Vesicle Geometries Enabled by Semiflexible Polymer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Methods
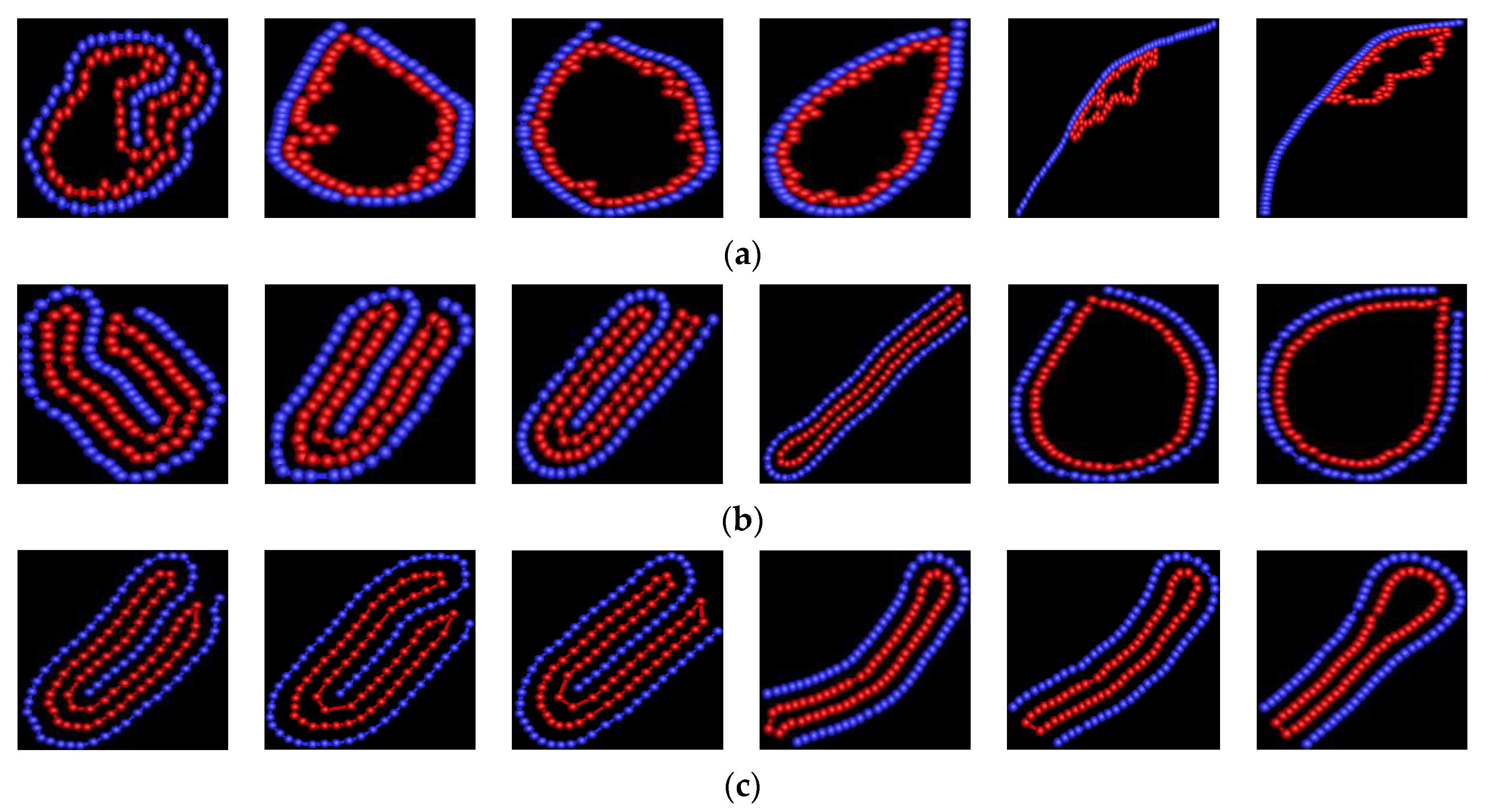
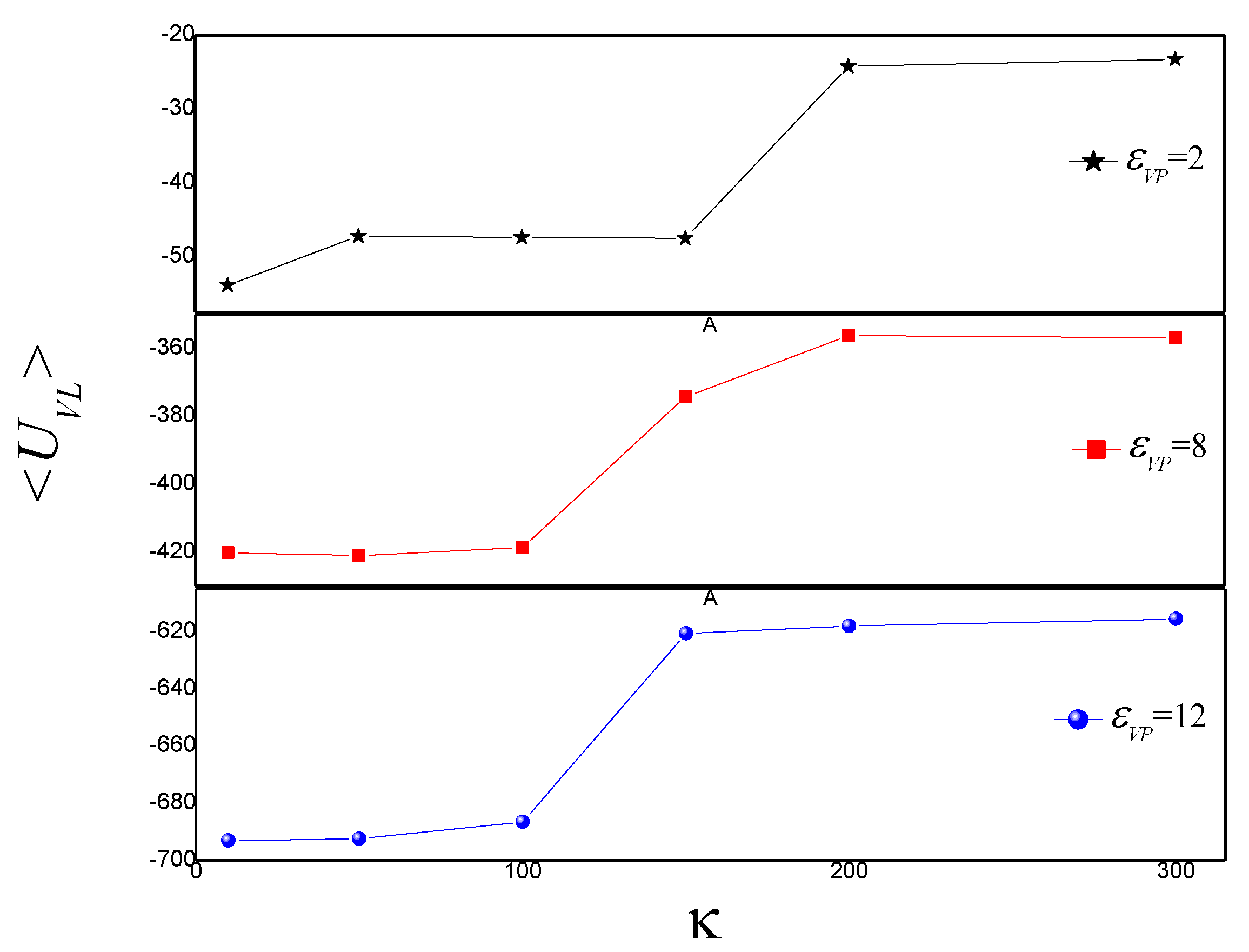
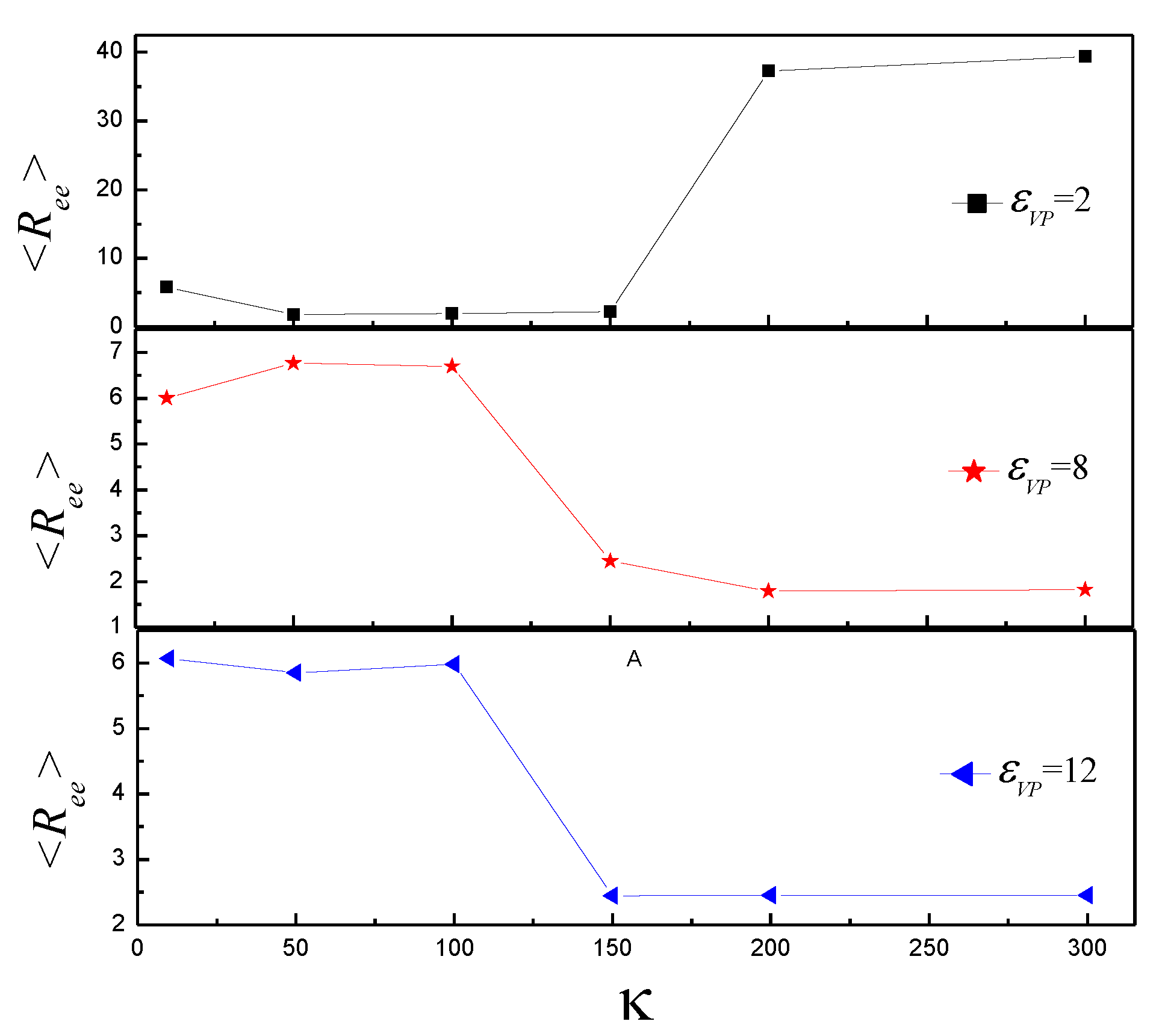
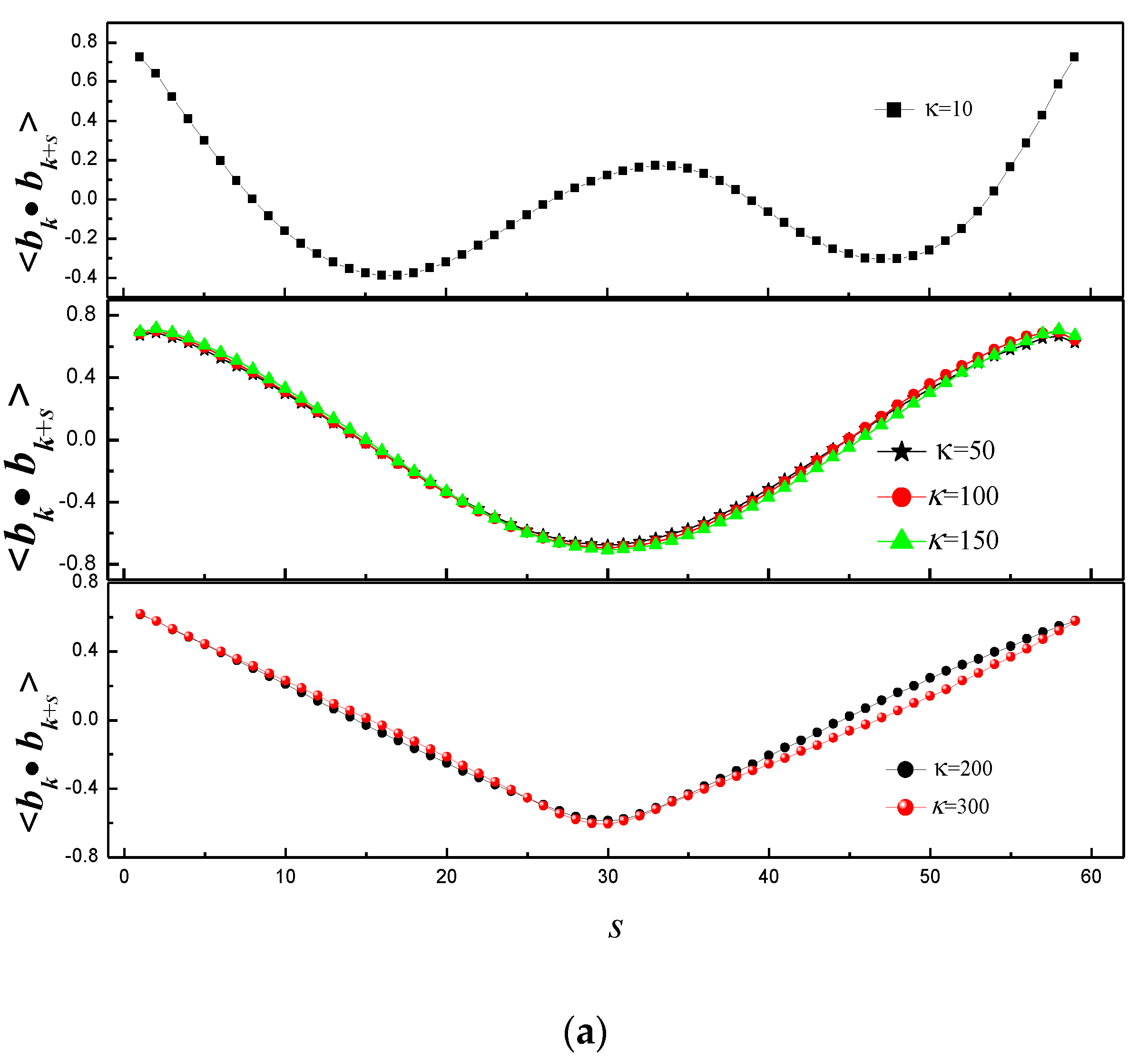
3. Results and Discussion
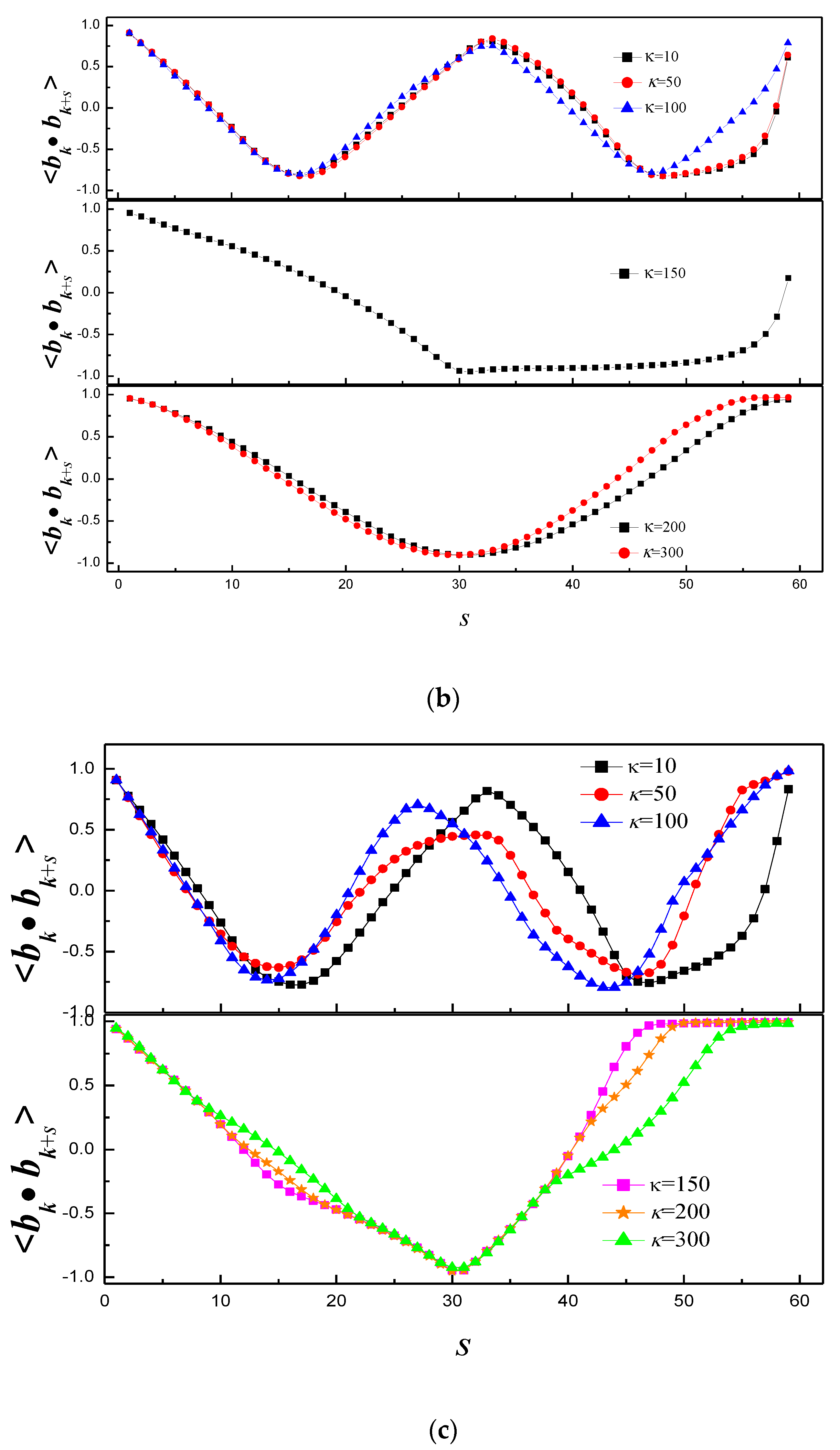
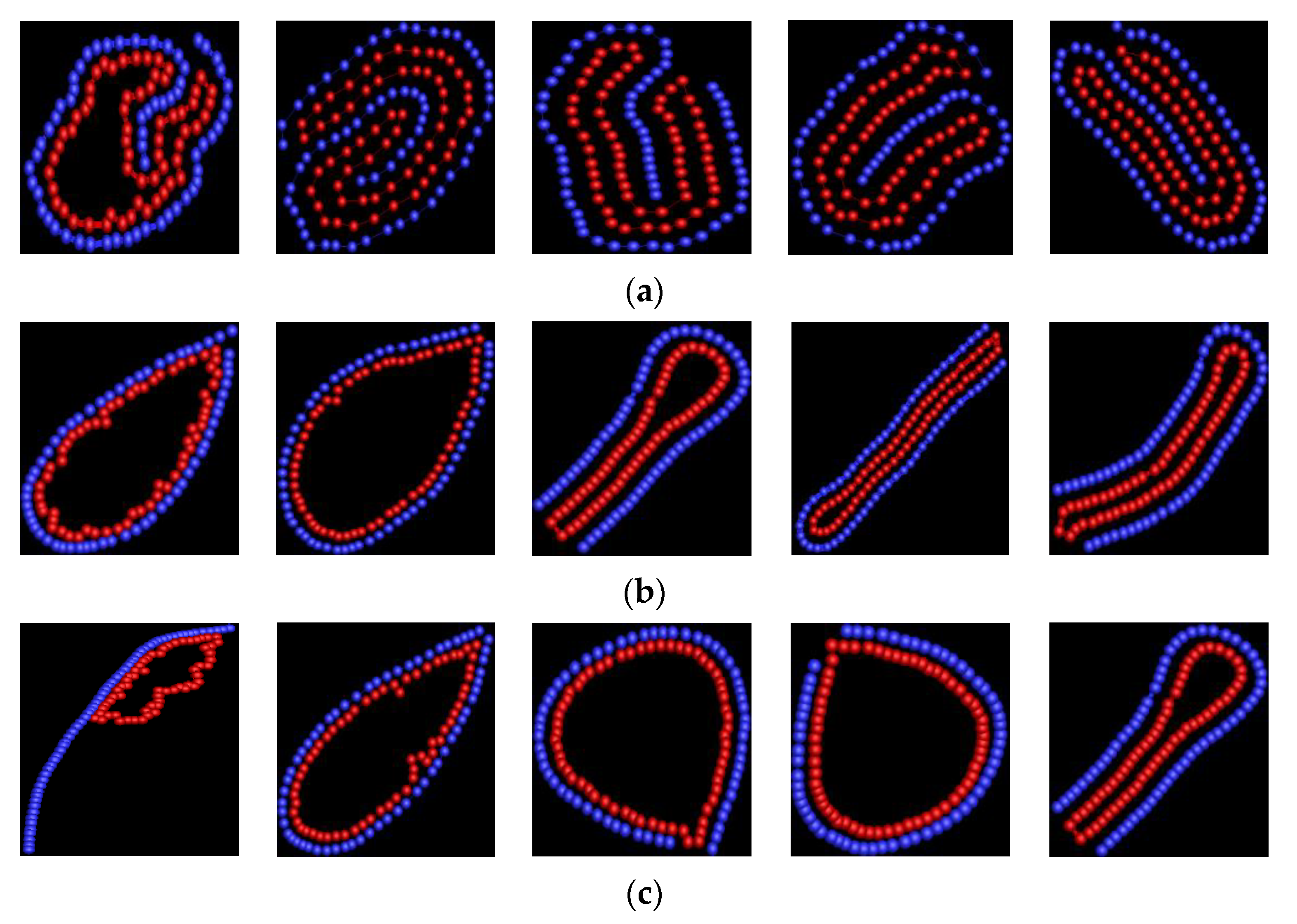
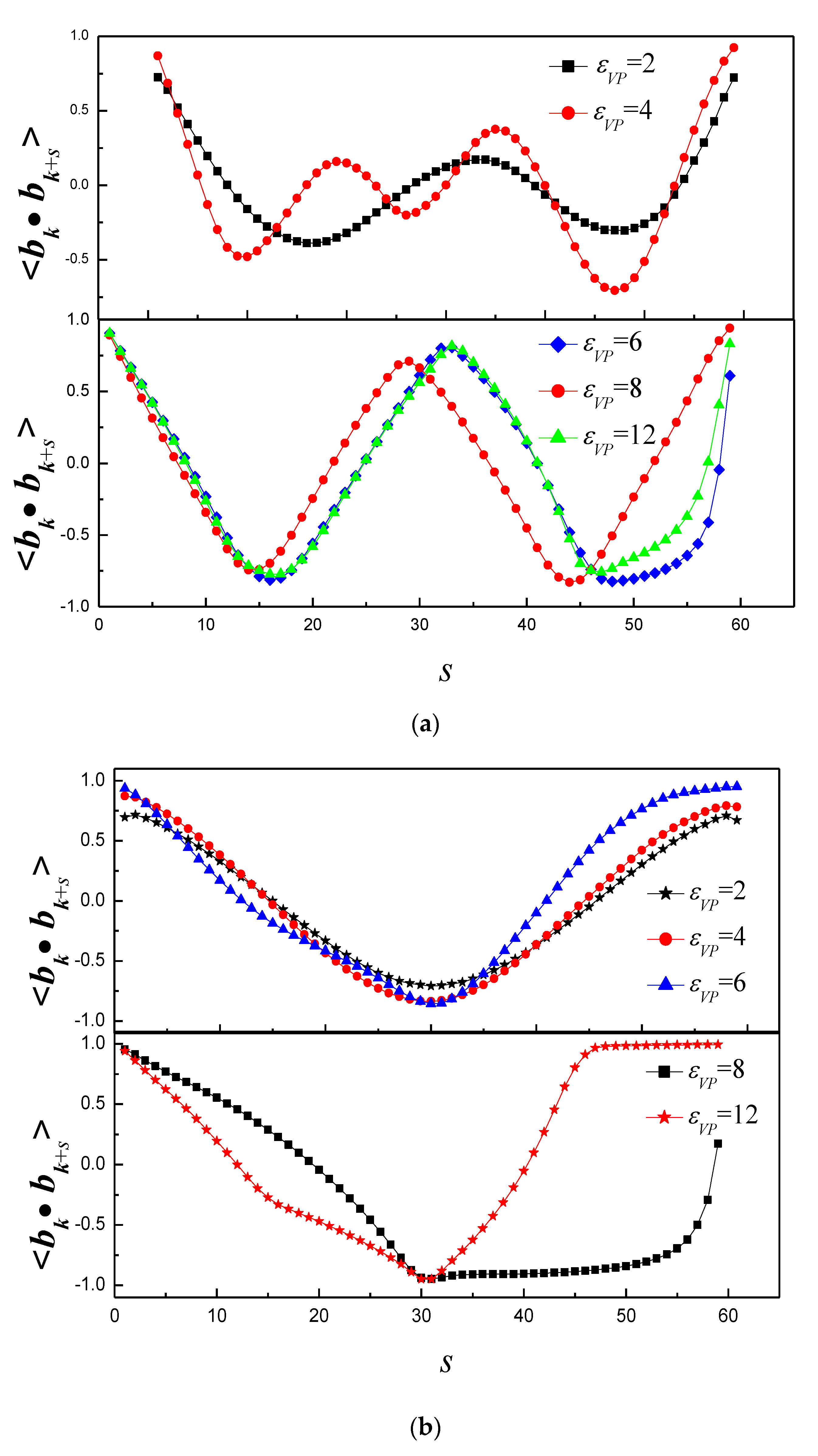
3.1. Effect of Bending Stiffness of Polymer on the Shape of Vesicles
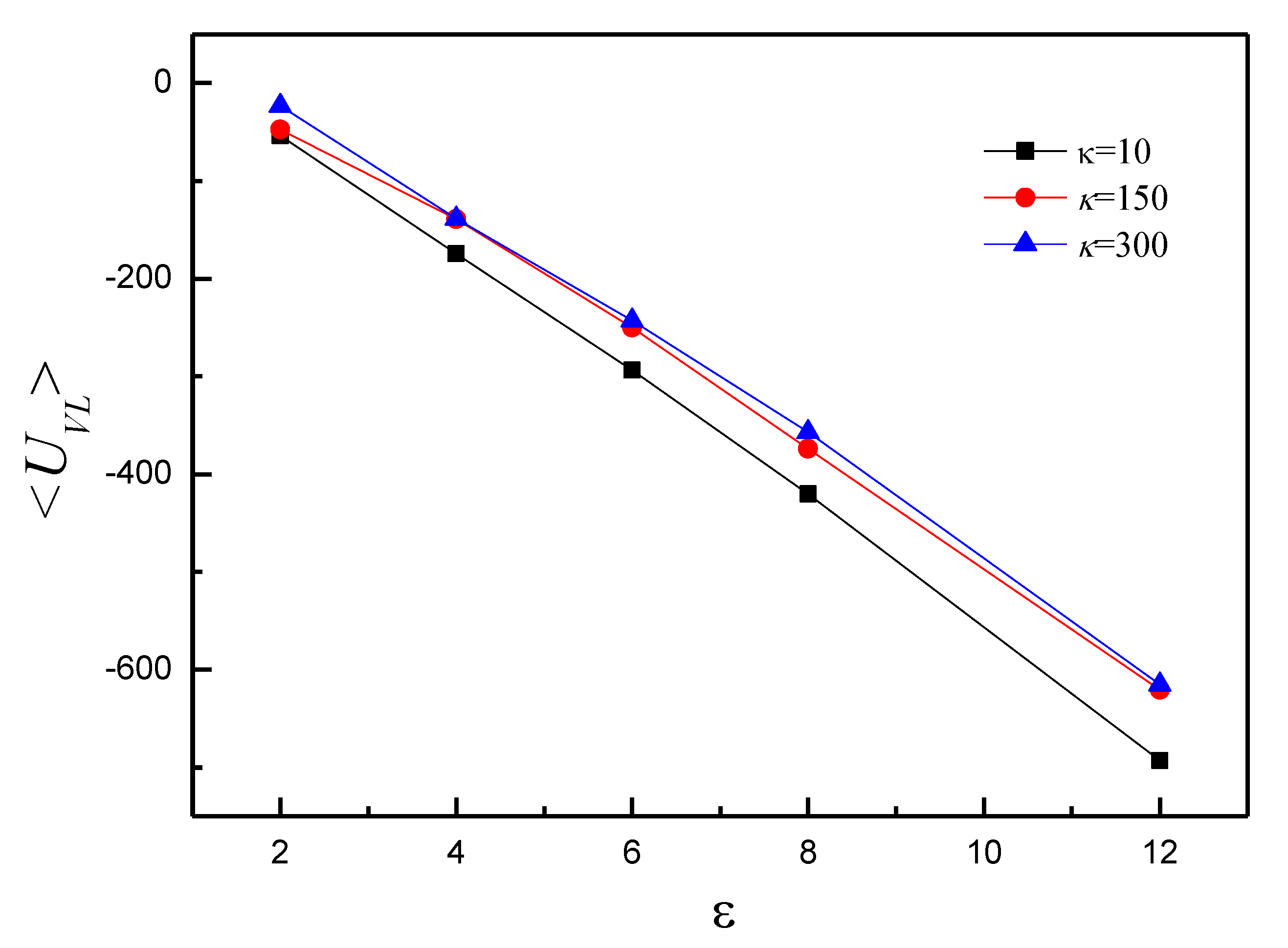
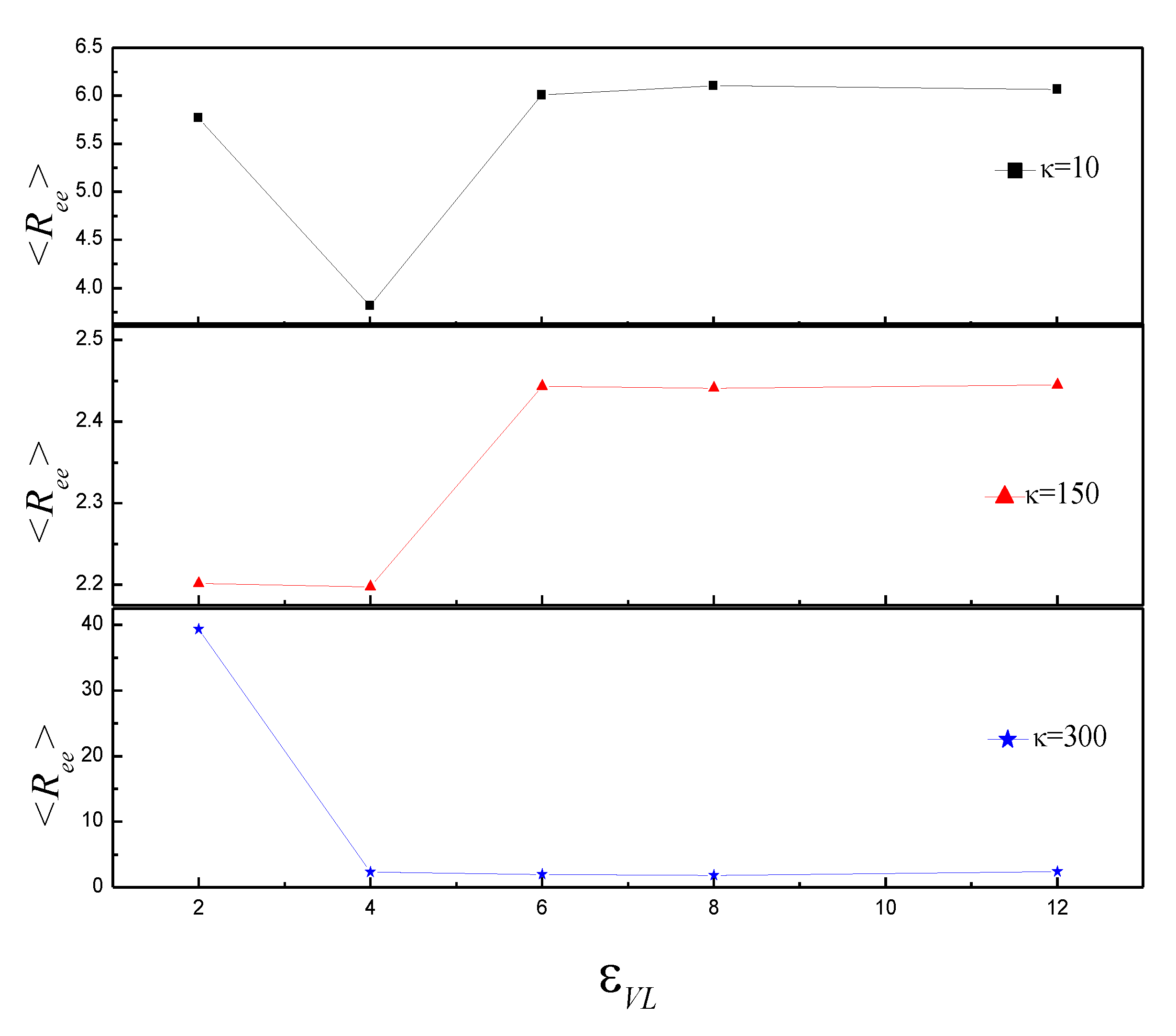
3.2. Effect of on the Shape of Vesicles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, F.; Engbers, G.H.; Feijen, J. Biodegradable polymersomes as a basis for artificial cells: Encapsulation, release and targeting. J. Control. Release 2005, 101, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, T.; Yang, Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, L. formation of controllable hydrophilic/hydrophobic drug delivery systems by electrospinning of vesicles. Langmuir 2015, 31, 5141–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonietti, M.; FÖrster, S. Vesicles and liposomes: A self-assembly principle beyond lipids. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.F.; Zhu, C.H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q.H. Broadband cross polarization converter with unity efficiency for terahertz waves based on anisotropic dielectric meta-reflect arrays. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Yuan, J.; Zheng, L. The formation of vesicles by N-dodecyl-N -methylpyrrolidinium bromide ionic liquid/copper dodecyl sulfate and application in the synthesis of leaflike Cu. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipowsky, R.; Sackmann, E. Structure and Dynamics of Membranes: From Cells to Vesicles. In Handbook of Biological Physics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 1–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Shillcock, J.C. Spontaneous vesicle self-assembly: A mesoscopic view of membrane dynamics. Langmuir 2012, 28, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Bao, M. Micelle-vesicle transitions in catanionic mixtures of SDS/DTAB induced by salt, temperature, and selective solvents: A dissipative particle dynamics simulation study. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, F.F.; Luan, Y.X.; Cao, W.T.; Ji, X.Q.; Zhao, L.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, Z.H. Formation of drug/surfactant catanionic vesicles and their application in sustained drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.Q.; Hou, W.G. Vesicle formation induced by layered double hydroxides in the catanionic surfactant solution composed of sodium dodecyl sulfate and dodecyltrimethylammoniu. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B.; Bray, D.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Essential Cell Biology; Garland Publishing: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Geng, T.; Li, Q.X.; Li, G.J.; Ju, H.B. Influences of temperature, pH and salinity on the surface property and self-assembly of 1:1 salt-free cataniomic surfactant. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 199, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Han, X.; Cheng, X.H.; Huang, J.B.; Liang, D.H.; Yu, C.L. pH-regulated molecular self-assemblies in a cationic-anionic surfactant system: From a “1-2” surfactant pair to a “1-1” surfactant pair. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13918–13924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Guo, K.K. Shape of vesicles encapsulating two aqueous phases. Soft Matter. 