Effect of Transglutaminase Pre-Crosslinking Treatment Incorporated with Glucono-δ-lactone on the Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Tofu
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
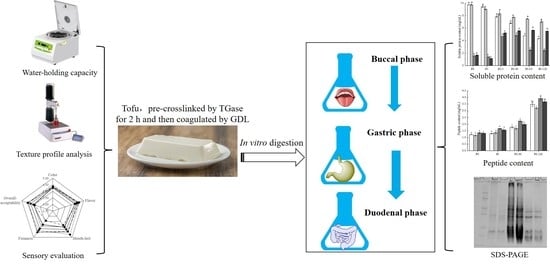
2.2. Soymilk and Tofu Preparation
2.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurement
2.4. Determination of Gelation Properties
2.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.6. In vitro digestion
2.7. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.8. Total Soluble Protein Content Measurement
2.9. Peptide Content Measurement
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Average Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
3.2. Electrophoresis of Soymilk Samples Treated by TGase Combined with GDL or Not
3.3. The WHC and Gel Strength
3.4. Sensory Evaluation
3.5. Protein Degradation
3.6. Bioaccessible Peptides
3.7. SDS-PAGE Profiles of Digesta
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jun, J.Y.; Jung, M.J.; Jeong, I.H.; Kim, G.W.; Sim, J.M.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, B.M. Effects of crab shell extract as a coagulant on the textural and sensorial properties of tofu (soybean curd). Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Tofu products: A review of their raw materials, processing conditions, and packaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3683–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.H.; Li, X.J.; Luo, S.Z.; Mu, D.D.; Zhong, X.Y.; Jiang, S.T.; Zheng, J.Z.; Zhao, Y.Y. Effects of organic acid coagulants on the physical properties of and chemical interactions in tofu. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 2017, 85, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, F.; Yang, B.; Lai, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, K.; Bu, G.; Fu, C.; Deng, Y. Preparation of organic tofu using organic compatible magnesium chloride incorporated with polysaccharide coagulants. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.H.; Li, L.; Wang, J.L.; Yang, X.Q. Formation and rheological properties of ‘cold-set’ tofu induced by microbial transglutaminase. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 2007, 40, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Cao, F.H.; Li, X.J.; Mu, D.D.; Zhong, X.Y.; Jiang, S.T.; Zheng, Z.; Luo, S.Z. Effects of different salts on the gelation behaviour and mechanical properties of citric acid-induced tofu. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, L. A new style of fermented tofu by Lactobacillus casei combined with salt coagulant. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Zare, F.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M. A comparison study of bioaccessibility of soy protein gel induced by magnesiumchloride, glucono-δ-lactone and microbial transglutaminase. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 2016, 71, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Rioux, L.E.; Britten, M.; Turgeon, S.L. In vitro bioaccessibility of peptides and amino acids from yogurt made with starch, pectin, or β-glucan. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 46, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Rui, X.; Dong, M.; Mariniello, L. Microbial transglutaminase-mediated polymerization in the presence of lactic acid bacteria affects antigenicity of soy protein component present in bio-tofu. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 53, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Guo, S. Texture characteristics of soymilk gels formed by lactic fermentation: A comparison of soymilk prepared by blanching soybeans under different temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Xing, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zare, F.; Li, W.; Dong, M. Protein bioaccessibility of soymilk and soymilk curd prepared with two Lactobacillus plantarum strains as assessed by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2016, 38, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Rui, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Dong, M. Effect of fermentation pH on protein bioaccessibility of soymilk curd with added tea polyphenols as assessed by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 11125–11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Azarpazhooh, E.; Simpson, B.K.; Rui, X. Effects of different satiety levels on the fate of soymilk protein in gastrointestinal digestion and antigenicity assessed by an in vitro dynamic gastrointestinal model. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7855–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Shih, T.W.; Chiu, C.P.; Pan, T.M.; Tsai, T.Y. Effects of lactic acid bacteria-fermented soy milk on melanogenesis in B16F0 melanocytes. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Fusco, A.; Al-Asmar, A.; Mariniello, L. Microbial transglutaminase as a tool to improve the features of hydrocolloid-based bioplastics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Zhao, X.H. Modified properties of a glycated and cross-linked soy protein isolate by transglutaminase and an oligochitosan of 5 kDa. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2017, 97, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, H.; Shen, X. Effect of ultrasound pretreatment on structural, physicochemical, rheological and gelation properties of transglutaminase cross-linked whey protein soluble aggregates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 74, 105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Soy protein isolates: A review of their composition, aggregation, and gelation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.F.; Yu, C.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Chen, S.T.; Tsai, H.Y. Microbial transglutaminase-induced polymerization of β-conglycinin and glycinin in soymilk: A proteomics approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Hu, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Ball-milling changed the physicochemical properties of SPI and its cold-set gels. J. Food Eng. 2017, 195, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, K.; Liu, S.; Adhikari, B.; Chen, J. Improvement of gelation properties of soy protein isolate emulsion induced by calcium cooperated with magnesium. J. Food Eng. 2019, 244, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Liu, S.; Miao, S.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Effects of transglutaminase pre-crosslinking on salt-induced gelation of soy protein isolate emulsion. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringgenberg, E.; Alexander, M.; Corredig, M. Effect of concentration and incubation temperature on the acid induced aggregation of soymilk. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Carpentieri, A.; Pasquino, R.; Dong, M.; Mariniello, L. Gelling behavior of bio-tofu coagulated by microbial transglutaminase combined with lactic acid bacteria. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonaro, M.; Maselli, P.; Nucara, A. Structural aspects of legume proteins and nutraceutical properties. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.F.; Yu, C.J.; Tsai, T.Y. Proteomic profiling of the coagulation of soymilk proteins induced by magnesium chloride. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, A.; Dave, A.; Singh, H. In vitro digestion of soymilk using a human gastric simulator: Impact of structural changes on kinetics of release of proteins and lipids. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ritzoulis, C.; Han, J.; Han, F.; Jin, W.; Liu, W. Particle degradation and nutrient bioavailability of soybean milk during in vitro digestion. Food Biophys. 2021, 16, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Time | Zeta Potential (mV) | Average Size (d/nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 h | −26.5 ± 0.7 a | 362.9 ± 3.2 d |
| 0.5 h | −33.7 ± 0.8 b | 442.2 ± 5.1 c |
| 1 h | −36.4 ± 1.7 b,c | 474.4 ± 26.1 c |
| 2 h | −37.9 ± 1.0 c | 547.3 ± 19.6 b |
| 3 h | −38.9 ± 3.4 c | 581.8 ± 12.0 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hui, T.; Xing, G. Effect of Transglutaminase Pre-Crosslinking Treatment Incorporated with Glucono-δ-lactone on the Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Tofu. Polymers 2022, 14, 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122364
Hui T, Xing G. Effect of Transglutaminase Pre-Crosslinking Treatment Incorporated with Glucono-δ-lactone on the Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Tofu. Polymers. 2022; 14(12):2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122364
Chicago/Turabian StyleHui, Tianran, and Guangliang Xing. 2022. "Effect of Transglutaminase Pre-Crosslinking Treatment Incorporated with Glucono-δ-lactone on the Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Tofu" Polymers 14, no. 12: 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122364
APA StyleHui, T., & Xing, G. (2022). Effect of Transglutaminase Pre-Crosslinking Treatment Incorporated with Glucono-δ-lactone on the Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Tofu. Polymers, 14(12), 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122364