Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties of Crumb Rubber Concrete after Elevated Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
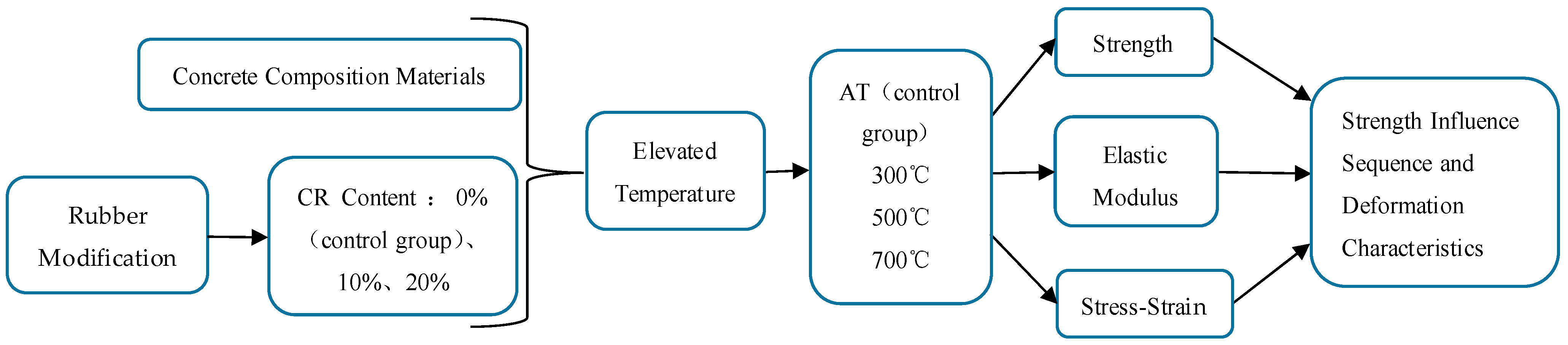
2. Materials and Methods
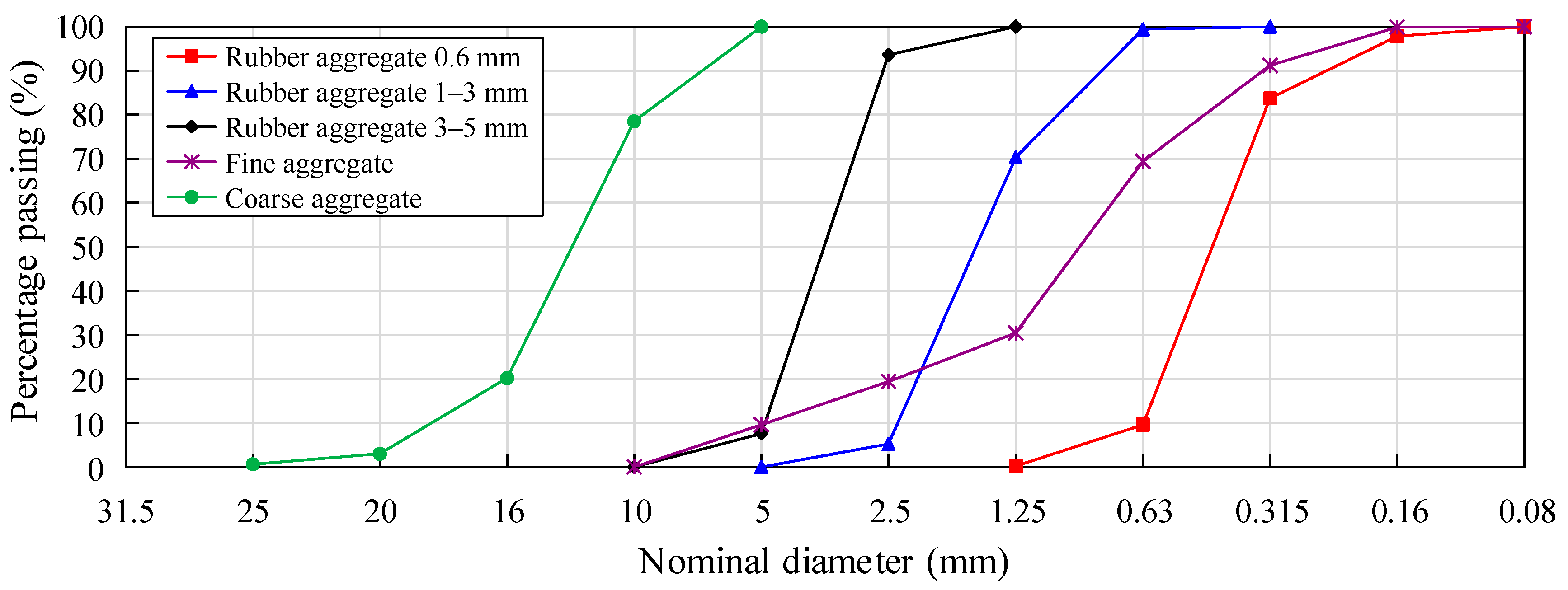
