Overview of Solar Steam Devices from Materials and Structures
Abstract
1. Background and Significance
2. Solar Steam Device
2.1. Working Principles of Solar Steam Technology
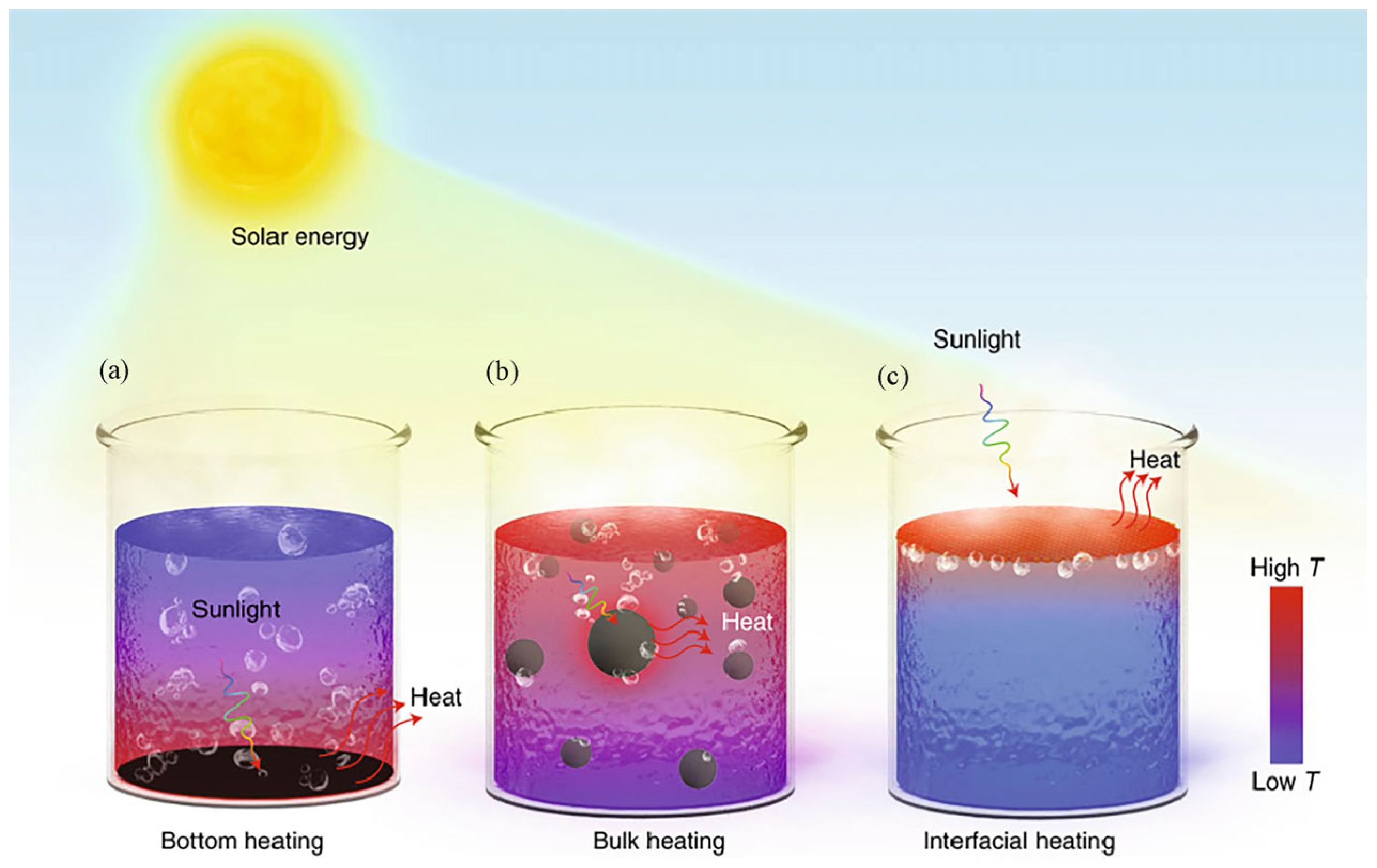
2.2. Types of Heating Systems and Solar Steam Generators
3. Photothermal Materials
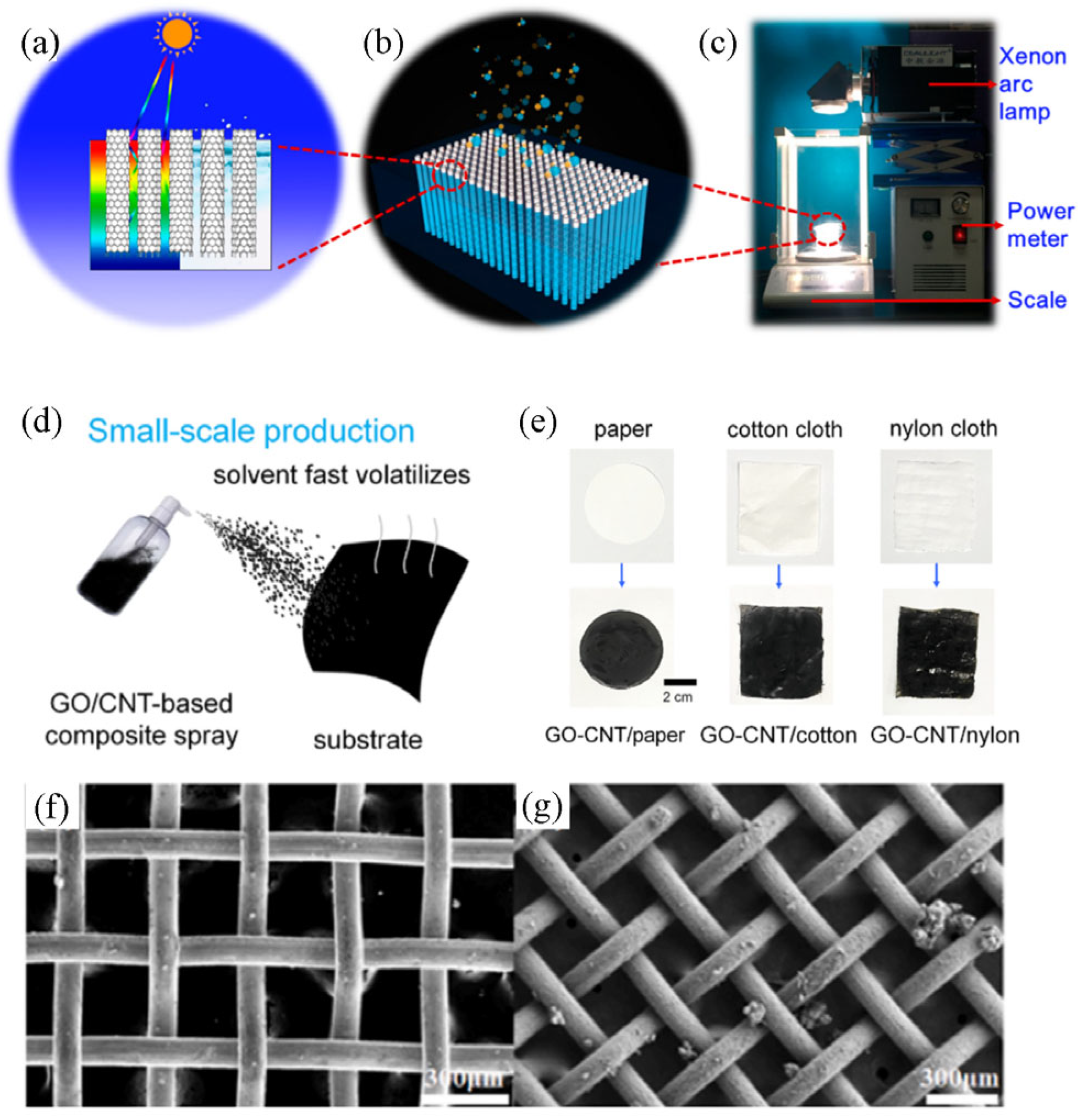
3.1. Carbon-Based Material
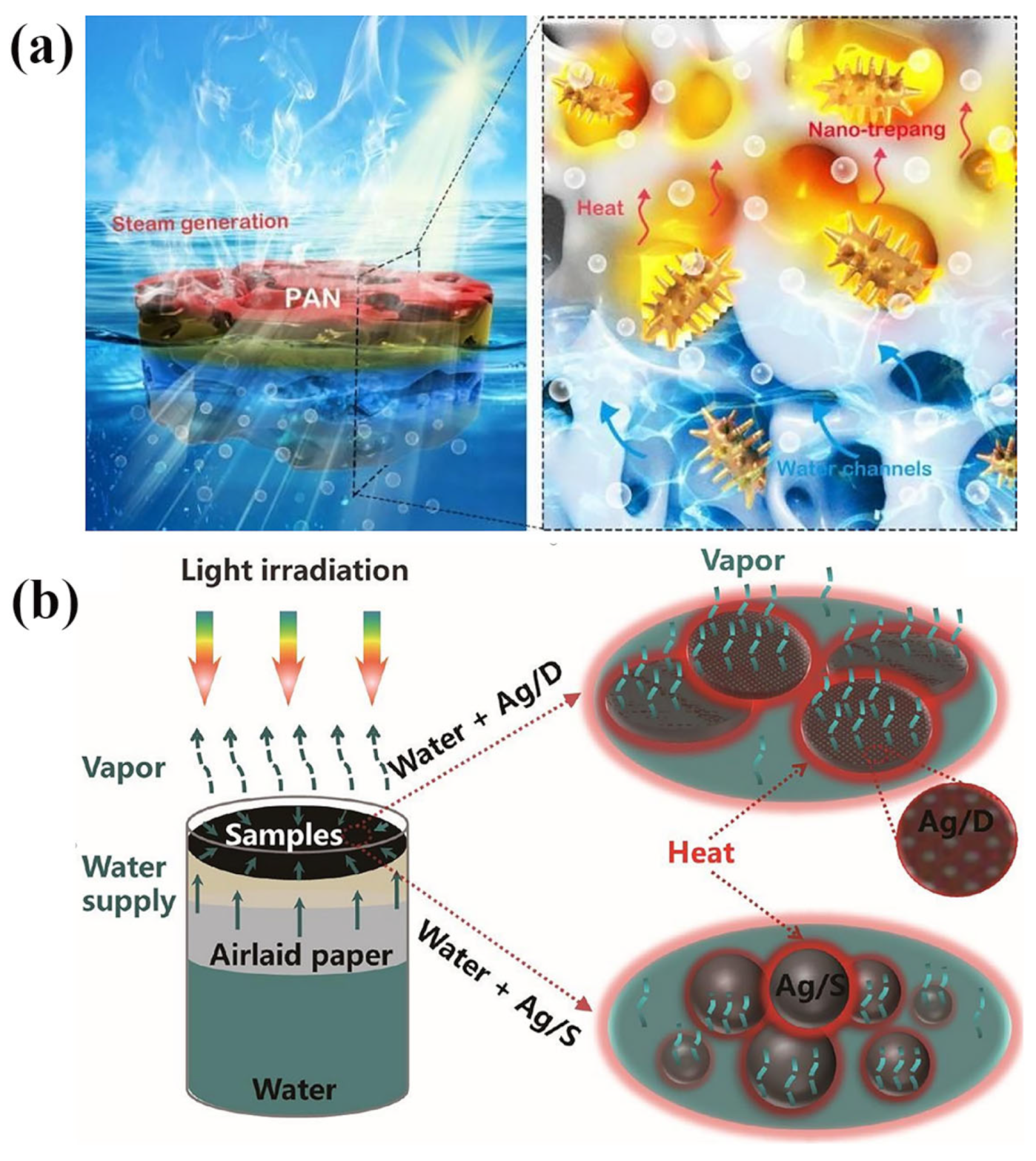
3.2. Plasma Metal
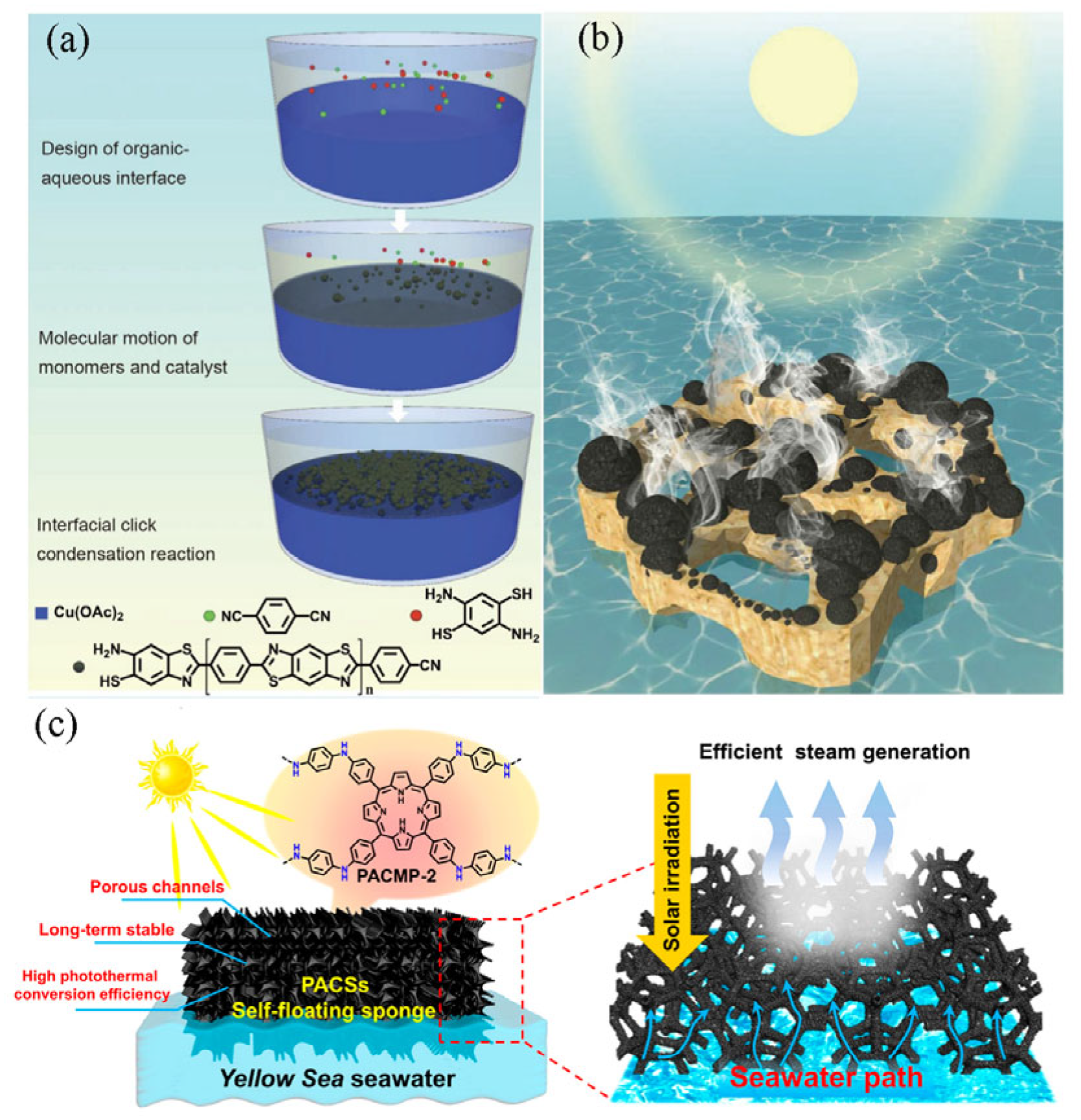
3.3. Conjugated Polymer
3.4. Inorganic Semiconductor
4. Design of Device Structure
4.1. Double-Layer Structure
4.2. Three-Dimensional Structure
4.3. Biomimetic Structure
4.4. Other Structures
5. Summary and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, H.; Geng, X.M.; Li, S.M.; Tu, H.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Bao, L.X.; Peng, Y.; Wan, Y.F. Multi-3D hierarchical biomass-based carbon particles absorber for solar desalination and thermoelectric power generator. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.T.; Liu, Z.; Gao, L.L.; He, Y.S.; Jin, B.W.; Meng, X.; Qi, Y.P.; Ye, C. Engineered Wood with Hierarchically Tunable Microchannels toward Efficient Solar Vapor Generation. Langmuir 2022, 38, 12773–12784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.H.; Chen, T.; Xu, J.L.; Yao, G.S.; Xie, J.; Cheng, Y.P.; Miao, Z.; Wang, K. Salt-rejecting solar interfacial evaporation. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2021, 2, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Xu, L.Q.; Cai, J.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Lv, B.Z.; Chao, J.B.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhao, Y.Q. A Stable Bilayer Polypyrrole-Sorghum Straw Evaporator for Efficient Solar Steam Generation and Desalination. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 6, 2100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Bian, F.G.; Sun, Z.Z. Porous wood-carbonized solar steam evaporator. Wood Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Functional materials in desalination: A review. Desalination 2019, 468, 114077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onggowarsito, C.; Feng, A.; Mao, S.; Nguyen, L.N.; Xu, J.Y.; Fu, Q. Water Harvesting Strategies through Solar Steam Generator Systems. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202201543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, E.S.; Benedict, M.A.; Desai, D.; Rivest, J.B. A redox-shuttled electrochemical method for energy-efficient separation of salt from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13411–13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, V.G.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Deng, S.G. Renewable and sustainable approaches for desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2641–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.X.; Li, Y.N.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.H.; Gong, L.; Zhang, T.; Sun, S.Y. Study of the Seawater Desalination Performance by Electrodialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Deng, H.; Fu, Q. Thermoelectric PEDOT: PSS Sheet/SWCNTs composites films with layered structure. Compos. Commun. 2021, 27, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Zhao, X.W.; Ye, L. Polyoxymethylene/Carbon Nanotube Self-Assembly Networks with Improved Electrical Conductivity for Engineering Functional Structural Materials. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 9606–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.C.; Fu, Q.; Deng, H. Recent progress in solar photothermal steam technology for water purification and energy utilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.K.; Tian, Z.Y.; Wang, F.; He, J.X.; Ye, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Sun, H.X.; Li, A. Enhanced solar-to-heat efficiency of photothermal materials containing an additional light-reflection layer for solar-driven interfacial water evaporation. