Effects of Input Parameter Range on the Accuracy of Artificial Neural Network Prediction for the Injection Molding Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
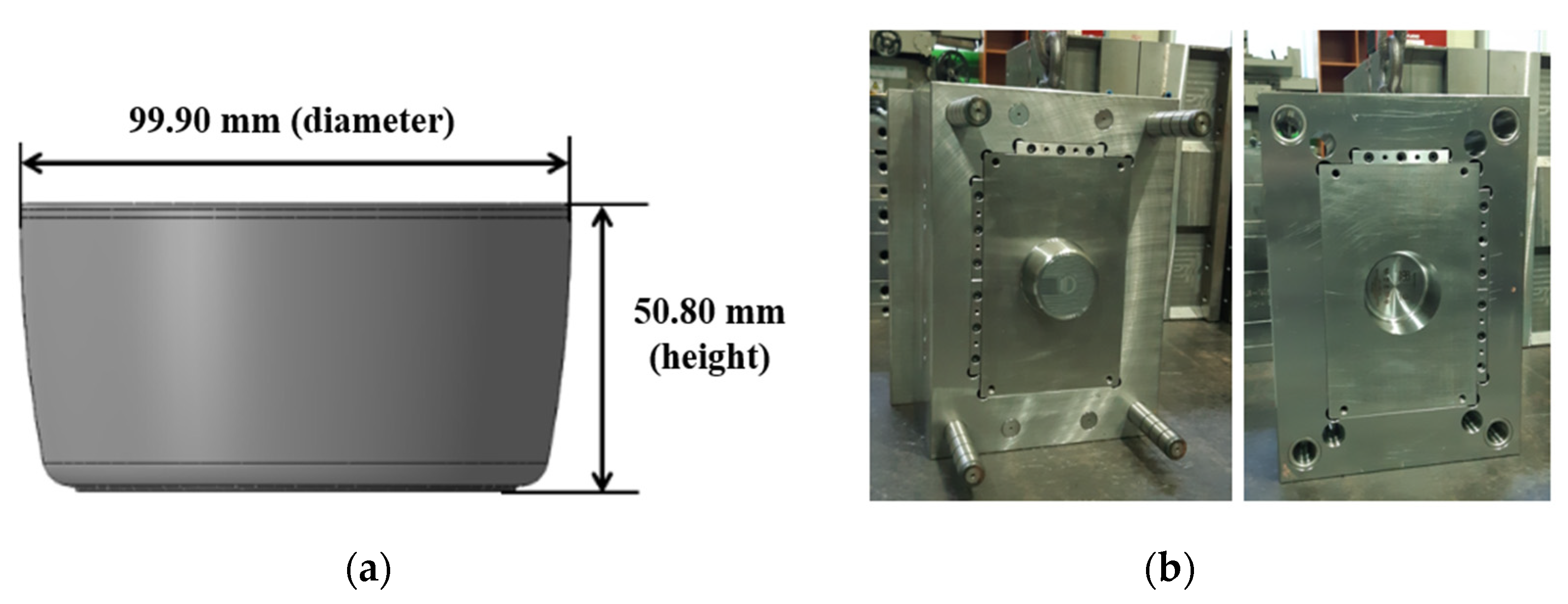
2.1. Material and Molding Equipment
2.2. Experimental Conditions
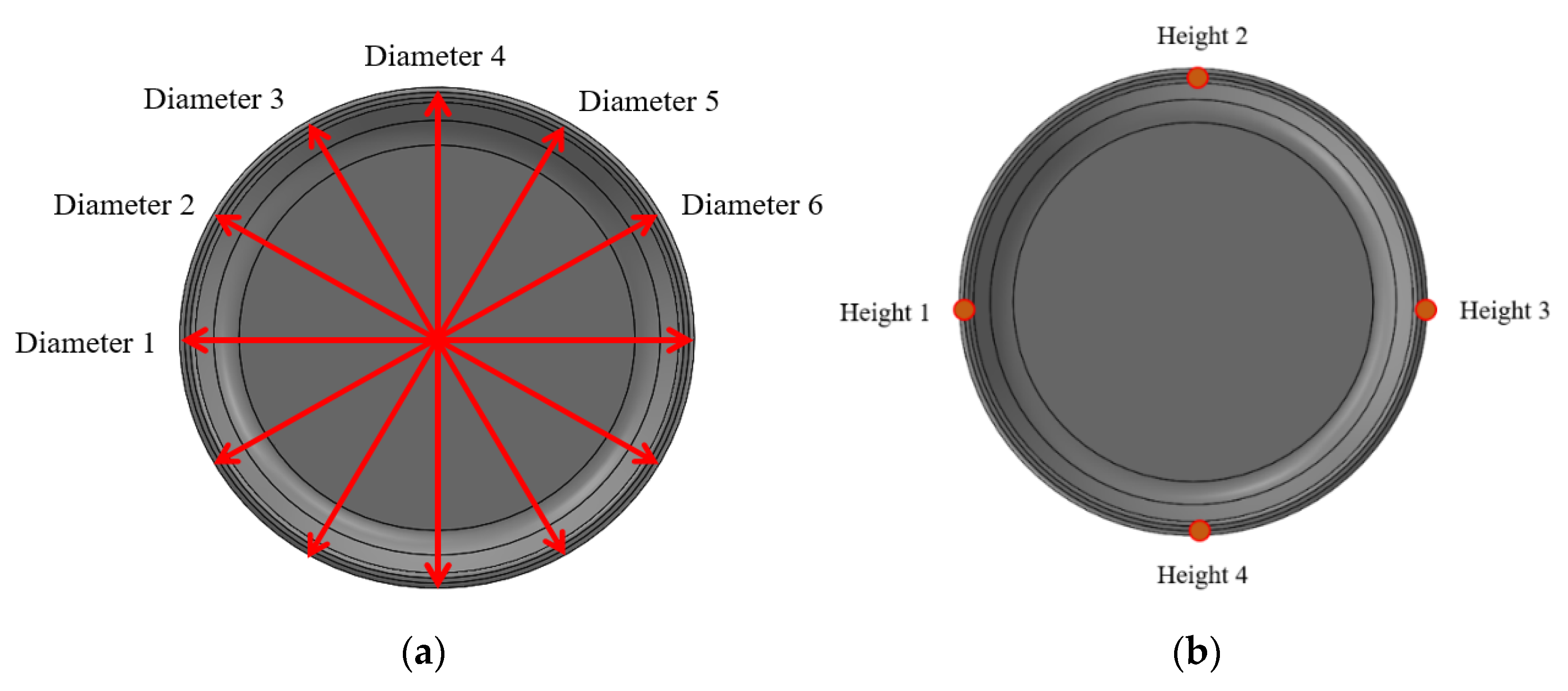
2.3. Measurement of Product Qualities
3. Building the Model to Predict the Product Qualities
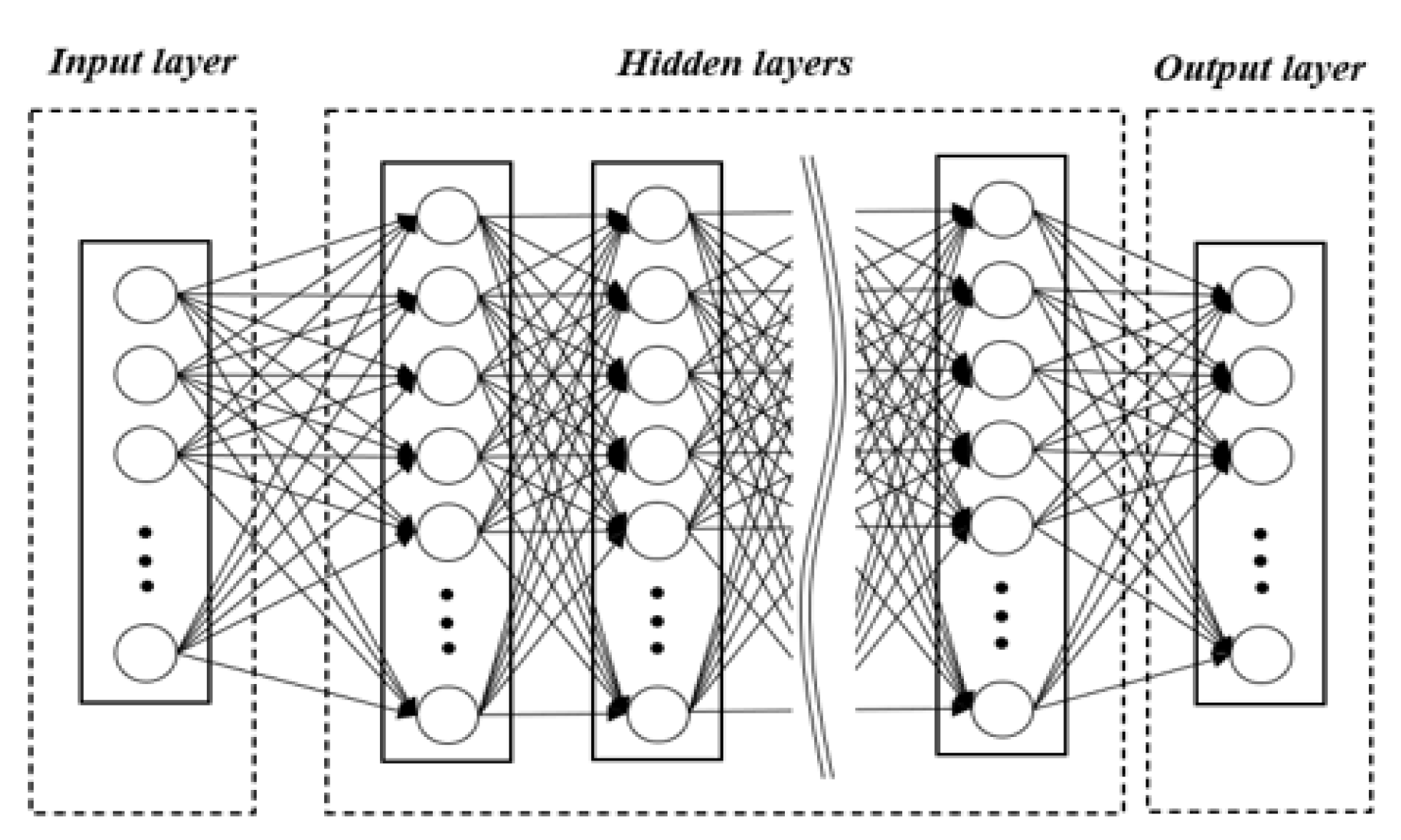
3.1. Artificial Neural Network
3.2. The Search for Optimal Hyper-Parameters
4. Results
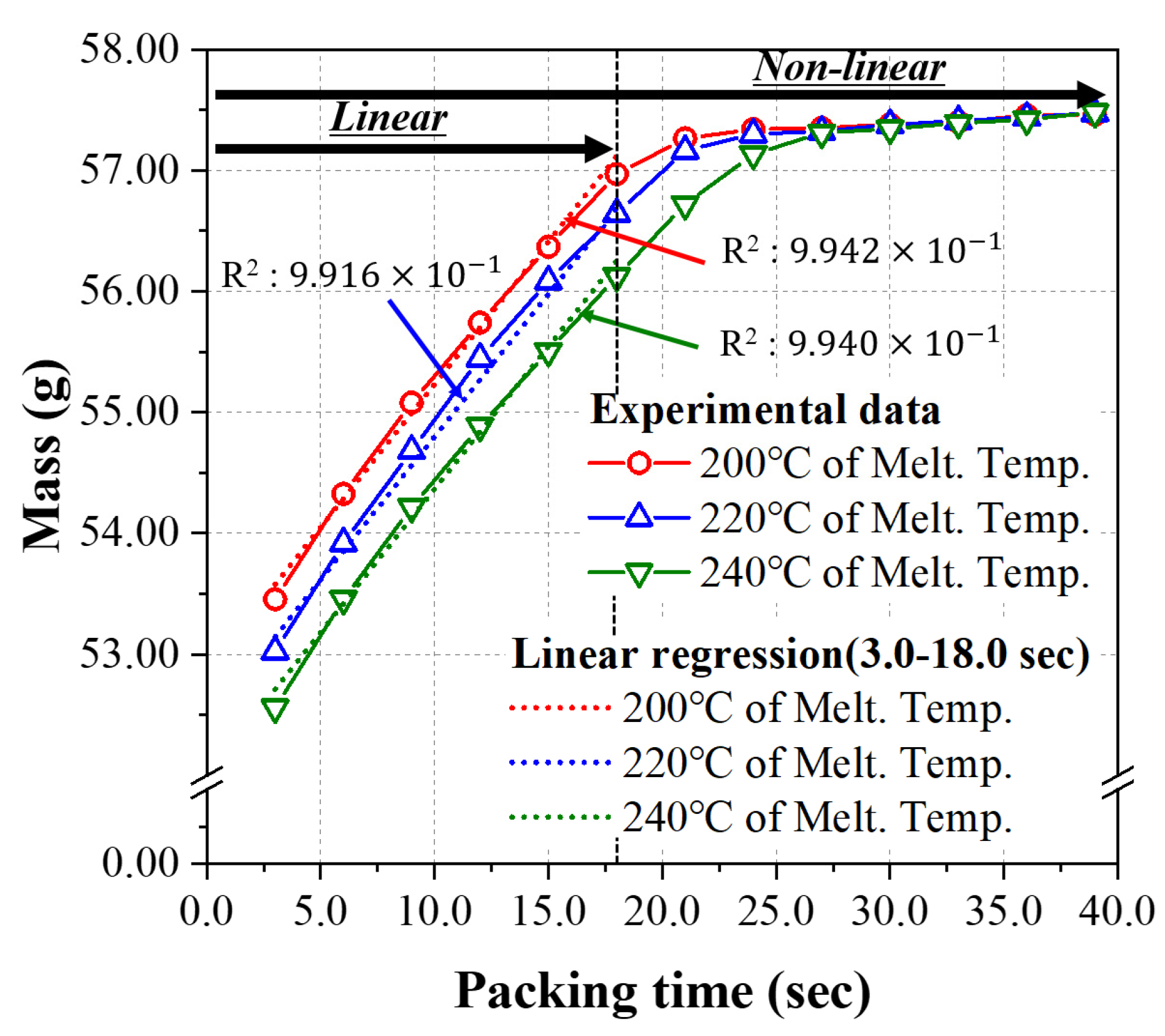
4.1. Injection Molding Experiment
4.2. The Prediction Models Learned by the Linear Relationship Group (Packing Time ≤ 18.0 s)
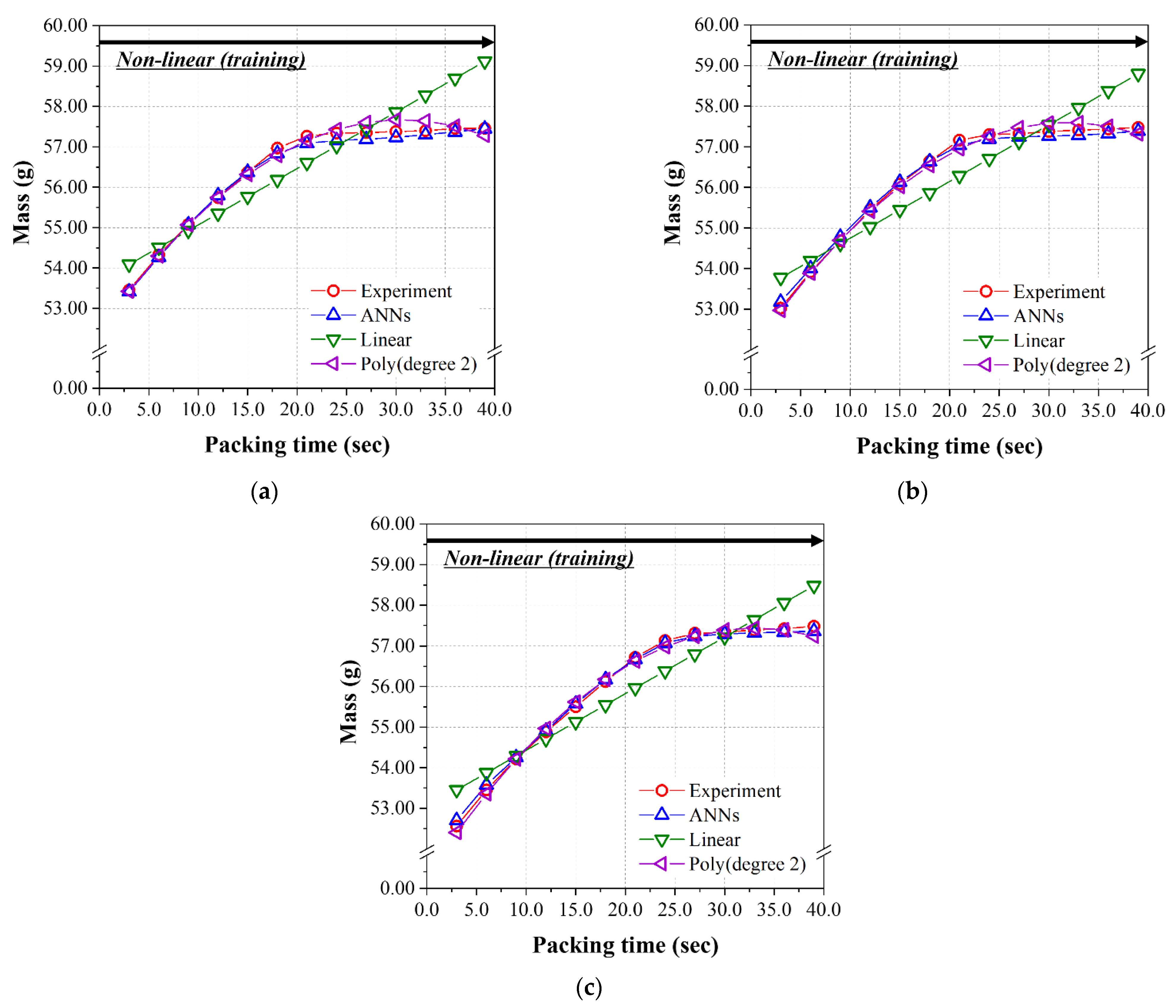
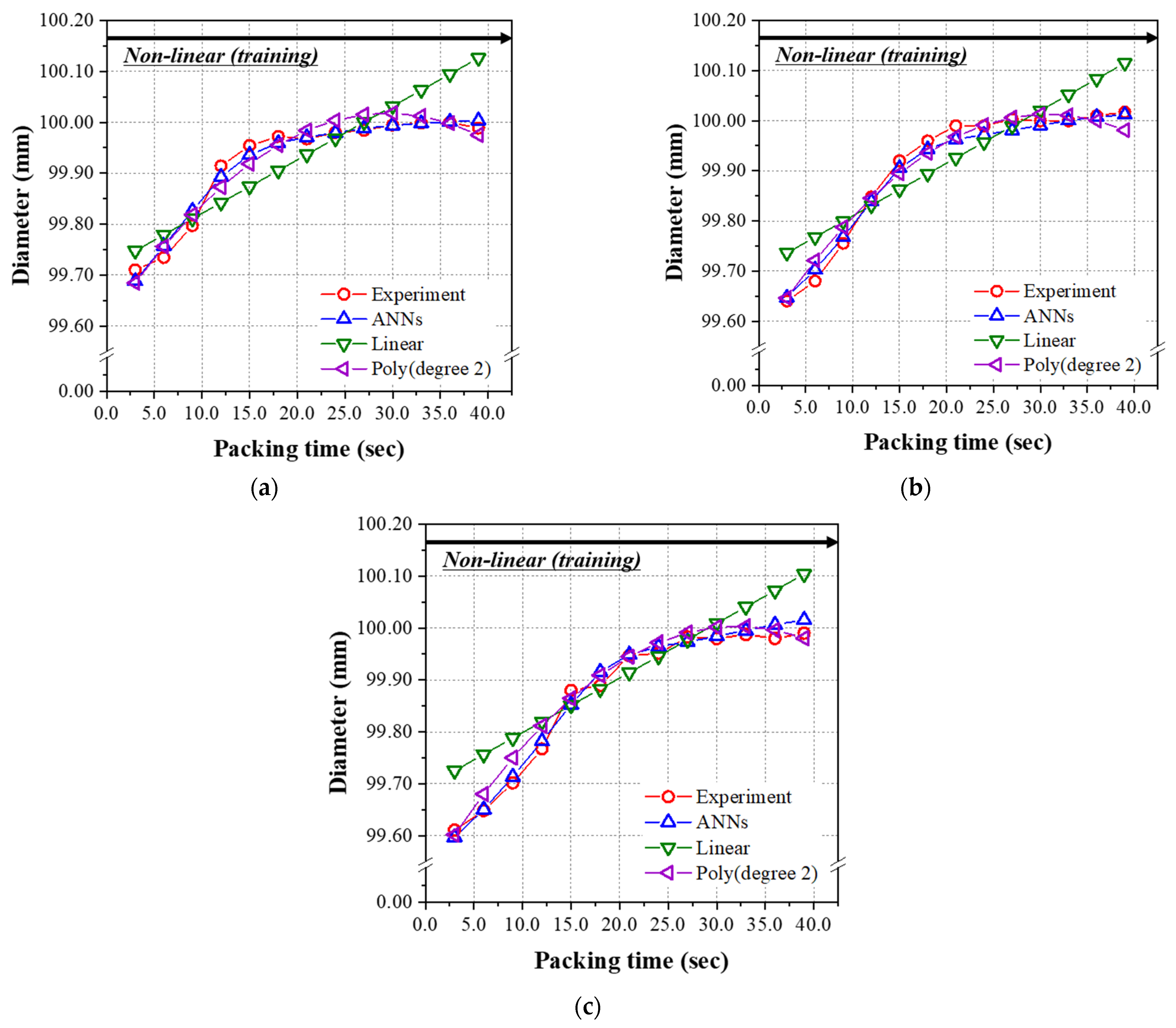
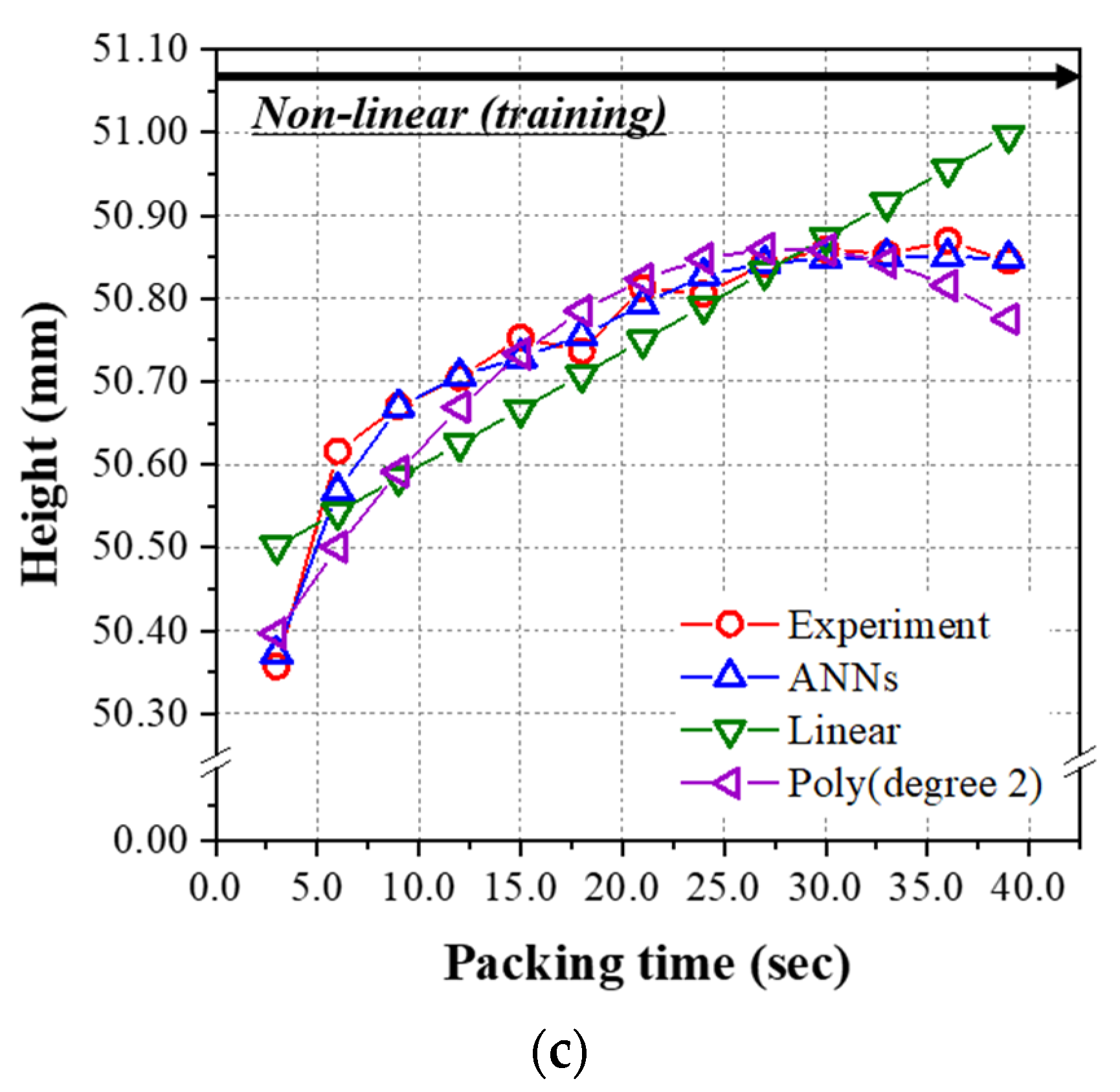
4.3. The Prediction Model Learned by the Non-Linear Relationship Group
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Mass (g) | Diameter (mm) | Height (mm) | Note | No. | Mass (g) | Diameter (mm) | Height (mm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 54.05 | 99.77 | 50.48 | L27 | 26 | 54.08 | 99.85 | 50.50 | Random |
| 2 | 55.89 | 99.88 | 50.72 | L27 | 27 | 55.29 | 99.93 | 50.68 | Random |
| 3 | 56.96 | 99.88 | 50.82 | L27 | 28 | 56.16 | 99.91 | 50.78 | Random |
| 4 | 54.33 | 99.73 | 50.59 | L27 | 29 | 56.22 | 99.92 | 50.79 | Random |
| 5 | 55.72 | 99.90 | 50.73 | L27 | 30 | 56.05 | 99.93 | 50.78 | Random |
| 6 | 57.17 | 99.95 | 50.88 | L27 | 31 | 54.11 | 99.79 | 50.51 | Random |
| 7 | 54.13 | 99.74 | 50.52 | L27 | 32 | 54.44 | 99.83 | 50.56 | Random |
| 8 | 55.69 | 99.92 | 50.77 | L27 | 33 | 57.07 | 100.00 | 50.92 | Random |
| 9 | 57.15 | 100.00 | 50.92 | L27 | 34 | 53.96 | 99.73 | 50.49 | Random |
| 10 | 54.24 | 99.69 | 50.57 | L27 | 35 | 57.06 | 99.93 | 50.90 | Random |
| 11 | 55.99 | 99.94 | 50.82 | L27 | 36 | 54.68 | 99.84 | 50.59 | Random |
| 12 | 57.31 | 100.02 | 50.95 | L27 | 37 | 55.49 | 99.86 | 50.74 | Random |
| 13 | 53.22 | 99.76 | 50.43 | L27 | 38 | 54.07 | 99.79 | 50.51 | Random |
| 14 | 54.86 | 99.90 | 50.61 | L27 | 39 | 56.02 | 99.99 | 50.75 | Random |
| 15 | 55.97 | 99.91 | 50.74 | L27 | 40 | 56.04 | 99.96 | 50.78 | Random |
| 16 | 53.75 | 99.77 | 50.45 | L27 | 41 | 54.92 | 99.89 | 50.65 | Random |
| 17 | 55.25 | 99.88 | 50.67 | L27 | 42 | 56.93 | 100.01 | 50.92 | Random |
| 18 | 56.22 | 99.89 | 50.77 | L27 | 43 | 56.53 | 100.02 | 50.85 | Random |
| 19 | 53.38 | 99.64 | 50.45 | L27 | 44 | 55.58 | 99.96 | 50.75 | Random |
| 20 | 54.87 | 99.92 | 50.67 | L27 | 45 | 56.12 | 100.02 | 50.81 | Random |
| 21 | 56.30 | 100.02 | 50.86 | L27 | 46 | 54.31 | 99.81 | 50.56 | Random |
| 22 | 53.89 | 99.71 | 50.51 | L27 | 47 | 53.52 | 99.79 | 50.43 | Random |
