Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Structural Properties of Bio-Active Films Based on Biological-Chemical Chitosan, a Novel Ramon (Brosimum alicastrum) Starch, and Quercetin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
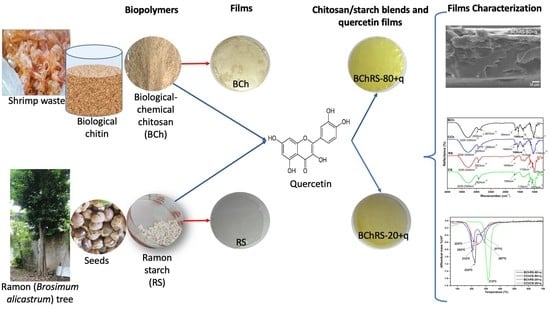
2.1. Preparation of Chitosan and Starch Films
2.2. Preparation of Chitosan-Starch-Quercetin-Based Films
2.3. Films Characterization
2.3.1. Physicochemical Properties: Thickness, Moisture, Water Solubility, Degree of Swelling of the Films, and Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
2.3.2. Mechanical Properties
2.3.3. Structural Properties
Thermogravimetric Analysis
FTIR Analysis
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.4. Bioactive Evaluation
DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity (RSADPPH)
ABTS+ Scavenging Activity (RSAABTS)
Antibacterial Activity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical, Mechanical and Bioactive Evaluation of Chitosan and Starch Films
3.1.1. Thickness, Moisture, Solubility, Swelling Index, and Water Vapor WVP
3.1.2. Mechanical Properties
3.1.3. Antioxidant Activity
3.1.4. Antimicrobial Activity
3.2. Structural Characteristics
3.2.1. TGA
3.2.2. FTIR Analysis
3.2.3. SEM
3.3. Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Bioactive Evaluation of Blended Chitosan/Starch Films
3.3.1. Thickness, Moisture, Solubility, Swelling Index, and Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
3.3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3.3. Antioxidant Activity
3.3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
3.4. Structural Characteristics of Blended Chitosan and Starch Films
3.4.1. TGA
3.4.2. FTIR Analysis
3.4.3. SEM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, R.; Zhang, X.; Yong, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Development and characterization of antioxidant active packaging and intelligent Al3+-sensing films based on carboxymethyl chitosan and quercetin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, N.; Naal-Ek, M.G.; Ayora-Talavera, T.; Shirai, K.; Román-Guerrero, A.; Fabela-Morón, M.F.; Cuevas-Bernardino, J.C. Effect of bio-chemical chitosan and gallic acid into rheology and physicochemical properties of ternary edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, A.; Lei, S.; Akhtar, H.M.S.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Jabbar, S.; Abid, M.; Hashim, M.M.; Zeng, X. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-based antimicrobial active food packaging film incorporated with apple peel polyphenols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yan, X.; Zhou, J.; Tong, J.; Su, X. Influence of chitosan concentration on mechanical and barrier properties of corn starch/chitosan films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giteru, S.G.; Coorey, R.; Bertolatti, D.; Watkin, E.; Johnson, S.; Fang, Z. Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of citral and quercetin incorporated kafirin-based bioactive films. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iñiguez-Moreno, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Calderón-Santoyo, M. An extensive review of natural polymers used as coatings for postharvest shelf-life extension: Trends and challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannini, D.; Dal Poggetto, G.; Malinconico, M.; Santagata, G.; Immirzi, B. Citrus pomace biomass as a source of pectin and lignocellulose fibers: From waste to upgraded biocomposites for mulching applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, M.A.C.d.; Levit, R.; Beres, C.; Bedani, R.; de Moreno, M.A.; Isay Saad, S.M.; Leblanc, J.G.J. Tropical fruit by-products water extracts of tropical fruit by-products as sources of soluble fibres and phenolic compounds with potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and functional properties. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Na, J.