A QbD Approach to Design and to Optimize the Self-Emulsifying Resveratrol–Phospholipid Complex to Enhance Drug Bioavailability through Lymphatic Transport
Abstract
:Highlights
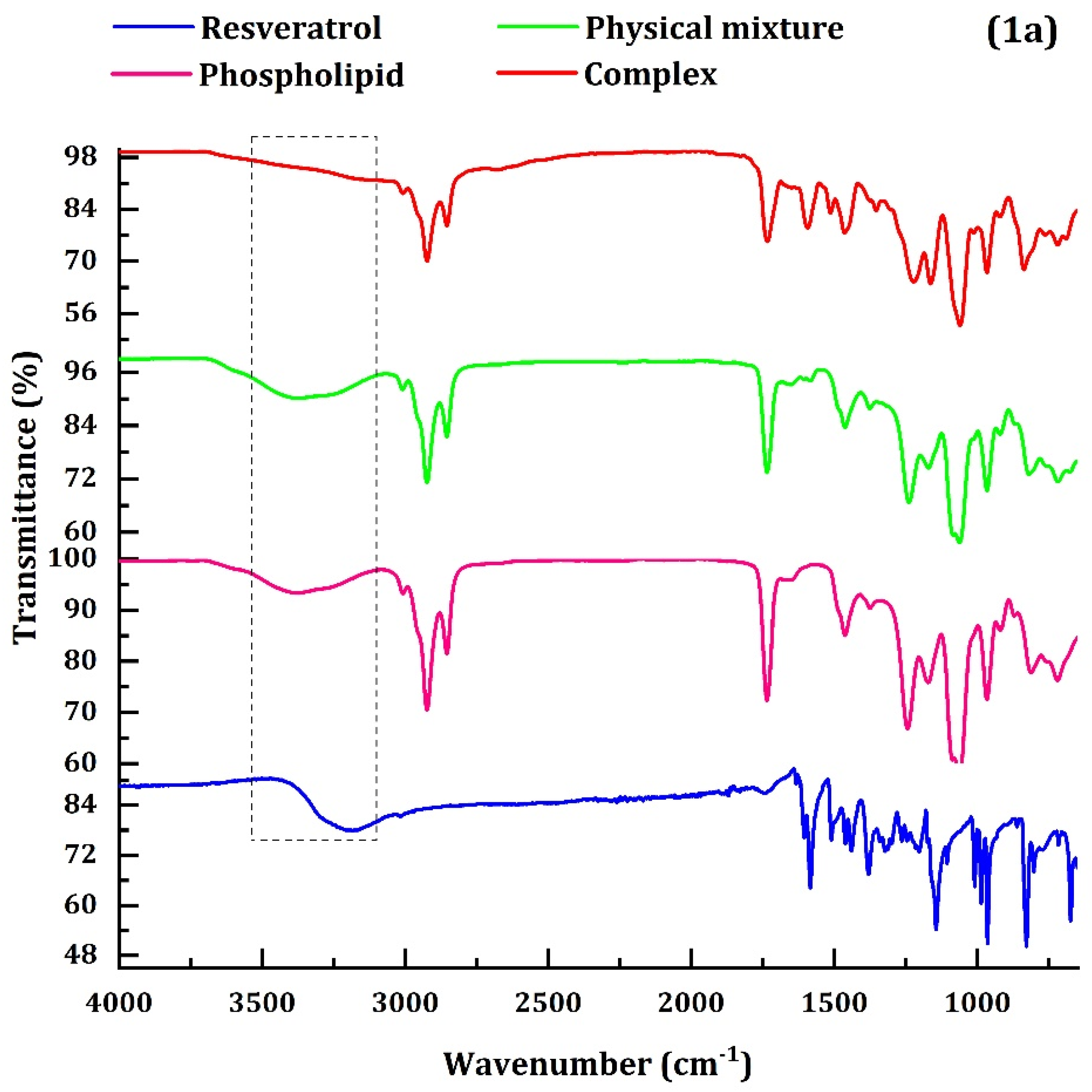
- The FTIR, DSC, and the XRD characterization confirmed the successful complex formation between resveratrol and phospholipid.
- The optimal SEDDS formulation exhibited Grade-A self-emulsion properties.
- Implementation of a QbD approach to select appropriate excipients and their concentrations facilitated lymphatic resveratrol transport, which increased bioavailability 48-fold.
