Polylactide/Carbon Black Segregated Composites for 3D Printing of Conductive Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Materials
2.2. Formation of the PLA/CB Composites
2.3. Formation of Filaments and FDM 3D Printing Process
2.4. Optical Microscopy
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7. WAXS
2.8. Measurements of the Electrical Conductivity
2.9. Static Mechanical Testing
2.10. Computer Modeling
3. Results
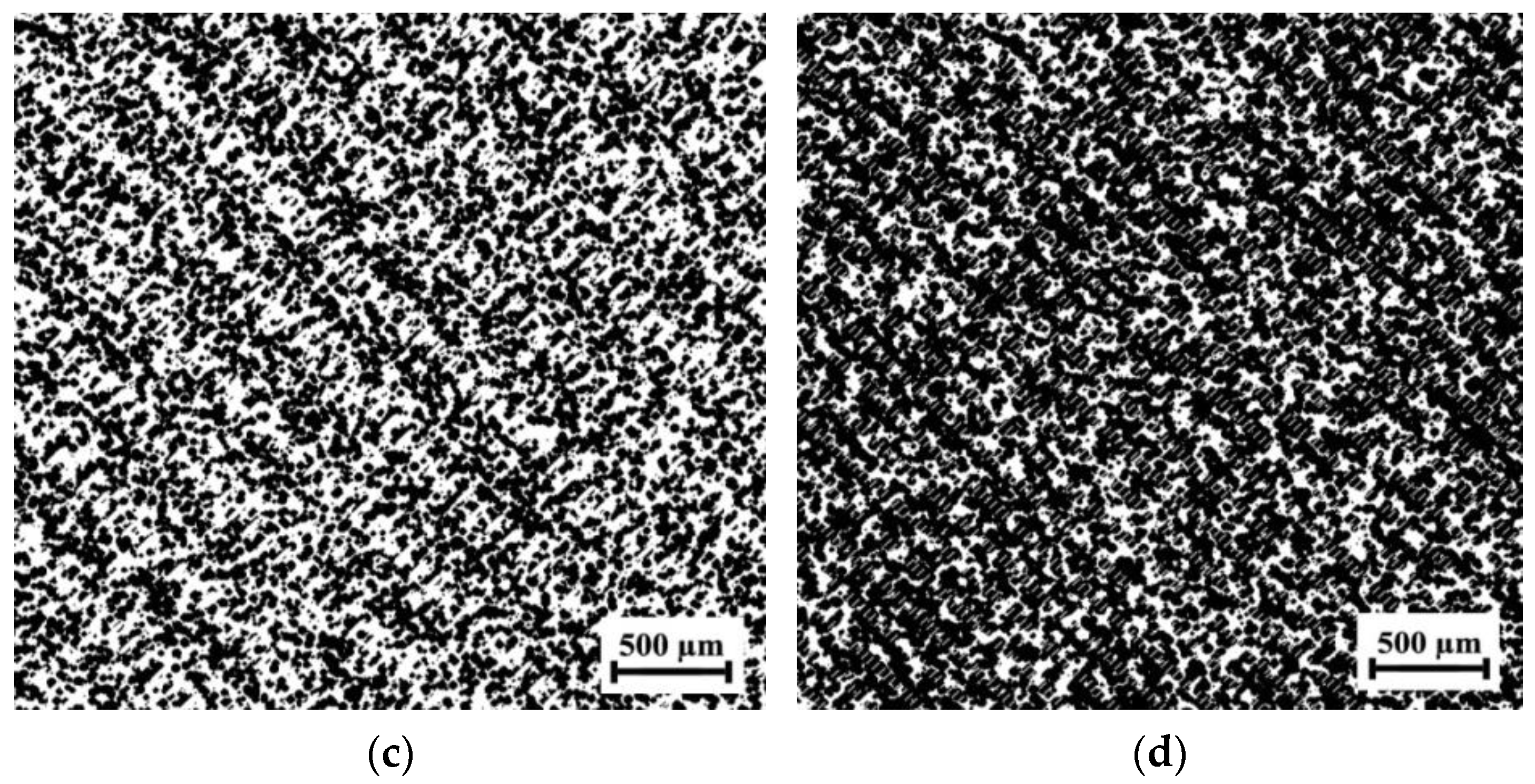
3.1. Modeling of the Segregated Structure of PLA/CB Composites
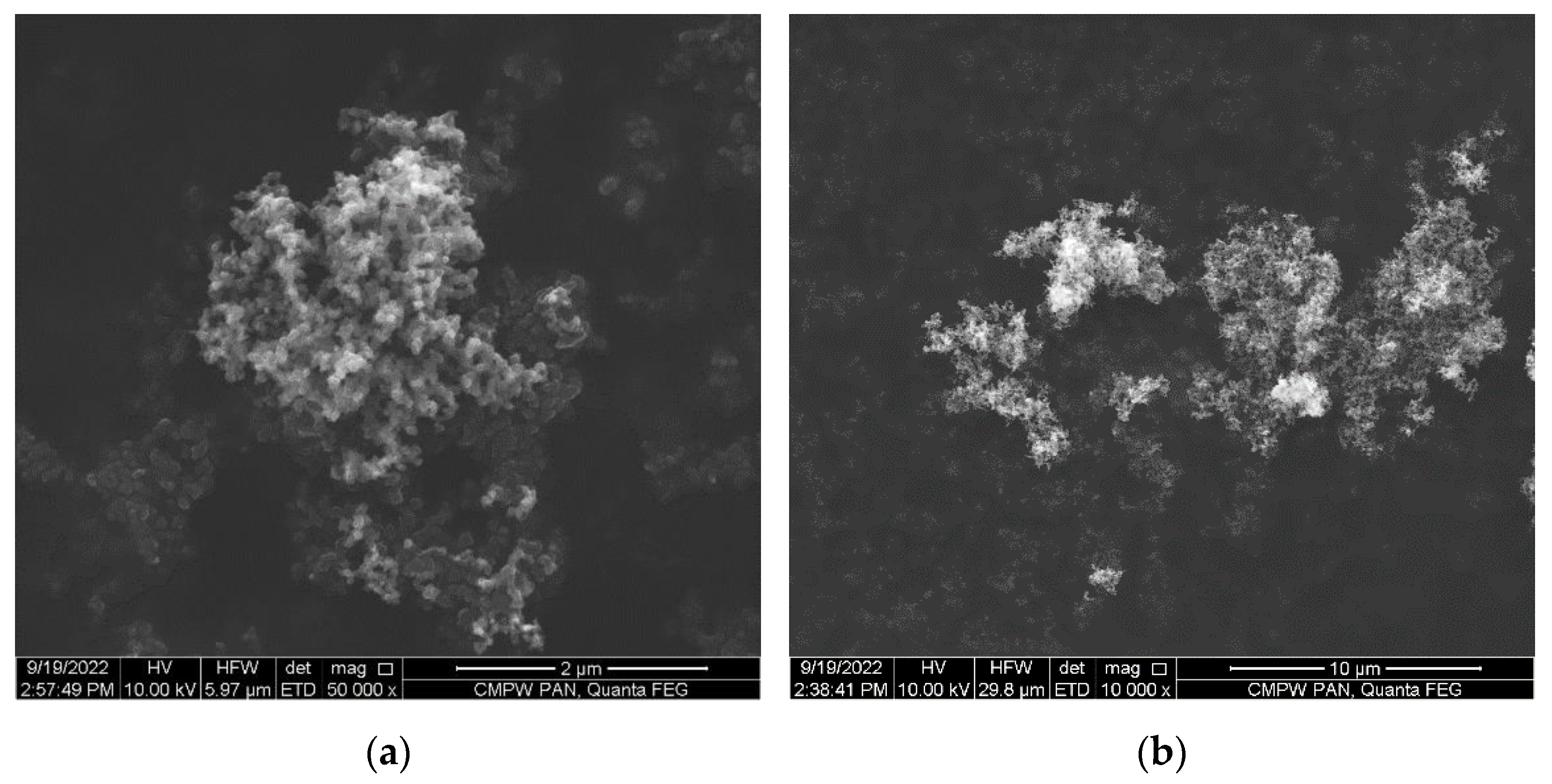
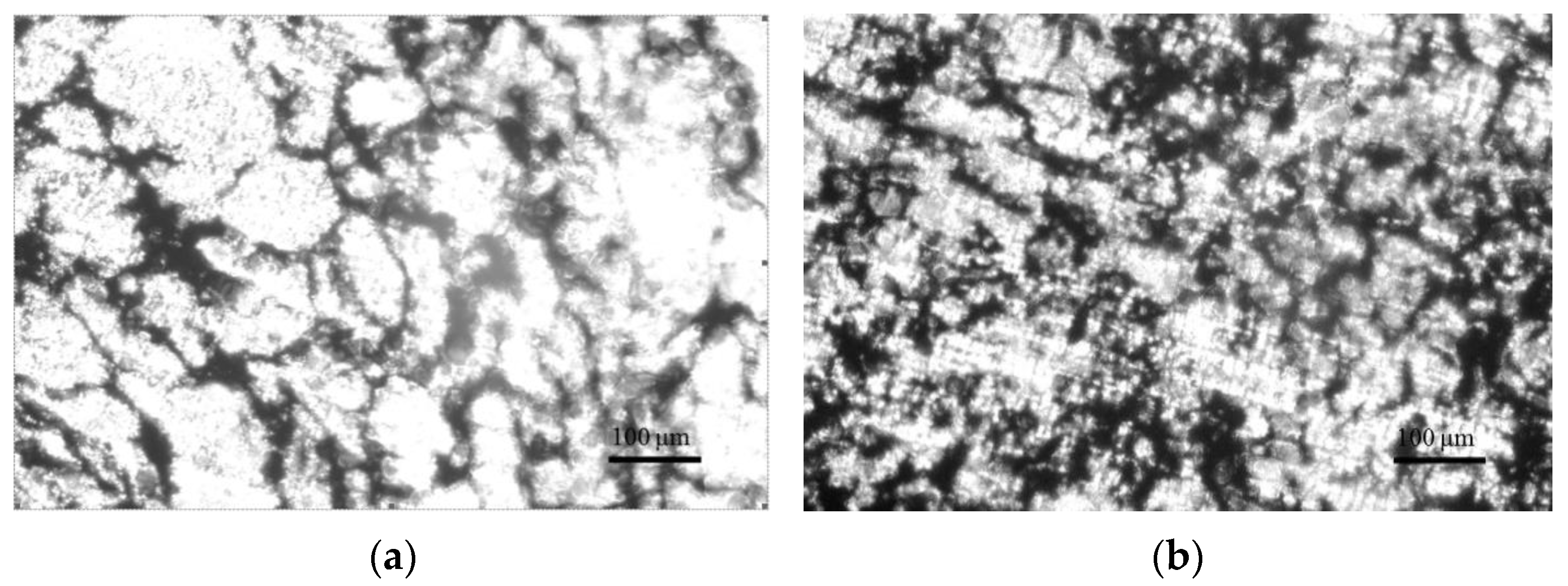
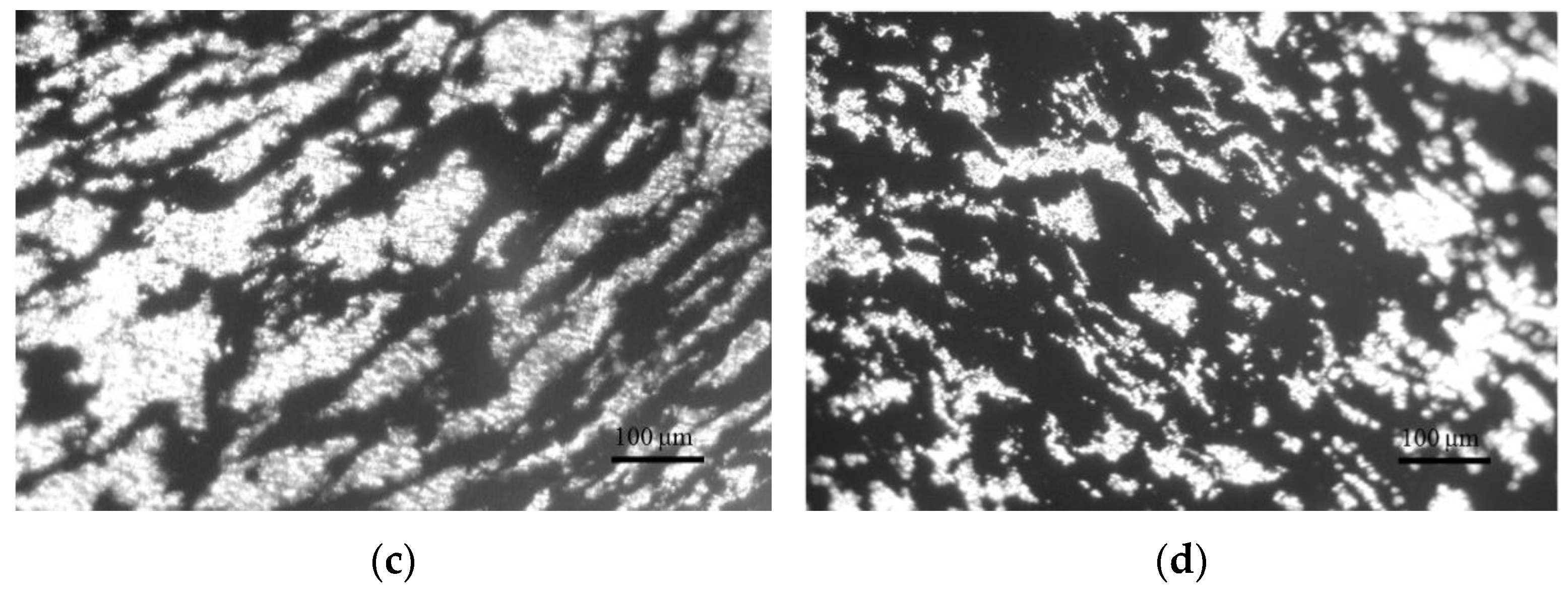
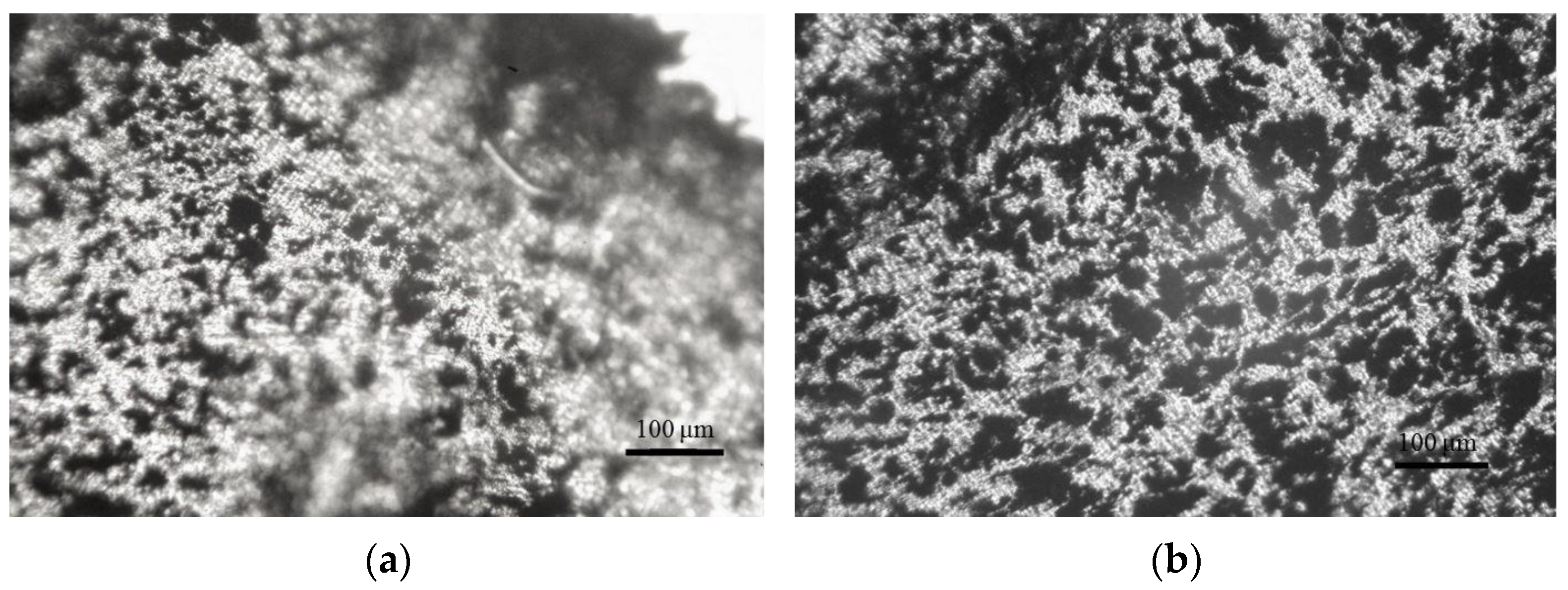
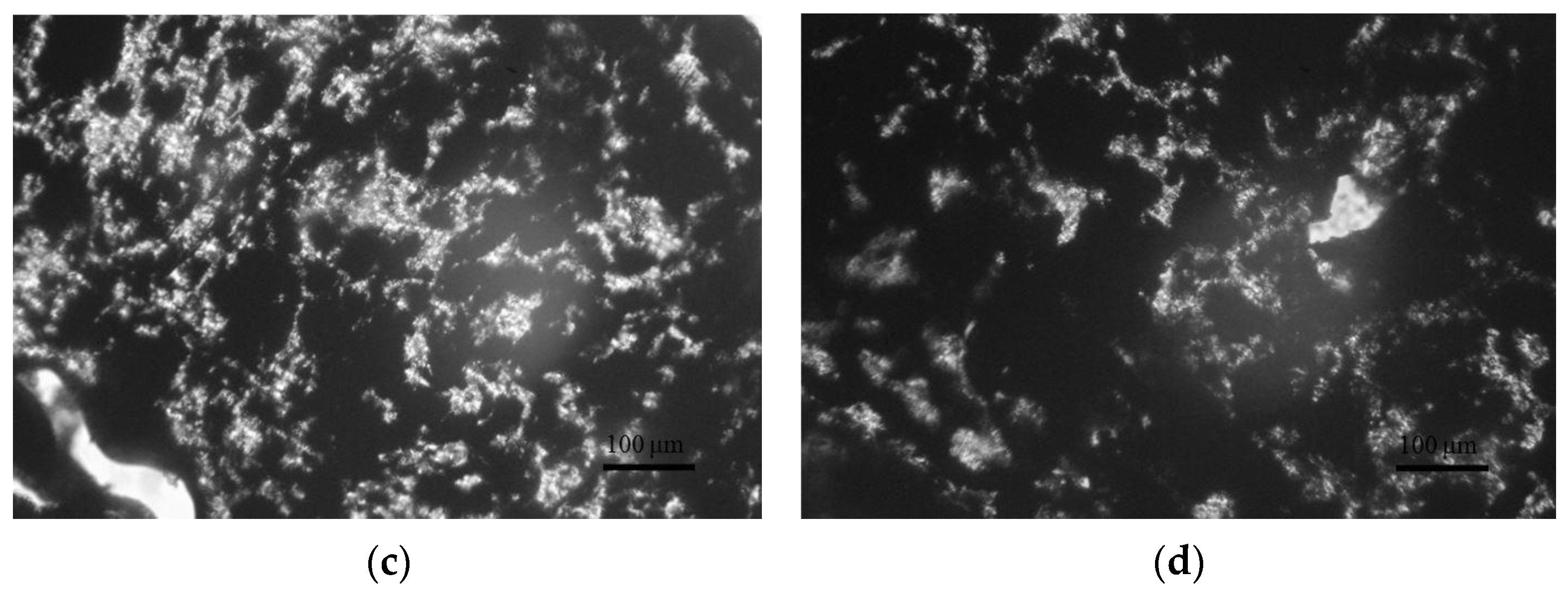
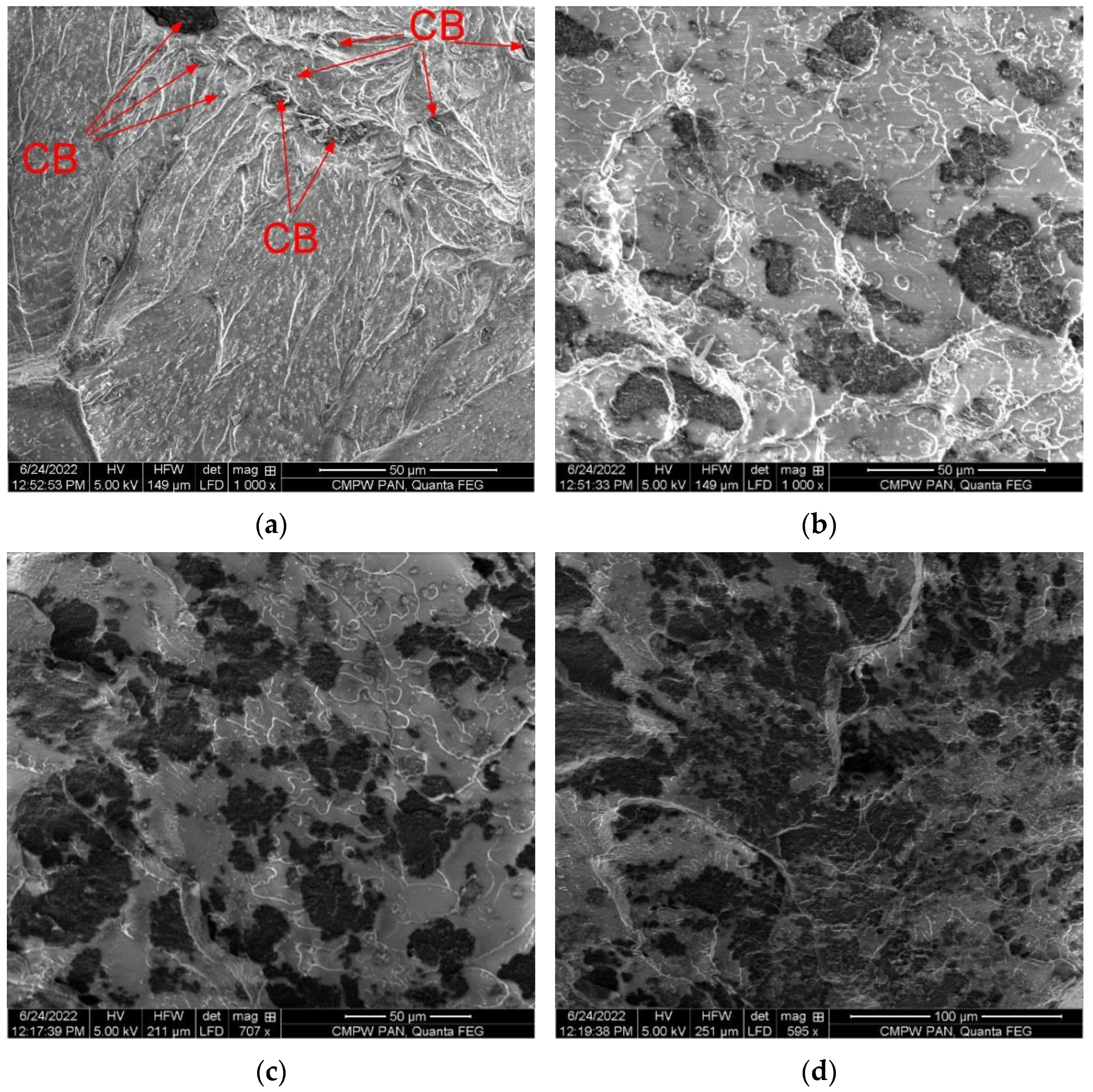
3.2. Morphology of the PLA/CB Composites, Filaments and 3D Specimens
3.3. Thermal Properties of the PLA/CB Composites, Filaments and 3D Specimens
3.4. WAXS
3.5. Electrical Conductivity of the Composites
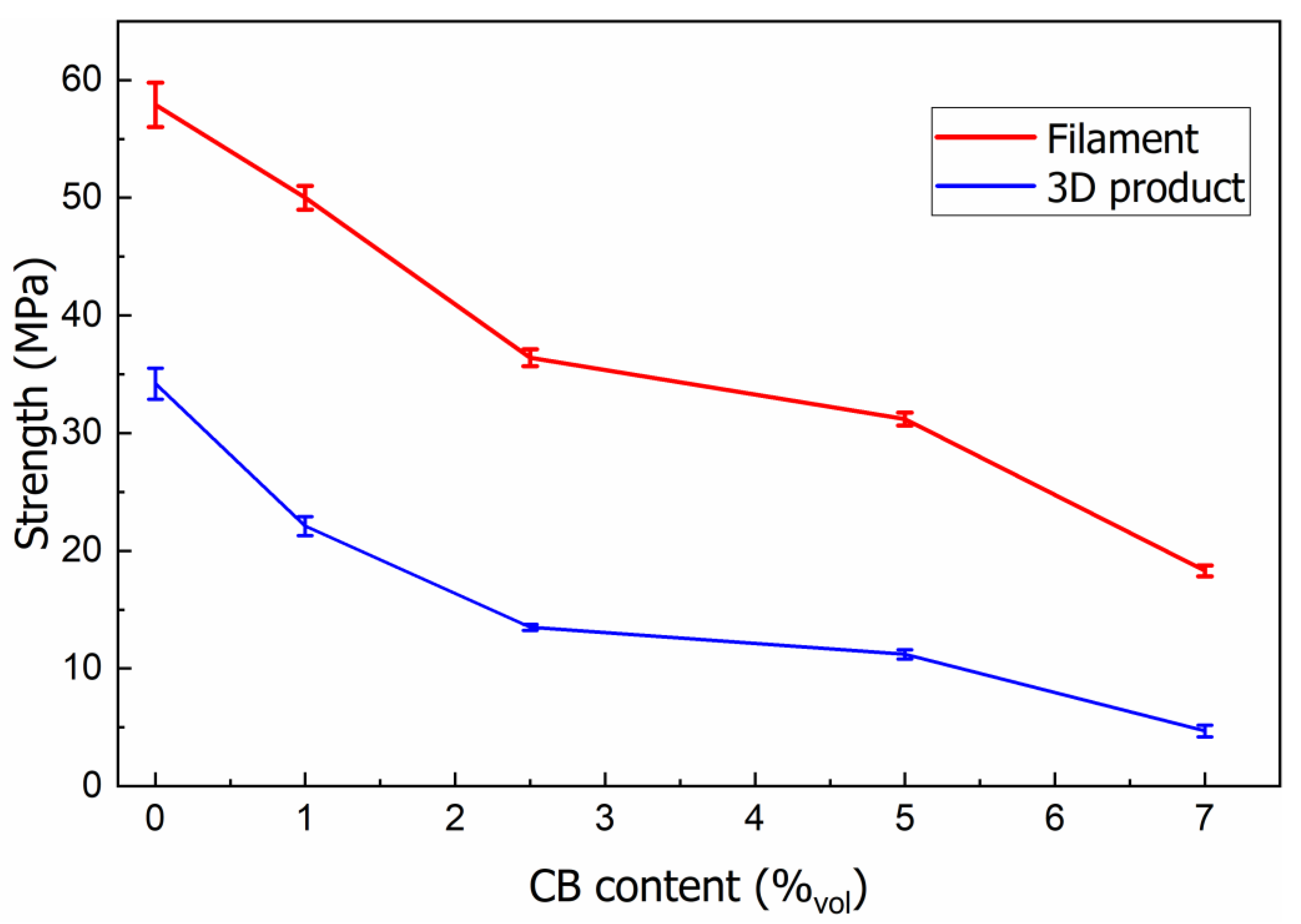
3.6. Mechanical Strength of the PLA/CB Filaments and 3D Specimens
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narayan, R.; Yoo, J.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting: Physical and chemical processes. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2021, 8, 030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.