The High Flux of Superhydrophilic-Superhydrophobic Janus Membrane of cPVA-PVDF/PMMA/GO by Layer-by-Layer Electrospinning for High Efficiency Oil-Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
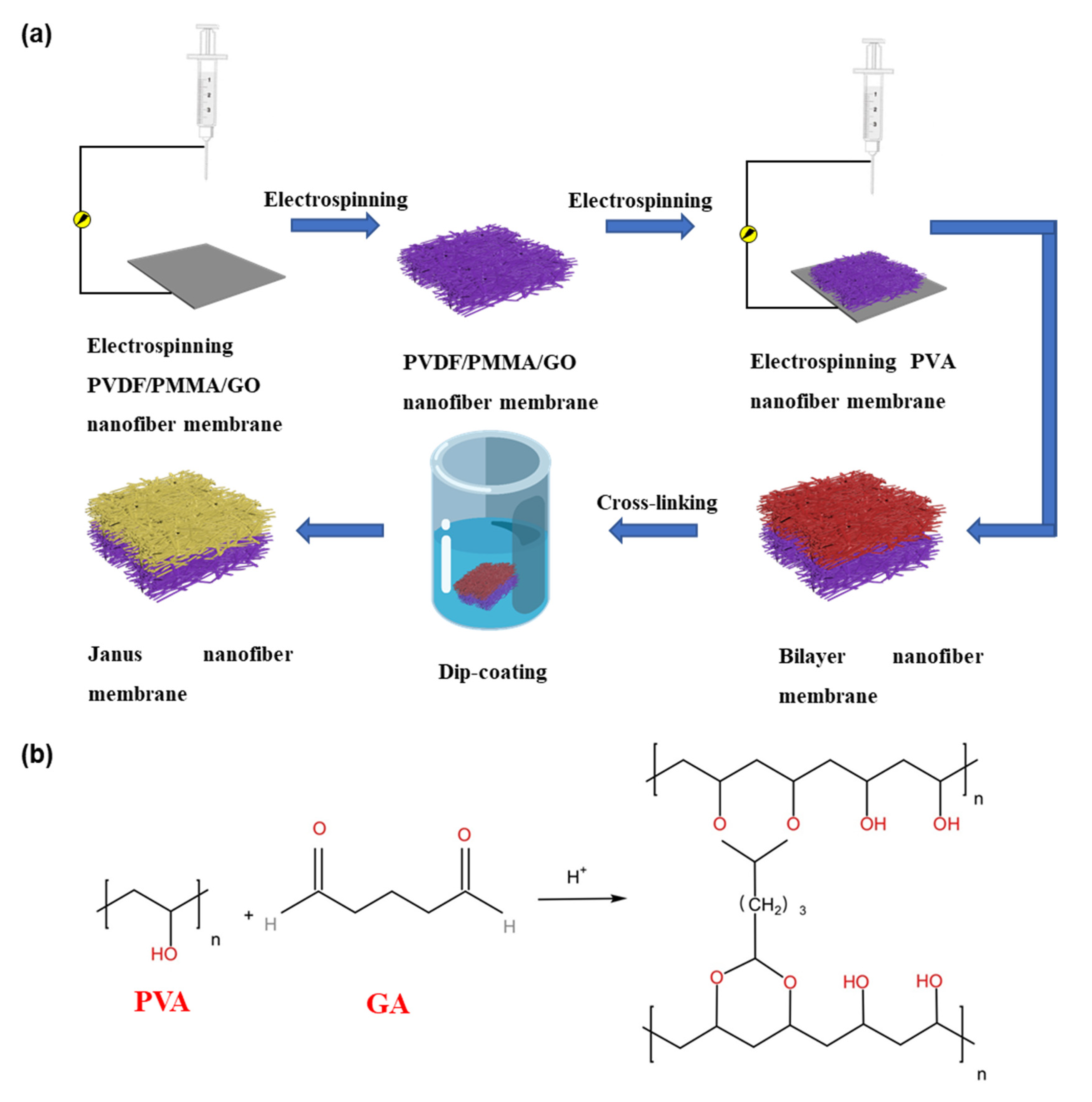
2.2. Preparation of Janus Composite Membrane
2.3. Preparation and Separation of Water-in-Oil Emulsions
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
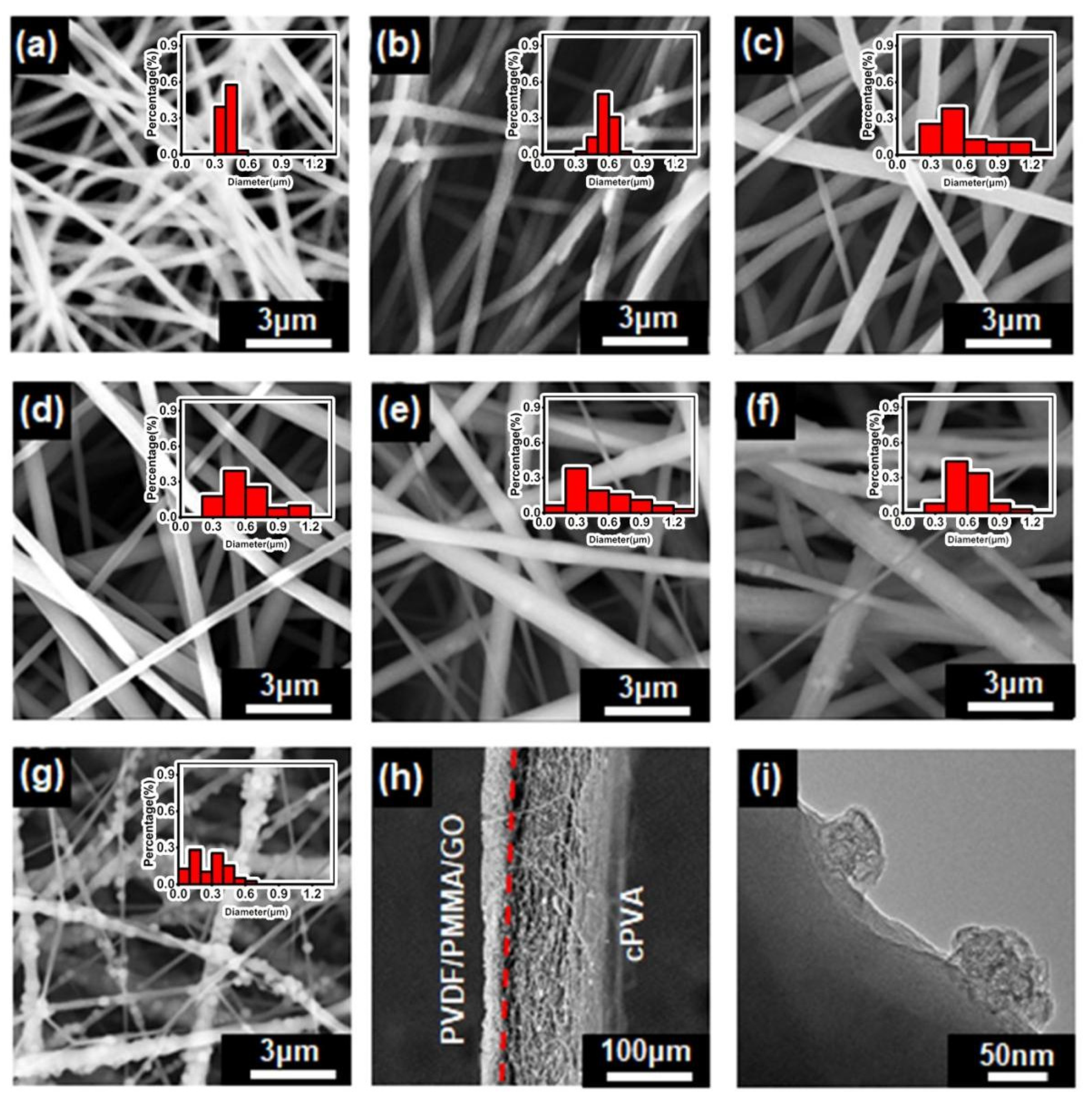
3.1. Characterization of Janus Composite Membrane
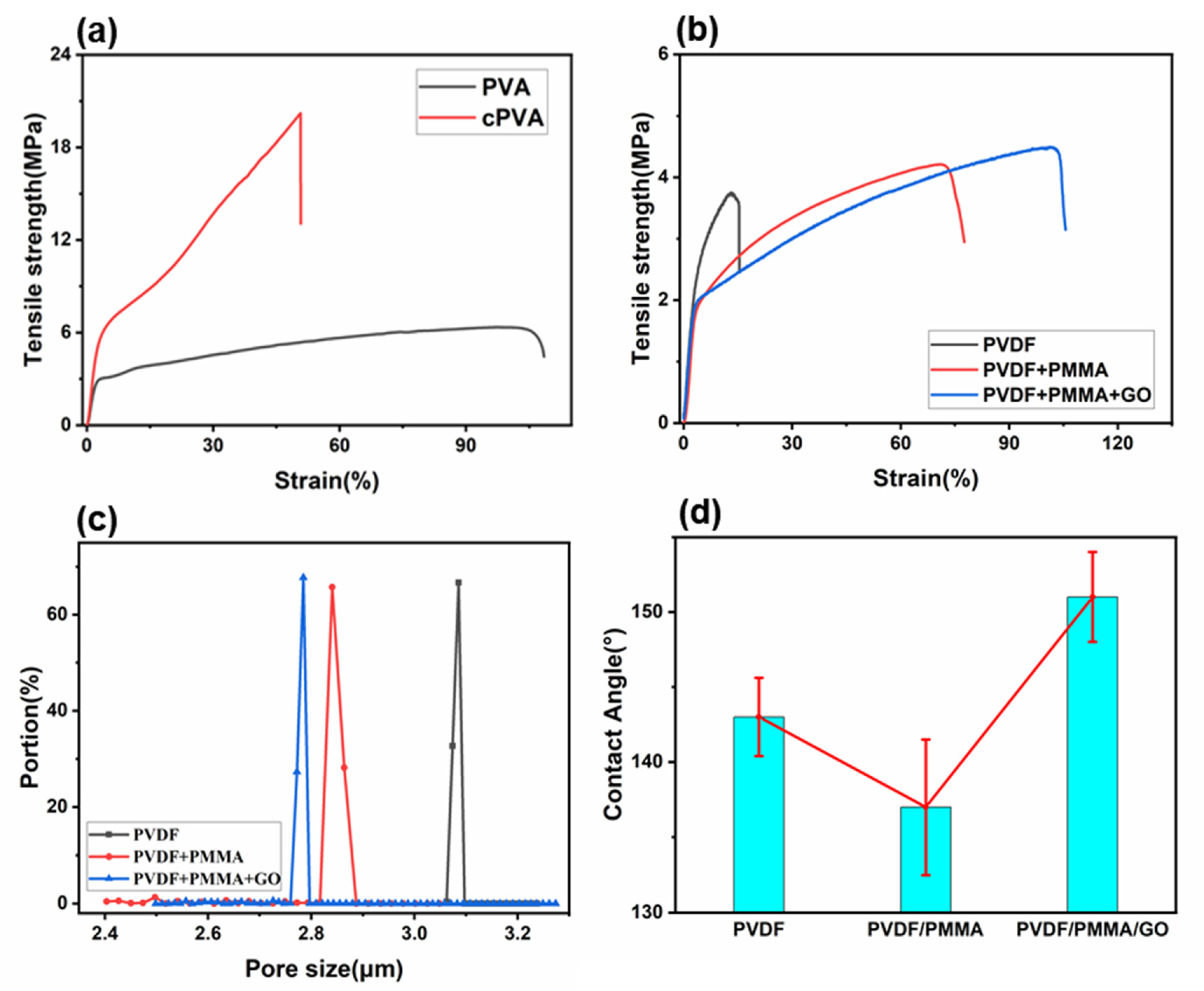
3.2. Mechanical Properties of Janus Composite Membrane
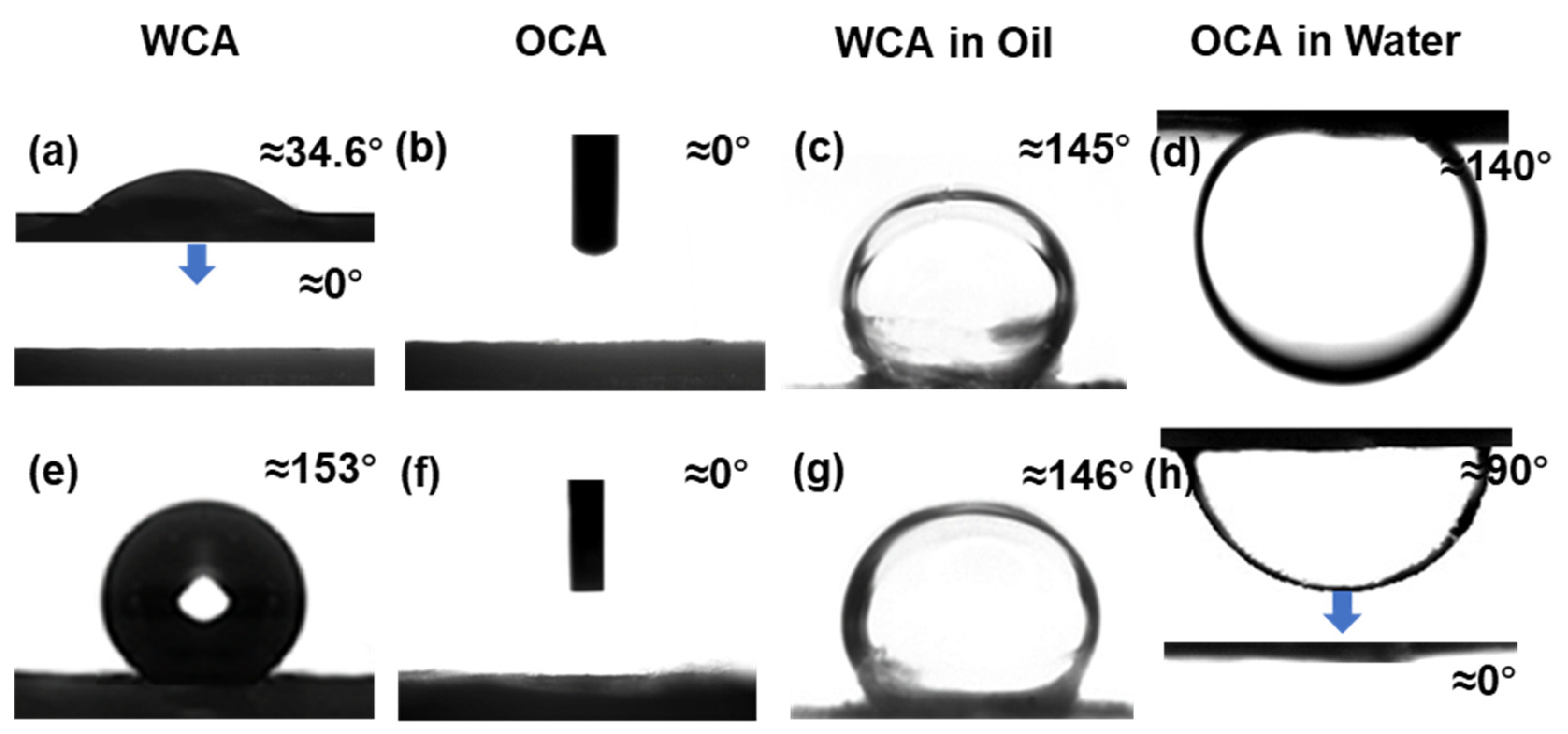
3.3. Wettability of Janus Composite Membrane
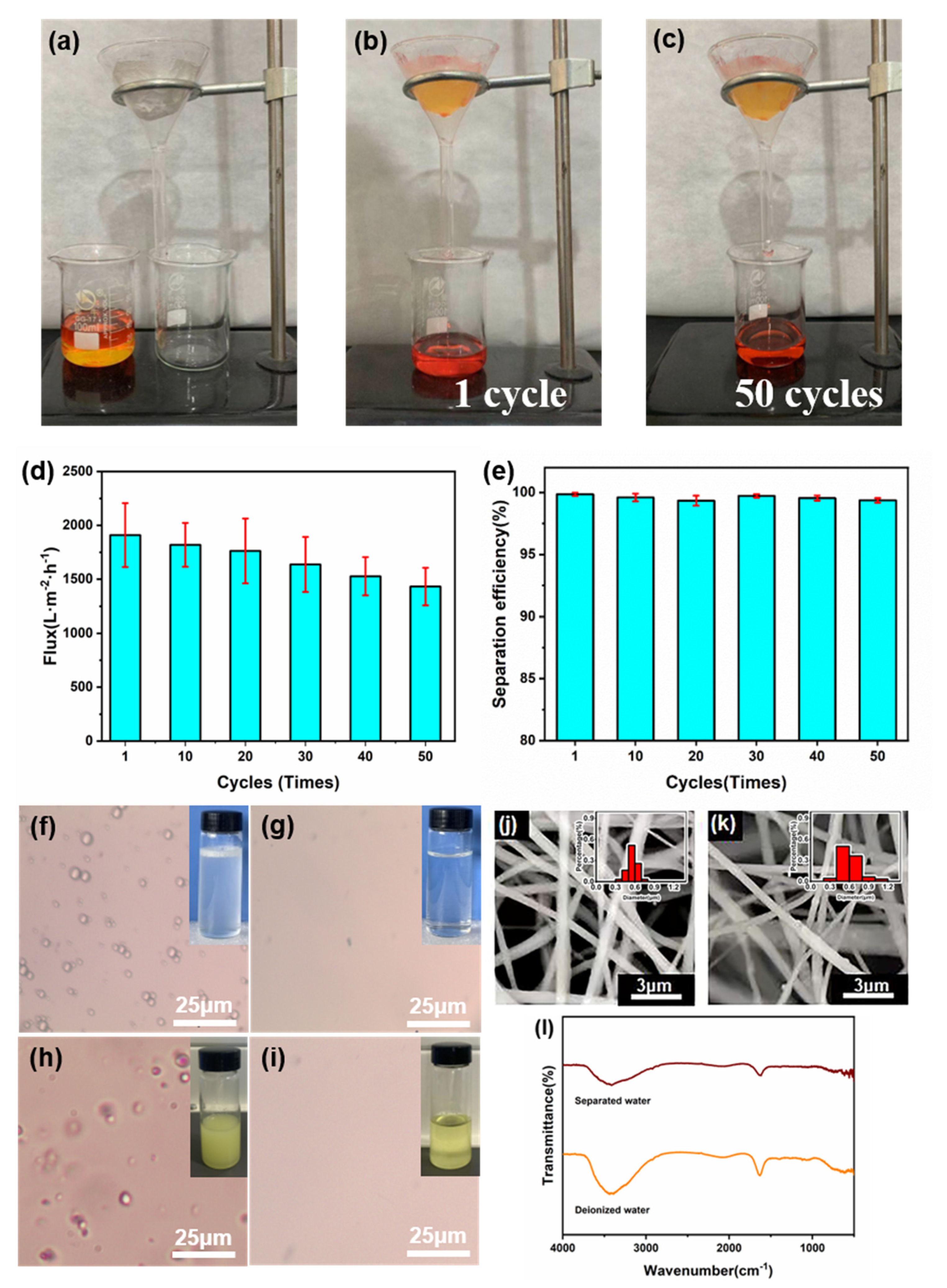
3.4. Oil-Water Separation Performance of Janus Membrane
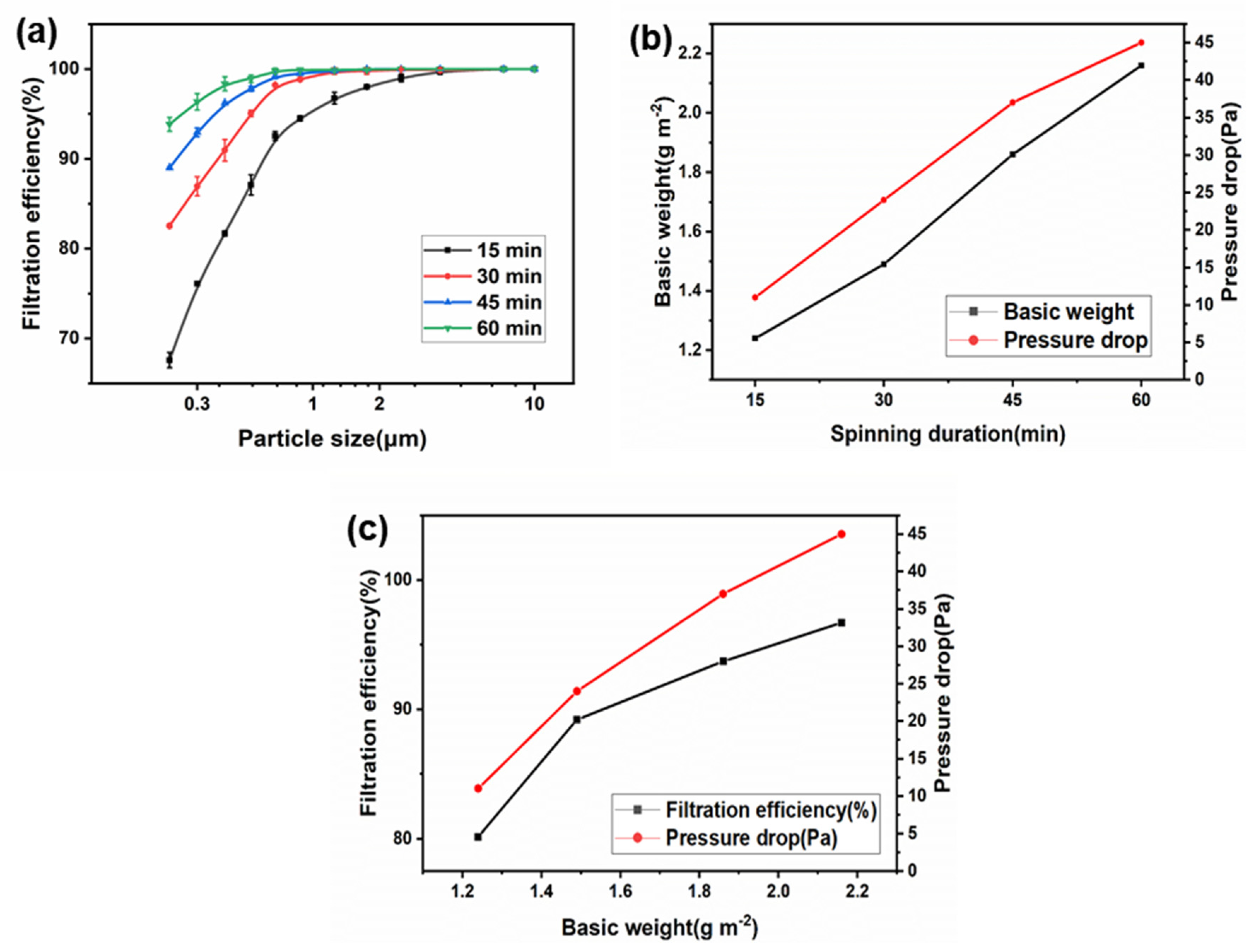
3.5. Filtration Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Polymeric and Ceramic Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, B.; Wang, T.; Liu, J. Direct photolithographic patterning of electrospun films for defined nanofibrillar microarchitectures. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, P.; Sobola, D.; Castkova, K.; Knapek, A.; Burda, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Dallaev, R.; Tofel, P.; Trcka, T.; Grmela, L.; et al. Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Electrospun Fibers Doped by Carbon Flakes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Nano-featured scaffolds for tissue engineering: A review of spinning methodologies. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Niu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X.; Song, L.; Zhao, R.; Ma, L.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, X. Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes: A Novel Solid Substrate for Microfluidic Immunoassays for HIV. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4770–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formo, E.; Lee, E.; Campbell, D.; Xia, Y. Functionalization of Electrospun TiO2 Nanofibers with Pt Nanoparticles and Nanowires for Catalytic Applications. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhou, Q.; Long, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y. Nanofibrous patterns by direct electrospinning of nanofibers onto topographically structured non-conductive substrates. