Utilization of Sulfonated Waste Polystyrene-Based Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanocomposites for Efficient Degradation of Calcon Dye
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Purification of Waste Polystyrene (WPS)
2.4. Synthesis of Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticle (CoFe2O4 MNp)
2.5. Synthesis of Sulfonated Waste Polystyrene (SWPS)
2.6. Synthesis of SWPS-Based Polymeric Magnetic Nanoparticle (SWPS/MNp)
2.7. Preparation of Calcon Dye Stock Solution
3. Result and Discussions
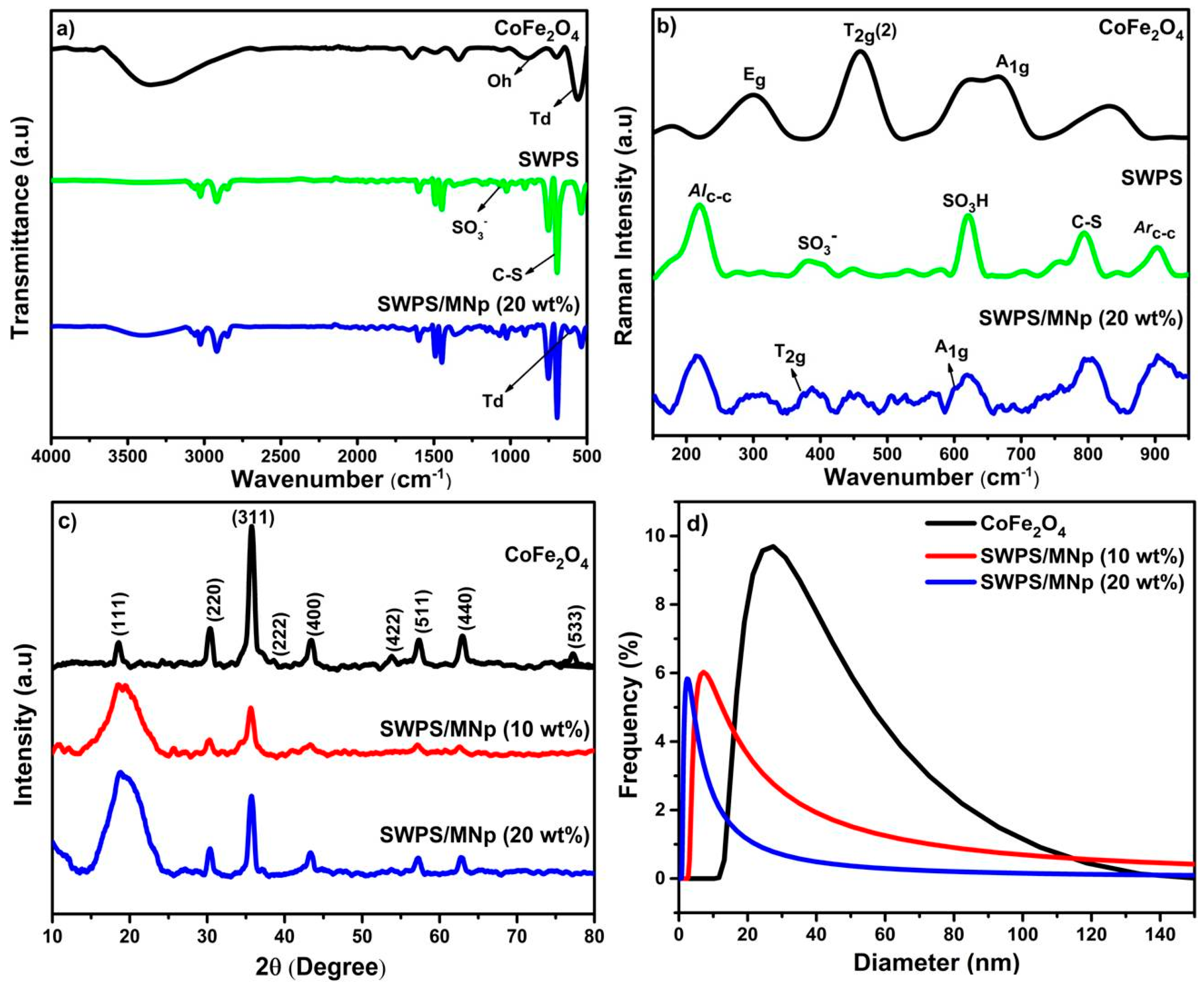
3.1. Synthesis of Polymeric Magnetic Nanoparticles (SWPS/MNp)
3.2. Structural Evaluation of SWPS
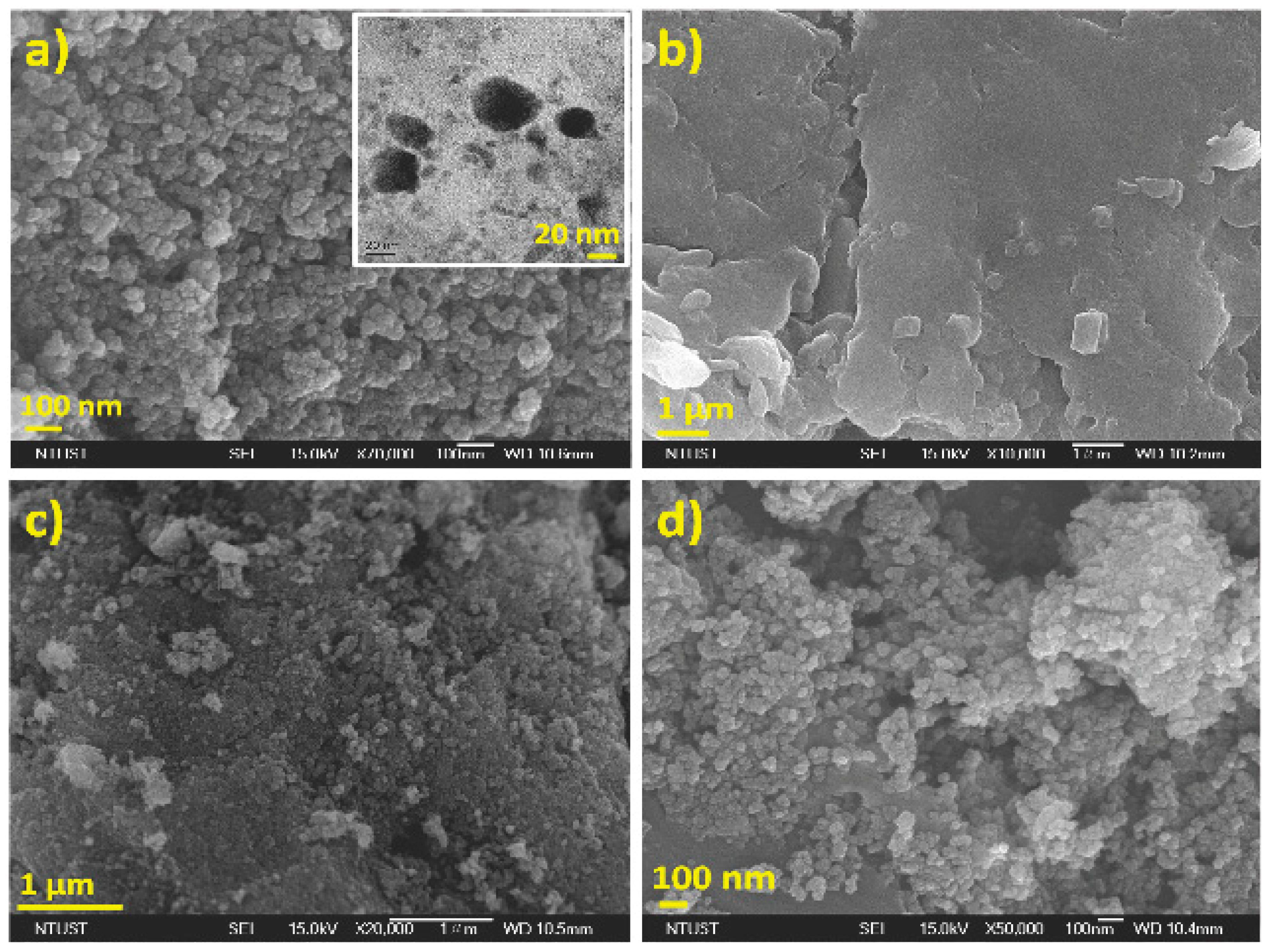
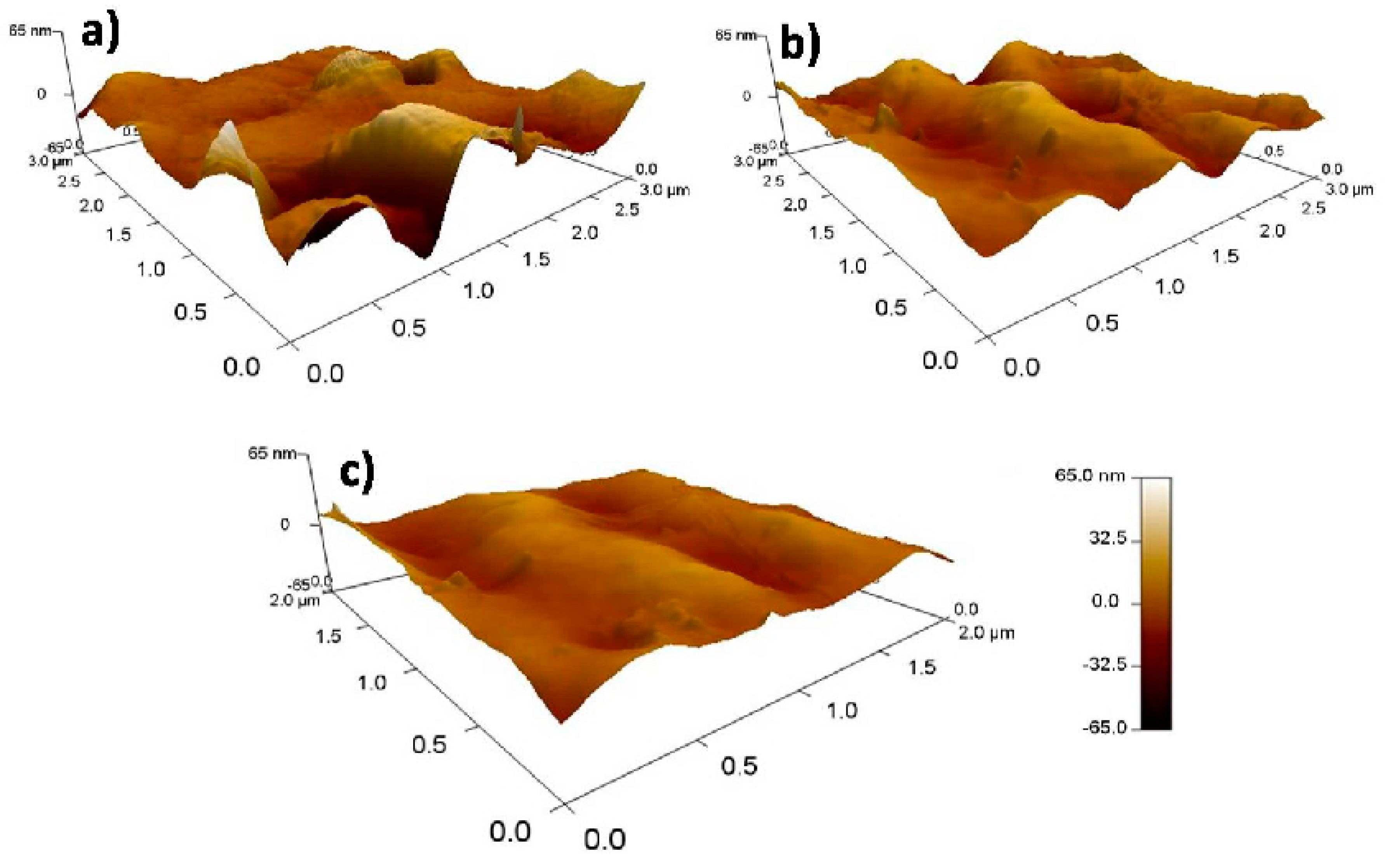
3.3. Particle Size and Morphological Studies
3.4. Thermal Stability
3.5. Determination of Band Gap Energy
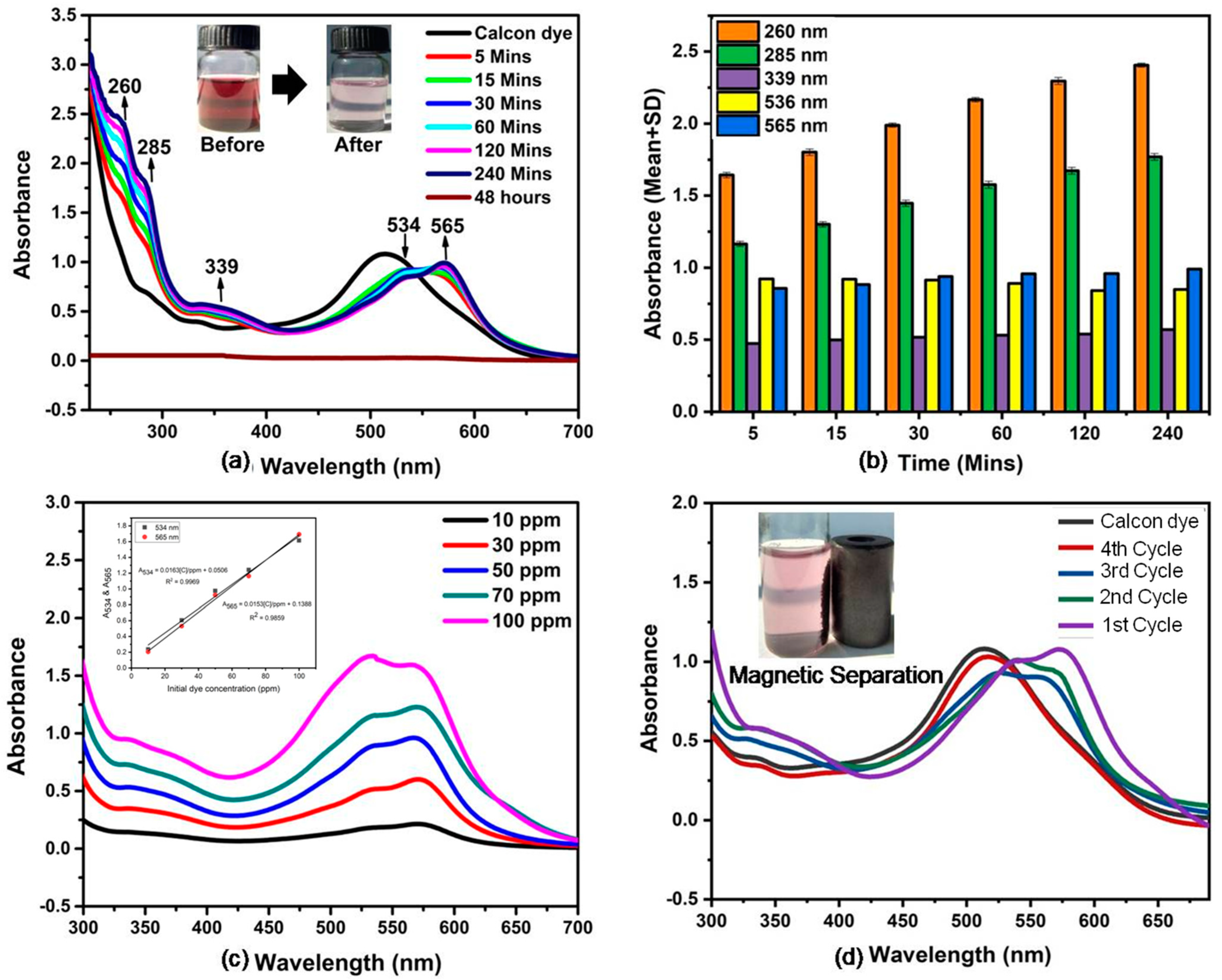
3.6. Degradation of Calcon Dye
3.7. Effect of Contact Time
3.8. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
3.9. Magnetic Separation and Reusable
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, I. New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5073–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, C.I.; Lloyd, J.R.; Guthrie, J.D. The removal of color from textiles wastewater using whole bacterial cells: A review. Dye. pigment. 2003, 58, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Q.; Lu, K.; Huang, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yu, S.; Gao, C. High efficient removal of dyes from aqueous solution through nano-filtration using diethanolamine-modified polyamide thin-film composite membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Pal, A. Microporous assembly of MnO2 nanosheets for malachite green degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 134, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Jannesar, R.; Goudarzi, A. Design and construction of nanoscale material for ultrasonic assisted adsorption of dyes: Application of derivative spectrophotometry and experimental design methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadand, R.F.; Nasab, S.J.H. Synthesis of calcon-imprinted magnetic chitosan nanoparticle as a novel adsorbent and its application in the selective removal of calcon dye from aqueous solution. Int. J. Bio. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.M.K.; Mahammadunnisa, S.; Ramaraju, B.; Sreedhar, B.; Subrahmanyam, C. Low-cost adsorbents from bio-waste for the removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 20, 4111–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, W.; Zhao, J. Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutants under visible-light irradiation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4206–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.D.; Faria, E.A.; Souza, J.; Prado, A.G. Preparation of photoactive chitosan–niobium (V) oxide composites for dye degradation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2006, 182, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by montmorillonite/CoFe2O4 composite with magnetic separation performance. Desalination 2011, 266, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Padhan, P.; Gupta, A. A Facile Thermolysis Route to Monodisperse Ferrite Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12374–12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhou, W.; Lu, R.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S. Superior adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2 core-shell microspheres for removal of congo red from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, M.; Rameshbabu, R.; Ramamurthi, K.; Arivanandhan, M. Enhanced dielectric and magnetic properties of polystyrene added CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 102, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sabagh, A.M.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Hamdy, A.; Killa, H.M.; Ghanem, R.T.M.; Morsi, R.E. Preparation and characterization of sulfonated polystyrene/magnetic nanoparticles for organic dye adsorption. Egy. J. Petro. 2018, 27, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Cong, H.; Peng, Q.; Yang, C. Synthesis and application of sulfonated polystyrene/ferroso ferric oxide/diazoresin nanocomposite microsphere for highly selective removal of dyes. Mat. Des. 2017, 135, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Cristine, A.D.; Gabriela, R.M.; Gonzalo, M.B.; Patricia, B.H.; Carmina, M.C.; Fernando, A. A novel sulfonated waste polystyrene/iron oxide nanoparticles composite: Green synthesis, characterization and application. J. Envir. Chem. Eng. 2019, 9, 102841. [Google Scholar]
- Salunkhe, A.B.; Khot, V.M.; Thorat, N.D.; Phadatare, M.R.; Sathish, C.I.; Dhawale, D.S.; Pawar, S.H. Polyvinyl alcohol functionalized CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for biomedical application. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2013, 264, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyki, M.H.; Alijani, H.; Fazli, Y. Solvent free synthesized MnFe2O4@polyamid resin as a novel green nanohybrid for fast removing Congo red. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyki, M.H.; Bayat, M.; Shemirani, F. Fabrication of core–shell structured magnetic nanocellulose base polymeric ionic liquid for effective biosorption of Congo red dye. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shen, Y.; Ling, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ge, M.; Pan, Z. Synthesis of Positively Charged Polystyrene Microspheres for the Removal of Congo Red, Phosphate, and Chromium(VI). ACS Omega 2019, 4, 6669–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, W.; Baigl, D.; Xie, M.; Chen, Y.; Pang, D. A micropillar-integrated smart micro-fluidic device for specific capture and sorting of cells. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 4713–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Z.; Dai, J.; Song, W. Synthesis and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 321, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułkowski, W.W.; Nowak, K.; Sułkowska, A.; Wolińska, A.; Bajdur, W.M.; Pentak, D.; Mikuła, B. Chemical Recycling of Polystyrene. Sulfonation with Different Sulfonation Agents. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 523, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułkowski, W.W.; Wolińska, A.; Szołtysik, B.; Bajdur, W.M.; Sułkowska, A. Preparation and properties of flocculants derived from polystyrene waste. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.H.; Omar, A.A.; Abdel-Moaty, S.A. Magnetic nanocomposites: Preparation and characterization of Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Col. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 281, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Salker, A.; Yusuf, S.; Meena, S. Influence of CO2+ distribution and spin–orbit coupling on the resultant magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 566, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.G.; Abrashev, M.V.; Iliev, M.N.; Gospodinov, M.M.; Meen, J.; Aroyo, M.I. Short range B-site ordering in the inverse spinel ferrite NiFe2O4. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Mat. Mater. Phy. 2010, 82, 024104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, K.S.A.; Bhowmik, R.N. Micro-structural characterization and magnetic study of Ni0.5Fe0.5O4 ferrite synthesized through co-precipitation route at different pH value. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 146, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, A.; Khot, V.; Thorat, N.; Phadatare, M.; Sathish, C.; Dhawale, D.; Pawar, S. Polyvinyl alcohol functionalized cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Deng, Z.; Khan, A.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wan, X.; Peng, X. Photothermal responsive ultrathin Cu-TCPP nanosheets/sulfonated polystyrene nanocomposite photo-switch proton conducting membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 620, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małgorzata, L.; Ruggeri, G.; Tomasz, W.; Artur, A.; Kamil, R.; Dominik, D.; Aleksandra, P.; Andrzej, P. Thermal Analysis of Plastics Used in the Food Industry. Materials 2022, 15, 248. [Google Scholar]