- The chylomicron flow blocking approach revealed that 91.3% of total systemically available resveratrol was transported through the intestinal lymphatic pathway.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Complex
3.1.1. Characterization Using FTIR, XRD, Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.1.2. Solubility Determination
3.2. QbD-Based Formulation-Development and Optimization Process
3.2.1. Defining QTPPs and QAs
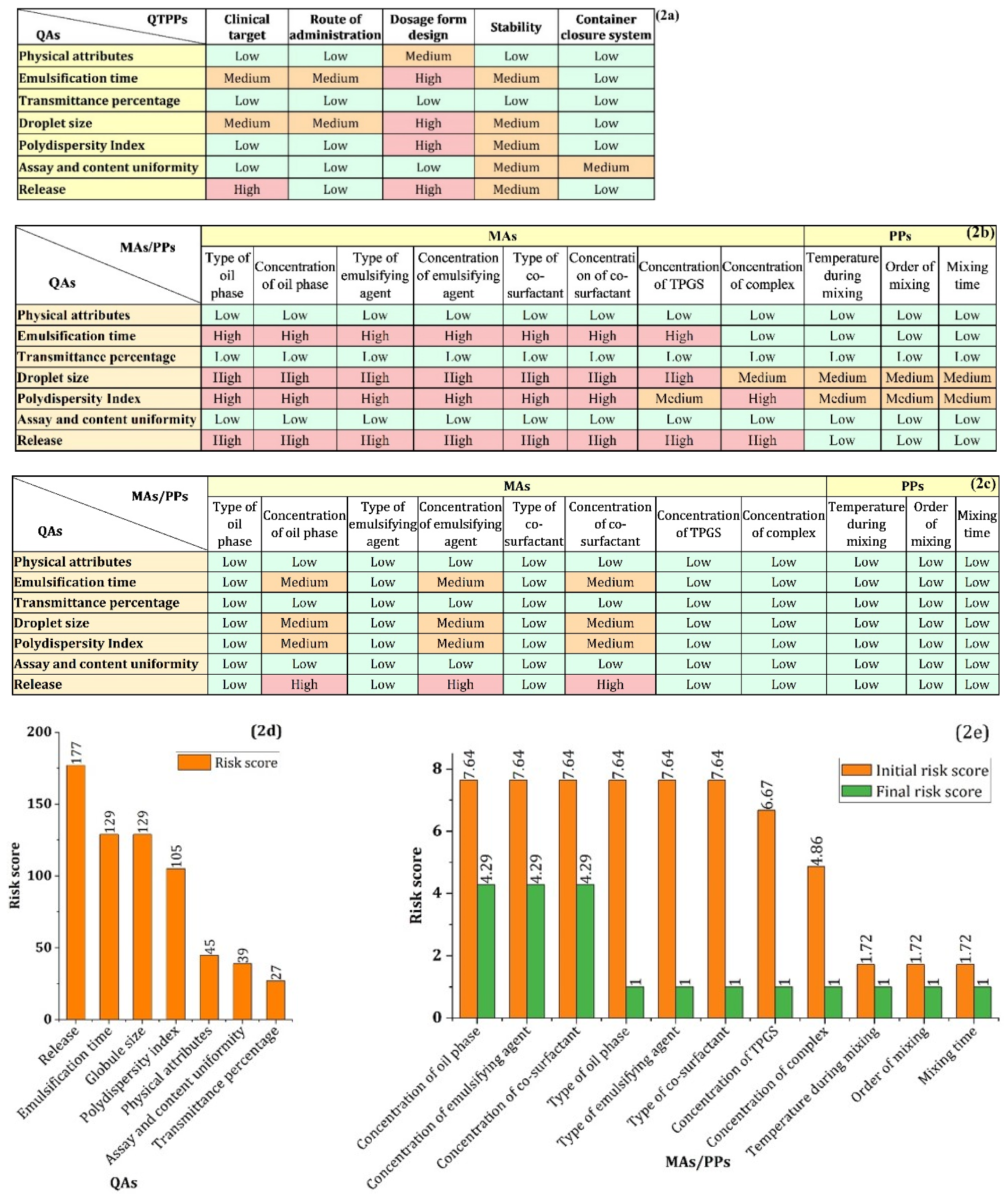
3.2.2. Risk Assessment (RA) Study
3.2.3. Risk Reduction by Experimental Approaches
Screening of Oil
Screening of Surfactant and Co-Surfactant
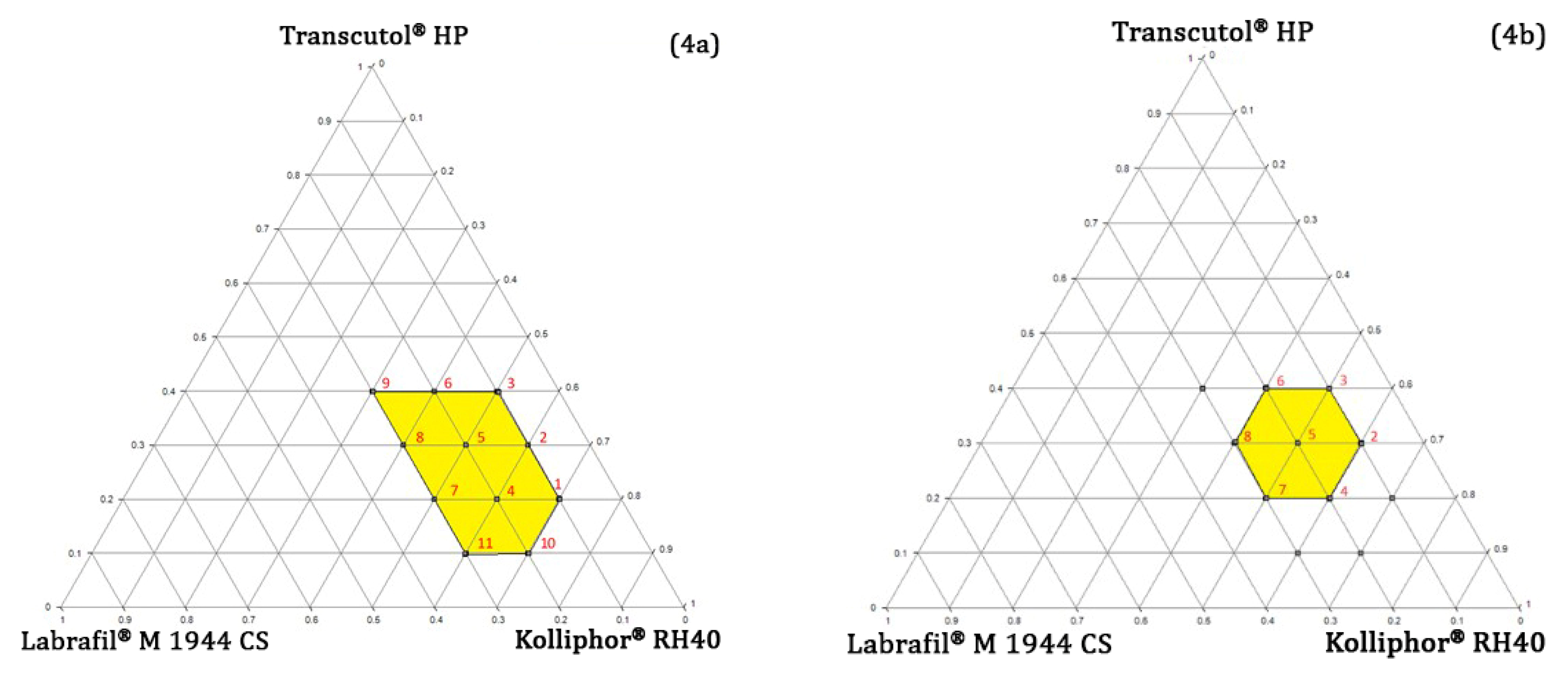
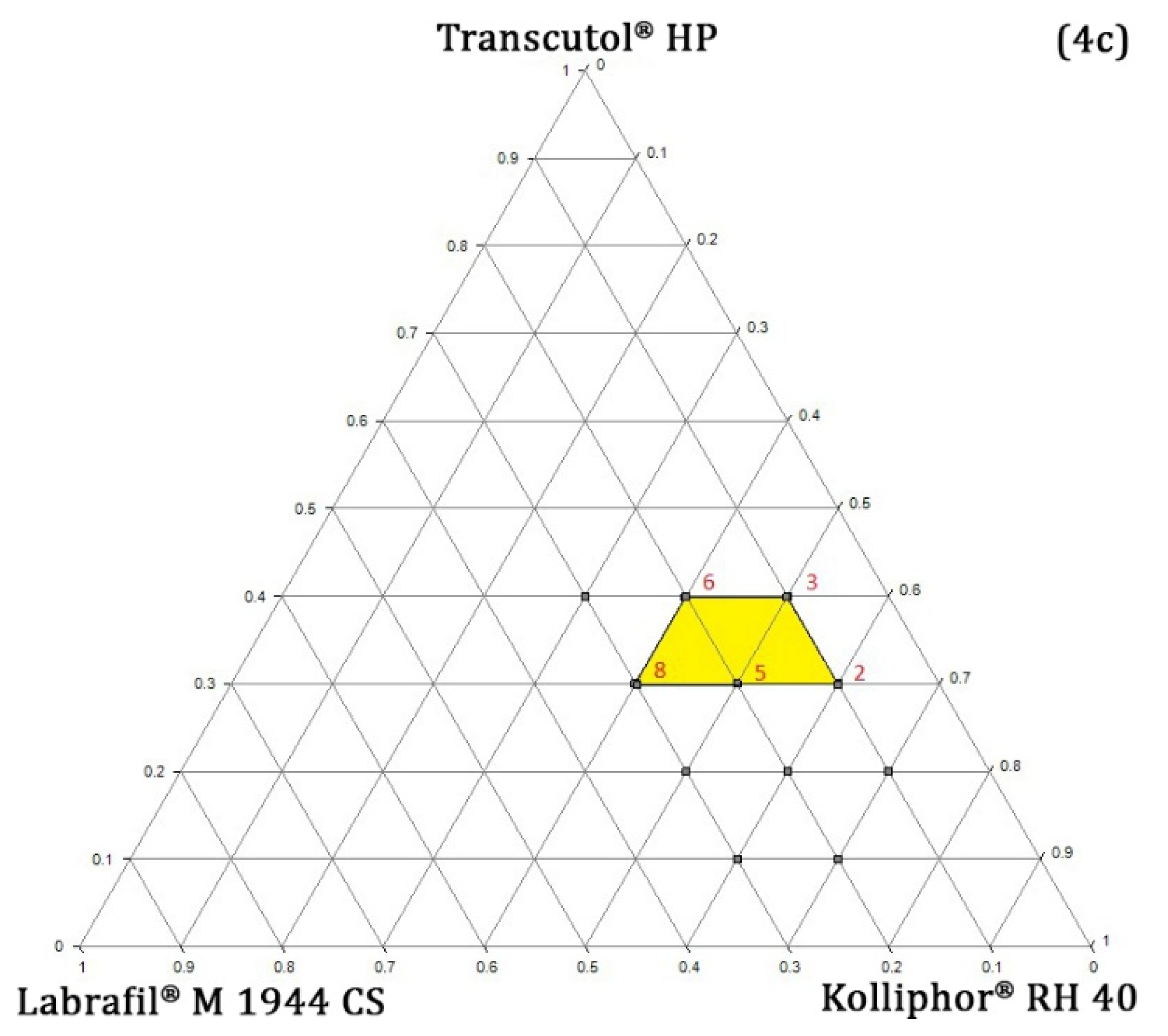
Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagram Study
Determination of TPGS and RPC Concentration
3.2.4. Preparation Procedure
3.2.5. Design of Experiment (DoE)
Generation and Verification of Design Space
3.3. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
Sample Preparation
3.4. HPLC Method
3.5. Characterization of SEDDS
3.5.1. Emulsification Time (ET)
3.5.2. Globule Size (GS) and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
3.5.3. Transmittance Percentage (TP)
3.5.4. In Vitro Drug Release
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Characterization of RPC
4.1.1. FTIR, RD and DSC
4.1.2. Solubility Studies
4.2. Determining QTTPs and CQAs
4.3. Risk Assessment
4.4. Risk Reduction of MAs by Experimental Approaches
4.4.1. Oil Phase
4.4.2. Surfactant and Co-Surfactant
4.4.3. Determining the Concentration Range of Oil, Surfactant, and Co-Surfactant
4.4.4. Determining the Optimal Concentration of TPGS and RPC
4.5. Mixer Design (DoE)
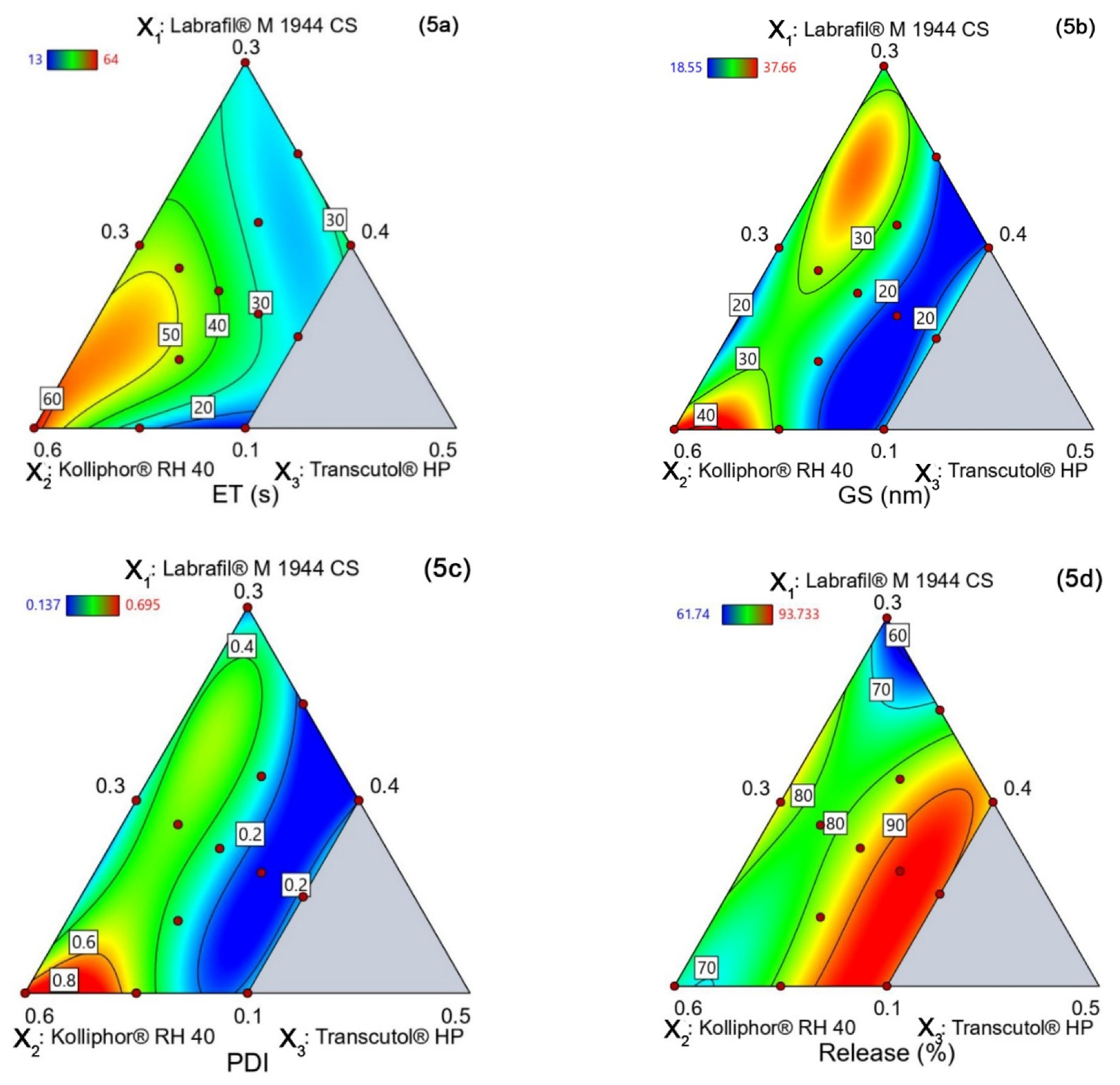
4.5.1. Emulsification Time (YET)
4.5.2. Globule Size (YGS)
4.5.3. PDI (YPDI)
4.5.4. Release (YRelease)
4.5.5. Design Space and Optimal Formulation
Verification of the Design Space
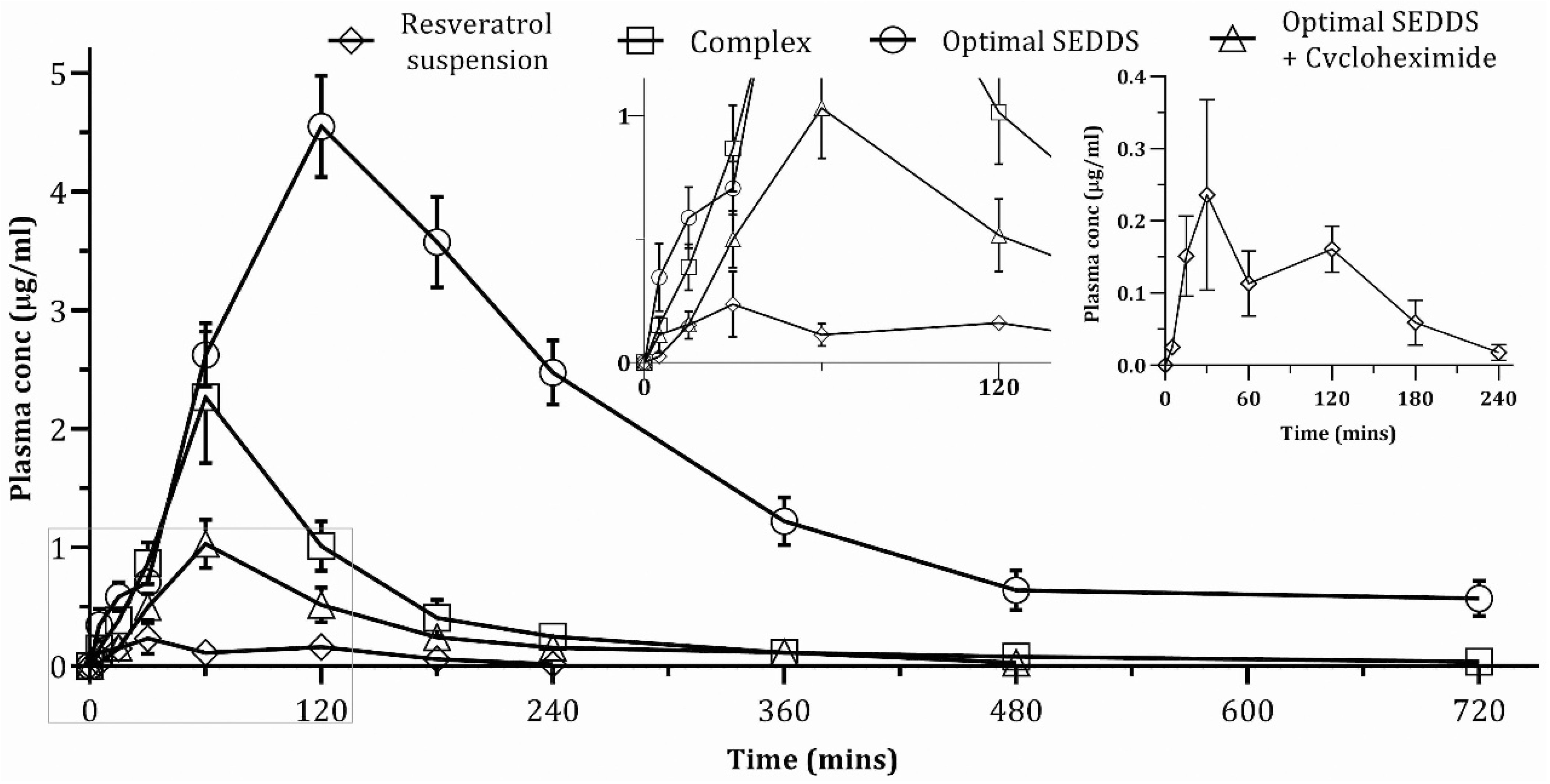
4.6. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berman, A.Y.; Motechin, R.A.; Wiesenfeld, M.Y.; Holz, M.K. The Therapeutic Potential of Resveratrol: A Review of Clinical Trials. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Summerlin, N.; Soo, E.; Thakur, S.; Qu, Z.; Jambhrunkar, S.; Popat, A. Resveratrol Nanoformulations: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quispe, C.; Mukazhanova, Z.; Knut, E.; Turgumbayeva, A.; Kipchakbayeva, A.; Seitimova, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Lobine, D.; Koay, A.; et al. Resveratrol-Based Nanoformulations as an Emerging Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Um, J.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A.; Ahn, K.S. The Role of Resveratrol in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smoliga, J.M.; Blanchard, O. Enhancing the Delivery of Resveratrol in Humans: If Low Bioavailability Is the Problem, What Is the Solution? Molecules 2014, 19, 17154–17172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amri, A.; Chaumeil, J.C.; Sfar, S.; Charrueau, C. Administration of Resveratrol: What Formulation Solutions to Bioavailability Limitations? J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Müllertz, A.; Rades, T. Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS)—The Splendid Comeback of an Old Technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 142, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.U.; Shah, K.U.; Shah, S.U.; Khan, I.U.; Khan, G.M.; Khan, A. From Nanoemulsions to Self-Nanoemulsions, with Recent Advances in Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS). Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniakov, I.; Domb, A.J.; Hoffman, A. Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems: An Update of the Biopharmaceutical Aspects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benet, L.Z.; Broccatelli, F.; Oprea, T.I. BDDCS Applied to over 900 Drugs. AAPS J. 2011, 13, 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, P.S.; Singh, N.; Sangamwar, A.T.; Bansal, A.K. Investigation of Need of Natural Bioenhancer for a Metabolism Susceptible Drug—Raloxifene, in a Designed Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, M.; Sikder, P.; Saha, A.; Shah, S.; Sultana, S.; Emran, T.; Banik, A.; Islam, Z.; Islam, M.S.; Sharker, S.M.; et al. QbD Approach towards Robust Design Space for Flutamide/Piperine Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System with Reduced Liver Injury. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Deng, S.; Huang, Y.; Xia, Z. Development of Phospholipid Complex Loaded Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System to Improve the Oral Bioavailability of Resveratrol. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, F.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Pan, R.L.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X.M.; Liao, Y.H. Involvement of the Inhibition of Intestinal Glucuronidation in Enhancing the Oral Bioavailability of Resveratrol by Labrasol Containing Nanoemulsions. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Pai, R.S. In Vitro and in Vivo Performance of Supersaturable Self-Nanoemulsifying System of Trans-Resveratrol. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaisamut, P.; Wanna, S.; Limsuwan, S.; Chusri, S.; Wiwattanawongsa, K.; Wiwattanapatapee, R. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability and Improved Biological Activities of a Quercetin/Resveratrol Combination Using a Liquid Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System. Planta Med. 2021, 87, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Garg, T.; Kushwah, V.; Thanki, K.; Agrawal, A.K.; Dora, C.P. α-Tocopherol as Functional Excipient for Resveratrol and Coenzyme Q10-Loaded SNEDDS for Improved Bioavailability and Prophylaxis of Breast Cancer. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Pai, R.S. Trans-Resveratrol Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SNEDDS) with Enhanced Bioavailability Potential: Optimization, Pharmacokinetics and in Situ Single Pass Intestinal Perfusion (SPIP) Studies. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Araújo, F.; Lopes, C.; Loureiro, A.; das Neves, J.; Marques, S.; Sarmento, B. Multicomponent Self Nano Emulsifying Delivery Systems of Resveratrol with Enhanced Pharmacokinetics Profile. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwana, V.; Jain, R.; Patel, K.; Nivsarkar, M.; Joshi, A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) of Efavirenz as Lymph Targeting Drug Delivery System: Elucidation of Mechanism of Uptake Using Chylomicron Flow Blocking Approach. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elz, A.S.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Porter, C.J.H.; Bowen, J.M.; Prestidge, C.A. Smart Design Approaches for Orally Administered Lipophilic Prodrugs to Promote Lymphatic Transport. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 676–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, C.J.H.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, W.N. Lipids and Lipid-Based Formulations: Optimizing the Oral Delivery of Lipophilic Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drescher, S.; van Hoogevest, P. The Phospholipid Research Center: Current Research in Phospholipids and Their Use in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumbhar, P.S.; Nadaf, S.; Manjappa, A.S.; Kumar, N.; Shinde, S.S.; Chopade, S.S.; Shete, A.S.; Disouza, J.I.; Sambamoorthy, U.; Kumar, S.A. D-α-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol Succinate: A Review of Multifarious Applications in Nanomedicines. OpenNano 2022, 6, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wu, J.; Fang, X.; Sha, X. A New Function of Vitamin E-TPGS in the Intestinal Lymphatic Transport of Lipophilic Drugs: Enhancing the Secretion of Chylomicrons. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 445, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, M.; Singh, A.; Amiji, M.M. Quality-by-Design Concepts to Improve Nanotechnology-Based Drug Development. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.; Beg, S.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, R.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B. Long-Chain Triglycerides-Based Self-Nanoemulsifying Oily Formulations (SNEOFs) of Darunavir with Improved Lymphatic Targeting Potential. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X. Pharmaceutical Quality by Design: Product and Process Development, Understanding, and Control. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, G.; Anzaghi, P.; Stefli, R. Resveratrol-Phospholipids Complexes, Their Preparation, and Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Composition Containing Same. U.S. Patent Application No. 10/471,706, 17 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Goos, P.; Jones, B.; Syafitri, U. I-Optimal Design of Mixture Experiments. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, D.H.; Ha, E.S.; Ha, D.H.; Sim, W.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Baek, I.H.; Park, H.; Choi, D.H.; et al. Development of a Resveratrol Nanosuspension Using the Antisolvent Precipitation Method without Solvent Removal, Based on a Quality by Design (QbD) Approach. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, M.H.; Sawant, K.K. Self Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System of Lurasidone Hydrochloride for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability by Lymphatic Targeting: In Vitro, Caco-2 Cell Line and in Vivo Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, M.; Rani, D.; Ulhosna, T.; Sharker, S.; Shohag, H.; Saiful, M.; Ray, S.K.; Rahman, M.S.; Mahmud, H. QbD Based Development of Resveratrol-Loaded Mucoadhesive Lecithin / Chitosan Nanoparticles for Prolonged Ocular Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avachat, A.M.; Patel, V.G. Self Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System of Stabilized Ellagic Acid–Phospholipid Complex with Improved Dissolution and Permeability. Saudi Pharm. J. 2015, 23, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; Yuan, H.; Xu, S. Preparation and in Vivo-in Vitro Evaluation of Polydatin-Phospholipid Complex with Improved Dissolution and Bioavailability. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res 2017, 9, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Zhen, N.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, D.; Huang, K. In Vitro Antioxidant and Antitumor Study of Zein/SHA Nanoparticles Loaded with Resveratrol. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, D.W.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, S.G.; Kang, M.H.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.W. Development and Optimization of a Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Atorvastatin Calcium by Using D-Optimal Mixture Design. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3865–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, V.; Nayak, P.; Yadav, N.; Singh, M.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Aljabali, A.A.A. Orally Administered Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System in Disease Management: Advancement and Patents. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Jain, A.; Kaur, R.; Saini, S.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B. Supersaturated LFCS Type III Self-Emulsifying Delivery Systems of Sorafenib Tosylate with Improved Biopharmaceutical Performance: QbD-Enabled Development and Evaluation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 839–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Jalil, A. Do Drug Release Studies from SEDDS Make Any Sense? J. Control. Release 2018, 271, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörgensen, A.M.; Friedl, J.D.; Wibel, R.; Chamieh, J.; Cottet, H.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Cosolvents in Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS): Do They Really Solve Our Solubility Problems? Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 3236–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buya, A.B.; Beloqui, A.; Memvanga, P.B.; Préat, V. Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems: From the Development to the Current Applications and Challenges in Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Yu, M.; Lei, M.; Tan, F.; Li, N. A Novel Topical Targeting System of Caffeine Microemulsion for Inhibiting UVB-Induced Skin Tumor: Characterization, Optimization, and Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xi, J.; Chang, Q.; Chan, C.K.; Meng, Z.Y.; Wang, G.N.; Sun, J.B.; Wang, Y.T.