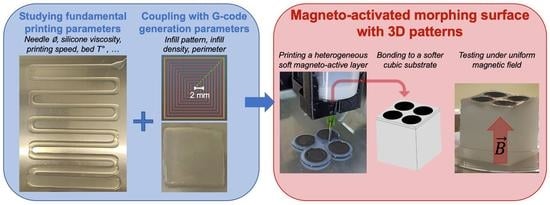
Towards 4D Printing of Very Soft Heterogeneous Magnetoactive Layers for Morphing Surface Applications via Liquid Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. D Printer
2.2. Syringes
2.3. Silicones, Particles, and Sample Preparation
2.4. Software
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Printing Properties of Silicone Lines
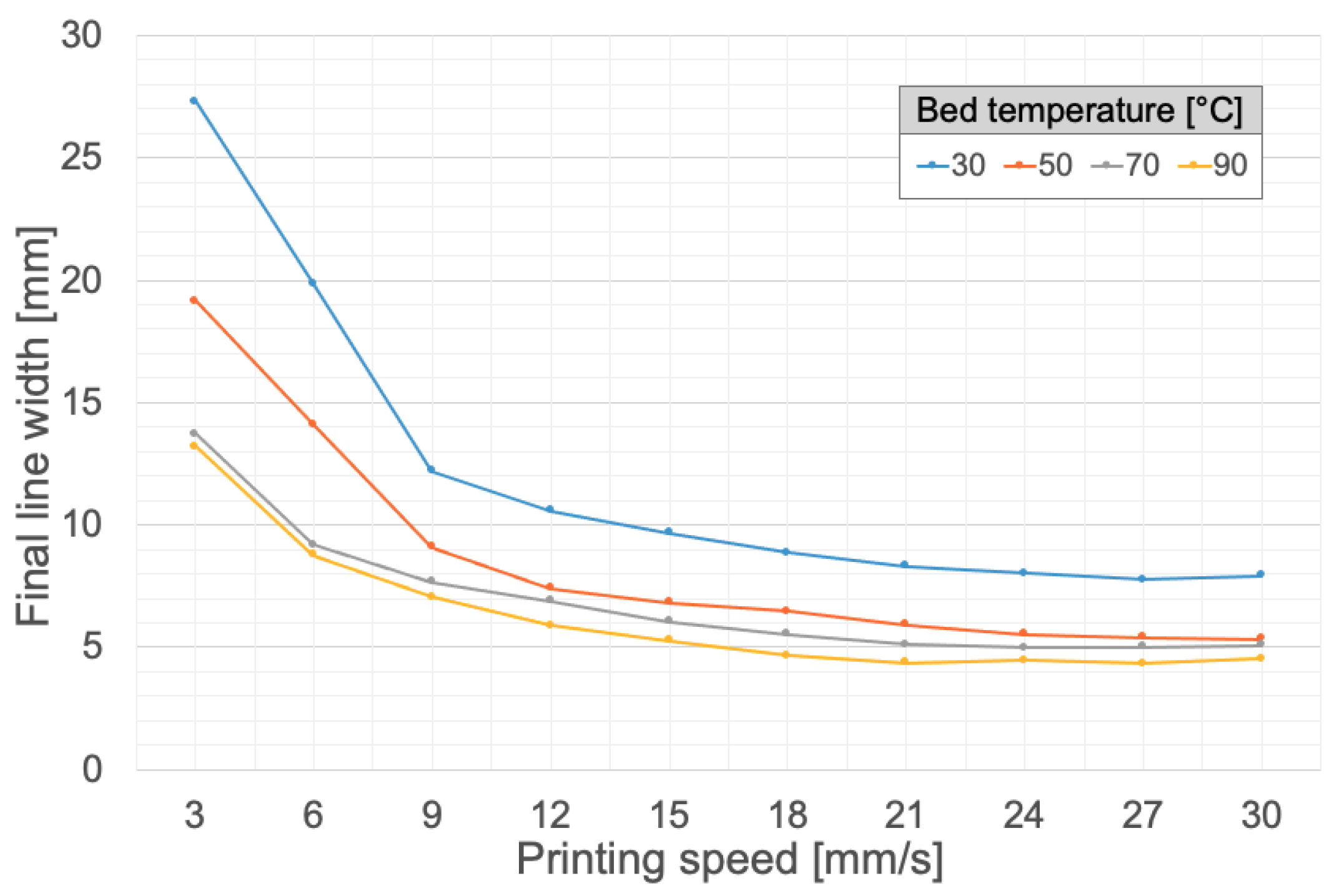
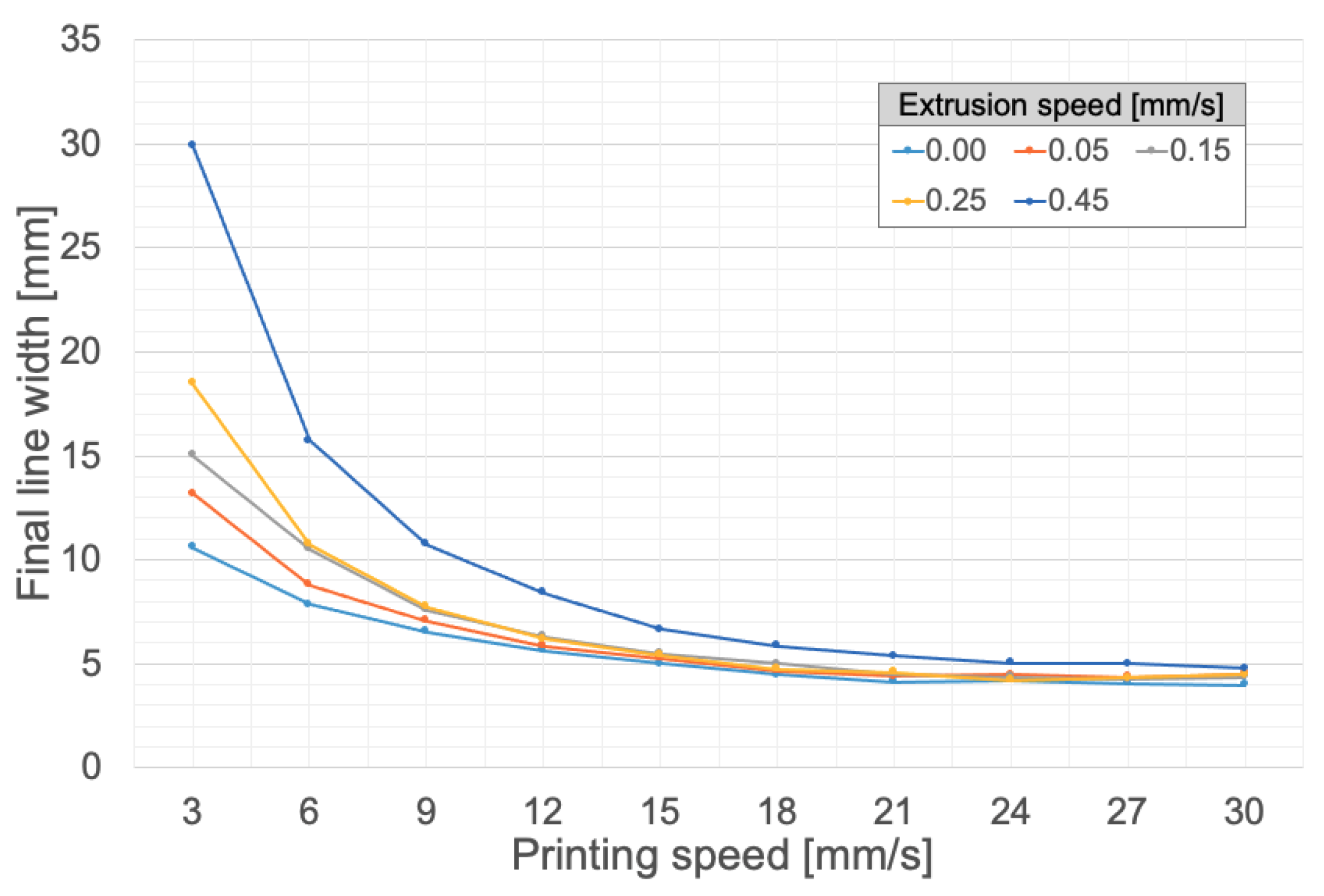
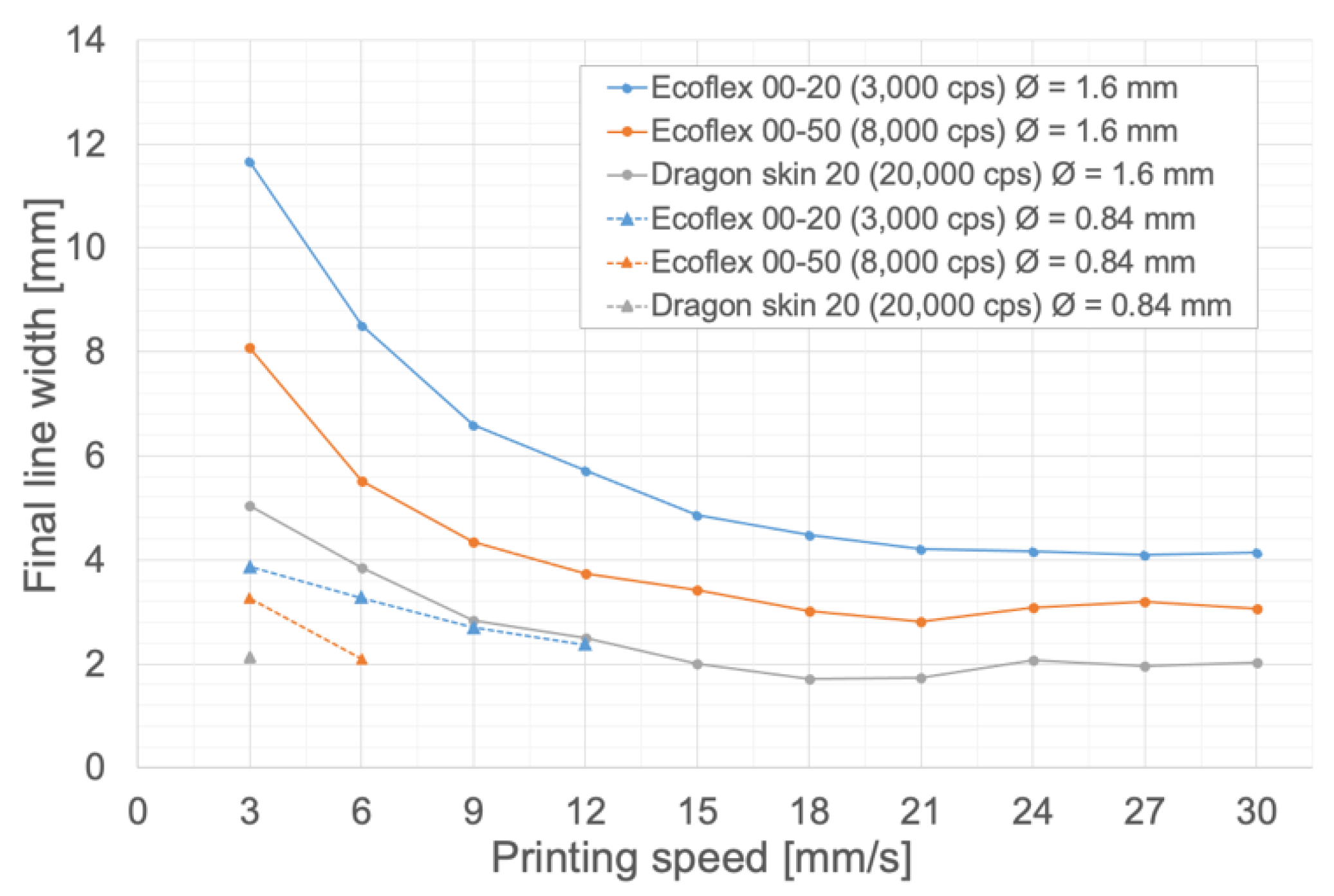
3.1.1. Influence of Printing Speed, Extrusion Speed, and Bed Temperature on the Final Line Width
3.1.2. Influence of Silicone Viscosity and Needle Diameter on the Final Line Width
3.1.3. Influence of Printing Height and Elapsed Time on the Final Line Width
3.2. Printing of Silicone Geometric Shapes
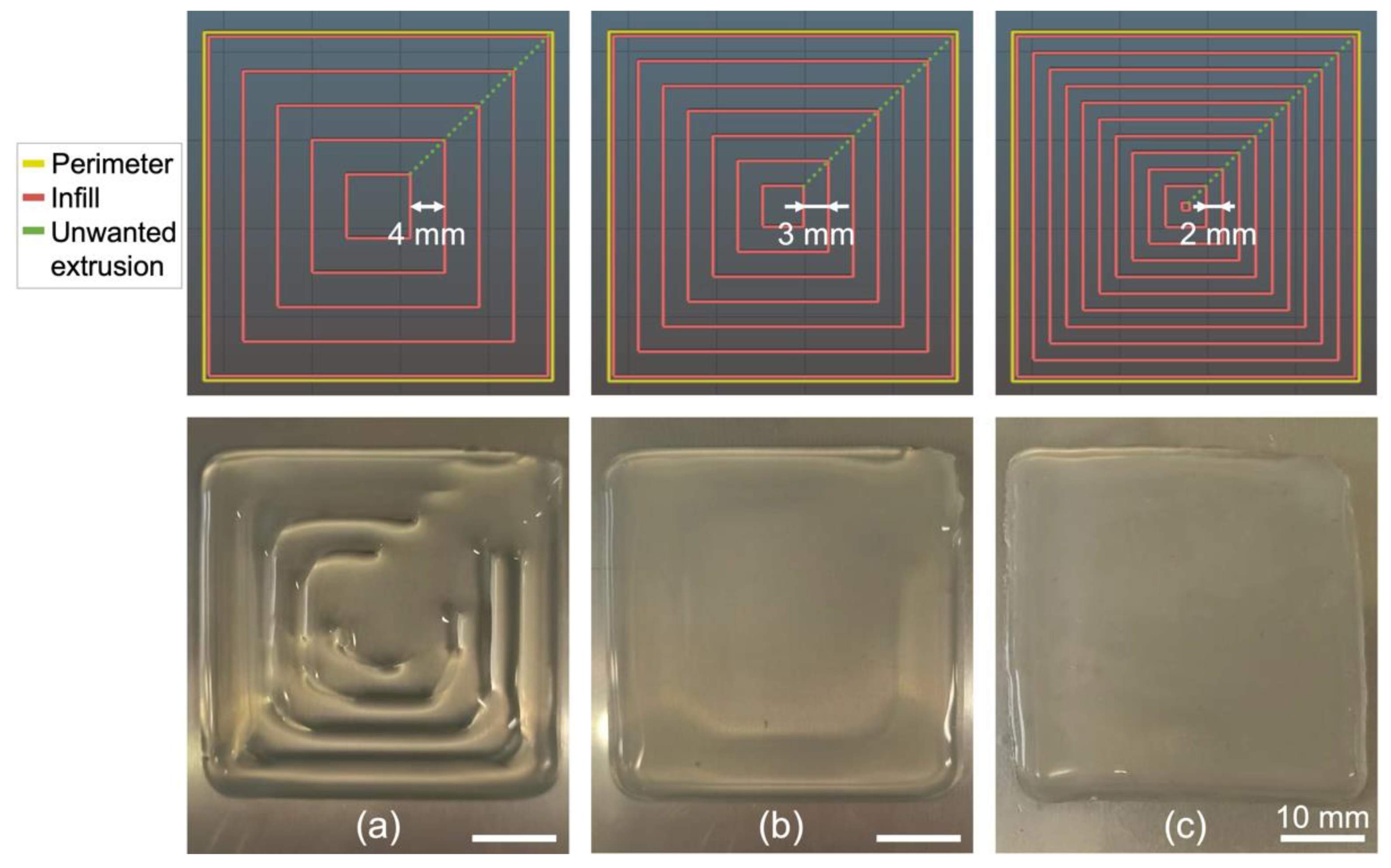
3.2.1. Influence of Infill Density and Infill Pattern on the Printing of a Square
3.2.2. Influence of Infill Pattern on the Printing of a Disc
3.3. Printing of a Heterogenous Magnetoactive Surface
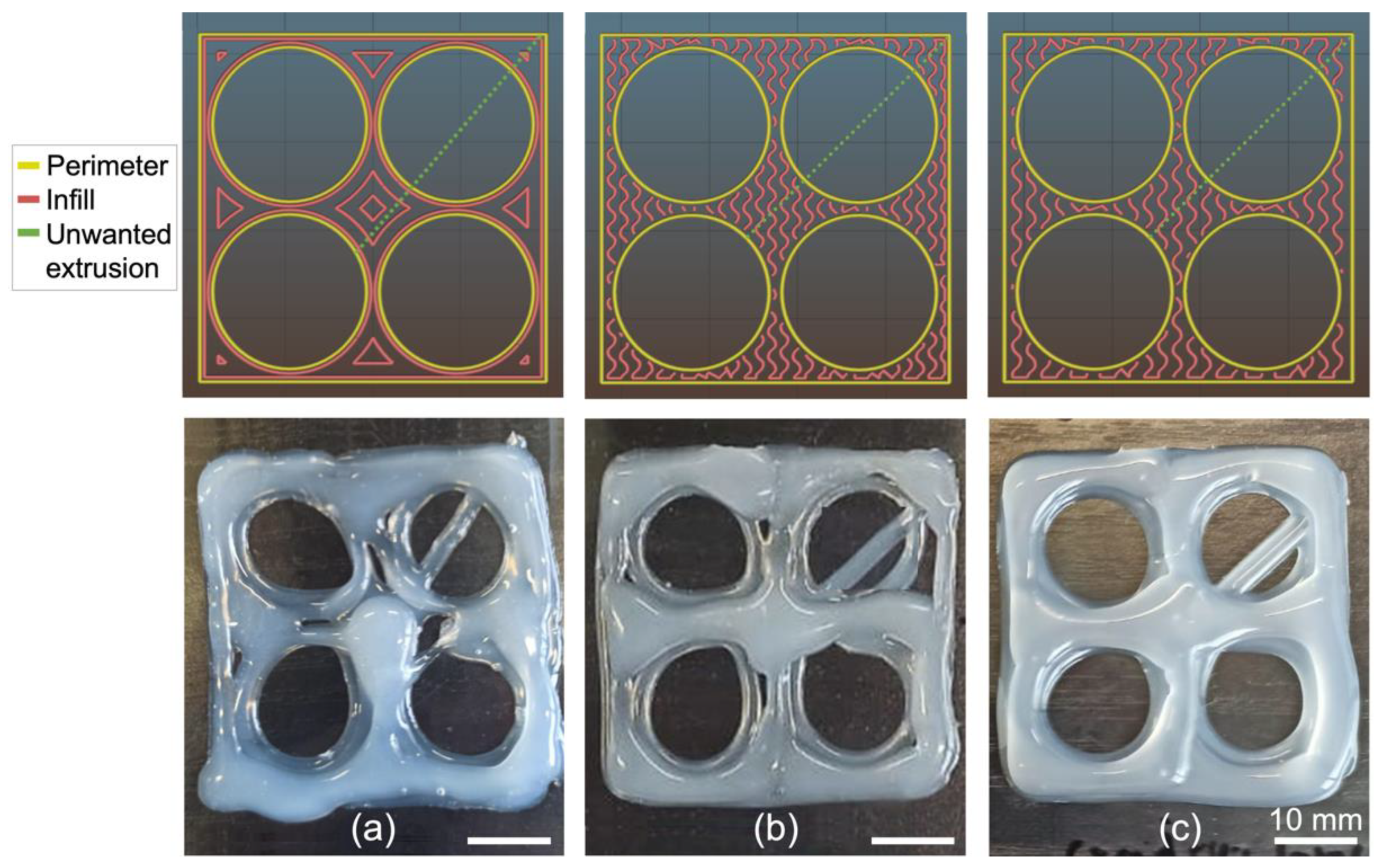
3.3.1. Influence of Infill Pattern on the Printing of a Square with Holes
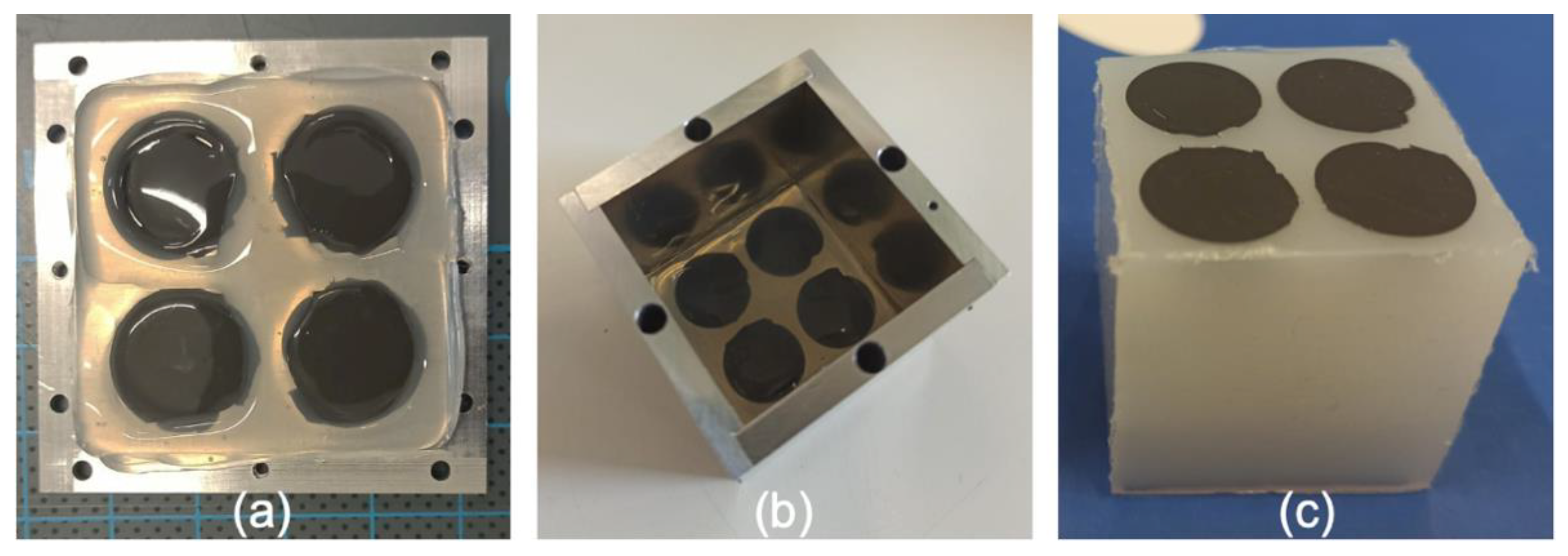
3.3.2. Printing of a Sequence of Four Discs
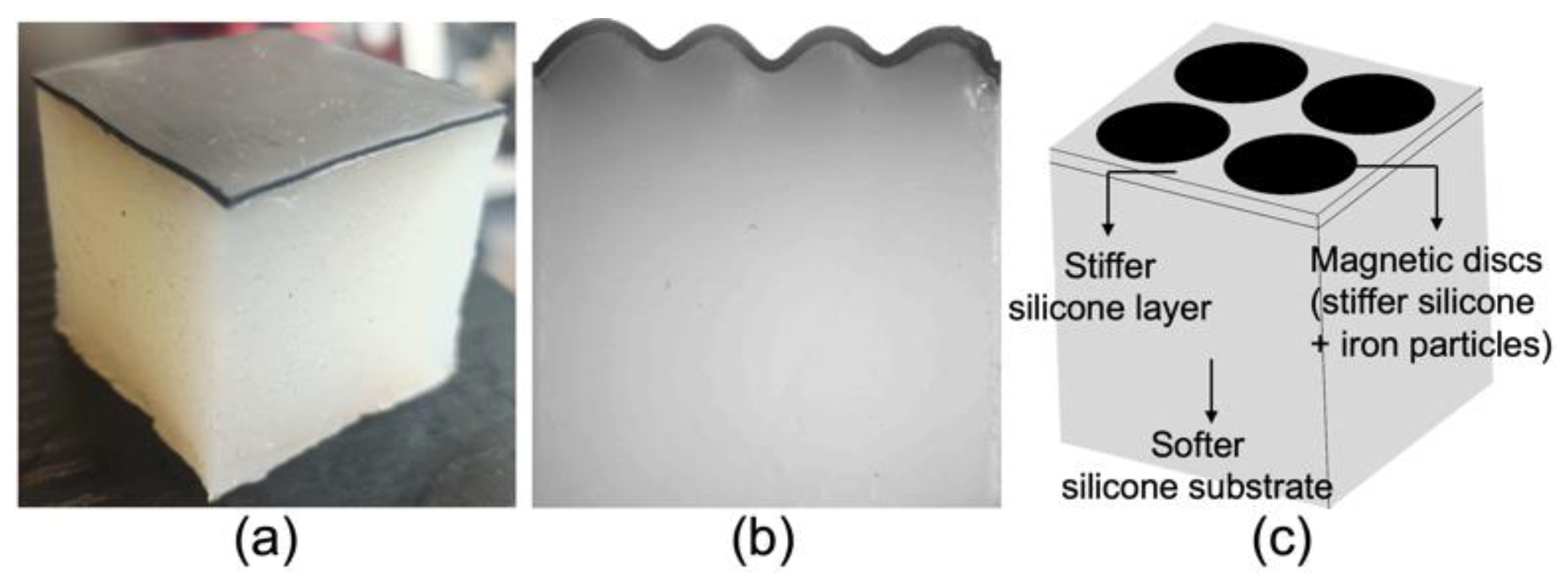
3.3.3. Printing of a Heterogeneous Magnetoactive Layer and Final Assembly
3.4. Testing under Magnetic Field and Comparison to a 2D Numerical Simulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Xu, Y. Magnetorheological Elastomers: Materials and Applications. In Smart and Functional Soft Materials; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 147–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Hu, W.; Ze, Q.; Sitti, M.; Zhao, R. Multifunctional Magnetic Soft Composites: A Review. Multifunct. Mater. 