Composition Effects on the Morphology of PVA/Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning of the PVA|CS Compositions
2.3. Morphology Characterization of the Electrospun Nanofibers
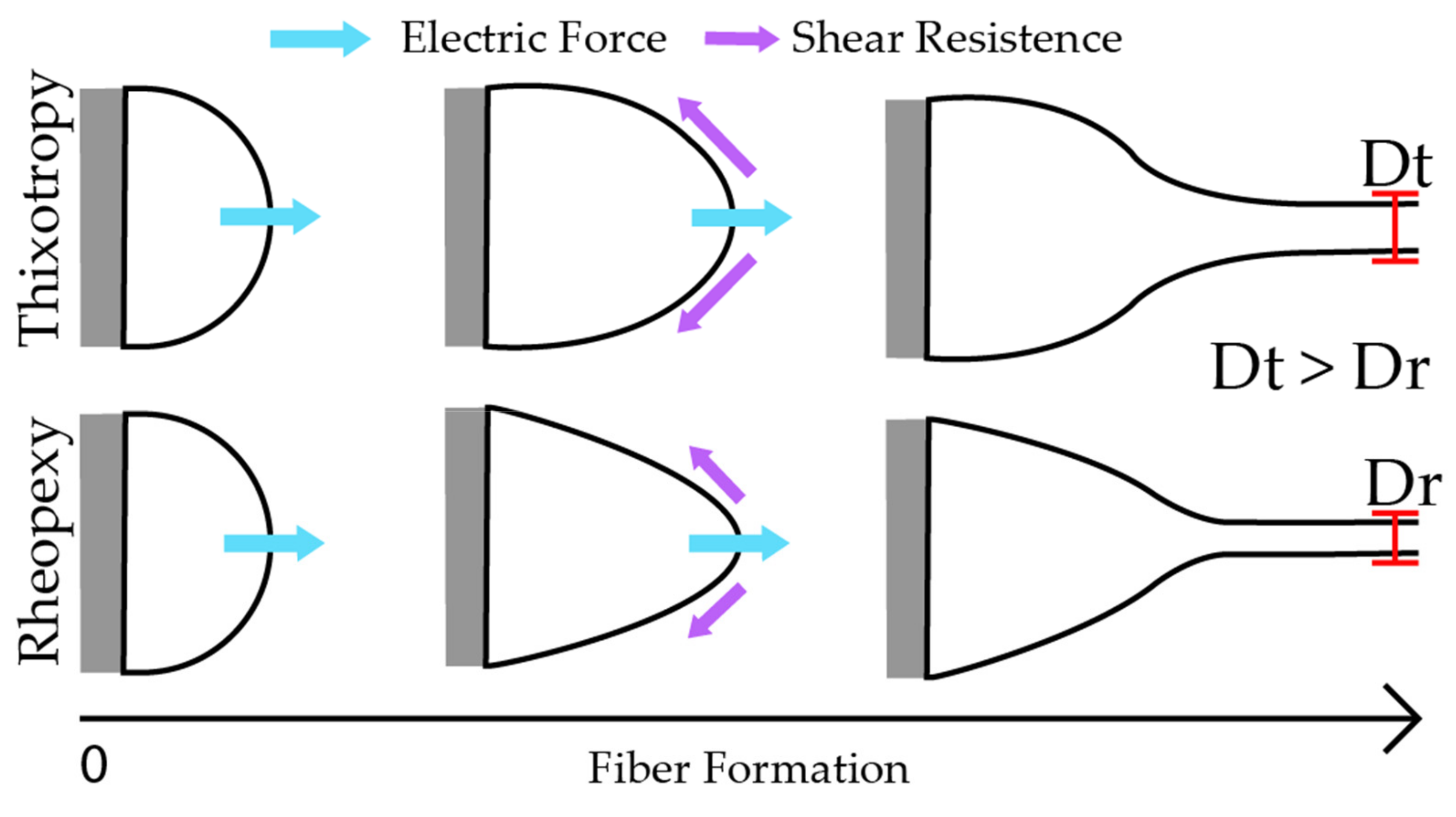
2.4. Electrical Conductivity and Rheology of the Formulations
2.5. Electrospinning of PVA|CS Compositions with Additives
3. Results and Discussion
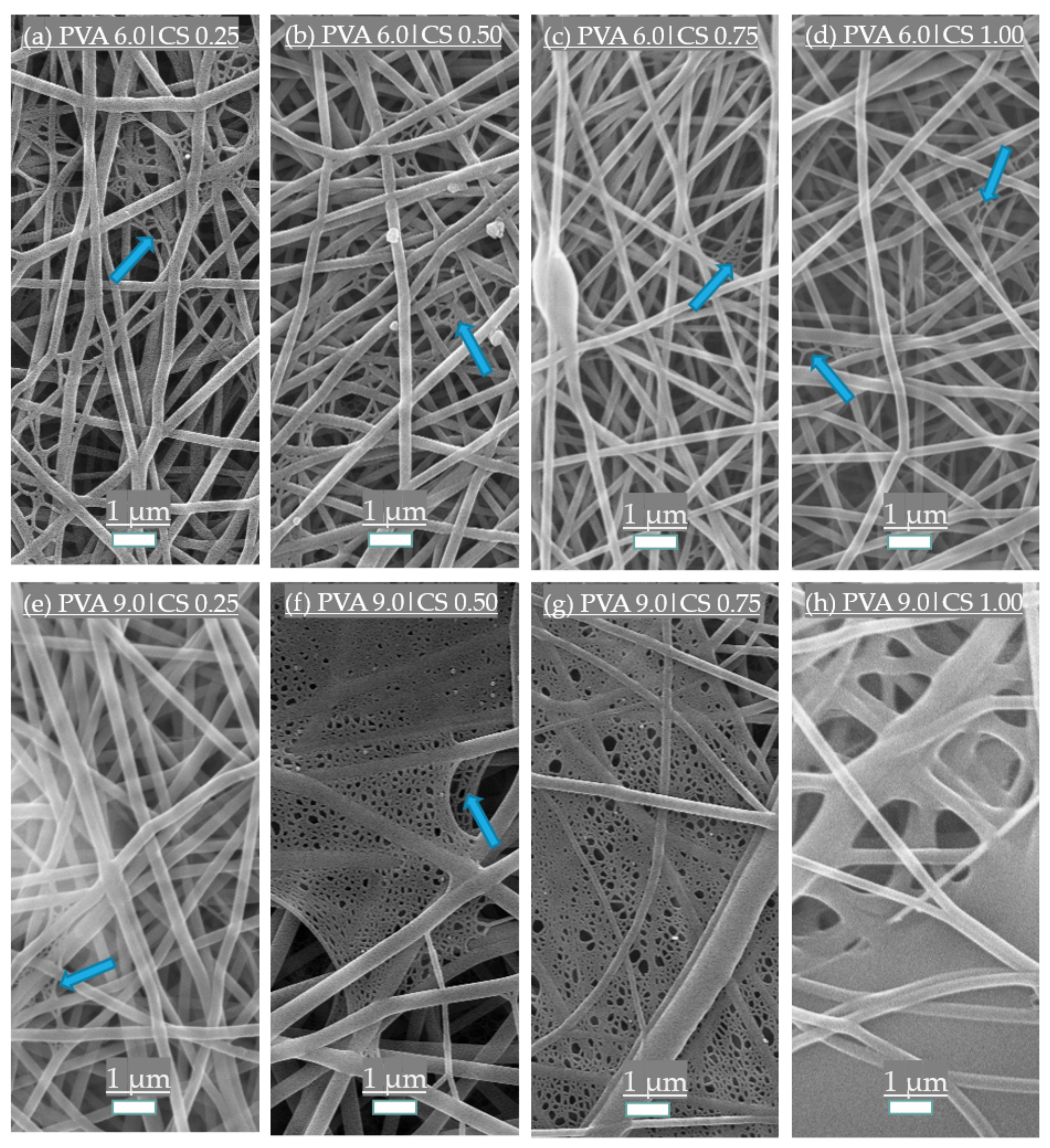
3.1. Morphological Structure of the Fibers
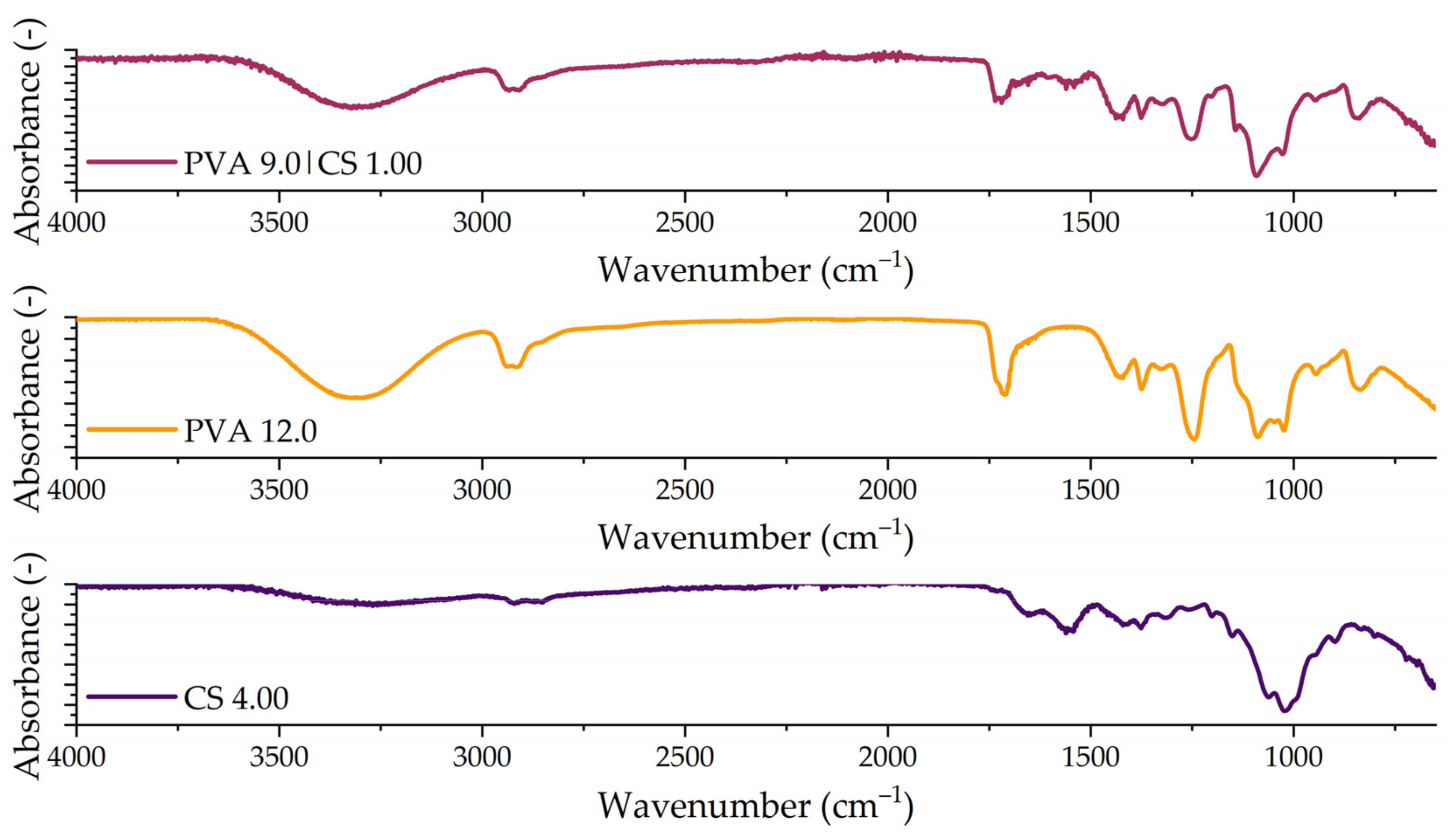
Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Fiber Optimization
3.2.1. Multilevel Factorial Design with Response Surface Analysis
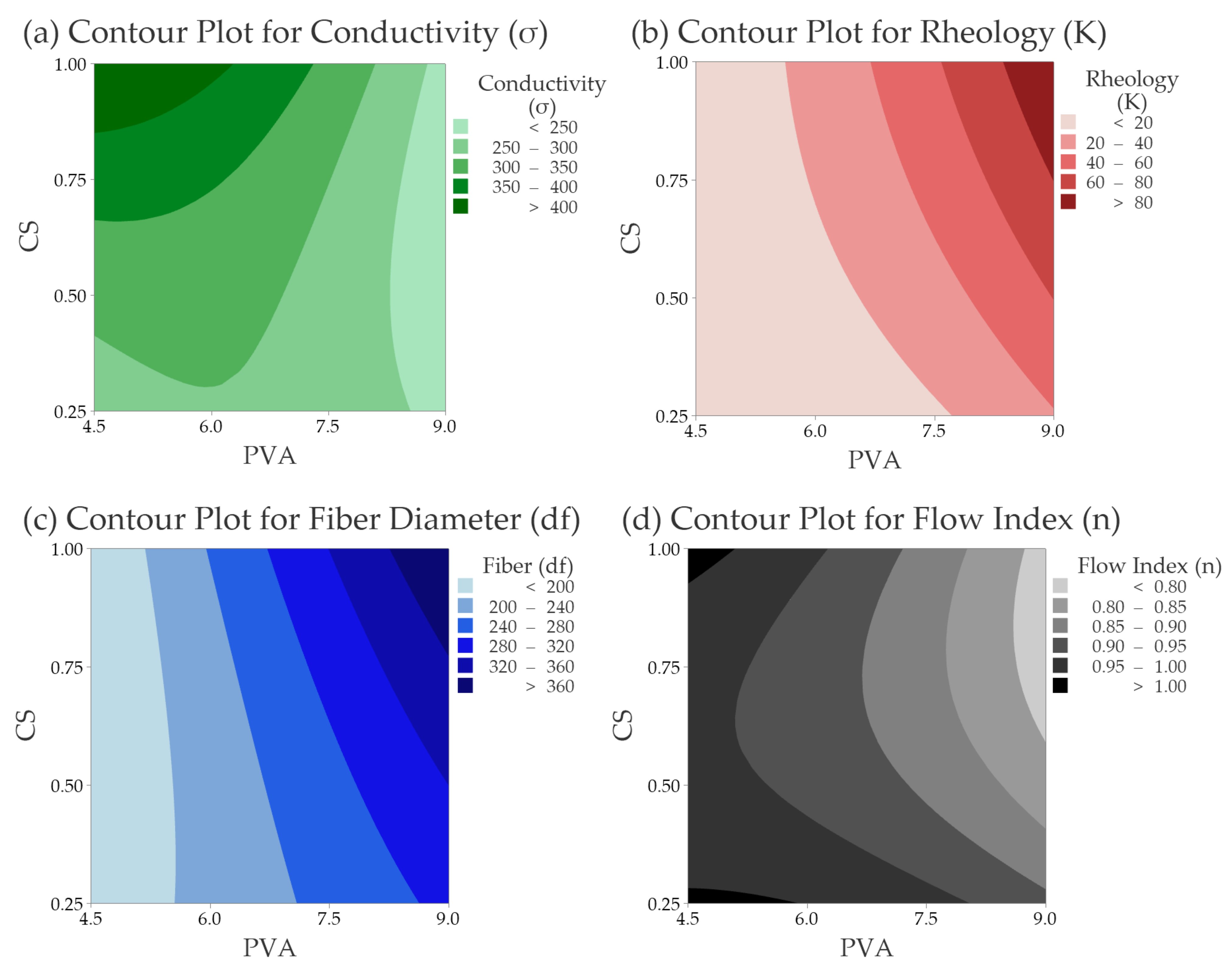
3.2.2. Electrical Conductivity (σ)
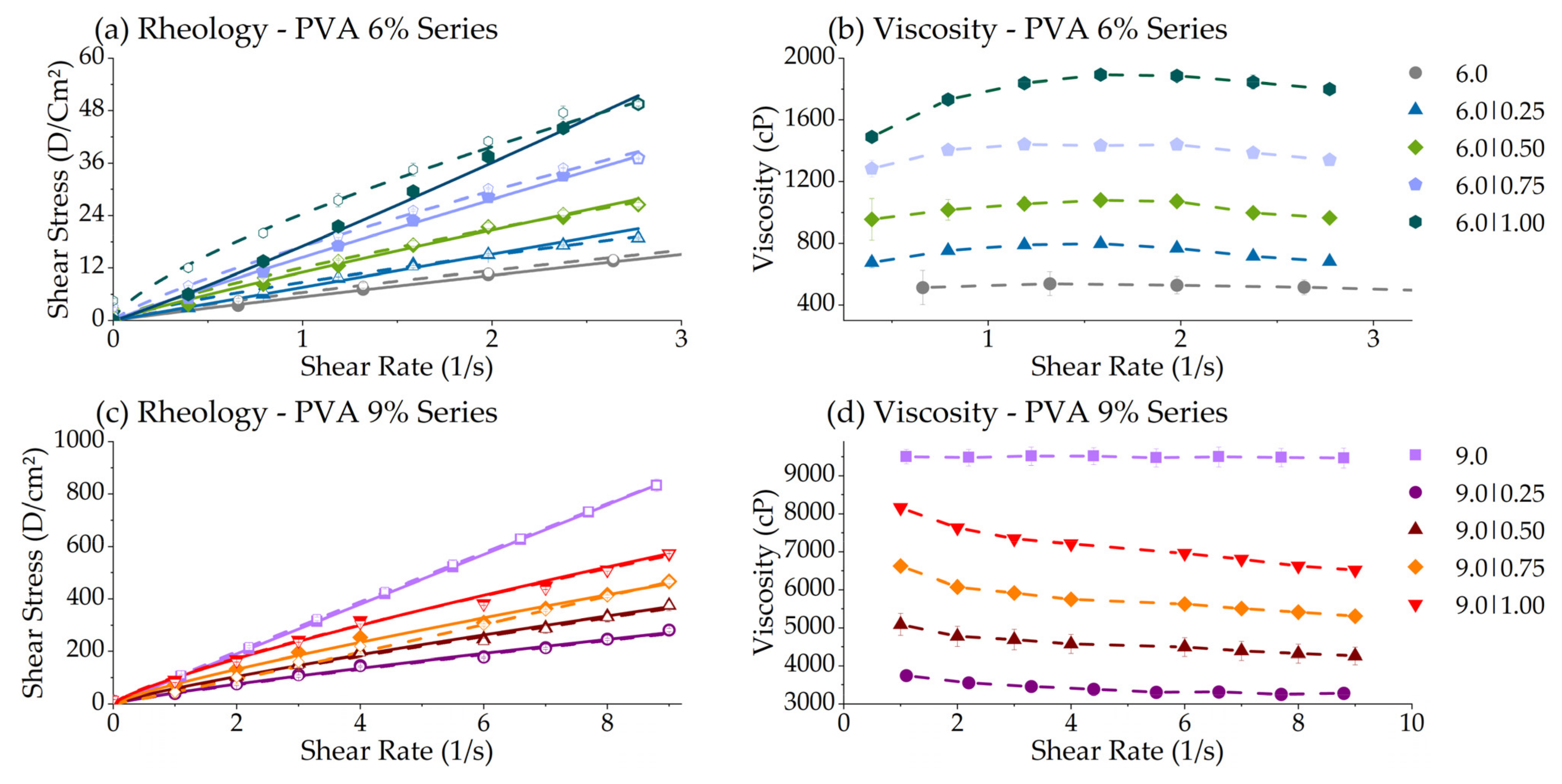
3.2.3. Rheology Consistency Index (K) & Flow Index (n)
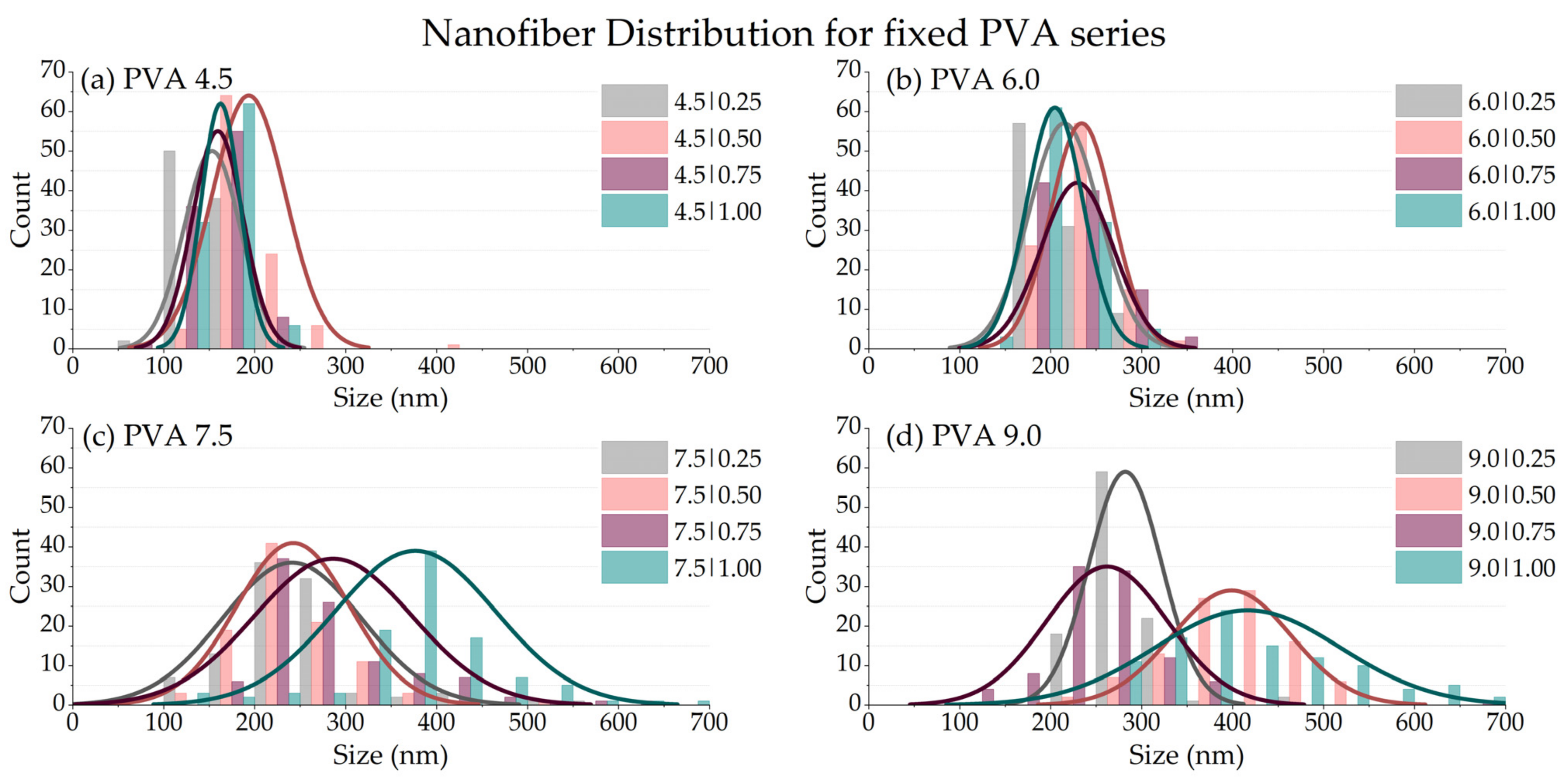
3.2.4. Fiber Size Diameter (df)
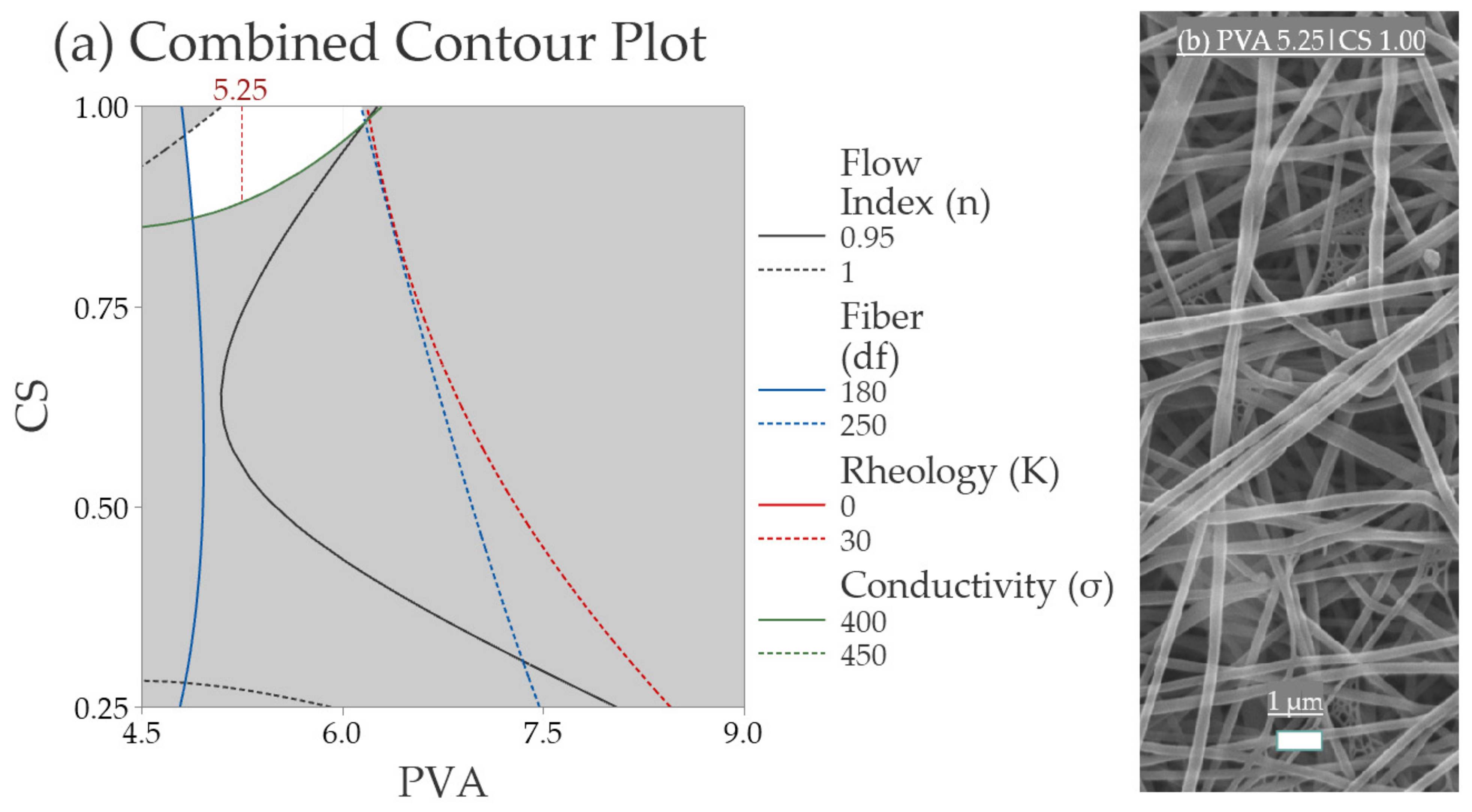
3.2.5. Validation of the Response Surface Analysis
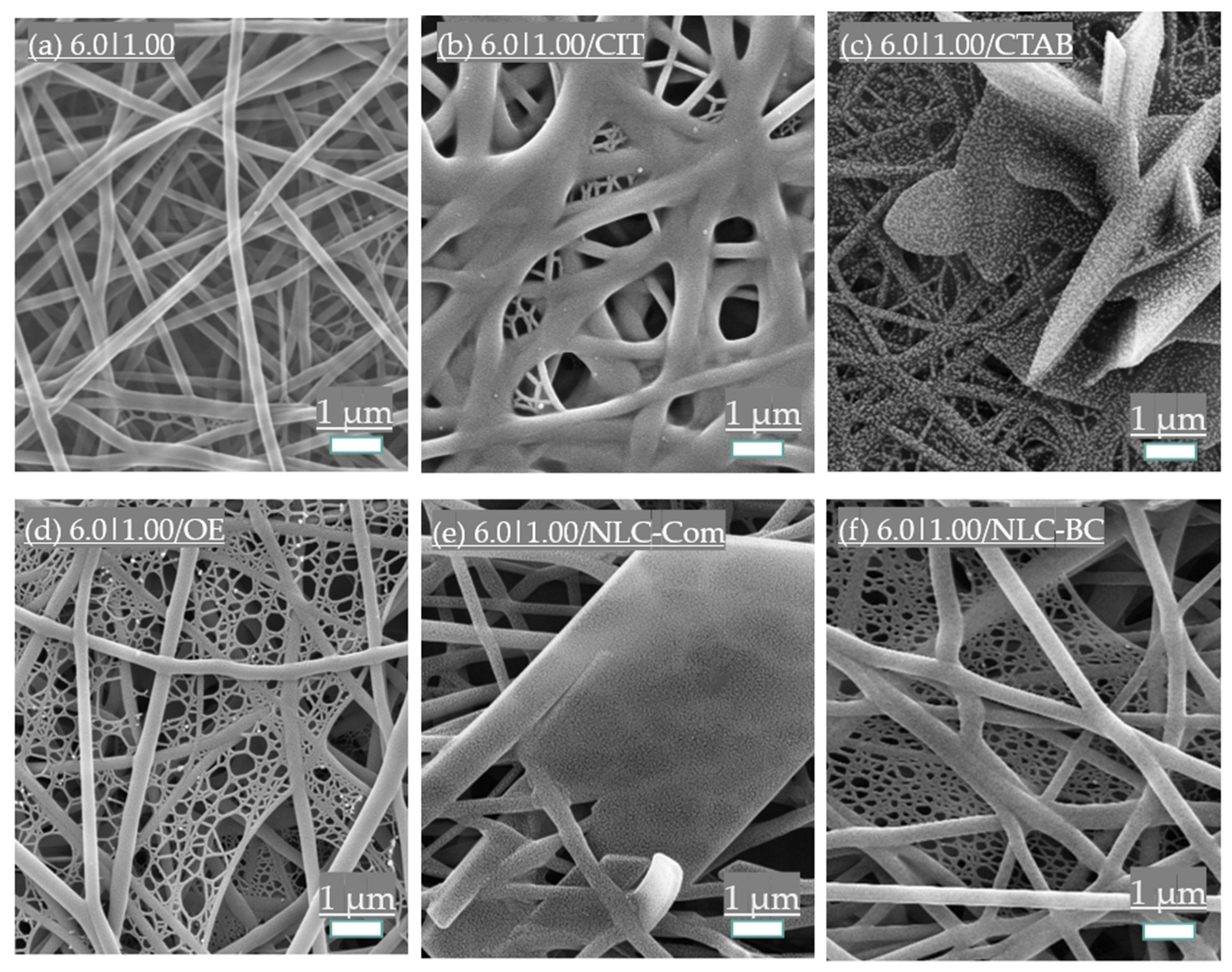
3.3. Additives Influence
3.3.1. Surfactant Addition
3.3.2. Essential Oil and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) Incorporation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.-W.; Wu, C.-Y.; Tepper, F.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.N. Removal and Retention of Viral Aerosols by a Novel Alumina Nanofiber Filter. J. Aerosol Sci. 2009, 40, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, C.; Lee, S.; Ryu, M.; Lee, J.; Lee, H. Electrospun Nanofiber Filters for Highly Efficient PM2.5 Capture. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, H.; Yan, C.; Sha, J.; Tang, H.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Y. Dual-Purpose High-Efficiency Air Filter Paper Loaded with Reactive Zirconium Hydroxide for the Filtration Aerosols and Degradation of Chemical Warfare Agents. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35245–35257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machry, K.; de Souza, C.W.O.; Aguiar, M.L.; Bernardo, A. Prevention of Pathogen Microorganisms at Indoor Air Ventilation System Using Synthesized Copper Nanoparticles. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 100, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi Le, V.C.; Yoon, S.; Kang, E.; Sheraz, M.; Uk Han, T.; Anus, A.; Duy Mai, H.; Choi, S.; Kim, S. A Capture and Inactivation System against Pathogens in Indoor Air Using Copper Nanoparticle Decorated Melamine Sponge Hybrid Air Filters. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2022, 1, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulevicius, J.; Kliucininkas, L.; Martuzevicius, D.; Krugly, E.; Tichonovas, M.; Baltrusaitis, J. Design and Characterization of Electrospun Polyamide Nanofiber Media for Air Filtration Applications. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Olya, M.E.