Sound Absorption Improvement in Porous Ferroelectret Polyethylene with Effective Piezoelectric Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
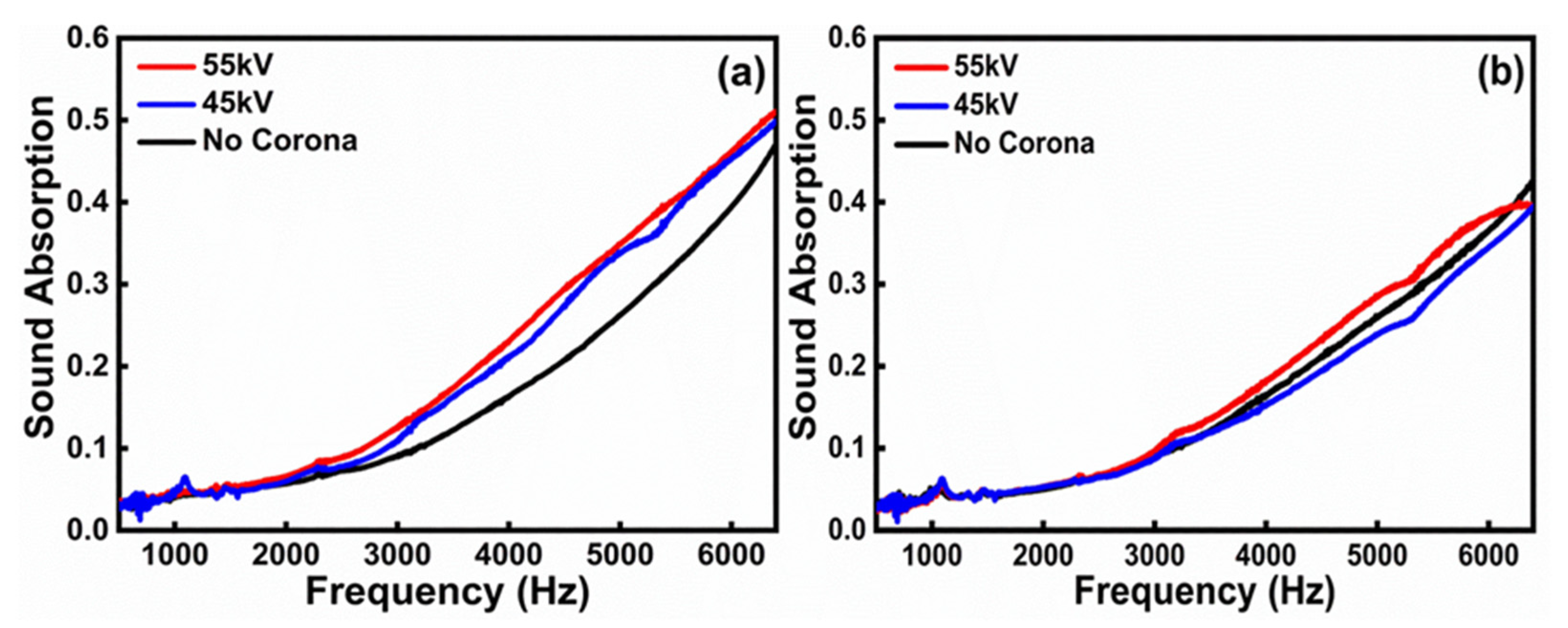
3.1. Sound Absorption Measurements
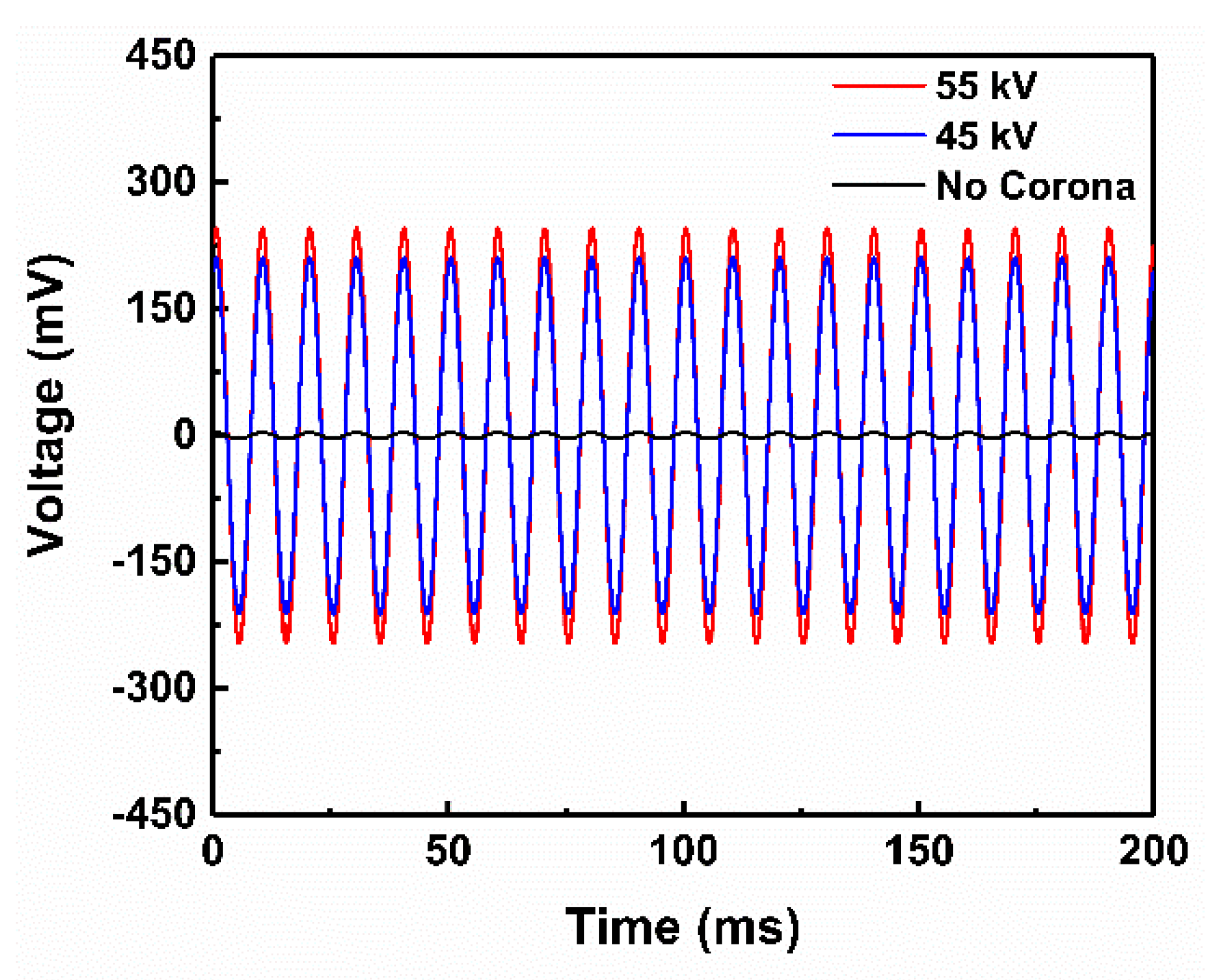
3.2. Analyses and Discussion
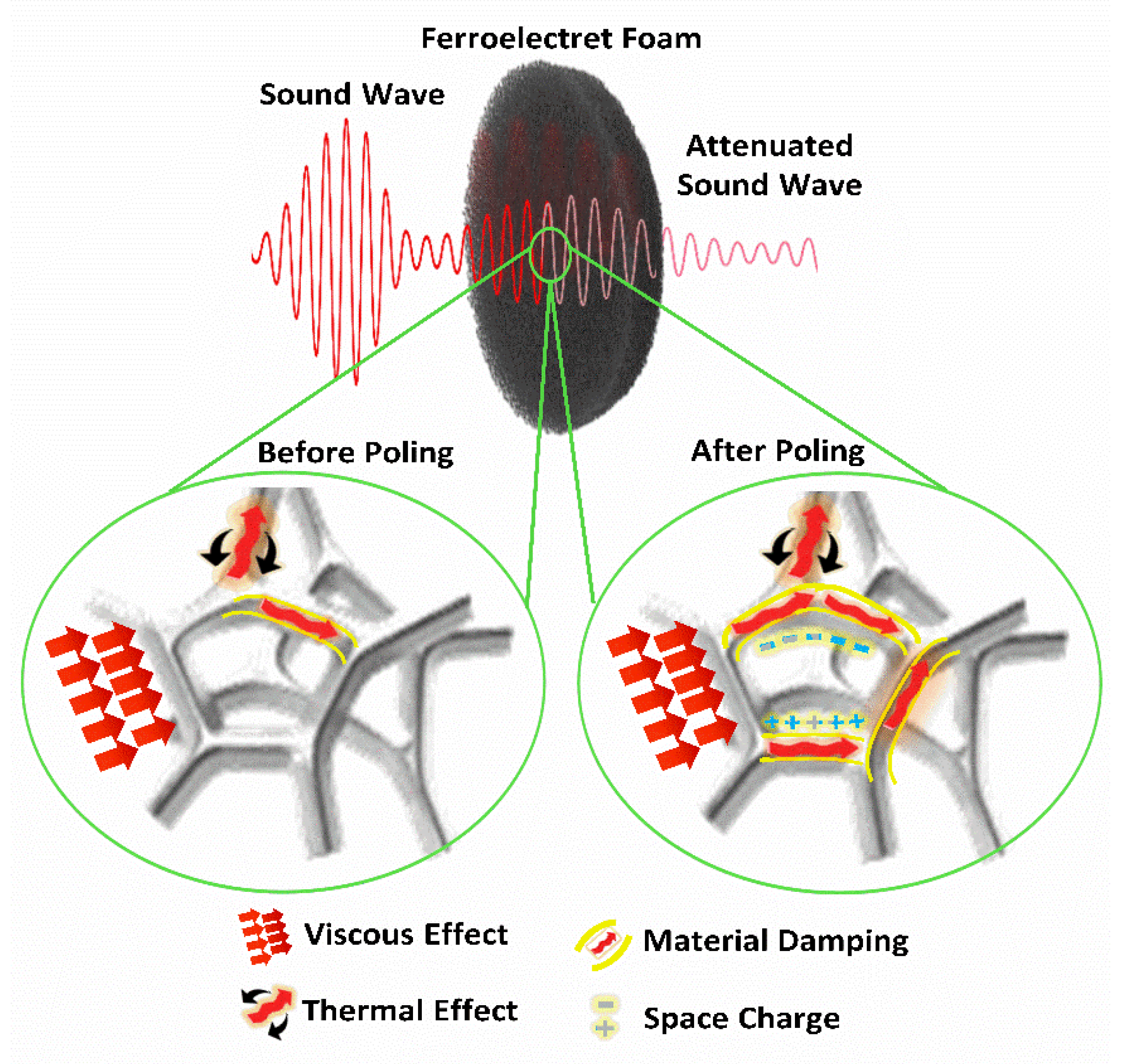
3.3. Theoretical Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Gong, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. The review of fiber-based sound-absorbing structures. Text. Res. J. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagartzazu, X.; Hervella-Nieto, L.; Pagalday, J.M. Review in Sound Absorbing Materials. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2008, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Wu, M.; Sun, H.; Yang, J.; Chen, M. Some Practical Acoustic Design and Typical Control Strategies for Multichannel Active Noise Control. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, J. A New Feedforward Hybrid Active Noise Control System. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2011, 18, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Shen, Y.; Wu, G. Improved sound absorption performance of synthetic fiber materials for industrial noise reduction: A review. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.J.; D’Antonio, P. Book Review: Acoustic Absorbers and Diffusers: Theory, Design and Application. Build. Acoust. 2005, 12, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everest, F.A.; Pohlmann, K.C. Master Handbook of Acoustics, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 193–238. [Google Scholar]
- Vér, I.L.; Beranek, L. L Noise and Vibration Control Engineering: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 215–277. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Peng, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y. Research Progress on Sound Absorption of Electrospun Fibrous Composite Materials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.; Nguyen, T.; Sinaie, S.; Heath, D.; Ngo, T. The low frequency structure-borne sound problem in multi-storey timber buildingsand potential of acoustic metamaterials: A review. Build. Environ. 