In-Depth Analysis of the High Strain Rate Compressive Behavior of RTM6 Epoxy Using Digital Image Correlation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The compression specimen should be short enough to achieve an early quasi-static stress equilibrium and to increase the achievable maximum strain rate, yet the sample length should be long enough to minimize the influence from the loading interfaces;
- A state of uniform stress and strain has to be achieved in the sample;
- The design of the compression specimen should prevent failure due to buckling and should reduce inertia effects during dynamic compression.
2. Materials and Methods
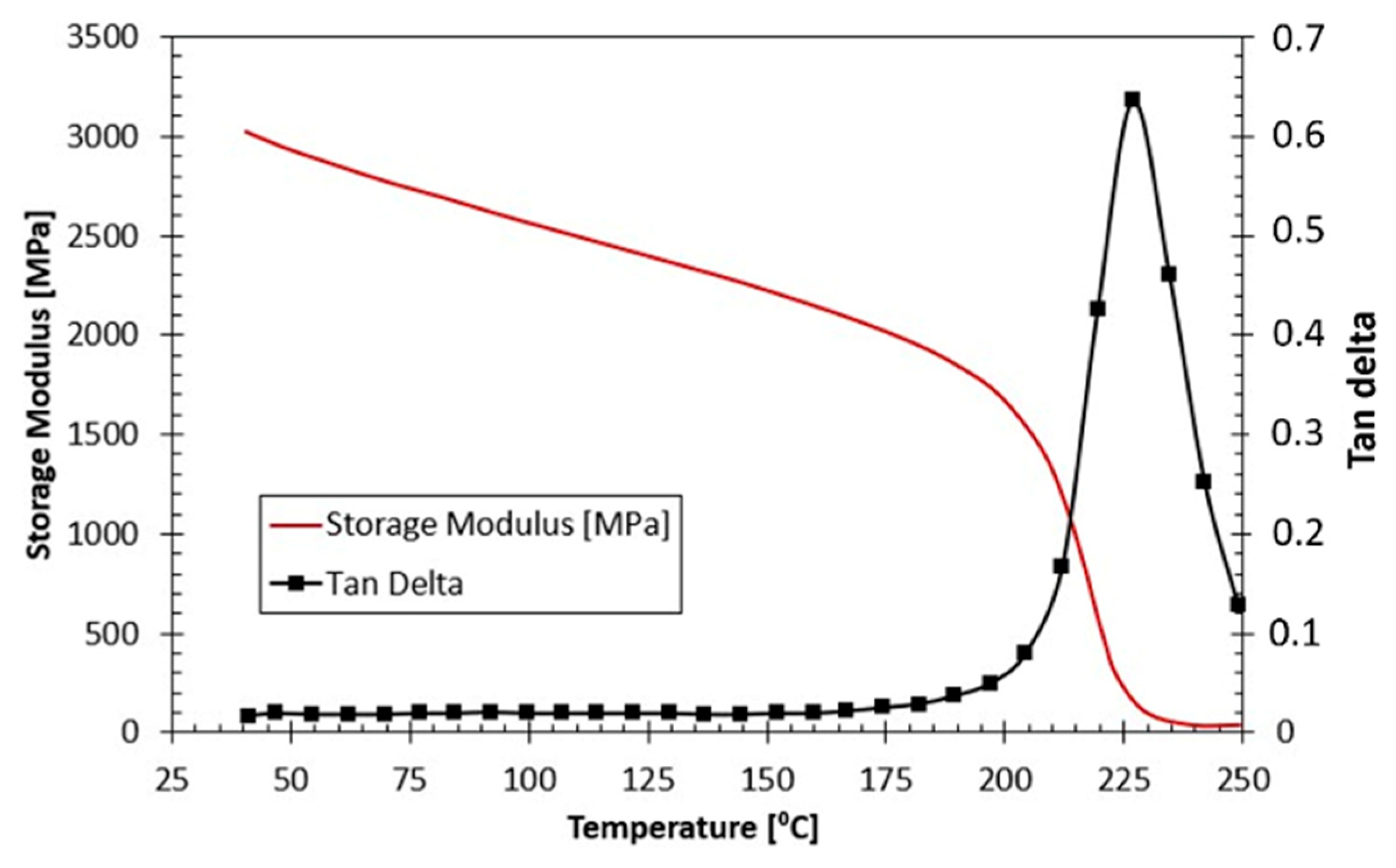
2.1. Specimen Materials and Geometry
2.2. Quasi-Static Testing
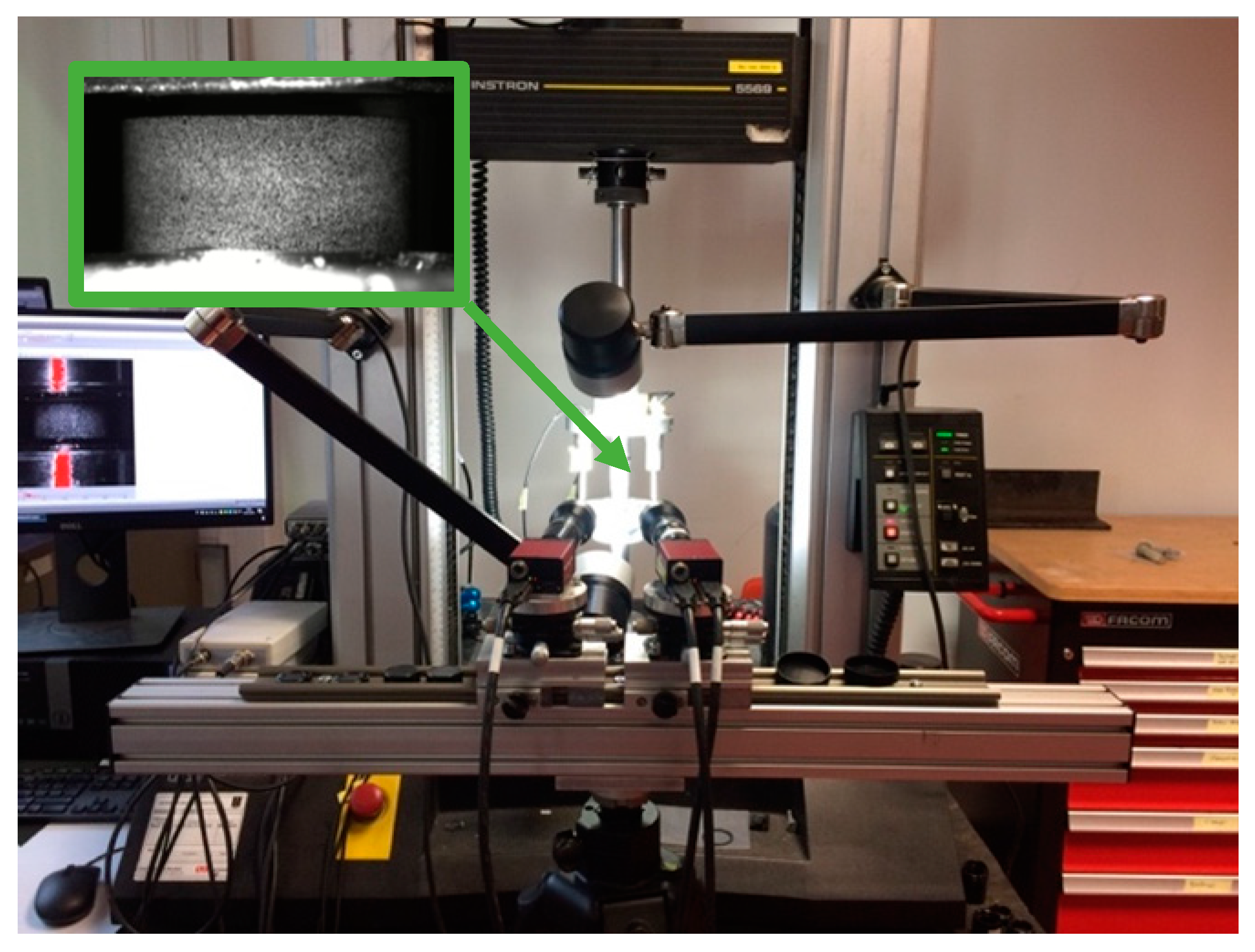
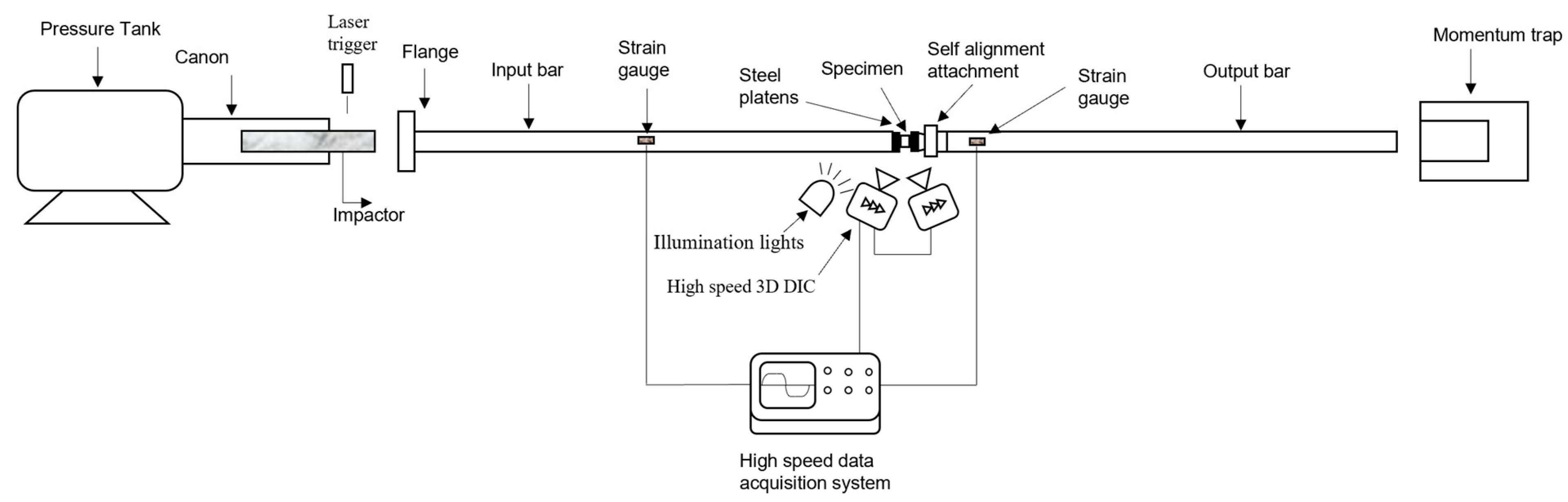
2.3. High Strain Rate Testing
2.4. Sample Fixing and Alignment
2.5. DIC Data Reduction and Processing Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
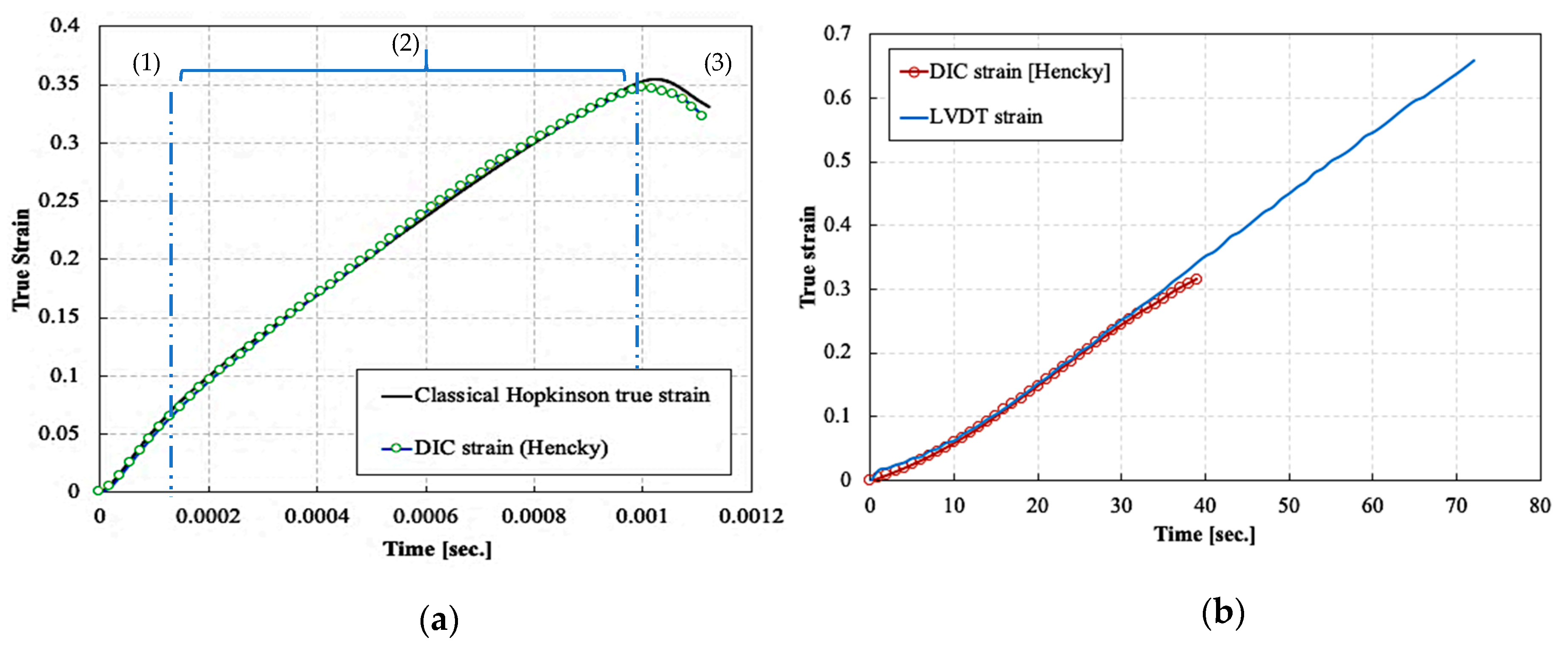
3.1. Quasi-Static Force Equilibrium and Strain Rate Evolution in the SHPB Tests
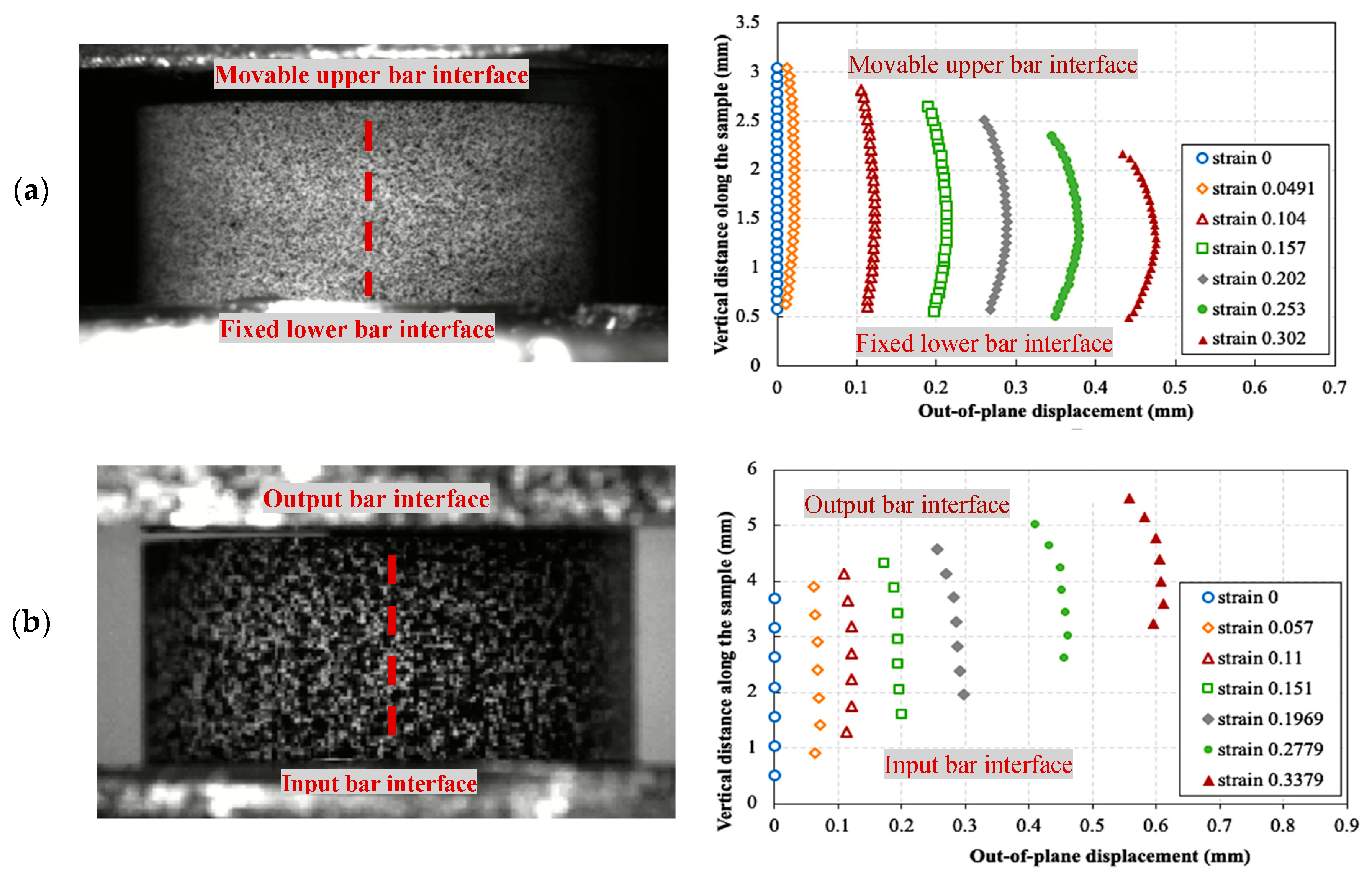
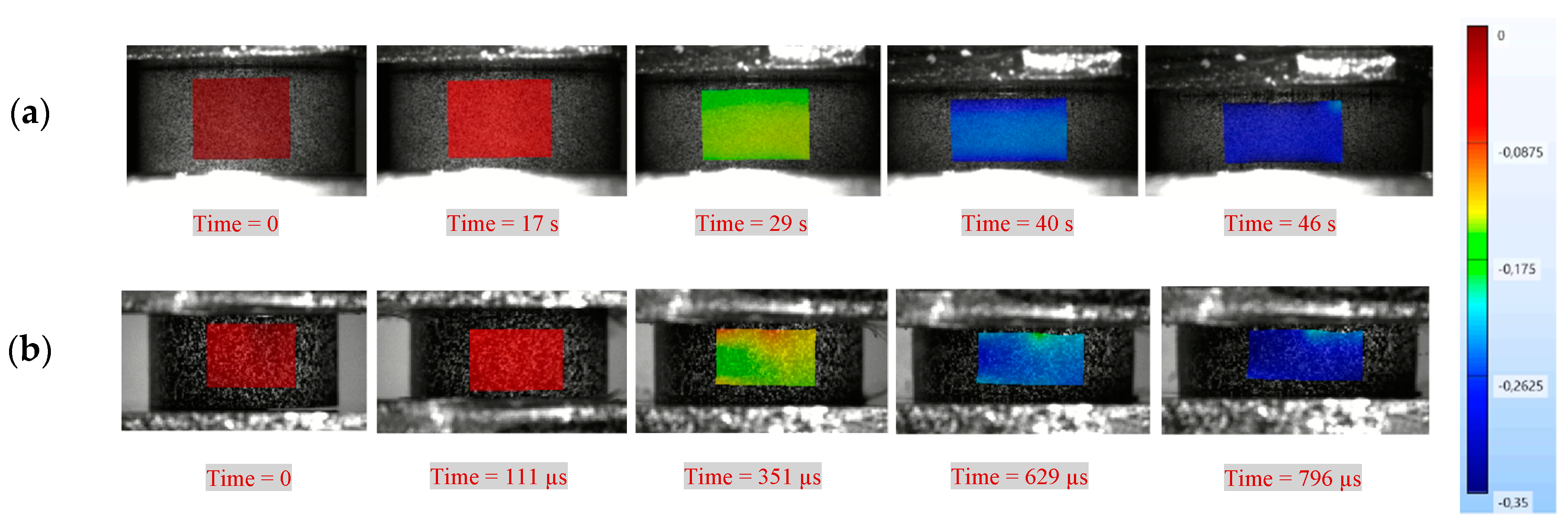
3.2. Interfacial Friction and Sample Barreling
