Recent Developments in the Application of Bio-Waste-Derived Adsorbents for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater: A Review
Abstract
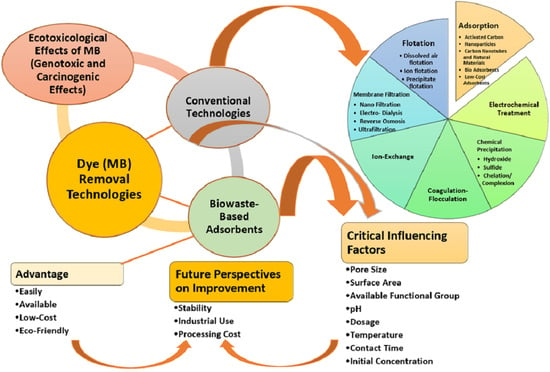
:1. Introduction
2. Carbon Structural Characteristics and Their Relationship to Adsorption Capacity
3. Wastewater Treatment Methods for MB’s Removal
3.1. Physical Techniques
3.2. Chemical Techniques
3.3. Biological Techniques
4. Adsorption
5. Adsorption Mechanism
6. Characterization and Formation of Carbon-Derived Adsorbents
Activated Carbons
7. Low-Cost Adsorbents
7.1. Natural Adsorbent
7.1.1. Clay
7.1.2. Siliceous
7.1.3. Zeolites
7.2. Bio Adsorbents
7.2.1. Bacterial
7.2.2. Fungal
7.2.3. Algae
7.2.4. Yeast
7.3. Agricultural and Industrial Materials’ Adsorbents
7.3.1. Agricultural Waste and Plant Adsorbents
7.3.2. Industrial Products
Fly Ash
Metal Hydroxide Sludge
Red Mud
7.4. Activated Carbon-Based Adsorbent Derived from Low-Cost Waste
Isotherm Equilibrium and Sorption Capacity of Biowaste-Derived Adsorbents
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pink Guava leaf | 250 | L-K2 | NA | 30 | 300 | [178] |
| Malted sorghum mash | 357.1 | L | 7.3 | 33 | 18 | [179] |
| Rice husk | 8.13 | L-K2 | 5.2 | 25 | NA | [180] |
| Water Hyacinth | 8.04 | L-K2 | 8 | 25 | 80 | [181] |
| Date stones | 398.19 | S-K2 | 7 | 30 | 270 | [182] |
| Oil palm shell | 133.13 | NA | NA | 30 | 10 | [183] |
| Swede rape straw | 246.4 | L | NA | 25 | NA | [184] |
| Pyrolysis of wheat | 12.03 | S | 8–9 | 20 | 50 | [185] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pea shells | 246.91 | L | 2–11.5 | 25 | 180 | [185] |
| Coconut fiber | 500 | L-K2 | 7.8 | 30 | 30 | [186] |
| Papaya leaves | 231.65 | L | 2–10 | 30 | 300 | [187] |
| Untreated Alfa grass | 200 | L-K2 | 12 | 20 | 180 | [188] |
| Neem leaf Powder | 401.6, 352.6 | F-K2 | 7 | 87 | 60 | [189] |
| Corn husk | 662.25 | F | 4 | 25 | 120 | [190] |
| Lagerstroemia microcarpa | 229.8 | L-K2 | NA | 30 | 360 | [191] |
| watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) | 489.80 | L-K2 | NA | 30 | 30 | [192] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | 95.19% | NA | 8.76 | 25 | 193 | [193] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron oxide-modified montmorillonite | 69.11 | L-K2 | 8 | 35 | 240 | [194] |
| Magnetic NaY Zeolite | 2.046 | L | 10.3 | 50 | 45 | [195] |
| Fe3O4 graphene/MWCNTs | 65.79 | L-K2 | 7 | 10 | 30 | [196] |
| Water hyacinth | 111.1 | L | 8-10 | 30 | 300 | [197] |
| Lantana camara stem | 19.84 | F-K2 | 3-11 | 20 | 60 | [198] |
| Natural peach gum (PG) | 298 | L-K2 | 6-10 | 25 | 30 | [199] |
| Activated fly ash (AFSH) | 14.28 | F-K2 | 3.0-10.0 | 20 | 100 | [200] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic biochar derived from empty fruit bunch | 31.25 | L-K2 | 2-10 | 25 | 120 | [201] |
| Magnetic adsorbent derived from corncob | 163.93 | L-K2 | NA | 25 | 500 | [202] |
| Fe3O4 bentonite | NA | K2 | 7 | NA | 20 | [203] |
| Magnetic chitosan/organic rectorite | 24.69 | L-K2 | 6 | 25 | 60 | [204] |
| Poly acrylic acid/MnFe2O4 | NA | K2 | 8.3 | 25 | NA | [205] |
| Fe3O4 xylan/poly acrylic acid | 438.6 | L-K2 | 8 | 25 | NA | [206] |
| Fe3O4 modified graphene sponge | 526 | L-K2 | 6 | NA | NA | [207] |
| Xanthate/Fe3O4 graphene oxide | 714.3 | L-K2 | 5.5 | 25 | 120 | [208] |
| Magnetic carbonate hydroxyapatite/ graphene oxide | 405.4 | L-K2 | 9.1 | 25 | 90 | [209] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palm shell | 163.3 | F-K2 | NA | 25 | NA | [210] |
| Fe3O4-activated montmorillonite | 106.38 | L-K2 | 7.37 | 20 | 25 | [211] |
| Clay (montmorillonite and vermaculti)/polyaniline/Fe3O4 | 184.5 | L-K2 | 6.3 | 25 | 30 | [212] |
| Magnetic chitosan/active charcoal | 200 | L-K2 | 7.73 | 25 | 200 | [99] |
| Fe3O4 /poly acrylic acid | 73.8 | L-K2 | NA | 45 | NA | [213] |
| Magnetized graphene oxide | 306.5 | L-K2 | 9 | 25 | 360 | [214] |
| Corn straw | 267.38 | F-K2 | 8 | 25 | 20 | [215] |
| Magnetic chitosan and graphene oxide | 243.31 | K2-L | 12 | 60 | 60 | [216] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time(min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn shell | 357.1 | L | 4 | 25 | 30 | [217] |
| Magnetic activated carbon | 2.046 | F-K2 | 10 | 25 | 120 | [218] |
| Magnetic halloysite nanotube nano-hybrid | 689.66 | L-K2 | 10 | 25 | 180 | [219] |
| Magnetic polyvinyl alcohol/laponite RD | 251 | L-K2 | 5.5 | 25 | 60 | [220] |
| Aegle marmelos leaves | 500 | F-K2 | 6 | 25 | 120 | [221] |
| Oak-acorn peel | 109.43 | L-K2 | 7 | 24 | 120 | [222] |
| Geopolymers | 15.95-20.22 | S-K2 | 4-12 | 25 | 80 | [223] |
| Ouricuri fiber | 31.7 | S-K2 | 5.5 | 25 | 5 | [224] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxymethyl/cellulose/ Fe3O4/SiO2 | 31.02 | L-K1 | 11 | NA | 60 | [225] |
| Cellulose-grafted | 7.5 | L | 8 | 5.5 | [226] | |
| NiFe2O4Ca/alginate | 1243 | R-K1 | 6.5 | 25 | 180 | [227] |
| Magnetic alginate | 161 | L | 7 | 20 | 120 | [228] |
| Magnetic hydrogel Nanocomposite of poly acrylic acid | 507.7 | L-K1 | 7 | 25 | 120 | [229] |
| Magnetized graphene oxide | 232.56 | L-K2 | 9 | 30 | 10 | [230] |
| Soursop | 55.397 | R-K2 | 5.5 | 25 | 300 | [231] |
| Sugarcane Bagasse | 17.434 | S-K2 | 5.5 | 25 | 300 | [231] |
| Palm sawdust | 53.476 | F-K2 | 8 | 25 | 120 | [232] |
| Eucalyptus sawdust | 99.009 | F-K2 | 6 | 20 | 60 | [232] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fir bark | 330.00 | F-K2 | NA | 25 | 40 | [233] |
| Pumpkin peel | 198.15 | L-K2 | 7 | 50 | 180 | [234] |
| Rice husk | 608 | L | 7 | 25 | 60 | [235] |
| date stones | 163.67 | F-K2 | 10 | 25 | 360 | [236] |
| Seaweed | 1279.00 | L-K2 | 4 | 25 | 50 | [237] |
| Moroccan cactus | 14.04 | L | 5 | 25 | 60 | [238] |
| Syagrus oleracea | 893.78 | L-K2 | 7 | 25 | 20 | [239] |
| Mentha plant | 588.24 | L | 10 | 25 | 30 | [240] |
| Palm leaf | 500 | L | 2 | 30-60 | 30 | [241] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kendu fruit peel | 144.90 | L-K2 | 6 | 25 | 100 | [242] |
| Magnesium oxide nanoparticles | 163.87 | L-K2 | 7.3 | 25 | 70 | [243] |
| Fava bean peel | 140.00 | L | 5.8 | 27 | NA | [244] |
| Dicarboxymethyl cellulose | 887.60 | L-K2 | 3 | 25 | 60 | [245] |
| Alginate-based beads | 400.00 | L-K1 | 7 | 25 | NA | [246] |
| Black cumin seeds | 16.85 | F-K2 | 4.8 | 25 | 20 | [247] |
| Dragon fruit peels | 195.2 | L-K1 | 3-10 | 50 | 60 | [248] |
| Litsea glutinosa seeds | 29.03 | L-K2 | 9 | 40 | 600 | [249] |
| Moringa oleifera leaf | 136.99 | F-K2 | 7 | 25 | 90 | [250] |
| Biosorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Most Appropriate Model | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grass waste | 364.2 | L | 10 | 45 | 15 | [251] |
| Mangosteen peel | 871.49 | L-K2 | 10 | 25 | 60 | [252] |
| Coconut shell | 156.25 | F-K2 | 4.9 | 25 | 360 | [253] |
| Core shell | 34.3 | L-K2 | 7 | 25 | 120 | [254] |
| Banana stem | 101.01 | F-K2 | 7 | 25 | 90 | [255] |
| Alginate beads | 769 | L-K2 | 8 | 30 | NA | [256] |
| Ulva lactuca | 344.83 | L-K2 | 11 | 25 | NA | [257] |
| Cassava Stem | 384.61 | L-K2 | 9.2 | 25 | 60 | [258] |
| Corncob | 864.58 | L-K2 | 5 | 25 | 360 | [259] |
8. Cost Analysis of Adsorbents
9. Regeneration and Economic Challenges of Bio-Waste-Derived Adsorbents
10. Management of Post-Adsorption Materials
10.1. Application as a Catalyst
10.2. Application in Ceramic Production
10.3. Application as Fertilizer
11. Cost-Effectiveness: Desorption versus Disposal
12. Limitations and Strategies
13. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamuddin. Xanthan gum/titanium dioxide nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 121, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Fixed-bed decolorization of Reactive Blue 172 by Proteus vulgaris NCIM-2027 immobilized on Luffa cylindrica sponge. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métivier-Pignon, H.; Faur-Brasquet, C.; Le Cloirec, P. Adsorption of dyes onto acti v ated carbon cloths: Approach of adsorption mechanisms and coupling of ACC with ultrafiltration to treat coloured wastewaters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 31, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaq, G.; Elmetwally, A.E. Bmim[OAc]-Cu2O/g-C3N4 as a multi-function catalyst for sonophotocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Ultrason Sonochem. 2019, 53, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbah, A.; Chouchane, H.; Abdelwahed, S.; Redissi, A.; Hamdi, M.; Kouidhi, S.; Neifar, M.; Masmoudi, A.S.; Cherif, A.; Mnif, W. PeptiDesalination Fixing Industrial Textile Dyes: A New Biochemical Method in Wastewater Treatment. J. Chem. 2020, 2019, 5081807. [Google Scholar]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Jamal, A.; Ilyas, M.; Zubair, M.; Khan, G.; Atieh, M.A. Bioremediation of dyes: Current status and prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Varjani, S.J.; Suganya, S. Treatment of dye wastewater using an ultrasonic aided nanoparticle stacked activated carbon: Kinetic and isotherm modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of Various Recent Wastewater Dye Removal Methods: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, D.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N. Ecotoxicological and health concerns of persistent coloring pollutants of textile industry wastewater and treatment approaches for environmental safety. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, A.; Fait, G. PesticiDesalination in surface waters: From edge-of-field to global modelling. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 36, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Mubarak, N.; Abdullah, E.C.; Nizamuddin, S.; Khalid, M.; Inamuddin. Recent trends in the synthesis of graphene and graphene oxide based nanomaterials for removal of heavy metals—A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 66, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K.; Rehman, Z. Application of Nanomaterials in the Remediation of Textile Effluents from Aqueous Solutions; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isloor, A.M.; Nayak, M.C.; Inamuddin; Prabhu, B.; Ismail, N.; Ismail, A.; Asiri, A.M. Novel polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)/nano tin oxide (SnO2) mixed matrix ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes: Fabrication, characterization and toxic dyes removal from aqueous solutions. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 139, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Development, characterization, and utilization of magnetized orange peel waste as a novel adsorbent for the confiscation of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, M.; Lorke, D.E.; Hasan, M.; Petroianu, G.A. Cellular and MolecularActions of Methylene Blue in the Nervous System. Med. Res. Rev. 2011, 31, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, M.M. Methylene blue as antidote for cyanide and carbon monoxide poisoning. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1933, 100, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.; Bharagava, R.N. Efficient degradation and detoxification of methylene blue dye by a newly isolated ligninolytic enzyme producing bacterium Bacillus albus MW407057. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Kim, D.S. Pristine and Modified Radix Angelicae Dahuricae (Baizhi) Residue for the Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: A Comparative Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharby, N.F.; Almutairi, R.S.; Mohamed, N.A. Adsorption Behavior of Methylene Blue Dye by Novel Crosslinked O-CM-Chitosan Hydrogel in Aqueous Solution: Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamics. Polymers 2021, 13, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owamah, H.I.; Chukwujindu, I.S.; Asiagwu, A.K. Biosorptive capacity of yam peels waste for the removal of dye from aqueous solutions. Civ. Environ. Res. 2013, 3, 36–48. [Google Scholar]
