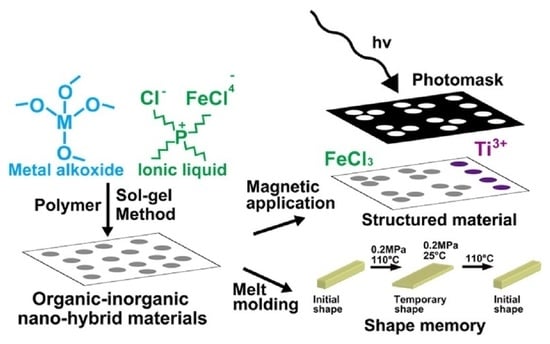
Skillful Control of Dispersion and 3D Network Structures: Advances in Functional Organic–Inorganic Nano-Hybrid Materials Prepared Using the Sol-Gel Method
Abstract
:1. Birth of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials
2. Preparation of Hybrid Materials Using the Sol-Gel Method
3. Creation of Nano-Hybrids Using Silane Coupling Agents
4. Birth of Ionic Liquids, from Designer Solvents to Functional Ionic Liquids
5. Ionic Liquids/Collaborations with Hybrid Materials
6. Creation of Functional Hybrids in the Presence of Ionic Liquids
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schubert, U.; Hüsing, N.; Lorenz, A. Hybrid inorganic-organic materials by sol-gel processing of organofunctional metal alkoxides. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 2010–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judeinstein, P.; Sanchez, C. Hybrid organic-inorganic materials: A land of multidisciplinarity. J. Mater. Chem. 1996, 6, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wilkes, G.L. Organic/inorganic hybrid network materials by the sol-gel approach. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottner, G. Hybrid sol-gel derived polymers: Applications of multifunctional materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3422–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Julián, B.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M. Applications of hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3559–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammeri, F.; Bourhis, E.L.; Rozesa, L.; Sanchez, C. Mechanical properties of hybrid organic-inorganic materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3787–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseri, W.R. Nanocomposites of polymers and inorganic particles: Preparation, structure, and properties. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.H.; Nagahara, L.A.; Thundat, T.; Mokarian-Tabari, P.; Furukawa, H.; Khosla, A. Organic-inorganic hybrid functional materials: An integrated platform for applied technologies. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B3137–B3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Tamai, K.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Konishi, S.; Katsuhara, M.; Ishiguro, M.; Murata, Y.; Yano, M. A silicon transporter in rice. Nature 2006, 440, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Tamai, K.; Konishi, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Katsuhara, M.; Yano, M. An efflux transporter of silicon in rice. Nature 2007, 448, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruet, B.J.F.; Qi, H.J.; Boyce, M.C.; Panas, R.; Tai, K.; Frick, L.; Ortiz, C. Nanoscale morphology and indentation of individual nacre tablets from gastropod mollusk Trochus niloticus. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 2400–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Nanofabrication and coloration study of artificial Morpho butterfly wings with aligned lamellae layers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dumanli, A.G.; Savin, T. Recent advances in the biomimicry of structural colors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6698–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Hannard, F.; Barthelat, F. Impact-resistant nacre-like transparent materials. Science 2019, 364, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, A.; Ishii, T.; Kato, T. Self-organized calcium carbonate with regular surface-relief structures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5299–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Kajiyama, S.; Kumamoto, A.; Nishimura, T.; Ikuhara, Y.; Yamato, M.; Kato, T. Stimuli-responsive hydroxyapatite liquid crystal with macroscopically controllable ordering and magneto-optical functions. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, N.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C.; Xia, J.; Dai, L.; Li, J. Dopamine-mediated biomineralization of calcium phosphate as a strategy to facilely synthesize functionalized hybrids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 10235–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.M.; Huang, K.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Chand, B.G.; Weng, C.J. Organic-acid-catalyzed sol-gel route for preparing poly(methyl methacrylate)-silica methacrylate)-silica hybrid materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, D. Electro-optic modulator based on novel organic-inorganic hybrid nonlinear optical materials. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2012, 48, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, R.; De, A. Conducting polymer nanocomposites: A brief overview. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.D. Structures and properties of ormosils. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1994, 2, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebelmen, M. Sur les produits de la decomposition des espèces minérales de la famille des silicates. Ann. Des Mines 1845, 7, 3–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mazdiyasni, K.S.; Dolloff, R.T.; Smith II, J.S. Preparation of high-purity submicron barium titanate powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1969, 52, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dislich, H. New routes to multicomponent oxide glasses. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1971, 10, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, G.; Schmidt, H. New materials for contact lenses prepared from Si- and Ti-alkoxides by the sol-gel process. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1984, 63, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutjens, J.M.; Fleer, G.J. Interaction between two adsorbed polymer layers. Macromolecules 1985, 18, 1882–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleer, G.J.; Scheutjens, J.M.H.M. Interaction between adsorbed layers of macromolecules. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 111, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosawa, F.; Asakura, S. Surface tension of high polymer solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1954, 22, 1255–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chujo, Y.; Saegusa, T. Organic polymer hybrids with silica gel formed by means of the sol-gel method. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1992, 100, 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chujo, Y. Organic-inorganic polymer hybrids. Polym. Mater. 1996, 6, 4793–4798. [Google Scholar]