2.1. Materials and Preparation of the CRC
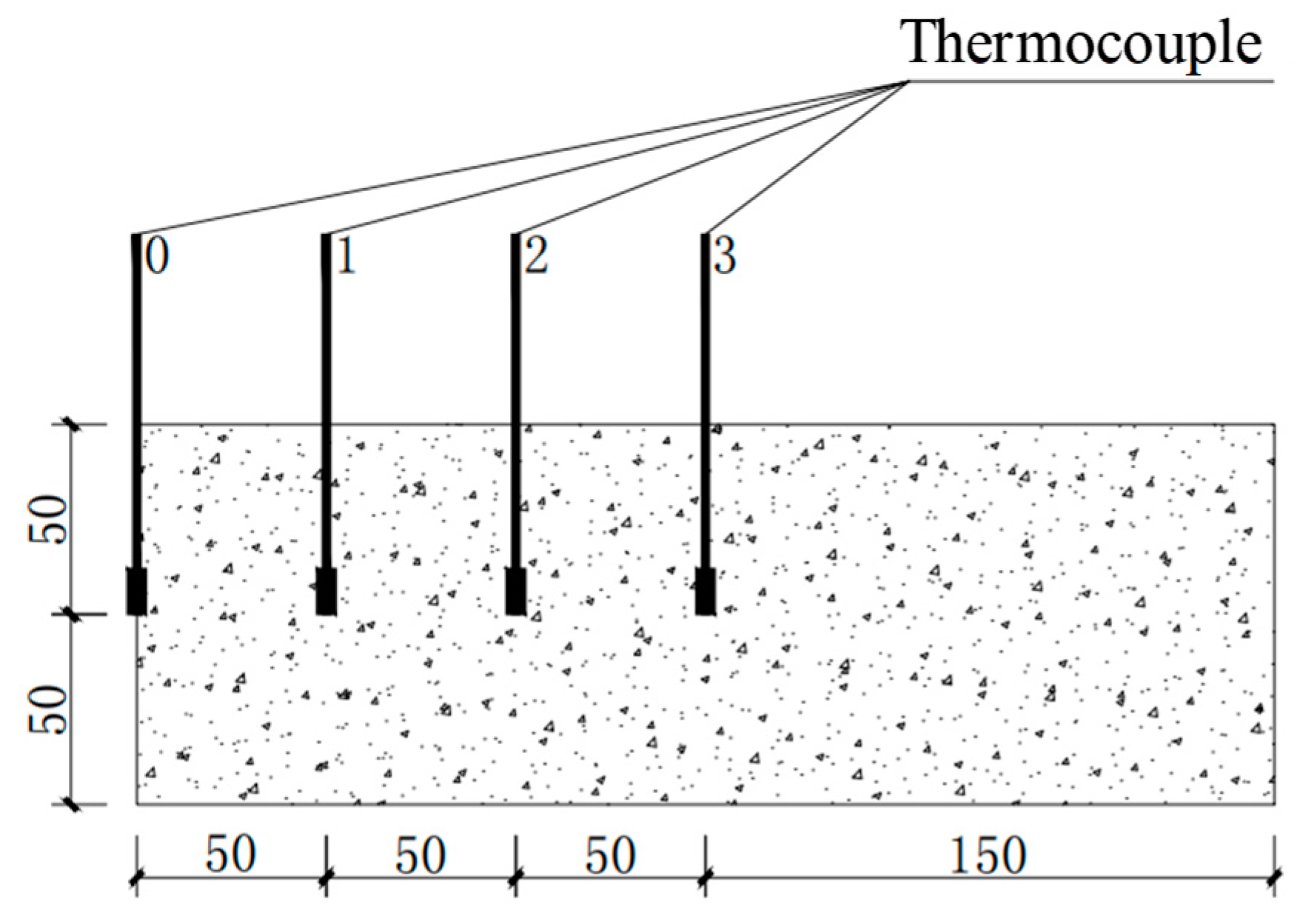
2.2. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
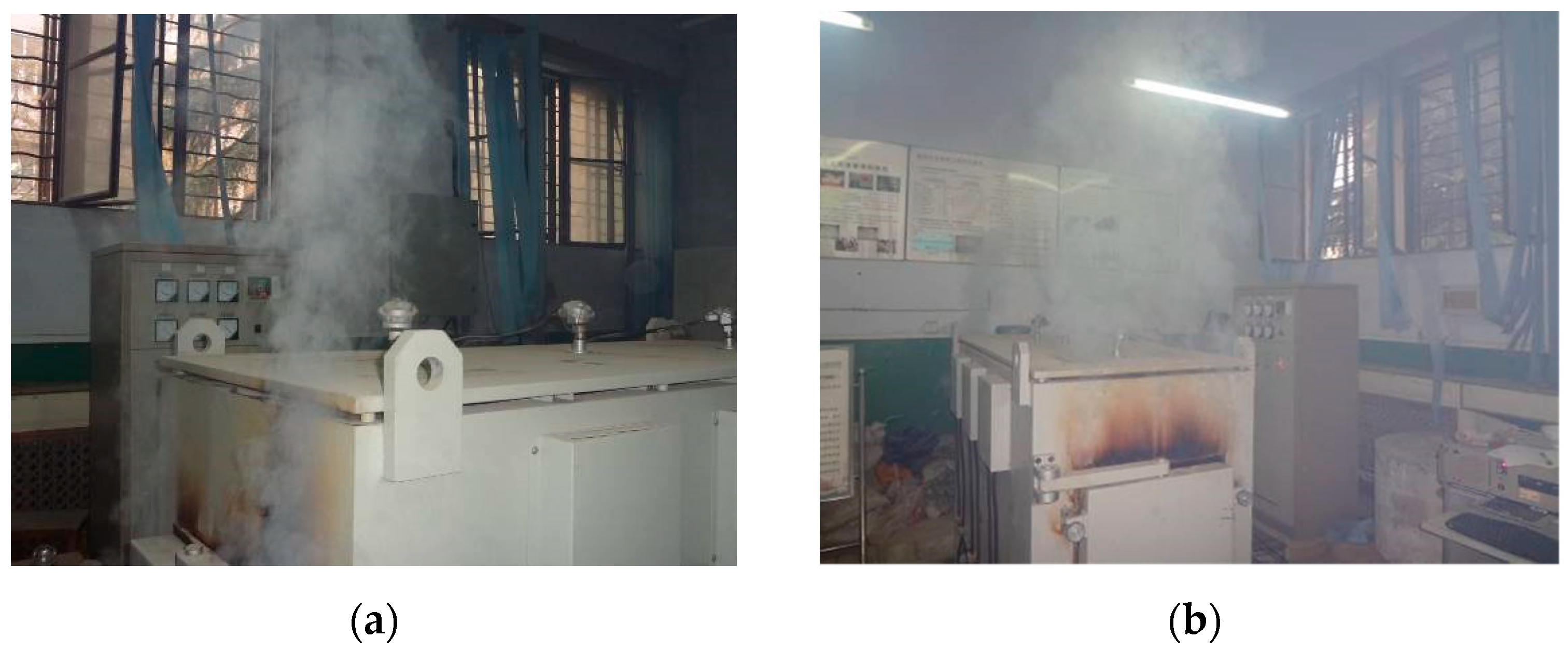
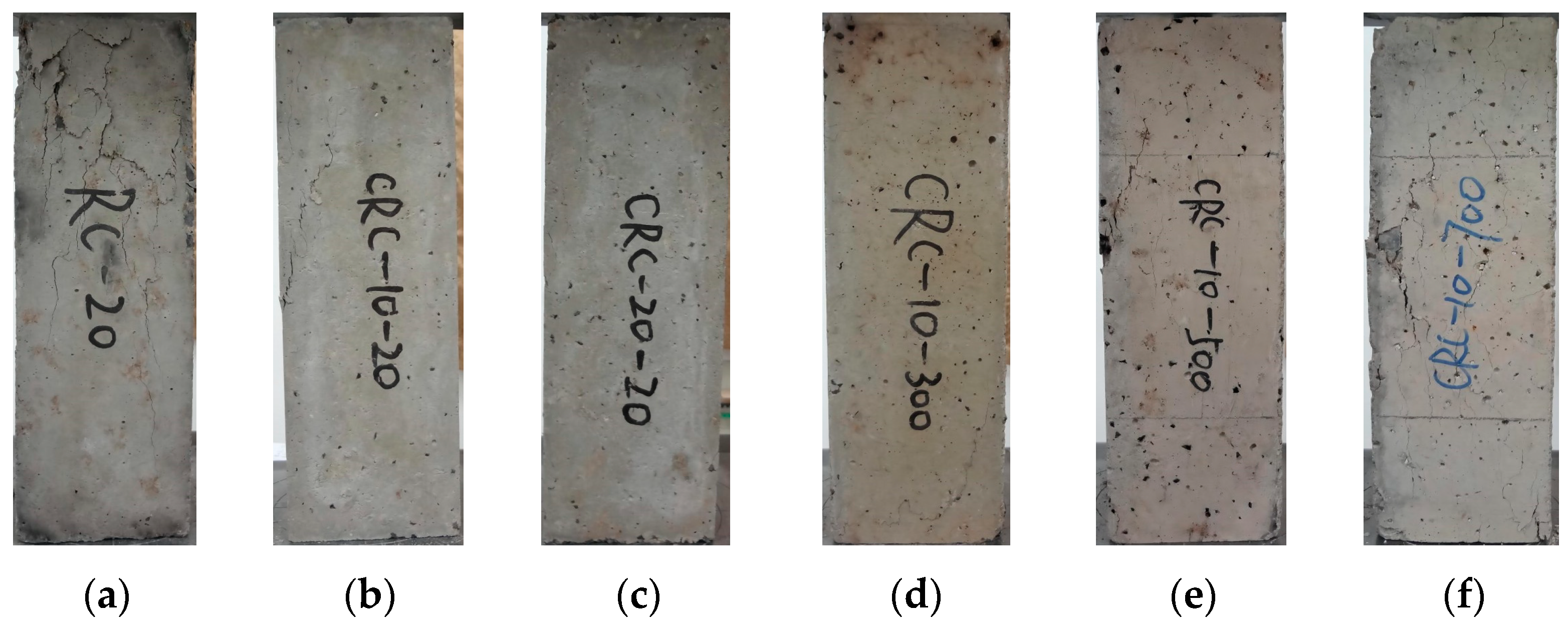
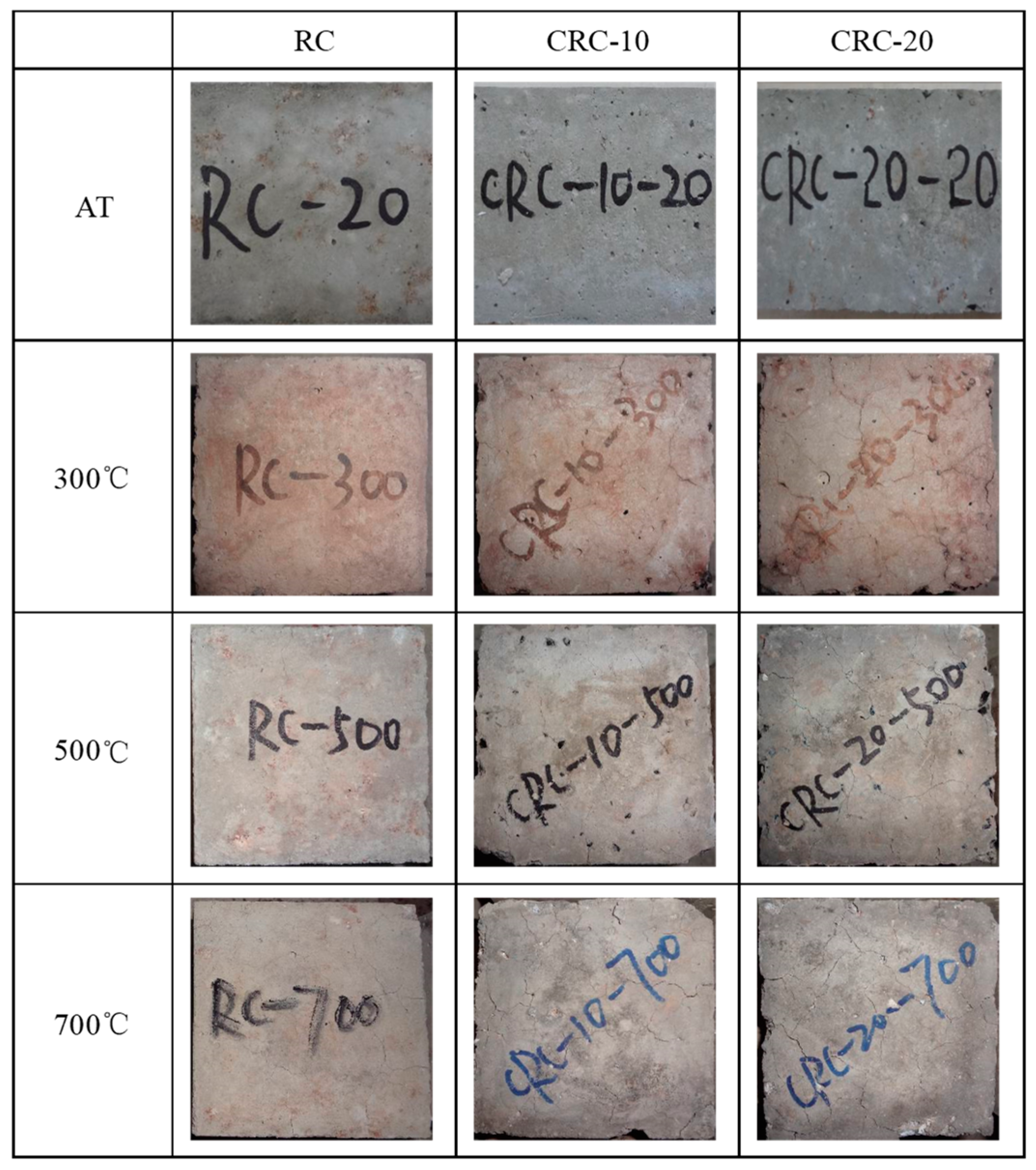
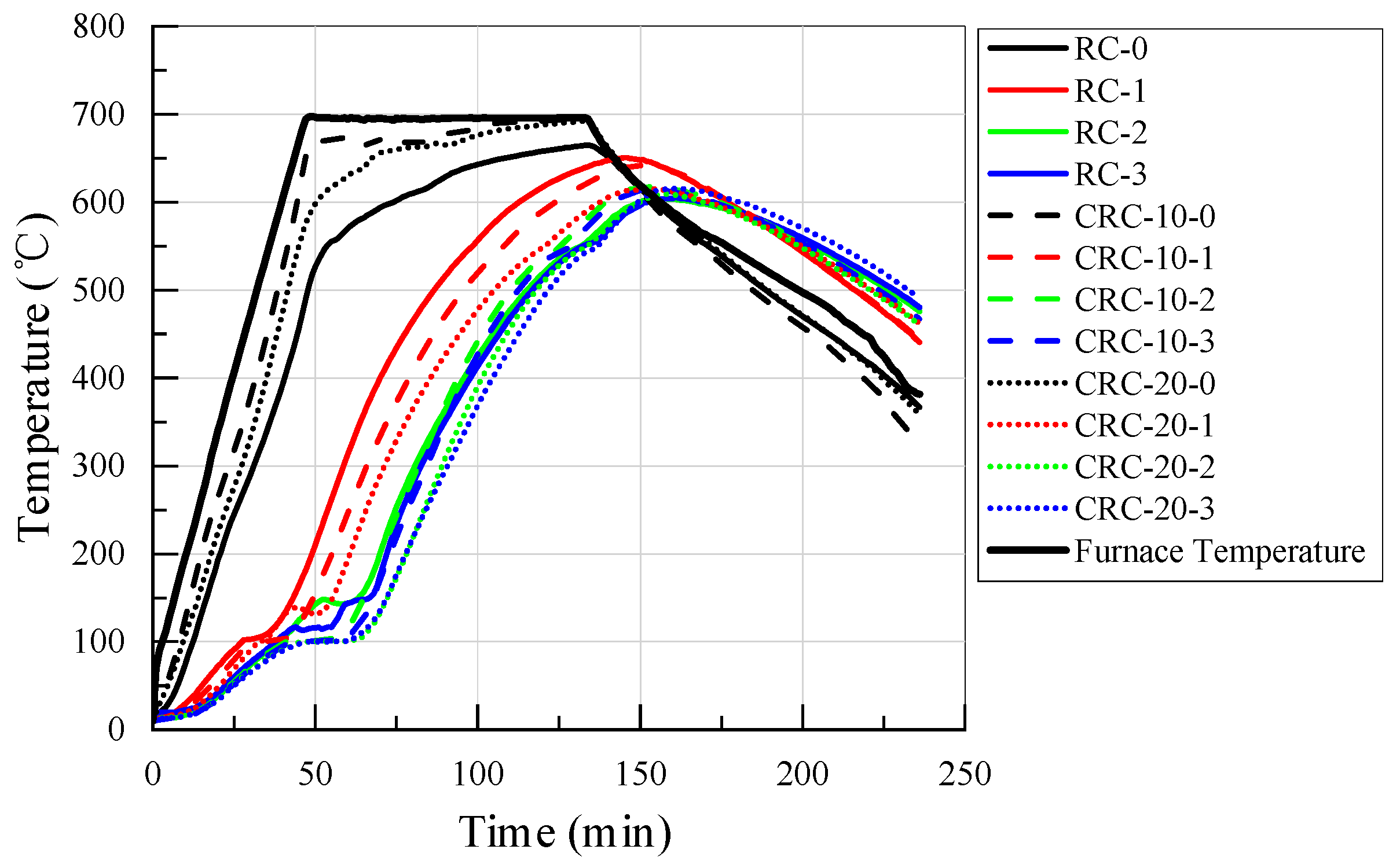