- Parhizkar, J.; Mohammad, H.H. Investigation and Comparison of Cobalt ferrite composite nanoparticles with individual Iron oxide and Cobalt oxide nanoparticles in azo dyes removal. J. Water. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2019, 4, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bodini, M.E.; Arancibia, V. Redox chemistry of 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene, 1,2-naphthosemiquinone and 1,2-naphthoquinone and their complexes with manganese(II) and manganese(III). Transit. Met. Chem. 1997, 22, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onunkwo, I.C.; Ejikeme, C.M.; Osuji, G.A. Synthesis and characterization of 1-amino-2-naphthol hydrochloride and dyeing potentials of 1-(1-phenylazo)-2-naphthol. Int. J. Chem. Mat. Res. 2020, 8, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, K.; Nachiyar, V. Biodegradation of the textile dye Mordant Black 17 (Calcon) by Moraxella osloensis isolated from textile effluent-contaminated site. World. J. Microbiol. Biotech. 2014, 30, 915–924. [Google Scholar]
- Olawale, O.O.; Umar, S.A. Synthesis and Dyeing Properties of Acid Dyes Derived from 1-amino-2-naphthol-4-sulphonic Acid. World J. Appl. Chem. 2019, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhm, A.E.; Stolz, A.; Ngai, K.L.; Knackmuss, H.J. Purification and characterization of a 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene dioxygenase from a bacterium that degrades naphthalenesulfonic acids. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 3795–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, A.; Mohammad, A.H.; Sanae, E.G.; Amina, A.; Zaina, Z.; Patrick, B. Nanostructural manganese oxide as an efficient eco-friendly catalyst for removing azo dye calcon from water. Mater. Today Proc. 2020; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Kangralkar, M.V.; Manjanna, J.; Momin, N.; Rane, K.; Nayaka, G.; Kangralkar, V.A. Photocatalytic degradation of hexavalent chromium and different staining dyes by ZnO in aqueous medium under UV light. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| S.No | Sample Code | Z-Average Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CoFe2O4 MNp | 27.5 | −31.6 |