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Synthesis of Polyacrylonitrile/Polyamidoamine Composite Nanofibers Using Electrospinning Technique and Their Dye Removal Capacity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yue, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, W.; Han, G. Preparation of Cellulose Acetate-Polyacrylonitrile Composite Nanofibers by Multi-Fluid Mixing Electrospinning Method: Morphology, Wettability, and Mechanical Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, V.; Truong, Y.B.; Easton, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Wang, L.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L. Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile/β-Cyclodextrin Composite Membranes for Simultaneous Air Filtration and Adsorption of Volatile Organic Compounds. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4268–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.W.F.; Sun, Q. Electrostatic Charged Nanofiber Filter for Filtering Airborne Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) and Nano-Aerosols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 116886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.W.F.; Sun, Q. Charged PVDF Multilayer Nanofiber Filter in Filtering Simulated Airborne Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Ambient Nano-Aerosols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 245, 116887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfim, D.P.F.; Cruz, F.G.S.; Guerra, V.G.; Aguiar, M.L. Development of Filter Media by Electrospinning for Air Filtration of Nanoparticles from PET Bottles. Membranes 2021, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sereshti, H.; Amini, F.; Najarzadekan, H. Electrospun Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Nanofibers as a New Adsorbent for Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Chromium(VI) in Environmental Water Samples. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 89195–89203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Sweetser, D. Recycled PET Nanofibers for Water Filtration Applications. Materials 2016, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfim, D.P.F.; Cruz, F.G.S.; Bretas, R.E.S.; Guerra, V.G.; Aguiar, M.L. A Sustainable Recycling Alternative: Electrospun PET-Membranes for Air Nanofiltration. Polymers 2021, 13, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Young, T.M.; Harper, D.P.; Wang, S. A Novel Method for Fabricating an Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Cellulose Nanocrystals Composite Nanofibrous Filter with Low Air Resistance for High-Efficiency Filtration of Particulate Matter. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8706–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.E.; Aguiar, M.; Guerra, V. Improved Filter Media with PVA/Citric Acid/Triton X-100 Nanofibers for Filtration of Nanoparticles from Air. Polym. Bull. 2020, 78, 6387–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulupi, M.; Haryadi, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Electrospinning PVA Nanofiber-Crosslinked by Glutaraldehyde. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 13, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, N.T.B.; Lee, B.-T. Electrospinning of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Gelatin Nanofiber Composites and Cross-Linking for Bone Tissue Engineering Application. J. Biomater. Appl. 2012, 27, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, R.; Sai Goutham, K.; Srivastava, C.M. Electrospun Sericin/PVA/Clay Nanofibrous Mats for Antimicrobial Air Filtration Mask. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, P.A.M.; Schneider, R.; dos Santos, D.M.; Otuka, A.J.G.; Mendonça, C.R.; Correa, D.S. Bilayered Electrospun Membranes Composed of Poly(Lactic-Acid)/Natural Rubber: A Strategy against Curcumin Photodegradation for Wound Dressing Application. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 163, 104889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Facure, M.H.M.; Alvarenga, A.D.; Chagas, P.A.M.; dos Santos, D.M.; Correa, D.S. Dye Adsorption Capacity of MoS2 Nanoflakes Immobilized on Poly(Lactic Acid) Fibrous Membranes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4881–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Fang, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, T.; Wang, X. Using Chitosan as a Thickener for Electrospinning Dilute PVA Solutions to Improve Fibre Uniformity. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3718–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, F.; Pei, H.; Li, J.; Cui, Z.; He, B. Antibacterial and Environmentally Friendly Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Blend Membranes for Air Filtration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaie, S.; Khorasani, M.T.; Zarrabi, A.; Moshtaghian, J. Wound Healing Properties of PVA/Starch/Chitosan Hydrogel Membranes with Nano Zinc Oxide as Antibacterial Wound Dressing Material. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 2220–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoni, H.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Valizadeh, M. Electrospinning of Chitosan Nanofibers: Processing Optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Kwon, O.-H.; Jang, J. Electrospinning of Chitosan Dissolved in Concentrated Acetic Acid Solution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.N.; Morozkina, S.N.; Uspenskaya, M.V. Study of the Nanofibers Fabrication Conditions from the Mixture of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Chitosan by Electrospinning Method. Polymers 2022, 14, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Sadeghi, K.; Seo, J. Recent Advances in Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Natural Polymer Based Films for Food Packaging Applications: A Review. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru Kamaci, U.; Peksel, A. Fabrication of PVA-Chitosan-Based Nanofibers for Phytase Immobilization to Enhance Enzymatic Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, W.A.; Sharafeldin, I.M.; Omar, M.M.; Allam, N.K. Novel Mineralized Electrospun Chitosan/PVA/TiO2 Nanofibrous Composites for Potential Biomedical Applications: Computational and Experimental Insights. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, M.S.; Bonfim, D.P.F.; Aguiar, M.L.; Oliveira, W.P. Electrospun Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibrous Mat Loaded with Green Propolis Extract, Chitosan and Nystatin as an Innovative Wound Dressing Material. J. Pharm. Innov. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldim, I.; Tonani, L.; von Zeska Kress, M.R.; Pereira Oliveira, W. Lippia Sidoides Essential Oil Encapsulated in Lipid Nanosystem as an Anti-Candida Agent. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 127, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Baldim, I.; Oliveira, W.P.; Rao, R.; Yadav, N.; Gama, F.M.; Mahant, S. SLN and NLC for Topical, Dermal, and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldim, I.; Paziani, M.H.; Grizante Barião, P.H.; von Z. Kress, M.R.; Oliveira, W.P. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Loaded with Lippia Sidoides Essential Oil as a Strategy to Combat the Multidrug-Resistant Candida Auris. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Edmondson, D.; Veiseh, O.; Matsen, F.A.; Zhang, M. Electrospun Chitosan-Based Nanofibers and Their Cellular Compatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6176–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Sheikh, F.A.; Kim, H.Y. Spider-Net within the N6, PVA and PU Electrospun Nanofiber Mats Using Salt Addition: Novel Strategy in the Electrospinning Process. Polymer 2009, 50, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstey, A.; Chang, E.; Kim, E.S.; Rizvi, A.; Kakroodi, A.R.; Park, C.B.; Lee, P.C. Nanofibrillated Polymer Systems: Design, Application, and Current State of the Art. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 113, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Singh, N.; Gupta, A.; Tiwari, S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Dhakate, S.R. Electrospun Chitosan–Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Nanofibers Loaded with Cerium for Efficient Removal of Arsenic from Contaminated Water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16669–16677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, D.; Sahoo, A.; Mohanty, B.; Anis, A.; Kulikouskaya, V.; Hileuskaya, K.; Agabekov, V.; Sarkar, P.; Ray, S.S.; Maji, S.; et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Chitosan Oligosaccharide-Based Blend Films. Gels 2021, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çay, A.; Miraftab, M.; Perrin Akçakoca Kumbasar, E. Characterization and Swelling Performance of Physically Stabilized Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan Nanofibres. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 61, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.-T.; Liu, J.-H. Fabrication and Characterization of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan Hydrogel Thin Films via UV Irradiation. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 4201–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Han, S.; Huang, M.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; He, J. Green Crosslinked Nanofibers Membrane Based on CS/PVA Combined with Polybasic Organic Acid for Tympanic Membrane Repair. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and Process Relationship of Electrospun Bioabsorbable Nanofiber Membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Taylor Cone and Jetting from Liquid Droplets in Electrospinning of Nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Yeneneh, A.M.; Sen, T.K.; Ang, H.M.; Kayaalp, A. A Comprehensive Review on Rheological Studies of Sludge from Various Sections of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants for Enhancement of Process Performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 257, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yördem, O.S.; Papila, M.; Menceloğlu, Y.Z. Effects of Electrospinning Parameters on Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Diameter: An Investigation by Response Surface Methodology. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.-E.; Lim, T.-C.; Ma, Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005; ISBN 978-981-256-415-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C.M.; Birs, I.R.; Copot, D.; Muresan, C.I.; Caponetto, R. Mathematical Modelling with Experimental Validation of Viscoelastic Properties in Non-Newtonian Fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramariuc, B.; Cramariuc, R.; Scarlet, R.; Manea, L.R.; Lupu, I.G.; Cramariuc, O. Fiber Diameter in Electrospinning Process. J. Electrost. 2013, 71, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-H. On the Height of Taylor Cone in Electrospinning. Results Phys. 2020, 17, 103096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Mata, G.C.; da Almeida, D.S.; de Oliveira, W.P.; Aguiar, M.L. Nanofibers functionalized with surfactants to Eliminate SARS-CoV-2 and other airborne pathogens. Conjecturas 2022, 22, 1929–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, O.; Emon, B.; Cheng, S.; Hong, L.; Chamorro, L.P.; Saif, M.T.A. Performance of Fabrics for Home-Made Masks against the Spread of COVID-19 through Droplets: A Quantitative Mechanistic Study. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2020, 40, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutledge, G.C.; Fridrikh, S.V. Formation of Fibers by Electrospinning. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, C.G.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Disruption of Electrospinning Due to Water Condensation into the Taylor Cone. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 26566–26576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Xia, Y. Maneuvering the Internal Porosity and Surface Morphology of Electrospun Polystyrene Yarns by Controlling the Solvent and Relative Humidity. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7070–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Controlling the Secondary Surface Morphology of Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers by Regulating the Solvent and Relative Humidity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, D.S.; Duarte, E.H.; Hashimoto, E.M.; Turbiani, F.R.B.; Muniz, E.C.; de Souza, P.R.; Gimenes, M.L.; Martins, L.D. Development and Characterization of Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers Modified by Cationic Surfactant. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallanezhad, P.; Nazockdast, H.; Ahmadi, Z.; Rostami, A. Fabrication and Characterization of Polycaprolactone/Chitosan Nanofibers Containing Antibacterial Agents of Curcumin and ZnO Nanoparticles for Use as Wound Dressing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1027351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golja, B.; Forte Tavčer, P.; University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Natural Sciences and Engineering, Department of Textiles, Graphic Arts and Design, 1000 Ljubljana, Snežniška 5, Slovenia. Textile Functionalisation by Printing Fragrant, Antimicrobial and Flame- Retardant Microcapsules. TEK 2016, 59, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, R.; Abbasipour, M. 5—Controlling Nanofiber Morphology by the Electrospinning Process. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Afshari, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 109–123. ISBN 978-0-08-100907-9. [Google Scholar]
- Haghi, A.K.; Akbari, M. Trends in Electrospinning of Natural Nanofibers. Phys. Status Solidi 2007, 204, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Feng, Y.-Y.; Xu, J.-X.; Kong, B.-H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Fabrication, Characterization, and Antibacterial Properties of Citric Acid Crosslinked PVA Electrospun Microfibre Mats for Active Food Packaging. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2021, 34, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Haider, A. (Eds.) Electrospinning and Electrospraying—Techniques and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-78984-701-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Influence of Solvents on the Formation of Ultrathin Uniform Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone) Nanofibers with Electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaj, A.F.; Elraies, K.A.; Mahmood, S.M.; Zulkifli, N.N.; Akbari, S.; Hussien, O.S. The Effect of Surfactant Concentration, Salinity, Temperature, and PH on Surfactant Adsorption for Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery: A Review. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Gong, X.; Jiao, W.; Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. In-Situ Electrospinning of Thymol-Loaded Polyurethane Fibrous Membranes for Waterproof, Breathable, and Antibacterial Wound Dressing Application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 592, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, W.; Wei, Q. Electrospun Thymol-Loaded Porous Cellulose Acetate Fibers with Potential Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial Electrospun Zein Nanofibrous Web Encapsulating Thymol/Cyclodextrin-Inclusion Complex for Food Packaging. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayari, P.; Jalilian, N.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Amini, S. Electrospun Cellulose Acetate /Polyacrylonitrile /Thymol /Mg-Metal Organic Framework Nanofibers as Efficient Sorbent for Pipette-Tip Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Anti-Cancer Drugs. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 173, 105217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Z.; Yaman, M.; Sağdıç, O.; Karabulut, E.; Yilmaz, M.T. Effect of Electrospun Thymol-Loaded Nanofiber Coating on Vitamin B Profile of Gilthead Sea Bream Fillets (Sparus Aurata). LWT 2018, 98, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-L.; Chuang, H.-S.; Lee, M.-H.; Wei, C.-L.; Lin, C.-F.; Tsai, Y.-C. Inhibition of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 by Thymol-Related Monoterpenoids. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1636–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Elnesr, S.S. A Review on the Beneficial Effect of Thymol on Health and Production of Fish. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, P.; Speranza, B.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M. A Study on the Antimicrobial Activity of Thymol Intended as a Natural Preservative. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Barbieri, R.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Gortzi, O.; Izadi, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Thymol: A Brief Review of the Literature. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.B.; Kulawik, P.; Ozogul, F.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ozogul, Y. Biological Activity of Plant-Based Carvacrol and Thymol and Their Impact on Human Health and Food Quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chitosan (CS) Content | Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6% | 8% | 10% | 12% | |