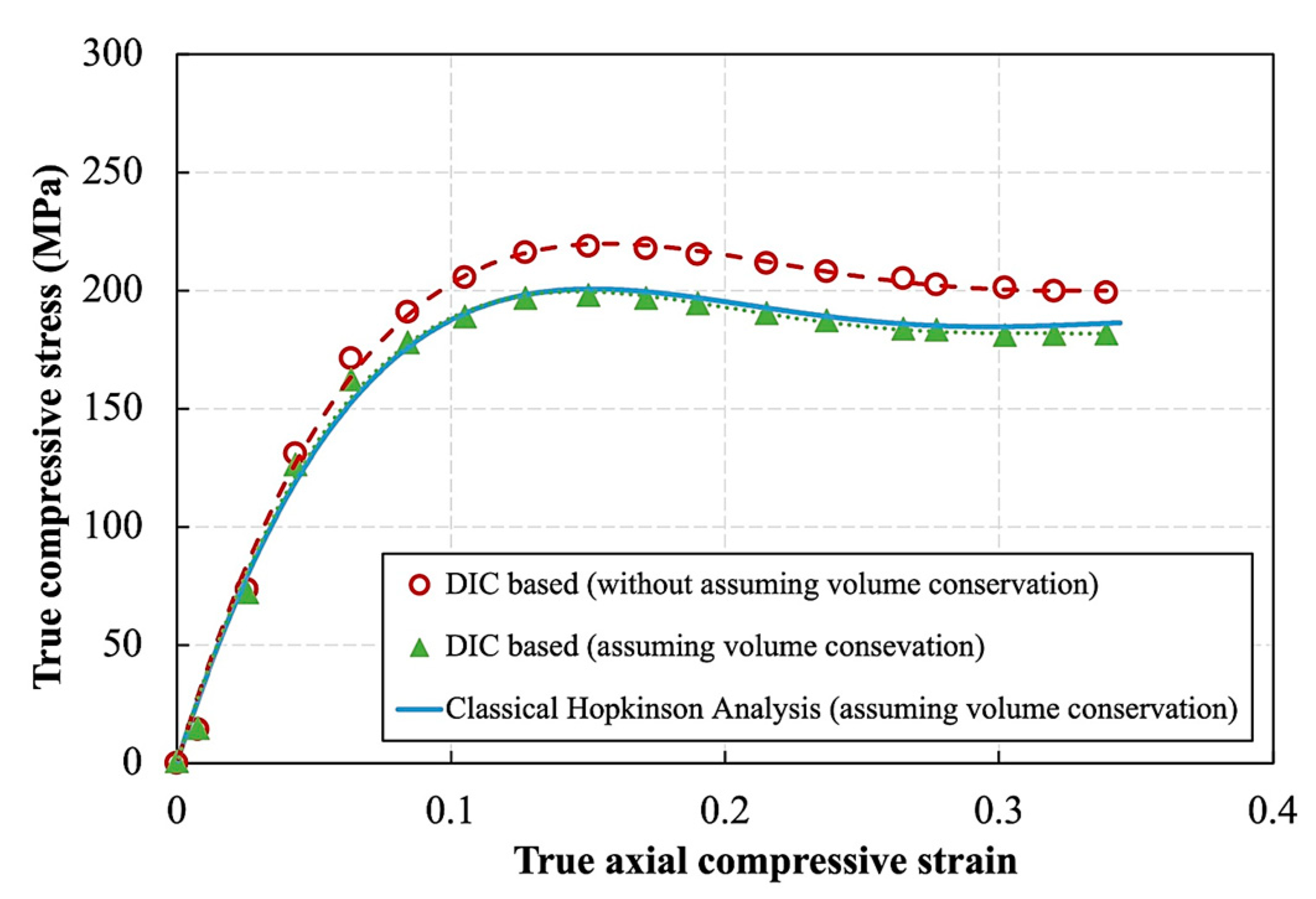
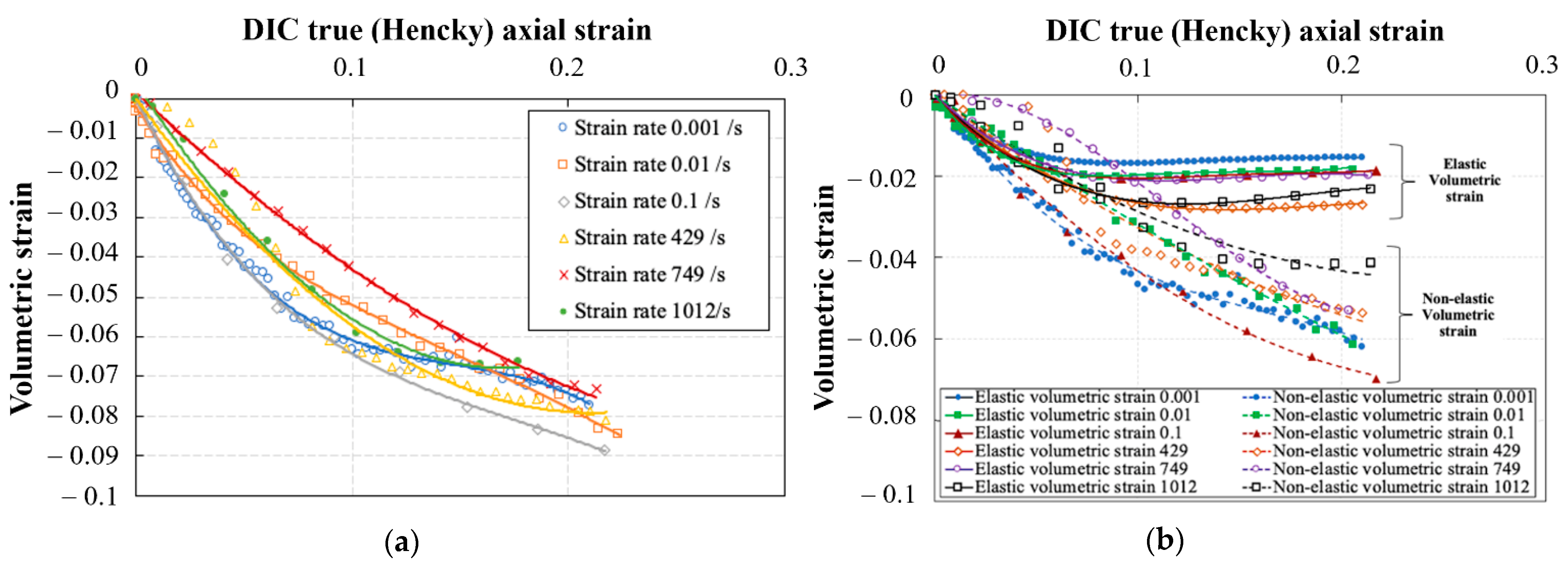
3.3. Axial Strain Homogeneity and Conservation of Volume
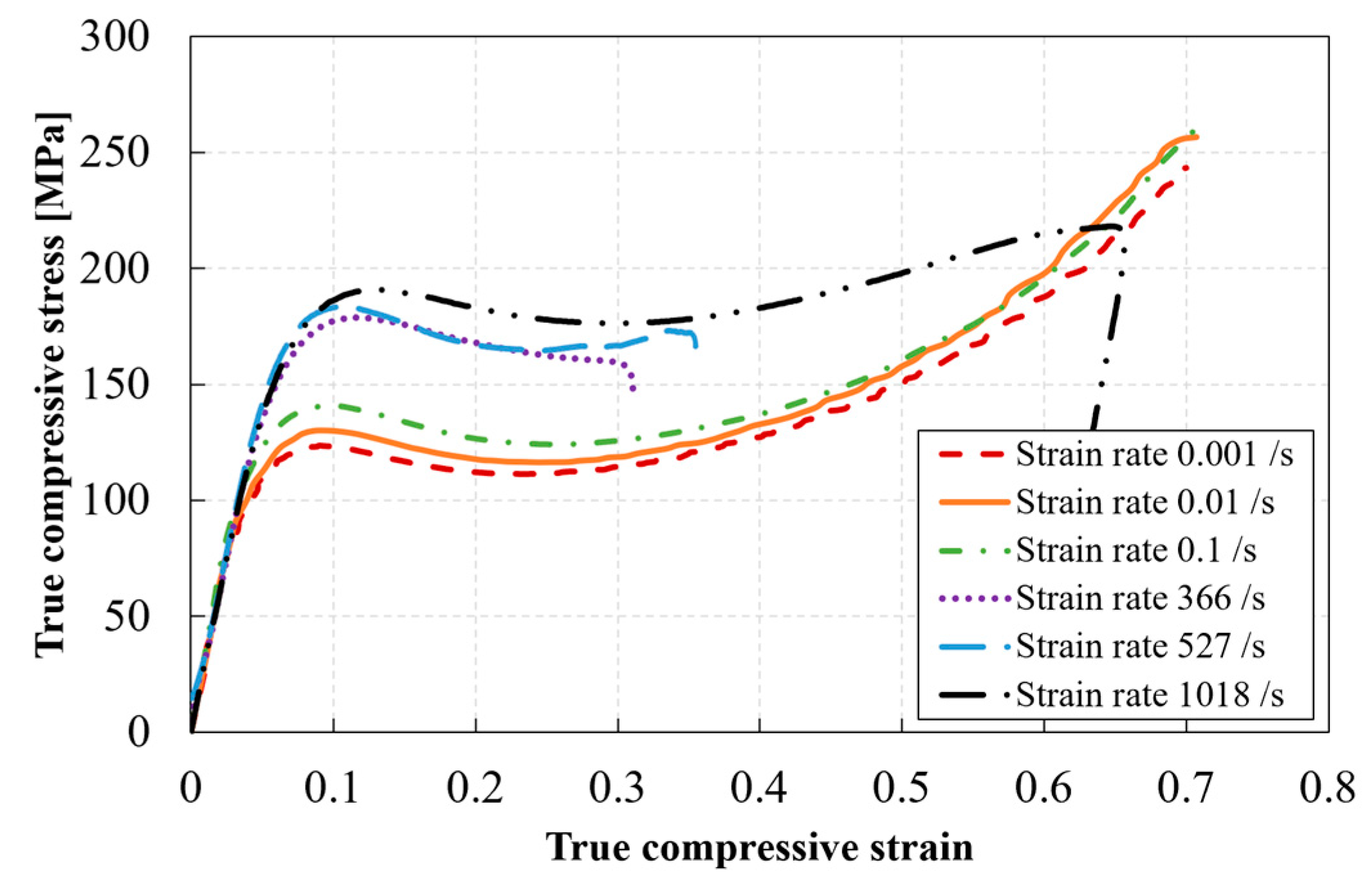
3.4. Compressive Stress–Strain Response of RTM6 Epoxy at Different Strain Rates
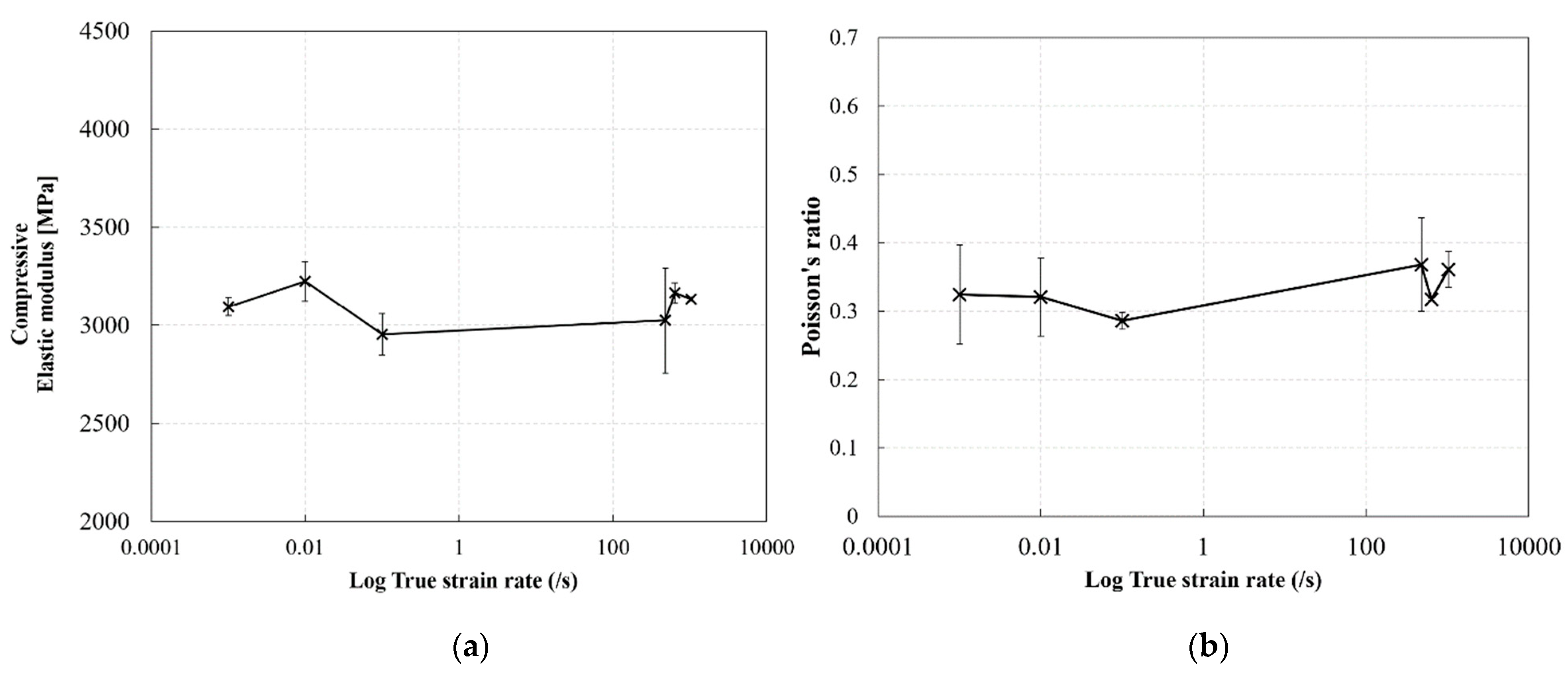
3.5. Effect of Strain Rate on the Elastic Modulus and Poisson’s Ratio of RTM6 Epoxy in Compression
3.6. Effect of Strain Rate on the Peak Yield Strength of the RTM6 Epoxy Resin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsieh, T.H.; Kinloch, A.J.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.C.; Sprenger, S. The mechanisms and mechanics of the toughening of epoxy polymers modified with silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2010, 51, 6284–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruckenberg, T.M.; Paton, R. (Eds.) Resin Transfer Moulding for Aerospace Structures; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; ISBN 978-94-010-5906-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-del Río, T.; Rodríguez, J. Compression yielding of epoxy: Strain rate and temperature effect. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, M.Y.; Liu, Y.; Chattopadhyay, A. Characterization of Epoxy Resin Including Strain Rate Effects Using Digital Image Correlation System. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2011, 25, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, J.D.; Ruggeri, C.R.; Goldberg, R.K.; Roberts, G.D.; Arnold, W.A.; Binienda, W.K. Measurement of Epoxy Resin Tension, Compression, and Shear Stress–Strain Curves over a Wide Range of Strain Rates Using Small Test Specimens. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2008, 21, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, C.A.; Bahlouli, N.; George, D.; Rémond, Y.; Ahzi, S. Identification of the dynamic behavior of epoxy material at large strain over a wide range of temperatures. Mech. Mater. 2020, 143, 103323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, X.; Kohlman, L.W.; Binienda, W.; Roberts, G.D.; Goldberg, R.K.; Benzerga, A.A. Determination of the intrinsic behavior of polymers using digital image correlation combined with video-monitored testing. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, N.K.; Shankar, P.J.; Kavala, V.R.; Ravikumar, G.; Pothnis, J.R.; Arya, H. High strain rate mechanical behavior of epoxy under compressive loading: Experimental and modeling studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, R.; Siviour, C.R.; Petrinic, N.; Wiegand, J. Experimental characterisation and constitutive modelling of RTM-6 resin under impact loading. Polymer 2008, 49, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelle, X.P.; Chevalier, J.; Bailly, C.; Pardoen, T.; Lani, F. Mechanical characterization and modeling of the deformation and failure of the highly crosslinked RTM6 epoxy resin. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2017, 21, 419–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerabek, M.; Major, Z.; Lang, R.W. Uniaxial compression testing of polymeric materials. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Pei, Z.; Tang, Z. Numerical and theoretical analysis of the inertia effects and interfacial friction in SHPB test systems. Materials 2020, 13, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Siviour, C.R.; Petrinic, N. The effect of strain rate, specimen geometry and lubrication on responses of aluminium AA2024 in uniaxial compression experiments. Exp. Mech. 2009, 49, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.Z.; Rusinek, A.; Jankowiak, T.; Abed, F.; Bernier, R.; Sutter, G. Influence of interfacial friction and specimen configuration in Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar system. Tribol. Int. 2015, 90, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, D.A. The effect of specimen dimensions on high strain rate compression measurements of copper. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1991, 24, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviour, C.R. High strain rate characterization of polymers. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1793, 060029. [Google Scholar]
- Tuninetti, V.; Gilles, G.; Péron-Lührs, V.; Habraken, A.M. Compression Test for Metal Characterization using Digital Image Correlation and Inverse Modeling. Procedia IUTAM 2012, 4, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.W.; Song, B. Split Hopkinson (Kolsky) Bar: Design, Testing and Applications; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4419-7981-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sunny, G.; Yuan, F.; Prakash, V.; Lewandowski, J. Design of inserts for split-hopkinson pressure bar testing of low strain-to-failure materials. Exp. Mech. 2009, 49, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.G.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Deng, Q.; Shen, L.; Mai, Y.W.; Guo, Y.Z.; Suo, T.; Hu, H.T.; Xie, F.Q.; et al. Determination of dynamic elastic modulus of polymeric materials using vertical split Hopkinson pressure bar. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2016, 108–109, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.W.; Rajendran, A.M.; Song, B.; Nie, X. Dynamic fracture of ceramics in armor applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, R. (Ed.) The Kolsky-Hopkinson Bar Machine: Selected Topics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9783319719191. [Google Scholar]
- Zotti, A.; Elmahdy, A.; Zuppolini, S.; Borriello, A.; Verleysen, P.; Zarrelli, M. Aromatic Hyperbranched Polyester/RTM6 Epoxy Resin for EXTREME Dynamic Loading Aeronautical Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmahdy, A.; Zotti, A.; Zuppolini, S.; Zarrelli, M.; Borriello, A.; Verleysen, P. Effect of Strain Rate and Silica Filler Content on the Compressive Behavior of RTM6 Epoxy—Based Nanocomposites. Polymers 2021, 13, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolsky, H. An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Materials at very High Rates of Loading. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1949, 62, 676–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.P.; Yee, A.F.; Moskala, E.J. The Molecular Basis for the Relationship between the Secondary Relaxation and Mechanical Properties of a Series of Polyester Copolymer Glasses. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 5944–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Correlation criterion | Zero normalized sum of square differences (ZNSSD) |
| Interpolation order | Bi-cubic spline |
| Shape function | Affine |
| Subset size (pixels) | 55 × 55 (quasi-static) and 21 × 21 (high strain rate) |
| Step size (pixels) | 10 |
| Strain window | 15 |
| Achieved Strain Rates for Elastic Modulus and Poisson’s Ratio (s−1) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Achieved Strain Rates for Peak Yield Strength (s−1) | True Peak Yield Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. dev. | Mean | Std. dev. | Mean | Std. dev. | ||
| 0.001 | 3242.733 | 256.889 | 0.3243 | 0.1256 | 0.001 | 116.403 | 6.2101 |
| 0.01 | 3358.254 | 91.116 | 0.3208 | 0.0985 | 0.01 | 125.318 | 4.2153 |
| 0.1 | 3250.859 | 314.344 | 0.2861 | 0.0178 | 0.1 | 135.196 | 7.8117 |
| 478.638 | 3293.361 | 185.774 | 0.3683 | 0.09698 | 365.760 | 184.840 | 8.2448 |
| 638.877 | 3307.398 | 251.415 | 0.3174 | 0.0017 | 527.334 | 191.603 | 11.305 |
| 1034.972 | 3270.952 | 182.501 | 0.3608 | 0.0375 | 1017.751 | 192.295 | 1.774 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmahdy, A.; Zotti, A.; Borriello, A.; Zarrelli, M.; Verleysen, P. In-Depth Analysis of the High Strain Rate Compressive Behavior of RTM6 Epoxy Using Digital Image Correlation. Polymers 2022, 14, 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091771
Elmahdy A, Zotti A, Borriello A, Zarrelli M, Verleysen P. In-Depth Analysis of the High Strain Rate Compressive Behavior of RTM6 Epoxy Using Digital Image Correlation. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091771
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmahdy, Ahmed, Aldobenedetto Zotti, Anna Borriello, Mauro Zarrelli, and Patricia Verleysen. 2022. "In-Depth Analysis of the High Strain Rate Compressive Behavior of RTM6 Epoxy Using Digital Image Correlation" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091771
APA StyleElmahdy, A., Zotti, A., Borriello, A., Zarrelli, M., & Verleysen, P. (2022). In-Depth Analysis of the High Strain Rate Compressive Behavior of RTM6 Epoxy Using Digital Image Correlation. Polymers, 14(9), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091771