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4993–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Fang, J.; Shao, H.; Ding, X.; Lin, T. High-sensitivity acoustic sensors from nanofibre webs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Gennes, P.G. Soft matter. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z. Janus Membranes: Exploring Duality for Advanced Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2016, 55, 13398–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xie, Y.; Hou, J.; Cheetham, A.K.; Chen, V.; Darling, S.B. Janus Membranes: Creating Asymmetry for Energy Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z. Asymmetric Surface Engineering for Janus Membranes. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1902064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Unidirectional water-penetration composite fibrous film via electrospinning. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5996–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Guo, Z. Superwetting Janus membranes: Focusing on unidirectional transport behaviors and multiple applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 12921–12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Ren, H.; Sun, F.; Lin, Q.; Lin, J.; Lou, C. Tuning the gradient structure of highly breathable permeable directional water transport in bi-layered Janus fibrous membranes using electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3529–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. Design of Gold nanorods Janus membrane for efficient and high-sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering and tunable surface plasmon resonance. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 721, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Mao, H.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Fan, Y. Underwater superoleophobic-underoil superhydrophobic Janus ceramic membrane with its switchable separation in oil/water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Q.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Bai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Shao, L. Constructing Scalable Superhydrophobic Membranes for Ultrafast Water-Oil Separation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3500–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. A Self-Pumping Dressing for Draining Excessive Biofluid around Wounds. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Continuous Spontaneous and Directional Water Transport in the Trilayered Fibrous Membranes for Functional Moisture Wicking Textiles. Small 2018, 14, 1801527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Pi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X. Novel Janus Fibrous Membranes with Enhanced Directional Water Vapor Transmission. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Kong, J.; Mu, C.; Zhao, C.; Thomas, N.L.; Lu, X. Materials design towards sport textiles with low-friction and moisture-wicking dual functions. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prince, J.A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Ayyanar, N.; Shanmugasundaram, T.S.; Singh, G. Nanofiber based triple layer hydro-philic/-phobic membrane—A solution for pore wetting in membrane distillation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jin, J.; Lin, S. Novel Janus Membrane for Membrane Distillation with Simultaneous Fouling and Wetting Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13304–13310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, L.; Song, C.; Shi, W.; Cui, F.; Wang, W. Breathable and asymmetrically superwettable Janus membrane with robust oil-fouling resistance for durable membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S. Janus porous membrane with conical nanoneedle channel for rapid unidirectional water transport. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10954–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Niu, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Lin, T. Dual-Layer Superamphiphobic/Superhydrophobic-Oleophilic Nanofibrous Membranes with Unidirectional Oil-Transport Ability and Strengthened Oil-Water Separation Performance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1400506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wang, N.; Man, X.; Cui, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, D.; Jiang, L.; et al. Interpenetrating Janus Membrane for High Rectification Ratio Liquid Unidirectional Penetration. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4124–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, N.; Hou, L.; Cui, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y. A bioinspired hybrid membrane with wettability and topology anisotropy for highly efficient fog collection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, X.; Long, J.; Cheng, X.; Pan, D.; Huang, Y.; Shao, L. Universal unilateral electro-spinning/spraying strategy to construct water-unidirectional Janus membranes with well-tuned hierarchical micro/nanostructures. Chem. Commun. 2019, 56, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganath, A.S.; Baji, A. Electrospun Janus Membrane for Efficient and Switchable Oil-Water Separation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.; Han, Q.; Zhao, S.; Tang, C.Y. Janus Membrane with Unparalleled Forward Osmosis Performance. Environ. Sci. Tech. Lett. 2019, 6, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Hu, X.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Flexible and Salt Resistant Janus Absorbers by Electrospinning for Stable and Efficient Solar Desalination. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Q.; Tian, J.; Xi, X.; Li, D.; Dong, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, G. Double anisotropic electrically conductive flexible Janus-typed membranes. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 18918–18930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Yu, W.; Ma, Q.; Li, D.; Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, G. Using special Janus nanobelt as constitutional unit to construct anisotropic conductive array membrane for concurrently affording color-tunable luminescence and superparamagnetism. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31608–31617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Ma, Q.; Qi, H.; Song, Y.; Tian, J.; Yu, W.; Dong, X.; Li, D.; Liu, G.; Wang, J. Utilizing modules of different functions to construct a Janus-type membrane and derivative 3D Janus-type tube displaying synchronous trifunction of conductive aeolotropism magnetism and luminescence. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 435602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, P.M.; Kandasubramanian, B. Heterogeneous wettable cotton based superhydrophobic Janus biofabric engineered with PLA/functionalized-organoclay microfibers for efficient oil-water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 7457–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Miao, D.; Zhao, J.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Biomimetic Fibrous Murray Membranes with Ultrafast Water Transport and Evaporation for Smart Moisture-Wicking Fabrics. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Kong, J.; Phua, S.L.; Zhao, C.; Thomas, N.L.; Lu, X. Tailoring surface hydrophilicity of porous electrospun nanofibers to enhance capillary and push-pull effects for moisture wicking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14087–14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pornea, A.M.; Puguan, J.M.C.; Deonikar, V.G.; Kim, H. Robust Janus nanocomposite membrane with opposing surface wettability for selective oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 236, 116297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Asymmetric water affinity on antibacterial electrospun sub-micro cellulose acetate Janus membrane. Mater. Lett. 2019, 256, 126607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Pan, K. Novel PAN/PVP Janus ultrafine fiber membrane and its application for biphasic drug release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5390–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Hou, J.; Xu, J.; Shan, B. Switchable oil/water separation with efficient and robust Janus nanofiber membranes. Carbon 2017, 115, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Geng, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, K. Novel magnetic-fluorescent bifunctional Janus nanofiber membrane. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wei, W.; Zhao, S.; Sun, M.; Wang, J. Fabrication of highly underwater oleophobic textiles through poly(vinyl alcohol) crosslinking for oil/water separation: The effect of surface wettability and textile type. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 52, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destaye, A.G.; Lin, C.K.; Lee, C.K. Glutaraldehyde vapor cross-linked nanofibrous PVA mat with in situ formed silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 4745–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lu, C.; Wang, F.; Dong, X. Piezoelectric property of PVDF/graphene composite films using 1H 1H 2H 2H-Perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane as a modifying agent. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 688, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, H.S.; Sadahira, C.M.; Souza, A.N.; Mansur, A.A.P. FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A critical analysis of the α β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.-D.; Xu, P.; Luo, X.; Zuo, X.-G.; Chen, F.; Ding, Y.-S. Effect of Graphene Modified by P[MMA-IL] on the Crystallization and Dielectric Behavior of PVDF Composite Film. Acta Polym. Sin. 2017, 5, 776–784. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Dong, T.; Hou, D.; Yao, J.; Han, L. Carbon nanotube based Janus composite membrane of oil fouling resistance for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 607, 118078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Shen, H.; Han, L.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, F.; Yang, S.; Yin, X. Mechanically Robust Janus Poly(lactic acid) Hybrid Fibrous Membranes toward Highly Efficient Switchable Separation of Surfactant-Stabilized Oil/Water Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 50879–50888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-M.; Hong, S.; Li, R.; Kim, I.S.; Wang, P. Janus Graphene Oxide-Doped Lamellar Composite Membranes with Strong Aqueous Stability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, S.; Wang, D.; Xu, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G. Facile fabricate a bioinspired Janus membrane with heterogeneous wettability for unidirectional water transfer and controllable oil-water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14398–14411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fu, L.; Zou, M.; Cao, A.; Du, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.H. Two-Dimensional Flexible Bilayer Janus Membrane for Advanced Photothermal Water Desalination. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, M.; Xu, Z. Janus Membranes with Charged Carbon Nanotube Coatings for Deemulsification and Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 9832–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J. An ultrathin bilayer membrane with asymmetric wettability for pressure responsive oil/water emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23477–23482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, H.; Ali, N.; Shah, A.U.H.A.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Hong, K.; Bilal, M. Effect of pH and salinity on stability and dynamic properties of magnetic composite amphiphilic demulsifier molecules at the oil-water interface. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kim, S.; Kallem, P.; Choi, H. Capillary effect in Janus electrospun nanofiber membrane for oil/water emulsion separation. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, N.; Tan, L.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X. Bioinspired Superwettable Covalent Organic Framework Nanofibrous Composite Membrane with a Spindle-Knotted Structure for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Emulsion Separation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16545–16554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Property | Water-in-Diesel Emulsions |
|---|---|
| Viscosity (mPa × S) | 3.52 |
| Density (g cm−3) | 0.82 |
| Surface tension (mN m−1) | 29.42 |
| Water content (%) | 5.8 |
| Membrane Side | θWA | θOA | θwater–in–oil | θoil–in–water | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Angle (°) | Wettability | Testing oil | Contact Angle (°) | Wettability | Contact Angle (°) | Wettability | Contact Angle (°) | Wettability | |
| cPVA | 0 | Hydrophilic | n-hexane | 0 | Oleophilic | 145 | Hydrophobic | 140 | Oleophobic |
| PVDF/PMMA/GO | 153 | Hydrophobic | n-hexane | 0 | Oleophilic | 146 | Hydrophobic | 0 | Oleophilic |
| Materials | Fabrication Method | Water Contact Angle of Hydrophobic Side | Major Applications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA-SiO2/PLA-CNTs | electrospinning | 142° | oil–water separation | [53] |