| 23 | 55.22 | 99.94 | 50.73 | L27 | 48 | 54.73 | 99.94 | 50.61 | Random |
| 24 | 56.60 | 100.05 | 50.92 | L27 | 49 | 54.47 | 99.80 | 50.61 | Random |
| 25 | 52.64 | 99.66 | 50.26 | L27 | 50 | 53.80 | 99.78 | 50.52 | Random |
| No. | Mass (g) | Diameter (mm) | Height (mm) | No. | Mass (g) | Diameter (mm) | Height (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 | 53.46 | 99.71 | 50.33 | 71 | 57.30 | 99.99 | 50.85 |
| 52 | 54.33 | 99.73 | 50.59 | 72 | 57.32 | 100.00 | 50.85 |
| 53 | 55.08 | 99.80 | 50.68 | 73 | 57.38 | 100.00 | 50.86 |
| 54 | 55.74 | 99.91 | 50.68 | 74 | 57.41 | 100.00 | 50.87 |
| 55 | 56.37 | 99.95 | 50.76 | 75 | 57.44 | 100.01 | 50.85 |
| 56 | 56.97 | 99.97 | 50.82 | 76 | 57.48 | 100.02 | 50.87 |
| 57 | 57.27 | 99.97 | 50.82 | 77 | 52.56 | 99.61 | 50.36 |
| 58 | 57.34 | 99.98 | 50.83 | 78 | 53.46 | 99.65 | 50.52 |
| 59 | 57.35 | 99.98 | 50.86 | 79 | 54.22 | 99.70 | 50.67 |
| 60 | 57.38 | 99.99 | 50.81 | 80 | 54.89 | 99.77 | 50.70 |
| 61 | 57.40 | 100.00 | 50.79 | 81 | 55.51 | 99.88 | 50.75 |
| 62 | 57.46 | 100.00 | 50.81 | 82 | 56.13 | 99.89 | 50.74 |
| 63 | 57.46 | 99.99 | 50.84 | 83 | 56.72 | 99.95 | 50.81 |
| 64 | 53.03 | 99.64 | 50.34 | 84 | 57.14 | 99.95 | 50.81 |
| 65 | 53.92 | 99.68 | 50.59 | 85 | 57.31 | 99.98 | 50.84 |
| 66 | 54.68 | 99.76 | 50.67 | 86 | 57.35 | 99.98 | 50.86 |
| 67 | 55.45 | 99.85 | 50.70 | 87 | 57.39 | 99.99 | 50.85 |
| 68 | 56.08 | 99.92 | 50.74 | 88 | 57.42 | 99.98 | 50.87 |
| 69 | 56.64 | 99.96 | 50.83 | 89 | 57.48 | 99.99 | 50.85 |
| 70 | 57.16 | 99.99 | 50.83 |
References
- Rosato, D.V.; Rosato, M.G. Injection Molding Handbook; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, C.; Pontes, A.J.; Viana, J.C.; Gaspar-Cunha, A. Modeling and optimization of the injection-molding process: A review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Q. Optimization of injection molding process parameters using combination of artificial neural network and genetic algorithm method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 183, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, B.; Szabó, F.; Hatos, I.; Suplicz, A.; Kovács, N.K.; Hargitai, H.; Tábi, T.; Kovács, J.G. Enhanced injection molding simulation of advanced injection molds. Polymers 2017, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hentati, F.; Hadriche, I.; Masmoudi, N.; Bradai, C. Optimization of the injection molding process for the PC/ABS parts by integrating Taguchi approach and CAE simulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 4353–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Bae, H.S.; Kwak, J.S. Dimensional optimization of electric component in ultra thin-wall injection molding by using Moldflow simulation. J. Korean Soc. Manuf. Process Eng. 2020, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, B.; Erzurumlu, T. Comparison of the warpage optimization in the plastic injection molding using ANOVA, neural network model and genetic algorithm. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 171, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Mao, H.; Hua, L.; Guo, W.; Shu, M. Back propagation neural network modeling for warpage prediction and optimization of plastic products during injection molding. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.C.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, K.H.; Kim, J.S. A study on the prediction of optimized injection molding condition using artificial neural network(ANN). Trans. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Na, J.W.; Park, K.H.; Yu, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, K.W.; Park, D.Y.; Park, S.J.; Rho, J.S.; Lee, S.C. Development of artificial neural network system to recommend process conditions of injection molding for various geometries. Adv. Intell. Sys. 2020, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gim, J.; Rhee, B. Novel Analysis Methodology of Cavity Pressure Profiles in Injection-Molding Processes Using Interpretation of Mchine Learning Model. Polymers 2021, 13, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, R.; Guo, G.; Chen, J.C.; Yoo, J.J.W. Shrinkage prediction of injection molded high polyethylene parts with taguchi/artificial neural network hybrid experimental design. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2020, 14, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinisch, J.; Lockner, Y.; Hopmann, C. Comparison of design of experiment methods for modeling injection molding experiments using artificial neural networks. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 61, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.C.; Huang, M.S. Quality Prediction for Injection Molding by Using a Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network. Polymers 2020, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.M.; Jong, W.R.; Chen, S.C. Transfer Learning Applied to Characteristic Prediction of Injection Molded Products. Polymers 2021, 13, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayyedian, M.; Dinc, A.; Mamedov, A. Optimization of Injection-Molding Process for Thin-Walled Polypropylene Part Using Artificial Neural Network and Taguchi Techniques. Polymers 2021, 13, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.C.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, K.H.; Kim, J.S. A study on the practical application of the integrated ANN system for manufacturing the target quality of the injection molded product. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Villiers, J.; Barnard, E. Backpropagation neural nets with one and two hidden layers. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1993, 4, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning (Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning Series); MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, R.; Marksll, R.J. Neural Smithing: Supervised Learning in Feedforward Artificial Neural Networks; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rudder, S. An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. An overview of multi-task learning. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Shu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K. Intelligent optical performance monitor using multi-task learning based artificial neural network. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 11281–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michelucci, U.; Venturini, F. Multi-task learning for multi-dimensional regression: Application to luminescence sensing. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Jamieson, K.; DeSalvo, G.; Rostamizadeh, A.; Talwalkar, A. Hyperband: A novel bandit-based approach to hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2017, 18, 6765–6816. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 20457:2018; Plastics Moulded Parts—Tolerances and Acceptance Conditions. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Yang, D.C. A Study on the Injection Molding Conditions for Manufacturing Target Quality Product Using Artificial Neural Network. Master’s Thesis, Dankook University, Yongin, Korea, 2021. Available online: http://lib.dankook.ac.kr/dcollection/common/orgView/000000196386 (accessed on 14 March 2022).
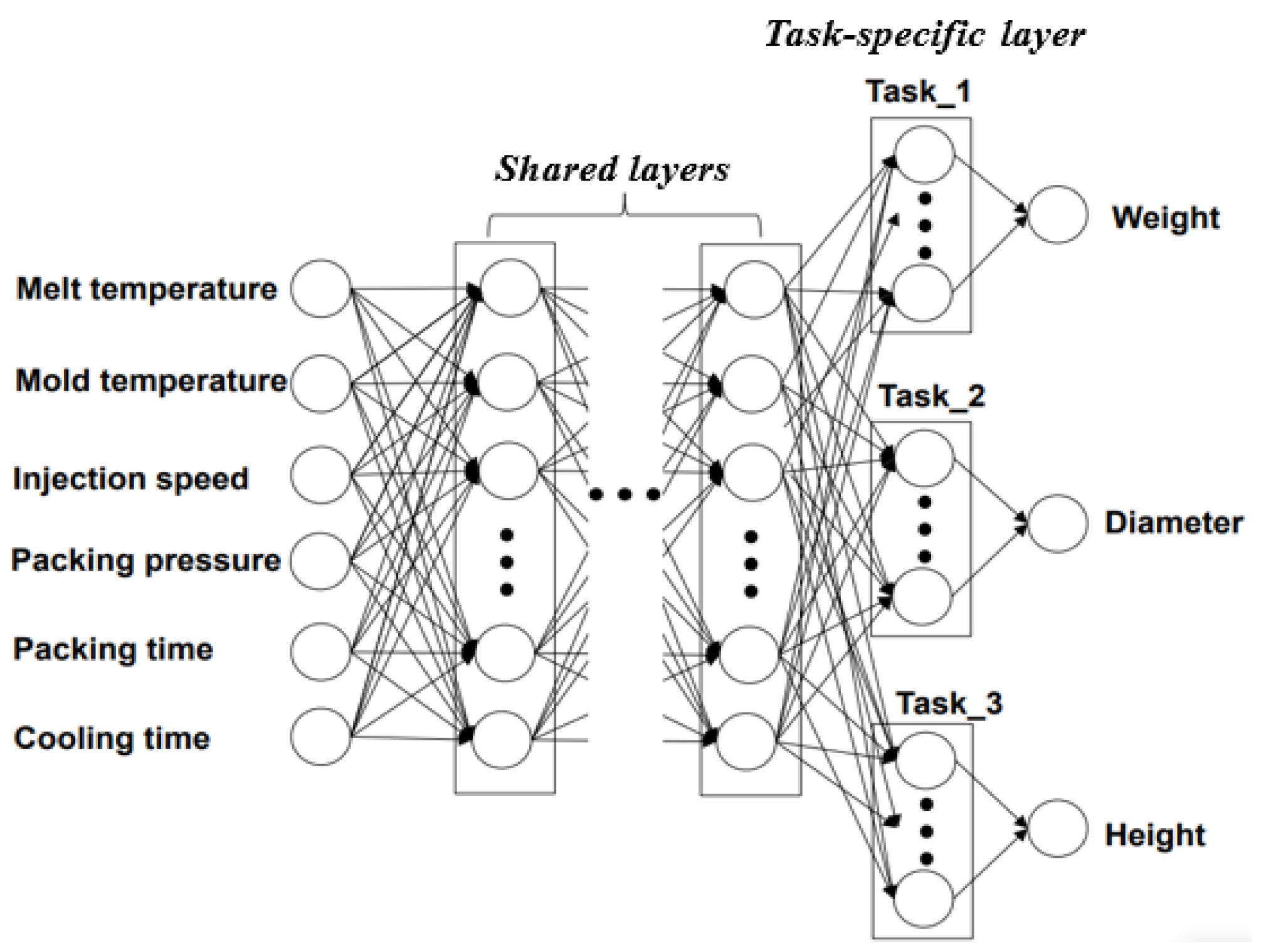
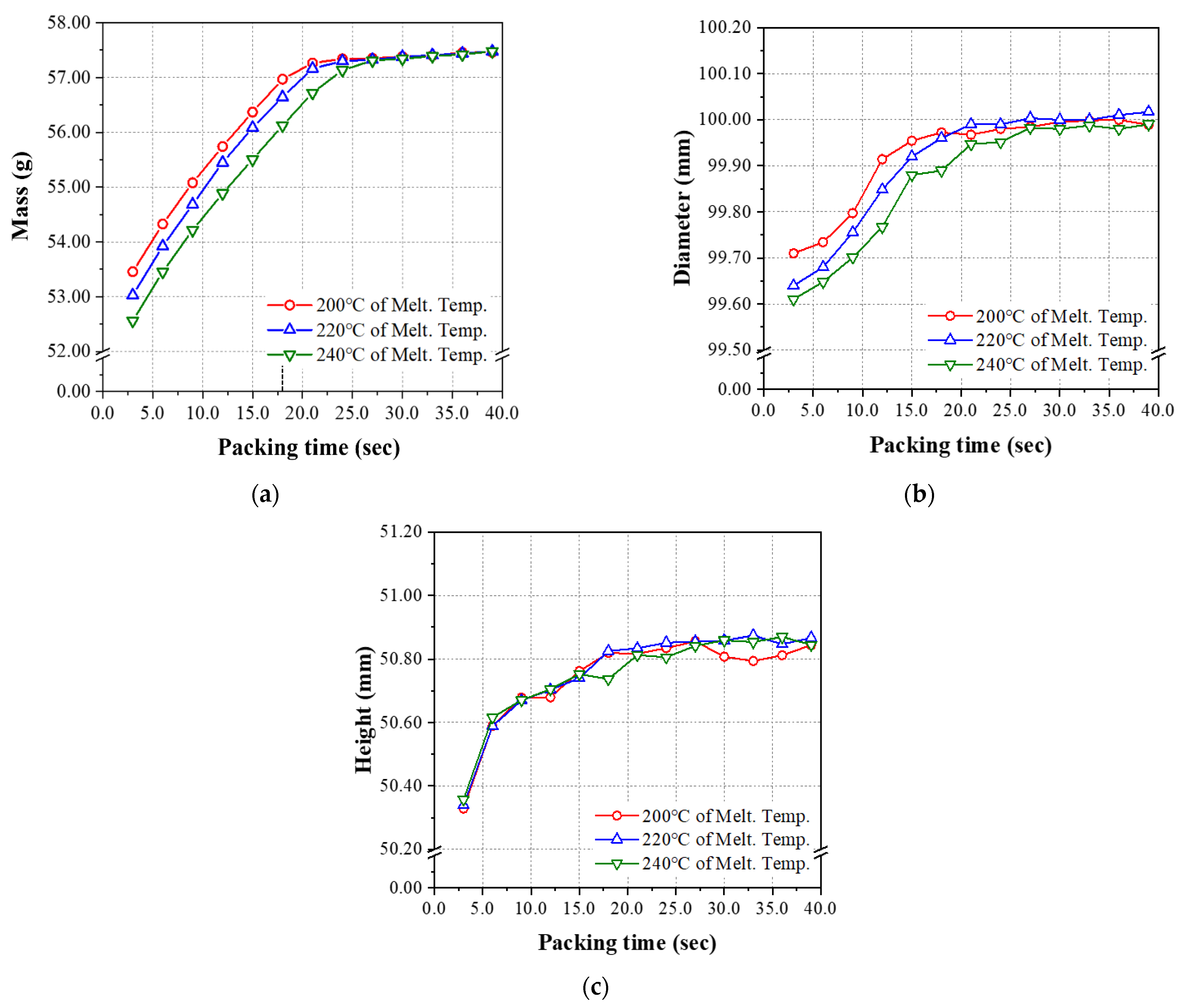

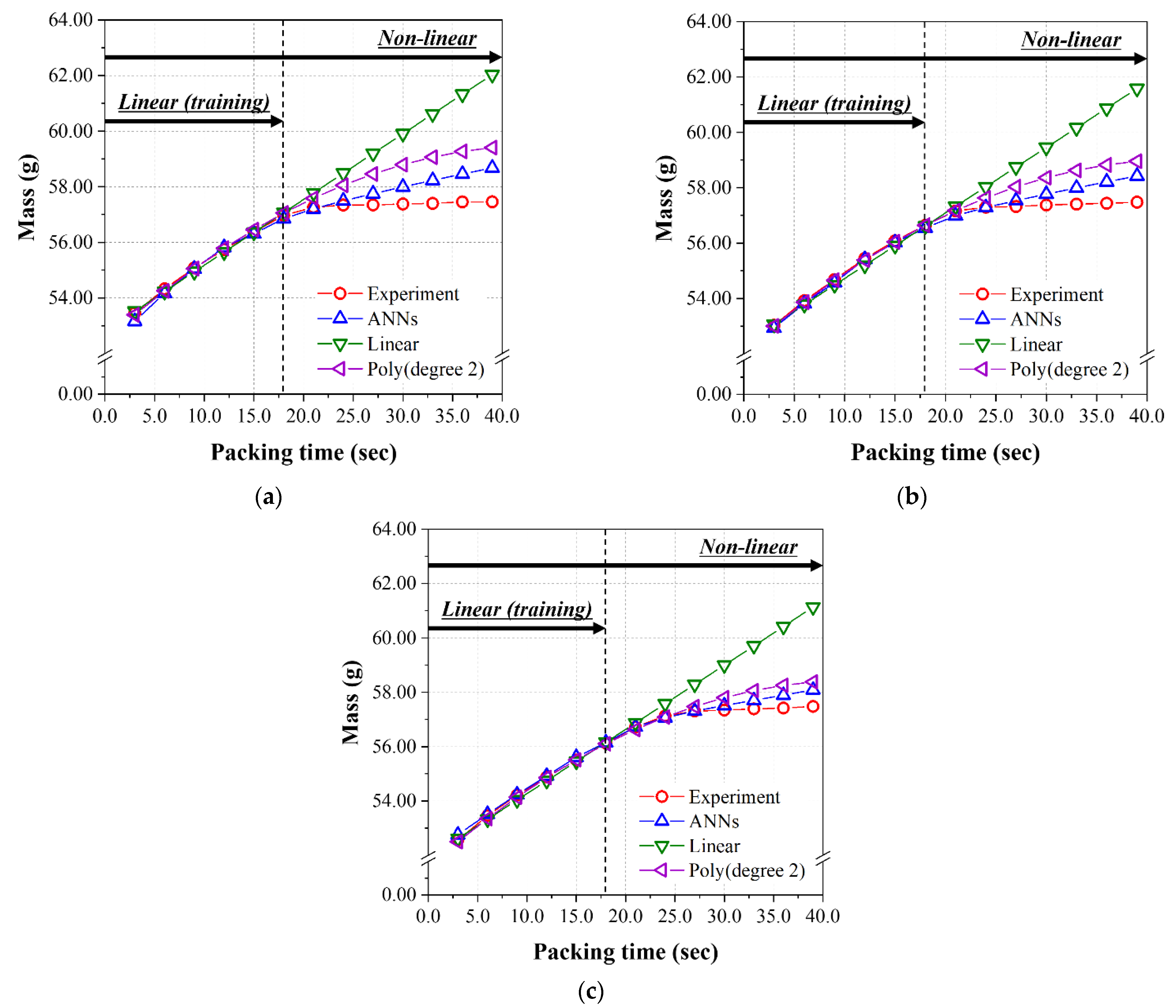

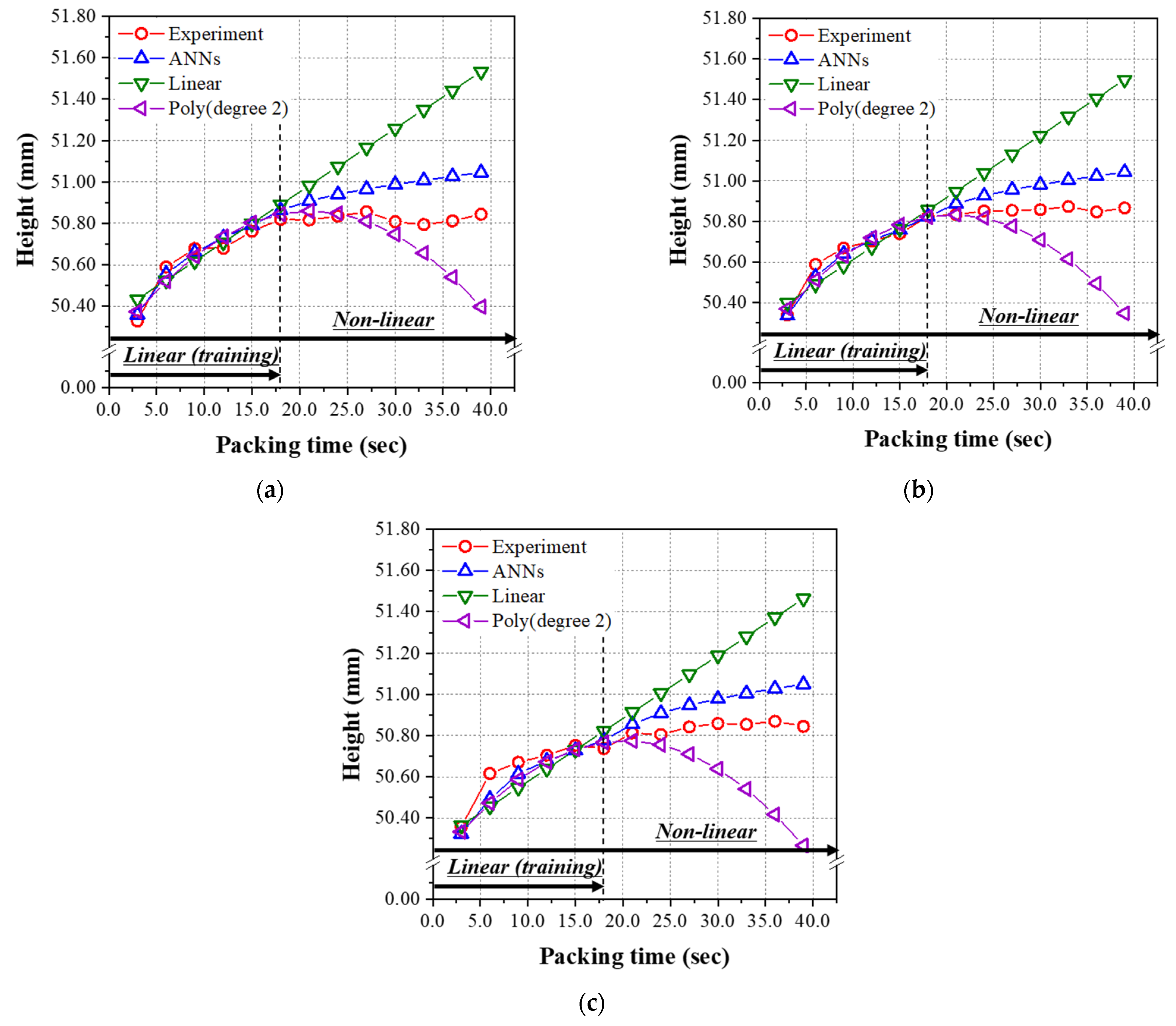


| Author | Product | Input Parameters | Output Parameters | The Number of Hidden Layers | The Number of Neurons per Hidden Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozcelik, B et al. [7] | Thin shell part (CAE) | 5 (Mold Temp., Melt Temp., Packing pressure, Packing time, Cooling time) | 1 (Warpage) | 2 hidden layers | 9 (1st)–9 (2nd) |
| Yin, F et al. [8] | Automobile glove component (CAE) | 5 (Mold Temp., Melt Temp., Packing pressure, Packing time, Cooling time) | 1 (Warpage) | 2 hidden layers | 20 (1st)–20 (2nd) |
| Yang, D. C. et al. [9] | Cup (experiment) | 10 (Melt Temp., Mold Temp., Injection speed, V/P switchover pressure, Packing pressure, Packing time, Cooling time, Back pressure, Plastification speed, Suck back) | 1 (Mass) | 2 hidden layers | 43 (1st)–40 (2nd) |
