Preparation, Properties and Water Dissolution Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide Mats Prepared by Solution Blow Spinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Materials
2.3. Characterization Methods
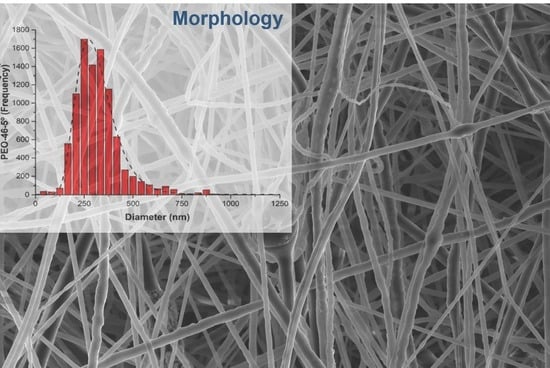
3. Results and Discussion
- (a)
- Image analysis. Permits obtaining the mean pore area, the number of pores and air area (Table 5). The results can be extrapolated to a 3D network of fibers assuming a homogeneous porosity throughout the sample.
- (b)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niazmand, R.; Razavizadeh, B.M. Active Polyethylene Films Incorporated with β-Cyclodextrin/Ferula Asafoetida Extract Inclusion Complexes: Sustained Release of Bioactive Agents. Polym. Test. 2021, 95, 107113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitoon, A.; Lim, L.T.; Scott-Dupree, C. Activated Release of Ethyl Formate Vapor from Its Precursor Encapsulated in Ethyl Cellulose/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Electrospun Nonwovens Intended for Active Packaging of Fresh Produce. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, N.; Ma, J. Water Redispersion and Cytotoxicity of Reducing End-Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals by Grafting Long-Chain Poly(Ethylene Oxide). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Fawal, G.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Mo, X.; Wang, H. Diethyldithiocarbamate/Silk Fibroin/Polyethylene Oxide Nanofibrous for Cancer Therapy: Fabrication, Characterization and in Vitro Evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldurini, S.; Abd El-Hady, B.M.; Shafaa, M.W.; Gad, A.A.M.; Tolba, E. A Multicompartment Vascular Implant of Electrospun Wintergreen Oil/ Polycaprolactone Fibers Coated with Poly(Ethylene Oxide). Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, O.M.; Iacob, A.T.; Mignon, A.; van Vlierberghe, S.; Baican, M.; Danu, M.; Ibănescu, C.; Simionescu, N.; Profire, L. Design, Preparation and In Vitro Characterization of Biomimetic and Bioactive Chitosan/Polyethylene Oxide Based Nanofibers as Wound Dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandehali, S.; Moghadassi, A.; Parvizian, F.; Hosseini, S.M.; Matsuura, T.; Joudaki, E. Advances in High Carbon Dioxide Separation Performance of Poly (Ethylene Oxide)-Based Membranes. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 46, 30–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojasiński, M.; Pilarek, M.; Ciach, T. Comparative Studies of Electrospinning and Solution Blow Spinning Processes for the Production of Nanofibrous Poly(L-Lactic Acid) Materials for Biomedical Engineering. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2014, 16, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Medeiros, E.S. Structural and Morphological Characterization of Micro and Nanofibers Produced by Electrospinning and Solution Blow Spinning: A Comparative Study. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 409572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Sheng, J. Study on Morphology of Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Mats. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Systematic Parameter Study for Ultra-Fine Fiber Fabrication via Electrospinning Process. Polymer 2005, 46, 6128–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiri, A.; Domínguez, J.E.; González-Benito, J. Morphology Optimization of Solution Blow Spun Polystyrene to Obtain Superhydrophobic Materials with High Ability of Oil Absorption. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution Blow Spinning: A New Method to Produce Micro- and Nanofibers from Polymer Solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kopperstad, P.; West, M.; Hedin, N.; Fong, H. Generation of Polymer Ultrafine Fibers through Solution (Air-) Blowing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Moraes, E.A.; Costa, R.G.F.; Afonso, A.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Medeiros, E.S. Nano and Submicrometric Fibers of Poly(D, L -Lactide) Obtained by Solution Blow Spinning: Process and Solution Variables. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 3396–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, K.; Gomez, C.; Zambrano, S.; Ramirez, M.; Hoyos, E.; Vasquez, H.; Lozan, K. Electrospinning to ForcespinningTM. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Zuníga, A.E.; Villela-Castrejón, J. Engineering and evaluation of forcespun functionalized carbon nano-onions reinforced poly (ε-caprolactone) composite nanofibers for pH-responsive drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Systematic Investigation on Parameters of Solution Blown Micro/Nanofibers Using Response Surface Methodology Based on Box-Behnken Design. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daristotle, J.L.; Behrens, A.M.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. A Review of the Fundamental Principles and Applications of Solution Blow Spinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34951–34963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutak, W.; Gelven, G.; Markle, C.; Palmer, X.L. Rapid Polymer Fiber Airbrushing: Impact of a Device Design on the Fiber Fabrication and Matrix Quality. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Z. Preparation of Solution Blown Polyamic Acid Nanofibers and Their Imidization into Polyimide Nanofiber Mats. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Parize, D.D.; Foschini, M.M.; de Oliveira, J.E.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Glenn, G.M.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution Blow Spinning: Parameters Optimization and Effects on the Properties of Nanofibers from Poly(Lactic Acid)/Dimethyl Carbonate Solutions. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4627–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaskova, M.; Peer, P.; Cermak, R.; Ponizil, P. Effect of Thermal Treatment on Crystallinity of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Electrospun Fibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Manuel, R.; Delgadillo, V.; Gonzalez-Ortiz, A. Engineering of carbon nano-onion bioconjugates for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Manuel, R.; Delgadillo, V. Design, fabrication and drug release potential of dual stimuli-responsive composite hydrogel nanoparticle interfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Deng, L.; Chen, J. Applications of poly(ethylene oxide) in controlled release tablet systems: A review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Moraes, E.A.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Glenn, G.M.; Medeiros, E.S. Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid) and Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Solvent Polymer Mixtures and Nanofibers Made by Solution Blow Spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 3672–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Benito, J.; Teno, J.; Torres, D.; Diaz, M. Solution Blow Spinning and Obtaining Submicrometric Fibers of Different Polymers. Int. J. Nanopart. Nanotechnol. 2017, 3, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.P.R.; Silva, G.G.; Caliman, V.; Rieumont, J.; de Miranda-Pinto, C.O.B.; Archanjo, B.S.; Neves, B.R.A. Morphology, Crystalline Structure and Thermal Properties of PEO/MEEP Blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3283–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrissopoulou, K.; Andrikopoulos, K.S.; Fotiadou, S.; Bollas, S.; Karageorgaki, C.; Christofilos, D.; Voyiatzis, G.A.; Anastasiadis, S.H. Crystallinity and Chain Conformation in PEO/Layered Silicate Nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9710–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, R.L. Polymer Heats of Fusion; Thermal Applications Note of TA Instruments: New Castle, DE, USA; Available online: http://www.tainstruments.com/pdf/literature/TN048.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- ASTM D882-10; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Dadol, G.C.; Kilic, A.; Tijing, L.D.; Lim, K.J.A.; Cabatingan, L.K.; Tan, N.P.B.; Stojanovska, E.; Polat, Y. Solution Blow Spinning (SBS) and SBS-Spun Nanofibers: Materials, Methods, and Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.T.G.; Rempel, S.P.; Agnol, L.D.; Bianchi, O. The Main Blow Spun Polymer Systems: Processing Conditions and Applications. J. Polym. Res. 2009, 27, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, M.L. The Viscosity of Dilute Solutions of Long-Chain Molecules. IV. Dependence on Concentration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1942, 64, 2716–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Pawlik, M. Intrinsic Viscosities and Huggins Constants of Guar Gum in Alkali Metal Chloride Solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, T.; Tadokoro, H.; Murahashi, S. Normal Vibrations of the Polymer Molecules of Helical Conformation. IV. Polyethylene Oxide and Polyethylene-d4 Oxide. J. Chem. Phys. 1964, 41, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucić, I.; Jurkin, T. FTIR Assessment of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Irradiated in Solid State, Melt and Aqeuous Solution. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rosa, C.G.; Sganzerla, W.G.; de Oliveira Brisola Maciel, M.V.; de Melo, A.P.Z.; da Rosa Almeida, A.; Ramos Nunes, M.; Bertoldi, F.C.; Manique Barreto, P.L. Development of Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Bioactive Nanocomposite Films Functionalized with Zein Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, H.; Luo, X.; Liang, S.; Tian, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Structure-Property Correlation of Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Based Form Stable Phase Change Materials with Different Crosslinking Structure. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 203, 110192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hsu, S.L. An Analysis of the Crystallization Behavior of Poly(Ethylene Oxide)/Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Blends by Spectroscopic and Calorimetric Techniques. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1984, 22, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jin, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L.; Rutledge, G.C. Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Silk Fibers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 6856–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, I. Analisis de Electrolitos Solidos Polimericos PEO/CF3CO2Li Por Difraccion de Rayos-X y SEM. Rev. Timbaga 2006, 1, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.D.; Hirvonen, J.K.; Beck Tan, N.C. Controlled Deposition of Electrospun Poly(Ethylene Oxide). Polymer 2001, 42, 8163–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malathi, M.; Tamilarasan, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyethylene Oxide Based Nano Composite Electrolyte. Sadhana 2014, 39, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chu, R.; Wu, R.; Wu, Q. Electrospun Polyethylene Oxide/Cellulose Nanocrystal Composite Nanofibrous Mats with Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Microstructures. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; Song, M. A Study of Crystallisation of Poly (Ethylene Oxide) and Polypropylene on Graphene Surface. Polymer 2015, 73, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Soto, P.J.; Ginés, J.M.; Arias, M.J.; Novák, C.; Ruiz-Conde, A.; García González, P. Effect of molecular mass on the melting temperature, enthalpy and entropy of hydroxy-terminated PEO. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2002, 67, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Wang, S.; Luo, J.; Sun, K.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Z.; Shi, Q. Thermal Analysis and Heat Capacity Study of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Phase Change Materials for Thermal Energy Storage Applications. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 128, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teno, J.; Corral, A.; Gorrasi, G.; Sorrentino, A.; Benito, J.G. Fibrous Nanocomposites Based on EVA40 Filled with Cu Nanoparticles and Their Potential Antibacterial Action. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 20, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S. Porosity of Fiber Mats from Different Polymer Solutions: Evaluating the Influence of Process and Solution Parameters. Master’s Thesis, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Washiyama, J.; Moteki, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Okuyama, K. Crystal Modification in Poly( Ethylene Succinate). Polym. J. 1995, 27, 1264–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bellan, L.M.; Kameoka, J.; Craighead, H.G. Measurement of the Young’s Moduli of Individual Polyethylene Oxide and Glass Nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, A.Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M. Determination of the Elastic Modulus of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Using a Photoisomerizing Dye. Chem. Phys. 2013, 422, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfield, R.W.; Barnet, F.R. Elastic Constanto of Bulk Polymers. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1972, 27, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Shen, X.X.; Branford-White, C.; White, K.; Zhu, L.M.; Annie Bligh, S.W. Oral Fast-Dissolving Drug Delivery Membranes Prepared from Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Ultrafine Fibers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, J.; Cui, Z.; Yu, D.G.; Annie Bligh, S.W. Testing of Fast Dissolution of Ibuprofen from Its Electrospun Hydrophilic Polymer Nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, A.; Larsson, A.; Andersson, Å.; Piculell, L. Swelling and Polymer Erosion for Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Tablets of Different Molecular Weights Polydispersities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Parameters Associated to the Solution | Parameters Associated to the Processing | Environment Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer concentration | Working distance, WD (distance from the tip of the capillary to the collector) | Temperature |
| Type of solvent and composition | Injection or feeding rate, FR (velocity at which the polymer solution is injected) | Humidity |
| Viscosity | Gas pressure, Ap | |
| Surface tension | Rotational speed of the collector, RSC | |
| Diameter of the capillary | ||
| Capillary protrusion from the nozzle exit | ||
| Polymer concentration | Working distance, WD (distance from the tip of the capillary to the collector) | Temperature |
| PEO-46 | PEO-55 | PEO-64 | PEO-73 | PEO-82 | PEO-91 | PEO-100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XXDR | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.76 |
| D (nm) | 34.4 | 35.2 | 34.0 | 33.5 | 34.0 | 34.5 | 35.8 |
| ε × 103 | 6.74 | 6.58 | 6.81 | 6.93 | 6.83 | 6.72 | 6.50 |
| (a) | PEO 46 | PEO 55 | PEO 64 | PEO 73 | PEO 82 | PEO 91 | PEO 100 | PEO Com |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm (°C) | 61.9 | 61.1 | 61.2 | 59.0 | 63.6 | 55.4 | 63.1 | 62.1 |
| ∆Hm (J/g) | 131.6 | 130.3 | 126.0 | 122.4 | 137.8 | 145.5 | 143.1 | 131.1 |
| χm (%) | 66.8 | 66.1 | 64.0 | 62.2 | 69.9 | 73.8 | 72.6 | 66.5 |
| (b) | PEO 46 | PEO 55 | PEO 64 | PEO 73 | PEO 82 | PEO 91 | PEO 100 | PEO Com |
| Tc (°C) | 41.1 | 46.6 | 43.1 | 44.7 | 43.8 | 44.9 | 43.7 | 43.1 |
| ∆Hc (J/g) | 121.1 | 126.5 | 117.8 | 129.3 | 123.4 | 133.4 | 130.8 | 88.0 |
| χc (%) | 61.5 | 64.2 | 59.8 | 65.6 | 62.7 | 67.7 | 66.4 | 44.6 |
| Sample | Tilt Angle (°) | <D> (nm) | Mean Diameter (nm) | σ (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEO-46 | −5 | 308 | 302 | 240 |
| 0 | 311 | 259 | ||
| 5 | 302 | 205 | ||
| 10 | 287 | 187 | ||
| PEO-55 | −5 | 346 | 301 | 302 |
| 0 | 232 | 268 | ||
| 5 | 316 | 232 | ||
| 10 | 309 | 193 | ||
| PEO-64 | −5 | 293 | 294 | 237 |
| 0 | 307 | 259 | ||
| 5 | 289 | 253 | ||
| 10 | 285 | 235 | ||
| PEO-73 | −5 | 290 | 304 | 180 |
| 0 | 315 | 239 | ||
| 5 | 324 | 227 | ||
| 10 | 329 | 246 | ||
| PEO-82 | −5 | 363 | 339 | 290 |
| 0 | 346 | 280 | ||
| 5 | 295 | 145 | ||
| 10 | 351 | 187 | ||
| PEO-91 | −5 | 280 | 294 | 225 |
| 0 | 306 | 212 | ||
| 5 | 274 | 201 | ||
| 10 | 315 | 238 | ||
| PEO-100 | −5 | 247 | 288 | 169 |
| 0 | 323 | 238 | ||
| 5 | 319 | 299 | ||
| 10 | 264 | 187 |
| PEO-46 | PEO-55 | PEO-64 | PEO-73 | PEO-82 | PEO-91 | PEO-100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Pore Area (μm) | 0.88 | 1.28 | 0.78 | 0.96 | 1.21 | 0.97 | 0.87 |
| PEO-46 | PEO-55 | PEO-64 | PEO-73 | PEO-82 | PEO-91 | PEO-100 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity (%) | Image Analysis | 39 | 31 | 37 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 36 |
| Gravimetry | 62 | 61 | 61 | 68 | 73 | 63 | 64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorente, M.Á.; González-Gaitano, G.; González-Benito, J. Preparation, Properties and Water Dissolution Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide Mats Prepared by Solution Blow Spinning. Polymers 2022, 14, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071299
Lorente MÁ, González-Gaitano G, González-Benito J. Preparation, Properties and Water Dissolution Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide Mats Prepared by Solution Blow Spinning. Polymers. 2022; 14(7):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071299
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorente, Miguel Ángel, Gustavo González-Gaitano, and Javier González-Benito. 2022. "Preparation, Properties and Water Dissolution Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide Mats Prepared by Solution Blow Spinning" Polymers 14, no. 7: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071299
APA StyleLorente, M. Á., González-Gaitano, G., & González-Benito, J. (2022). Preparation, Properties and Water Dissolution Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide Mats Prepared by Solution Blow Spinning. Polymers, 14(7), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071299