2020, 3, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarini, S.; Hossain, M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D. Recent Advances in Hard-Magnetic Soft Composites: Synthesis, Characterisation, Computational Modelling, and Applications. Compos. Struct. 2022, 279, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, J.M.; Clark, S.M.; Schlotter, W.F.; Nichols, M.E. Magnetostrictive Phenomena in Magnetorheological Elastomers. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2002, 16, 2412–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Read, D.; Gulley, G. Magnetostriction of Field-Structured Magnetoelastomers. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 51507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodelot, L.; Voropaieff, J.-P.; Pössinger, T. Experimental Investigation of the Coupled Magneto-Mechanical Response in Magnetorheological Elastomers. Exp. Mech. 2018, 58, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, X.; Dong, X.; Ou, J. Magnetostrictive Effect of Magnetorheological Elastomer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Semerenko, D.A. Magnetodeformational Effect of the Magnetoactive Elastomer and Its Possible Applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 412, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, J.M.; Nichols, M.E.; Elie, L.D.; Clark, S.M. Controllable-Stiffness Components Based on Magnetorheological Elastomers. In Smart Structures and Materials 2000: Smart Structures and Integrated Systems; Wereley, N.M., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 3985, pp. 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Farshad, M.; le Roux, M. A New Active Noise Abatement Barrier System. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, F.C.; Pao, Y.