| Lee, C.H et al. [10] | 36 different products (CAE, experiment) | 9 (Overall volume, Cavity volume, Overall surface area, Cavity surface area, Filling time, Melt Temp., Mold Temp., Packing pressure, Packing time) | 1 (Weight) | 2 hidden layers | 28 (1st)–28 (2nd) |
| Gim, J. et al. [11] | Spiral (experiment) | 10 (Time and pressure value from sensor) | 1 (Part weight) | 1 hidden layer | 8 |
| Abdul, R et al. [12] | Tensile specimens (experiment) | 3 (Injection speed, Holding time, Cooling time) | 2 (Length shrinkage, Width shrinkage) | 1 hidden layer | 4 (1st) |
| Heinisch, J et al. [13] | Plate (CAE) | 6 (Mold Temp., Melt Temp., Injection time, Packing pressure, Packing time, Cooling time) | 3 (Weight, length, width) | 1 hidden layer | 5 (1st) |
| Ke, K. C. et al. [14] | IC tray (experiment) | 1~11 (Combinations of 11 pressure sensor signal) | 3 points of width | 1 hidden layer | 1~33 (1st) |
| Huang, Y. M. et al. [15] | Circle plate (CAE) | 5 (Injection speed, Packing time, Mold Temp., Melt Temp.) | 3 (Injection pressure, Cooling time, Z shrinkage) | 2 hidden layers | 7 (1st)–3 (2nd) |
| 5 (Injection pressure, Cooling time, X, Y, Z shrinkage) | 2 hidden layers | 11 (1st)–7 (2nd) | |||
| Moayyedian, M. et al. [16] | Circle plate (CAE) | 4 (Filing time, Cooling time, Packing time, Melt temperature) | 3 (Short shot, Shrinkage rate, Warpage) | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| Yang, D. C. et al. [17] | LEGO (experiment) | 8 (Melt Temp., Mold Temp., Injection speed, Packing pressure, Packing time, Cooling time, Back pressure, Screw speed) | 5 (Mass, Pressure at the end of fill, X, Y, Z Length) | 1 hidden layer | 11 (1st) |
| Properties | Standard | Condition | Unit | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | Specific gravity | ASTM D792 | - | - | 0.94 |
| Melt flow rate | ASTM D1238 | 230 °C, 2.16 kg | g/10 min | 13.0 | |
| Mechanical | Tensile strength (3.2 mm) | ASTM D638 | 50 mm/min | kgf/cm2 | 270 |
| Flexural strength (6.4 mm) | ASTM D790 | 10 mm/min | kgf/cm2 | 360 | |
| Thermal | Heat deflection Temp. (6.4 mm) | ASTM D648 | 4.6 kg | °C | 125 |
| Item | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Clamping force | 150 | ton |
| Screw diameter | 32.0 | mm |
| Max. injection speed | 1000 | mm/s |
| Max. injection pressure | 3500 | bar |
| Max. injection stroke | 120 | mm |
| Conditions | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melt temperature (°C) | 200 | 220 | 240 |
| Mold temperature (°C) | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| Injection speed (mm/s) | 40 | 70 | 100 |
| Packing pressure (bar) | 150 | 200 | 250 |
| Packing time (s) | 6.0 | 12.0 | 18.0 |
| Cooling time (s) | 38 | 48 | 58 |