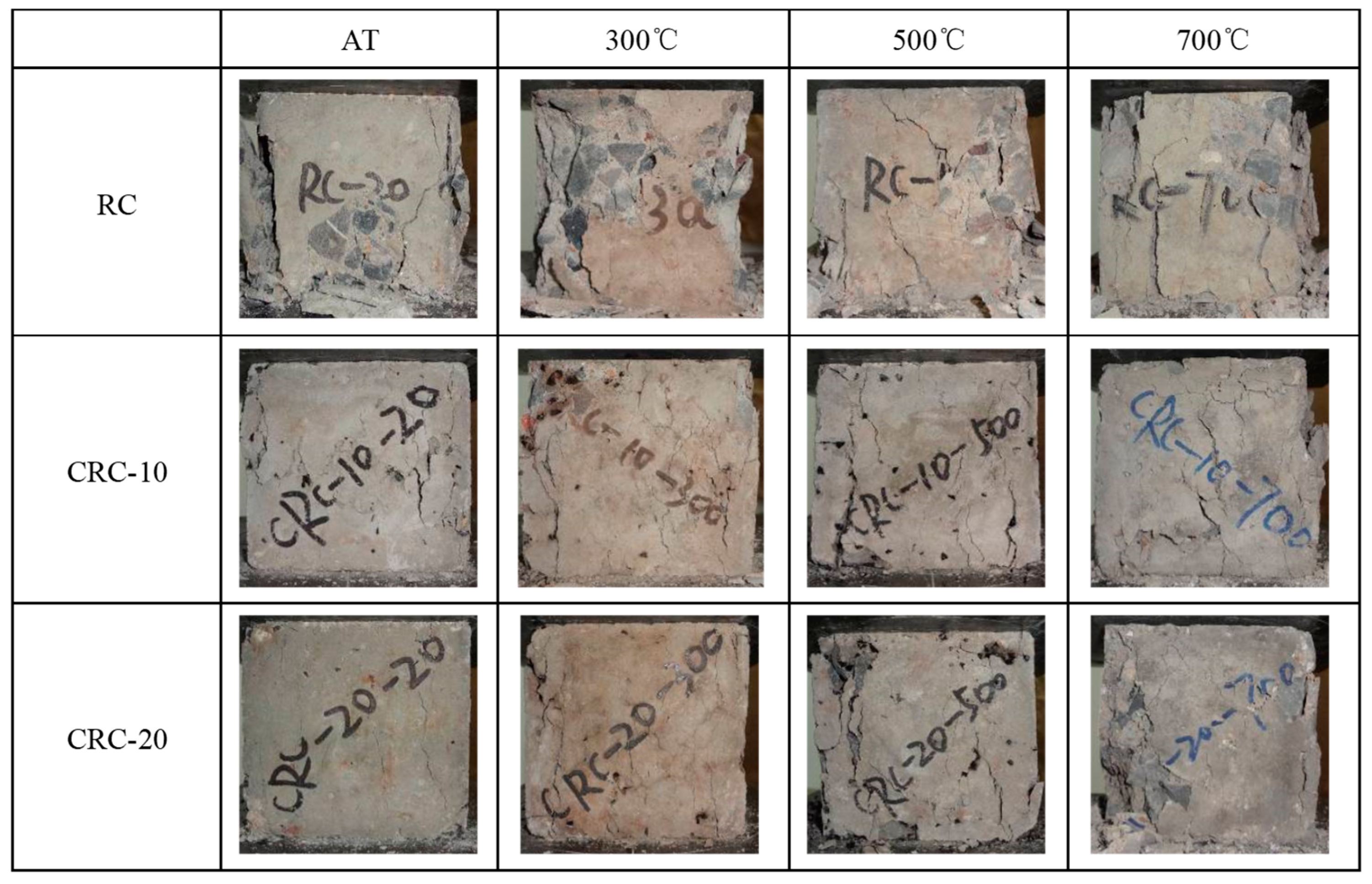
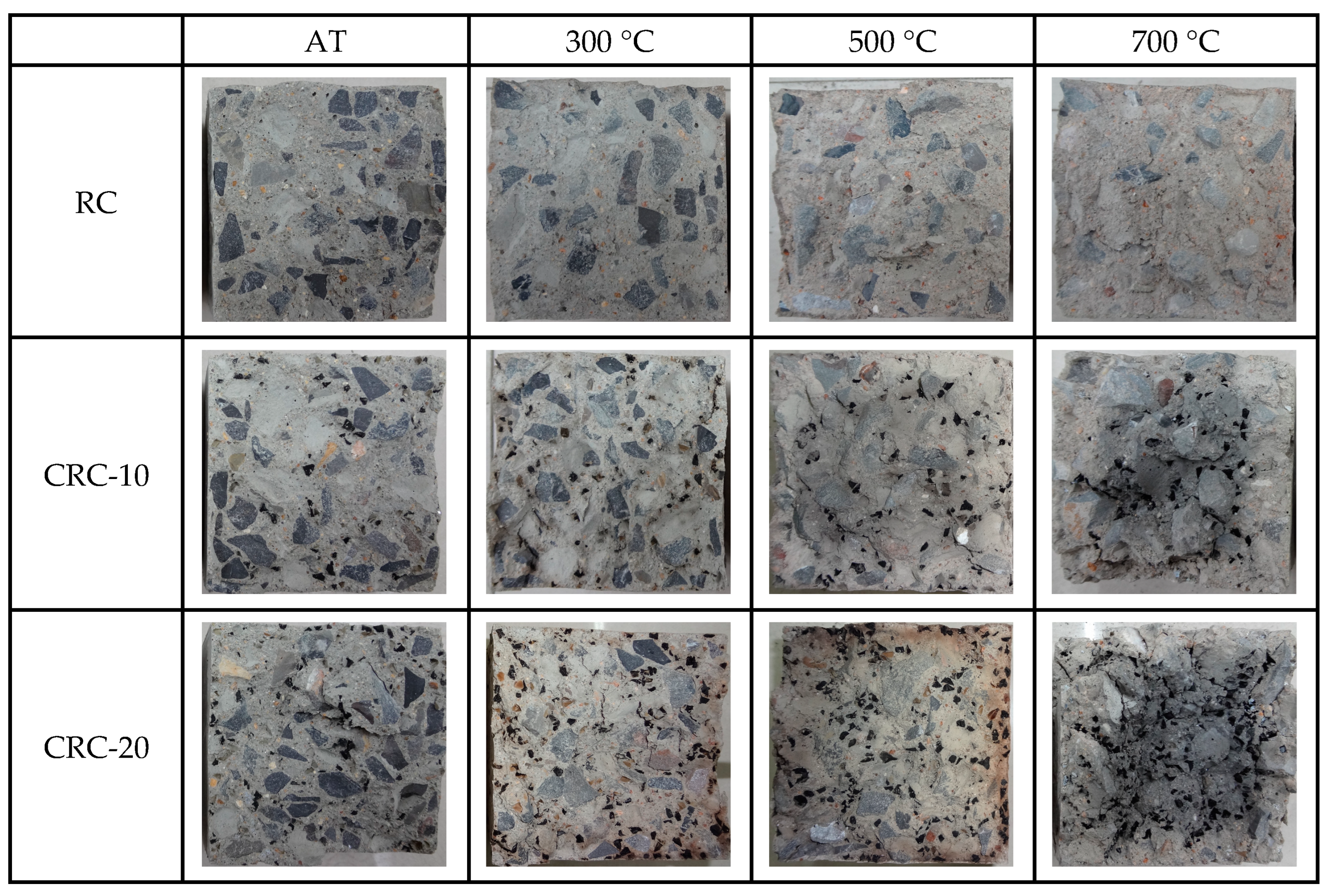
3.1. Elevated Temperature Test Phenomenon
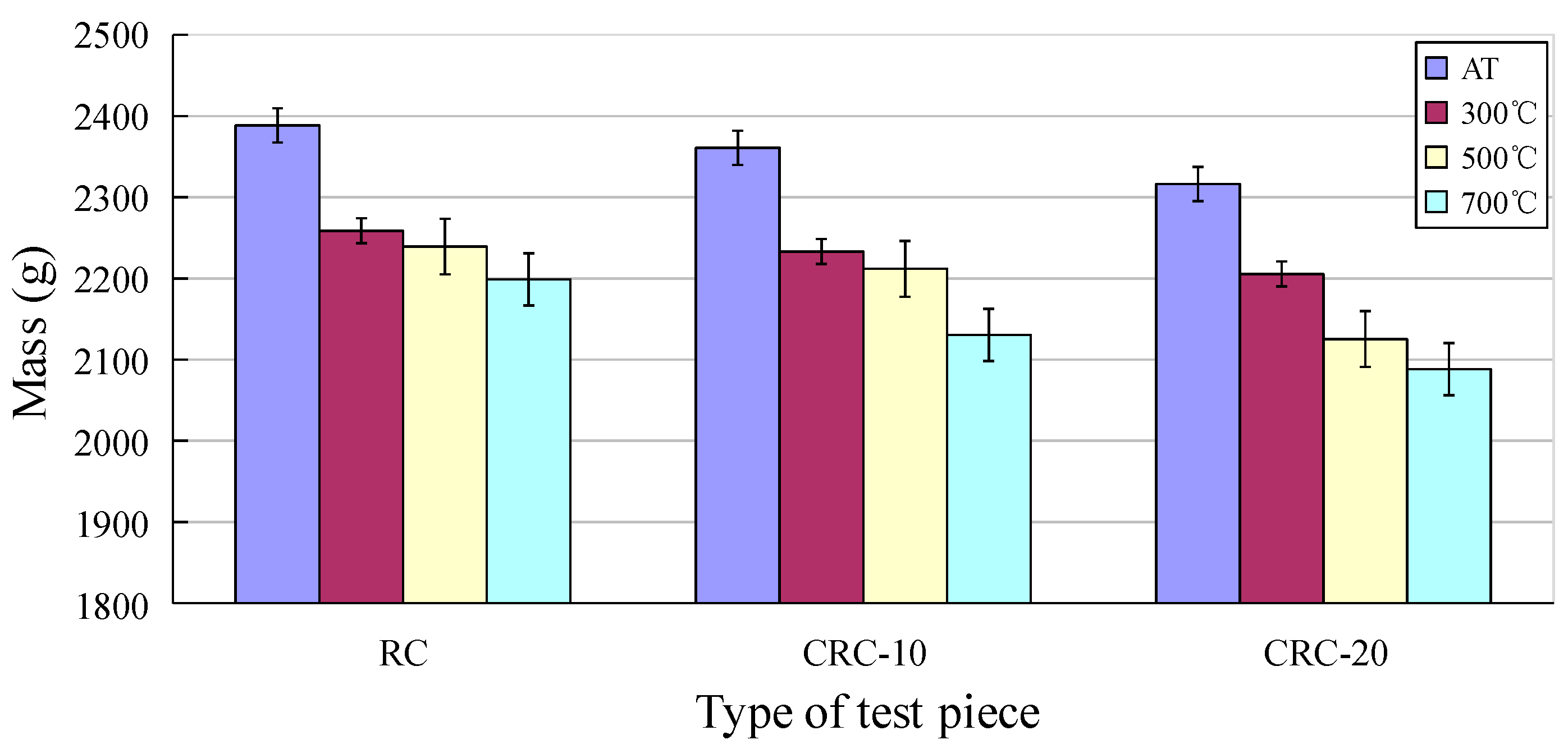
3.2. Quality Loss of the CRC
3.3. Thermal Conductivity Characteristics of the CRC
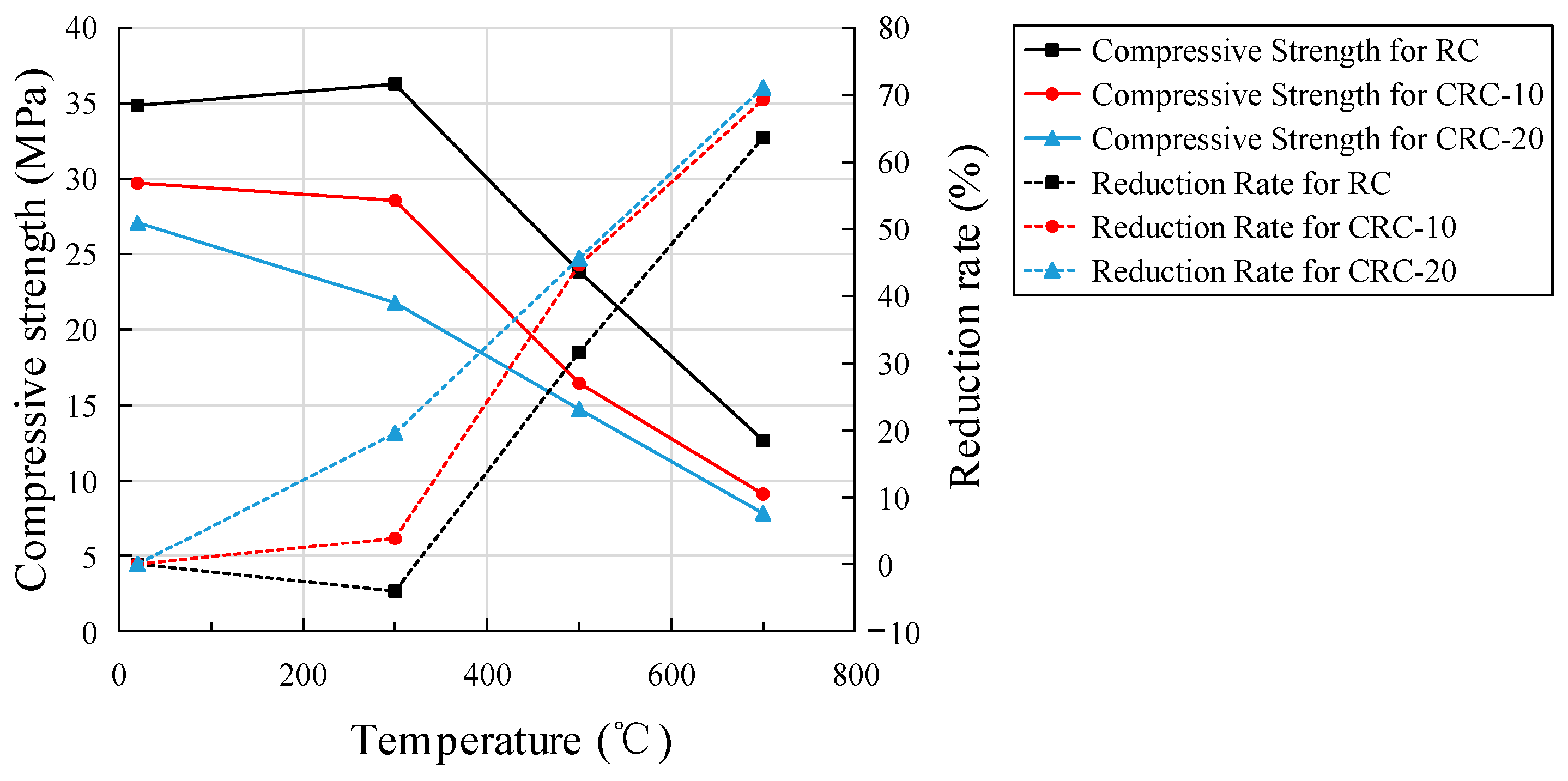
