Silk Fibroin Conjugated with Heparin Promotes Epithelialization and Wound Healing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
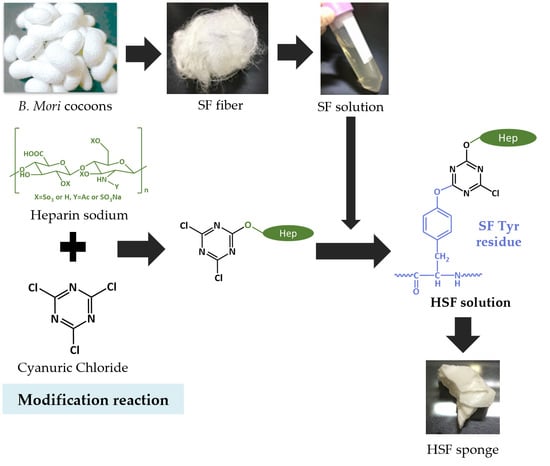
2.1. Preparation of SF Aqueous Solution
2.2. Modification of SF with Heparin
2.3. SF-Heparin Reaction Confirmation by Solution-State 1H NMR
2.4. Secondary Structure Analysis by Solid-State 13C CP/MAS NMR
2.5. Evaluation of Film Surface Properties
2.6. Water Absorption
2.7. Dynamic Viscoelasticity Evaluation
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. Evaluation of Cell Proliferation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SF-Heparin Conjugation Reaction Confirmation
3.2. Secondary Structure Analysis
3.3. Heparin Coverage of Film Surface
3.4. Evaluation of Water Absorption
3.5. Dynamic Viscoelasticity Evaluation
3.6. Cell Proliferation In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guerra, A.; Belinha, J.; Jorge, R.N. Modelling Skin Wound Healing Angiogenesis: A Review. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 459, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, S.C.; Huang, C.; Chan, B.P.; Du, Y. Physical Properties of Implanted Porous Bioscaffolds Regulate Skin Repair: Focusing on Mechanical and Structural Features. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1700894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malafaya, P.B.; Silva, G.A.; Reis, R.L. Natural-Origin Polymers as Carriers and Scaffolds for Biomolecules and Cell Delivery in Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.A.; Wolfe, P.S.; Garg, K.; McCool, J.M.; Rodriguez, I.A.; Bowlin, G.L. The Use of Natural Polymers in Tissue Engineering: A Focus on Electrospun Extracellular Matrix Analogues. Polymers 2010, 2, 522–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Rheinwald, H.G. Epidermal Growth Factor and the Multiplication of Cultured Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Nature 1977, 265, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrus, R.B.H.; Rameli, M.A.B.P.; Cheong, L.K.; Xian, L.J.; Hui, C.K.; Latiff, M.B.A.; Saim, A. Bin Allogeneic Bilayered Tissue-Engineered Skin Promotes Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Ovine Model. Biomed. Res. 2014, 25, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Millán-Rivero, J.E.; Martínez, C.M.; Romecín, P.A.; Aznar-Cervantes, S.D.; Carpes-Ruiz, M.; Cenis, J.L.; Moraleda, J.M.; Atucha, N.M.; García-Bernal, D. Silk Fibroin Scaffolds Seeded with Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Re-Epithelialization and Reduce Formation of Scar Tissue after Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, J.; Warkentin, T.E.; Shaughnessy, S.G.; Anand, S.S.; Halperin, J.L.; Raschke, R.; Granger, C.; Ohman, E.M.; Dalen, J.E. Heparin and Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Mechanisms of Action, Pharmacokinetics, Dosing, Monitoring, Efficacy, and Safety. Chest 2001, 119, 64S–94S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrby, K.; Nordenhem, A. Dalteparin, a Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin, Promotes Angiogenesis Mediated by Heparin-Binding VEGF-A in Vivo. APMIS 2010, 118, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Xue, W. Acceleration of Skin Regeneration in Full-Thickness Burns by Incorporation of BFGF-Loaded Alginate Microspheres into a CMCS–PVA Hydrogel. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.R.; Won, J.E.; Jeon, E.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.; Jo, H.; Jang, J.H.; Shin, U.S.; Kim, H.W. Fibroblast Growth Factors: Biology, Function, and Application for Tissue Regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. 2010, 2010, 218142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakata, Y.; Kimura, R.; Nanba, D.; Iwamoto, R.; Tokumaru, S.; Morimoto, C.; Yokota, K.; Nakamura, M.; Sayama, K.; Mekada, E.; et al. Heparin-Binding EGF-like Growth Factor Accelerates Keratinocyte Migration and Skin Wound Healing. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Johnstone, B.H.; Cook, T.G.; Liang, Z.; Traktuev, D.; Cornetta, K.; Ingram, D.A.; Rosen, E.D.; March, K.L. Suppression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Production Impairs the Ability of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells to Promote Ischemic Tissue Revascularization. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 3234–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, S.; Sumi, M.; Kajimoto, K.; Nakazawa, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Takabayashi, C.; Asakura, T.; Sata, M. Long-Term Patency of Small-Diameter Vascular Graft Made from Fibroin, a Silk-Based Biodegradable Material. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 51, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantawong, P.; Tanaka, T.; Uemura, A.; Shimada, K.; Higuchi, A.; Tajiri, H.; Sakura, K.; Murakami, T.; Nakazawa, Y.; Tanaka, R. Silk Fibroin-Pellethane® Cardiovascular Patches: Effect of Silk Fibroin Concentration on Vascular Remodeling in Rat Model. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Kojima, K.; Otaka, A.; Takeda, Y.S.; Tomita, N.; Tamada, Y. Quantitative Evaluation of Fibroblast Migration on a Silk Fibroin Surface and TGFBI Gene Expression. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkhipova, A.Y.; Nosenko, M.A.; Malyuchenko, N.V.; Zvartsev, R.V.; Moisenovich, A.M.; Zhdanova, A.S.; Vasil’eva, T.V.; Gorshkova, E.A.; Agapov, I.I.; Drutskaya, M.S.; et al. Effects of Fibroin Microcarriers on Inflammation and Regeneration of Deep Skin Wounds in Mice. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, D.; Mandal, B.B. Silk Biomaterials in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration Therapeutics: From Bench to Bedside. Acta Biomater. 2020, 103, 24–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, M.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Fatahi, Y.; Khademhosseini, A.; Kaplan, D.L. Overview of Silk Fibroin Use in Wound Dressings. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalathevan, P.; Ooi, P.S.; Loo, Y.L. Silk-Based Biomaterials in Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2018, 31, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shi, D.; Han, Z.; Dong, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, W.; Yi, Q. Heparinized Silk Fibroin Hydrogels Loading FGF1 Promote the Wound Healing in Rats with Full-Thickness Skin Excision. Biomed. Eng. Online 2019, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.-Z. Fine Organization of Bombyx Mori Fibroin Heavy Chain Gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, M.E.; Krieger, J.R.; Tellier, L.E.; McFaline-Figueroa, J.; Temenoff, J.S.; Botchwey, E.A. Dual Affinity Heparin-Based Hydrogels Achieve Pro-Regenerative Immunomodulation and Microvascular Remodeling. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seib, F.P.; Herklotz, M.; Burke, K.A.; Maitz, M.F.; Werner, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Multifunctional Silk-Heparin Biomaterials for Vascular Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakır, C.O.; Ozturk, M.T.; Tuzlakoglu, K. Design of Antibacterial Bilayered Silk Fibroin-Based Scaffolds for Healing of Severe Skin Damages. Mater. Technol. 2018, 33, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestari, M.; Muller, V.; Rodrigues, J.H.D.S.; Nakamura, C.V.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Preparing Silk Fibroin Nanofibers through Electrospinning: Further Heparin Immobilization toward Hemocompatibility Improvement. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphya, A.R.; David, L. Kaplan Biomedical Applications of Chemically-Modified Silk Fibroin. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6443–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytemiz, D.; Fukuda, Y.; Higuchi, A.; Asano, A.; Nakazawa, C.T.; Kameda, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Nakazawa, Y. Compatibility Evaluation of Non-Woven Sheet Composite of Silk Fibroin and Polyurethane in the Wet State. Polymers 2018, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, Y.; Tsukada, M.; Aiba, S.; Minoura, N. Chemical Modification of Silk Fibroin with N-Acetyl-Chito-Oligosaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1996, 18, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, Y.; Minoura, N.; Miyashita, T. Preparation and Characterization of Conjugates of Silk Fibroin and Chitooligosaccharides. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2002, 280, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponedel’kina, I.Y.; Odinokov, V.N.; Lukina, E.S.; Tyumkina, T.V.; Khalilov, L.M.; Dzhemilev, U.M. Chemical Modification of Heparin. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2006, 32, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakazawa, Y.; Yazawa, K.; Holland, G.P.; Yarger, J.L. Silk Structure Studied with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2013, 69, 23–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, W.; Christ, M.D.; Rabenstein, D.L. Determination of the Primary Structures of Heparin- and Heparan Sulfate-Derived Oligosaccharides Using Band-Selective Experiments. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, T.; Okushita, K.; Williamson, M.P. Analysis of the Structure of Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin by NMR. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgo, K.; Niemczura, W.P.; Muroi, T.; Onizuka, A.K.; Kumashiro, K.K. Wideline Separation (WISE) NMR of Native Elastin. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8899–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Target Sites in SF | Cyanuric Chloride | Heparin Sodium | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSF2 | 20 | 20 | 2 |
| HSF3 | 20 | 20 | 3 |
| HSF4 | 20 | 20 | 4 |
| HSF5 | 20 | 20 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hama, R.; Aytemiz, D.; Moseti, K.O.; Kameda, T.; Nakazawa, Y. Silk Fibroin Conjugated with Heparin Promotes Epithelialization and Wound Healing. Polymers 2022, 14, 3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173582
Hama R, Aytemiz D, Moseti KO, Kameda T, Nakazawa Y. Silk Fibroin Conjugated with Heparin Promotes Epithelialization and Wound Healing. Polymers. 2022; 14(17):3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173582
Chicago/Turabian StyleHama, Rikako, Derya Aytemiz, Kelvin O. Moseti, Tsunenori Kameda, and Yasumoto Nakazawa. 2022. "Silk Fibroin Conjugated with Heparin Promotes Epithelialization and Wound Healing" Polymers 14, no. 17: 3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173582
APA StyleHama, R., Aytemiz, D., Moseti, K. O., Kameda, T., & Nakazawa, Y. (2022). Silk Fibroin Conjugated with Heparin Promotes Epithelialization and Wound Healing. Polymers, 14(17), 3582. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173582