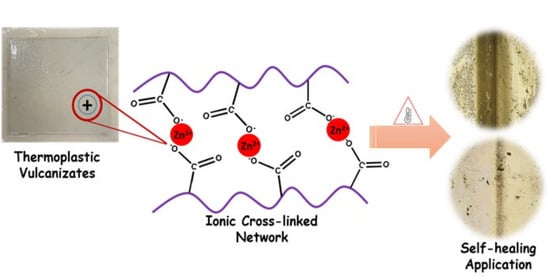
Design of Self-Healing EPDM/Ionomer Thermoplastic Vulcanizates by Ionic Cross-Links for Automotive Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Thermoplastic Vulcanizates
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of Thermoplastic Vulcanizates for Self-Healing Application
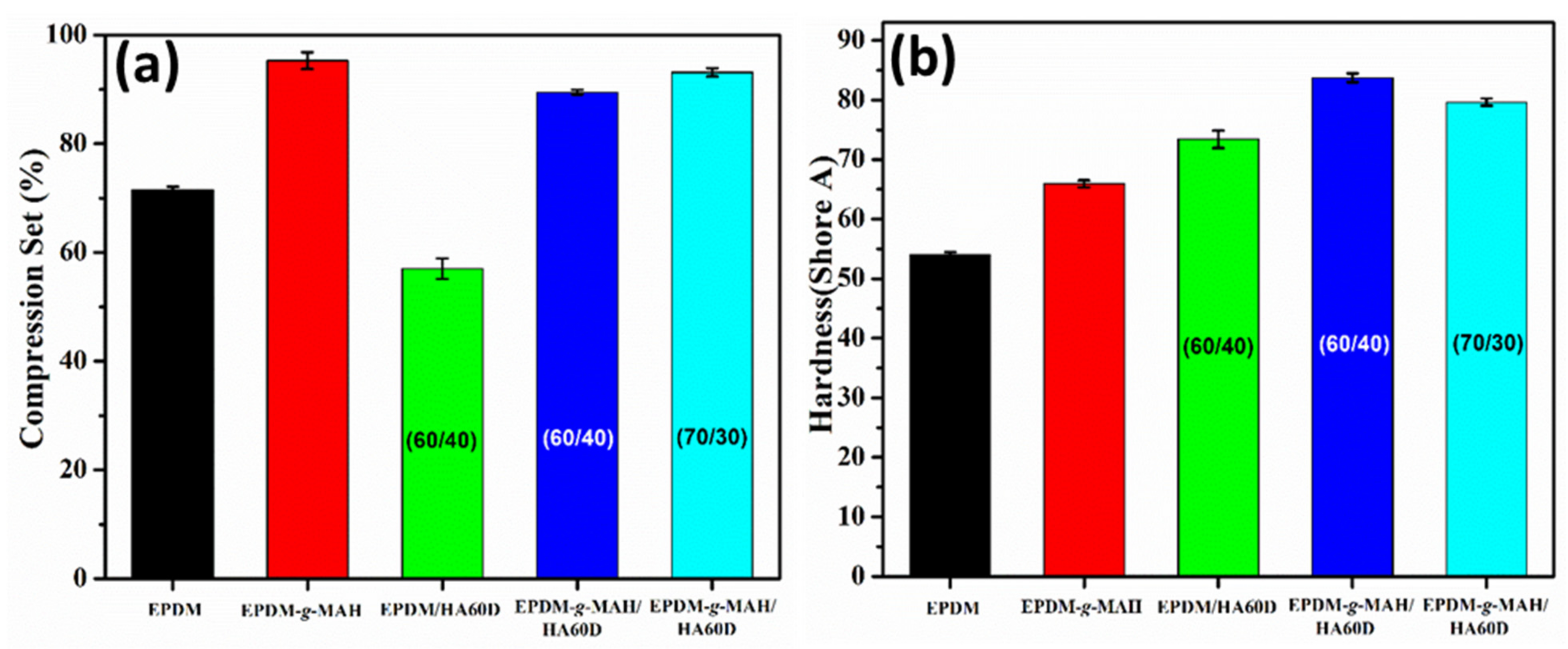
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Thermal Analysis
3.4. SEM Analysis
3.5. Self-Healing Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sazali, N.; Mohamed, M.A.; Hir, Z.A.M. Self-Healable Tires: Self-Healing Smart Materials and Allied Applications; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 99–122. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.P.; Qian, H.J.; Lu, Z.Y.; Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q. Crack healing and reclaiming of vulcanized rubber by triggering the rearrangement of inherent sulfur cross-linked networks. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4315–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, P.; Tournilhac, F.; Soulié-Ziakovic, C.; Leibler, L. Self-healing and thermoreversible rubber from supramolecular assembly. Nature 2008, 451, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Pongwisuthiruchte, A.; Debnath, S.C.; Potiyaraj, P. Application of cellulose as green filler for the development of sustainable rubber technology. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100140–100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, B.; Jia, D. Recyclable and self-healing rubber composites based on thermoreversible dynamic covalent bonding. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 129, 105709–105716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo-Morera, J.; Santana, M.H.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A. Giving a Second Opportunity to Tire Waste: An Alternative Path for the Development of Sustainable Self-Healing Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Compounds Overcoming the Magic Triangle of Tires. Polymers 2019, 11, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, A.; Sallat, A.; Böhme, F.; Suckow, M.; Basu, D.; Wießner, S.; Stöckelhuber, K.W.; Voit, B.; Heinrich, G. Ionic Modification Turns Commercial Rubber into a Self-Healing Material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20623–20630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Cao, L.; Yuan, D.; Chen, Y. Design of Novel Self-Healing Thermoplastic Vulcanizates Utilizing Thermal/Magnetic/Light-Triggered Shape Memory Effects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 40996–41002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, C.N.; Kloxin, C.J. Covalent Adaptable Networks: Reversible Bond Structures Incorporated in Polymer Networks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4272–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stukalin, E.B.; Cai, L.H.; Kumar, N.A.; Leibler, L.; Rubinstein, M. Self-Healing of Unentangled Polymer Networks with Reversible Bonds. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 7525–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.P.; Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q. Self-healing, Reshaping, and Recycling of Vulcanized Chloroprene Rubber: A Case Study of Multitask Cyclic Utilization of Cross-linked Polymer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cui, R.; Fu, L.; Lin, B. Recyclable and heat-healable epoxidized natural rubber/bentonite composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 167, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuana, Z.; Ye, L. Construction of sacrificial bonds and hybrid networks in EPDM rubber towards mechanical performance enhancement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasi, P.; Santana, M.H.; Carretero-González, J.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A. Thermo-reversible crosslinked natural rubber: A Diels-Alder route for reuse and self-healing properties in elastomers. Polymer 2019, 175, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ca, L.; Fan, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y. A robust and stretchable cross-linked rubber network with recyclable and self-healable capabilities based on dynamic covalent bonds. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 4922–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Bhowmick, A.K. Sustainable self-healing elastomers with thermoreversible network derived from biomass via emulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Nie, J.; Wu, W.; Fu, L.; Lin, B. Design of self-healable supramolecular hybrid network based on carboxylated styrene butadiene rubber and nano-chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgar, L.M.; Duin, M.V.; Broekhuis, A.A.; Picchioni, F. Use of Diels-Alder Chemistry for Thermoreversible Cross-Linking of Rubbers: The Next Step toward Recycling of Rubber Products? Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7096–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, R. Ionomer as Self-healing Polymers. In Self-Healing Materials: An Alternative Approach to 20 Centuries of Materials Science, 1st ed.; Van Der Zwaag, S., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Q.; Xiong, H.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Reinforcing self-healing and Re-processable ionomers with carbon black: An investigation on the network structure and molecular mobility. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 216, 109035–109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, B.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y. Zinc dimethacrylate induced in situ interfacial compatibilization turns EPDM/PP TPVs into a shape memory material. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4539–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Lin, B.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y. Design of Self-Healing Supramolecular Rubbers by Introducing Ionic Cross-Links into Natural Rubber via a Controlled Vulcanization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17728–17737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sahu, P.; Bhajiwala, H.; Mohanty, S.; Gupta, V.; Bhowmick, A.K. Synthesis, characterization and properties of self-healable ionomeric carboxylated styrene-butadiene polymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 14986–14999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, X.