3.4. Cube Compressive Strength
3.5. Splitting Tensile Strength
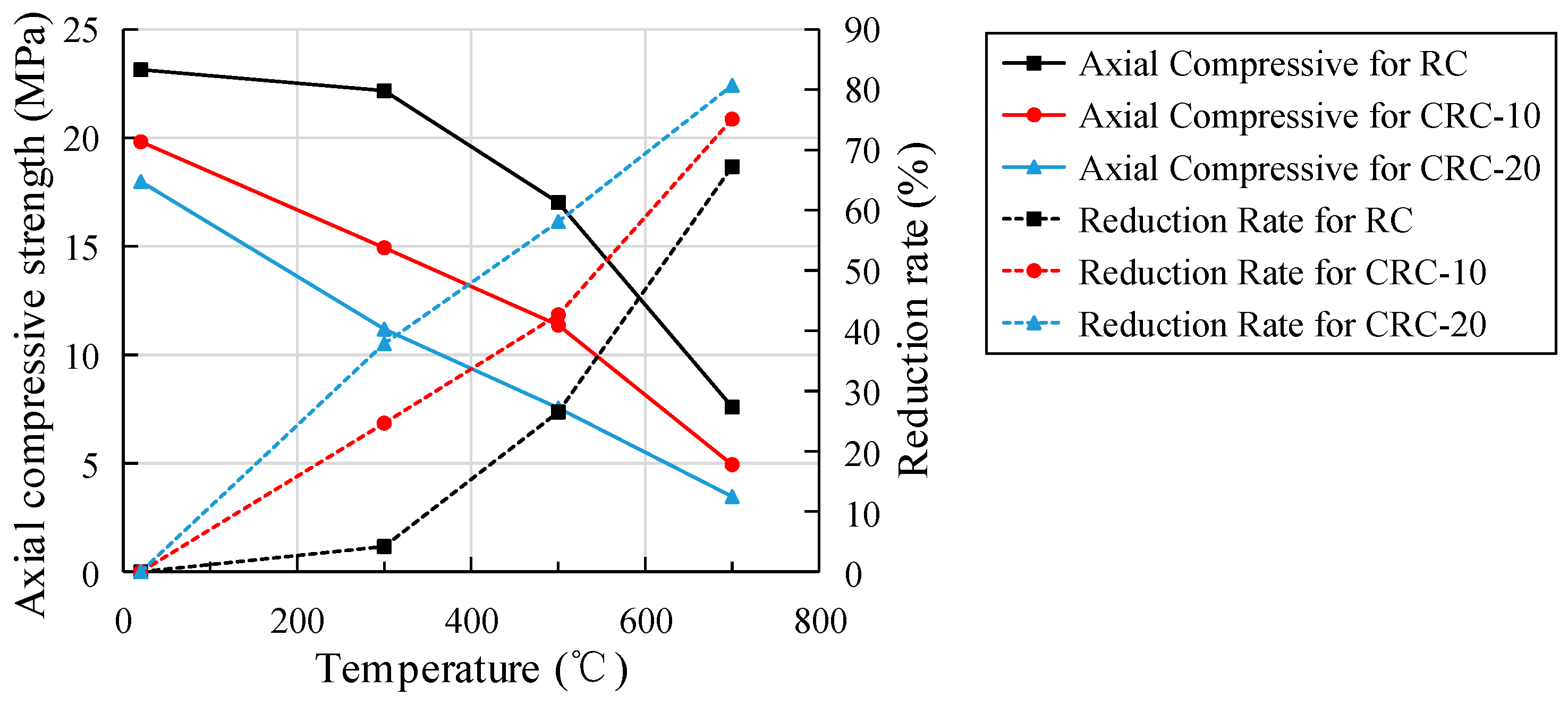
3.6. Axial Compressive Strength
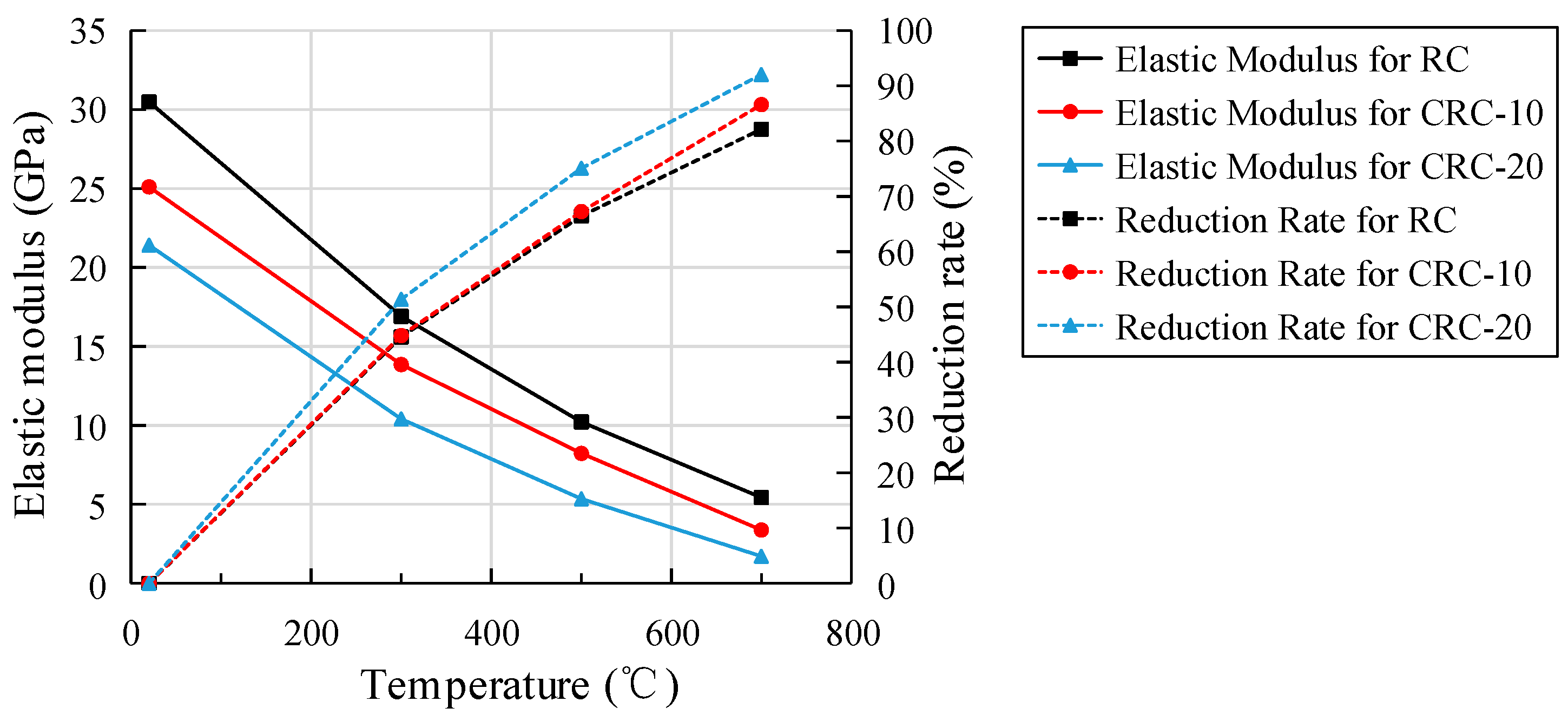
3.7. Elastic Modulus under Static Pressure
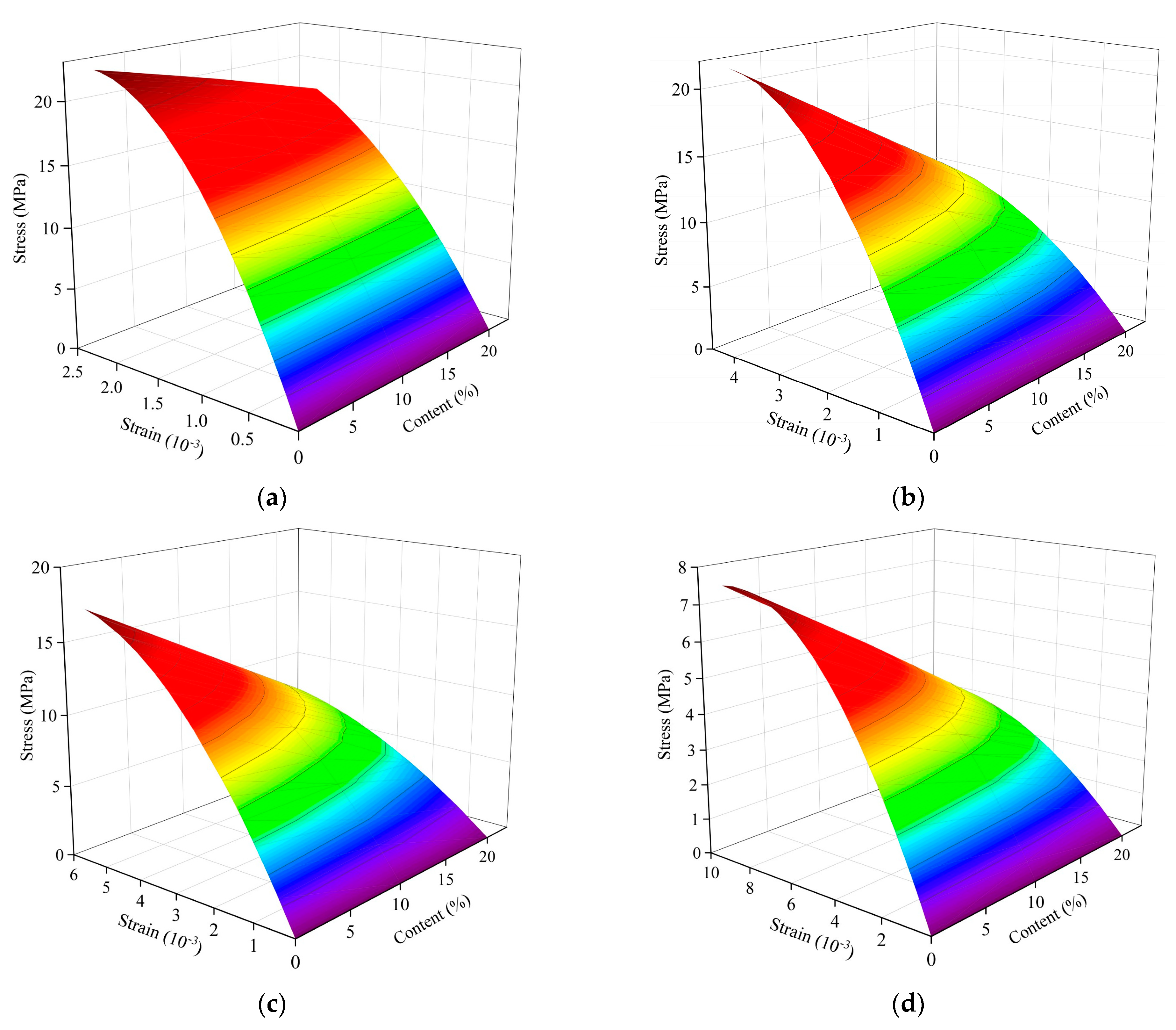