- Muhamad Ng, S.N.; Idrus, S.; Ahsan, A.; Tuan Mohd Marzuki, T.N.; Mahat, S.B. Treatment of wastewater from a food and beverage industry using conventional wastewater treatment integrated with membrane bioreactor system: A pilot-scale case study. Membranes 2021, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erabee, I.K.; Ahsan, A.; Jose, B.; Aziz, M.M.A.; Ng, A.W.M.; Idrus, S.; Daud, N.N.N. Adsorptive Treatment of Landfill Leachate using Activated Carbon Modified with Three Different Methods. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Lv, K. Novel polymer material for efficiently removing methylene blue, Cu (II) and emulsified oil droplets from water simultaneously. Polymers 2018, 10, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vakili, M.; Rafatullah, M.; Salamatinia, B.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Tan, K.B.; Gholami, Z.; Amouzgar, P. Application of chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for dye removal from water and wastewater: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.I.; Khalid, R.; Najeeb, J.; Hussain, Z. Fundamentals and photocatalysis of methylene blue dye using various nanocatalytic assemblies—A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Magsorbents: Potential candidates in wastewater treatment technology—A review on the removal of methylene blue dye. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 500, 166408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, E.; Ediati, R.; Kusumawati, Y.; Bahruji, H.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Prasetyoko, D. Review on recent advances of carbon based adsorbent for methylene blue removal from waste water. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 16, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhou, Z. Citrus pectin derived porous carbons as a superior adsorbent toward removal of methylene blue. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 243, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, S.; Yue, Q.; Wu, Y.; Gao, B. Chemical preparation of crab shell-based activated carbon with superior adsorption performance for dye removal from wastewater. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Ghazanfarkhani, M.D.; Khodadoust, S.; Sohrabi, N.; Oftade, M. Acceleration of methylene blue adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from dross licorice by ultrasonic: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2548–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Peng, L. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by modified expanded graphite powder. Desalination 2009, 249, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Halwany, M. Study of adsorption isotherms and kinetic models for Methylene Blue adsorption on activated carbon developed from Egyptian rice hull (Part II). Desalination 2010, 250, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarinejad, Z.; Rahmanian, O.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Heidari, M. Enhancement of methylene blue adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from Date Press Cake by low frequency ultrasound. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 264, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ahmad, T.; Hashim, R. Comparison of surface properties of wood biomass activated carbons and their application against rhodamine B and methylene blue dye. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, S.; Tay, T.; Ucar, S.; Erdem, M. Activated carbons from waste biomass by sulfuric acid activation and their use on methylene blue adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6214–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption characteristics of industrial solid waste derived activated carbon prepared by microwave heating for methylene blue. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 99, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, K.L.; Ng, D.H. Synthesis and characterization of cotton-made activated carbon fiber and its adsorption of methylene blue in water treatment. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 46, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherifi, H.; Fatiha, B.; Salah, H. Kinetic studies on the adsorption of methylene blue onto vegetal fiber activated carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 282, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhai, K.; He, C.; Li, Q.; Guo, P. Methylene Blue Adsorption from Aqueous Solution by Loofah Sponge-Based Porous Carbons. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.A.; Feng, R.; Malik, A.; Khan, S.Z.; Shi, Y.; Bhutta, A.J.; Shah, A.H. Combining Microwave Pretreatment with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enhanced Biogas and Hydrogen Yield from Green Algae. Processes 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, X. A Modified Method for Enhancing Adsorption Capability of Banana Pseudostem Biochar towards Methylene Blue at Low Temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meili, L.; Lins, P.V.; Zanta, C.L.P.S.; Soletti, J.I.; Ribeiro, L.M.O.; Dornelas, C.B.; Silva, T.L.; Vieira, M.G.A. MgAl-LDH/Biochar composites for methylene blue removal by adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.S.; Wu, C.W.; Adebajo, M.O.; Jin, G.C.; Yu, W.H.; Ji, S.F.; Zhou, C.H. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto porous cellulose- derived carbon/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Biochar/g-C3N4 Composites for Methylene Blue in Aqueous Solution. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 2394184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, Q.; Shi, W.; Xing, Y.; Hou, Y. A Polyoxoniobate/g-C3N4 Nanoporous Material with High Adsorption Capacity of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, T.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; et al. Comparative study of methylene blue dye adsorption onto activated carbon, graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Cui, J. Chitosan-derived three-dimensional porous carbon for fast removal of methylene blue from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narvekar, A.A.; Fernandes, J.B.; Tilve, S.G. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on glycerol based carbon materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1714–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Jiang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, W. An ultra-high surface area mesoporous carbon prepared by a novel MnO-templated method for highly effective adsorption of methylene blue. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Z.; Ma, G.; Kong, D.; Xiong, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y. Heteroatom-doped porous carbons with enhanced carbon dioxide uptake and excellent methylene blue adsorption capacities. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 257, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, O.; Tunç, S.; Polat, T.G.; Bozoğlan, B.K. Synthesis of magnetic oxidized multiwalled carbon application in cationic Methylene Blue dye adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Lee, X. Impregnation of multiwall carbon nanotubes in alginate beads dramatically enhances their adsorptive ability to aqueous methylene blue. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 133, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilo, M.; Lebovka, N.; Barany, S. Mechanism of Methylene Blue adsorption on hybrid laponite-multi-walled carbon nanotube particles. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 42, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, X. Wrapping carbon nanotubes with poly (sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue and its mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Mirza, B.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue dye on nanocomposite multi-walled carbon nanotube functionalized thiol (MWCNT-SH) as new adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wen, X.; Mijowska, E.; Tang, T.; Chen, X. A facile approach to prepare porous cup-stacked carbon nanotube with high performance in adsorption of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonune, A.; Ghate, R. Developments in wastewater treatment methods. Desalination 2004, 167, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinakis, A.S.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Arvaniti, O.S.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Samaras, V.G.; Ajibola, A.; Mamais, D.; Lekkas, T.D. Contribution of primary and secondary treatment on the removal of benzothiazoles, benzotriazoles, endocrine disruptors, pharmaceuticals and perfluorinated compounds in a sewage treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Yan, M.; Tan, X.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Song, B.