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 2932–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Qin, Y.; Jia, F.F.; Li, Y.M.; Song, S.X. Magnetic MoS2 nanosheets as recyclable solar-absorbers for high-performance solar steam generation. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahi, R.; Morikawa, T.; Ohwaki, T.; Aoki, K.; Taga, Y. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science 2001, 293, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.P.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.D.; Gong, F.; Pei, X.D.; Wang, W.B.; Li, H.; Zeng, W.; Wu, M.Q.; Papavassiliou, D.V. Molybdenum and tungsten disulfides-based nanocomposite films for energy storage and conversion: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 908–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagfeldt, A.; Grätzel, M. Molecular photovoltaics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Mende, L.; Fechtenkotter, A.; Mullen, K.; Moons, E.; Friend, R.H.; MacKenzie, J.D. Self-organized discotic liquid crystals for high-efficiency organic photovoltaics. Science 2001, 293, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sai, H.; Yugami, H.; Kanamori, Y.; Hane, K. Solar selective absorbers based on two-dimensional W surface gratings with submicron periods for high-temperature photothermal conversion. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2003, 79, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Emerging investigator series: The rise of nano-enabled photothermal materials for water evaporation and clean water production by sunlight. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.F.; Mu, X.J.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.Q.; Wei, A.Y.; Tian, Y.Z.; Zhu, G.S.; Xu, H.R.; et al. Integrated photothermal aerogels with ultrahigh-performance solar steam generation. Nano Energy 2020, 74, 104857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, B.; Li, J.L.; Zhu, J. Interfacial solar vapor generation: Materials and structural design. ACC Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Xie, W.R.; Zhu, J. Interfacial solar steam/vapor generation for heating and cooling. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermel, P.; Yazawa, K.; Gray, J.L.; Xu, X.; Shakouri, A. Hybrid strategies and technologies for full spectrum solar conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2776–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregambi, C.; Chirone, R.; Montagnaro, F.; Salatino, P.; Solimene, R. Heat transfer in directly irradiated fluidized beds. Sol. Energy 2016, 129, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Wang, W.B.; Li, H.; Xia, D.D.; Dai, Q.W.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, M.Z.; Li, J.; Papavassiliou, D.V.; Xiao, R. Solid waste and graphite derived solar steam generator for highly-efficient and cost-effective water purification. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sui, Y.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Cai, Z.S.; Xu, B. An all-day solar-driven vapor generator via photothermal and Joule-heating effects. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25178–25186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.T.; Huang, K.L.; Meng, X.C. Review on solar-driven evaporator: Development and applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 119, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Ni, G.; Song, C.Y.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.B.; Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Deng, T. Solar driven interfacial evaporation. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.K.; Fu, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.B. Diameter effect of gold nanoparticles on photothermal conversion for solar steam generation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4815–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, D.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhao, Q.; Xing, B.S. Advances and challenges of broadband solar absorbers for efficient solar steam generation. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 2264–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Gao, T.T.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.J.; Luo, W.; Song, J.W.; Hitz, E.; Jia, C.; Zhou, Y.B.; Yang, B.; et al. 3D-printed, all-in-one evaporator for high-efficiency solar steam generation under 1 sun illumination. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.B.; Dong, K.J.; Peng, L.H.; Bian, L.; Sun, Q.; Luo, W.M.; Zhang, B.B. Round-the-clock interfacial solar vapor generator enabled by form-stable phase change materials with enhanced photothermal conversion capacity. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 277, 116634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Chen, T.; Xu, J.L.; Li, G.; Wang, K.Y. Solar evaporation for simultaneous steam and power generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Ma, H.X.; Guo, D.; Guo, P.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, M.Q.; Wu, S.; Bao, C.L. Multiscale Preparation of Graphene Oxide/Carbon Nanotube-Based Membrane Evaporators by a Spray Method for Efficient Solar Steam Generation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 7198–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Liao, W.L.; Chen, D.Z.; Deng, Z.W.; Liu, X.; Shang, B. A water supply tunable bilayer evaporator for high-quality solar vapor generation. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 7913–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Li, Y.R.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y.D.; Fan, Z.H.; Han, X.; Wang, W.Y.; Lin, T.; Zhu, Z.T. Nanomaterial design for efficient solar-driven steam generation. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 6112–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.X.; Guo, Y.H.; Yu, G.H. Carbon materials for solar water evaporation and desalination. Small 2021, 17, 2007176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.X.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, C.H.; Liu, F.; Sun, H.X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liang, W.D.; Li, A. High-performance salt-rejecting and cost-effective superhydrophilic porous monolithic polymer foam for solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 16308–16318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Tao, Y.B.; Kong, F.G.; Li, P. The emerging development of solar evaporators in materials and structures. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.H.; Lai, Y.J.; Zhao, B.Y.; Bradley, R.; Wu, W.P. Photothermal materials for efficient solar powered steam generation. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 636–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, X.X.; Hao, Z.K.; Han, S.B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.Y. Photothermal-based nanomaterials and photothermal-sensing: An overview. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 220, 114883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Yin, K.B.; Zhang, Z.H. Hierarchically structured black gold film with ultrahigh porosity for solar steam generation. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, S.L.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, X.H. Janus carbon nanotube sponges for highly efficient solar-driven vapor generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.M.; Wu, Y.M.; Yi, J.; Yang, Y.H.; Shen, M.L.; Yang, Z.H.; Peng, S.; Min, X.; Yang, X.X.; Xiong, J.; et al. Full cattail leaf-based solar evaporator with square water transport channels for cost-effective solar vapor production. Cellulose 2023, 30, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kospa, D.A.; Ahmed, A.I.; Samra, S.E.; Ibrahim, A.A. High efficiency solar desalination and dye retention of plasmonic/reduced graphene oxide based copper oxide nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15184–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.H.; Zhao, B.Y.; Wu, W.P.; Yang, H.Y.; Ning, Y.S.; Lai, Y.J.; Bradley, R. Steam Generation: Low Cost, Robust, Environmentally Friendly Geopolymer–Mesoporous Carbon Composites for Efficient Solar Powered Steam Generation. Adv. Funct. Mater 2018, 21, 1870332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Q.; Chen, D.H.; Wang, Q.; Ying, Y.B.; Gao, W.L.; Xie, L.J. Recent advances in applications of carbon nanotubes for desalination: A review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Huang, X.H.; Wu, W. Graphene-based stand-alone networks for efficient solar steam generation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.S.; Hu, M.