-T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rai, A. Fused deposition modelling (FDM) based 3D and 4D Printing: A state of art review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastic in a Coil with Special Properties [Electronic Resource]. Available online: https://pro3d.com.ua/g75852675-plastik-kotushtsi-spets (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Palenzuela, C.L.M.; Novotny, F.; Krupicka, P.; Sofer, Z.; Pumera, M. 3D-printed graphene/polylactic acid electrodes promise high sensitivity in electroanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5753–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneckov, E.; Bousa, M.; Lachmanov, S.N.; Rathouský, J.; Gal, M.; Sebechlebská, T.; Kolivoska, V. 3D printed polylactic acid/carbon black electrodes with nearly ideal electrochemical behaviour. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 857, 113745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.Y.; Duoss, E.B.; Motala, M.J.; Guo, X.; Park, S.I.; Xiong, Y.; Yoon, J.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Rogers, J.A.; Lewis, J.A. Omnidirectional printing of flexible, stretchable, and spanning silver microelectrodes. Science 2009, 323, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, K.; Heijmans, T.; van Bennekom, S.; Woldhuis, H.; Wijnia, S.; de With, G.; Friedrich, H. 3D printing of CNT- and graphene-based conductive polymer nanocomposites by fused deposition modeling. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A. Conductive polymer-based electro-conductive textile composites for electromagnetic interferenceshielding: A review. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 47, 2228–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathies, T.; Senthil, P.; Prakash, C. Application of 3D printed PLA-carbon black conductive polymer composite in solvent sensing. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, S.J.; Bradley, R.J.; Purssell, C.P.; Billson, D.R.; Hutchins, D.A. A simple, low-cost conductive composite material for 3D printing of electronic sensors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S. Characterization of Electrical Heating of Graphene/PLA Honeycomb Structure Composite Manufactured by CFDM 3D Printer. Fash. Text. 2020, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekce, H.S.; Kumlutas, D.; Tavman, I.H. Effect of Particle Shape on Thermal Conductivity of Copper Reinforced Polymer Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2007, 26, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, B.W.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Then, Y.Y.; Loo, Y.Y. Mechanical, thermal, and morphology properties of poly(lactic acid) plasticized with poly(ethylene glycol) and epoxidized palm oil hybrid plasticizer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, S.; Gong, S.; O’Neill, E.; Rowell, R.M.; Krzysik, A.M. Polylactide-pine wood flour composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Islam, M.S.; Hassan, A.; Mohamad Haafiz, K.M.; Arjmandi, R.; Inuwa, I.M. Mechanical properties and morphological characterization of PLA/chitosan/epoxidized natural rubber composites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, S.M.; Gefle, O.S.; Amitov, E.T.; Berchuk, D.Y.; Zhuravlev, D.V. Influence of heavy metal powders on rheological properties of poly(lactic acid). Russ. Phys. J. 2017, 60, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureto, J.; Tomasi, J.; King, J.A.; Pearce, J.M. Thermal properties of 3-D printed polylactic acid-metal composites. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 2, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizundia, E.; Oleaga, A.; Salazar, A.; Sarasua, J.R. Nano- and microstructural effects on thermal properties of poly(L-lactide)/multi-wall carbon nanotube composites. Polymer 2012, 53, 2412–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory; Revised second edition; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pridoehl, M.; Behrens, U.; Bernhardt, S.; Klaar, A.-K.; Karsa-Wilberforce, S. Use and Production of Coated Flaments for Extrusion-Based 3D Printing Processes. U.S. Patent 9,193,110 B2 (45), 24 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, S.M.; Gefle, O.S.; Amitov, E.T.; Zhuravlev, D.V.; Berchuk, D.Y.; Mikutskiy, E.A. Mechanical properties of PLA-based composites for fused deposition modeling technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 97, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.; Lima, P.; Krause, B.; Pötschke, P.; Lafont, U.; Gomes, J.R.; Abreu, C.S.; Paiva, M.C.; Covas, J.A. Electrically Conductive Polyetheretherketone Nanocomposite Filaments: From Production to Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2018, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirado-Garcia, I.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D.; Garzon-Hernandez, S.; Rusinek, A.; Robles, G.; Martinez-Tarifa, J.; Arias, A. Conductive 3D printed PLA composites: On the interplay of mechanical, electrical and thermal behaviours. Compos. Struct. 