Phase Behaviors of ABA Star Polymer and Nanoparticles Confined in a Sphere with Soft Inner Surface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Numerical Results and Discussions
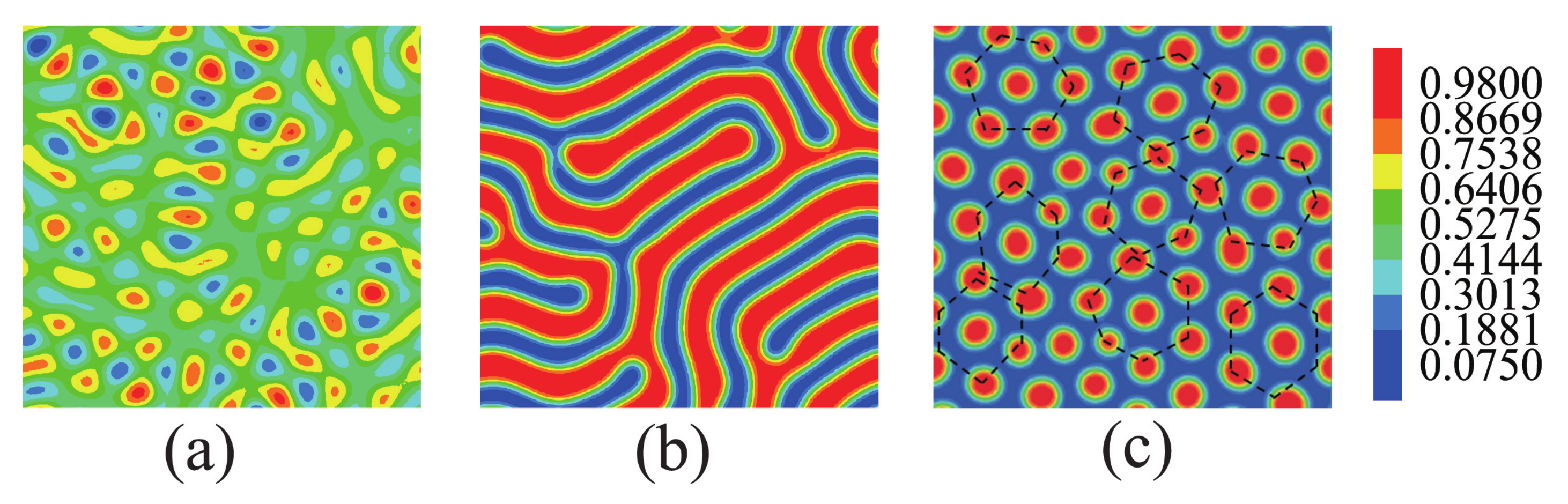
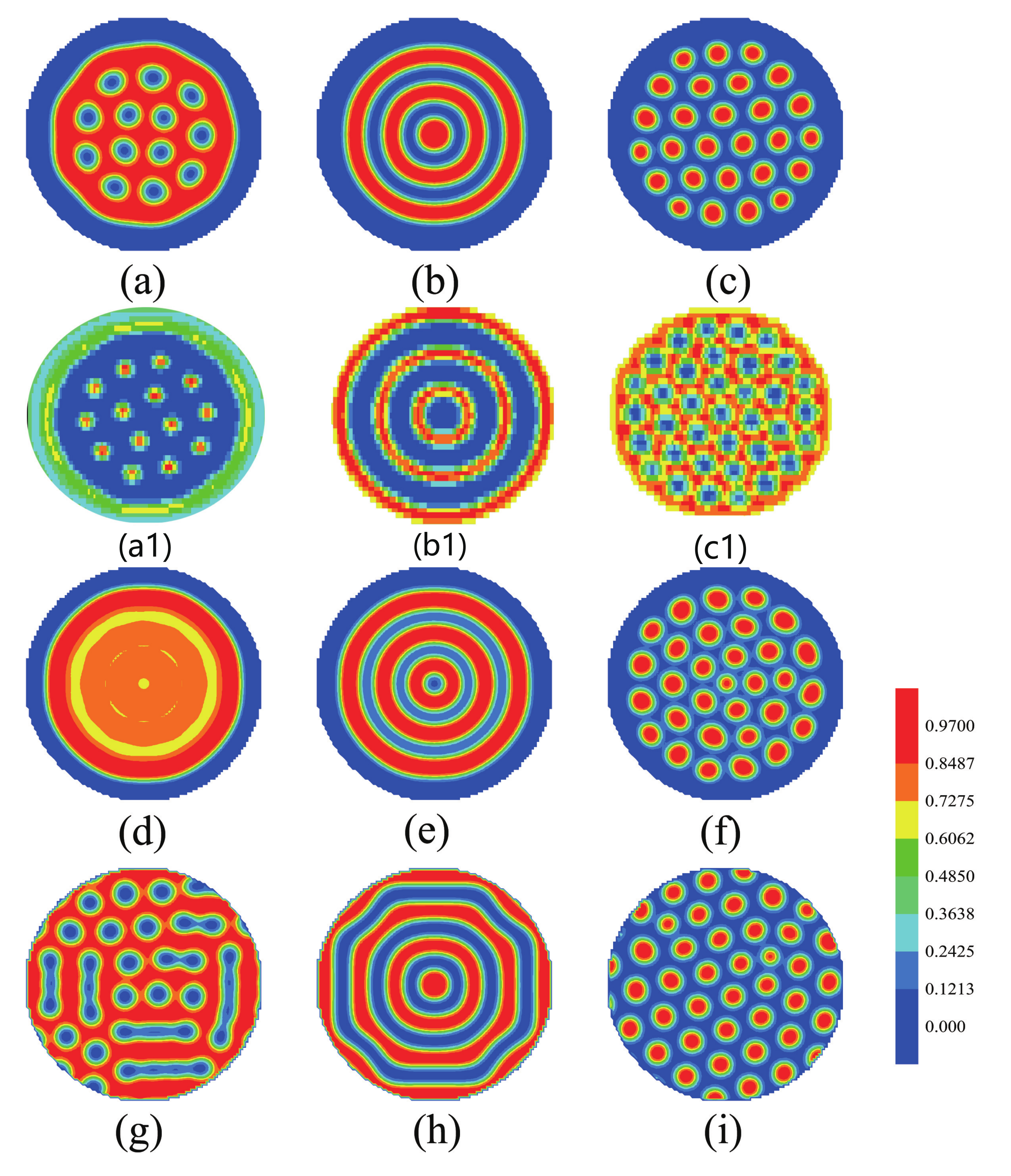
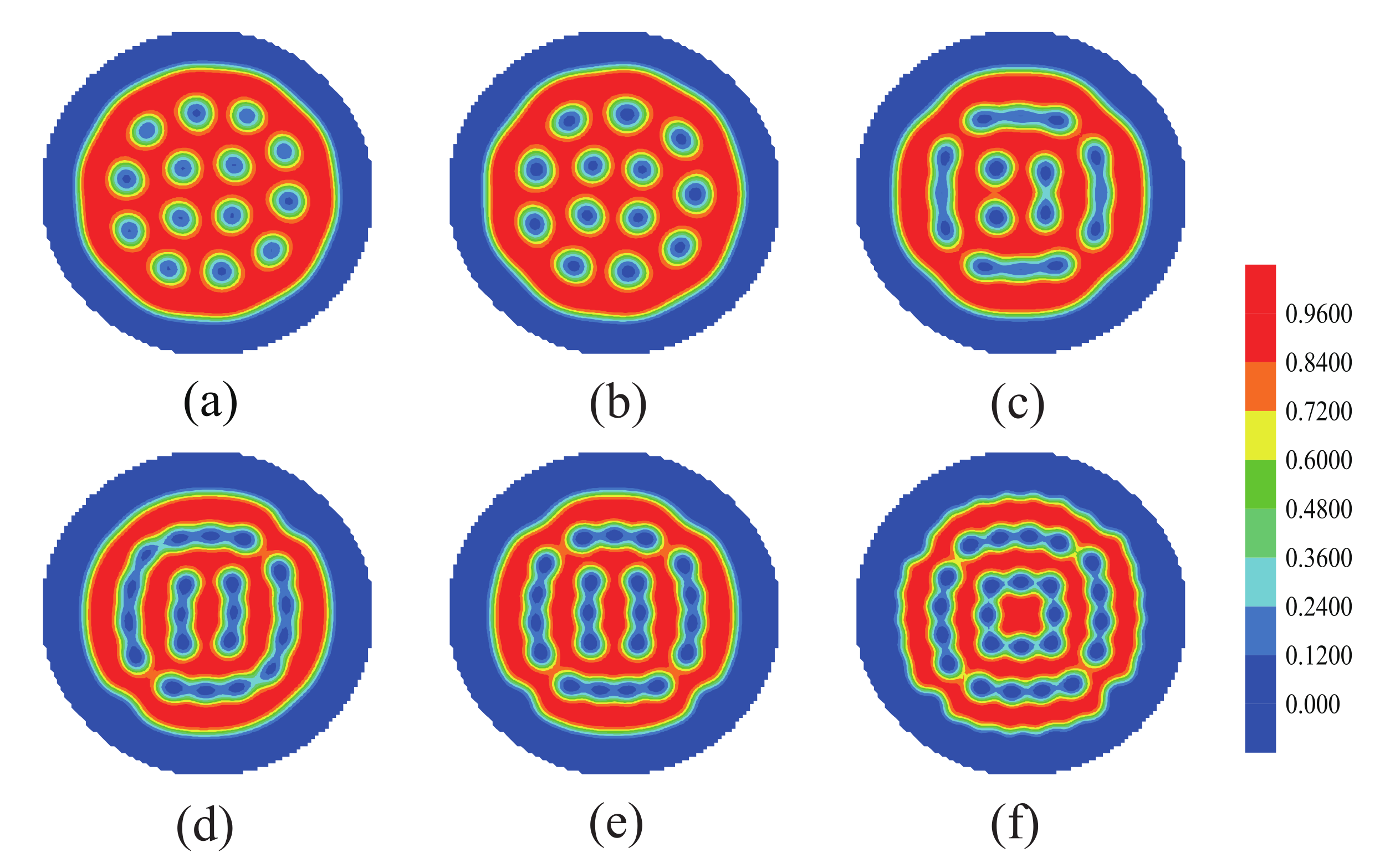
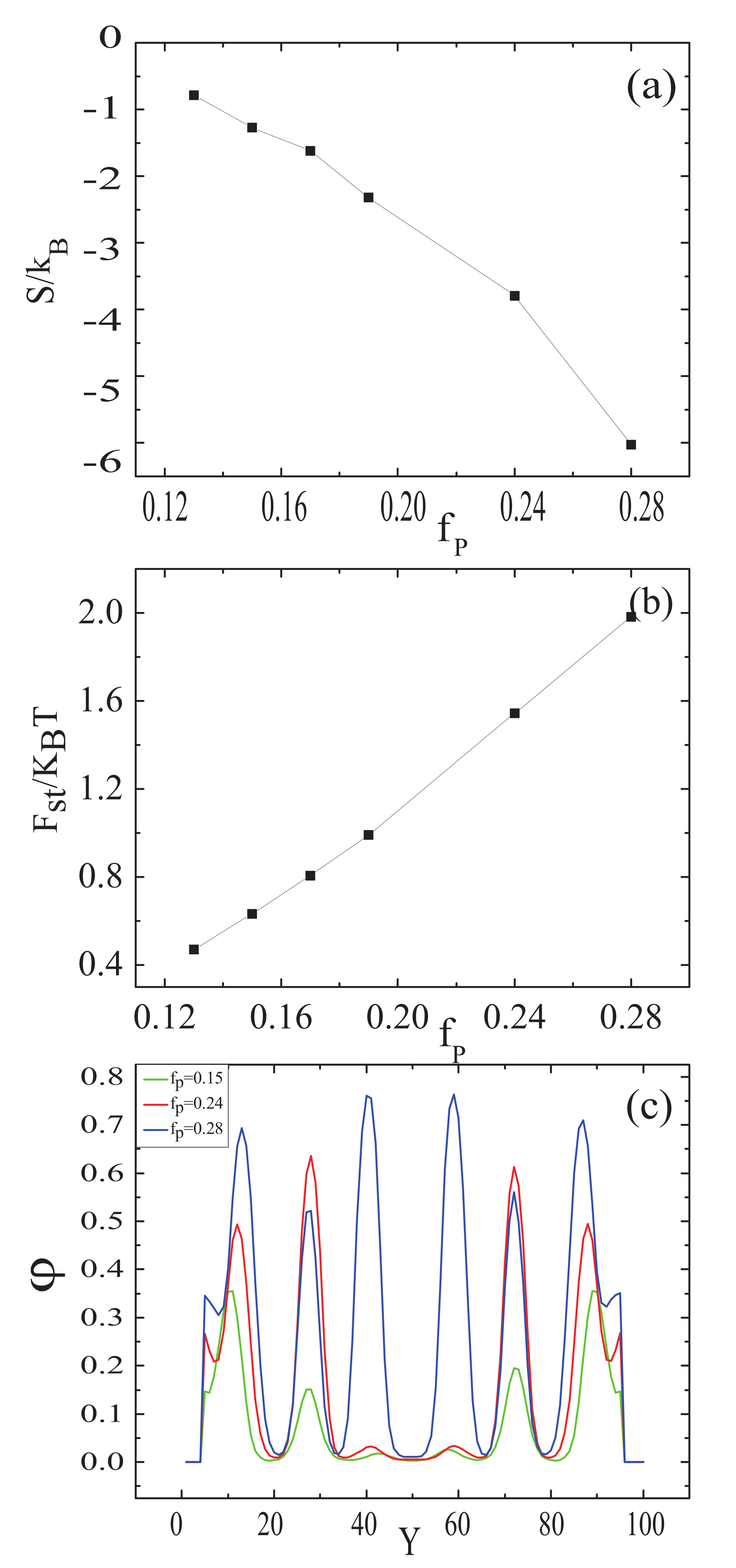
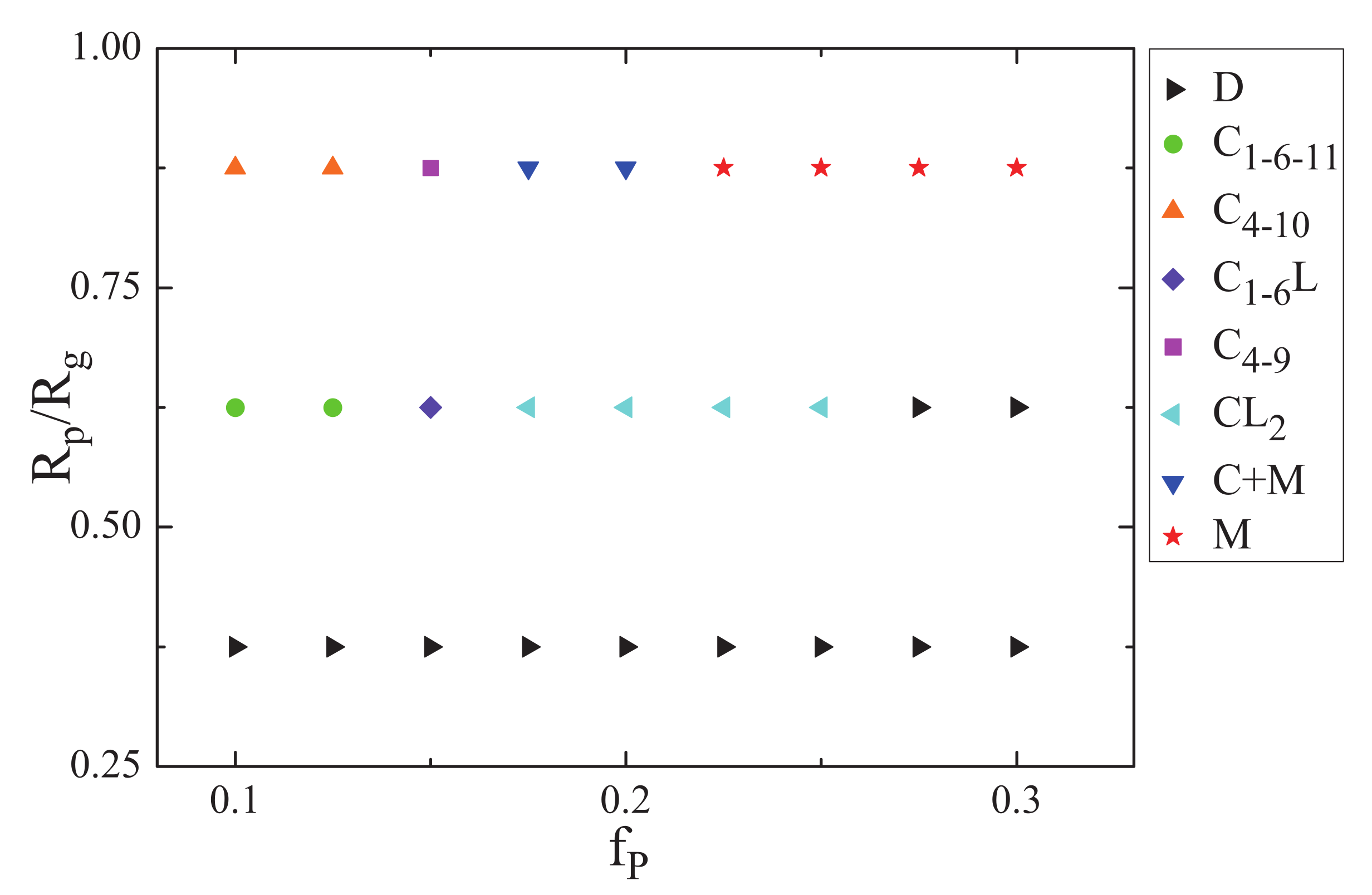
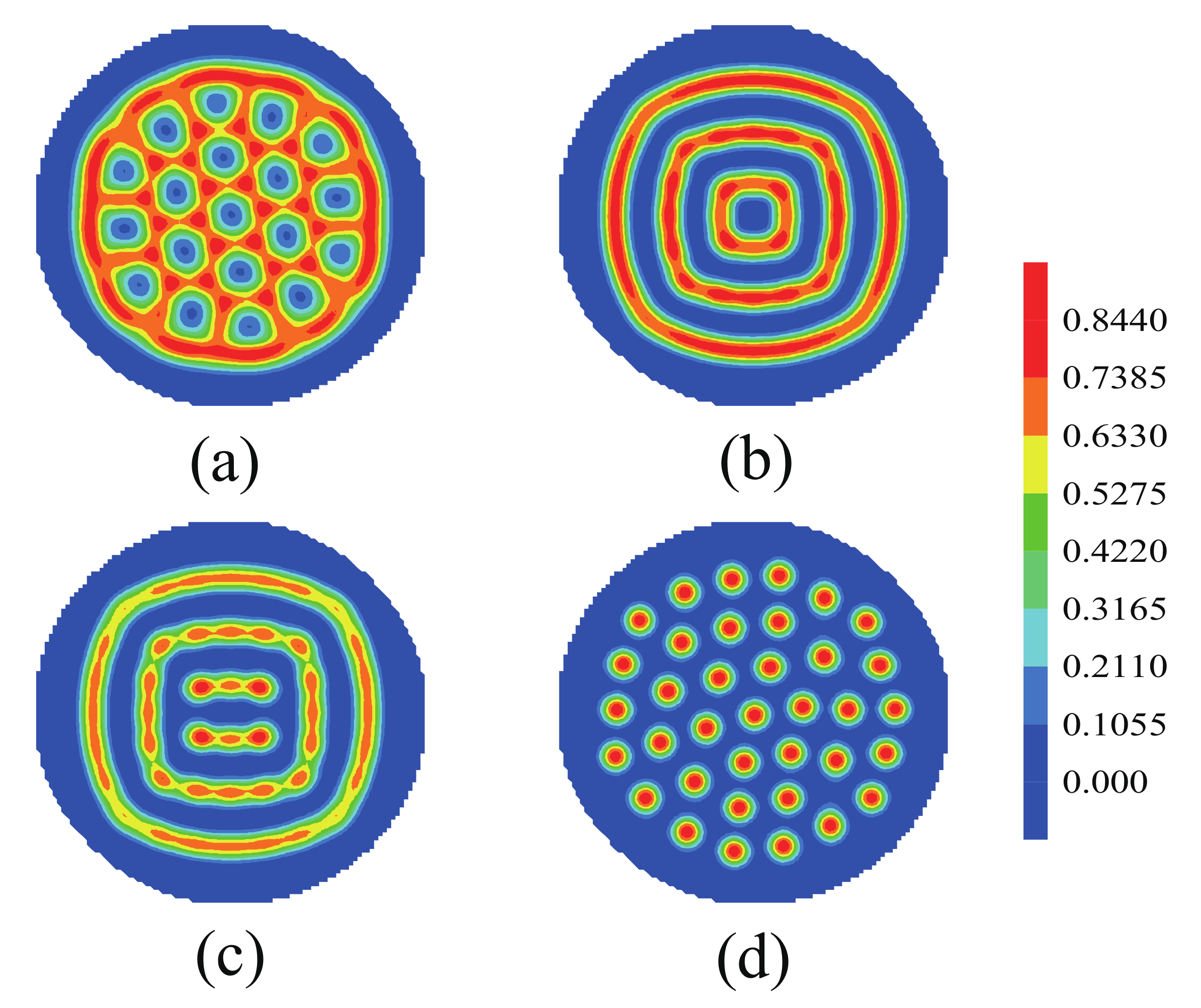
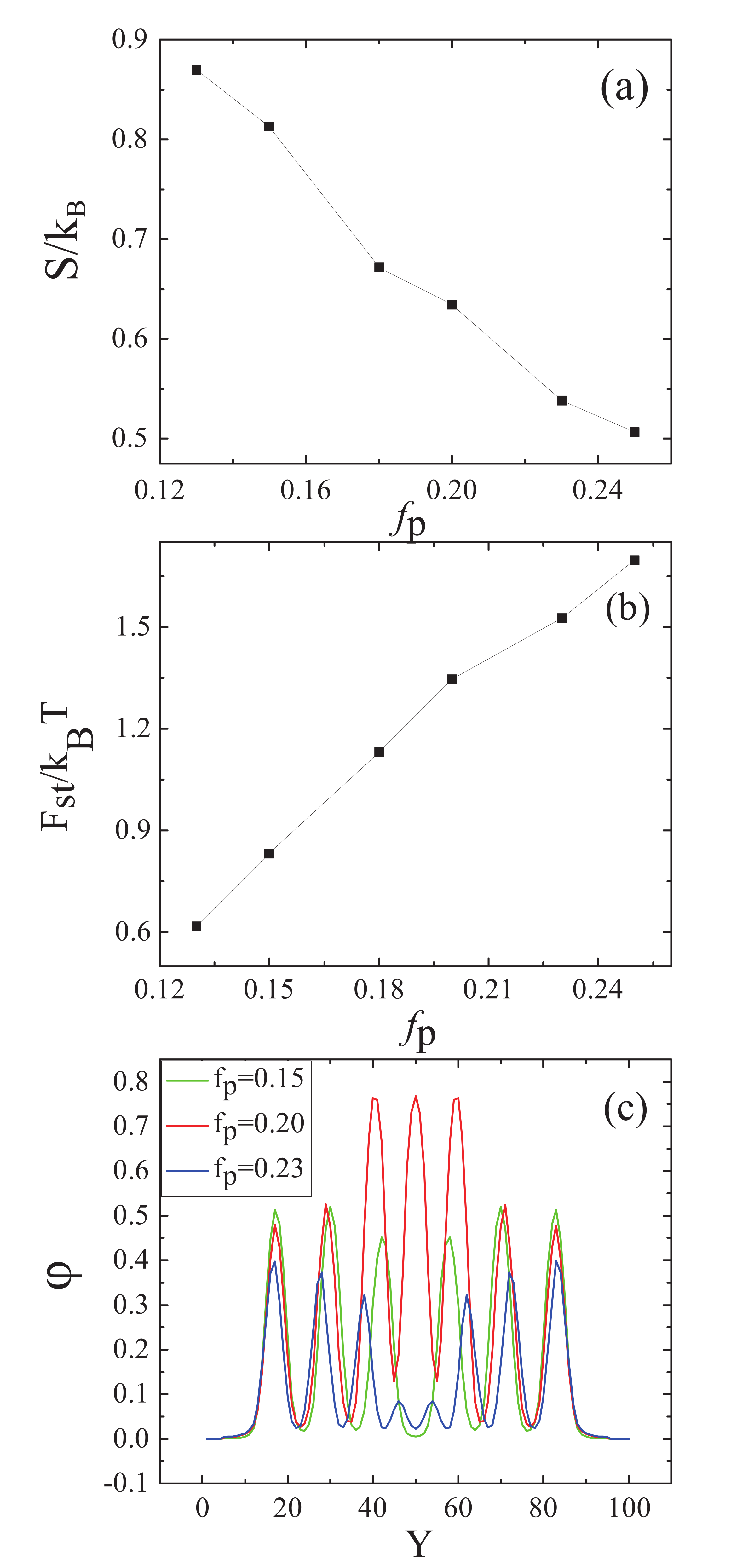
3.1. Nanoparticles Interact with the B Blocks
3.2. Nanoparticles Interact with the A Blocks and the Homopolymer Brushes
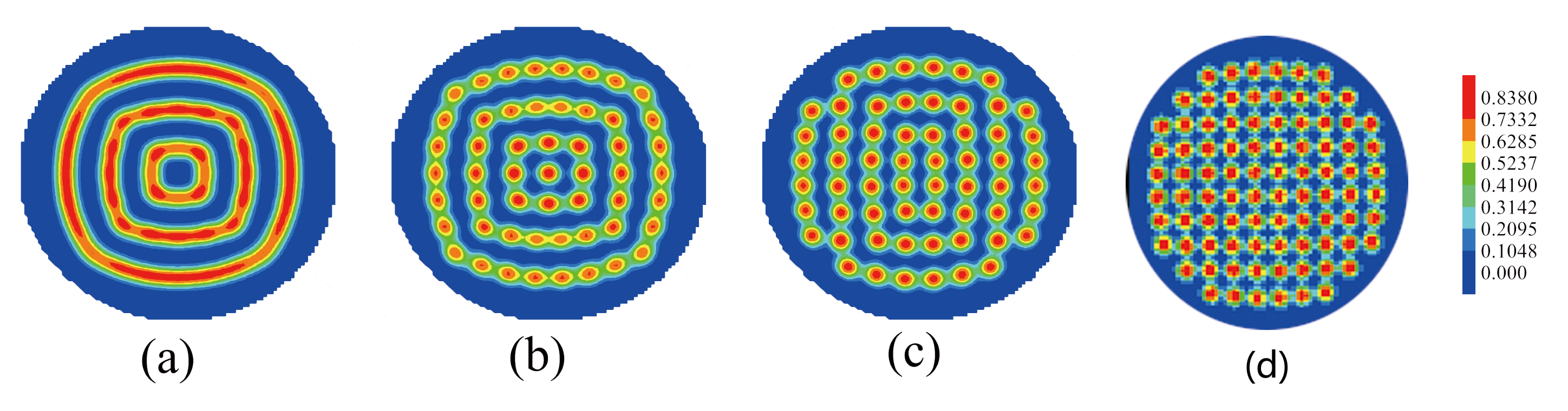
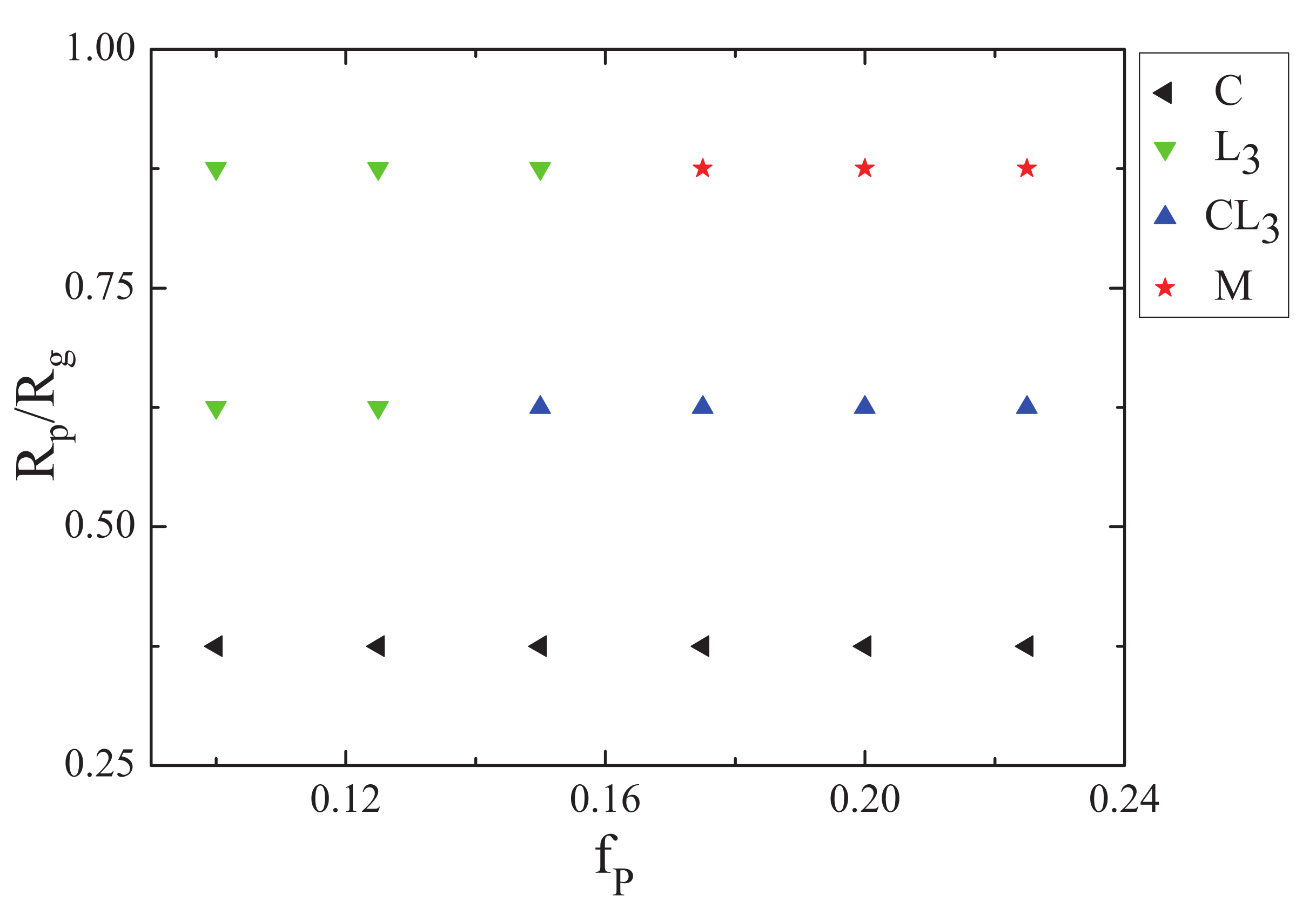
3.3. The Effect of Sphere Radius on the Morphologies of the Mixture of ABA Star Polymers and Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarkar, B.; Alexandridis, P. Block copolymer–nanoparticle composites: Structure, functional properties, and processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 40, 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winey, K.I.; Vaia, R.A. Polymer nanocomposites. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaia, R.A.; Giannelis, E.P. Polymer nanocomposites: Status and opportunities. MRS Bull. 2001, 26, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Qiang, Y.C.; Li, W.H. Regulate the Stability of Gyroids of ABC-Type Multiblock Copolymers by Controlling the Packing Frustration. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.T.; Li, W.h. Laves Phases Formed in the Binary Blend of AB4 Miktoarm Star Copolymer and A-Homopolymer. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunpetch, P.; Man, X.; Kawakatsu, T.; Doi, M. Translocation of a vesicle through a narrow hole across a membrane. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 134901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, S.I.; Braun, P.V. Molecular manipulation of microstructures: Biomaterials, ceramics, and semiconductors. Science 1997, 277, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiner, S.; Wagner, H.D. The material bone: Structure-mechanical function relations. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1998, 28, 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.A. Simulating the co-encapsulation of drugs in a “smart” core-shell-shell polymer nanoparticle. Eur. Phys. J. E 2014, 37, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, G. Rigid biological systems as models for synthetic composites. Science 2005, 310, 1144–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schexnailder, P.; Schmidt, G. Nanocomposite polymer hydrogels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorovsky, K.; Chou, L.Y.T.; Chan, W.C.W. Controlling DNA–nanoparticle serum interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13600–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.; Cho, Y.T.; Fang, N.X. Additive Manufacturing of Functional Microarchitected Reactors for Energy, Environmental, and Biological Applications. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2021, 8, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Kong, J. Integration of electrochemistry in micro-total analysis systems for biochemical assays: Recent developments. Talanta 2009, 80, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenhar, R.; Norsten, T.B.; Rotello, V.M. Polymer-mediated nanoparticle assembly: Structural control and applications. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, Y.; Urbas, A.M.; Bawendi, M.G.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Thomas, E.L. Block copolymers as photonic bandgap materials. J. Light. Technol. 1999, 17, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.K.; Qiang, X.; Mller, A.H.E. Self-Assembly of block copolymers into internally ordered microparticles. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 102, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fei, X.; Qi, P.; Lin, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Buehler, M.J.; Ling, S. Biological material interfaces as inspiration for mechanical and optical material designs. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 12279–12336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamley, I.W. Nanotechnology with soft materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1692–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockstaller, M.R.; Mickiewicz, R.A.; Thomas, E.L. Block copolymer nanocomposites: Perspectives for tailored functional materials. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, A.C.; Emrick, T.; Russell, T.P. Nanoparticle polymer composites: Where two small worlds meet. Science 2006, 314, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, L. Polymer matrix hybrid composites: The efficient way of improved performance. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, S. Polymer/carbon nanotube nano composite fibers–a review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6069–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B. Polymer-guided assembly of inorganic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 465–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoheisel, T.N.; Hur, K.; Wiesner, U.B. Block copolymer-nanoparticle hybrid self-assembly. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 40, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, J.; Ginzburg, V.V.; Balazs, A.C. Thermodynamic behavior of particle/diblock copolymer mixtures: Simulation and theory. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8085–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Thompson, R.B.; Jasnow, D.; Balazs, A. Effect of nanoscopic particles on the mesophase structure of diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 4855–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Thompson, R.B.; Jasnow, D.; Balazs, A.C. Entropically driven formation of hierarchically ordered nanocomposites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 155503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, E.; Liu, F.; Blisko, J.; Li, Y.; Tsyrenova, A.; Mort, R.; Vorst, K.; Curtzwiler, G.; Yong, X.; Jiang, S. Self-assembly in biobased nanocomposites for multifunctionality and improved performance. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4321–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Shou, Z.; Balazs, A.C. Predicting the morphologies of confined copolymer/nanoparticle mixtures. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7730–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Tong, C.; Zhu, Y. Self-consistent-field and hybrid particle-field theory simulation of confined copolymer and nanoparticle mixtures. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Tong, C.; Zhu, Y. Phase behaviors of diblock copolymer-nanoparticle films under nanopore confinement. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 094903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ye, X.; Edwards, B.J. A self-consistent field study of diblock copolymer/charged particle system morphologies for nanofiltration membranes. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 244909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevi, A.; Halivni, S.; Oded, M.; Müller, A.H.E.; Banin, U.; Shenhar, R. Co-assembly of A–B diblock copolymers with B′-type nanoparticles in thin films: Effect of copolymer composition and nanoparticle shape. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3022–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Ganesan, V.; Riggleman, R.A. Perspective: Outstanding theoretical questions in polymer-nanoparticle hybrids. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, J.; Thorkelsson, K.; Bai, P.; Rancatoreb, B.J.; Xu, T. Toward functional nanocomposites: Taking the best of nanoparticles, polymers, and small molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2654–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombly, D.M.; Pryamitsyn, V.; Ganesan, V. Interfacial properties of statistical copolymer brushes in contact with homopolymer melts. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 154903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, R.; Pelissetto, A.; Randisi, F. Thermodynamics of star polymer solutions: A coarse-grained study. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 146, 244908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chremos, A.; Douglas, J.F. Polyelectrolyte association and solvation. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 163305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, M.; Perahia, D.; Grest, G.S. Effects of interaction strength of associating groups on linear and star polymer dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 074903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.P.; Prunty, T.M.; O’Neil, C.M. All-or-none folding of a flexible polymer chain in cylindrical nanoconfinement. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 094901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Ma, Y. Phase behavior of nanoparticle–copolymer films confined between polymer-grafted surfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.B.; Ginzburg, V.V.; Matsen, M.W.; Balazs, A.C. Predicting the mesophases of copolymer-nanoparticle composites. Science 2001, 292, 2469–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.B.; Ginzburg, V.V.; Matsen, M.W.; Balazs, A. Block copolymer-directed assembly of nanoparticles: Forming mesoscopically ordered hybrid materials. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liang, H.; Shi, A.C. Origin of microstructures from confined asymmetric diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 7329–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y. Morphology and phase diagram of complex block copolymers: ABC linear triblock copolymers. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 031803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, P. A density functional theory of melting. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, P.; Evans, R. A simple density functional theory for inhomogeneous liquids: Wetting by gas at a solid-liquid interface. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnahan, N.F.; Starling, K.E. Equation of state for nonattracting rigid spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, P.; Matsen, M.W. Efficiency of pseudo-spectral algorithms with Anderson mixing for the SCFT of periodic block-copolymer phases. Eur. Phys. J. E 2011, 34, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liang, H.; Shi, A.C. Microstructures of a cylinder-forming diblock copolymer under spherical confinement. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8938–8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Lin, S. Self-assembly behavior of amphiphilic block copolymer/nanoparticle mixture in dilute solution studied by self-consistent-field theory/density functional theory. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 5582–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Liao, Q.; Qin, L. Phase Behaviors of ABA Star Polymer and Nanoparticles Confined in a Sphere with Soft Inner Surface. Polymers 2022, 14, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081610
Sun M, Zhang Z, Li Y, Li W, Liao Q, Qin L. Phase Behaviors of ABA Star Polymer and Nanoparticles Confined in a Sphere with Soft Inner Surface. Polymers. 2022; 14(8):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081610
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Minna, Zhiwei Zhang, Ying Li, Wen Li, Qingwei Liao, and Lei Qin. 2022. "Phase Behaviors of ABA Star Polymer and Nanoparticles Confined in a Sphere with Soft Inner Surface" Polymers 14, no. 8: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081610
APA StyleSun, M., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Li, W., Liao, Q., & Qin, L. (2022). Phase Behaviors of ABA Star Polymer and Nanoparticles Confined in a Sphere with Soft Inner Surface. Polymers, 14(8), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081610