- Chujo, Y. Organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1996, 1, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chujo, Y.; Tamaki, R. New preparation methods for organic-inorganic polymer hybrids. MRS Bull. 2001, 26, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, T.; Chujo, Y. Organic-inorganic polymer hybrids prepared by the sol-gel method. Compos. Interfaces 2005, 11, 539–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aelion, R.; Loebel, A.; Eirich, F. Hydrolysis of ethyl silicate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 5705–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, T. Preparation and properties of esters of polyorthotitanic acid. J. Polym. Sci. 1951, 7, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.C.; Carter, D.G. Metal oxide alkoxide polymers, part I. The hydrolysis of some primary alkoxides of zirconium. Can. J. Chem. 1961, 39, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Ribot, F. Design of hybrid organic-inorganic materials synthesized via sol-gel chemistry. New J. Chem. 1994, 18, 1007–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.K. Organically modified silicates as inorganic-organic polymers. ACS Symp. Ser. 1988, 360, 333–344. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H. Inorganic-organic composites by sol-gel techniques. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1989, 171, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, H.K. Aspects of chemistry and chemical processing of organically modified ceramics. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1990, 180, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, H.; Krug, H. Sol-gel-based inorganic-organic composite materials. ACS Symp. Ser. 1994, 572, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Ikake, H.; Hashimoto, W.; Kawai, M.; Kamiyama, N.; Shimizu, S.; Kurita, K.; Yano, S. Optical properties and microstructures of poly(tetramethylene)/titania hybrid materials with protection against UV-rays. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2002, 59, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yada, K.; Tanaka, S.; Ikake, H.; Shimizu, S.; Kurita, K. Preparation and physical properties of poly(propylene glycol)/titania hybrid materials. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2006, 63, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deb, S.K. Optical and photoelectric properties and color centers in thin films of tungsten oxide. Philos. Mag. 1973, 27, 801–822. [Google Scholar]
- Ikake, H.; Hashimoto, W.; Obara, T.; Kurita, K.; Yano, S. Photochromic properties and microstructures of poly(tetramethylene oxide)/tungsten trioxide hybrid materials. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2000, 57, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikake, H.; Fukuda, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Kurita, K.; Yano, S. Microstructures of poly(ethylene glycol)/tungsten oxide hybrid films exhibiting photochromic properties. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2002, 59, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leaustic, A.; Babonneau, F.; Livage, J. Photoreactivity of WO3 dispersions: Spin trapping and electron spin resonance detection of radical intermediates. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 4193–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, R.J.; Guzman, A.M.; Rabalais, J.W. Photochromism and electrochromism in amorphous transition metal oxide films. Acc. Chem. Res. 1978, 11, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, A.; Iyoko, Y.; Kakimoto, M.; Imai, Y. Preparation of a new class of polyimide-silica hybrid films by the sol-gel process. Polym. J. 1992, 24, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.A.; Hedrick, J.L.; Miller, R.D.; Pietro, R.D. Crosslinked networks based on trimethoxysilyl functionalized poly(amic ethyl ester) chain extendable oligomers. Polymer 1997, 38, 3129–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, W.C. Synthesis and optical properties of polyimide-silica hybrid thin films. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4242–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, R.; Ikake, H.; Shimizu, S.; Kurita, K. Preparation of polyimide/silica hybrid materials. Polym. Prepr. Jpn. 2008, 57, 688. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, S.; Ikake, H.; Shimizu, S. Features and applications of polyimide/magnesia hybrid films. Jpn. Plast. 2018, 69, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids. Clean. Prod. Process. 1999, 1, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Keim, W. Ionic liquids—New solutions for transition metal catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3772–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids—From molten salts to neoteric solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids—Solvents of the future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids—A taste of the future. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Weiner, J. Ueber einige Abkömmlinge des Propylamins. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1888, 21, 2669–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walden, V.P. Ueber die Molekulargrösse und elektrisele Leitfähigkeit einiger gesehmolzenen Salze. Bull. l’Acad. Impér. Sci. 1914, 8, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworotko, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 13, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, N.; Athanassov, Y.; Armand, M.; Bonhôte, P.; Pettersson, H.; Azam, A.; Grätzel, M. The performance and stability of ambient temperature molten salts for solar cell applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieniecka-Rosłonkiewicz, A.; Pernak, J.; Kubis-Feder, J.; Ramani, A.; Robertson, A.J.; Seddon, K.R. Synthesis, anti-microbial activities, and anti-electrostatic properties of phosphonium-based ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.M.; Liu, W.M. Tribological performance of phosphonium-based ionic liquids for an aluminum-on-steel system and opinions on lubrication mechanism. Wear 2006, 261, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Mao, H.; Yan, F. Synthesis of pyrrolidinium-type poly(ionic liquid) membranes for antibacterial applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10504–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Hamaguchi, H. Discovery of a magnetic ionic liquid [bmim]FeCl4. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 1590–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Otsuka, A.; Saito, G.; Natsume, S.; Nishibori, E.; Takata, M.; Sakata, M.; Takahashi, M.; Yoko, T. Conducting and magnetic properties of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (EMI) salts containing paramagnetic irons: Liquids [EMI][MIII Cl4 ] (M = Fe and Fe0:5Ga0:5) and solid [EMI]2[FeIICl4]. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 78, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, P.; Ni, R.; Meng, J. Creating magnetic ionic liquid-molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction of lysozyme. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21850–21856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Correia, D.M.; Fernandes, L.C.; García-Astrain, C.; Tariq, M.; Esperança, J.M.S.; Bermudez, V.Z.; Méndez, S.L. Magnetic ionic liquid/polymer composites: Tailoring physico-chemical properties by ionic liquid content and solvent evaporation temperature. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 178, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Wada, M.; Ohno, H. Cellulose dissolution with polar ionic liquids under mild conditions: Required factors for anions. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.M.; Abraham, M.H.; Taft, R.W. Linear solvation energy relationships. 23. A comprehensive collection of the solvatochromic parameters, p*, α, and β, and some methods for simplifying the generalized solvatochromic equation. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.; Gräsvik, J.; Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Deconstruction of lignocellulosic biomass with ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 550–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, M.; Fukaya, Y.; Ohno, H. Extraction of polysaccharides from bran with phosphonate or phosphinate-derived ionic liquids under short mixing time and low temperature. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, T.; Watanabe, M. Macromolecules in ionic liquids: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Kurita, K.; Furusaka, M. Segment-segment interactions of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in aqueous methanol solutions by using small-angle scattering. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2002, 74, S389–S391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.P.; Brazel, C.S.; Benton, M.G.; Mays, J.W.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Application of ionic liquids as plasticizers for poly(methyl methacrylate)methacrylate). Chem. Commun. 2002, 13, 1370–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Ikake, H.; Shimizu, S. Compound, Dispersant, Complex, Dispersion, and Method for Producing Complex. JP. Patent No. JP6736121, 5 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, S.; Ishizu, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kaneko, T.; Toyama, T.; Shimizu, S.; Ikake, H. Improvement of the transparency, mechanical, and shape memory properties of polymethylmethacrylate/titania hybrid films using tetrabutylphosphonium chloride. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 4761–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Tomono, M.; Fukumoto, K.; Kubodera, M.; Kato, N.; Kaneko, T.; Toyama, T.; Shimizu, S.; Ikake, H. Melt-moldable copolymethacrylate/titania thermoreversible polymer networks with shape memory. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5654–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Aya, S.; Araoka, F.; Ishida, Y.; Kikkawa, A.; Kriener, M.; Taguchi, Y.; Ebina, Y.; Sasaki, T.; et al. Reversible switching of the magnetic orientation of titanate nanosheets by photochemical reduction and autoxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16396–16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, S.; Kurebayashi, S.; Sanae, G.; Watanabe, S.; Kaneko, T.; Toyama, T.; Shimizu, S.; Ikake, H. Polycarbonate/titania hybrid films with localized photo-induced magnetic-phase transition. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikake, H.; Hara, S.; Kurebayashi, S.; Kubodera, M.; Watanabe, S.; Hamada, K.; Shimizu, S. Development of a magnetic hybrid material capable of photoinduced phase separation of iron chloride by shape memory and photolithography. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 7849–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikake, H.; Hara, S.; Shimizu, S. Skillful Control of Dispersion and 3D Network Structures: Advances in Functional Organic–Inorganic Nano-Hybrid Materials Prepared Using the Sol-Gel Method. Polymers 2022, 14, 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163247
Ikake H, Hara S, Shimizu S. Skillful Control of Dispersion and 3D Network Structures: Advances in Functional Organic–Inorganic Nano-Hybrid Materials Prepared Using the Sol-Gel Method. Polymers. 2022; 14(16):3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163247
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkake, Hiroki, Shuta Hara, and Shigeru Shimizu. 2022. "Skillful Control of Dispersion and 3D Network Structures: Advances in Functional Organic–Inorganic Nano-Hybrid Materials Prepared Using the Sol-Gel Method" Polymers 14, no. 16: 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163247
APA StyleIkake, H., Hara, S., & Shimizu, S. (2022). Skillful Control of Dispersion and 3D Network Structures: Advances in Functional Organic–Inorganic Nano-Hybrid Materials Prepared Using the Sol-Gel Method. Polymers, 14(16), 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163247