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Lin, B.; Liang, X. Design of “Zn2+ Salt-Bondings” Cross-Linked Carboxylated Styrene Butadiene Rubber with Reprocessing and Recycling Ability via Rearrangements of Ionic Cross-linkings. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6981–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.T.; Lee, K.H.; Sinha, T.K.; Oh, J.S. Comparison of ultrasonic-treated rice husk carbon with the conventional carbon black towards improved mechanical properties of their EPDM composites. Carbon Lett. 2021, 31, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, J.A.; Ahmad, S.H.; Ratnam, C.T.; Mahamood, M.A.; Yaakub, J.; Mohamad, N. Effects of EPDM-g-MAH compatibilizer and internal mixer processing parameters on the properties of NR/EPDM blends: An analysis using response surface methodology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42199–42214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Ingredients | EPDM/HA60D (60/40) Loading (phr) a | EPDM-g-MAH/HA60D (60/40) Loading (phr) a | EPDM-g-MAH/HA60D (70/30) Loading (phr) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 100 | ----- | ----- |
| EPDM-g-MAH | ----- | 100 | 100 |
| HA60D | 66.7 | 66.7 | 42.8 |
| Zinc oxide | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Stearic acid | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| MBTS b | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| TMTD c | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Sulfur | 1.5 | 1.5/2.0/3.0 | 1.5 |
| Sample (wt%) | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | Second | ||
| EPDM | −47 | 22 | |
| EPDM-g-MAH | −55 | 162 | |
| HA60D | 26 | 82 | |
| EPDM/HA60D (60/40) | −42 | 84 | |
| EPDM-g-MAH/HA60D (60/40) | −51 | 81 | 166 |
| EPDM-g-MAH/HA60D (70/30) | −51 | 82 | 164 |
| Sample (wt%) | Self-Healing Property (%) |
|---|---|
| EPDM-g-MAH/HA60D (60/40) | 87.4 |
| EPDM-g-MAH/HA60D (70/30) | 88.6 |
| EPDM/HA60D (60/40) | ---- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, W.S.; Sahu, P.; Park, S.M.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, N.I.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, J.S. Design of Self-Healing EPDM/Ionomer Thermoplastic Vulcanizates by Ionic Cross-Links for Automotive Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061156
Jin WS, Sahu P, Park SM, Jeon JH, Kim NI, Lee JH, Oh JS. Design of Self-Healing EPDM/Ionomer Thermoplastic Vulcanizates by Ionic Cross-Links for Automotive Application. Polymers. 2022; 14(6):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061156
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Woo Seok, Pranabesh Sahu, Sung Min Park, Jun Ha Jeon, Nam Il Kim, Jae Hyeon Lee, and Jeong Seok Oh. 2022. "Design of Self-Healing EPDM/Ionomer Thermoplastic Vulcanizates by Ionic Cross-Links for Automotive Application" Polymers 14, no. 6: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061156
APA StyleJin, W. S., Sahu, P., Park, S. M., Jeon, J. H., Kim, N. I., Lee, J. H., & Oh, J. S. (2022). Design of Self-Healing EPDM/Ionomer Thermoplastic Vulcanizates by Ionic Cross-Links for Automotive Application. Polymers, 14(6), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061156