Rubber Rail Pad Reinforced by Modified Silica Using GPTMS and Sulfenamide Accelerator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
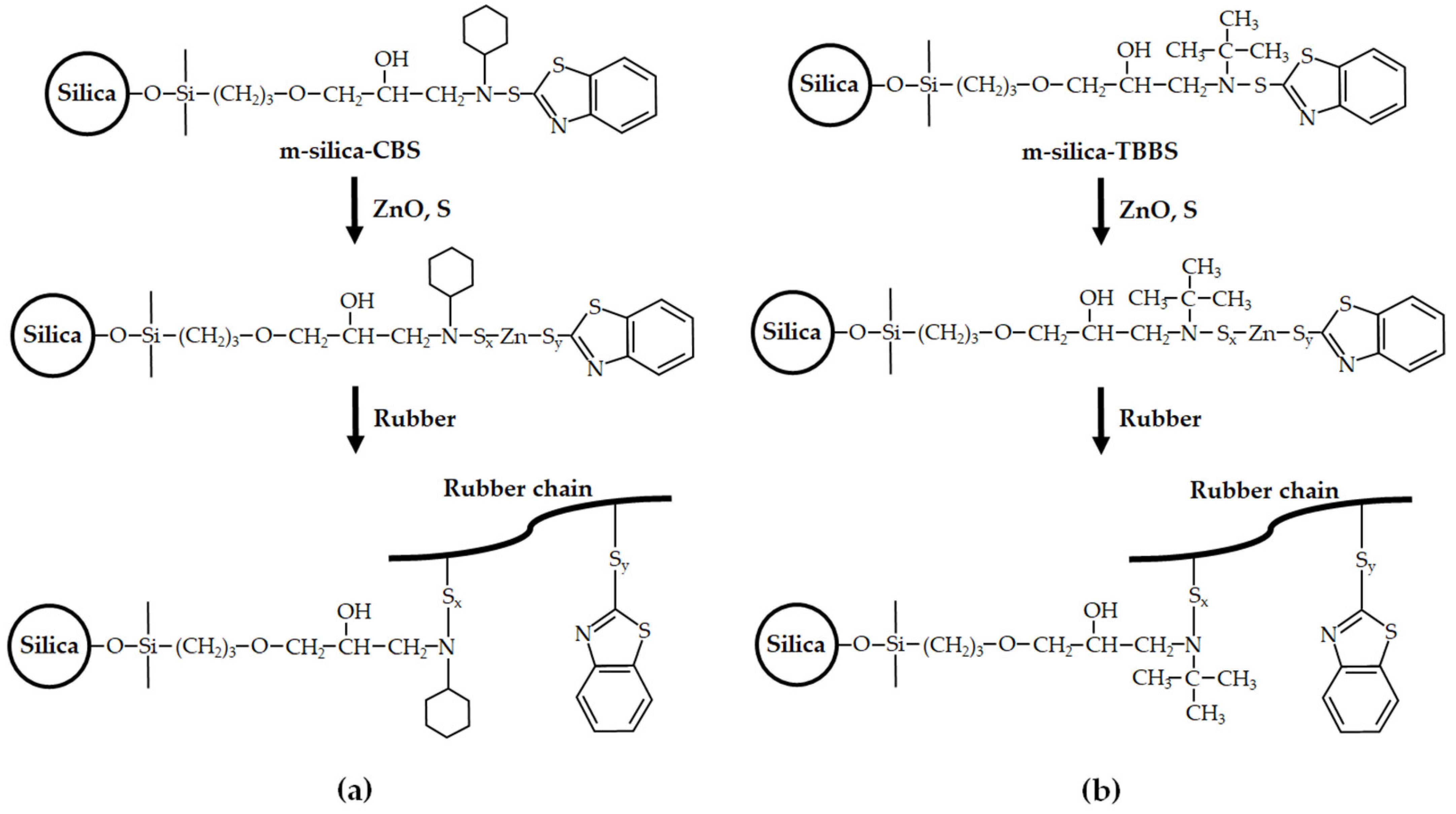
2.2. Surface Modification of Silica
2.3. Compounding and Vulcanization
2.4. Rheological Characteristics and Mechanical Properties
2.5. Crosslink Density
2.6. Static Spring and Deformation Testing of Rubber Rail Pad
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Modified Silica
3.2. Rheological Characteristics
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Crosslink Density
3.5. The Static Spring and Deformation Testing of Rubber Rail Pad
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerspacher, M.; O’Farrel, C.P.; Nikiel, L.; Yang, H.H. Furnace carbon black characterization: Continuing saga. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1996, 69, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, J.; Niedermeier, W.; Luginsland, H.D. The effect of filler-filler and filler-elastomer interaction on rubber reinforcement. Compos. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Q.; Weng, P.; Guo, B. Remarkably improving performance of carbon black-filled rubber composites by incorporating MoS2 nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 132, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Kohjiya, S. Reinforcement mechanism of carbon black (CB) in natural rubber vulcanizates: Relationship between CB aggregate and network structure and viscoelastic properties. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 1418–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Rajasekar, R.; Kang, D.J.; Ahang, Z.X.; Pal, S.K.; Das, C.K.; Kim, J.K. Effect of fillers on natural rubber/high styrene rubber blends with nano silica: Morphology and wear. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Han, D.; Ye, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Chemical and physical interaction between silane coupling agent with long arms and silica and its effect on silica/natural rubber composites. Polymer 2018, 135, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, C.S.J.; Bipinbal, P.K.; Sunil, K.N. Viscoelastic behavior of silica filled natural rubber composites-Correlation of shear with elongational testing. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jia, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wu, L.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D. Novel functional silica nanoparticals for rubber vulcanization and reinforcement. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 144, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, R.; Sreelekshimi, R.V.; Menon, A.R.R. Cetryltrimethyl ammonium bromide modified kaolin as a reinforcing filler for natural rubber. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, G.C.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bhowmick, A.K. Influence of nanoclay on adhesion of EPDM vulcanizate. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghari, H.S.; Jalali-Arani, A. Nanocomposites based on natural rubber, organoclay and nano-calcium carbonate: Study on the structure, cure behavior, static and dynamic-mechanical properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghari, H.S.; Shakouri, Z.; Shirazi, M.M.A. Evaluation of microstructure of natural rubber/nano-calcium carbonate nanocomposites by solvent transport properties. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2014, 43, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Mathialagan, M. Comparative study on the effect of partial replacement of silica or calcium carbonate by bentonite on the properties of EPDM composites. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramorino, G.; Bignotti, F.; Pandini, S.; Ricco, T. Mechanical reinforcement in natural rubber/organoclay nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, F.; Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; Wan, J.; Jia, D. Stryrene-butadiene rubber/halloysite nanotubes nanocomposites modified by sorbic acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7329–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloskovska, E.; Nies, E.; Hristova-Bogaerds, D.; Van Duin, M.; De With, G. Influence of reaction parameters on the structure of in situ rubber/silica compounds synthesized via sol-gel reaction. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Hou, Y.Q.; Ning, N.Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Tian, M.; Mi, J.G. Theoretical insight into dispersion of silica nanoparticles in polymer melts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 9940–9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsri, S.; Rattanasom, N. Mechanical and damping properties of silica/natural rubber composites prepared from latex system. Polym. Test. 2011, 30, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-oui, P.; Sirisinha, C.; Thepsuwan, U.; Hatthapanit, K. Comparison of reinforcing efficiency between Si-69 and Si-264 in a conventional vulcanization system. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanawanidchai, S.; Loykulnant, S.; Sae-oui, P.; Maneevas, N.; Sirisinha, C. Development of eco-friendly coupling agent for precipitated silica filled natural rubber compounds. Polm. Test. 2014, 34, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.G.; Lin, C.J.; Bogoslovov, R.B.; Rackaitis, M.; Sadhukhan, P.; Quinn, J.D.; Roland, C.M. Flocculation, reinforcement, and glass transition effects in silica-filled styrene-butadiene rubber. Chem. Technol. 2011, 84, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Torbati-Fard, N.; Kiyani, H.; Razzaghi-Kashani, M. Comparative role of interface in reinforcing mechanisms of nano silica modified by silanes and liquid rubber in SBR composites. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntako, R. The rubber damper reinforced by modified silica fume (mSF) as an alternative reinforcing filler in rubber industry. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Zeng, X.; Chen, W.; Luo, Q.; Hu, Z.; Jia, D. Nonsolvent-assisted surface modification of silica by silane and antioxidant for rubber reinforcement. Polym. Test. 2019, 78, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntako, R. Effect of modified silica fume using MPTMS for the enhanced EPDM foam insulation. Polymers 2021, 13, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengloyluan, K.; Sahakaro, K.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M. Silica-reinforced tire tread compounds compatibilized by using epoxidized natural rubber. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 51, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, M.; Conzatti, L.; Costa, G.; Falqui, L.; Turturro, A.; Valenti, B.; Negroni, F. Surface modification of silica: 1. Thermodynamic aspects and effect on elastomer reinforcement. Polymer 2005, 46, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansarifar, A.; Azhar, A.; Ibrahim, N.; Shiah, S.F.; Lawton, J.M.D. The use of a silanised silica filler to reinforce and crosslink natural rubber. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2005, 25, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoeythornkhajhornchai, P.; Samthong, C.; Somwangthanaroj, A. Influence of sulfonamide accelerators on cure kinetics and properties of natural rubber foam. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, J.; Ghorai, S.; Jalan, A.K.; Roy, M.; De, D. Manifestation of accelerator type and vulcanization system on the properties of silica-reinforced SBR/devulcanize SBR blend vulcanizates. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2636–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahakaro, K.; Pongpaiboon, C.; Nakason, C. Improved mechanical properties of NR/EPDM blends by controlling the migration of curative and filler via reactive processing technique. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, H.; Ismail, H.; Azura, A.R. Optimisation of accelerators and vulcanizing systems on thermal stability of natural rubber/recycled ethylene-propylene-diene-monomer blends. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donley, M.S.; Mantz, R.A.; Khramov, A.N.; Balbyshev, V.N.; Kasten, L.S.; Gaspar, D.J. The self-assembled nanophase particle (SNAP) process: A nanoscience approach to coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2003, 47, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, L.; Joseph, K.U.; Joseph, R. Swelling behavior of isora/natural rubber composites in oils used in automobiles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2006, 29, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiranobe, C.T.; Ribeiro, G.D.; Torres, G.B.; Prado dos Reis, E.A.; Cabrera, F.C.; Job, A.E.; Paim, L.L.; Jose dos Santos, R. Cross-linked density determination of natural rubber compounds by different analytical techniques. Mat. Res. 2021, 4 (Suppl. S1), e20210041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Khorrami, M.K.; Vatanparast, H.; Ghasemzadeh, H. Prediction of surface tension of solution in the presence of hydrophilic silica nanoparticle and anionic surfactant by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and chemometric methods. Spectrochim. Acta. A 2021, 255, 119697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidalgo, A.M.; Ilharco, L.M. Tailoring the structure and hydrophobic properties of amorphous silica by silylation. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2012, 158, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Jia, Z.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D. Surface modification of silica with N-cyclohexyl-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide for styrene-butadiene rubber composites with dramatically improved mechanical property. Mater. Lett. 2015, 145, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, L.M.S.; Azevedo, J.B.; Diniz, M.F.; Silva, L.M.; Dutra, R.C.L. Characterization of additives in NR formulations by TLC-IR (UATR). Polimeros 2018, 28, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Lu, W.; He, Z.; Qi, G.; Li, J.; Hu, X. Effect of silane treatment on mechanical properties of polyurethane/mesoscopic fly ash composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khimi, S.R.; Pickering, K.L. A new method to predict optimum cure time of rubber compound using dynamic mechanical analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, I.; Ismail, H.; Azura, A.R. The comparison of alkanolamide and silane coupling agent on the properties of silica-filled natural rubber (SMR-L) compounds. Polym. Test. 2014, 40, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, B.; Waddell, W. The science of rubber compounding. In The Science and Technology of Rubber, 4th ed.; Mark, J.E., Erman, B., Roland, C.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 417–471. [Google Scholar]
- Changjie, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Junwei, G.; Junping, Z.; Youqiang, S.; Yuhang, W. Cure characteristics and mechanical properties of styrene-butadiene rubber/hydrogenated acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber/silica composites. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formela, K.; Wasowicz, D.; Formela, M.; Hejna, A.; Haponiuk, J. Curing characteristics, mechanical and thermal properties of reclaimed ground tire rubber cured with various vulcanizing systems. Iran. Polym. J. 2015, 24, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luginsland, H.D.; Fröhlich, J.; Wehmeier, A. Influence of different silanes on the reinforcement of silica-filled rubber compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2002, 75, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Tan, S.; Poh, B.T. Curing and mechanical properties of nitrile and natural rubber blends. J. Elastomers Plast. 2001, 33, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabbagh, S.A.; Yehia, A. Detection of crosslink density by different methods for natural rubber blended with SBR and NBR. Egypt. J. Solids 2007, 30, 157–173. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiei, S.; Shojaei, A. Vulcanization kinetics and reversion behavior of natural rubber/styrene-butadiene rubber blend filled with nanodiamond-The role of sulfur curing system. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 81, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayeemase, N.; Ismail, H.; Azura, A.R. Blending of natural rubber/recycled ethylene-propylene-diene monomer: Cure behaviors and mechanical properties. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2013, 52, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, L.; Ye, X.; Han, D. Surface modification of silica nanoparticles by a polyxyethylene sorbitan and silane coupling agent to prepare high-performance rubber composites. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Nizami, S.N.; Raza, N.Z.; Mahmood, K. Mechanical, swelling and thermal aging properties of marble sludge-natural rubber composites. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2012, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Bi, W.; Zhao, S. Influence of crosslink density on mechanical properties of natural rubber vulcanizates. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2011, 50, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Materials (phr *) | Unfilled | Silica (Unmodified) | m-silica | m-silica-CBS | m-silica-TBBS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STR 20CV | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| N-774 | - | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| Silica | - | 35 | - | - | - |
