Size-Dependent Diffusion and Dispersion of Particles in Mucin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
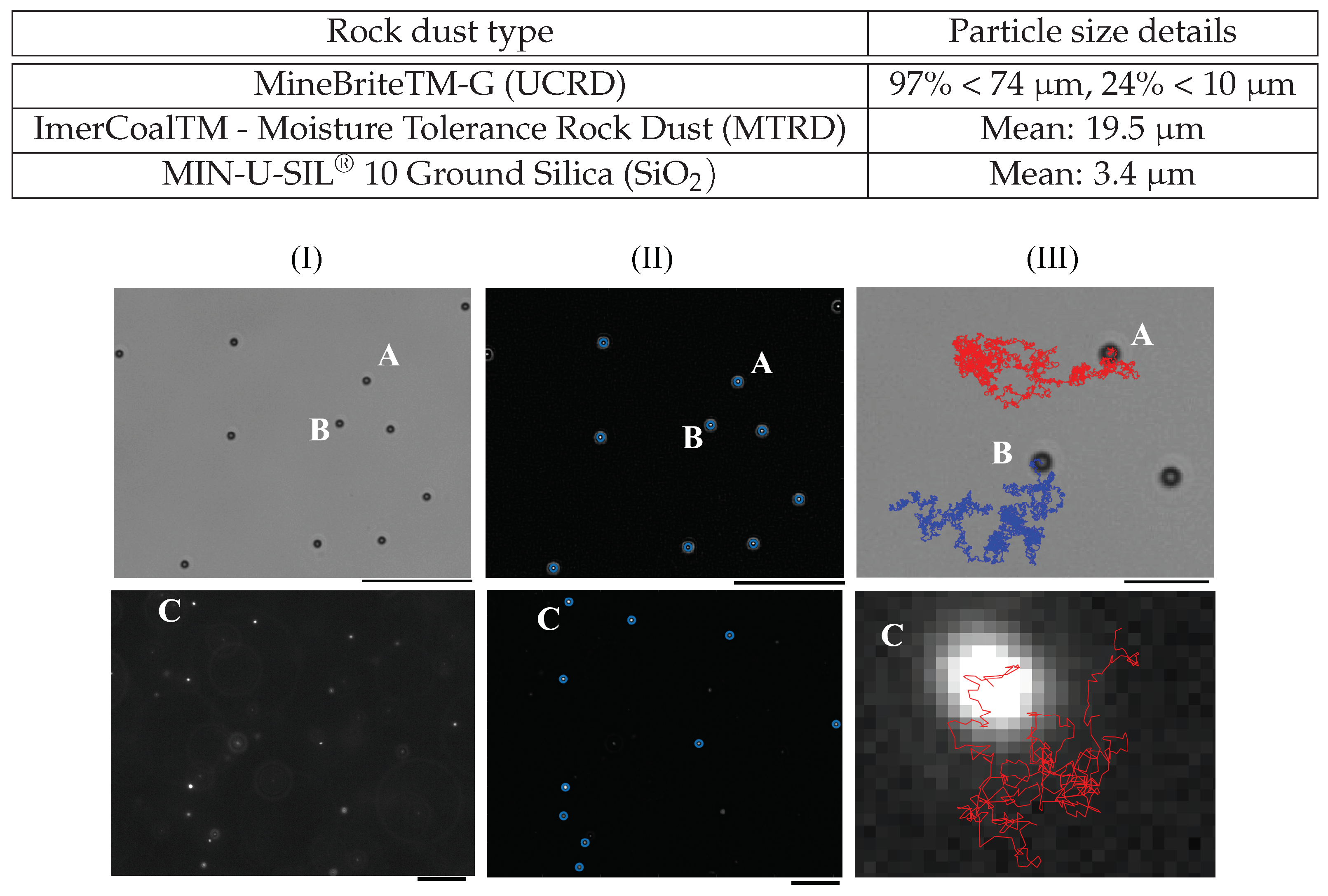
2.1. Preparation of Control Mucin and Mucin Loaded with Anti-Caking Agent (Rock Dust)
2.2. CMC Sample Preparation
2.3. Slide Preparation for Particle Tracking and Microrheology
2.4. Optical Setup for Microrheology
