Effect of Flaxseed Gum on the Textural, Rheological, and Tribological Properties of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. SPI Solution Preparation
2.2.2. FG Extraction
2.2.3. SPI-FG Gels Preparation
2.3. Texture Analysis and Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.4. Particle Size
2.5. Tribology
2.6. Viscoelasticity
2.7. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Viscoelastic Properties
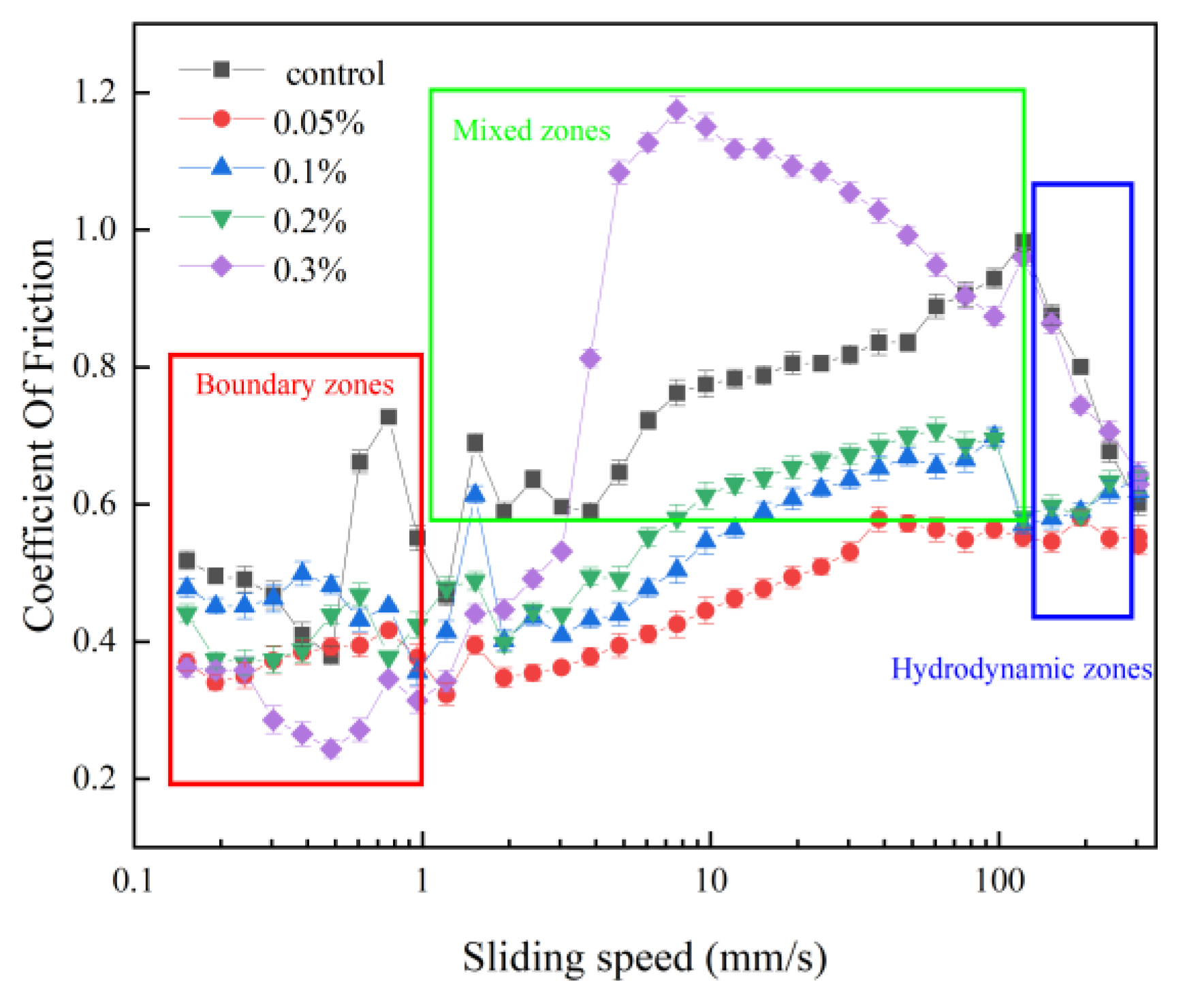
3.2. Tribology
3.3. Particle Size Distribution
3.4. Texture Analysis and Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahbazizadeh, S.; Naji-Tabasi, S.; Shahidi-Noghabi, M.; Pourfarzad, A. Development of cress seed gum hydrogel and investigation of its potential application in the delivery of curcumin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6505–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, A.; Dar, A.H.; Pandey, V.K.; Shams, R.; Khan, S.; Panesar, P.S.; Kennedy, J.F.; Fayaz, U.; Khan, S.A. Recent insights into polysaccharide-based hydrogels and their potential applications in food sector: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Zhu, L.; Qi, X.G.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.C. Characteristics of low-fat whipped cream containing protein-based fat replacers. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 76, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Yue, X.; Shao, J.; Li, M.; Li, Z. Polysaccharides, proteins, and their complex as microencapsulation carriers for delivery of probiotics: A review on carrier types and encapsulation techniques. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Marchioni, E. Protein-Based High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions: A Review of Their Fabrication, Composition and Future Perspectives in the Food Industry. Foods 2023, 12, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Dong, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, H. Improved viability of probiotics encapsulated in soybean protein isolate matrix microcapsules by coacervation and cross-linking modification. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, H.; Wu, D.; Lin, D.; Qin, W.; Meng, D.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Q. Rheological and textural properties of acid-induced soybean protein isolate gel in the presence of soybean protein isolate hydrolysates or their glycosylated products. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazizadeh, S.; Naji-Tabasi, S.; Shahidi-Noghabi, M. Development of soy protein/sodium alginate nanogel-based cress seed gum hydrogel for oral delivery of curcumin. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verfaillie, D.; Janssen, F.; Van Royen, G.; Wouters, A.G. A systematic study of the impact of the isoelectric precipitation process on the physical properties and protein composition of soy protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, S. Characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by glucono-δ-lactone: Effects of the protein concentration during preheating. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-H.; Kuo, M.-I. Effect of microwave heating on the viscoelastic property and microstructure of soy protein isolate gel. J. Texture Stud. 2011, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourouis, I.; Pang, Z.; Liu, X. Recent advances on uses of protein and/or polysaccharide as fat replacers: Textural and tribological perspectives: A review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 11, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, Y. An overview of classifications, properties of food polysaccharides and their links to applications in improving food textures. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Campbell, L.J.; Euston, S.R. Influence of sugars on the characteristics of glucono-δ-lactone-induced soy protein isolate gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.-H.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-J.; Adhikari, B. Effect of LBG on the gel properties of acid-induced SPI gels. LWT 2017, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gan, J.; Ji, A.; Song, S.; Yin, L. Development of double network gels based on soy protein isolate and sugar beet pectin induced by thermal treatment and laccase catalysis. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Chen, Q.; Cai, Q.; Fan, Y.; Wilde, P.J.; Rong, Z.; Zeng, X. Gelation of soybean protein and polysaccharides delays digestion. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-J.; Bi, C.-H.; Adhikari, B. Effect of gums on the rheological characteristics and microstructure of acid-induced SPI-gum mixed gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elboutachfaiti, R.; Delattre, C.; Quéro, A.; Roulard, R.; Duchêne, J.; Mesnard, F.; Petit, E. Fractionation and structural characterization of six purified rhamnogalacturonans type I from flaxseed mucilage. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Cui, S.; Wu, Y.; Goff, H. Flaxseed gum from flaxseed hulls: Extraction, fractionation, and characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Mantovani, R.; Raposo, M.; Coimbra, M.; Vicente, A.; Cunha, R. Effect of extraction temperature on rheological behavior and antioxidant capacity of flaxseed gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Mai, Y.; Gao, L.; Ou, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Peng, X. Flaxseed gum reduces body weight by regulating gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.-H.; Chi, S.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Alkhatib, A.; Huang, Z.-G.; Liu, Y. Effect of flax gum on the functional properties of soy protein isolate emulsion gel. LWT 2021, 149, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, D.; Adhikari, B. Effect of flaxseed gum on the rheological properties of peanut protein isolate dispersions and gels. LWT 2016, 74, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M. Food rheology—Texture and fundamental properties. In Food Process Engineering Principles and Data; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2023; pp. 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- De Wijk, R.A.; Prinz, J.F. The role of friction in perceived oral texture. Food Qual. Prefer. 2005, 16, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Tong, F.; Jiang, S.; Chen, C.; Liu, X. Particle characteristics and tribo-rheological properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions: Effect of heating and incorporation of flaxseed gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, P.; Dowling, K.; Adhikari, R.; Barrow, C.J.; Adhikari, B. Effect of extraction temperature on composition, structure and functional properties of flaxseed gum. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, B.; ZhiHua, P.; Xinqi, L.; Jatoi, M.A.; Rashid, M.T. Influence of different extraction techniques on recovery, purity, antioxidant activities, and microstructure of flaxseed gum. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3168–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S.; Zhu, L. Acid-induced gelation behavior of soybean protein isolate with high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.H.; Tang, J.; Paulson, A.T. Texture profile and turbidity of gellan/gelatin mixed gels. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Donkor, P.O.; Ren, X.; Wu, J.; Agyemang, K.; Ayim, I.; Ma, H. Effect of ultrasound pretreatment with mono-frequency and simultaneous dual frequency on the mechanical properties and microstructure of whey protein emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Xu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Bansal, N.; Liu, X. Comparison of rheological, tribological, and microstructural properties of soymilk gels acidified with glucono-δ-lactone or culture. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niknam, R.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Ayaseh, A.; Rezagholi, F. The effects of Plantago major seed gum on steady and dynamic oscillatory shear rheology of sunflower oil-in-water emulsions. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, R.; Bea, L.L.; Hidalgo, M.E.; Risso, P.H. Microstructural and textural characteristics of soy protein isolate and tara gum cold-set gels. LWT 2019, 113, 108286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Fang, C.; Yang, H. Thermal-responsive self-healing hydrogel based on hydrophobically modified chitosan and vesicle. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Marangoni, A.G. Peculiar frequency dependence of the storage modulus in a plastic disperse system. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Song, Q.; Xie, J. Gel properties and interactions of Mesona blumes polysaccharide-soy protein isolates mixed gel: The effect of salt addition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.R.; Lopes-Da-Silva, J.A. Effect of the molecular weight of a neutral polysaccharide on soy protein gelation. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Pang, Z. Tribo-rheological properties of acid milk gels with different types of gelatin: Effect of concentration. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7849–7862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Jiang, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, S.; Xie, J. Influence of Mesona blumes polysaccharide on the gel properties and microstructure of acid-induced soy protein isolate gels. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Physicochemical properties of a ginkgo seed protein-pectin composite gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, J.G.; Wu, N.F.; Fan, M.M.; Shen, X.L.; Chen, M.T.; Jiang, A.M.; Lai, L.-S. Effect of hsian-tsao gum (HG) content upon rheological properties of film-forming solutions (FFS) and physical properties of soy protein/hsian-tsao gum films. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 50, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X. Effect of different hydrocolloids on tribological and rheological behaviors of soymilk gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmanová, J.; Mason, J.; Batchelor, H. Tribology provides an in vitro tool that correlated to in vivo sensory data on the mouthfeel of coated tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gu, W.; Bourouis, I.; Sun, M.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Pang, Z. Lubrication behaviors of core-shell structured particles formed by whey proteins and xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.C.; Bhandari, B.R.; Prakash, S. Tribo-rheology and sensory analysis of a dairy semi-solid. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriele, A.; Spyropoulos, F.; Norton, I.T. A conceptual model for fluid gel lubrication. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selway, N.; Stokes, J.R. Insights into the dynamics of oral lubrication and mouthfeel using soft tribology: Differentiating semi-fluid foods with similar rheology. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Malairaj, S.; Brohi, S.A.; Boateng, E.F.; Zhang, W. Impact of unripe banana flour on water states, rheological behaviour and structural properties of myofibrillar protein composite gel. LWT 2020, 125, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, D.P.; Roberts, R.F.; Coupland, J.N. Effect of pH on the properties of soy protein–pectin complexes. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Abdalhai, M.; Emmanuel, M.; Qian, H. Texture, rheological properties and microstructure of soy protein gels coagulated by CaSO4 and the effect of soybean soluble polysaccharide on the gel performance. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Raak, N.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Acid-induced gelation of enzymatically cross-linked caseinates: Small and large deformation rheology in relation to water holding capacity and micro-rheological properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 619, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Deeth, H.; Yang, H.; Prakash, S.; Bansal, N. Evaluation of tilapia skin gelatin as a mammalian gelatin replacer in acid milk gels and low-fat stirred yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 3436–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Sample | G′ (Pa) | G″ (Pa) | tan δ | η * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 966.22 | 259.74 | 0.269 | 181.98 |
| 0.05% | 1487.82 | 276.95 | 0.186 | 243.27 |
| 0.1% | 697.84 | 158.05 | 0.226 | 115.38 |
| 0.2% | 898.07 | 199.51 | 0.222 | 146.42 |
| 0.3% | 1493.42 | 284.52 | 0.191 | 244.88 |
| 100 °C | Average Particle Size (μm) | D10 | D50 | D90 | Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.54 ± 0.45 a | 0.27 ± 0.08 a | 9.85 ± 0.47 a | 43.72 ± 0.88 a | 4.41 ± 0.38 b |
| 0.05% | 21.43 ± 0.29 b | 10.23 ± 1.00 b | 22.85 ± 0.96 b | 49.05 ± 5.07 b | 1.70 ± 0.13 a |
| 0.1% | 22.72 ± 0.72 c | 10.78 ± 2.44 b | 22.90 ± 0.42 b | 61.99 ± 4.72 c | 2.24 ± 0.33 a |
| 0.2% | 40.94 ± 3.26 d | 17.47 ± 0.37 c | 43.17 ± 0.39 c | 94.19 ± 2.33 d | 1.78 ± 0.40 a |
| 0.3% | 49.90 ± 1.75 e | 20.59 ± 0.44 d | 56.97 ± 1.34 d | 102.88 ± 1.80 e | 1.44 ± 0.19 a |
| 100 °C Treatment | Water Holding Capacity (%) | Hardness (g) | Viscosity (mJ) | Elasticity (mm) | Cohesiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 91.20 ± 3.21 bc | 40.65 ± 0.77 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 3.73 ± 0.04 d | 0.30 ± 0.01 a |
| 0.05% | 90.42 ± 0.47 b | 41.45 ± 0.49 a | 0.24 ± 0.04 d | 4.04 ± 0.00 e | 0.37 ± 0.04 c |
| 0.1% | 92.71 ± 1.58 c | 14.15 ± 0.60 b | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 1.94 ± 0.16 b | 0.43 ± 0.07 d |
| 0.2% | 91.60 ± 3.22 bc | 12.15 ± 0.67 b | 0.08 ± 0.01 b | 2.87 ± 0.31 c | 0.55 ± 0.042 e |
| 0.3% | 82.40 ± 2.79 a | 11.45 ± 0.40 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 c | 2.87 ± 0.31 c | 0.32 ± 0.045 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Ma, P.; Jiang, S.; Bourouis, I.; Pang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, P. Effect of Flaxseed Gum on the Textural, Rheological, and Tribological Properties of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels. Polymers 2023, 15, 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132834
Chen C, Ma P, Jiang S, Bourouis I, Pang Z, Liu X, Wang P. Effect of Flaxseed Gum on the Textural, Rheological, and Tribological Properties of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels. Polymers. 2023; 15(13):2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132834
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cunshe, Peipei Ma, Siyuan Jiang, Imane Bourouis, Zhihua Pang, Xinqi Liu, and Pengjie Wang. 2023. "Effect of Flaxseed Gum on the Textural, Rheological, and Tribological Properties of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels" Polymers 15, no. 13: 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132834
APA StyleChen, C., Ma, P., Jiang, S., Bourouis, I., Pang, Z., Liu, X., & Wang, P. (2023). Effect of Flaxseed Gum on the Textural, Rheological, and Tribological Properties of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels. Polymers, 15(13), 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132834