2021, 265, 113744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Q. Electrostatic adsorption method for preparing electrically conducting ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/graphene nanosheets composites with a segregated network. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 89, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacubowicz, J.; Narkis, M.; Benguigui, L. Electrical and dielectric properties of segregated carbon black–polyethylene systems. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Xu, L.; Pang, H.; Yan, D.X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.Q.; Tang, J.H.; Li, Z.M. Preparation and properties of carbon black/polymer composites with segregated and double-percolated network structures. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 4892–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolisnyk, R.; Korab, M.; Iurzhenko, M.; Masiuchok, O.; Mamunya, Y. Development of heating elements based on conductive polymer composites for electrofusion welding of plastics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, 50418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemicals reactions. Kolloid-Z. Fuer Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Dechief, A.L.; Paint, Y. Polylactide (PLA)-halloysite nanaocomposites: Production, morphology and key-properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, S.; Anandjiwala, R.; Ray, S. Mechanical, thermal, and fire properties of polylactide/starch blend/clay composites. J. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 113, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamunya, Y. Carbon nanotubes as conductive filler in segregated polymer composites—Electrical properties. In Carbon Nanotubes—Polymer Nanocomposites; Yellampalli, S., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; Chapter 9; pp. 173–196. ISBN 978-953-307-498-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mamunya, Y.P.; Davydenko, V.V.; Pissis, P.; Lebedev, E.V. Electrical and thermal conductivity of polymers filled with metal powders. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, M. Enthalpy relaxation and recovery in amorphous materials. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1994, 169, 211–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, M.A.; Mondal, A.; Sengupta, A. Effect of physical aging on glass transition and enthalpy relaxation in PLA polymer filament. In Proceedings of the International Conference RAMSB-2018, Material Science and Biophysics, Mangalore, India, 23–25 January 2018; pp. 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, M.; Lee, S.C.; Jeong, Y.G. Influences of physical aging on enthalpy relaxation behavior, gas permeability, and dynamic mechanical property of polylactide films with various D-isomer contents. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Zhu, B.; Inoue, Y. Enthalpy Relaxation and Embrittlement of Poly(L-lactide) during Physical Aging. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 9664–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrasa, J.O.; Montero, A.F.; Ferrari, B.; Pastor, J.Y. Characterisation and modelling of PLA filaments and evolution with time. Polymers 2021, 13, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bhandari, B.; Zhou, W. Glass transition and enthalpy relaxation of amorphous food saccharides: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5701–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, P.; Imre, B.; Bere, J.; Móczó, J.; Pukánszky, B. Physical ageing and molecular mobility in PLA blends and composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 122, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tsou, C.-H.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.-S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Ge, F.; Liu, P.; De Guzman, M.R. Conductivity and mechanical properties of carbon black-reinforced poly(lactic acid) (PLA/CB) composites. Iran. Polym. J. 2021, 30, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





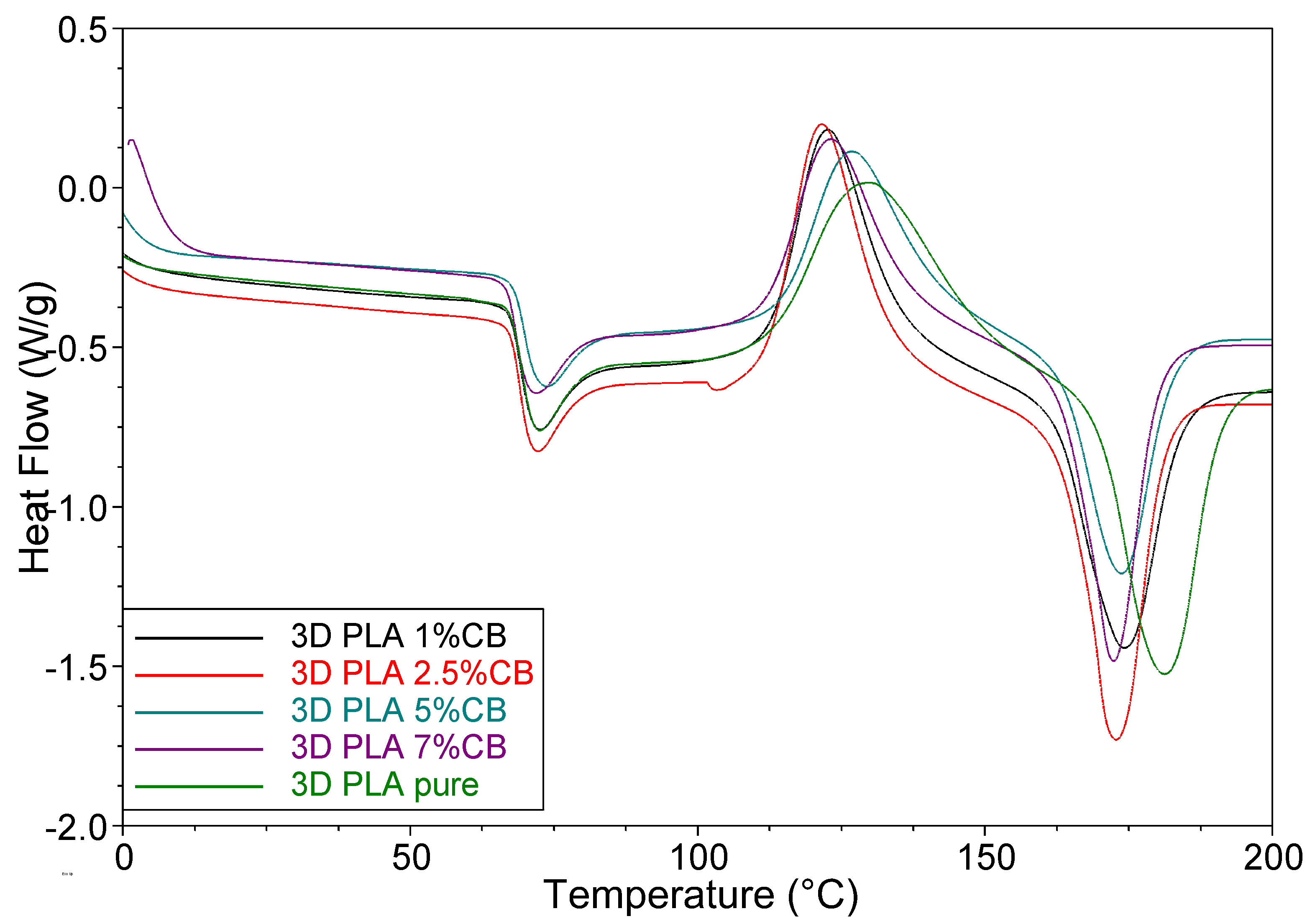
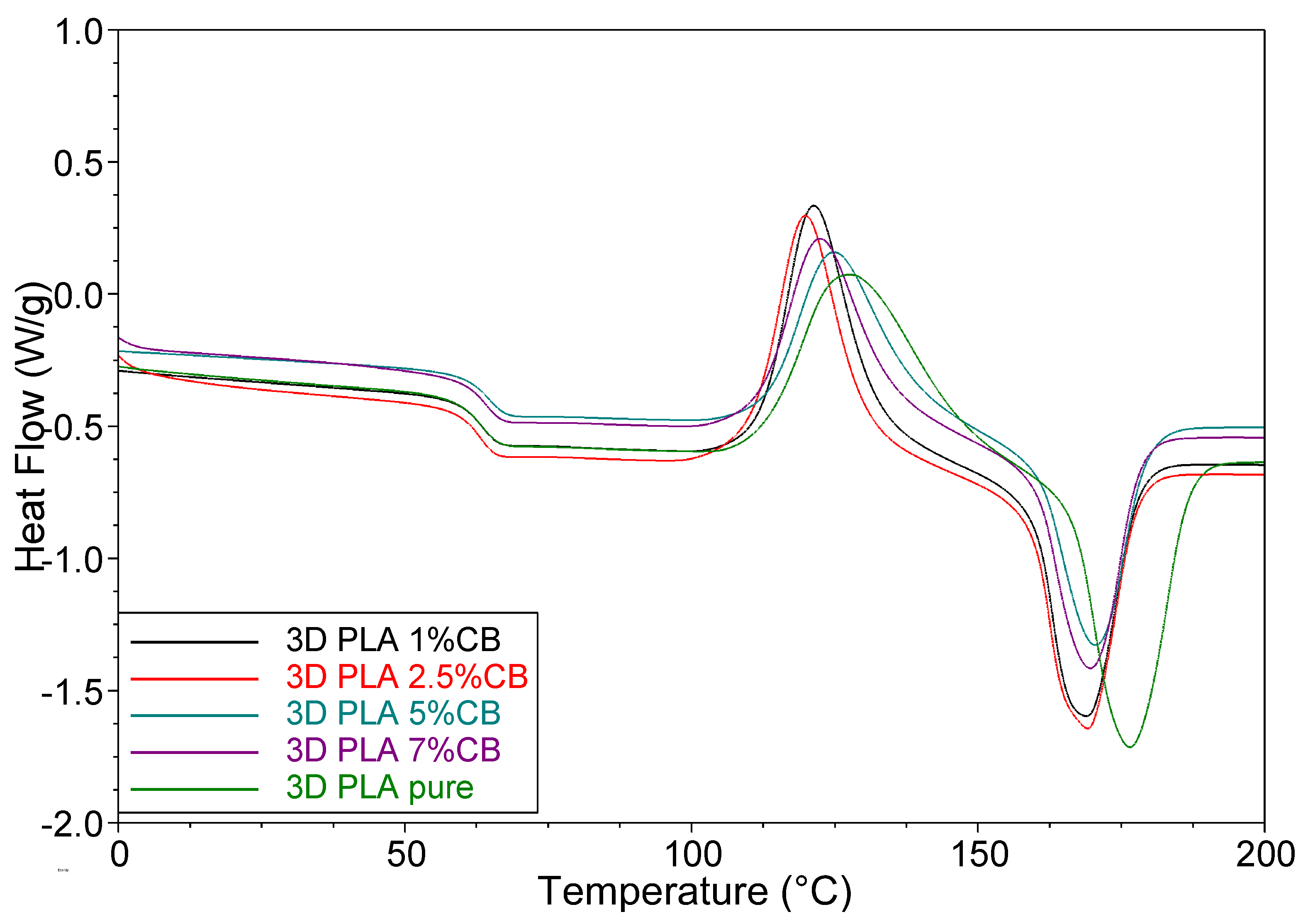

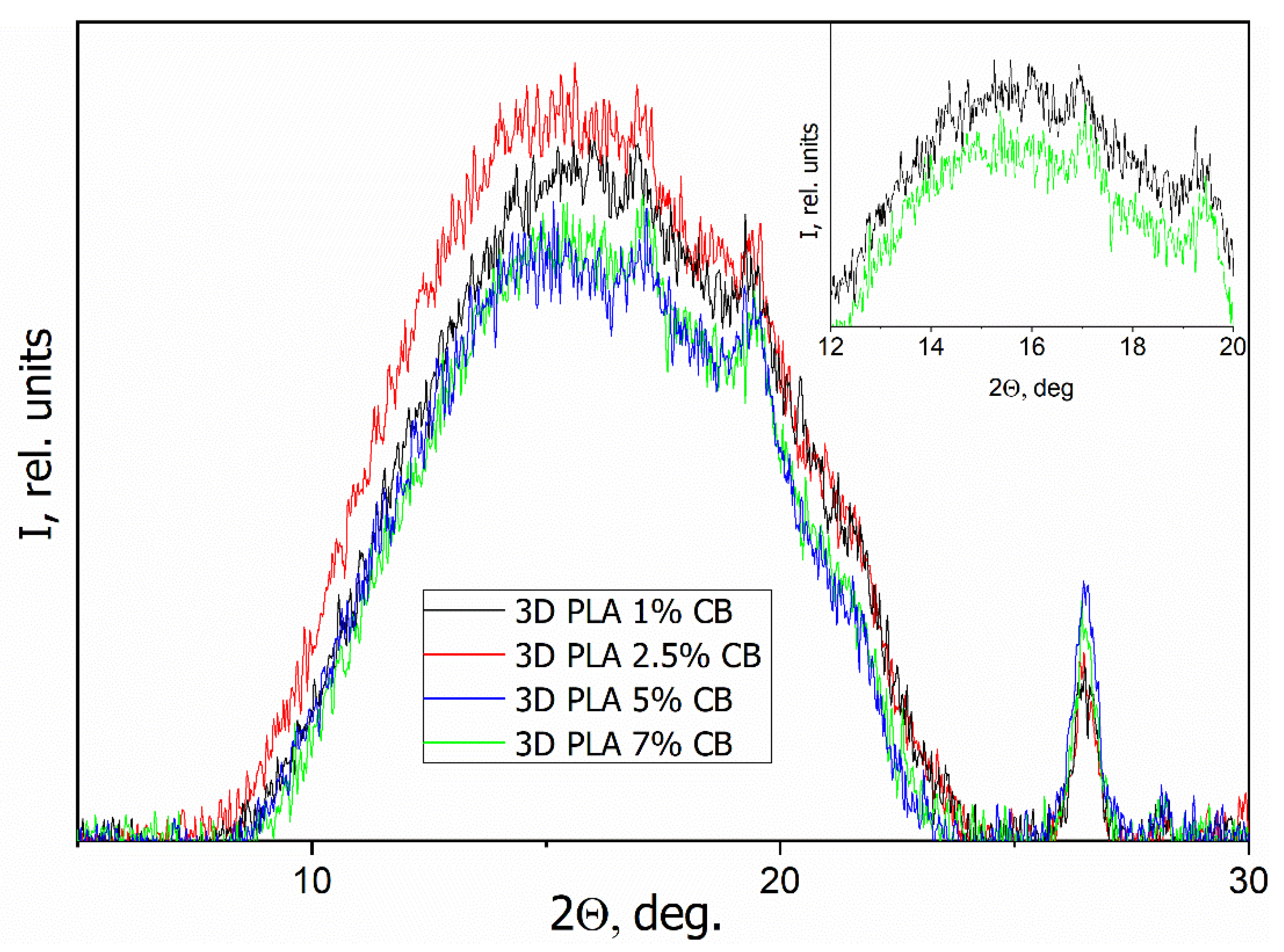

| Filler Content φ, vol.% | Tg, °C | Tcc, °C | ΔHcc, J/g | Tm, °C | ΔHm, J/g | Xc, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filaments (Ⅰ run) | ||||||
| 0 | 67.8 | 106.8 | 17.9 | 173.1 | 18.5 | 0.68 |
| 1 | 66.7 | 120.2 | 23.7 | 173.2 | 25.0 | 1.57 |
| 2.5 | 67.0 | 125.3 | 20.2 | 173.8 | 21.3 | 1.40 |
| 5 | 67.9 | 128.5 | 17.6 | 174.3 | 19.1 | 1.20 |
| 7 | 67.2 | 126.1 | 17.1 | 173.2 | 19.6 | 3.06 |
| 3D specimens (Ⅰ run) | ||||||
| 0 | 69.4 | 129.8 | 40.5 | 181.0 | 42.5 | 2.26 |
| 1 | 69.1 | 122.6 | 35.5 | 174.2 | 37.9 | 2.60 |
| 2.5 | 69.1 | 121.6 | 37.2 | 172.7 | 40.8 | 3.97 |
| 5 | 69.8 | 126.9 | 28.8 | 173.7 | 31.8 | 3.47 |