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Gao, J.; Han, L.; Lu, S.Y.; Cao, H.Q.; Wu, X.L.; Li, B.J. Efficient Carbon-Based Catalyst Derived from Natural Cattail Fiber for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 274, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yin, J.C.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.B. Design and optimization of solar steam generation system for water purification and energy utilization: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2019, 58, 226–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, V.D.; Choi, H.S. Carbon-based sunlight absorbers in solar-driven steam generation devices. Glob. Chall. 2018, 2, 1700094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Cordero, J.R.; Hernandez-Cordero, J. Heat generation and conduction in PDMS-carbon nanoparticle membranes irradiated with optical fibers. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 96, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Huang, H.B.; Li, H.L.; Sun, Y.K.; Xue, Y.H.; Xiao, S.N.; Yang, J.H. Carbon materials for solar-powered seawater desalination. New Carbon Mater. 2021, 36, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, H.M.; Jian, M.Q.; Li, Y.S.; Xia, K.L.; Zhang, M.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, M.; Zheng, Q.S.; et al. Extremely black vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays for solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28596–28603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.H.; Zhang, P.P.; Yao, H.Z.; Cheng, H.H.; Li, C.; Qu, L.T. Reduced graphene oxide–based spectrally selective absorber with an extremely low thermal emittance and high solar absorptance. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wei, N.; Xu, R.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Gong, L.; Cui, H.Z. Porous Ni/CNTs composite membrane as solar absorber for highly efficient solar steam generation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 243, 111815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.M.; Yu, J.L.; Ma, C.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wu, D.X.; Zhu, H.T. Carbonized daikon for high efficient solar steam generation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 191, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Zhao, C.X.; Sun, H.X.; Zhu, Z. Carbonized tofu as photothermal material for highly efficient solar steam generation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 9213–9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.N.; Wang, X.G. Use of in-situ polymerization in the preparation of graphene/polymer nanocomposites. New Carbon Mater. 2020, 35, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, W.; He, J.X.; Sun, H.X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liang, W.D.; Li, A. Superwetting monolithic hollow-carbon-nanotubes aerogels with hierarchically nanoporous structure for efficient solar steam generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahanayaka, M.; Liu, B.; Srikanth, N.; Zhou, K. Ionised graphene oxide membranes for seawater desalination. Desalination 2020, 496, 114637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.P.; Li, J.; Lv, L.X.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L.T. Vertically aligned graphene sheets membrane for highly efficient solar thermal generation of clean water. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5087–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.J.; Kuang, Y.D.