| 1% | 4.5|0.25 | 6.0|0.25 | 7.5|0.25 | 9.0|0.25 |
| 2% | 4.5|0.50 | 6.0|0.50 | 7.5|0.50 | 9.0|0.50 |
| 3% | 4.5|0.75 | 6.0|0.75 | 7.5|0.75 | 9.0|0.75 |
| 4% | 4.5|1.00 | 6.0|1.00 | 7.5|1.00 | 9.0|1.00 |
| Response | Model | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| σ (mS·cm−1) | −73 + 109.0 PVA + 266 CS − 7.90 PVA × PVA + 150 CS × CS − 50.4 PVA × CS | 0.001 |
| K (Dyn·cm−2) | 57.5 − 22.3 PVA − 53.5 CS + 1.951 PVA × PVA − 15.5 CS × CS + 16.92 PVA × CS | 0.000 |
| df (nm) | 108 + 17.5 PVA − 224 CS − 0.02 PVA × PVA + 46 CS × CS + 34.7 PVA × CS | 0.005 |
| n | 0.949 + 0.055 PVA − 0.268 CS − 0.00487 PVA × PVA + 0.381 CS × CS − 0.0429 PVA × CS | 0.128 |
| Chitosan Content | Polyvinyl Alcohol Content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 4.5 | 6.0 | 7.5 | 9.0 | |
| 0.00 | - | 238.1 ± 6.9 | 231.9 ± 6.8 | 249.7 ± 15.6 | 286.4 ± 30.4 |
| 0.25 | 519.9 ± 7.0 | 312.9 ± 17.8 | 254.3 ± 2.6 | 247.6 ± 7.9 | 278.8 ± 6.1 |
| 0.50 | 826.5 ± 6.7 | 326.9 ± 6.2 | 301.8 ± 10.4 | 300.8 ± 1.7 | 180.5 ± 12.5 |
| 0.75 | 1176.3 ± 8.2 | 347.9 ± 7.2 | 363.2 ± 4.1 | 350.9 ± 8.6 | 195.3 ± 11.9 |
| 1.00 | 1505.9 ± 14.5 | 445.9 ± 4.5 | 396.2 ± 5.6 | 369.7 ± 1.9 | 211.8 ± 8.6 |
| Chitosan (CS) Content (% w/w) | Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Content (% w/w) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.5 | 6.0 | 7.5 | 9.0 | |
| 0.25 | 153.1 ± 31.2 | 214.8 ± 38.7 | 240.9 ± 76.8 | 282.4 ± 40.2 |
| 0.50 | 193.4 ± 40.5 | 234.0 ± 34.4 | 242.3 ± 62.6 | 398.8 ± 65.5 |
| 0.75 | 159.3 ± 27.8 | 229.1 ± 39.9 | 286.2 ± 87.1 | 261.8 ± 66.6 |
| 1.00 | 162.4 ± 21.2 | 204.4 ± 32.2 | 376.7 ± 89.0 | 416.4 ± 101.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mata, G.C.d.; Morais, M.S.; Oliveira, W.P.d.; Aguiar, M.L. Composition Effects on the Morphology of PVA/Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers 2022, 14, 4856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224856
Mata GCd, Morais MS, Oliveira WPd, Aguiar ML. Composition Effects on the Morphology of PVA/Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers. 2022; 14(22):4856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224856
Chicago/Turabian StyleMata, Gustavo Cardoso da, Maria Sirlene Morais, Wanderley Pereira de Oliveira, and Mônica Lopes Aguiar. 2022. "Composition Effects on the Morphology of PVA/Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers" Polymers 14, no. 22: 4856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224856
APA StyleMata, G. C. d., Morais, M. S., Oliveira, W. P. d., & Aguiar, M. L. (2022). Composition Effects on the Morphology of PVA/Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers, 14(22), 4856. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224856







