickering stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Kaplan, D.L.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Oral Delivery of Curcumin Using Silk Nano- and Microparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3885–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; Reverchon, E.; De Marco, I. Zein/diclofenac sodium coprecipitation at micrometric and nanometric range by supercritical antisolvent processing. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 27, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlang, B.; Pawar, Y.B.; Bansal, A.K. Identification of permeability-related hurdles in oral delivery of curcumin using the Caco-2 cell model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, R.; Karki, R.; Chandrashekarappa, J.; Santhanam, M.; Shankar, A.K.K.; Joshi, H.K.; Divakar, G. Enhanced Water Dispersibility of Curcumin Encapsulated in Alginate-Polysorbate 80 Nano Particles and Bioavailability in Healthy Human Volunteers. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2019, 7, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, P.V.; Bhingare, C.L.; Nikam, R.Y.; Pawar, S.A. Development and validation of UV Spectrophotometric method for the estimation of Curcumin in cream formulation. Pharm. Methods 2013, 4, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, S.; Grove, D.; Lindberg, K.A.; Reynolds, G.; Sivarajah, A.; Pinnell, S.R. Regulation of collagen synthesis by ascorbic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 2879–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebouche, C.J. Ascorbic acid and carnitine biosynthesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 1147s–1152s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.M.; Qu, Z.C.; Meredith, M.E. Mechanisms of ascorbic acid stimulation of norepinephrine synthesis in neuronal cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levine, M.; Rumsey, S.C.; Daruwala, R.; Park, J.B.; Wang, Y. Criteria and Recommendations for Vitamin C Intake. JAMA 1999, 281, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padayatty, S.J.; Katz, A.; Wang, Y.; Eck, P.; Kwon, O.; Lee, J.H.; Chen, S.; Corpe, C.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.K.; et al. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: Evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, C.I.; Zúñiga, F.A.; Salas-Burgos, A.; Mardones, L.; Ormazabal, V.; Vera, J.C. Vitamin C transporters. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 64, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc, C.W. Cancer: The preconditioning factor in pathogenesis; a new etiologic approach. Arch. Pediatrics 1954, 71, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Roa, F.J.; Peña, E.; Gatica, M.; Escobar-Acuña, K.; Saavedra, P.; Maldonado, M.; Cuevas, M.E.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Rivas, C.I.; Muñoz-Montesino, C. Therapeutic Use of Vitamin C in Cancer: Physiological Considerations. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Labuza, T.P. Destruction of ascorbic acid as a function of water activity. J. Food Sci. 1975, 40, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, T.; Matsuda, K.; Shouji, H. Improvement in site-specific intestinal absorption of furosemide by Eudragit L100-55. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gousous, J.; Tsume, Y.; Fu, M.; Salem, I.I.; Langguth, P. Unpredictable Performance of pH-Dependent Coatings Accentuates the Need for Improved Predictive in Vitro Test Systems. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4209–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziolek, M.; Grimm, M.; Becker, D.; Iordanov, V.; Zou, H.; Shimizu, J.; Wanke, C.; Garbacz, G.; Weitschies, W. Investigation of pH and Temperature Profiles in the GI Tract of Fasted Human Subjects Using the Intellicap(®) System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KAUNITZ, J.D.; AKIBA, Y. Review article: Duodenal bicarbonate—mucosal protection, luminal chemosensing and acid–base balance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovesen, L.; Bendtsen, F.; Tage-Jensen, U.; Pedersen, N.T.; Gram, B.R.; Rune, S.J. Intraluminal pH in the stomach, duodenum, and proximal jejunum in normal subjects and patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Gastroenterology 1986, 90, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Basit, A.W. A paradigm shift in enteric coating: Achieving rapid release in the proximal small intestine of man. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2010, 147, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, K.; Kalantzis, C.; Papadopoulos, A.A.; Apostolopoulos, P.; Rokkas, T.; Kalantzis, N.; Ladas, S.D. Video-capsule endoscopy gastric and small bowel transit time and completeness of the examination in patients with diabetes mellitus. Dig. Liver Dis. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Gastroenterol. Ital. Assoc. Study Liver 2007, 39, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusev, P.A.; Andrews, K.W.; Savarala, S.; Tey, P.-T.; Han, F.; Oh, L.; Pehrsson, P.R.; Dwyer, J.T.; Betz, J.M.; Kuszak, A.J.; et al. Disintegration and Dissolution Testing of Green Tea Dietary Supplements: Application and Evaluation of United States Pharmacopeial Standards. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glube, N.; Moos, L.V.; Duchateau, G. Capsule shell material impacts the in vitro disintegration and dissolution behaviour of a green tea extract. Results Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, W.; Omar, T.; Patel, H.; Rodriguez, D.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Pasinetti, G.M.; Murrough, J.W.; Muzzio, F.J.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Dissolution Study on Grape Polyphenol Hard Gelatin Capsule Dietary Supplements. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 780260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, D.-J. 3-O-Ethyl-L-Ascorbic Acid Doped Enteric-Coated Gelatin Capsules towards the Advanced Oral Curcumin Delivery for Cancers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112207
Lim D-J. 3-O-Ethyl-L-Ascorbic Acid Doped Enteric-Coated Gelatin Capsules towards the Advanced Oral Curcumin Delivery for Cancers. Polymers. 2022; 14(11):2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112207
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Dong-Jin. 2022. "3-O-Ethyl-L-Ascorbic Acid Doped Enteric-Coated Gelatin Capsules towards the Advanced Oral Curcumin Delivery for Cancers" Polymers 14, no. 11: 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112207
APA StyleLim, D.-J. (2022). 3-O-Ethyl-L-Ascorbic Acid Doped Enteric-Coated Gelatin Capsules towards the Advanced Oral Curcumin Delivery for Cancers. Polymers, 14(11), 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112207