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Feng, Z. Reutilization of food waste: One-step extration, purification and characterization of ovalbumin from salted egg white by aqueous two-phase flotation. Foods 2019, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Canche, N.G.; Carrillo, J.G.; Escobar-Morales, B.; Salgado-Tránsito, I.; Pacheco, N.; Pech-Cohuo, S.C.; Peña-Cruz, M.I. Physicochemical and Optical Characterization of Citrus aurantium Derived Biochar for Solar Absorber Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiao, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, D.; Feng, Z.; Liu, C. Preparation and evaluation of a novel high internal phase Pickering emulsion based on whey protein isolate nanofibrils derived by hydrothermal method. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo-Huchin, V.M.; Ac-Chim, D.M.; Chim-Chi, Y.A.; Ríos-Soberanis, C.R.; Ramos, G.; Yee-Madeira, H.T.; Ortiz-Fernández, A.; Estrada-León, R.J.; Pérez-Pacheco, E. Huaya (Melicoccus bijugatus) seed flour as a new source of starch: Physicochemical, morphological, thermal and functional characterization. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 3299–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-León, R.; Moo-Huchin, V.; Ríos-Soberanis, C.; Betancur-Ancona, D.; May-Hernández, L.; Carrillo-Sánchez, F.; Cervantes-Uc, J.; Pérez-Pacheco, E. The effect of isolation method on properties of parota (Enterolobium cyclocarpum) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pacheco, E.; Moo-Huchin, V.; Estrada-León, R.; Ortiz-Fernández, A.; May-Hernández, L.; Ríos-Soberanis, C.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Isolation and characterization of starch obtained from Brosimum alicastrum Swarts Seeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pacheco, E.; Estrada-León, R.J.; Duch, E.S.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Betancur-Ancona, D.; Moo-Huchin, V.M. Partial characterization of starch obtained from Ramon (Brosimum alicastrum Swartz), oxidized under different conditions. Starch-Stärke 2017, 69, 1600233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.M.; Pardo-Tejeda, E. Brosimum alicastrum (Moraceae): Uses and potential in Mexico. Econ. Bot. 1982, 36, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguin-Maciel, E.; Larqué-Saavedra, A.; Lappe-Oliveras, P.E.; Barahona-Pérez, L.F.; Alzate-Gaviria, L.; Chablé-Villacis, R.; Domínguez-Maldonado, J.; Pacheco-Catalán, D.; Ruíz, H.A.; Tapia-Tussell, R. Consolidated bioprocess for bioethanol production from raw flour of Brosimum alicastrum seeds using the native strain of trametes hirsuta bm-2. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moo-Huchin, V.; Cabrera-Sierra, M.; Estrada-León, R.; Ríos-Soberanis, C.; Betancur-Ancona, D.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Ortiz-Fernández, A.; Estrada-Mota, I.; Pérez-Pacheco, E. Determination of some physicochemical and rheological characteristics of starch obtained from Brosimum alicastrum Swartz seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Soberanis, C.R.; Estrada-León, R.J.; Moo-Huchin, V.M.; Cabrera-Sierra, M.J.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Pérez-Pacheco, E. Utilization of ramon seeds (Brosimum alicastrum swarts) as a new source material for thermoplastic starch production. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Fernández, A.; Carrillo-Sánchez, F.; May-Hernández, L.; Estrada-León, R.; Carrillo-Escalante, H.; Hernández-Sánchez, F.; Valadez-Gonzalez, A. Design of experiments for optimization a biodegrable adhesive based on ramon starch (Brosimum alicastrum Sw.). Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 73, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssell, P.; Lahtinen, R.; Lahelin, M.; Myllärinen, P. Oxygen permeability of amylose and amylopectin films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 47, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, N.; Garnica-Gonzalez, M.; Gimeno, M.; Bárzana, E.; Trombotto, S.; David, L.; Shirai, K. Structural characterization of chitin and chitosan obtained by biological and chemical methods. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3285–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásconez, M.B.; Flores, S.K.; Campos, C.A.; Alvarado, J.; Gerschenson, L.N. Antimicrobial activity and physical properties of chitosan–tapioca starch based edible films and coatings. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.L.; Wu, J.M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G. Antimicrobial and physical properties of sweet potato starch films incorporated with potassium sorbate or chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, J.; Atarés, L.; Vargas, M.; Chiralt, A. Properties of wheat starch film-forming dispersions and films as affected by chitosan addition. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, K.M.; Yoksan, R. Morphological characteristics and barrier properties of thermoplastic starch/chitosan blown film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Song, X.; Li, Y. Antimicrobial, physical and mechanical properties of kudzu starch–chitosan composite films as a function of acid solvent types. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.P.; Vaz, A.F.; Silva, H.D.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A.; Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G. Development and characterization of an active chitosan-based film containing quercetin. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2015, 8, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Agustini, T.W. Physico-mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin film from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket incorporated with essential oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Tian, B.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Jiang, B.; Feng, Z. Preparation and characterization of coating based on protein nanofibers and polyphenol and application for salted duck egg yolks. Foods 2020, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Feng, Z.; Tian, B. Separation, structural characteristics and biological activity of lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides separated by aqueous two-phase system. LWT 2021, 147, 111617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shi, L.; Ren, Z.; Hao, G.; Chen, J.; Weng, W. Characterization of emulsion films prepared from soy protein isolate at different preheating temperatures. J. Food Eng. 2021, 309, 110697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Gastelú, G.; Barrera, G.N.; Ribotta, P.D.; Igarzabal, C.I.Á. Preparation and characterization of soy protein films reinforced with cellulose nanofibers obtained from soybean by-products. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongdeesoontorn, W.; Mauer, L.J.; Wongruong, S.; Sriburi, P.; Rachtanapun, P. Physical and antioxidant properties of cassava starch–carboxymethyl cellulose incorporated with quercetin and TBHQ as active food packaging. Polymers 2020, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phoopuritham, P.; Thongngam, M.; Yoksan, R.; Suppakul, P. Properties of antioxidant cellulose ether films containing selected plant extracts. In Proceedings of the 5th International Packaging Congress & Exhibition, Izmir, Turkey, 22–24 November 2007; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Božič, M.; Gorgieva, S.; Kokol, V. Homogeneous and heterogeneous methods for laccase-mediated functionalization of chitosan by tannic acid and quercetin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, E.; Marín, V.; Aburto, J.; Beltrán, H.; Shirai, K.; Villanueva, S.; Sandoval, G. Enzymatic Modification of Chitosan with Quercetin and Its Application As Antioxidant Edible Films1. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2012, 48, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Mehrotra, G.; Bhartiya, P.; Singh, A.; Dutta, P. Preparation, physicochemical and biological evaluation of quercetin based chitosan-gelatin film for food packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongdeesoontorn, W.; Mauer, L.J.; Wongruong, S.; Sriburi, P.; Reungsang, A.; Rachtanapun, P. Antioxidant Films from Cassava Starch/Gelatin Biocomposite Fortified with Quercetin and TBHQ and Their Applications in Food Models. Polymers 2021, 13, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-López, H.; Pech-Cohuo, S.C.; Ayora-Talavera, T.; Cuevas-Bernardino, J.C.; Ramos-Díaz, A.; Espinosa-Andrews, H.; Shirai, K.; Pacheco, N. Deacetylation of chitin obtained by biological method and its application in melipona honey-incorporated antimicrobial biofilms. MRS Adv. 2021, 6, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech-Cohuo, S.C.; Hernandez-Colula, J.; Gonzalez-Canche, N.G.; Salgado-Transito, I.; Uribe-Calderon, J.