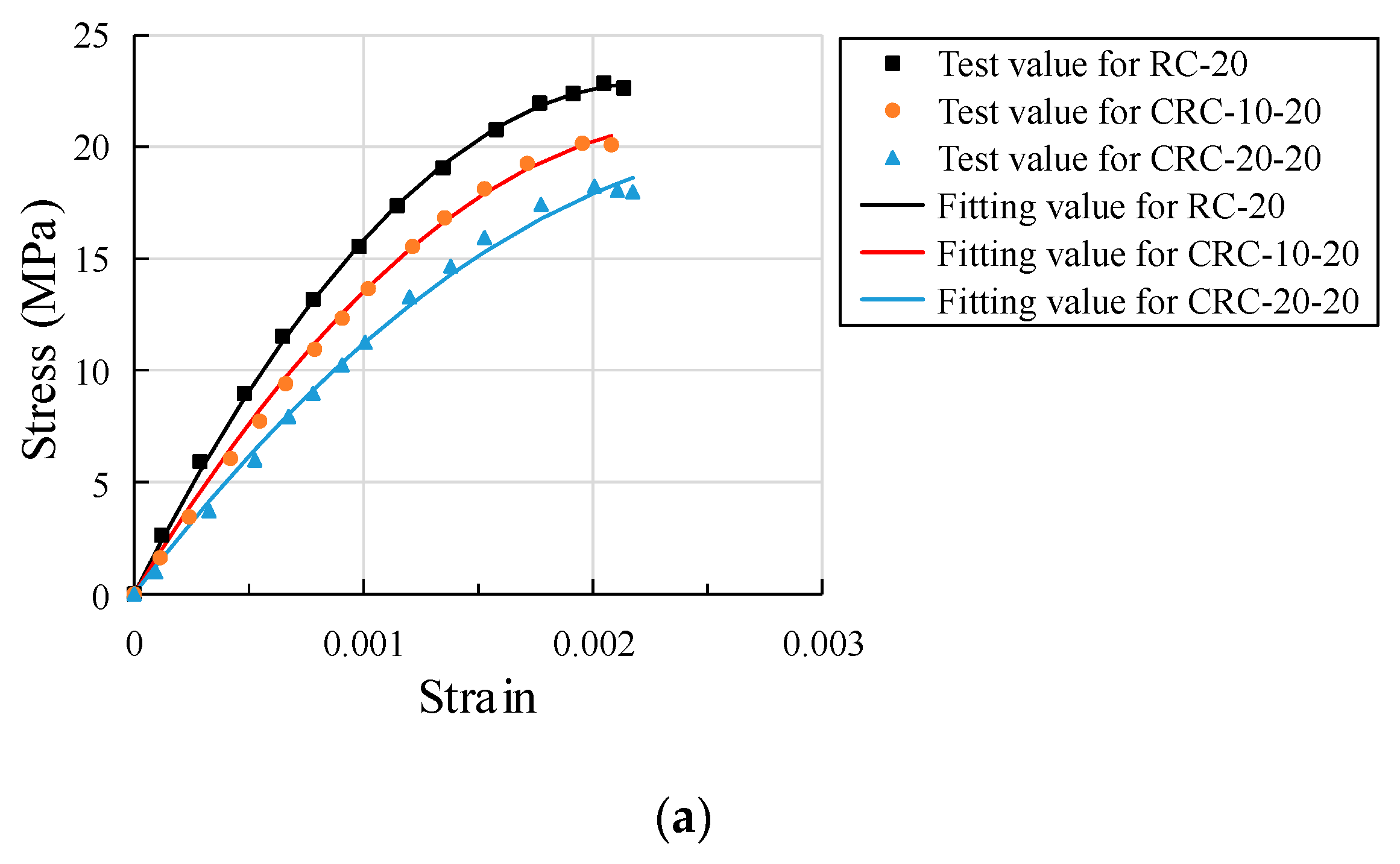
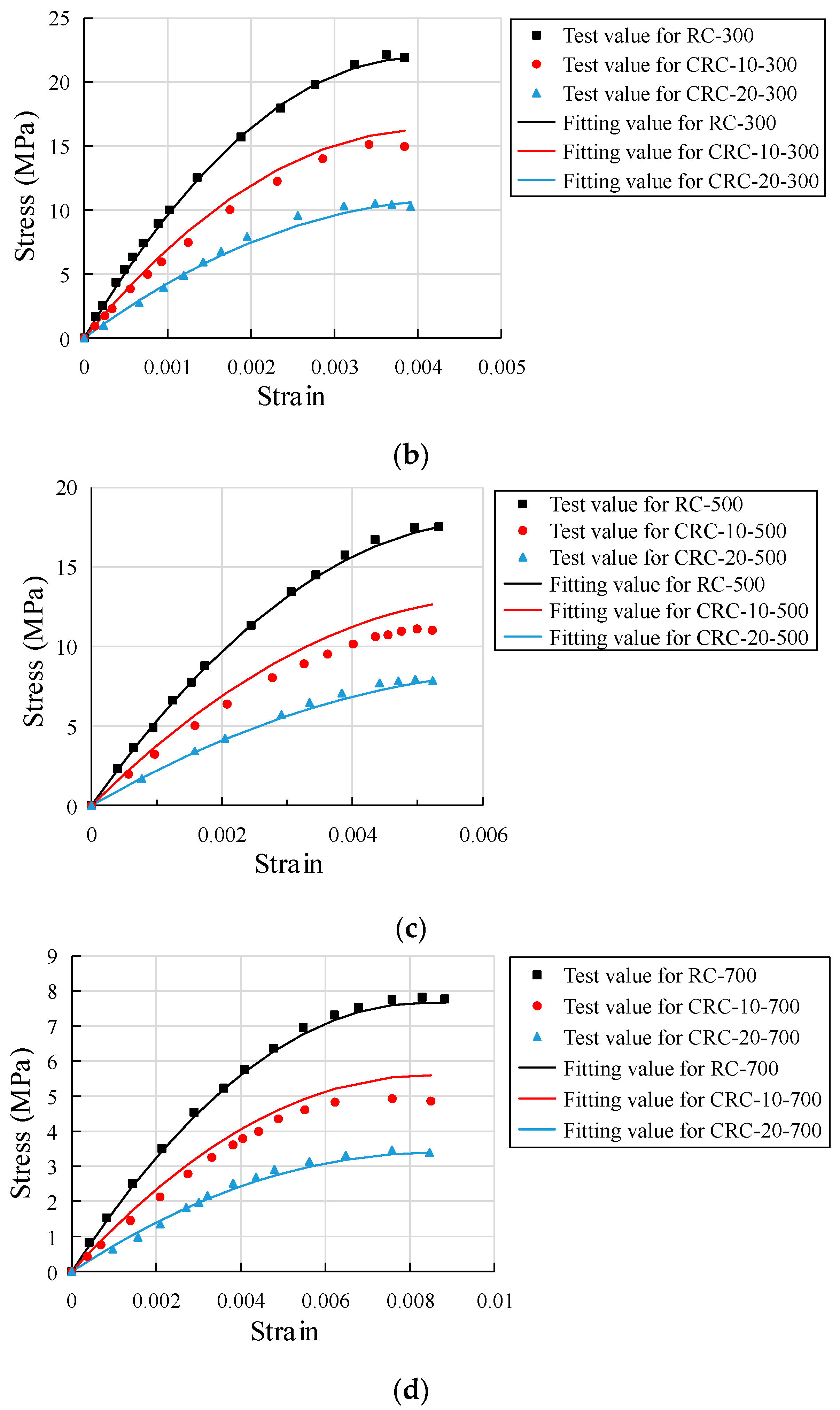
3.8. Uniaxial Compression Stress-Strain Relationship
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the increase in heating temperature, the apparent color of the specimen becomes lighter, the surface cracks of the specimen become wider, and the mass loss of the specimen increases. With the increase in crumb rubber content, the cracks on the surface of the specimen become wider, the mass loss becomes larger, and the heat conduction rate of concrete decreases.