2.5. Image Filtering and Pre-Tracking Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
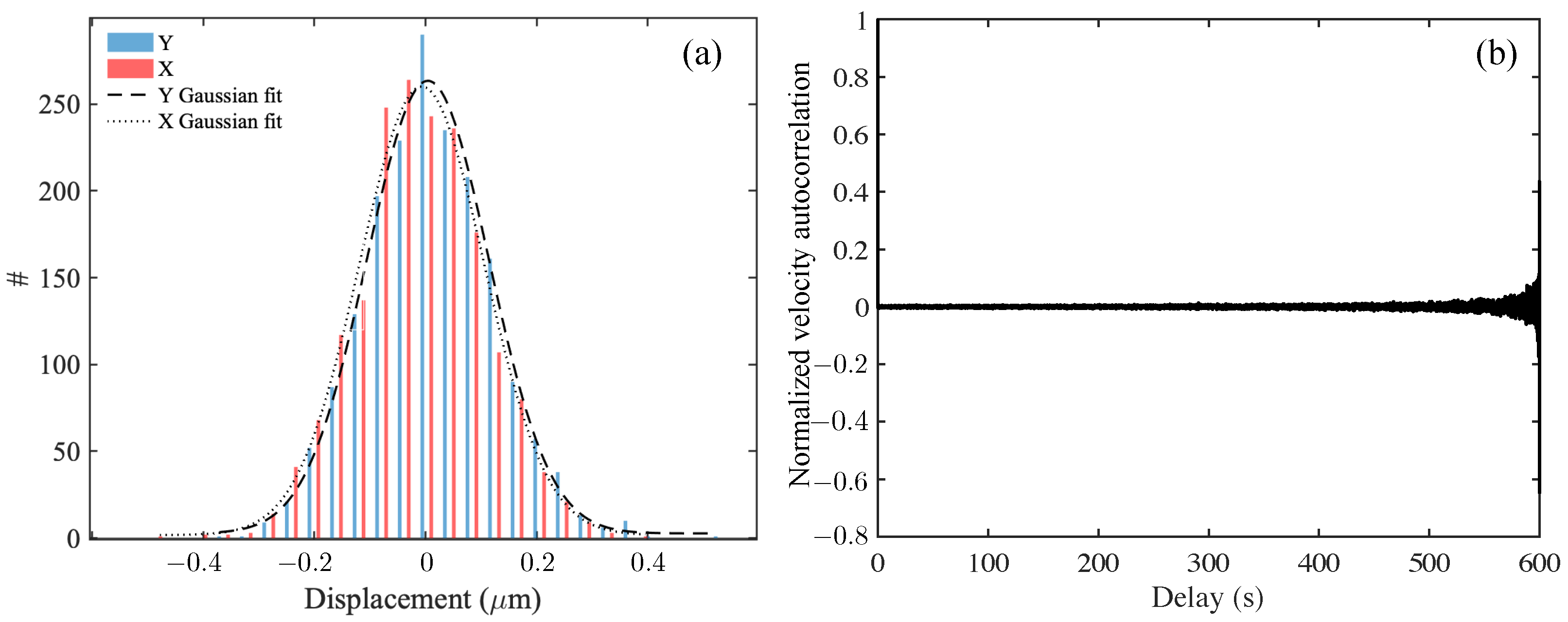
2.7. Velocity Correlation, Diffusion, and Dispersion of Tracers
2.8. Diffusion of Tracers in Viscoelastic CMC
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reconstituted Mucin Solutions Behave as Very Weakly Viscoelastic Fluids
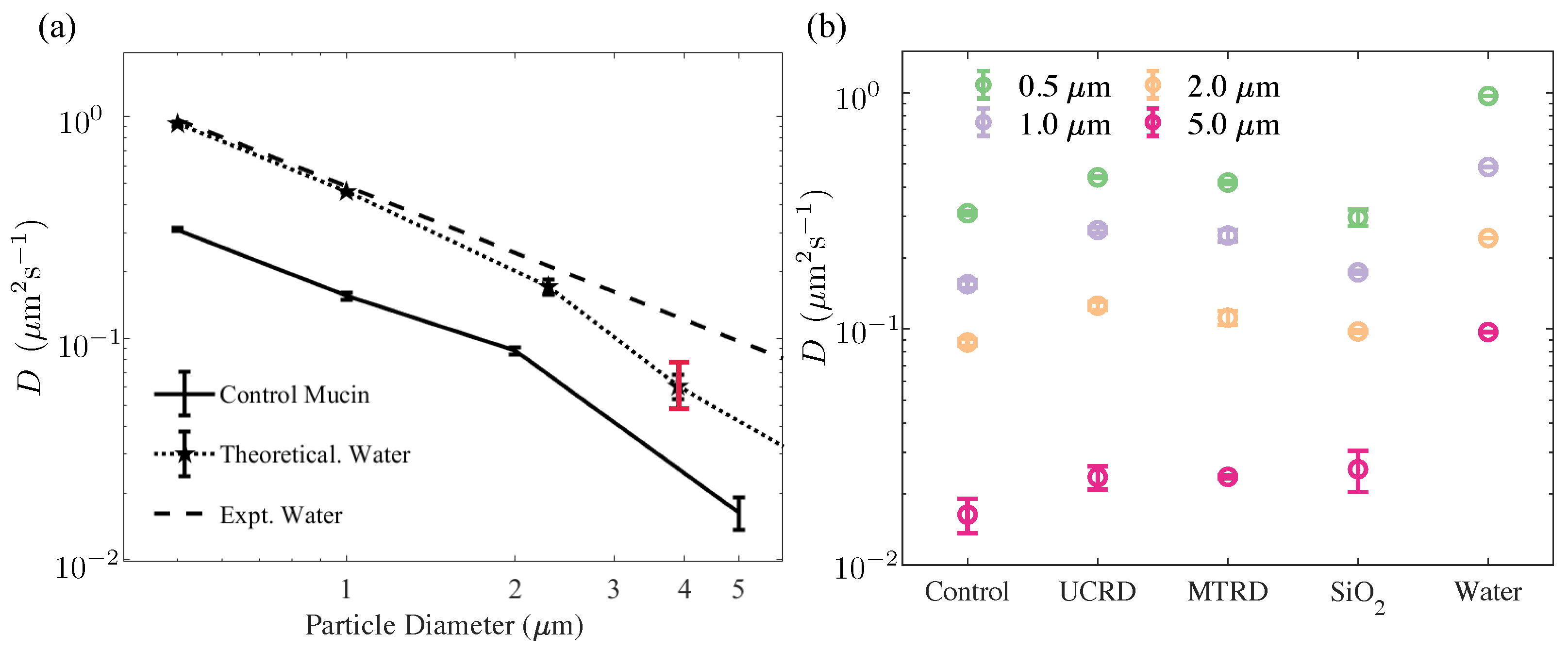