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Cuevas-Bernardino, J.C.; Ayora-Talavera, T.; Pacheco, N. Starch from Ramon seed (Brosimum alicastrum) obtained by two extraction methods. MRS Adv. 2021, 6, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, M.; Alemán, A.; Romani, V.P.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Montero, P.; Prentice, C. Effects of agar films incorporated with fish protein hydrolysate or clove essential oil on flounder (Paralichthys orbignyanus) fillets shelf-life. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui, L.; Xie, M.; Hu, B.; Zhou, L.; Yin, D.; Zeng, X. A comparative study on chitosan/gelatin composite films with conjugated or incorporated gallic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Baloch, Z.; Khalid, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L. Starch-based antimicrobial films functionalized by pomegranate peel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, A.B.; Sellamuthu, P.S.; Nambiar, R.B.; Sadiku, E.R. Development of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan bio-nanocomposite films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals isolated from rice straw. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-López, H.A. Extraction of Biopolymers from Agro-Industrial Wastes and Their Application in Forming Honey Functionalized Films (Extracción de Biopolímeros a Partir de Desechos Agroindustriales y su Aplicación en la Formación de Películas Funcionalizadas con Miel); Centro de Investigación y Asistencia en Tecnología y Diseño del Estado de Jalisco: Merida, Mexico, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Escárcega-Galaz, A.A.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; López-Cervantes, J.; Sanches-Silva, A.; Madera-Santana, T.J.; Paseiro-Losada, P. Mechanical, structural and physical aspects of chitosan-based films as antimicrobial dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-López, H.; Pech-Cohuo, S.C.; Herrera-Pool, E.; Medina-Torres, N.; Cuevas-Bernardino, J.C.; Ayora-Talavera, T.; Espinosa-Andrews, H.; Ramos-Díaz, A.; Trombotto, S.; Pacheco, N. Structural and Physicochemical Characterization of Chitosan Obtained by UAE and its Effect on the Growth Inhibition of Pythium ultimum. Agriculture 2020, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, K.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Li, P. The production of fully deacetylated chitosan by compression method. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villalobos, K.; Rojas, H.; González-Paz, R.; Granados, D.B.; González-Masís, J.; Baudrit, J.V.; Corrales-Ureña, Y.R. Production of starch films using propolis nanoparticles as novel bioplasticizer. J. Renew. Mater. 2017, 5, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Li, L. Thermal decomposition of corn starch with different amylose/amylopectin ratios in open and sealed systems. Cereal Chem. 2009, 86, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dutta, P.; Kumar, H.; Kureel, A.K.; Rai, A.K. Synthesis of chitin-glucan-aldehyde-quercetin conjugate and evaluation of anticancer and antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kureel, A.K.; Dutta, P.; Kumar, S.; Rai, A.K. Curcumin loaded chitin-glucan quercetin conjugate: Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant, in vitro release study, and anticancer activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Brahmakumar, M.; Abraham, T.E. Microstructural imaging and characterization of the mechanical, chemical, thermal, and swelling properties of starch–chitosan blend films. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 2006, 82, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Characterization of edible starch–chitosan film and its application in the storage of Mongolian cheese. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 57, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourtoom, T.; Chinnan, M.S. Preparation and properties of rice starch–chitosan blend biodegradable film. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantala, J.; Rachtanapun, C.; Rachtanapun, P. Effect of molecular sizes, sources of chitosan and plasticizer types on properties of carboxymethyl chitosan films. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Freienbach, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 611–614. [Google Scholar]