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.P.T. Facile assembled biochar-based nanocomposite with improved graphitization for efficient photocatalytic activity driven by visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 250, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. An overview of dye removal via activated carbon adsorption process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 9, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saratale, R.G.; Sun, Q.; Munagapati, V.S.; Saratale, G.D.; Park, J.; Kim, D.S. The use of eggshell membrane for the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Batch, kinetics and reusability studies. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.; Singh, K.; Arora, S. Removal of Synthetic Textile Dyes From Wastewaters: A Critical Review on Present Treatment Technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 807–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Pan, F.; Sun, P.; Fu, J. An overview of nanomaterials applied for removing dyes from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15882–15904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, N.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Rathi, G.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Inamuddin; Asiri, A.M. Nano-Engineered Adsorbent for the Removal of Dyes from Water: A Review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2020, 16, 14–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K.; Baig, U. Synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles and their performance towards methyl orange dye removal: Characterisation, adsorption and response surface methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 211, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K. Suhas Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.M.; Haghighi, R. Chemical catalytic reaction and biological oxidation for treatment of non-biodegradable textile effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 95, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulalia, M.; Tenorio, P. Valorización De Residuos Agroindustriales Como Adsorbentes Para La Remoción De Fármacos De Uso Común De Aguas Contami-Nadas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Unuabonah, E.I.; Adie, G.U.; Onah, L.O.; Adeyemi, O.G. Multistage optimization of the adsorption of methylene blue dye onto defatted Carica papaya seeds. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, M.A.; Shehadeh, I.; Ahmed, A.; Al-zamly, A. Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by Using Gypsum as a Low Cost Adsorbent. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 55, 608–613. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Li, G.; Wang, D.; Feng, C.; Tang, H. Removal of direct dyes by coagulation: The performance of preformed polymeric aluminum species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y. Decolorization and COD removal of secondary yeast wastewater effluents by coagulation using aluminum sulfate. Desalination 2008, 225, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Bajpai, M. The flocculation performance of Tamarindus mucilage in relation to removal of vat and direct dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.G.; Gu, R.R. Synthesis of polyamine flocculants and their potential use in treating dye wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Choi, S.-P.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Shim, W.-G.; Moon, H. Evaluation of the performance of adsorption and coagulation processes for the maximum removal of reactive dyes. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 69, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, T.N.T.M.; Idrus, S.; Musa, M.A.; Wahab, A.M.A.; Jamali, N.S.; Man, H.C.; Ng, S.N.M. Enhancement of Bioreactor Performance Using Acclimatised Seed Sludge in Anaerobic Treatment of Chicken Slaughterhouse Wastewater: Laboratory Achievement, Energy Recovery, and Its Commercial-Scale Potential. Animals 2021, 11, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.; Mcmullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of dyes in textile e ‚ uent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Biores. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.; Jadhav, A.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Miino, M.C.; Damiani, S. Treatments for color removal from wastewater: State of the art. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyuncu, I.; Güney, K. Membrane-Based Treatment of Textile Industry Wastewaters. Encycl. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Ahmad, A.L.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption of reactive dye onto cross-linked chitosan/oil palm ash composite beads. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 136, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Gupta, V.K.; Sikarwar, S. Adsorption and desorption studies on hazardous dye Naphthol Yellow S. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Nayak, A.; Saleh, T.A.; Barakat, M.A. Adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution onto carbon nanotubes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 193–194, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, R.K.; Saibaba, K.V.N.; Shaik, K.B. Dye Removal by Adsorption: A Review. J. Bioremediation Biodegrad. 2016, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piaskowski, K.; Świderska-Dąbrowska, R.; Zarzycki, P.K. Dye removal from water and wastewater using various physical, chemical, and biological processes. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. Biomass-derived porous carbonaceous materials and their composites as adsorbents for cationic and anionic dyes: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Cheng, S.; Xia, H.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, S. Copper loaded on activated carbon as an efficient adsorbent for removal of methylene blue. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14395–14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uğurlu, M.; Gürses, A.; Açıkyıldız, M. Comparison of textile dyeing effluent adsorption on commercial activated carbon and activated carbon prepared from olive stone by ZnCl2 activation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhong, W.; Wei, W. Enhanced methylene blue adsorption onto activated reed-derived biochar by tannic acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, E.; Ali, S.N.; Al-Busafi, S.; Al Lawati, H. Preparation and characterization of surface functionalized activated carbons from date palm leaflets and application for methylene blue removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2713–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, X.; Ning, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Liu, S. Influence of sodium dodecyl sulfate coating on adsorption of methylene blue by biochar from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 70, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaer, H.; Kaya, I. Synthesis, characterization of magnetic chitosan/active charcoal composite and using at the adsorption of methylene blue and reactive blue4. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 232, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, D.; Dhandapani, B.; Panchamoorthy, G.K.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Ramakrishnan, S.R. Comparison of surface-engineered superparamagnetic nanosorbents with low-cost adsorbents of cellulose, zeolites and biochar for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3181–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, K.; Li, L.Y. Adsorption of organic stormwater pollutants onto activated carbon from sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Degs, Y.S.; El-Barghouthi, M.I.; El-Sheikh, A.H.; Walker, G.M. Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 77, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.A.; Nuh, A.; Rasid, Z.A.; Abu, A.; Tanasta, Z.; Hassan, M.Z.; Mahmud, J. Tensile behaviours of single-walled carbon nanotubes: Dehnungsverhalten einwandiger Kohlenstoffnanoröhren. Mater. Werkst. 2018, 49, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, L.; Shin, C.H.; Ryu, M.H.; Cai, J. Study on the copper (II)-doped MIL-101 (Cr) and its performance in VOCs adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28109–28119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Fu, Y. Synthesis of high-performance hierarchically porous carbons from rice husk for sorption of phenol in the gas phase. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.Z.; Wang, L.; Cheng, G.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.B. Adsorption properties of regenerative materials for removal of low concentration of toluene. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tahriri, M.; Del Monico, M.; Moghanian, A.; Yaraki, M.T.; Torres, R.; Yadegari, A.; Tayebi, L. Graphene and its derivatives: Opportunities and challenges in dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, C.J.; Yoo, M.J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.H. High-performance materials for effective sorptive removal of formaldehyde in air. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, A.; Boukoussa, B. Structural, textural and toluene adsorption properties of microporous–mesoporous zeolite omega synthesized by different methods. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8096–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, L.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, M. Metal-organic frameworks/carbon-based materials for environmental remediation: A state-of-the-art mini-review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cai, W.; Liu, L. Hydrothermal carbonization synthesis of Al-pillared montmorillonite@carbon composites as high performing toluene adsorbents. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, H.; Tan, X.; Lv, A. Adsorption performance of hydrophobically modified silica gel for the vapors of n-hexane and water. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, H.-J.; Pan, L.-L.; Zhang, C.-L.; Liu, X.-K. Reversely swellable porphyrin-linked microporous polyimide networks with super-adsorption for volatile organic compounds. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart, J.; Otero, M. Dye adsorption by sewage sludge-based activated carbons in batch and fixed-bed systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Inorg, O. Microporous activated carbons from a bituminous coal. Fuel 1996, 75, 966–970. [Google Scholar]