2022, 224, 109531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.F.; Atalla, N. Propagation of Sound in Porous Media: Modelling Sound Absorbing Materials, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 73–107. [Google Scholar]
- Fahy, F.J. Foundations of Engineering Acoustics, 1st ed.; Academic: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 140–179. [Google Scholar]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of Propagation of Elastic Waves in a Fluid Saturated Porous Solid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, C. Acoustics of porous media with inner resonators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 4717–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qiu, X.; Kang, J. Active noise attenuation in ventilation windows. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirshekarloo, M.S.; Tan, C.Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Yao, K.; Cui, F.; Pandit, S.M.; Chong, S.H.; Tan, S.T. Transparent piezoelectric film speakers for windows with active noise mitigation function. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 137, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.-K. Broadband transmission noise reduction of smart panels featuring piezoelectric shunt circuits and sound-absorbing material. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szu Cheng, L.; Mirshekarloo, M.S.; Yao, K. Effects of equivalent series resistance on the noise mitigation performance of piezoelectric shunt damping. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 057005. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, K. Advanced Piezoelectric Materials: Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimabady, M.; Statharas, E.C.; Yao, K.; Mirshekarloo, M.S.; Chen, S.; Tay, F.E.H. Hybrid local piezoelectric and conductive functions for high performance airborne sound absorption. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 241601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.; Yao, K.; Yousry, Y.M.