Shockproof Deformable Infrared Radiation Sensors Based on a Polymeric Rubber and Organic Semiconductor H2Pc-CNT Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
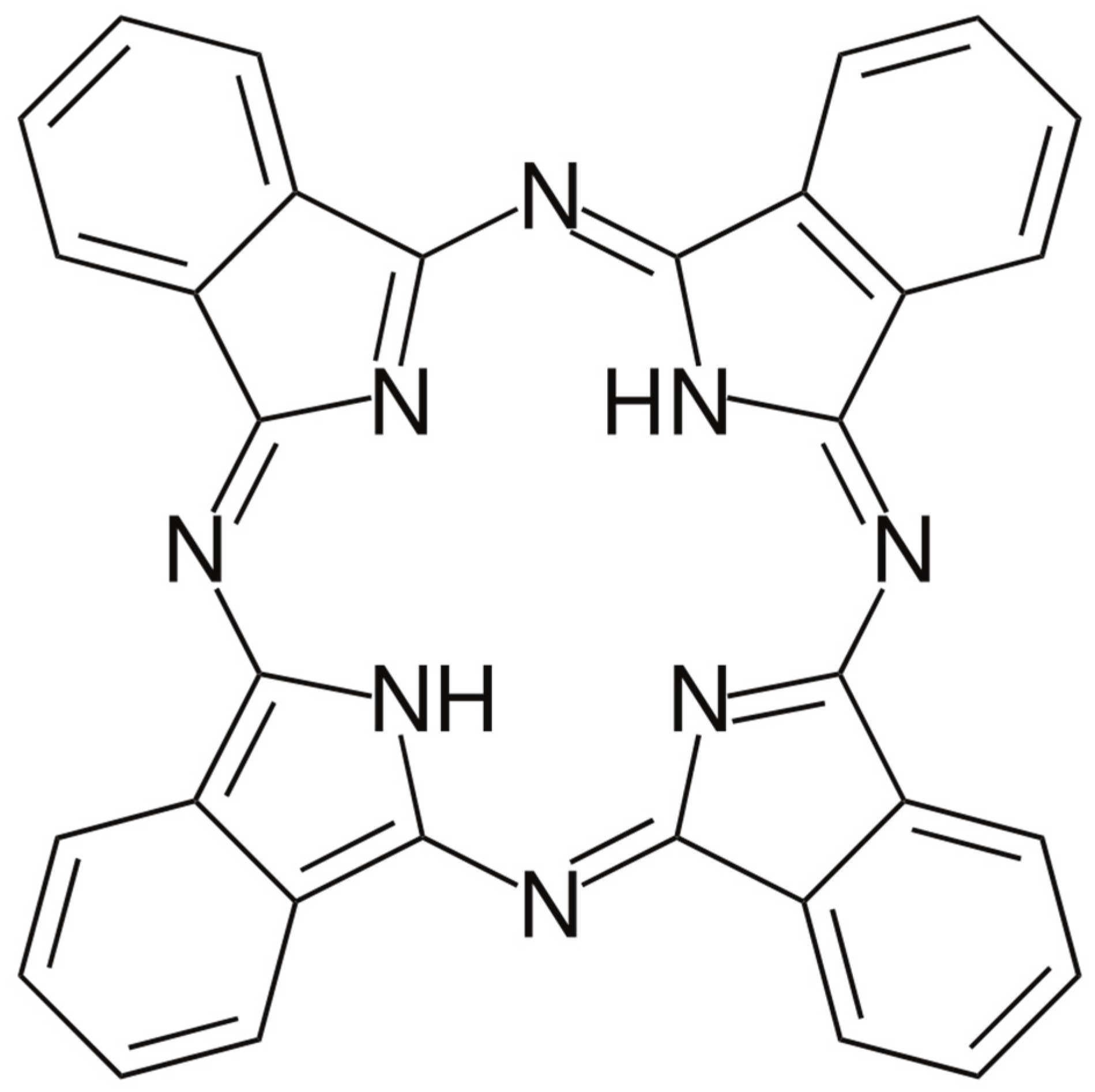
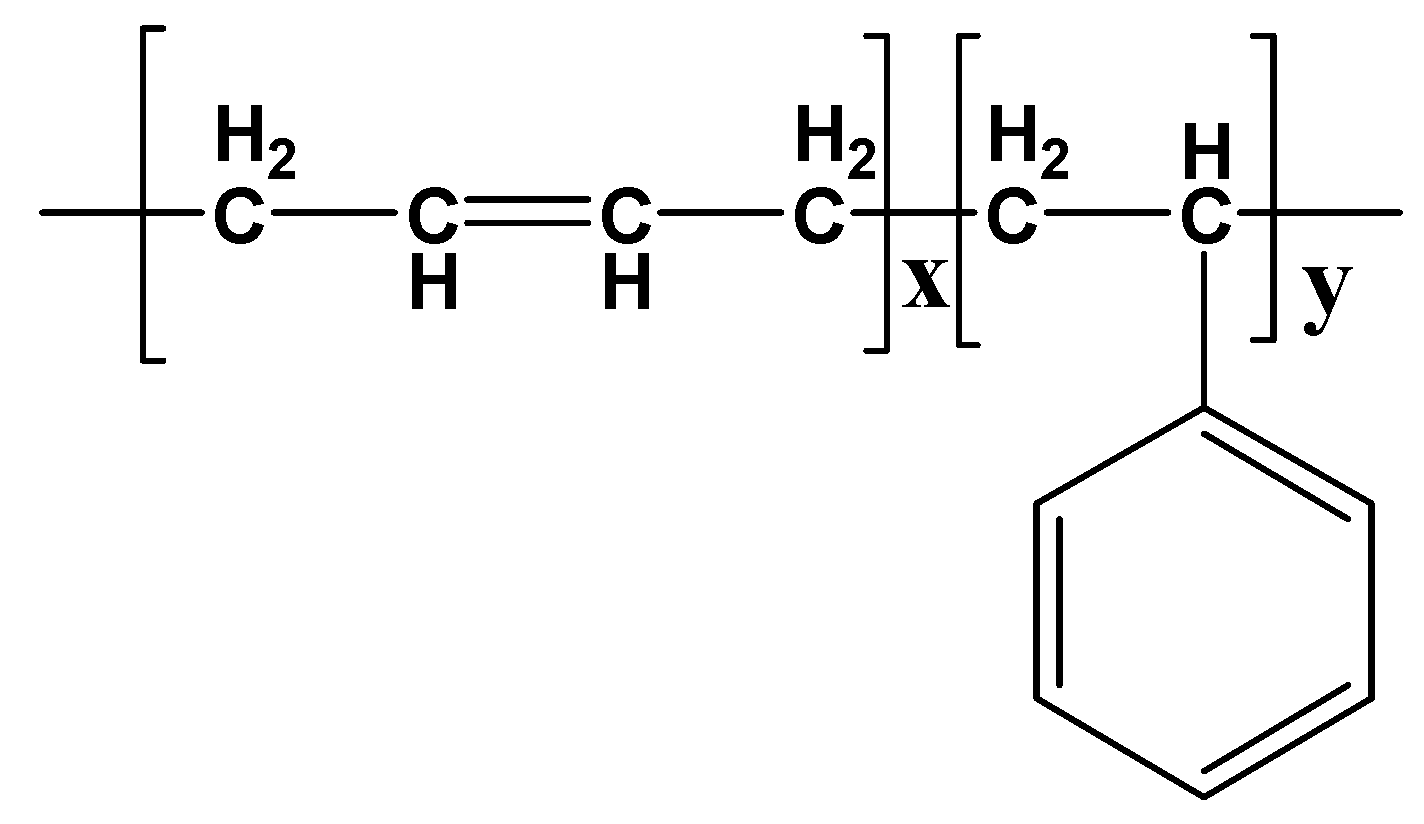
2.1. Materials
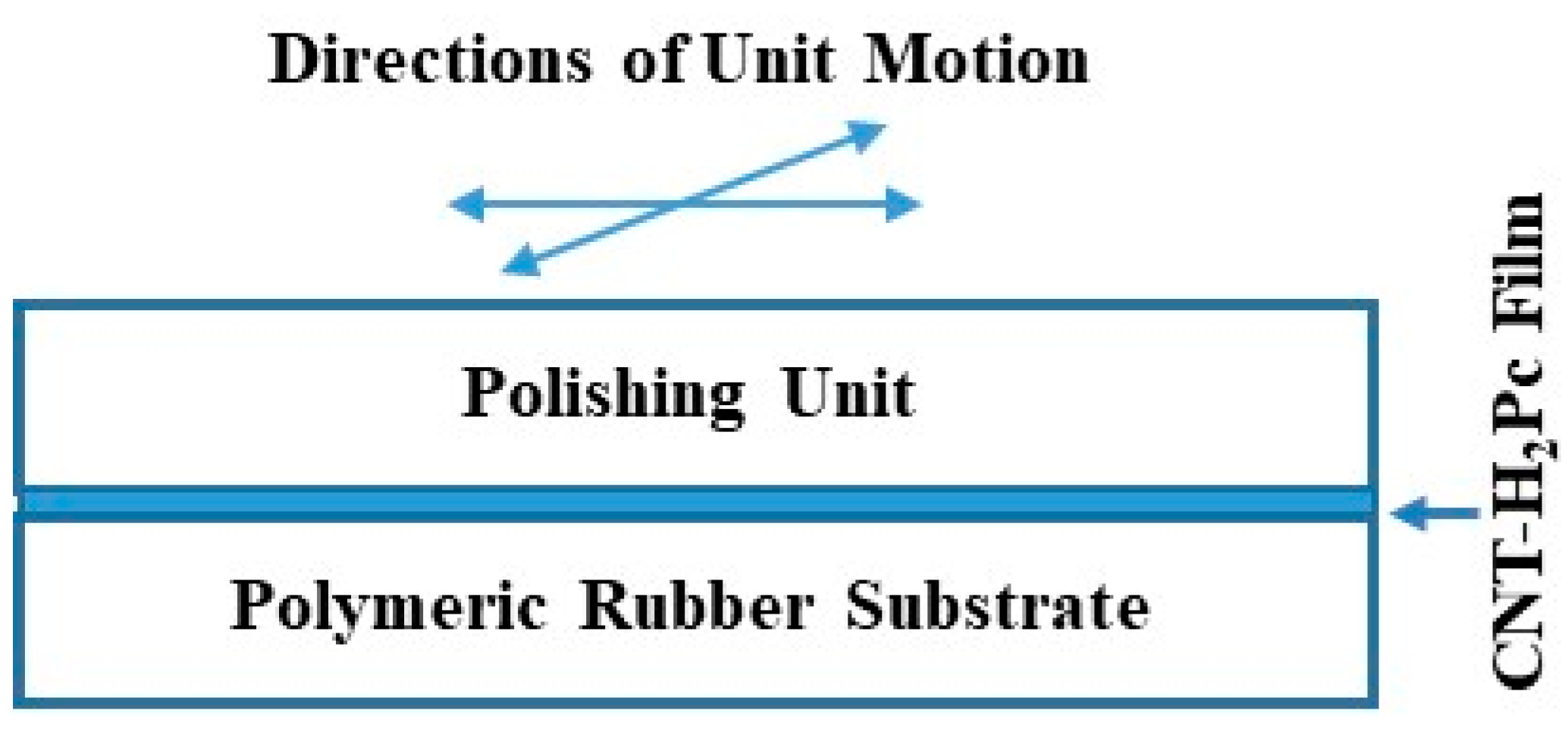
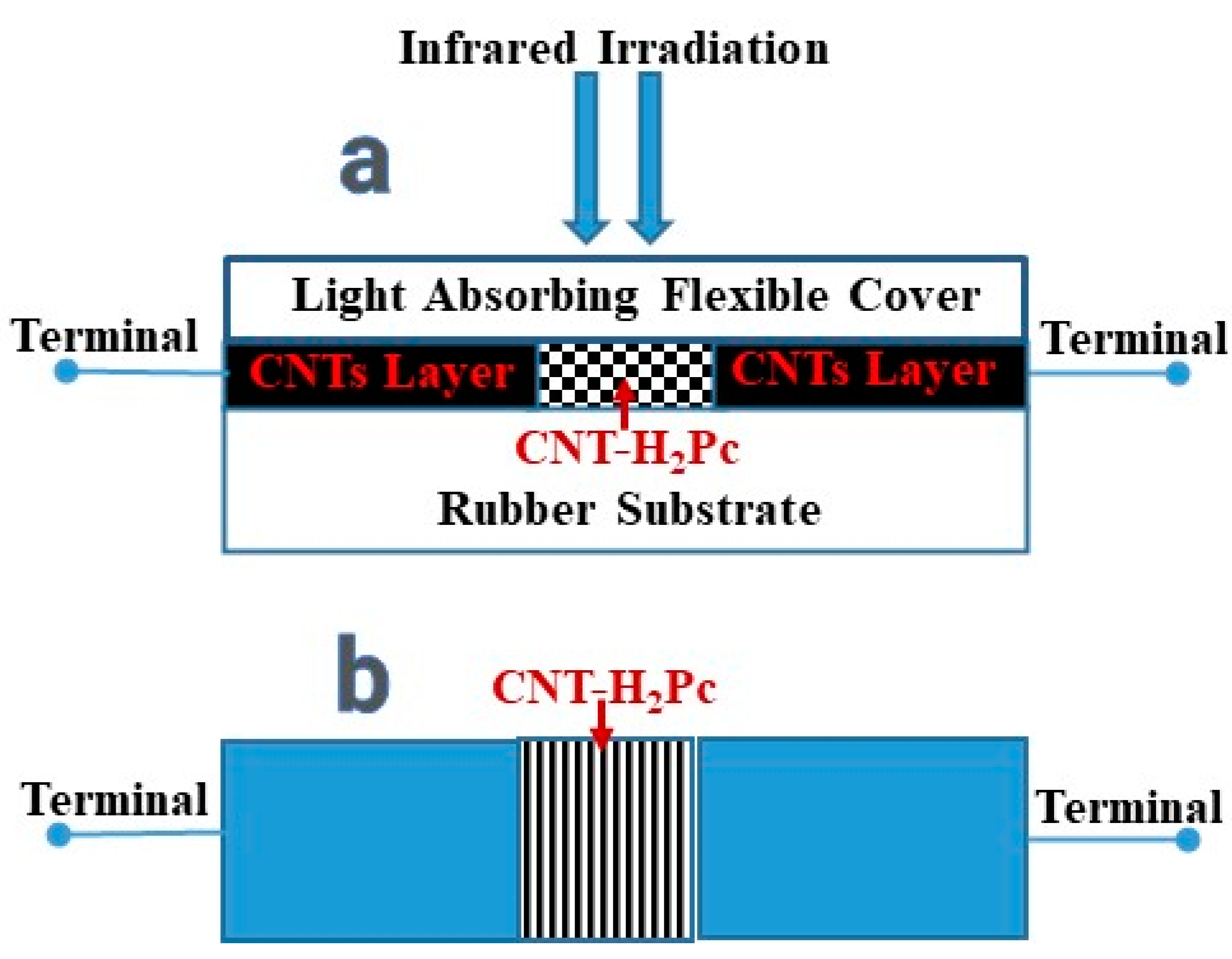
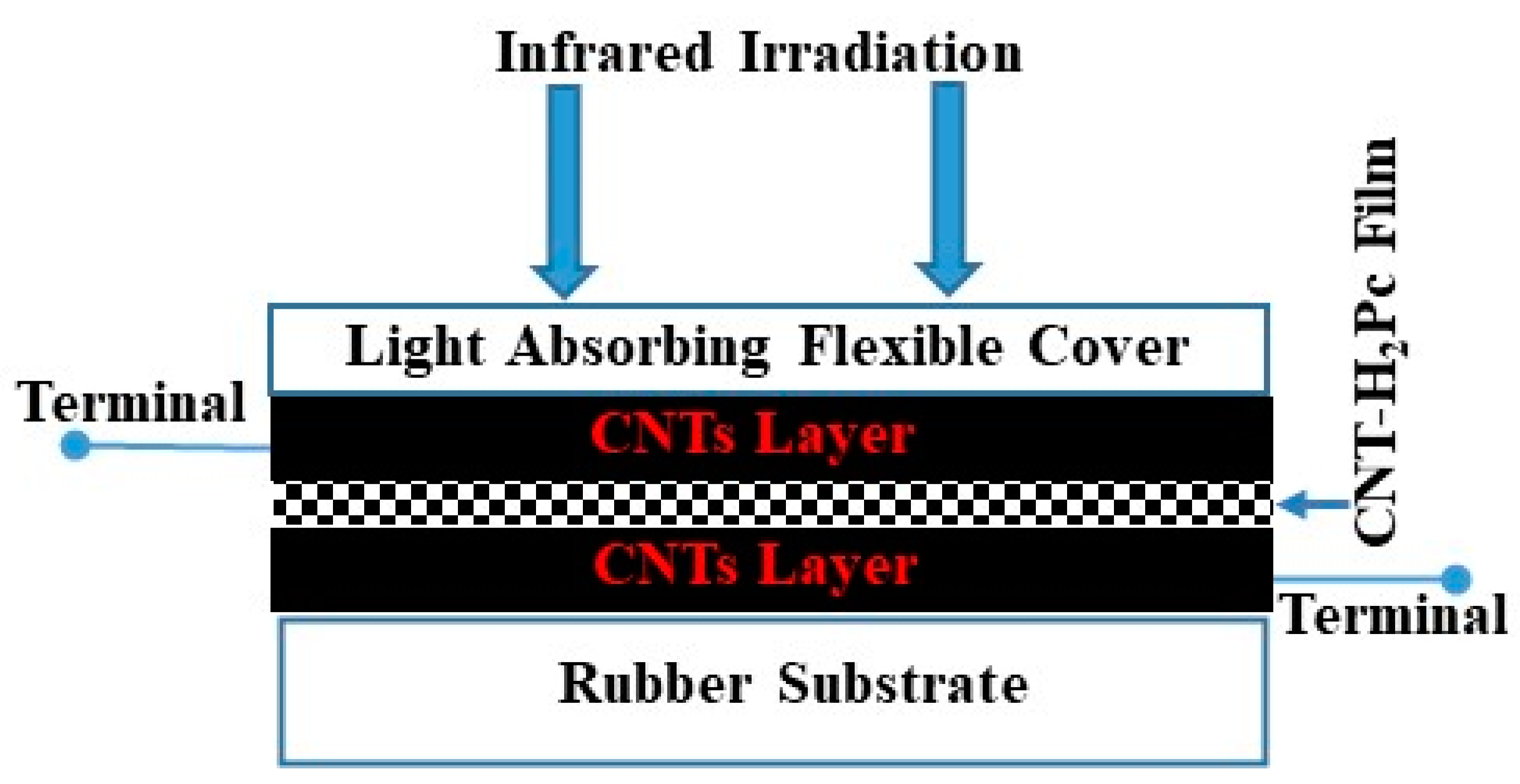
2.2. Methods
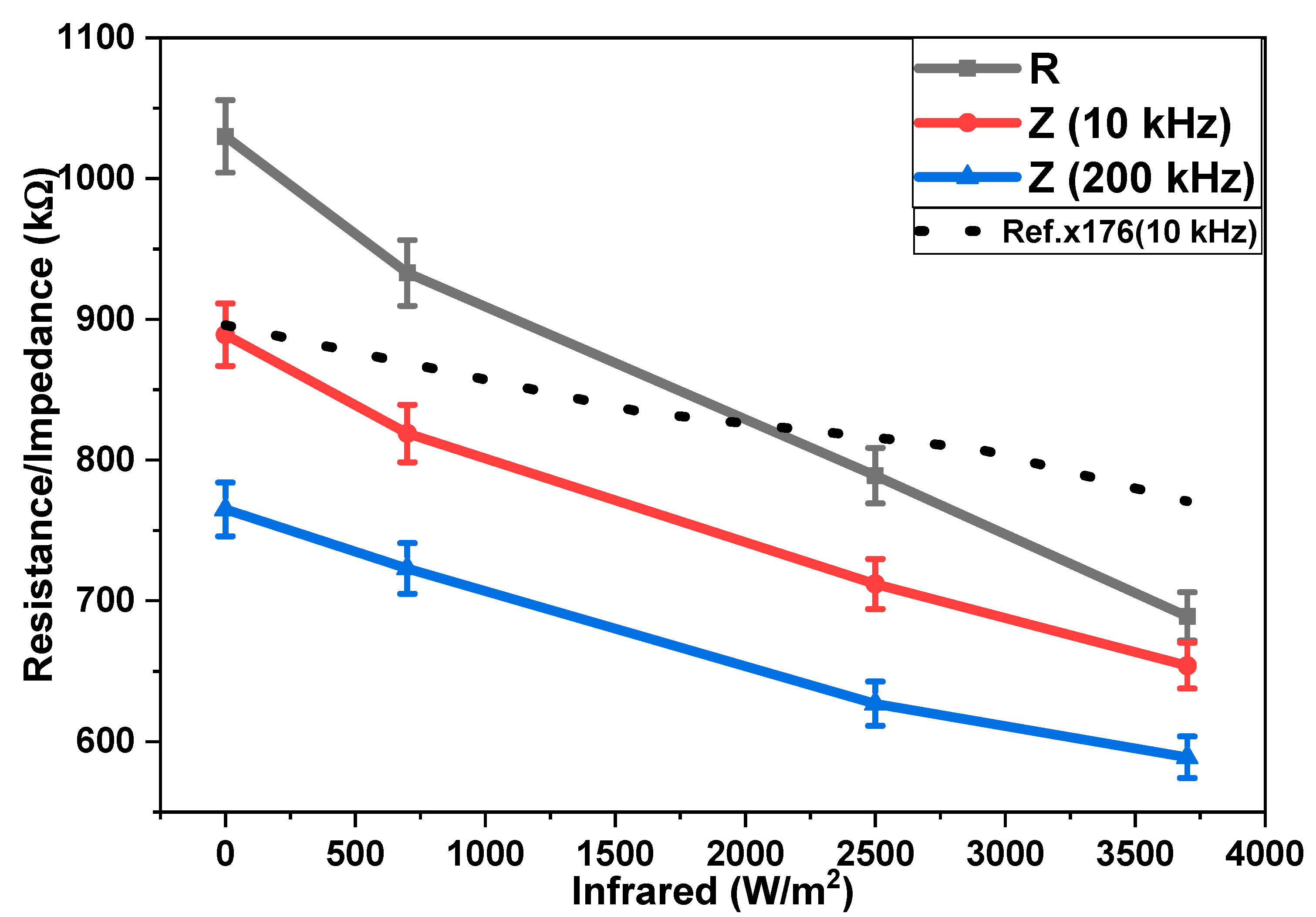
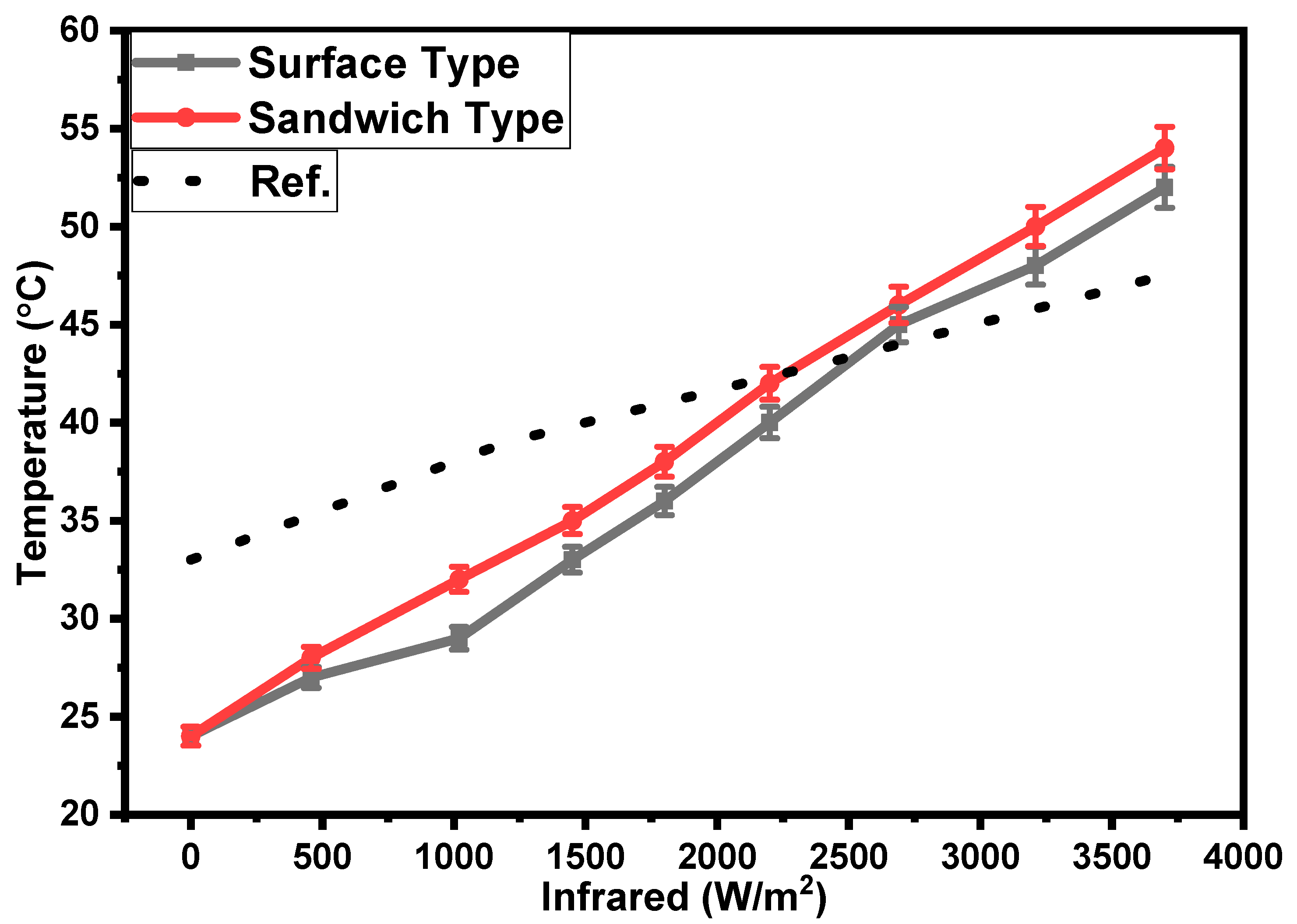
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogt, H. Bolometer Having an Organic Semiconductor Layer Arrangement. European Patent Office EP 1994384 B1, 27 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kettle, J.; Chang, S.-W.; Horie, M. IR Sensor based on low bandgap organic photodiode with up-converting phosphor. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3221–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Kim, H.; Azoulay, J.D.; Ng, T.N. Emerging design and characterization guidelines for polymer-based infrared photodetectors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3144–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Cheng, J.; Pisano, A.; Cauley, T.H., III. Infrared Sensor Systems and Devices. U.S. Patent 7,547,886, 16 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Siegmund, B.; Mischok, A.; Benduhn, J.; Zeika, O.; Ullbrich, S.; Nehm, F.; Böhm, M.; Spoltore, D.; Fröb, H.; Körner, C. Organic narrowband near-infrared photodetectors based on intermolecular charge-transfer absorption. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Fukuda, K.; Wang, M.; Lee, C.; Yokota, T.; Jin, H.; Jinno, H.; Kimura, H.; Zalar, P.; Matsuhisa, N. Ultraflexible Near-Infrared Organic Photodetectors for Conformal Photoplethysmogram Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddiard, K.C. Semiconductor Film Bolometer Thermal Infrared Detector. U.S. Patent 5,369,280, 11 December 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Ma, D. Development of organic semiconductor photodetectors: From mechanism to applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1800522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.-H.; Lee, J.W.; Manders, J.R.; So, F. Multi-spectral imaging with infrared sensitive organic light emitting diode. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5946. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nahass, M.; Farid, A.; Attia, A.; Ali, H. Structural properties and UV to NIR absorption spectra of metal-free phthalocyanine (H~ 2Pc) thin films. FIZIKA A-ZAGREB- 2006, 15, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, T.J.; Vera-Reveles, G.; González, G.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, J.M.; Linhardt, R.J.; Navarro-Contreras, H.; González, F.J. Bolometric properties of semiconducting and metallic single-walled carbon nanotube composite films. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaikie, A.; Miller, D.; Alemán, B.J. A fast and sensitive room-temperature graphene nanomechanical bolometer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, M.; Morita, S. Infrared sensor with precisely patterned Au black absorption layer. In Infrared Technology and Applications XXIV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Hyseni, G.; Caka, N.; Hyseni, K. Infrared thermal detectors parameters: Semiconductor bolometers versus pyroelectrics. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 2010, 9, 238–247. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G. Image Sensors Made from Organic Semiconductors. U.S. Patent 6,300,612, 09 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kweon, O.Y.; Kim, H.; Yoo, J.H.; Han, S.G.; Oh, J.H. Recent advances in organic sensors for health self-monitoring systems. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 8569–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouklin, N.; Tzolov, M.; Straus, D.; Yin, A.; Xu, J. Infrared absorption properties of carbon nanotubes synthesized by chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 4463–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfattner, R.; Lebedev, V.; Laukhina, E.; Kumar, S.C.; Esteban-Martin, A.; Ramaiah-Badarla, V.; Ebrahim-Zadeh, M.; de Arquer, F.P.G.; Konstantatos, G.; Laukhin, V. A Highly Sensitive Pyroresistive All-Organic Infrared Bolometer. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A.; Shahi, M.; Brill, J.W.; Fabiano, S.; Crispin, X. Conducting-Polymer Bolometers for Low-Cost IR-Detection Systems. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Reveles, G.; Simmons, T.J.; Bravo-Sánchez, M.; Vidal, M.; Navarro-Contreras, H.; González, F.J. High-sensitivity bolometers from self-oriented single-walled carbon nanotube composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3200–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xing, W.; Li, H.; Xie, Z.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Fundamental researches on graphene/rubber nanocomposites. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2019, 2, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chani, M.T.S.; Karimov, K.S.; Asiri, A.M. Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Powder Based Multifunctional Pressure, Displacement and Gradient of Temperature Sensors. Semiconductors 2020, 54, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chani, M.T.S.; Karimov, K.S.; Asiri, A.M. Impedimetric humidity and temperature sensing properties of the graphene–carbon nanotubes–silicone adhesive nanocomposite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 6419–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N.; Karimov, K.S. Shock-proof and supple multiplex sensor based on Silicon composite fabricated through an energy-free technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 112902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chani, M.T.S.; Asiri, A.M. Deformable organic semiconductor sensors based on metal free phthalocyanine for pressure and compressive displacement monitoring. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 2022, 17, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Qasuria, T.A.; Fatima, N.; Karimov, K.S.; Ibrahim, M.A. A novel and stable ultraviolet and infrared intensity sensor in impedance/capacitance modes fabricated from degraded CH3NH3PbI3-xClx perovskite materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12795–12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, S.; Nagaya, T.; Ogata, F.; Maruoka, Y.; Sato, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Avoiding thermal injury during near-infrared photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT): The importance of NIR light power density. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, U.; Parret, R.; Nanot, S.; Bruna, M.; Borini, S.; De Fazio, D.; Zhao, Z.; Lidorikis, E.; Koppens, F.H.L.; Ferrari, A.C.; et al. Graphene-based mid-infrared room-temperature pyroelectric bolometers with ultrahigh temperature coefficient of resistance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitigala, P.K.D.D.P.; Jayaweera, P.V.V.; Matsik, S.G.; Perera, A.G.U.; Liu, H.C. Highly sensitive GaAs/AlGaAs heterojunction bolometer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knite, M.; Ozols, K.; Fuith, A.; Aulika, I.; Orlovs, R. Photo-thermal