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.J.; Huang, H.; Jia, C.; Zhao, X.P.; Hitz, E.; et al. Lightweight, mesoporous, and highly absorptive all-nanofiber aerogel for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.X.; Wu, J.B.; Li, F.H.; Guo, Q.Q.; Fan, H.L.; Zhao, H.M. A low-cost lotus leaf-based carbon film for solar-driven steam generation. New Carbon Mater. 2020, 35, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Xu, J.L.; Wang, K.Y. Solar water evaporation by black photothermal sheets. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Fang, W.Z.; Ying, W.; Chen, D.K.; Li, Z.Y.; Deng, Z.; Gao, C.; Peng, X.S. A robust asymmetric porous SWCNT/Gelatin thin membrane with salt-resistant for efficient solar vapor generation. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Dong, X.L.; Hsiung, C.E.; Zhu, Y.H.; Liu, L.M.; Han, Y. Microporous cokes formed in zeolite catalysts enable efficient solar evaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6860–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeson, M.J.; Dasog, M. Plasmonic metal nitrides for solar-driven water evaporation. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. 2020, 6, 3169–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Li, S.L.; Cui, X.; Wan, Y.P.; Xiao, Y.F.; Tian, S.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.X.; Zhao, Q.; Lee, C.S. A broadband aggregation-independent plasmonic absorber for highly efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 10742–10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, U.M.; Barclay, M.; Seo, D.H.; Park, M.J.; MacLeod, J.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Motta, N.; Shon, K.H.; Ostrikov, K.K. Utilization of plasma in water desalination and purification. Desalination 2021, 500, 114903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, H.Z.; Yu, J.Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, J. Plasmon-enhanced solar vapor generation. Nanophotonics 2019, 8, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Miao, L.; Tanemura, S. Morphology control of Ag polyhedron nanoparticles for cost-effective and fast solar steam generation. Sol. RRL 2017, 1, 1600023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.J.; Su, Y.S.; Su, H.L.; Guo, C.P.; Zhang, D. Ag/diatomite for highly efficient solar vapor generation under one-sun irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17817–17821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.F.; Mu, H.C.; Xu, Y.L.; Song, C.W.; Liu, Y.M. Silver nanoparticles-polydopamine-wax gourd: An antimicrobial solar evaporator with enhanced steam generation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 8949–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, Z.F.; Ou, W.T.; Lin, P.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, Y. Narrow-bandgap light-absorbing conjugated polybenzobisthiazole: Massive interfacial synthesis, robust solar-thermal evaporation and thermoelectric power generation. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2491–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Shi, W.; Yu, G.H. Materials for solar-powered water evaporation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 5, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Su, Y.N.; Wei, D.Y.; Sun, H.X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liang, W.D.; Li, A. Salt-Resistant Photothermal Materials Based on Monolithic Porous Ionic Polymers for Efficient Solar Steam Generation. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 8746–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Shen, L.; Zhang, C.X.; Gao, H.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Lin, P.; Zhang, H.X.; Xia, Y.Y. Polyacid doping-enabled efficient solar evaporation of polypyrrole hydrogel. Desalination 2021, 505, 114766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Z.; He, J.X.; Sun, H.X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liang, W.D.; Li, A. Robust aerogels based on conjugated microporous polymer nanotubes with exceptional mechanical strength for efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18183–18190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Mu, P.; Fan, Y.K.