| Exp. No. | Melt Temperature (°C) | Mold Temperature (°C) | Injection Speed (mm/s) | Packing Pressure (bar) | Packing Time (s) | Cooling Time (s) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 40 | 40.0 | 150 | 6.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 2 | 200 | 40 | 40.0 | 150 | 12.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 3 | 200 | 40 | 40.0 | 150 | 18.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 4 | 200 | 50 | 70.0 | 200 | 6.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 5 | 200 | 50 | 70.0 | 200 | 12.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 6 | 200 | 50 | 70.0 | 200 | 18.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 7 | 200 | 60 | 100.0 | 250 | 6.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 8 | 200 | 60 | 100.0 | 250 | 12.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 9 | 200 | 60 | 100.0 | 250 | 18.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 10 | 220 | 40 | 70.0 | 250 | 6.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 11 | 220 | 40 | 70.0 | 250 | 12.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 12 | 220 | 40 | 70.0 | 250 | 18.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 13 | 220 | 50 | 100.0 | 150 | 6.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 14 | 220 | 50 | 100.0 | 150 | 12.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 15 | 220 | 50 | 100.0 | 150 | 18.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 16 | 220 | 60 | 40.0 | 200 | 6.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 17 | 220 | 60 | 40.0 | 200 | 12.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 18 | 220 | 60 | 40.0 | 200 | 18.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 19 | 240 | 40 | 100.0 | 200 | 6.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 20 | 240 | 40 | 100.0 | 200 | 12.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 21 | 240 | 40 | 100.0 | 200 | 18.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 22 | 240 | 40 | 40.0 | 250 | 6.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 23 | 240 | 50 | 40.0 | 250 | 12.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 24 | 240 | 50 | 40.0 | 250 | 18.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 25 | 240 | 60 | 70.0 | 150 | 6.0 | 58 | L27 |
| 26 | 240 | 60 | 70.0 | 150 | 12.0 | 38 | L27 |
| 27 | 240 | 60 | 70.0 | 150 | 18.0 | 48 | L27 |
| 28 | 214 | 55 | 82.7 | 204 | 16.3 | 52 | Random |
| 29 | 204 | 44 | 43.4 | 202 | 13.9 | 41 | Random |
| 30 | 203 | 46 | 93.6 | 205 | 13.7 | 45 | Random |
| 31 | 202 | 54 | 83.4 | 213 | 6.6 | 48 | Random |
| 32 | 206 | 43 | 61.6 | 221 | 6.9 | 39 | Random |
| 33 | 212 | 44 | 53.3 | 240 | 17.0 | 52 | Random |
| 34 | 212 | 51 | 90.8 | 224 | 6.1 | 48 | Random |