2014, 10, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Y.; Yao, Z.W.; de la Cruz, M.O. Vesicle geometries enabled by dynamically trapped states. ACS Nano. 2016, 10, 2287–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.Z.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, H.D.; Yang, Y.L. Shape of fluid vesicles anchored by rigid rod. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 9698–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiergeist, C.; Lipowsky, R. Elastic properties of polymer-decorated membranes. J. Phys. II 1996, 6, 1465–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Gennes, P.-G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornell University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.W.; Sung, W. Membrane curvature induced by polymer adsorption. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 041910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auth, T.; Gompper, G. Self-avoiding linear and star polymers anchored to membranes. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 051801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breidenich, M.; Netz, R.R.; Lipowsky, R. Adsorption of polymers anchored to membranes. Eur. Phys. J. E 2001, 5, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipowsky, R. Bending of Membranes by Anchored Polymers. Europhys. Lett. 1998, 30, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipowsky, R.; Doebereiner, H.G.; Hiergiest, C.; Indrani, V. Membrane curvature induced by polymers and colloids. Physica A 1998, 249, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, K.K.; Wang, J.F.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, H.D.; Yang, Y.L. Shapes of fluid vesicles anchored by polymer chains. Soft Matter. 2009, 5, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Neimark, A.V. Adsorption-driven translocation of polymer chain into nanopore. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Chai, A.H.; Yang, Y.F.; Li, X.M.; Li, P.; Dai, R.Y. The semiflexible polymer translocation into laterally unbounded region between two parallel flat membranes. Polymers 2016, 8, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panja, D.; Barkema, G.T.; Kolomeisky, A.B. Through the eye of the needle: Recent advances in understanding biopolymer translocation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 4977–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.X.; Chen, C.H.; Rehaman, A.U.; Liang, H.J. Local coil-helix transition of semiflexible polymers confined in spheres. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 6836–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, D.T.; Schnabel, S.; Landau, D.P.; Bachmann, M. From flexible to stiff: Systematic analysis of structural phases for single semiflexible polymers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 028103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnabel, S.; Janke, W.; Bachmann, M. Advanced multicanonical Monte Carlo methods for efficient simulations of nucleation processes of polymers. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 4454–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, B.A.; Neuhaus, T. Multicanonical ensemble: A new approach to simulate first-order phase transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Laudau, D.P. Efficient, multiple-range random walk algorithm to calculate the density of states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 2050–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eslami, H.; Das, S.; Zhou, T.H.; Müller-Plathe, F. How alcoholic disinfectants affect coronavirus model membranes: Membrane fluidity, permeability, and disintegration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 10374–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Khanjari, N.; Müller-Plathe, F. Self-assembly mechanisms of triblock janus particles. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzav, E.; Adda-Bedia, M.; Boudaoud, A. A statistical approach to close packing of elastic rods and to DNA packaging in viral capsids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18900–18904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Sullivan, D.; Yuan, X. Model for wormlike polymers confined between hard wall. Europhys. Lett. 2005, 72, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Gharibi, A.; Müller-Plathe, F. Mechanisms of nucleation and solid-solid-phase transitions in triblock janus assemblies. J. Chem. Theory. Comput. 2021, 17, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Guo, K.K.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, H.D.; Yang, Y.L. Predicting shapes of polymer chain anchored fluid vesicles. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 041908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesi, A.; Pasquali, M.; Mackkintosh, F.C. Collapse of a semiflexible polymer in poor solvent. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 0219161–02191610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drube, F.; Alim, K.; Witz, G.; Dietler, G.; Frey, E. Excluded volume effects on semiflexible ring polymers. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Kang, N.; Chai, A.; Lu, D.; Luo, S.; Yang, Z. Vesicle Geometries Enabled by Semiflexible Polymer. Polymers 2022, 14, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040757
Li P, Kang N, Chai A, Lu D, Luo S, Yang Z. Vesicle Geometries Enabled by Semiflexible Polymer. Polymers. 2022; 14(4):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040757
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ping, Nianqiang Kang, Aihua Chai, Dan Lu, Shuiping Luo, and Zhiyong Yang. 2022. "Vesicle Geometries Enabled by Semiflexible Polymer" Polymers 14, no. 4: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040757
APA StyleLi, P., Kang, N., Chai, A., Lu, D., Luo, S., & Yang, Z. (2022). Vesicle Geometries Enabled by Semiflexible Polymer. Polymers, 14(4), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040757