-H. Magnetoelastic Buckling of a Thin Plate. J. Appl. Mech. 1968, 35, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbal, F.; Wang, Y.; Lyonnet, F.; Bacri, J.-C.; Hocquet, T.; Devaud, M. A Refined Theory of Magnetoelastic Buckling Matches Experiments with Ferromagnetic and Superparamagnetic Rods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7135–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lum, G.Z.; Ye, Z.; Dong, X.; Marvi, H.; Erin, O.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. Shape-Programmable Magnetic Soft Matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6007–E6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Chung, S.E.; Choi, S.-E.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S. Programming Magnetic Anisotropy in Polymeric Microactuators. Nat. Mat. 2011, 10, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Lum, G.Z.; Mastrangeli, M.; Sitti, M. Small-Scale Soft-Bodied Robot with Multimodal Locomotion. Nature 2018, 554, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Salehizadeh, M.; Onaizah, O.; Diller, E. Millimeter-Scale Flexible Robots with Programmable Three-Dimensional Magnetization and Motions. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaav4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Kim, Y.; Chester, S.A.; Sharma, P.; Zhao, X. Mechanics of Hard-Magnetic Soft Materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 124, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Du, H. A State-of-the-Art Review on Magnetorheological Elastomer Devices. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, R.; Choi, S.-B.; Ferdaus, M.M. A State of Art on Magneto-Rheological Materials and Their Potential Applications. J. Intel. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 2051–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bira, N.; Dhagat, P.; Davidson, J.R. A Review of Magnetic Elastomers and Their Role in Soft Robotics. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, R.D.; Dubé, M.; Therriault, D. Three-Dimensional Printing of Multifunctional Nanocomposites: Manufacturing Techniques and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5794–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truby, R.L.; Lewis, J.A. Printing Soft Matter in Three Dimensions. Nature 2016, 540, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahati, M.; Ahmadvand, P.; Safaee, S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lyu, Z.; Chen, R.; Li, L.; Lin, Y. Smart Polymers and Nanocomposites for 3D and 4D Printing. Mater. Today 2020, 40, 215–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmero, E.M.; Rial, J.; de Vicente, J.; Camarero, J.; Skårman, B.; Vidarsson, H.; Larsson, P.-O.; Bollero, A. Development of Permanent Magnet MnAlC/Polymer Composites and Flexible Filament for Bonding and 3D-Printing Technologies. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018, 19, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Lv, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Leng, J. 4D-Printed Biodegradable and Remotely Controllable Shape Memory Occlusion Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1906569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Fu, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Gan, R.; Yu, M. Versatile Magnetorheological Plastomer with 3D Printability, Switchable Mechanics, Shape Memory, and Self-Healing Capacity. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 183, 107817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xuan, S.; Sun, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Gong, X. 3D Printing Magnetic Actuators for Biomimetic Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 30127–30136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Yan, C.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F. Multimaterials 3D Printing for Free Assembly Manufacturing of Magnetic Driving Soft Actuator. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Baynojir Joyee, E.; Pan, Y. Correlation Between Microscale Magnetic Particle Distribution and Magnetic-Field-Responsive Performance of Three-Dimensional Printed Composites. J. Micro Nano Manuf. 2017, 6, 010904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lantean, S.; Barrera, G.; Pirri, C.F.; Tiberto, P.; Sangermano, M.; Roppolo, I.; Rizza, G. 3D Printing of Magnetoresponsive Polymeric Materials with Tunable Mechanical and Magnetic Properties by Digital Light Processing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratson, G.M.; Xu, M.; Lewis, J.A. Direct Writing of Three-Dimensional Webs. Nature 2004, 428, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.A. Direct Ink Writing of 3D Functional Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yuk, H.; Zhao, R.; Chester, S.A.; Zhao, X. Printing Ferromagnetic Domains for Untethered Fast-Transforming Soft Materials. Nature 2018, 558, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Yang, W.; Wang, R.; Gao, S.; Li, B.; Li, Q. 4D Printing of Complex Structures with a Fast Response Time to Magnetic Stimulus. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 36435–36442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Parada, G.A.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X. Ferromagnetic Soft Continuum Robots. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaax7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, S.; Okello, L.B.; Golbasi, N.; Hankwitz, J.P.; Liu, J.A.-C.; Tracy, J.B.; Velev, O.D. 3D-Printed Silicone Soft Architectures with Programmed Magneto-Capillary Reconfiguration. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yi, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L. 4D Printing of Magnetoactive Soft Materials for On-Demand Magnetic Actuation Transformation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4174–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.K.; Paudel, M.; Li, L. Development of Hybrid Magnetorheological Elastomers by 3D Printing. Polymer 2018, 149, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.K.; Paudel, M.; Li, L. Line-Patterned Hybrid Magnetorheological Elastomer Developed by 3D Printing. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 31, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, T.J.; Hudson, A.; Pusch, K.; Lee, A.; Feinberg, A.W. 3D Printing PDMS Elastomer in a Hydrophilic Support Bath via Freeform Reversible Embedding. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plott, J.; Shih, A. The Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing of Moisture-Cured Silicone Elastomer with Minimal Void for Pneumatic Actuators. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liravi, F.; Toyserkani, E. A Hybrid Additive Manufacturing Method for the Fabrication of Silicone Bio-Structures: 3D Printing Optimization and Surface Characterization. Mater. Des. 2018, 138, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, E.; Pan, H.M.; Sing, S.L.; Bajpai, R.; Song, J.; Yeong, W.Y. 3D Direct Printing of Silicone Meniscus Implant Using a Novel Heat-Cured Extrusion-Based Printer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiQ 320–3D Printing from Liquid Silicone. Available online: https://www.innovatiq.com/en/products/3d-printers/liq-320/ (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Feng, J.; Xuan, S.; Lv, Z.; Pei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, X. Magnetic-Field-Induced Deformation Analysis of Magnetoactive Elastomer Film by Means of DIC, LDV, and FEM. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3246–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikher, Y.L.; Stolbov, O.V.; Stepanov, G.V. Deformation of a Circular Ferroelastic Membrane in a Uniform Magnetic Field. Tech. Phys. 2008, 53, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, C.; Bodelot, L.; Danas, K. Experiments and Numerical Implementation of a Boundary Value Problem Involving a Magnetorheological Elastomer Layer Subjected to a Nonuniform Magnetic Field. J. Appl. Mech. 2021, 88, 071004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarra, E.; Bodelot, L.; Danas, K. Two-Field Surface Pattern Control via Marginally Stable Magnetorheological Elastomers. Soft Matter. 2017, 13, 6576–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psarra, E.; Bodelot, L.; Danas, K. Wrinkling to Crinkling Transitions and Curvature Localization in a Magnetoelastic Film Bonded to a Non-Magnetic Substrate. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 133, 103734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danas, K.; Kankanala, S.V.; Triantafyllidis, N. Experiments and Modeling of Iron-Particle-Filled Magnetorheological Elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2012, 60, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mateos, M.A.; Gonzalez-Rico, J.; Nunez-Sardinha, E.; Gomez-Cruz, C.; Lopez-Donaire, M.L.; Lucarini, S.; Arias, A.; Muñoz-Barrutia, A.; Velasco, D.