- Illa, M.J. Activated Carbons from Spanish Coals. 2. Chemical Activation. Energy Fuels 1996, 10, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Karaca, S.; Gürses, A.; Bayrak, R. Effect of some pre-treatments on the adsorption of methylene blue by Balkaya lignite. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, A.; Shahzad, M.; Kashif, S.; Muhammad, M.; Rabia, A.; Saba, A. Comparative study of adsorptive removal of congo red and brilliant green dyes from water using peanut shell. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2012, 11, 828–832. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Kumar, R. Adsorptive removal of congo red dye from aqueous solution using bael shell carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T.K. Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent: Equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnav, V.; Chandra, S.; Daga, K. Adsorption Studies of Zn (II) Ions from wastewater using Calotropis procera as an adsorbent. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2012, 1, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Kannadasan, T.; Velmurugan, S.; Muthu, S.; Vinoth Kumar, P. Biosorption of Chromium (VI) from Industrial Effluent using Neem Leaf Adsorbent. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2013, 3, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, E.; Jimoh, A.; Odigure, J.O. Heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater by activated carbon prepared from coconut shell Heavy Metals Removal from Industrial Wastewater by Activated Carbon Prepared from Coconut Shell. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2013, 2231, 606X. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.; Kathane, P. Superparamagnetic PVA-Alginate Microspheres as Adsorbent for Cu2+ ions Removal from Aqueous Systems. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 2, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, G.; Khan, J.; Singh, N.K. Application and efficacy of low-cost adsorbents for metal removal from contaminated water: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 2958–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichi, T.; Takagi, K. Clay minerals as photochemical reaction fields. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2000, 1, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, M.; Abak, H.; Alkan, M. Adsorption of methylene blue onto hazelnut shell: Kinetics, mechanism and activation parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysztafkiewicz, A.; Binkowski, S.; Jesionowski, T. Adsorption of dyes on a silica surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 199, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolard, C.D.; Strong, P.J.; Erasmus, C.R. Evaluation of the use of modified coal ash as a potential sorbent for organic waste streams. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.N.; Ram, R.N. Removal of basic dye from waste-water using silica as adsorbent. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 77, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kirnaji, N.P.; Bagewadi, C.S. Decohering Environment And Coupled Quantum States And Internal Resonance In Coupled Spin Systems And The Conflict Between Quantum Gate Operation And Decoupling A Cormorant-Barnacle Model. Adv. Phys. Theor. Appl. 2002, 6, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, O.; Armagan, B.; Turan, M.; Çelik, M.S. Comparison of the adsorption characteristics of azo-reactive dyes on mezoporous minerals. Dye. Pigment. 2004, 62, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzaferri, G.; Brühwiler, D.; Megelski, S.; Pfenniger, M.; Pauchard, M.; Hennessy, B.; Maas, H.; Devaux, A.; Graf, U. Playing with dye molecules at the inner and outer surface of zeolite L. Solid State Sci. 2000, 2, 421–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, A.; Valiyaveettil, S. Chemical transformation of soya waste into stable adsorbent for enhanced removal of methylene blue and neutral red from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Fatima, B.; Tara, N.; Rathi, G.; Chaudhry, S.A. Recent advances in remediation of synthetic dyes from wastewaters using sustainable and low-cost adsorbents. In The Impact and Prospects of Green Chemistry for Textile Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 471–507. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, E.J.R.; Corso, C.R. Decolorization and removal of toxicity of textile azo dyes using fungal biomass pelletized. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasar, A.; Mashkoor, F. Application of polyaniline-based adsorbents for dye removal from water and wastewater—a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5333–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni Law, X.; Cheah, W.Y.; Chew, K.W.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Park, Y.-K.; Ho, S.-H.; Show, P.L. Microalgal-based biochar in wastewater remediation: Its synthesis, characterization and applications. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, V.; Saravanan, K.; Sivarajasekar, N.; Suriyanarayanan, N. Bioremediation of dye bearing effluents using microbial biomass. Ecol. Environ. Conserv. 2016, 22, S423–S434. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, U.; Manna, S.; Sengupta, S.; Das, P.; Datta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Bhowal, A. Dye Removal Using Microbial Biosorbents. In Green Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 253–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, C.I.; Lloyd, J.R.; Guthrie, J.T. The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: A review. Dye. Pigment. 2003, 58, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvajith, M.; Reddy, G.K.K.; Nancharaiah, Y.V. Textile dye biodecolourization and ammonium removal over nitrite in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Nagpal, G.; Agrawal, S. Rachna Water purification by using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 187–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Reng, X.; Zhou, J.; Qin, W. Dye-decolorization of a newly isolated strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens W36. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jin, M.R.; Chung, C.H.; Yun, Y.S.; Jahng, K.Y.; Yu, K.Y. Biosorption of cationic basic dye and cadmium by the novel biosorbent Bacillus catenulatus JB-022 strain. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kousha, M.; Tavakoli, S.; Daneshvar, E.; Vazirzadeh, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Central composite design optimization of Acid Blue 25 dye biosorption using shrimp shell biomass. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 207, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upendar, G.; Dutta, S.; Chakraborty, J.; Bhattacharyya, P. Removal of methylene blue dye using immobilized bacillus subtilis in batch & column reactor. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 3467–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.B.; Ebrahim, S.E. Removal of methylene blue and congo red dyes by pretreated fungus biomass-equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2020, 66, 84–100. [Google Scholar]
- Argumedo-Delira, R.; Gómez-Martínez, M.J.; Uribe-Kaffure, R. Trichoderma biomass as an alternative for removal of congo red and malachite green industrial dyes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Azin, E.; Kamyabi, A.; Moghimi, H. Biosorption performance and cell surface properties of a fungal-based sorbent in azo dye removal coupled with textile wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, Ü.D. Treatment of dyeing wastewater including reactive dyes (Reactive Red RB, Reactive Black B, Remazol Blue) and Methylene Blue by fungal biomass. Water SA 2013, 39, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; et al. Utilizations of agricultural waste as adsorbent for the removal of contaminants: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, R.; Kothari, R.; Singh, H.M.; Ahmad, S.; Ashokkumar, V.; Tyagi, V. Production of algal biomass for its biochemical profile using slaughterhouse wastewater for treatment under axenic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essekri, A.; Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Laabd, M.; Ajmal, Z.; El Ouardi, M.; Addi, A.A.; Albourine, A. Novel citric acid-functionalized brown algae with a high removal efficiency of crystal violet dye from colored wastewaters: Insights into equilibrium, adsorption mechanism, and reusability. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2021, 23, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, R.; Baldikova, E.; Pospiskova, K.; Maderova, Z.; Safarikova, M.; Safarik, I. Magnetically modified Sargassum horneri biomass as an adsorbent for organic dye removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.K.; Raut, S.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Raut, S. Fungal decolouration and degradation of azo dyes: A review. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2016, 30, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Datta, S.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Sharma, K.; Samuel, J.; Singh, J. Current advancement and future prospect of biosorbents for bioremediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 135895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najar, J.A.; Lutfee, T.; Alwan, N.F. The action of yeast as an adsorbent in wastewater treatment: A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Scientific Conference on Environment and Sustainable Development, Baghdad, Iraq, 1–2 June 2021; Volume 779, p. 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscasso, F.; Bezus, B.; Garmendia, G.; Vero, S.; Curutchet, G.; Cavello, I.; Cavalitto, S. Debaryomyces hansenii F39A as biosorbent for textile dye removal. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2021, 53, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semião, M.A.; Haminiuk, C.W.I.; Maciel, G.M. Residual diatomaceous earth as a potential and cost effective biosorbent of the azo textile dye Reactive Blue 160. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-H.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Kao, T.