| 7 | 68.3 | 123.2 | 31.4 | 172.3 | 35.4 | 4.78 |
| 3D specimens (Ⅱ run) | ||||||
| 0 | 63.3 | 127.4 | 45.9 | 176.5 | 47.5 | 1.66 |
| 1 | 63.6 | 121.3 | 38.7 | 168.9 | 40.4 | 1.87 |
| 2.5 | 63.3 | 119.9 | 39.3 | 169.1 | 40.9 | 1.77 |
| 5 | 64.7 | 124.9 | 33.3 | 170.5 | 34.7 | 1.63 |
| 7 | 64.2 | 122.5 | 34.5 | 169.6 | 36.2 | 2.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masiuchok, O.; Iurzhenko, M.; Kolisnyk, R.; Mamunya, Y.; Godzierz, M.; Demchenko, V.; Yermolenko, D.; Shadrin, A. Polylactide/Carbon Black Segregated Composites for 3D Printing of Conductive Products. Polymers 2022, 14, 4022. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194022
Masiuchok O, Iurzhenko M, Kolisnyk R, Mamunya Y, Godzierz M, Demchenko V, Yermolenko D, Shadrin A. Polylactide/Carbon Black Segregated Composites for 3D Printing of Conductive Products. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):4022. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasiuchok, Olha, Maksym Iurzhenko, Roman Kolisnyk, Yevgen Mamunya, Marcin Godzierz, Valeriy Demchenko, Dmytro Yermolenko, and Andriy Shadrin. 2022. "Polylactide/Carbon Black Segregated Composites for 3D Printing of Conductive Products" Polymers 14, no. 19: 4022. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194022
APA StyleMasiuchok, O., Iurzhenko, M., Kolisnyk, R., Mamunya, Y., Godzierz, M., Demchenko, V., Yermolenko, D., & Shadrin, A. (2022). Polylactide/Carbon Black Segregated Composites for 3D Printing of Conductive Products. Polymers, 14(19), 4022. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194022