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D. Magneto-Mechanical System to Reproduce and Quantify Complex Strain Patterns in Biological Materials. Appl. Mat. Today 2022, 27, 101437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Silicone | Working Time (min) | Mixing Ratio | Mixed Viscosity (cps) | Shore Hardness (ASTM D-2240) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecoflex 00-20 | 30 | 1A:1B | 3000 | 00-20 |
| Ecoflex 00-50 | 18 | 1A:1B | 8000 | 00-50 |
| Ecoflex 00-10 | 30 | 1A:1B | 14,000 | 00-10 |
| Dragon Skin 20 | 25 | 1A:1B | 20,000 | 20A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brusa da Costa Linn, L.; Danas, K.; Bodelot, L. Towards 4D Printing of Very Soft Heterogeneous Magnetoactive Layers for Morphing Surface Applications via Liquid Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2022, 14, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091684
Brusa da Costa Linn L, Danas K, Bodelot L. Towards 4D Printing of Very Soft Heterogeneous Magnetoactive Layers for Morphing Surface Applications via Liquid Additive Manufacturing. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091684
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrusa da Costa Linn, Lucas, Kostas Danas, and Laurence Bodelot. 2022. "Towards 4D Printing of Very Soft Heterogeneous Magnetoactive Layers for Morphing Surface Applications via Liquid Additive Manufacturing" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091684
APA StyleBrusa da Costa Linn, L., Danas, K., & Bodelot, L. (2022). Towards 4D Printing of Very Soft Heterogeneous Magnetoactive Layers for Morphing Surface Applications via Liquid Additive Manufacturing. Polymers, 14(9), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091684