-H. Removal Potential of Basic Dyes and Lead from Water by Brewer’s Yeast Biomass. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2019, 77, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. A review on agro-industrial waste (AIW) derived adsorbents for water and wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, F.; Kepekci, R.A. Bioremoval of Malachite green from water sample by forestry waste mixture as potential biosorbent. Microchem. J. 2017, 132, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhlifi, F.; Chraibi, S.; Alami, M. Evaluation of the adsorption kinetics and equilibrium. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 3, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Aziz, N. Adsorption of direct dye on palm ash: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemioǧlu, B. Adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solution onto calcium-rich fly ash. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 274, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, K.; Sahu, J.N.; Meikap, B.C.; Biswas, M.N. Removal of methylene blue from wastewater using fly ash as an adsorbent by hydrocyclone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, P.; Datta, S. Assessment on thermodynamics and kinetics parameters on reduction of methylene blue dye using flyash. Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 12, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.C.R.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Waste metal hydroxide sludge as adsorbent for a reactive dye. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Boyjoo, Y.; Choueib, A.; Zhu, Z.H. Removal of dyes from aqueous solution using fly ash and red mud. Water Res. 2005, 39, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tor, A.; Cengeloglu, Y. Removal of congo red from aqueous solution by adsorption onto acid activated red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I.; Saini, V.K. Removal of chlorophenols from wastewater using red mud: An aluminum industry waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4012–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabbas, K.; Zabat, N.; Hocini, I. Study of the chemical pretreatment of a nonconventional low-cost biosorbent (Callitriche obtusangula) for removing an anionic dye from aqueous solution. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2021, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S.K.U.S.; Charaya, M.U. Biosorption: The Removal of Toxic Dyes From Industrial Effluent Using Phytobiomass- a Review. Plant Arch. 2021, 21, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccin, J.S.; Cadaval, T.R.S.A.; De Pinto, L.A.A.; Dotto, G.L. Adsorption isotherms in liquid phase: Experimental, modeling, and interpretations. In Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., Mendoza-Castillo, D., Reynel, Á., Vila, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9783319581361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Shen, C.; Li, Y.N.; Ying, Z.; Duan, Y. Kinetics and Mechanism Study of Mercury Adsorption by Activated Carbon in Wet Oxy-Fuel Conditions. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, L.; Tian, Z.; Huang, D.; Xu, H. A smart reaction-based fluorescence probe for ratio detection of hydrazine and its application in living cells. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Shitu, A.; Ibrahim, A. Removal of methylene blue using low cost adsorbent: A review. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2014, 4, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Oyelude, E.O.; Appiah-takyi, F. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using alkali-modified malted sorghum mash. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2012, 36, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.S.U.; Kim, I.; Han, J.-I. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by sugar extracted spent rice biomass. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, M.; Sharma, A.K.; Srivastava, J.K.; Yadav, J.S. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous solution using water hyacinth root powder as a low cost adsorbent. Int. J. Chem. Sci. Appl. 2012, 3, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Dhedan, S.K. Equilibrium isotherms and kinetics modeling of methylene blue adsorption on agricultural wastes-based activated carbons. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 2012, 317, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Dynamic adsorption behavior of methylene blue onto oil palm shell granular activated carbon prepared by microwave heating. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, G.; Qiao, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, L. Methylene blue adsorption onto swede rape straw (Brassica napus L.) modified by tartaric acid: Equilibrium, kinetic and adsorption mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Ma, D.; Han, R. Characterization of bio-char from pyrolysis of wheat straw and its evaluation on methylene blue adsorption. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 46, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aoh, H.A.; Yahya, R.; Maah, M.J.; Bin Abas, M.R. Adsorption of methylene blue on activated carbon fiber prepared from coconut husk: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 6720–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishni, R.; Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B. Adsorption of methylene blue onto papaya leaves: Comparison of linear and nonlinear isotherm analysis. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 6712–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumi, L.B.; Hamdi, L.; Salem, Z.; Allia, K. Batch adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by untreated Alfa grass. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 53, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Vashi, R.T. A Comparison Study of Removal of Methylene Blue Dye by Adsorption on Neem Leaf Powder (Nlp) and Activated Nlp. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2012, 21, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaie, M.; Ghasemi, N.; Moradi, B.; Rahimi, M. Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater by Adsorption onto ZnCl2 Activated Corn Husk Carbon Equilibrium Studies. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 383985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kini Srinivas, M.; Saidutta, M.B.; Murty, V.R.C.; Kadoli Sandip, V. Adsorption of basic Dye from Aqueous Solution using HCl Treated Saw Dust (Lagerstroemia microcarpa): Kinetic, Modeling of Equilibrium, thermodynamic. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 2, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmipathy, R.; Sarada, N. Adsorptive removal of basic cationic dyes from aqueous solution by chemically protonated watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) rind biomass. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 6175–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, E.-C.; Ong, S.-T.; Hung, Y.-T.; Ha, S.-T. Removal of basic dyes from aqueous solution using sugarcane bagasse: Optimization by Plackett—Burman and Response Surface Methodology. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 7109–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, L.; Almeida, C.A.P.; Naidek, N.; Viante, M.F.; Lopes, M.C.; Debacher, N.A. Adsorption characteristics of montmorillonite clay modi fi ed with iron oxide with respect to methylene blue in aqueous media. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, M.; Javanbakht, V.; Esmaili, J. Synthesis of zeolite/nickel ferrite/sodium alginate bionanocomposite via a co-precipitation technique for efficient removal of water-soluble methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, M.; Wang, C.; Ao, Y.; Hou, J.; Qian, J. Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption of methylene blue by a magnetic graphene-carbon nanotube composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamadi, C.; Mawere, E. High adsorption of dyes by water hyacinth fixed on alginate. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 12, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuda, O.S.; Olayiwola, A.O.; Alade, A.O.; Farombi, A.G.; Adebisi, S.A. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution using steam-activated carbon produced from Lantana camara stem. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 5, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, J.; He, B.; Zhang, F.; Li, H. Peach gum for efficient removal of methylene blue and methyl violet dyes from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Sharma, G.C.; Chattopadhyaya, M.; Sharma, Y.C. Kinetic and equilibrium modeling for the adsorptive removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions on of activated fly ash (AFSH). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, N.M.; Fo, Y.T.; Al-Salim, H.S.; Sahu, J.N.; Abdullah, E.C.; Nizamuddin, S.; Jayakumar, N.S.; Ganesan, P. Removal of Methylene Blue and Orange-G from Waste Water Using Magnetic Biochar. Int. J. Nanosci. 2015, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Miao, M.; Cheng, B.; Zhu, S. Novel synthesis of a versatile magnetic adsorbent derived from corncob for dye removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H. Magnetized bentonite by Fe3O4 nanoparticles treated as adsorbent for methylene blue removal from aqueous solution: Synthesis, characterization, mechanism, kinetics and regeneration. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, H.; Peng, Y.; Luo, J. Chitosan/organic rectorite composite for the magnetic uptake of methylene blue and methyl orange. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ding, Z.; Cai, M.; Jian, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis and high-efficiency methylene blue adsorption of magnetic PAA/MnFe2O4 nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, B.; Jing, Z.; Wang, H. Preparation and adsorption property of xylan/poly (acrylic acid) magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel adsorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 118, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Wu, R.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, F.; Yang, H.; Ming, Z.; Yang, S. Magnetic graphene sponge for the removal of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Guo, X.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Yan, L.; Yan, T.; Du, B. Removal of mercury and methylene blue from aqueous solution by xanthate functionalized magnetic graphene oxide: Sorption kinetic and uptake mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Gao, L.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Mechanism of Pb(ii) and methylene blue adsorption onto magnetic carbonate hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 9759–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.; Eu, N.C.; Ibrahim, S.; Kim, H.; Yoon, Y.; Jang, M. Recyclable magnetite-loaded palm shell-waste based activated carbon for the effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qiao, N.; Hu, M.; Ma, H. Adsorption of methylene blue onto Fe 3 O 4/activated montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 115, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A. Preparation, characterization and application on dye adsorption of a well-de fi ned two-dimensional superparamagnetic clay/polyaniline/Fe3O4 nanocomposite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132–133, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Bao, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Magnetic Responsive Metal-Organic Frameworks Nanosphere with Core-Shell Structure for Highly Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 8693189123. [Google Scholar]