electrical resistance response of polyisoprene/nanographite composites. Polymer 2016, 85, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata, M. Chapter 10—Silicon infrared focal plane arrays. In Handbook of Infra-Red Detection Technologies; Henini, M., Razeghi, M., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 353–392. [Google Scholar]
- Niklaus, F.; Pejnefors, J.; Dainese, M.; Häggblad, M.; Hellström, P.-E.; Wallgren, U.; Stemme, G.; Flir, B.; Ab, S.; Danderyd, S.; et al. Characterization of transfer-bonded silicon bolometer arrays. Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2004, 5406, 521–530. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Deng, X.; Xiang, L.; Xu, K.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y. Preparation and Bolometric Responses of MoS2 Nanoflowers and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite Network. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezcan, D.S.; Eminoglu, S.; Akar, O.S.; Akin, T. A low cost uncooled infrared microbolometer focal plane array using the CMOS n-well layer. In Proceedings of Technical Digest. MEMS 2001. 14th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (Cat. No.01CH37090), Interlaken, Switzerland, 25 January 2001; pp. 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Neamen, D.A. Semiconductor Physics and Devices: Basic Principles; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Li, L.; Geng, D.; Liu, M. A review for polaron dependent charge transport in organic semiconductor. Org. Electron. 2018, 61, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, M.; Smida, A.; Kossi, S.E. Effect of polaron formation in conduction and dielectric behavior in La0.7Sr0.25K0.05MnO3 oxide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 6014–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chani, M.T.S.; Asiri, A.M.; Karimov, H. Fabrication of Flexible Conductive Films, with Semiconductive Material, Formed with Rubbing-in Technology for Elastic or Deformable Devices. U.S. Patent 10,994,387, 04 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, T.; Davison, R.; Hargreaves, M. Engineering Mathematics: A Modern Foundation for Electrical, Elctronic, and Control Engineers; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]


| Sr. # | Sensing Materials | Fabrication Technology | Device Design | TCR (%/K) | Sensitivity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Single-crystal Si | SOI Process | Diode | 0.5–0.7 | - | [31] |
| 2 | SWCNT composite | High-pressure method | Bolometer | −2.94 | 1.2 × 108 cm Hz1/2/W | [20] |
| 3 | Polycrystalline silicon | CMOS process | Microbolometer | −0.52 | 218.2 Ω/°C | [32] |
| 4 | MoS2-CNT composite | Facile hydrothermal process | - | 0.25 | - | [33] |
| 5 | Polysilicon | CMOS process | Infrared microbolometer | 0.34 to 0.58 | 2.2 × 108 cm Hz1/2/W | [34] |