- Zamudio-Flores, P.B.; Torres, A.V.; Salgado-Delgado, R.; Bello-Pérez, L.A. Influence of the oxidation and acetylation of banana starch on the mechanical and water barrier properties of modified starch and modified starch/chitosan blend films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Adhikari, R.; Guo, Q.; Adhikari, B. Preparation and characterization of glycerol plasticized (high-amylose) starch–chitosan films. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelissari, F.M.; Grossmann, M.V.; Yamashita, F.; Pineda, E.A.G. Antimicrobial, mechanical, and barrier properties of cassava starch− chitosan films incorporated with oregano essential oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7499–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Elhussieny, A.; Ali, K.; Samy, I.; Everitt, N. Extraction of degradable bio polymer materials from shrimp shell wastes by two different methods. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 012004. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, S.; Annamareddy, S.H.K.; Abanti, S.; Rath, P.K. Physicochemical properties and characterization of chitosan synthesized from fish scales, crab and shrimp shells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.F.; Trotta, A.; Fossey, S.; Nagarajan, S.; Nagarajan, R.; Samuelson, L.A.; Kumar, J. Enzymatic synthesis and characterization of polyquercetin. J. Macromol. Sci. Part. A Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 47, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Abraham, T.E. Characterisation of ferulic acid incorporated starch–chitosan blend films. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Gopakumar, D.A.; Olaiya, N.; Zarlaida, F.; Alfian, A.; Aprinasari, C.; Alfatah, T.; Rizal, S.; Khalil, H.A. Evaluation of the thermomechanical properties and biodegradation of brown rice starch-based chitosan biodegradable composite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinotti, A.; Garcia, M.A.; Martino, M.N.; Zaritzky, N.E. Study on microstructure and physical properties of composite films based on chitosan and methylcellulose. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norajit, K.; Kim, K.M.; Ryu, G.H. Comparative studies on the characterization and antioxidant properties of biodegradable alginate films containing ginseng extract. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramza, A.; Korczak, J. Tea constituents (Camellia sinensis L.) as antioxidants in lipid systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Navajas, Y.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Sendra, E.; Perez-Alvarez, J.; Fernández-López, J. In vitro antibacterial and antioxidant properties of chitosan edible films incorporated with Thymus moroderi or Thymus piperella essential oils. Food Control 2013, 30, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, R.; Sivakumar, S.; Kaur, H. Antimicrobial edible films in food packaging: Current scenario and recent nanotechnological advancements-a review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Sellimi, S.; Rinaudo, M.; Jellouli, K.; Nasri, M. Influence of acetylation degree and molecular weight of homogeneous chitosans on antibacterial and antifungal activities. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 185, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Film | BCh i | CCh ii | RS iii | CS iv |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.14 ± 0.002 a | 0.15 ± 0.009 a | 0.06 ± 0.006 b | 0.06 ± 0.002 b |
| Moisture (%) | 19.13 ± 1.78 b | 18.71 ± 1.74 b | 32.31 ± 1.23 a | 15.39 ± 0.22 c |