- Online, V.A.; Deng, J.; Zhou, X.; Bai, R. Removal of mercury (II) and methylene blue from a wastewater environment with magnetic graphene oxide: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and mechanism. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 82523–82536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Huang, Z. Synthesis of citric acid functionalized magnetic graphene oxide coated corn straw for methylene blue adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, F.; Duan, H.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C. The preparation of novel adsorbent materials with efficient adsorption performance for both chromium and methylene blue. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıntıg, E.; Altundag, H.; Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A. Effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using magnetic loaded activated carbon as novel adsorbent. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 122, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzerr, S.; Darwish, M.; Mahvi, A.H. Simultaneous removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic reactive red 198 dyes using magnetic activated carbon nanoparticles: Equilibrium, and kinetics analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 2017, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Zhan, Y.; Long, Z.; Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Long, Z.; Zeng, G.; He, Y. Core @ double-shell structured magnetic halloysite nanotube nano-hybrid as efficient recyclable adsorbent for methylene blue removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, G.R.; Soleymani, M.; Sabzi, M.; Azimi, H.; Atlasi, Z. Novel magnetic polyvinyl alcohol/laponite RD nanocomposite hydrogels for efficient removal of methylene blue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2617–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Devi, A.; Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Sarma, A. Developing a biosorbent from Aegle Marmelos leaves for removal of methylene blue from water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 14, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Kadiyala, V.; Palanisami, T.; Yong, B.L.; Ravi, N.; Mallavarapu, M. Quercus robur acorn peel as a novel coagulating adsorbent for cationic dye removal from aquatic ecosystems. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 101, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingi, F.M.; Mbuvi, H.M.; Ng’ang’a, M.M.; Mwangi, H. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Methylene blue by Geopolymers Derived from Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Methylene Blue by Geopolymers Derived from Common Clay and Rice Husk. Phys. Chem. 2017, 7, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meili, L.; Da Silva, T.S.; Henrique, D.C.; Soletti, J.I.; de Carvalho, S.H.V.; Fonseca, E.J.D.S.; de Almeida, A.R.F.; Dotto, G.L. Ouricuri (Syagrus coronata) fiber: A novel biosorbent to remove methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirak, M.; Abdollahiyan, A.; Eftekhari-Sis, B.; Saraei, M. Carboxymethyl cellulose coated Fe3O4@SiO2 core—Shell magnetic nanoparticles for methylene blue removal: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Cellulose 2017, 25, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, H.; Beyki, M.H.; Kaveh, R.; Fazli, Y. Rapid biosorption of methylene blue by in situ cellulose-grafted poly 4-hydroxybenzoic acid magnetic nanohybrid: Multivariate optimization and isotherm study. Polym. Bull. 2017, 75, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Humelnicu, A.C.; Samoila, P.; Pascariu, P.; Harabagiu, V. Optimized formulation of NiFe2O4@Ca-alginate composite as a selective and magnetic adsorbent for cationic dyes: Experimental and modeling study. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 125, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, D.; Queiros Campos, J.; Checa-Fernandez, B.L.; Marins, J.A.; Lomenech, C.; Hurel, C.; Godeau, G.D.; Raboisson-Michel, M.; Verger-Dubois, G.; Obeid, L.; et al. Adsorption of Organic Dyes on Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Part I: Mechanisms and Adsorption-Induced Nanoparticle Agglomeration. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 19086–19098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooresmaeil, M.; Mansoori, Y.; Mirzaeinejad, M.; Khodayari, A.L.I. Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue by Novel Magnetic Hydrogel Nanocomposites of Poly(acrylic acid). Adv. Polym. Technol. 2016, 37, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.H.; Alias, N.H.; Shahruddin, M.Z.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Him, N.R.N.; Lau, W.J. Adsorption kinetics of methylene blue dyes onto magnetic graphene oxide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2803–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meili, L.; Lins, P.; Costa, M.; Almeida, R.; Abud, A.K.; Soletti, J.; Dotto, G.L.; Tanabe, E.; Sellaoui, L.; de Carvalho, S.H.V.; et al. Adsorption of methylene blue on agroindustrial wastes: Experimental investigation and phenomenological modelling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 141, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, H.; Foroutan, R. Adsorptive Behavior of Methylene Blue onto Sawdust of Sour Lemon, Date Palm, and Eucalyptus as Agricultural Wastes. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 40, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Fan, M.; Zhao, W. Synthesis of activated carbon from biowaste of fir bark for methylene blue removal. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashid, J.; Tehreem, F.; Rehman, A.; Kumar, R. Synthesis using natural functionalization of activated carbon from pumpkin peels for decolourization of aqueous methylene blue. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, L.; Thapa, M.; Shrestha, R.; Maji, S.; Pradhananga, R.; Ariga, K. Rice Husk-Derived High Surface Area Nanoporous Carbon Materials with Excellent Iodine and Methylene Blue Adsorption Properties. C J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gherbia, A.; Chergui, A.; Yeddou, A.R.; Selatnia Ammar, S.; Boubekeur, N. Removal of methylene blue using activated carbon prepared from date stones activated with NaOH. Glob. Nest J. 2019, 21, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Huang, P.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Yuan, T.; Sun, R. Compressive alginate sponge derived from seaweed biomass resources for methylene blue removal from wastewater. Polymers 2019, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakr, F.; Alahiane, S.; Sennaoui, A.; Dinne, M.; Bakas, I.; Assabbane, A. Removal of cationic dye (Methylene Blue) from aqueous solution by adsorption on two type of biomaterial of South Morocco. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, K.J.L.; de Souza dos Santos, G.E.; de Sá, Í.M.G.L.; de Carvalho, S.H.V.; Soletti, J.I.; Meili, L.; da Silva Duarte, J.L.; Bispo, M.D.; Dotto, G.L. Syagrus oleracea–activated carbon prepared by vacuum pyrolysis for methylene blue adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16470–16481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, A.P.; Kumar, V.; Singh, D.P. A combined effect of adsorption and reduction potential of biochar derived from Mentha plant waste on removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Alazba, A.A.; Amin, M.T. Synthesis, characterization, and application of date palm leaf waste-derived biochar to remove cadmium and hazardous cationic dyes from synthetic wastewater. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Pahi, S.; Sahu, J.K.; Sahu, U.K.; Patel, R.K. Kendu (Diospyros melanoxylon Roxb) fruit peel activated carbon—an efficient bioadsorbent for methylene blue dye: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22579–22592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, V.R.; Kanidarapu, N.R.; Vangalapati, M. Methylene blue adsorption by magnesium oxide nanoparticles immobilized with chitosan (CS-MgONP): Response surface methodology, isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2020, 39, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Novel approach for effective removal of methylene blue dye from water using fava bean peel waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago, D.; Chagas, R.; Ferreira, M.; Velizarov, S.; Coelhoso, I. A novel cellulose-based polymer for efficient removal of methylene blue. Membranes 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, I.; Abu Haija, M.; Kannan, P.; Banat, F. Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Water Using High-Performance Alginate-Based Beads. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabede, P.M.; Shooto, N.D.; Naidoo, E.B. Removal of methylene blue dye and lead ions from aqueous solution using activated carbon from black cumin seeds. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 33, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Saud Abdulhameed, A.; Wilson, L.D.; Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Rizwan Khan, M. High surface area and mesoporous activated carbon from KOH-activated dragon fruit peels for methylene blue dye adsorption: Optimization and mechanism study. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.U.; Le, H.S.; Hoang, H.Y.; Tran, V.A.; Doan, V.D.; Le, T.T.N.; Sirotkin, A.; Le, V.T. Natural core-shell structure activated carbon beads derived from Litsea glutinosa seeds for removal of methylene blue: Facile preparation, characterization, and adsorption properties. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 110481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, T.H.; Nguyen, V.T.; Dung, N.Q.; Chu, M.N.; Van Kiet, D.; Ngan, T.T.K.; Van Tan, L. Study on methylene blue adsorption of activated carbon made from Moringa oleifera leaf. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 38, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, A.S.; Firdaus Hum, N.N.M.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Jawad, A.H.; Wilson, L.D.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Alothman, Z.A. Statistical modeling and mechanistic pathway for methylene blue dye removal by high surface area and mesoporous grass-based activated carbon using K2CO3activator. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Feng, R.; Zou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhou, P. Efficient removal of methylene blue using the mesoporous activated carbon obtained from mangosteen peel wastes: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 315, 110904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yağmur, H.K.; Kaya, İ. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic ZnCl2-activated carbon produced from coconut shell for the adsorption of methylene blue. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1232, 130071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, T.; Shen, J.; Meng, Y.; Tong, S.; Guan, Q.; Xia, X. Core-shell structured magnetic carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel nanosorbents for effective adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Polymers 2021, 13, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misran, E.; Bani, O.; Situmeang, E.M.; Purba, A.S. Banana stem based activated carbon as a low-cost adsorbent for methylene blue removal: Isotherm, kinetics, and reusability. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 61, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamin, N.U.; Khan, A.S.; Nasrullah, A.; Iqbal, J.; Ullah, Z.; Din, I.U.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, S.Z. Activated carbon-alginate beads impregnated with surfactant as sustainable adsorbent for efficient removal of methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; Shoaib, A.G.M.; El Sikaily, A.; Mohamed, A.E.D.A.; Hassan, A.F. Evaluation of Cationic Methylene Blue Dye Removal by High Surface Area Mesoporous Activated Carbon Derived from Ulva lactuca. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.S.; Amini, M.H.M.; Danish, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R. Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Isotherms of Methylene Blue Adsorption Study onto Cassava Stem Activated Carbon. Water 2021, 13, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Qu, K.; Cheng, Y.; You, Y.; Huang, Z.; Umar, A.; Ibrahim, Y.S.A.; Algadi, H.; Castañeda, L.; Colorado, H.A.; et al. Corncob-derived Activated Carbon for Efficiently Adsorption Dye in Sewage. ES Food Agrofor. 2021, 4, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgariu, L.; Escudero, L.B.; Bello, O.S.; Iqbal, M.; Nisar, J.; Adegoke, K.A.; Alakhras, F.; Kornaros, M.; Anastopoulos, I. The utilization of leaf-based adsorbents for dyes removal: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 728–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praveen, S.; Gokulan, R.; Pushpa, T.B.; Jegan, J. Techno-economic feasibility of biochar as biosorbent for basic dye sequestration. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.S.; Adegoke, K.A.; Sarumi, O.O.; Lameed, O.S. Functionalized locust bean pod (Parkia biglobosa) activated carbon for Rhodamine B dye removal. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moosavi, S.; Lai, C.W.; Gan, S.; Zamiri, G.; Akbarzadeh Pivehzhani, O.; Johan, M.R. Application of efficient magnetic particles and activated carbon for dye removal from wastewater. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20684–20697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H. Review on solvent desorption study from exhausted adsorbent. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.D.; Das, S.; Kumar, R.; Doley, R.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Vermiremoval of methylene blue using Eisenia fetida: A potential strategy for bioremediation of synthetic dye-containing effluents. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Basak, B.B.; Ponnuchamy, M. Performance of activated carbon derived from Cymbopogon winterianus distillation waste for scavenging of aqueous toxic anionic dye Congo red: Comparison with commercial activated carbon. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1970–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiru, M.; Zango, Z.U.; Haruna, M.A. Cationic Dyes Removal Using Low-Cost Banana Peel Biosorbent. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 8, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Debeli, D.K.; Shan, G.; Pan, P. Selective adsorption and high recovery of La3+ using graphene oxide/poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide-maleic acid) cryogel. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, A.; Momeni, F.; Derakhshani, E. Efficiency of ultrasonic process in the regeneration of graphene nanoparticles saturated with humic acid. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 70, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Xu, G. Adsorption of potentially toxic elements in water by modified biochar: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudyal, H.; Ohto, K.; Kawakita, H.; Inoue, K. Recovery of fluoride from water through adsorption using orange-waste gel, followed by desorption using saturated lime water. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Mei, Y.; Chen, D.; He, S.; Luo, Y. Recycling Spent Cr Adsorbents as Catalyst for Eliminating Methylmercaptan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3669–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avinash, A.; Murugesan, A. Judicious Recycling of Biobased Adsorbents for Biodiesel Purification: A Critical Review. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, e13077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Halder, G. A Review on the Sorptive Elimination of Fluoride from Contaminated Wastewater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 6, ISBN 3432754078. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, J.; Goswamee, R.L. Use of carbon coated ceramic barriers for adsorptive removal of fluoride and permanent immobilization of the spent adsorbent barriers. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolinko, P.A.; Smirniotis, P.G.; Kozlov, D.V.; Vorontsov, A.V. Cr modified TiO2-loaded MCM-41 catalysts for UV-light driven photodegradation of diethyl sulfide and ethanol. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2012, 232, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Rao, F.; Changmei, S.; Rongjun, Q.; Ying, Z. Silica gel-based adsorbents prepared via homogeneous and heterogeneous routes: Adsorption properties and recycling as heterogeneous catalysts. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ying, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, J. Rapid and selective removal of Hg(II) ions and high catalytic performance of the spent adsorbent based on functionalized mesoporous silica/poly(m-aminothiophenol) nanocomposite. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Roy, S.K.; Talukdar, A.K. Effective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by diamino-functionalised mesoporous MCM-48 and selective oxidation of cyclohexene and ethylbenzene over the Cr containing spent adsorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4707–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.K.; Garg, R. A comprehensive review on removal of arsenic using activated carbon prepared from easily available waste materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13295–13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Kim, J.A.; Yun, Y.-S. Valorisation of post-sorption materials: Opportunities, strategies, and challenges. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 242, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbinnen, B.; Block, C.; Van Caneghem, J.; Vandecasteele, C. Recycling of spent adsorbents for oxyanions and heavy metal ions in the production of ceramics. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, A.; Ramrakhiani, L.; Mukherjee, D.; Mishra, U.; Halder, A.; Mandal, A.K.; Ghosh, S. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles for arsenic remediation in water and sludge utilization. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 795–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bădescu, I.S.; Bulgariu, D.; Ahmad, I.; Bulgariu, L. Valorisation possibilities of exhausted biosorbents loaded with metal ions—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, K.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, S.; Ikram, S. Synthesis, Characterization, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics of EDTA-Modified Chitosan-Carboxymethyl Cellulose as Cu (II) Ion Adsorbent. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 17425–17437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdallah, M.M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Walker, G.; Leahy, J.J.; Kwapinski, W. Batch and Continuous Systems for Zn, Cu, and Pb Metal Ions Adsorption on Spent Mushroom Compost Biochar. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7296–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Hussain, Q.; Akmal, M.; Riaz, M.; Hu, H.; Ijaz, S.S.; Iqbal, M.; Abro, S.; Mehmood, S.; Ahmad, M. Sugarcane bagasse-derived biochar reduces the cadmium and chromium bioavailability to mash bean and enhances the microbial activity in contaminated soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Z. Biochar as an adsorbent for inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus removal from water: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26297–26309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, R.E.; Luna, A.S.; Torres, A.R. Operating parameters for bio-oil production in biomass pyrolysis: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 129, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, T.; Strezov, V.; Evans, T.J. Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis: A review of product properties and effects of pyrolysis parameters. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1126–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.J.; Paul, N.A.; de Nys, R.; Roberts, D.A. Good for sewage treatment and good for agriculture: Algal based compost and biochar. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 200, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Cagnetta, G.; Wang, W.; Meng, P.; Liu, D.; Yu, G. Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelmanov, G.; Semiat, R. Iron (Fe+3) oxide/hydroxide nanoparticles-based agglomerates suspension as adsorbent for chromium (Cr+6) removal from water and recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Singh, P.K.; Samadder, S.R. Regeneration of adsorbents and recovery of heavy metals: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1461–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



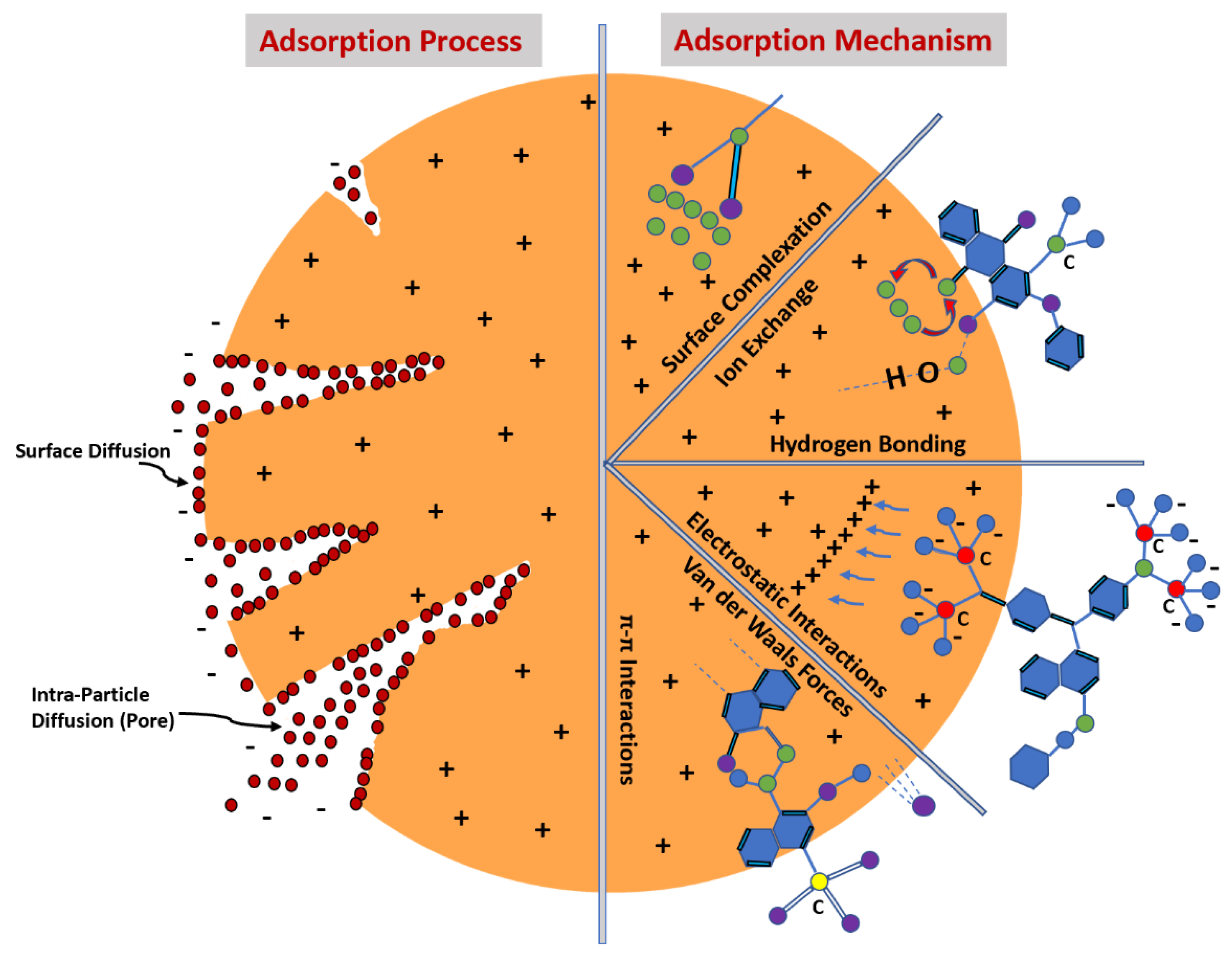



| No | Adsorbents | Surface Area (m2/g) | Diameter, ɸ (nm) | Qmax (mg/g) | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Activated charcoal | 4.445–2854 | 1.0–15.9 | 0.71–1030 | [35,36,37,38,39,40,41] |
| 2 | Biochar | 2.05–2054.49 | 2.29–20.57 | 2.06–1282.6 | [42,43,44] |
| 3 | Modified activated carbon and modified biochar | 4.02–1229 | 1.038–7.477 | 9.72–986.8 | [45,46,47] |
| 4 | Carbon graphics and modifications | 32–295.56 | 2–50 | 41.67–847 | [45,47,48,49] |
| 5 | Porous Carbon | 21–3496 | 0.74–5.45 | 8.96–1791 | [50,51,52,53] |
| 6 | Carbon Nanotube | 140–558.7 | 2.19–25 | 33.4–1189 | [49,54,55,56,57,58,59] |
| Technologies | Benefits | Drawbacks | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced oxidation process | At normal atmospheric pressure and temperature, the dyes are degraded efficiently, and organic contaminants are transformed into carbon dioxide. | Significant operating and maintenance expenses; inflexibility | [69,73] |
| Chemical precipitation | Simple; low-cost; can manage high pollutant loads; is easy to use; has an integrated physio-chemical process; and results in a significant reduction in COD. | Contains a huge amount of chemicals and generates a lot of sludge | [82] |
| Ion exchange | Absence of sludge; requires less time; water of superior purity is generated; and an effective decolorization procedure is used. No adsorbent loss during regeneration | pH has a significant effect on performance; not suitable for all colors; costly in terms of recharging and the formation of significant amounts of sludge | [73,81] |
| Electrochemical | Chemicals are either unnecessary or are limited; the process is quick; suited to both insoluble and soluble dyes, with a lower COD. | High operating expenses; rising electricity prices; sludge formation; contamination from chlorinated organics and heavy metals as a result of indirect oxidation | [65,69] |
| Oxidation | Dyes are completely degraded, and the reaction time is minimal. | pH maintenance; catalyst required for optimal treatment; high cost | [69,83] |
| Ozonation | Disinfection that is quick and effective, as well as equipment installation that is simple; no volume growth in the gas phase | A relatively brief half-life; costly process; hazardous by-products and intermediates in manufacturing; strict pH control of effluent | [81,84] |
| Hydrogen peroxide | Oxidation causes water-insoluble colors to decolorate; reduction in COD; and non-toxic by-products of manufacturing | Increased reaction time; increased need for space; more costly | [65] |
| Fenton reagents | Removal of both soluble and insoluble dyes with effective decolorization | Sludge production | [63] |
| Sodium hypochloride | Cleavage of azo bonds develops and accelerates | Production of aromatic amines | [63] |
| Electrochemical destruction | The breakdown products are not dangerous. | Electricity is costly | [63] |
| Coagulation–Flocculation | A wide range of physiochemical approaches used for color elimination; the coagulating agent entirely removes dyes from remediated wastewater; it is effective and simple to operate, and as a result decolorization occurs completely. | Recycling high-priced chemicals is impractical; not suited for very water-soluble colors; generates colorful coagulated solid waste; produces hazardous sludge; raises TDS in treated wastewater; is not ecologically sustainable. | [65,82] |
| Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration | Effective with all types of dyes | Extreme operational pressure, significant energy consumption, high price of membrane, limited lifespan, and concentrated production of sludge | [83,85,86] |
| Reverse osmosis | The most efficient decolorizing and desalting technology, with maximal salt removal, and high-quality water | Extreme pressure and operating costs, as well as membrane clogging, are involved on a frequent basis. | [83,86] |
| Biological techniques (aerobic and anaerobic) | Low-cost, environmentally friendly, and non-dangerous product; is fully mineralized. | Dye biodegradability is lower, extremely dependent on reaction circumstances, design and operation inflexibility, requires a vast land area, and the requires a longer period for decolorization | [69] |
| Adsorption technique | Highly efficient and easy; simple and adaptable to a wide variety of pollutants; excellent capacity to remove a wide variety of impurities; economical; adsorbents can be made from wastes; potential regeneration of the adsorbent | Adsorbents’ compositions influence their efficacy; their chemical modification is necessary to boost their adsorption capacity; certain adsorbents are highly expensive. | [83,86] |
| Classifications | Adsorbents | Formation | Benefits | Drawbacks | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition of carbon | Activated carbon | Carbonized and activated (e.g., lignite, coal, peat, wood) | Large and specific chemical functional groups; large surface area; large pore volume | Hygroscopicity; pore resistance; flammability; incomplete desorption; high permeability | [104] |
| Biochar | Formed under moderate pyrolysis conditions in an inert environment | Abundant resources; highly efficient; affordable; low energy usage | Plug hole; flammability; hygroscopicity; gas release | [105] | |
| Carbon fiber, activated | A microfilament fiber | Hydrophobic and efficient | Expensive | [106] | |
| Graphene | 2D graphene is made up of carbon sheets hexagonal that portion three extra carbon atoms’ sp2 hybridized orbitals | Superior electrical conductivity; a large amount of physical specific surface area; great mechanical strength | Synthesis is difficult and dangerous | [107] | |
| Carbon nanotubes | The cylindrical structure is composed of carbon atoms that have undergone sp2 hybridization. | Strong thermal stability; good electrical conductivity; wide surface area; inherent hydrophobicity | Serious aggregation | [108] | |
| Materials containing oxygen | Zeolite | Zeolite is composed of an endless (3D) arrangement of TO4 tetrahedra in a crystalline aluminosilicate frame (T is Al or Si) | High adsorption capacity; huge surface area; tunable porosity; incombustibility; hydrothermal and chemical stability; good hydrophobicity | The synthetic technique is intricate, lengthy, and costly | [109] |
| Frameworks of metal organic | Metal ions or coordination clusters containing organic ligands are created in a single-, two-, or three-dimensional manners. | Extremely large surface area; outstanding thermal stability; oxidizable porous structure; simplicity of functionalization | A large vacuum space; a weak dispersion force; an unsuitable environment for coordination; an inadequate number of active metal catalyst areas; expensive preparation costs | [110] | |
| Clay | Clay is a layered aluminosilicate mineral that contains water and is found in rocks and soils | Strong thermal stability; excessive heat resistance; great surface area; a special micro-porous medium; inexpensive cost | Because of its underdeveloped pore structure, clay’s adsorption affinity for carbon-based gases is restricted | [111] | |
| Silica gel | Silica gel is a three-dimensional tetrahedral inorganic substance with silicol groups on its surface | Low density; substantial porous surface area; multiple functional groupings; excellent mechanical, thermal, and chemical stabilities | Hygroscopicity | [112] | |
| Organic polymers | Macroporous and hyper cross-linked polymers | Other known porous materials have a higher density than organic polymers made of light nonmetallic components such as C, H, O, N, and B | Large specific surface area; excellent porosity; low weight; excellent thermal stability, repeatability, and hydrophobicity | Complex synthesis | [113] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamad, H.N.; Idrus, S. Recent Developments in the Application of Bio-Waste-Derived Adsorbents for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040783
Hamad HN, Idrus S. Recent Developments in the Application of Bio-Waste-Derived Adsorbents for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater: A Review. Polymers. 2022; 14(4):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040783
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamad, Hamad Noori, and Syazwani Idrus. 2022. "Recent Developments in the Application of Bio-Waste-Derived Adsorbents for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater: A Review" Polymers 14, no. 4: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040783
APA StyleHamad, H. N., & Idrus, S. (2022). Recent Developments in the Application of Bio-Waste-Derived Adsorbents for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater: A Review. Polymers, 14(4), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040783