| 6 | CNT-H2Pc | Rubbing-in technology | Sandwich-type bolometer | −1.1 | 0.87 Ω/(W/m2) | Current Study |
| Surface-type bolometer | −1.2 | −92.2 Ω/(W/m2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chani, M.T.S.; Karimov, K.S.; Kamal, T.; Fatima, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Asiri, A.M. Shockproof Deformable Infrared Radiation Sensors Based on a Polymeric Rubber and Organic Semiconductor H2Pc-CNT Composite. Polymers 2023, 15, 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122691
Chani MTS, Karimov KS, Kamal T, Fatima N, Rahman MM, Asiri AM. Shockproof Deformable Infrared Radiation Sensors Based on a Polymeric Rubber and Organic Semiconductor H2Pc-CNT Composite. Polymers. 2023; 15(12):2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122691
Chicago/Turabian StyleChani, Muhammad Tariq Saeed, Khasan S. Karimov, Tahseen Kamal, Noshin Fatima, Mohammed M. Rahman, and Abdullah M. Asiri. 2023. "Shockproof Deformable Infrared Radiation Sensors Based on a Polymeric Rubber and Organic Semiconductor H2Pc-CNT Composite" Polymers 15, no. 12: 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122691
APA StyleChani, M. T. S., Karimov, K. S., Kamal, T., Fatima, N., Rahman, M. M., & Asiri, A. M. (2023). Shockproof Deformable Infrared Radiation Sensors Based on a Polymeric Rubber and Organic Semiconductor H2Pc-CNT Composite. Polymers, 15(12), 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122691