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Zheng, Y. Formulation Development and Bioavailability Evaluation of a Self-Nanoemulsified Drug Delivery System of Oleanolic Acid. Aaps Pharmscitech 2009, 10, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valicherla, G.R.; Dave, K.M.; Syed, A.A.; Riyazuddin, M.; Gupta, A.P.; Singh, A.; Wahajuddin; Mitra, K.; Datta, D.; Gayen, J.R. Formulation Optimization of Docetaxel Loaded Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System to Enhance Bioavailability and Anti-Tumor Activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butreddy, A.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M.A. Quality-by-Design in Hot Melt Extrusion Based Amorphous Solid Dispersions: An Industrial Perspective on Product Development. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 158, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Song, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Pan, W.; Yang, X. Preparation and Pharmacokinetics Evaluation of Oral Self-Emulsifying System for Poorly Water-Soluble Drug Lornoxicam. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malkani, A.; Date, A.A.; Hegde, D. Celecoxib Nanosuspension: Single-Step Fabrication Using a Modified Nanoprecipitation Method and in Vivo Evaluation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2014, 4, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Y. Development and Characterization of Promising Cremophor EL-Stabilized o/w Nanoemulsions Containing Short-Chain Alcohols as a Cosurfactant. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19815–19827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yildiz, H.M.; McKelvey, C.A.; Marsac, P.J.; Carrier, R.L. Size Selectivity of Intestinal Mucus to Diffusing Particulates Is Dependent on Surface Chemistry and Exposure to Lipids. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.; Shi, Y.; Han, Y.; Shao, Y.; Qi, M.; Li, B. Exploring uncertainty in deep learning for construction of prediction intervals. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.12593. [Google Scholar]
- Debevec, V.; Srčič, S.; Horvat, M. Scientific, Statistical, Practical, and Regulatory Considerations in Design Space Development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marier, J.F.; Vachon, P.; Gritsas, A.; Zhang, J.; Moreau, J.P.; Ducharme, M.P. Metabolism and Disposition of Resveratrol in Rats: Extent of Absorption, Glucuronidation, and Enterohepatic Recirculation Evidenced by a Linked-Rat Model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijayakumar, M.R.; Vajanthri, K.Y.; Balavigneswaran, C.K.; Mahto, S.K.; Mishra, N.; Muthu, M.S.; Singh, S. Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, in Vitro Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility of Vitamin E TPGS Coated Trans Resveratrol Liposomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuche, K.; Bhargavi, N.; Dora, C.P.; Jain, S. Drug-Phospholipid Complex—A Go through Strategy for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Bu, H. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Loading Candesartan Cilexetil Enhance Oral Bioavailability: In Vitro Characteristics and Absorption Mechanism in Rats. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Patel, M. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Nintedanib Esylate with Nanostructured Lipid Carriers by Lymphatic Targeting: In Vitro, Cell Line and in Vivo Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.; Bahadur, P.; Tiwari, S. Nanocarriers Based on Vitamin E-TPGS: Design Principle and Molecular Insights into Improving the Efficacy of Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, A.; Hoffman, A. Evaluation of a Chylomicron Flow Blocking Approach to Investigate the Intestinal Lymphatic Transport of Lipophilic Drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.F.; Zhou, J.; Hu, X.; Cong, Z.Q.; Liu, C.Y.; Pan, R.L.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X.M.; Liao, Y.H. Improving Oral Bioavailability of Resveratrol by a UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Inhibitory Excipient-Based Self-Microemulsion. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 114, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| QTPPs | Target | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical target | Improving the bioavailability of resveratrol through lymphatic transport | Resveratrol undergoes extensive fast pass metabolism, and <1% becomes systemically bioavailable. |
| Route of Administration | Oral | The most convenient route of drug administration. |
| Dosage form design | Self-emulsifying drug delivery system | SEDDS offers higher drug loading and improved biopharmaceutical attributes of the loaded drug. |
| Stability | Six months (at least) | SEDDS is a preconcentrate dosage form that could be stored for a long time. |
| Container closure system | Amber glass container | Resveratrol undergoes photolytic degradation in the presence of light. |
| CQAs | Target | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Physical attributes | No unpleasant color, odor, and taste | Those unpleasant attributes of formulation reduce the patient acceptability. |
| Transmittance percentage | ≥90% | The transmittance percentage of ≥90% denotes ultrafine globules and is essential to maintain the class of Grade-A SEDDS, which can be used to characterize during the initial development of SEDDS instead of DLS [37]. |
| Emulsification time | 1–60 s | Rapid self-emulsion formation (within 60 s) is a requirement for Grade A self-emulsion [38]. |
| Droplet size | 10–50 nm | The globule size of ≤100 nm is the specification for Grade-A self-emulsion [37]. However, the globule size of <30 nm aid in permeation of the unstirred water layer and mucous layer. |
| Polydispersity index | 0.2 | The lower PDI values indicate a narrow globule size distribution and monodispersed globule. |
| Assay and content uniformity | 100% | Assay and content uniformity are necessary to ensure the safety and efficacy of the drug product. |
| Release | 80–100% at 8 h | A higher percentage of the drug needs to be released in the desired time. |
| Run | Labrafil® M 1944 CS (X1) | Kolliphor® RH 40 (X2) | Transcutol® HP (X3) | Emulsification Time, s (YET) | Globule Size, nm (YGS) | PDI (YPDI) | Release, % (YRelease) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1625 | 0.4625 | 0.375 | 34.31 | 18.55 | 0.137 | 93.73 |