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Open-cell poly (vinylidene fluoride) foams with polar phase for enhanced airborne sound absorption. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 092903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statharas, E.C.; Yao, K.; Zhang, L.; Salloum, R.; Mohamed, A.M.; Tay, F.E.H. Theoretical analysis on hybrid local piezoelectric and conductive effect on sound absorption performance of porous poly (vinylidene fluoride). Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 086204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.; Yao, K.; Yousry, Y.M.; Wang, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Enhanced airborne sound absorption effect in poly(vinylidene fluoride)/(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-nanofiber composite foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.; Yao, K.; Yousry, Y.M.; Wang, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Open-cell P(VDF-TrFE)/MWCNT Nanocomposite Foams with Local Piezoelectric and Conductive Effects for Passive Airborne Sound Absorption. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 214102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Gerhard-Multhaupt, R.; Künstler, W.; Wedel, A.; Danz, R. High surface-charge stability of porous polytetrafluoroethylene electret films at room and elevated temperatures. J. Phys. D 1999, 32, L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychkov, D.; Altafim, R.A.P.; Qiu, X.; Gerhard, R. Treatment with orthophosphoric acid enhances the thermal stability of the piezoelectricity in low-density polyethylene ferroelectrets. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 124105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, G.M. Electrets, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 81–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, Y.; Yousry, Y.M.; Nobeshima, T.; Iumsrivun, C.; Sakai, H.; Uemura, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Yao, K. Electromechanically Active As-Electrospun Polystyrene Fiber Mat: Significantly High Quasistatic/Dynamic Electromechanical Response and Theoretical Modeling. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Ding, X.; Fang, J.; Niu, H.; Wang, W.; Lang, C.; Lin, T. Efficient conversion of sound noise into electric energy using electrospun polyacrylonitrile membranes. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Corona Voltage (kV) | d33 After Corona (pC/N) | d33 After Annealing (pC/N) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | <1 | <1 |
| 45 | 17 | <1 |
| 55 | 21 | <1 |
| Parameter | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Poling voltage (kV) | 0 | 45 | 55 |
| Input acoustic power (nW) | 70.5 | 70.5 | 70.5 |
| Total acoustic power absorbed (nW) | 31.7 | 35.2 | 36.7 |
| Output voltage (mV) | 0 | 100 | 130 |
| Additional acoustic power absorbed after poling (nW) | – | 3.5 | 5.0 |
| Experimental electrical power generated (nW) | – | 1.1 | 2.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yousry, Y.M.; Statharas, E.C.; Yao, K.; Mohamed, A.M.; Lim, P.C.; Tay, F.E.H. Sound Absorption Improvement in Porous Ferroelectret Polyethylene with Effective Piezoelectric Mechanism. Polymers 2022, 14, 4843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224843
Yousry YM, Statharas EC, Yao K, Mohamed AM, Lim PC, Tay FEH. Sound Absorption Improvement in Porous Ferroelectret Polyethylene with Effective Piezoelectric Mechanism. Polymers. 2022; 14(22):4843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224843
Chicago/Turabian StyleYousry, Yasmin Mohamed, Eleftherios Christos Statharas, Kui Yao, Ayman Mahmoud Mohamed, Poh Chong Lim, and Francis Eng Hock Tay. 2022. "Sound Absorption Improvement in Porous Ferroelectret Polyethylene with Effective Piezoelectric Mechanism" Polymers 14, no. 22: 4843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224843
APA StyleYousry, Y. M., Statharas, E. C., Yao, K., Mohamed, A. M., Lim, P. C., & Tay, F. E. H. (2022). Sound Absorption Improvement in Porous Ferroelectret Polyethylene with Effective Piezoelectric Mechanism. Polymers, 14(22), 4843. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224843