| 2 | SWPS/MNp (10 wt%) | 2.3 | −43.7 |
| 3 | SWPS/MNp (20 wt%) | 1.1 | −46.2 |
| S.No | Metal Catalyst (mg) | Experimental Conditions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Na-MnO2/SnO2(50) | Dark Temperature—Room; Time—24 h; pH: 3 | [38] |
| 2 | Chitosan/Fe3O4 (50) | Temperature—25 °C; Time—240 min; pH: 3 | [6] |
| 3 | ZnO (50) | UV irradiation (250 W); Time—260 min; pH: 4.5 | [39] |
| 4 | SWPS/CoFe2O4 (50) | Natural Light; Temperature—Ambient; Time—240 min; pH: Natural | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srinivasan, V.; Sumalatha, V.; Prasannan, A.; Govindarajan, S. Utilization of Sulfonated Waste Polystyrene-Based Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanocomposites for Efficient Degradation of Calcon Dye. Polymers 2022, 14, 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142909
Srinivasan V, Sumalatha V, Prasannan A, Govindarajan S. Utilization of Sulfonated Waste Polystyrene-Based Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanocomposites for Efficient Degradation of Calcon Dye. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142909
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrinivasan, Vennila, Vasam Sumalatha, Adhimoorthy Prasannan, and Sankar Govindarajan. 2022. "Utilization of Sulfonated Waste Polystyrene-Based Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanocomposites for Efficient Degradation of Calcon Dye" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142909
APA StyleSrinivasan, V., Sumalatha, V., Prasannan, A., & Govindarajan, S. (2022). Utilization of Sulfonated Waste Polystyrene-Based Cobalt Ferrite Magnetic Nanocomposites for Efficient Degradation of Calcon Dye. Polymers, 14(14), 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142909