| 2 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 26.12 | 21.79 | 0.157 | 72.82 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 44.97 | 22.89 | 0.274 | 86.24 |
| 4 | 0.175 | 0.475 | 0.35 | 41.17 | 25.77 | 0.301 | 86.02 |
| 5 | 0.1875 | 0.4875 | 0.325 | 47.21 | 31.69 | 0.476 | 78.39 |
| 6 | 0.2125 | 0.4375 | 0.35 | 23.89 | 26.08 | 0.3 | 82.18 |
| 7 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 13.21 | 22.08 | 0.249 | 90.43 |
| 8 | 0.15 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 22.87 | 23.875 | 0.2435 | 90.47 |
| 9 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 26.11 | 24.88 | 0.189 | 61.74 |
| 10 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 64.55 | 37.66 | 0.695 | 78.81 |
| 11 | 0.1 | 0.55 | 0.35 | 25.26 | 28.79 | 0.518 | 82.47 |
| 12 | 0.1375 | 0.5125 | 0.35 | 43.88 | 22.56 | 0.33 | 83.45 |
| 13 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 36.43 | 21.31 | 0.192 | 85.74 |
| PK Parameters | Resveratrol Suspension | RPC | Optimal SEDDS | Optimal SEDDS + Cycloheximide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area under curve, AUC0–720min (µg /mL × min) | 24.31 ± 4.31 | 257.15 ± 40.26 | 1167.39 ± 103.20 | 130.43 ± 21.14 |
| Area under curve, AUC0–∞ (µg /mL × min) | 25.31 ± 4.98 | 267.04 ± 41.62 | 1353.11 ± 170.97 | 134.37 ± 22.03 |
| Tmax (min) | 30 | 60 | 120 | 60 |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 0.24 ± 0.12 | 2.27 ± 0.51 | 4.55 ± 0.39 | 1.03 ± 0.19 |
| Plasma half-life, t1/2 (min) | 35.5 ± 11.97 | 185.02 ± 44.78 | 217.26 ± 83.28 | 88.16 ± 16.3 |
| Mean residence time, MRT (min) | 100.75 ± 14.13 | 184.3 ± 15.95 | 357.33 ± 70.65 | 153.46 ± 21.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gausuzzaman, S.A.L.; Saha, M.; Dip, S.J.; Alam, S.; Kumar, A.; Das, H.; Sharker, S.M.; Rashid, M.A.; Kazi, M.; Reza, H.M. A QbD Approach to Design and to Optimize the Self-Emulsifying Resveratrol–Phospholipid Complex to Enhance Drug Bioavailability through Lymphatic Transport. Polymers 2022, 14, 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153220
Gausuzzaman SAL, Saha M, Dip SJ, Alam S, Kumar A, Das H, Sharker SM, Rashid MA, Kazi M, Reza HM. A QbD Approach to Design and to Optimize the Self-Emulsifying Resveratrol–Phospholipid Complex to Enhance Drug Bioavailability through Lymphatic Transport. Polymers. 2022; 14(15):3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153220
Chicago/Turabian StyleGausuzzaman, Syed Abul Layes, Mithun Saha, Shahid Jaman Dip, Shaiful Alam, Arup Kumar, Harinarayan Das, Shazid Md. Sharker, Md Abdur Rashid, Mohsin Kazi, and Hasan Mahmud Reza. 2022. "A QbD Approach to Design and to Optimize the Self-Emulsifying Resveratrol–Phospholipid Complex to Enhance Drug Bioavailability through Lymphatic Transport" Polymers 14, no. 15: 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153220
APA StyleGausuzzaman, S. A. L., Saha, M., Dip, S. J., Alam, S., Kumar, A., Das, H., Sharker, S. M., Rashid, M. A., Kazi, M., & Reza, H. M. (2022). A QbD Approach to Design and to Optimize the Self-Emulsifying Resveratrol–Phospholipid Complex to Enhance Drug Bioavailability through Lymphatic Transport. Polymers, 14(15), 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153220










