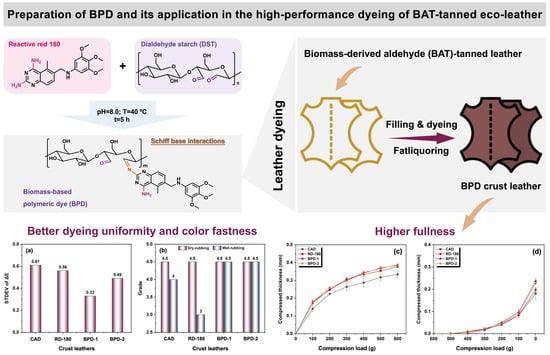
Novel Biomass-Based Polymeric Dyes: Preparation and Performance Assessment in the Dyeing of Biomass-Derived Aldehyde-Tanned Leather
Abstract
Share and Cite
Ding, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Remón, J.; Wang, K.; Bao, L.; Pang, X. Novel Biomass-Based Polymeric Dyes: Preparation and Performance Assessment in the Dyeing of Biomass-Derived Aldehyde-Tanned Leather. Polymers 2023, 15, 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102300
Ding W, Zhang Y, Li S, Remón J, Wang K, Bao L, Pang X. Novel Biomass-Based Polymeric Dyes: Preparation and Performance Assessment in the Dyeing of Biomass-Derived Aldehyde-Tanned Leather. Polymers. 2023; 15(10):2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102300
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Wei, Yinuo Zhang, Shuolin Li, Javier Remón, Kanglei Wang, Lihong Bao, and Xiaoyan Pang. 2023. "Novel Biomass-Based Polymeric Dyes: Preparation and Performance Assessment in the Dyeing of Biomass-Derived Aldehyde-Tanned Leather" Polymers 15, no. 10: 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102300
APA StyleDing, W., Zhang, Y., Li, S., Remón, J., Wang, K., Bao, L., & Pang, X. (2023). Novel Biomass-Based Polymeric Dyes: Preparation and Performance Assessment in the Dyeing of Biomass-Derived Aldehyde-Tanned Leather. Polymers, 15(10), 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102300