- (2)
- An elevated temperature has a great influence on the strength and elastic modulus of CRC. With the increase in heating temperature, the cube compressive strength of the control group increases slightly at 300 °C, while the cube compressive strength of the CRC decreases, and the split tensile strength, axial compressive strength, and elastic modulus of the control group and CRC all decrease. However, the integrity of the CRC specimen after failure is better, and the plastic failure characteristics are more obvious.
- (3)
- The cubic compressive strength, splitting tensile strength, axial compressive strength, and elastic modulus decrease more obviously with the increase in crumb rubber content. The degree of influence of elevated temperature on strength and elastic modulus is as follows: splitting tensile strength > elastic modulus > axial compressive strength > cubic compressive strength.
- (4)
- With the increase in heating temperature, the stress-strain curve tends to be flat, the peak stress decreases, and the corresponding peak strain obviously increases. At the same temperature, the peak stress decreases more with the increase in crumb rubber content, but the corresponding peak strain is basically the same. After multiple nonlinear regression analyses and the fitting of stress-strain data from three kinds of crumb rubber mixtures, the stress-strain fitting curves of specimens with different crumb rubber mixtures are obtained. The fitting results are basically consistent with the experimental results.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddika, A.; Al Mamun, A.; Alyousef, R.; Amran, Y.H.M.; Aslani, F.; Alabduljabbar, H. Properties and utilizations of waste tire rubber in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarivan, J.Z.; Khaleel, H.Y. Mechanical and durability properties of self-compacted concrete incorporating waste crumb rubber as sand replacement: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11301. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ling, T.; Mo, K.H. Functions and impacts of plastic/rubber wastes as eco-friendly aggregate in concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, Z. Enhancement of dynamic damping in eco-friendly railway concrete sleepers using waste-tyre crumb rubber. Materials 2018, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ince, C.; Shehata, B.M.; Derogar, S.; Ball, R.J. Towards the development of sustainable concrete incorporating waste tyre rubbers: A long-term study of physical, mechanical & durability properties and environmental impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130223. [Google Scholar]
- Alyousef, R.; Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, A.; Aslam, F.; Joyklad, P.; Alabduliabbar, H. Potential use of recycled plastic and rubber aggregate in cementitious materials for sustainable construction: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trilok, G.; Salman, S.; Ravi, K.S.; Sandeep, C. Behaviour of waste rubber powder and hybrid rubber concrete in aggressive environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Blessen, S.T.; Ramesh, C.G. A comprehensive review on the applications of waste tire rubber in cement concrete. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Turatsinze, A.; Granju, J.L.; Bonnet, S. Positive synergy between steel fibres and rubber aggregates: Effect on the resistance of cement-based mortars to shrinkage cracking. Cement. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, L.K.; Gamal, Y.A. Properties of rubberized concrete prepared from different cement types. Recycling 2022, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijana, H.N.; Emmanuel, K.N.; Naida, A.; Ivana, M.; Tanja, K. Modelling the influence of waste rubber on compressive strength of concrete by artificial neural networks. Materials 2019, 12, 561. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, M.M.; El-Dieb, A.S.; El-Wahab, M.A.; Abdel-Hameed, M.E. Mechanical, fracture, and microstructural investigations of rubber concrete. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2008, 20, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sisi, A.A.; Elkilani, A.M.; Salim, H.A. Investigation of the effect of crumb rubber on the static and dynamic response of reinforced concrete panels. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Cheng, B.Q. Mechanical properties of alkali-activated concrete containing crumb rubber particles. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.F.; Huang, X.Y.; Li, H.M.; Cao, Z.; Yang, Z.J.; Hao, D.Y.; Min, K.; Li, W.C.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; et al. Numerical simulation of fatigue life of rubber concrete on the mesoscale. Polymers 2023, 15, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pang, J.; Chen, Q.; Yao, W. Study on mechanical properties and pore structure of hybrid fiber reinforced rubber concrete. Crystals 2021, 11, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.L. Analysis of uniaxial compression mechanical properties of rubber powder recycled coarse aggregate concrete based on strain energy theory. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6767428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Sadek, D.M. Behavior of alkali-activated slag pastes blended with waste rubber powder under the effect of freeze/thaw cycles and severe sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.Y.; Chen, A.J.; Liu, H.D. Effect of waste tire rubber particles on concrete abrasion resistance under high-speed water flow. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2021, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J.; Lai, D.; Yu, T.; Huang, D. Rubberized geopolymer concrete: Dependence of mechanical properties and freeze-thaw resistance on replacement ratio of crumb rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Farzad, H.; Emadaldin, M.G. Evaluating the synergic effect of waste rubber powder and recycled concrete aggregate on mechanical properties and durability of concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00639. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, T.L.; Sih, Y.K.; Yu, B.; Susilawati, S.; Izni, Z.; Suvash, C.P.; Mavinakere, E.R. Thermal and mechanical properties of concrete incorporating silica fume and waste rubber powder. Polymers 2022, 14, 4858. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, L. Utilization of waste tire rubber powder in concrete. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2015, 22, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alireza, K.; Yaser, P.D. Investigation of flexural capacity of concrete containing liquid silicone rubber. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 6668283. [Google Scholar]
- Safeer, A.; Ayesha, F.; Syed, M.S.; Muhammad, J.M.; Shahid, A.; Mujasim, A.R. Effect of particle sizes and dosages of rubber waste on the mechanical properties of rubberized concrete composite. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8460. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, S.; Feng, S.; Shu, L.; Tang, C. Improvement mechanism of the mechanical properties and pore structure of rubber lightweight aggregate concrete with S95 slag. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osama, Y.; Abdelrahman, S.; Ahmed, M.T. Performance of crumb rubber concrete made with high contents of heat pre-treated rubber and magnetized water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 2160–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulaziz, A.; Abdulrahman, A.; Aref, A.; Husain, A.; Tarek, A.; Yousef, A.S. Behavior of ternary blended cementitious rubberized mixes reinforced with recycled tires steel fibers under different types of impact loads. Structures 2022, 45, 2292–2305. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, R.R.; De, P.H.; Bonfim, W.B.; Silva, I.D.; Pinto, H.S. Recycling of tire rubber and concrete residue in the production of concrete bricks: Dosing and optimization. Matéria 2021, 26, e13027. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, F.Q.; Zhu, H.; Yasser, E.I.; Musa, A. Durability and property study of decade old crumb rubber concrete cored specimens. Materials 2022, 15, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignozzi, M.C.; Sandrolini, F. Tyre rubber waste recycling in self-compacting concrete. Cement. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Gao, S.; Xu, P. The application of rubber aggregate combined permeable concrete mixture in sponge city construction. Coatings 2023, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmet, G.; Erhan, G.; Ganjeena, K. Abrasion and freezing–thawing resistance of pervious concretes containing waste rubbers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Ren, S.S.; Sun, C.J.; Zhang, J.Z.; Jiang, H.G.; Yao, Z.Y. Extruded tire crumb-rubber recycled polyethylene melt blend as asphalt composite additive for enhancing the performance of binder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04019373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, V.R. Properties of concrete at elevated temperatures. ISRN Civil. Eng. 2014, 2014, 468510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, W.; Feng, W.; Chen, J.; Bao, D.; Li, L. Compressive properties of rubber-modified recycled aggregate concrete subjected to elevated temperatures. Construct. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.T.; Carino, N.J. Code provisions for high strength concrete strengthtemperature relationship at elevated temperatures. Mater. Struct. 2003, 36, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.D.; Alam, N.; Nadjai, A.; Nigro, E.; Ali, F. Finite element modelling for structural performance of slim floors in fire and influence of protection materials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11291. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, A.M.; Roszilah, H.; Azrul, A.M.; Amrul, K.A. A review of precast concrete beam-to-column connections subjected to severe fire conditions. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 23, 8831120. [Google Scholar]
- Noman, M.; Yaqub, M.; Abid, M.; Musarat, M.A.; Vatin, N.I.; Usman, M. Effects of low-cost repair techniques on restoration of mechanical properties of fire-damaged concrete. Front. Mater. 2022, 8, 801464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, P. Investigating the role of swelling-degradation degree of crumb rubber on CR/SBS modified porous asphalt binder and mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.B.; Amir, A.S.; Nader, A.Z.; Kamyar, K.; Vivian, W.Y. Impact of elevated temperatures on the structural performance of recycled rubber concrete: Experimental and mathematical modeling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 255, 119374. [Google Scholar]
- Saberian, M.; Shi, L.; Sidiq, A.; Li, J.; Setunge, S.; Li, C.Q. Recycled concrete aggregate mixed with crumb rubber under elevated temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpalaskas, A.C.; Matikas, T.E.; Aggelis, D.G. Acoustic emission of fire damaged fiber reinforced concrete. SPIE 2016, 9806, 320–328. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Phuong, T. Cement mortar containing crumb rubber coated with geopolymer: From microstructural properties to compressive strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 383, 131284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.D.; Zeng, Z.X. Measures to strengthen bond strength of rubber concrete interface. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power 2010, 31, 57–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khaliq, W.; Kodur, V. Effect of high temperature on tensile strength of different types of high-strength concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2011, 108, 394–403. [Google Scholar]
- Lie, T.T.; Irwin, R.J. Method to calculate the fire resistance of reinforced concrete columns with rectangular cross section. ACI Struct. J. 1993, 90, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F. The Experimental Studies and Analysis on Temperature Field of Concrete Members. Doctoral Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulaziz, A.; Abdulrahman, A.; Aref, A.; Husain, A.; Yousef, A.S. Development of metakaolin-based geopolymer rubberized concrete: Fresh and hardened properties. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Najib, N.G.; Camille, A.I.; Samer, A.F. Rubber concrete: Mechanical and dynamical properties. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2018, 9, e00184. [Google Scholar]
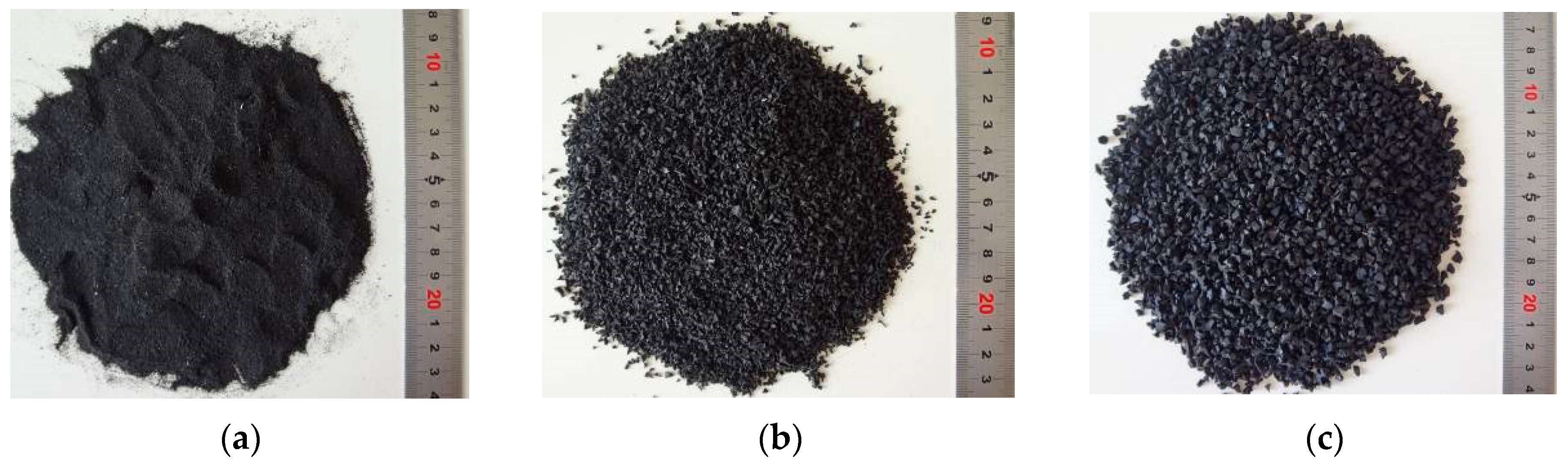
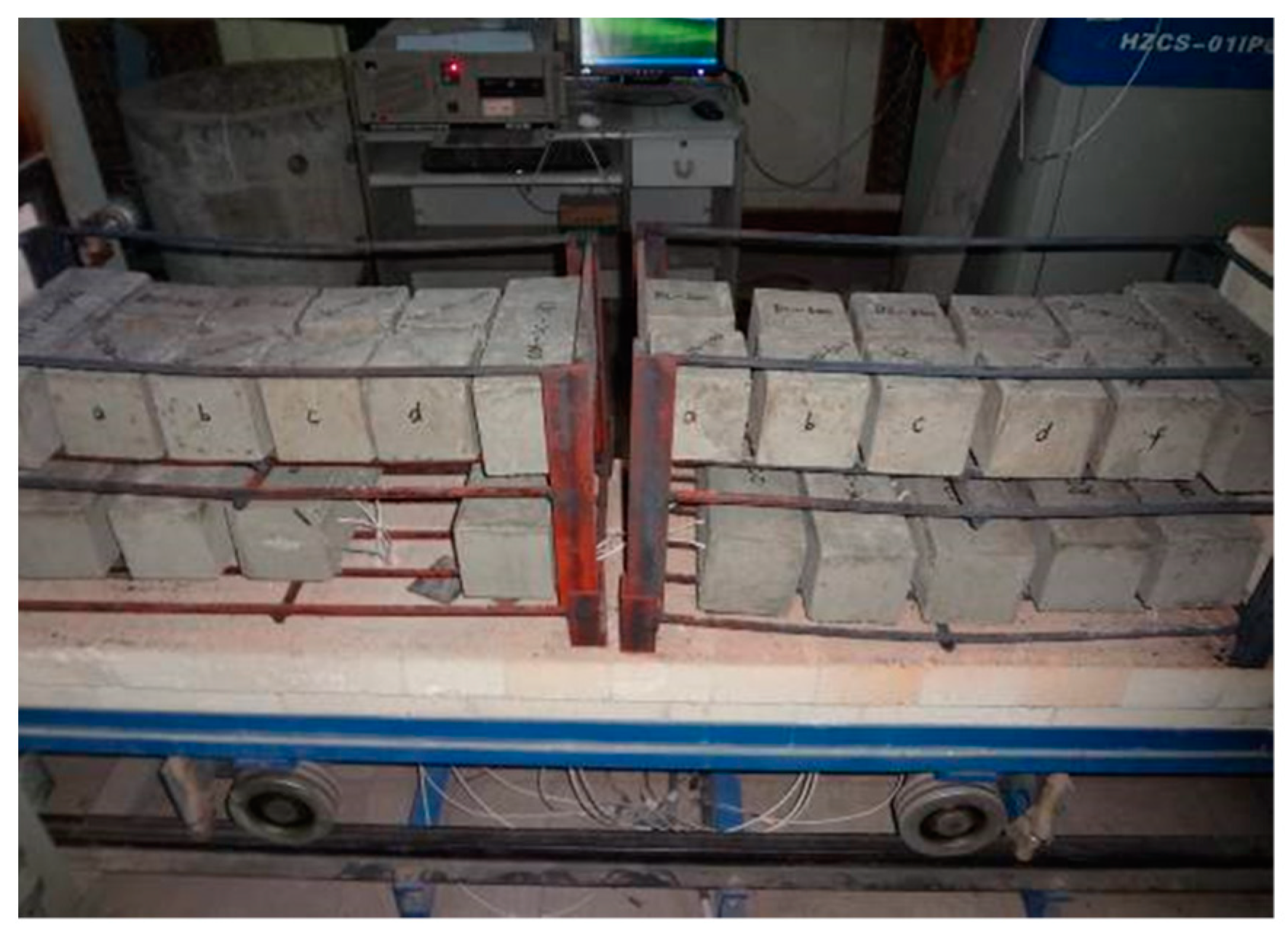










| Fineness/% | Alkali Content/% | Setting Time/min | Flexural Strength/MPa | Compressive Strength/MPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Setting Time | Final Setting Time | 3 d | 28 d | 3 d | 28 d | ||
| <10 | 0.56 | 153 | 203 | 5.6 | 8.7 | 30 | 56 |
| Specimen | Cement | Crumb Rubber | Fine Aggregate | Coarse Aggregate | Fly Ash | Water | Water-Reducing Agent | Water-Cement Ratio | Sand Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC | 280 | 0 | 848 | 1037 | 70 | 175 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| CRC-10 | 280 | 34.7 | 763.2 | 1037 | 70 | 175 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 0.42 |
| CRC-20 | 280 | 69.4 | 678.4 | 1037 | 70 | 175 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 0.40 |
| Specimen | Heating Temperature | Cube Compressive (100 mm × 100 mm × 100 mm) | Splitting Tensile (100 mm × 100 mm × 100 mm) | Axial Compressive (100 mm × 100 mm × 300 mm) | Elastic Modulus (100 mm × 100 mm × 300 mm) | Stress-Strain (100 mm × 100 mm × 300 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC-20 | AT | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| CRC-10-20 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| CRC-20-20 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| RC-300 | 300 °C | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| CRC-10-300 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| CRC-20-300 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| RC-500 | 500 °C | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| CRC-10-500 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| CRC-20-500 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| RC-700 | 700 °C | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| CRC-10-700 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| CRC-20-700 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Type | RC | CRC-10 | CRC-20 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCS/% | ACS/% | EM/% | STS/% | CCS/% | ACS/% | EM/% | STS/% | CCS/% | ACS/% | EM/% | STS/% | |
| AT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 °C | −4.04 | 4.19 | 44.55 | 19.42 | 3.87 | 24.67 | 44.82 | 43.16 | 19.57 | 37.82 | 51.38 | 61.54 |
| 500 °C | 31.66 | 26.49 | 66.47 | 72.57 | 44.64 | 42.63 | 67.25 | 80.16 | 45.61 | 58.06 | 75.06 | 81.36 |
| 700 °C | 63.67 | 67.2 | 82.15 | 86.17 | 69.32 | 75.08 | 86.57 | 90.88 | 71.09 | 80.7 | 92.01 | 92.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Lv, Z.; Bai, Y.; Han, G.; Li, D. Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties of Crumb Rubber Concrete after Elevated Temperature. Polymers 2023, 15, 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143102
Han Y, Lv Z, Bai Y, Han G, Li D. Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties of Crumb Rubber Concrete after Elevated Temperature. Polymers. 2023; 15(14):3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yang, Zhishuan Lv, Yaqiang Bai, Guoqi Han, and Dongqiao Li. 2023. "Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties of Crumb Rubber Concrete after Elevated Temperature" Polymers 15, no. 14: 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143102
APA StyleHan, Y., Lv, Z., Bai, Y., Han, G., & Li, D. (2023). Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties of Crumb Rubber Concrete after Elevated Temperature. Polymers, 15(14), 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143102