| Solubilty (%) | 24.68 ± 3.97 b | 27.74 ± 1.76 b | 52.47 ± 5.53 a | 49.53 ± 041 a |
| Swelling (%) | 32.00 ± 0.22 c | 103.50 ± 0.84 b | 111.90 ± 5.92 b | 240.44 ± 18.45 a |
| WVP × 10−9 (g m−1 s−1 Pa−1) | 6.75 ± 0.11 a | 7.80 ± 1.69 a | 2.26 ± 0.38 b | 2.48 ± 0.31 b |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 2.43 ± 0.08 a | 3.05 ± 0.74 a | 2.49 ± 0.12 a | 3.20 ± 0.45 a |
| Elongation at break (%) | 25.29 ± 0.11 a | 18.01 ± 0.41 b | 17.43 ± 0.38 b | 7.93 ± 0.95 c |
| Elastic modulus (MPa) | 11.35 ± 0.07 c | 25.83 ± 0.77 b | 50.54 ± 3.37 a | 1.22 ± 0.05 d |
| DPPH (μgTEAC/mL) | 2.63 ± 0.31 a | 2.83 ± 0.15 a | NP | NP |
| ABTS (μgTEAC/mL) | 6.06 ± 0.67 a | 6.69 ± 1.20 a | NP | NP |
| Inhibition (%) for gram possitive, S. aureus | 33.62 ± 5.45 a | 29.86 ± 2.45 a | NP | NP |
| Inhibition (%) for gram negative, S. typhimurium | 28.64 ± 0.65 a | 27.31 ± 2.30 a | NP | NP |
| Film | BChRS-80+q i | CChCS-80+q ii | BChRS-20+q iii | CChCS-20+q iv |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.15 ± 0.008 a | 0.13 ± 0.009 a | 0.07 ± 0.005 b | 0.04 ± 0.002 c |
| Moisture (%) | 36.45 ± 1.58 b | 42.84 ± 0.26 a | 17.25 ± 1.09 d | 21.85 ± 1.97 c |
| Solubilty (%) | 56.47 ± 6.62 a | 51.71 ± 0.31 a | 52.06 ± 4.27 a | 36.44 ± 3.76 b |
| Swelling (%) | 81.24 ± 3.91 b | 11.56 ± 1.59 c | 121.69 ± 6.59 a | 70.75 ± 6.17 b |
| WVP × 10−9 (g m−1 s−1 Pa−1) | 6.76 ± 1.57 a | 6.00 ± 1.36 ab | 3.43 ± 0.45 ab | 2.14 ± 0.02 b |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 0.56 ± 0.03 c | 3.61 ± 0.29 b | 0.68 ± 0.09 c | 7.47 ± 0.05 a |
| Elongation at break (%) | 4.80 ± 0.35 d | 20.10 ± 0.83 b | 9.14 ± 0.68 c | 34.50 ± 0.18 a |
| Elastic modulus (MPa) | 9.86 ± 0.70 c | 16.97 ± 0.57 b | 6.72 ± 0.09 b | 40.78 ± 2.15 a |
| DPPH (μgTEAC/mL) | 3.70 ± 0.29 a | 3.60 ± 0.33 a | 3.21 ± 0.20 a | 3.31 ± 0.02 a |
| ABTS (μgTEAC/mL) | 14.06 ± 1.89 a | 20.23 ± 2.32 a | 18.81 ± 2.15 a | 19.48 ± 5.32 a |
| Inhibition % for gram possitive, S. aureus | 41.56 ± 3.81 a | 37.97 ± 3.82 a | 19.41 ± 1.83 b | 14.30 ± 0.56 b |
| Inhibition (%) for gram negative, S. typhimurium | 44.07 ± 5.73 a | 38.47 ± 3.28 a | 17.29 ± 2.30 b | 10.03 ± 0.56 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pech-Cohuo, S.C.; Martín-López, H.; Uribe-Calderón, J.; González-Canché, N.G.; Salgado-Tránsito, I.; May-Pat, A.; Cuevas-Bernardino, J.C.; Ayora-Talavera, T.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Pacheco, N. Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Structural Properties of Bio-Active Films Based on Biological-Chemical Chitosan, a Novel Ramon (Brosimum alicastrum) Starch, and Quercetin. Polymers 2022, 14, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071346
Pech-Cohuo SC, Martín-López H, Uribe-Calderón J, González-Canché NG, Salgado-Tránsito I, May-Pat A, Cuevas-Bernardino JC, Ayora-Talavera T, Cervantes-Uc JM, Pacheco N. Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Structural Properties of Bio-Active Films Based on Biological-Chemical Chitosan, a Novel Ramon (Brosimum alicastrum) Starch, and Quercetin. Polymers. 2022; 14(7):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071346
Chicago/Turabian StylePech-Cohuo, Soledad Cecilia, Héctor Martín-López, Jorge Uribe-Calderón, Nancy Guadalupe González-Canché, Iván Salgado-Tránsito, Alejandro May-Pat, Juan Carlos Cuevas-Bernardino, Teresa Ayora-Talavera, José Manuel Cervantes-Uc, and Neith Pacheco. 2022. "Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Structural Properties of Bio-Active Films Based on Biological-Chemical Chitosan, a Novel Ramon (Brosimum alicastrum) Starch, and Quercetin" Polymers 14, no. 7: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071346
APA StylePech-Cohuo, S. C., Martín-López, H., Uribe-Calderón, J., González-Canché, N. G., Salgado-Tránsito, I., May-Pat, A., Cuevas-Bernardino, J. C., Ayora-Talavera, T., Cervantes-Uc, J. M., & Pacheco, N. (2022). Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Structural Properties of Bio-Active Films Based on Biological-Chemical Chitosan, a Novel Ramon (Brosimum alicastrum) Starch, and Quercetin. Polymers, 14(7), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071346