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, H.X.; Liang, W.D.; Li, A. Highly efficient solar steam generation of bilayered ultralight aerogels based on N-rich conjugated microporous polymers nanotubes. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 126, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Meng, N.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Liao, Y.Z. Scalable fabrication of conjugated microporous polymer sponges for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4522–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, I.; Seo, D.H.; McDonagh, A.M.; Shon, H.K.; Tijing, L. Semiconductor photothermal materials enabling efficient solar steam generation toward desalination and wastewater treatment. Desalination 2021, 500, 114853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, C.M.; Pattani, V.P.; Rasch, M.; Panthani, M.G.; Koo, B.; Tunnell, J.W.; Korgel, B.A. Copper selenide nanocrystals for photothermal therapy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Kuang, Y.D.; Hu, L.B. Challenges and opportunities for solar evaporation. Joule 2019, 3, 683–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Wu, S.L.; Wang, H.L.; Wu, Q.Y.; Yang, H.C. Photothermal devices for sustainable uses beyond desalination. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2021, 2, 2000056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, Y.B.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, L.X.; Chen, C.; Yuan, B.L.; Fu, M.L. Enhanced Solar Evaporation Using a Scalable MoS2-Based Hydrogel for Highly Efficient Solar Desalination. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2022, 134, e202208587. [Google Scholar]
- Irshad, M.S.; Wang, X.B.; Abbasi, M.S.; Arshad, N.; Chen, Z.H.; Guo, Z.Z.; Yu, L.; Qian, J.W.; You, J.; Mei, T. Semiconductive, flexible MnO2 NWs/chitosan hydrogels for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 3887–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.A.; Garg, P.; Bera, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dutta, S.; Kumar, H.; Bera, A. Narrow-Bandgap LaMO3 (M = Ni, Co) nanomaterials for efficient interfacial solar steam generation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 612, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Jiang, Q.S.; Wu, X.; Ghim, D.; Derami, H.G.; Chou, P.I.; Jun, Y.S.; Singamaneni, S. Advances in solar evaporator materials for freshwater generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 24092–24123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.S.; Singamaneni, S. Water from wood: Pouring through pores. Joule 2017, 1, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Jia, X.H.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.Z.; Song, H.J. Wood-based solar interface evaporation device with self-desalting and high antibacterial activity for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 47029–47037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.S.; Huang, P.R.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Ju, X.; Du, X.Z. Experimental study on the radiative properties of open-cell porous ceramics. Sol. Energy 2017, 149, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhou, X.Y.; Shi, Y.; Qian, X.; Alexander, M.; Zhao, X.P.; Mendez, S.; Yang, R.G.; Qu, L.T.; Yu, G.H. Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, C.L.; Liu, S.; Zhong, J.X. High performance of carbon-particle/bulk-wood bi-layer system for solar steam generation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 4830–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Jia, F.F.; Huang, A.H.; Qin, Y.; Song, S.X.; Li, Y.M.; Arroyo, M.A.C. MoS2@ sponge with double layer structure for high-efficiency solar desalination. Desalination 2020, 481, 114359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, D.Q.; Wang, Y.D.; Xu, H.L.; Lu, C.H.; Yang, X.F. Surface patterning of two-dimensional nanostructure-embedded photothermal hydrogels for high-yield solar steam generation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 10366–10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wu, D.X.; Huang, C.L.; Rao, Z.H. Skeleton double layer structure for high solar steam generation. Energy 2019, 183, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.B.; Li, W.; Li, Z.T.; Fang, B.Z. Solar thermal harvesting based on self-doped nanocermet: Structural merits, design strategies and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Wu, X.; Gao, T.