| 35 | 200 | 52 | 50.0 | 215 | 17.6 | 39 | Random |
| 36 | 229 | 51 | 46.2 | 153 | 11.7 | 45 | Random |
| 37 | 228 | 49 | 53.2 | 217 | 12.3 | 58 | Random |
| 38 | 222 | 51 | 63.7 | 167 | 8.7 | 51 | Random |
| 39 | 219 | 50 | 41.4 | 156 | 16.3 | 52 | Random |
| 40 | 228 | 46 | 96.5 | 154 | 16.7 | 57 | Random |
| 41 | 228 | 46 | 62.5 | 191 | 10.9 | 46 | Random |
| 42 | 219 | 42 | 98.4 | 237 | 17.9 | 41 | Random |
| 43 | 220 | 43 | 55.8 | 241 | 14.8 | 44 | Random |
| 44 | 233 | 42 | 50.8 | 198 | 13.5 | 55 | Random |
| 45 | 238 | 53 | 41.6 | 221 | 17.2 | 40 | Random |
| 46 | 234 | 48 | 68.2 | 222 | 8.8 | 41 | Random |
| 47 | 233 | 44 | 84.9 | 171 | 6.7 | 55 | Random |
| 48 | 234 | 43 | 56.9 | 176 | 11.1 | 48 | Random |
| 49 | 239 | 49 | 41.2 | 234 | 8.6 | 52 | Random |
| 50 | 240 | 49 | 76.1 | 241 | 6.4 | 51 | Random |
| Exp. No. | Melt Temperature (°C) | Mold Temperature (°C) | Injection Speed (mm/s) | Packing Pressure (bar) | Packing Time (s) | Cooling Time (s) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51– 63 | 200 | 50 | 70 | 200 | 3.0–39.0 (interval: 3) | 38 | Non-linear case |
| 64– 76 | 220 | 50 | 70 | 200 | 3.0–39.0 (interval: 3) | 38 | Non-linear case |
| 77– 89 | 240 | 50 | 70 | 200 | 3.0–39.0 (interval: 3) | 38 | Non-linear case |
| Hyper-Parameters | Range | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Seed number | 0–50 | Step size was 1 |
| Batch size | 16, 32, 64, … | Increased in multiples of 2 until it could cover the number of learning data |
| Optimizer | Adams [26] | Fixed |
| Learning rate | 0.0001–0.01 [26] | Step size was 0.0001 |
| Beta 1 | 0.1–1.0 [26] | Step size was 0.1 |
| Bata 2 | 0.9, 0.99, 0.999, 0.999 [26] | - |
| Number of hidden layers | 1–5 (shared layers) 1 (task-specific layer) | Step size was 1 (task-specific layer was fixed as one layer) |
| Number of neurons | 3–18 | Step size was 1 |
| Initializer | He normal (hidden layer) Xavier normal (output layer) | - |
| Activation function | Elu (hidden layer) Linear (output layer) | - |
| Drop number | 0.0–0.4 | Step size was 0.1 |
| Coefficient of batch normalization | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 | - |
| Hyper-Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Seed number | 16 |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Optimizer | Adams |
| Learning rate | 0.0069 |
| Beta 1 | 0.6 |
| Beta 2 | 0.9 |
| Number of hidden layers | 3 (shared layers) 1 (specific-task layer) |
| Number of neurons | 17–13–13 (shared layers) 13 (specific-task layers for mass) 9 (specific-task layers for diameter) 8 (specific-task layers for height) |
| Initializer | He normal (hidden layers) Xavier normal (output layer) |
| Activation function | Elu |