| m-silica | - | - | 35 | - | - |
| m-silica-CBS | - | - | - | 35 | - |
| m-silica-TBBS | - | - | - | - | 35 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Stearic acid | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6PPD | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TBzTD | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| DPG | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Sulphur | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| FTIR Peak (cm−1) | Assignment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica (Unmodified) | m-silica | m-silica-CBS | m-silica-TBBS | |
| - | - | 761 | - | Ortho-substituted aromatic ring |
| 799 | 814 | 817 | 821 | Symmetric stretching vibration of siloxane |
| - | - | - | 1020 | C–N stretching |
| 1090 | 1090 | 1085 | 1083 | Asymmetric stretching vibration of siloxane |
| - | 1197 | 1195 | 1195 | Pure vibration of methoxy groups |
| - | - | 14,301,484 | 14,301,484 | Benzothiazole |
| - | 28,452,943 | 28,402,946 | 28,402,942 | C–H stretching of CH3 and CH2 |
| Properties | Unfilled | Silica (Unmodified) | m-silica | m-silica-CBS | m-silica-TBBS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxmimum torque (MH), lb-in | 2.74 | 10.64 | 12.69 | 13.59 | 14.79 |
| Minimum torque (ML), lb-in | 0.49 | 2.53 | 3.26 | 2.83 | 2.48 |
| Differential torque (MH-ML), lb-in | 2.25 | 8.11 | 9.43 | 10.76 | 12.31 |
| Optimum cure time (t90), second | 2.52 | 9.83 | 11.75 | 12.51 | 13.56 |
| Properties | Unfilled | Silica (Unmodified) | m-silica | m-silica-CBS | m-silica-TBBS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 26 ± 1 | 57 ± 1 | 58 ± 1 | 61 ± 1 | 63 ± 1 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 11.18 ± 0.22 | 15.49 ± 0.32 | 17.77 ± 0.18 | 19.88 ± 0.20 | 23.36 ± 0.18 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 940 ± 20 | 580 ± 30 | 560 ± 30 | 540 ± 20 | 525 ± 20 |
| 100% Modulus (MPa) | 1.32 ± 0.02 | 1.70 ± 0.04 | 1.98 ± 0.02 | 2.42 ± 0.01 | 2.72 ± 0.02 |
| 300% Modulus (MPa) | 2.38 ± 0.03 | 5.76 ± 0.02 | 7.91 ± 0.05 | 10.83 ± 0.03 | 12.27 ± 0.03 |
| Tear strength (kN/m) | 19.77 ± 0.05 | 50.45 ± 0.02 | 56.11 ± 0.03 | 61.54 ± 0.04 | 71.08 ± 0.02 |
| Reinforcing index (RI) | 1.80 | 3.39 | 3.99 | 4.48 | 4.51 |
| Properties | Unfilled | Silica (Unmodified) | m-silica | m-silica-CBS | m-silica-TBBS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swelling index (%) | 572 | 531 | 485 | 454 | 435 |
| Crosslink density (mol/cm3) | 7.11 × 10−5 | 8.16 × 10−5 | 9.66 × 10−5 | 10.92 × 10−5 | 11.83 × 10−5 |
| Formulation | Displacement (mm) | Static Spring (N/mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load at 45 N | Load at 55 N | ||
| Unfilled | 0.865 | 0.970 | 95.238 |
| Silica (unmodified) | 0.494 | 0.523 | 344.828 |
| m-silica | 0.361 | 0.383 | 454.545 |
| m-silica-CBS | 0.360 | 0.378 | 555.556 |
| m-silica-TBBS | 0.347 | 0.364 | 588.235 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suntako, R. Rubber Rail Pad Reinforced by Modified Silica Using GPTMS and Sulfenamide Accelerator. Polymers 2022, 14, 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091767
Suntako R. Rubber Rail Pad Reinforced by Modified Silica Using GPTMS and Sulfenamide Accelerator. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091767
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuntako, Rudeerat. 2022. "Rubber Rail Pad Reinforced by Modified Silica Using GPTMS and Sulfenamide Accelerator" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091767
APA StyleSuntako, R. (2022). Rubber Rail Pad Reinforced by Modified Silica Using GPTMS and Sulfenamide Accelerator. Polymers, 14(9), 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091767