| PVDF-M-CNT | coating | 115.3° | membrane distillation | [52] |
| c-PVA/f-CNT | coating | 157° | oil–water separation | [41] |
| PCFE/GO/JGO | coating | 90° | water treatments | [54] |
| HP-PET/GNs-PET | coating | 95.3° | oil–water separation | [55] |
| AuNR/SWNT | coating | 110° | photothermal water desalination | [56] |
| CNTs/MPPM | coating | 158° | oil–water separation | [57] |
| PAN/CNTs | coating | 100° | oil–water separation | [44] |
| polydopamine-coated SWCNT/SWCNT | coating | 104° | oil–water separation | [58] |
| cPVA/PVDF-PMMA-GO | electrospinning | 153° | oil–water separation | This work |
| Materials | Flux | Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA-SiO2/PLA-CNTs | 1457 L m−2 h−1 | 99.1% | [53] |
| HP-PET/GNs-PET | ≈1875 L m−2 h−1 | 99.0% | [55] |
| PNIPAM-PVDF/PVDF | 1500 L m−2 h−1 | 96.0% | [32] |
| PAN/PS | 430 L m−2 h−1 | - | [60] |
| COF-DhaTab/PAN | 1100 L m−2 h−1 | 99.9% | [61] |
| cPVA/PVDF-PMMA-GO | 1910 L m−2 h−1 | 99.9% | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Shi, J.; Ning, X.; Long, Y.-Z.; Zheng, J. The High Flux of Superhydrophilic-Superhydrophobic Janus Membrane of cPVA-PVDF/PMMA/GO by Layer-by-Layer Electrospinning for High Efficiency Oil-Water Separation. Polymers 2022, 14, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030621
Wu H, Shi J, Ning X, Long Y-Z, Zheng J. The High Flux of Superhydrophilic-Superhydrophobic Janus Membrane of cPVA-PVDF/PMMA/GO by Layer-by-Layer Electrospinning for High Efficiency Oil-Water Separation. Polymers. 2022; 14(3):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030621
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Han, Jia Shi, Xin Ning, Yun-Ze Long, and Jie Zheng. 2022. "The High Flux of Superhydrophilic-Superhydrophobic Janus Membrane of cPVA-PVDF/PMMA/GO by Layer-by-Layer Electrospinning for High Efficiency Oil-Water Separation" Polymers 14, no. 3: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030621
APA StyleWu, H., Shi, J., Ning, X., Long, Y.-Z., & Zheng, J. (2022). The High Flux of Superhydrophilic-Superhydrophobic Janus Membrane of cPVA-PVDF/PMMA/GO by Layer-by-Layer Electrospinning for High Efficiency Oil-Water Separation. Polymers, 14(3), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030621