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X.F.; Chen, G.Y.; Xu, H.L. Same materials, bigger output: A reversibly transformable 2D–3D photothermal evaporator for highly efficient solar steam generation. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Gu, Y.F.; Liu, P.F.; Wang, P.F.; Miao, L.; Liu, J.; Wei, A.Y.; Mu, X.J.; Zhu, J. Development and evolution of the system structure for highly efficient solar steam generation from zero to three dimensions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.F.; Li, H.; Wang, W.B.; Huang, J.G.; Xia, D.D.; Liao, J.X.; Wu, M.Q.; Papavassiliou, D.V. Scalable, eco-friendly and ultrafast solar steam generators based on one-step melamine-derived carbon sponges toward water purification. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darre, N.C.; Toor, G.S. Desalination of water: A review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Zhu, J.T.; Zhang, L.B. Three-dimensionally structured polypyrrole-coated setaria viridis spike composites for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9027–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Shi, Y.; Li, R.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Jin, Y.; Wang, P. Nature-inspired, 3D origami solar steam generator toward near full utilization of solar energy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28517–28524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Shin, D.; Baitha, M.N.; Ryu, Y.; Urbas, A.M.; Park, W.; Kim, K. High-efficiency solar vapor generation boosted by a solar-induced updraft with biomimetic 3D structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29602–29611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Bai, B.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.L. Low-cost and facile fabrication of a candle soot/adsorbent cotton 3D-interfacial solar steam generation for effective water evaporation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 221, 110876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.X.; Li, B.B.; Xu, C.L.; Zhang, R.H.; Wang, Y.F. Biomimetic Janus photothermal membrane for efficient interfacial solar evaporation and simultaneous water decontamination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.K.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, X.Z. Flower-inspired bionic sodium alginate hydrogel evaporator enhancing solar desalination performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Li, L.; He, N.; Wang, H.N.; Wang, B.S.; Dong, T.Y.; Jiang, B.; Tang, D. Bioinspired hierarchical evaporator via cell wall engineering for highly efficient and sustainable solar desalination. Ecomat 2022, 4, e12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Guan, W.; Wang, P.; Feng, J.G.; Song, N.; Dong, H.Z.; Yu, L.Y.; Sui, L.; Gan, Z.X.; et al. A self-floating and integrated bionic mushroom for highly efficient solar steam generation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 612, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, W.; Zada, I.; Zhang, Y.X.; Gu, J.J.; Liu, Q.L.; Su, H.L.; Pantelić, D.; Jelenković, B.; Zhang, D. 3D-structured carbonized sunflower heads for improved energy efficiency in solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Hao, L.; Zhang, B.Y.; Niu, R.; Gong, J.; Tang, T. High-performance solar vapor generation by sustainable biomimetic snake-scale-like porous carbon. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2020, 4, 5522–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Y.D.; Wu, P.; Zhao, J.Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X.F.; Xu, H.L. Dual-zone photothermal evaporator for antisalt accumulation and highly efficient solar steam generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 30, 2102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, J.L.; Wu, S.Y.; Di, Y.S.; Liu, C.H.; Dong, L.F.; Yu, L.Y.; Gan, Z.X. Solar-Driven Airflow-Enhanced All-Daytime Solar Steam Generation Based on Inverse-Bowl-Shaped Graphene Aerogels. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Han, D.T.; Guo, C.W.; Huang, C.L. Facile preparation of MnO2-deposited wood for high-efficiency solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 4, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Jiang, D.G.; Huo, B.B.; Ding, M.C.; Huang, C.C.; Jia, D.D.; Li, H.X.; Liu, C.Y.; Liu, J.Q. Scalable and robust bilayer polymer foams for highly efficient and stable solar desalination. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.B.; Fan, C.; Sun, Y.J. Multilevel design strategies of high-performance interfacial solar vapor generation: A state of the art review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.M.; Chen, C.J.; Kuang, Y.D.; Mi, R.Y.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Kong, W.Q.; Gan, W.T.; Xie, H.; Hitz, E.; et al. Nature-inspired salt resistant bimodal porous solar evaporator for efficient and stable water desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.Y.; Guo, H.S.; Zhu, Y.N.; Bai, H.Y.; Zhao, W.Q.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, J.; Cao, M.Y.; Zhang, L. Fully superhydrophilic, self-floatable, and multi-contamination-resistant solar steam generator inspired by seaweed. Engineering 2023, 20, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials | Evaporation Rate (kg·m−2·h−1) | Photothermal Conversion Efficiency | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-based material | rGO/sodium alginate | 1.60 | 83.00% | [59] |
| CNTs/porous nickel mesh | 2.13 | 94.3% | [62] | |
| Durable charred tofu | 1.65 | 87.26% | [64] | |
| Plasma metal | Gold nanostructured plasmon | 2.70 | 79.30% | [75] |
| Spherical silver nanoparticles | 1.01 | 82.45% | [78] | |
| AgNPs/PDA | 1.70 | 83.21% | [80] | |
| Conjugated polymer | Conjugated polyphenylene diazole microspheres | 2.96 | 90.30% | [81] |
| Polypyrrole hydrogel | 1.90 | 89.00% | [84] | |
| Novel porphyrin/aniline-based conjugated microporous polymer | 1.31 | 86.3% | [87] | |
| Inorganic semiconductor | MoS2 | 3.29 | 93.40% | [92] |
| MnO2/CS | 1.78 | 90.60% | [93] | |
| LaNiO3 | 2.30 | 83.00% | [94] |
| Structures | Evaporation Rate (kg·m−2·h−1) | Evaporation Efficiency | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Double-layer structure | Carbon particles/boxwood | 1.00 | 65.00% | [100] |
| Carbon particles/cellulose sponge | 1.50 | 90.00% | [103] | |
| Three-dimensional structure | A carbon-coated polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/convection flower | 3.31 | 166.10% | [111] |
| rGO/cellulose sponge | 4.35 | 178.80% | [105] | |
| Biomimetic structure | Biomimetic mushroom | 1.67 | 104.8% | [116] |
| Carbonized sunflower | 1.51 | 100.4% | [117] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Yin, Z.; Hou, Y.; Yin, C.; Yin, Z. Overview of Solar Steam Devices from Materials and Structures. Polymers 2023, 15, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122742
Liu C, Yin Z, Hou Y, Yin C, Yin Z. Overview of Solar Steam Devices from Materials and Structures. Polymers. 2023; 15(12):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122742
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chang, Zhenhao Yin, Yue Hou, Chengri Yin, and Zhenxing Yin. 2023. "Overview of Solar Steam Devices from Materials and Structures" Polymers 15, no. 12: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122742
APA StyleLiu, C., Yin, Z., Hou, Y., Yin, C., & Yin, Z. (2023). Overview of Solar Steam Devices from Materials and Structures. Polymers, 15(12), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122742