| Drop number | 0.0–0.2–0.2 (shared layers) 0.0 (specific-task layers for mass) 0.3 (specific-task layers for diameter) 0.3 (specific-task layers for height) |
| Coefficient of batch normalization | 0.001 (mass), 0.01 (diameter), 0.001 (height) |
| Prediction Model | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | Diameter | Height | |
| ANN | |||
| Linear regression | |||
| Polynomial regression of degree 2 | |||
| Prediction Model | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | Diameter | Height | |
| ANN | |||
| Linear regression | |||
| Polynomial regression of degree 2 | |||
| Hyper-Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Seed number | 35 |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Optimizer | Adams |
| Learning rate | 0.0073 |
| Beta 1 | 0.5 |
| Beta 2 | 0.9 |
| Number of hidden layers | 2 (shared layers) 1 (specific-task layer) |
| Number of neurons | 6–5 (shared layers) 4 (specific-task layers for mass) 3 (specific-task layers for diameter) 4 (specific-task layers for height) |
| Initializer | He normal (hidden layers) Xavier normal (output layer) |
| Activation function | Elu |
| Drop number | 0.0–0.0 (shared layers) 0.2 (specific-task layers for mass) 0.1 (specific-task layers for diameter) 0.0 (specific-task layers for height) |
| Coefficient of batch normalization | 0.001 (mass), 0.01 (diameter), 0.001 (height) |
| Prediction Model | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | Diameter | Height | |
| ANN | |||
| Linear regression | |||
| Polynomial regression of degree 2 | |||
| Prediction Model | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | Diameter | Height | |
| ANN | |||
| Linear regression | |||
| Polynomial regression of degree 2 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Yang, D.; Yoon, K.; Kim, J. Effects of Input Parameter Range on the Accuracy of Artificial Neural Network Prediction for the Injection Molding Process. Polymers 2022, 14, 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091724
Lee J, Yang D, Yoon K, Kim J. Effects of Input Parameter Range on the Accuracy of Artificial Neural Network Prediction for the Injection Molding Process. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091724
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Junhan, Dongcheol Yang, Kyunghwan Yoon, and Jongsun Kim. 2022. "Effects of Input Parameter Range on the Accuracy of Artificial Neural Network Prediction for the Injection Molding Process" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091724
APA StyleLee, J., Yang, D., Yoon, K., & Kim, J. (2022). Effects of Input Parameter Range on the Accuracy of Artificial Neural Network Prediction for the Injection Molding Process. Polymers, 14(9), 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091724






