Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Polyamide Composites Doped with 2D Graphitic Carbon Nitride
Abstract
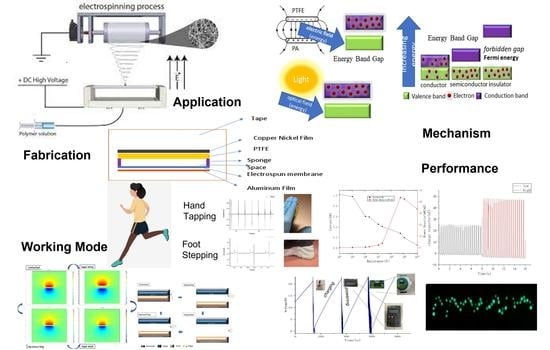
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of g-C3N4
2.3. Fabrication of the PA66 Membrane
2.4. Material Characterization and Measurement of Electrical Output Performance
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yao, T.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Shang, J. Self-Powered Non-Contact Triboelectric Rotation Sensor with Interdigitated Film. Sensors 2020, 20, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wu, M. Interfacial modification boosted permittivity and triboelectric performance of liquid doping composites for high-performance flexible triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Tao, B.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H. Multidimensional Force Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Electronic Skin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56320–56328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seol, M.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.; Byun, K.E.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, H.J.; Park, S. Triboelectric Series of 2D Layered Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e18012102018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peymanfar, R.; Selseleh-Zakerin, E.; Ahmadi, A. Tailoring energy band gap and microwave absorbing features of graphite-like carbon nitride (g-C3N4). J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 867, 159039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Fan, H.; Fu, K.; Lei, S.; Hu, Q.; Huang, H.; He, G. Protonation of Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4) for an Electrostatically Self-Assembling Carbon@g-C3N4 Core–Shell Nanostructure toward High Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7093–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Takanabe, K.; Maeda, K.; Domen, K.; Epping, J.D.; Fu, X.; Antonietti, M.; Wang, X. Synthesis of a carbon nitride structure for visible-light catalysis by copolymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Maeda, K.; Thomas, A.; Takanabe, K.; Xin, G.; Carlsson, J.M.; Domen, K.; Antonietti, M. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhang, D. Synthesis and Electrochemical Behavior of Two Microporous Polyoxomolybdates. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 79–82, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Boyer, C.; Li, G.; Yu, Y.; Allioux, F.-M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Wang, C.-H.; Zhang, J. Electrospun liquid metal/PVDF-HFP nanofiber membranes with exceptional triboelectric performance. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Shen, C.; Guo, Z. Carbon Nanotubes-Adsorbed Electrospun PA66 Nanofiber Bundles with Improved Conductivity and Robust Flexibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14150–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Shao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Bian, Z. Self-cleaning triboelectric nanogenerator based on TiO2 photocatalysis. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvarts, A.G.; Xu, Y.; Min, G.; Athanasiadis, I.; Kaczmarczyk, L.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Pearce, C.J. Finite-element modelling of triboelectric nanogenerators accounting for surface roughness. In Proceedings of the UKACM 2021 Conference, Loughborough, UK, 14–16 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z. Theoretical foundations of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 1087–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical modeling of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Dynamical charge transfer model for high surface charge density triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasena, R.D.I.G.; Jayawardena, K.D.G.I.; Mills, C.A.; Deane, J.H.B.; Anguita, J.V.; Dorey, R.A.; Silva, S.R.P. Triboelectric nanogenerators: Providing a fundamental framework. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Tang, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Xu, L.; Guo, H.; Lin, P.; Li, D.; et al. Three-dimensional ultraflexible triboelectric nanogenerator made by 3D printing. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.; Chen, W.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, Y. Facile Synthesis of Self-Assembled g-C3N4 with Abundant Nitrogen Defects for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10200–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qi, P. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle and graphene oxide nanosheet composites as a bactericidal agent for water disinfection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.J.; Tan, L.L.; Ng, Y.H.; Yong, S.T.; Chai, S.P. Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4)-Based Photocatalysts for Artificial Photosynthesis and Environmental Remediation: Are We a Step Closer To Achieving Sustainability? Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7159–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, M.; Jiang, C.; Guan, X.; Yang, Y. Scalable core–spun coating yarn-based triboelectric nanogenerators with hierarchical structure for wearable energy harvesting and sensing via continuous manufacturing. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Gao, Y.; Li, M. Conductive Composite Fiber with Customizable Functionalities for Energy Harvesting and Electronic Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 49927–49935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Han, J.; Huang, J.; Chung, K.Y. Interfacial Polarization and Dual Charge Transfer Induced High Permittivity of Carbon Dots-Based Composite as Humidity-Resistant Tribomaterial for Efficient Biomechanical Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Han, J.; Huang, J.; Fu, H. A Polycation-Modified Nanofillers Tailored Polymer Electrolytes Fiber for Versatile Biomechanical Energy Harvesting and Full-Range Personal Healthcare Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-F.; Xu, Q.-Q.; Qi, J.-L.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Yin, J.-Z. Isolated Single Atoms Anchored on N-Doped Carbon Materials as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Electrochemical and Organic Reactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14630–14656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Cardone, G.; Restrepo, D.; Zavattieri, P.D.; Baker, T.S.; Tezcan, F.A. Self-assembly of coherently dynamic, auxetic, two-dimensional protein crystals. Nature 2016, 533, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmacher, P.; Gachot, C.; Eder, S.J. Visualization of microstructural mechanisms in nanocrystalline ferrite during grinding. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Liao, Y.; Fan, J.; Xiang, Q. Recent advances in crystalline carbon nitride for photocatalysis. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 91, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Xu, B.; Wu, M.; Jing, T.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y. Breathable, washable and wearable woven-structured triboelectric nanogenerators utilizing electrospun nanofibers for biomechanical energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Xu, B.; Xin, J.H.; Guan, X.; Yang, Y. Series to parallel structure of electrode fiber: An effective method to remarkably reduce inner resistance of triboelectric nanogenerator textiles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 12331–12339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.; Wen, J.; Hua, T.; Kan, C.-W. Graphene-based in-planar supercapacitors by a novel laser-scribing, in-situ reduction and transfer-printed method on flexible substrates. J. Power Sources 2019, 420, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Xu, B.; Bao, Q.; Lam, Y. Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Polyamide Composites Doped with 2D Graphitic Carbon Nitride. Polymers 2022, 14, 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153029
Xiao Y, Xu B, Bao Q, Lam Y. Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Polyamide Composites Doped with 2D Graphitic Carbon Nitride. Polymers. 2022; 14(15):3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153029
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yana, Bingang Xu, Qi Bao, and Yintung Lam. 2022. "Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Polyamide Composites Doped with 2D Graphitic Carbon Nitride" Polymers 14, no. 15: 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153029
APA StyleXiao, Y., Xu, B., Bao, Q., & Lam, Y. (2022). Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Polyamide Composites Doped with 2D Graphitic Carbon Nitride. Polymers, 14(15), 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153029