3.2. Diffusivity of Tracers Decreases Inversely with Tracer Diameter
3.3. Diffusivity in Rock Dust-Laden Mucin Formulations Is Larger Than in the Bare Mucin
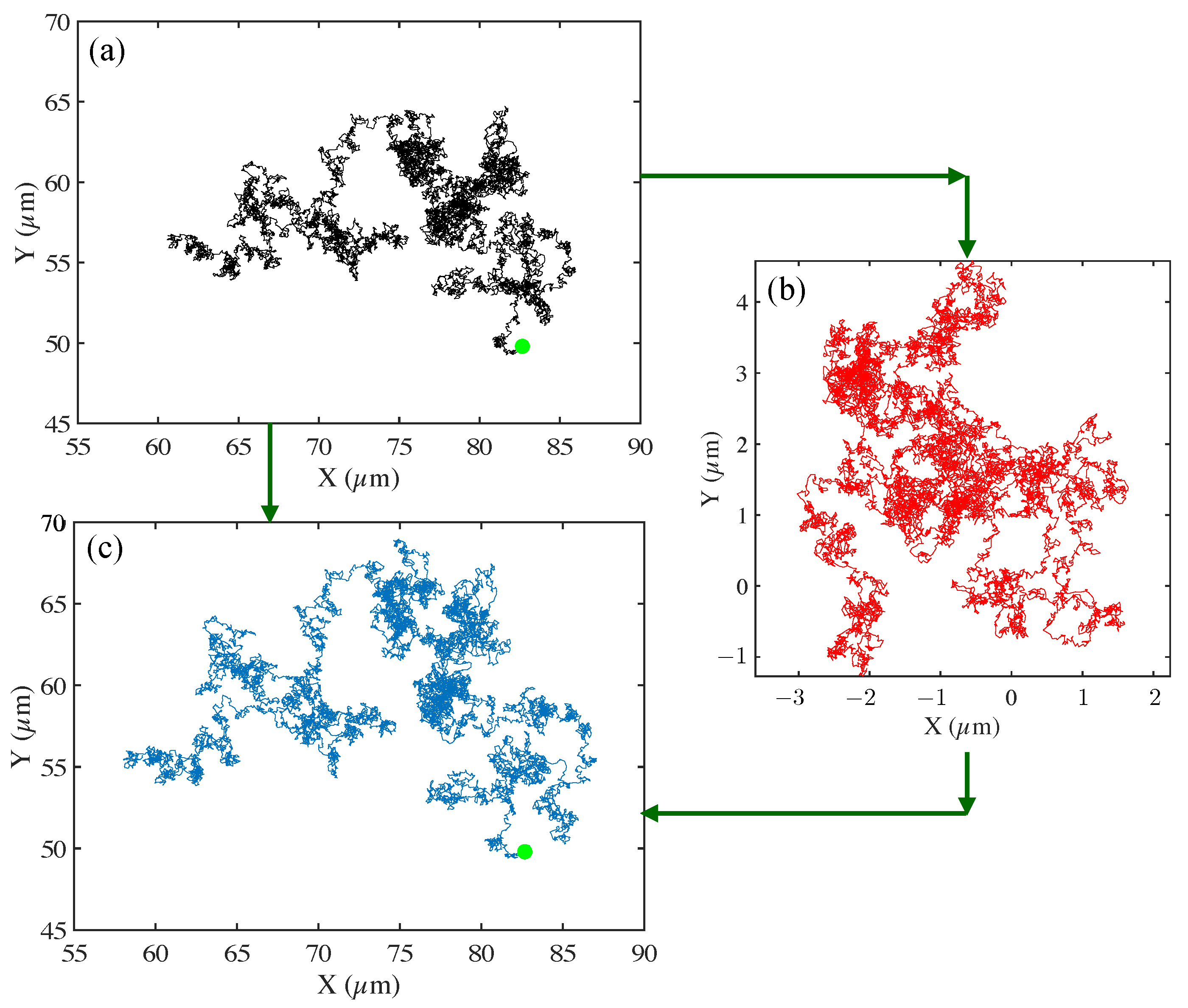
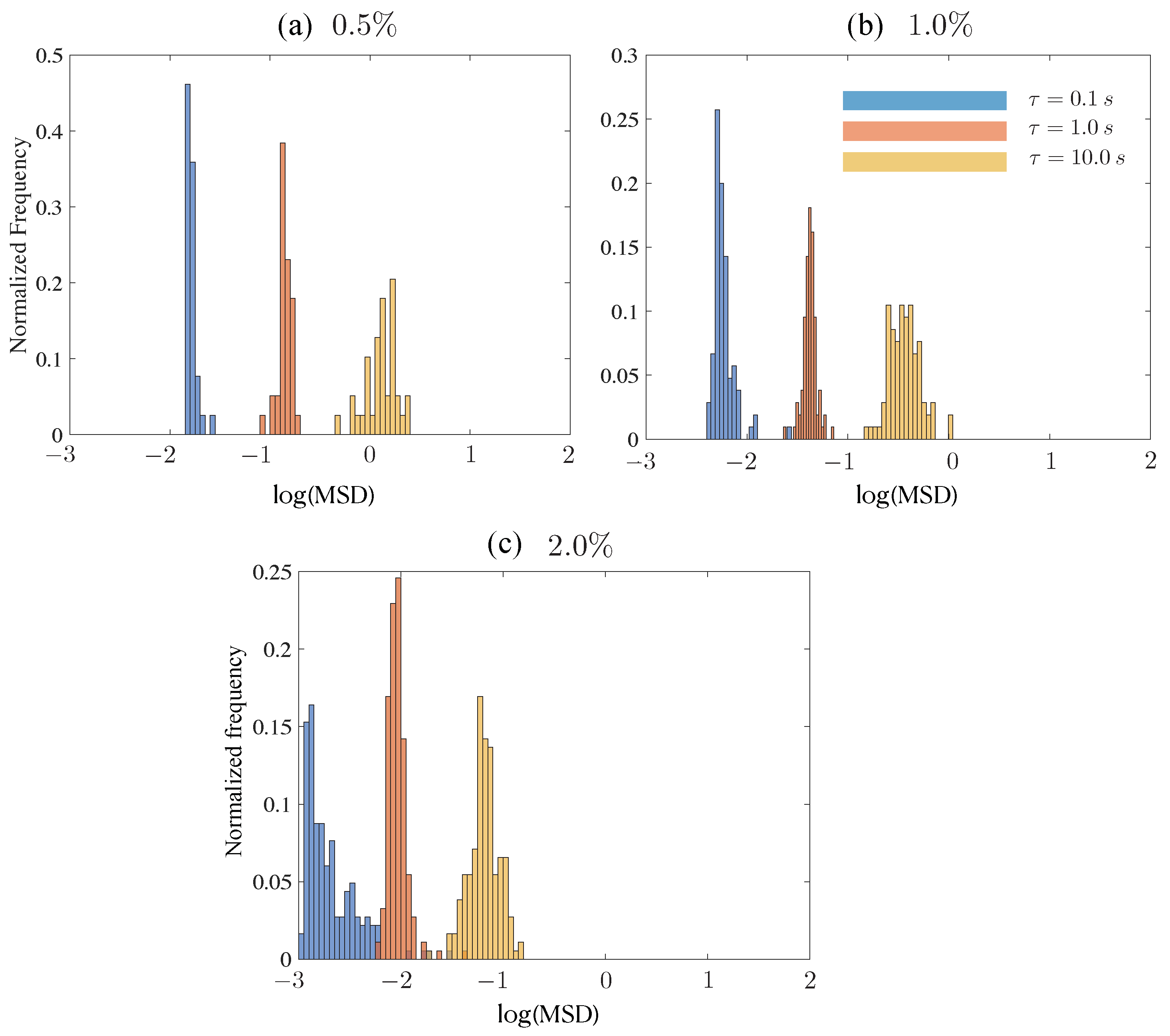
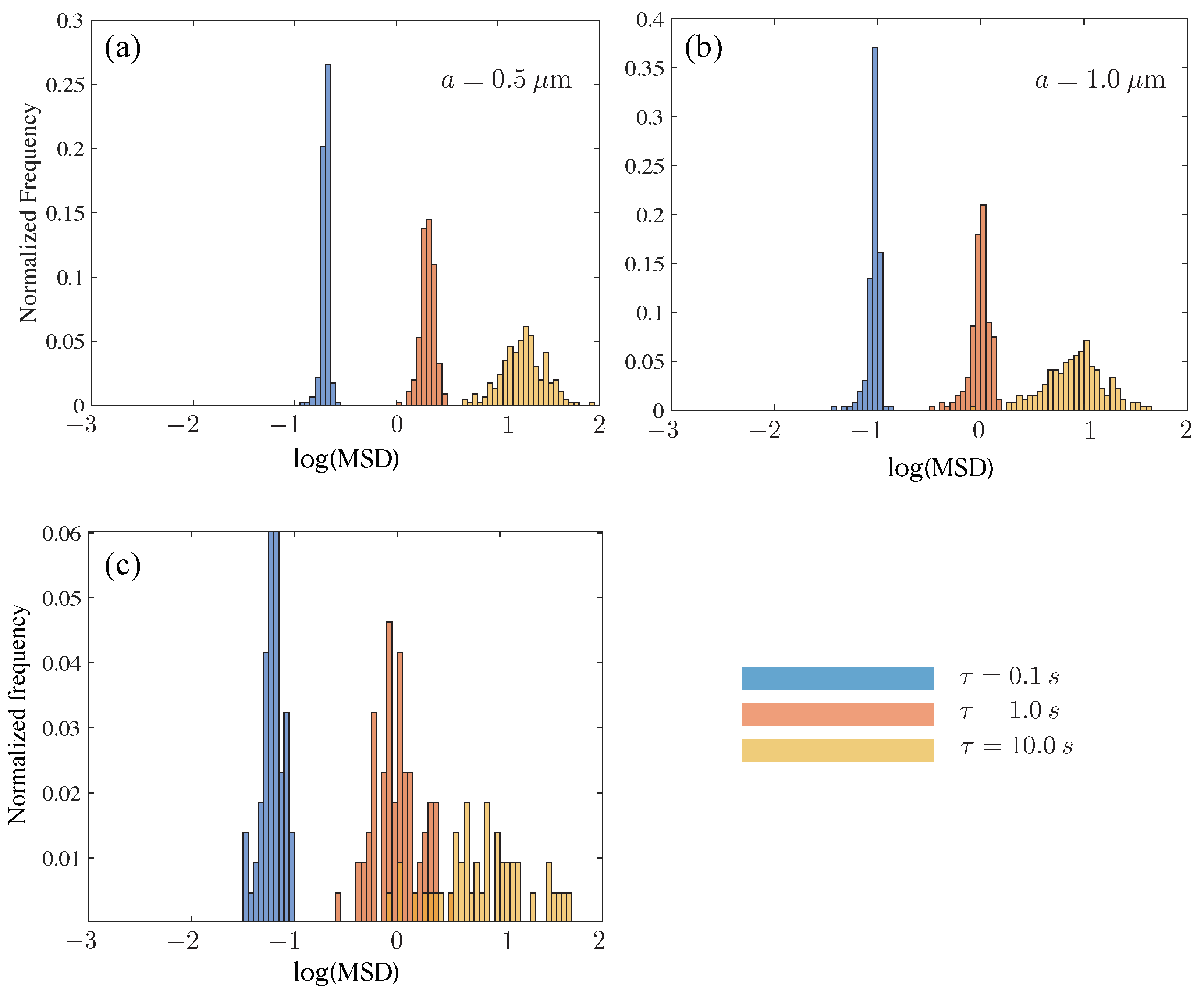
3.4. Tracer Squared Displacements Highlight Effects of Heterogeneity and Transient Trapping
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSD | Mean Square Displacement |
| CMC | Carboxymethylcellulose |
References
- Thornton, D.J.; Sheehan, J.K. From Mucins to Mucus. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2004, 1, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, D.J.; Rousseau, K.; McGuckin, M.A. Structure and Function of the Polymeric Mucins in Airways Mucus. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 459–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pednekar, D.D.; Liguori, M.A.; Marques, C.N.H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Z.; Amoako, K.; Gu, H. From Static to Dynamic: A Review on the Role of Mucus Heterogeneity in Particle and Microbial Transport. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 2825–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansil, R.; Celli, J.P.; Hardcastle, J.M.; Turner, B.S. The Influence of Mucus Microstructure and Rheology in Helicobacter pylori Infection. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Georgiades, P.; Pudney, P.D.A.; Thornton, D.J.; Waigh, T.A. Particle tracking microrheology of purified gastrointestinal mucins. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.; Snary, D. The structure and function of gastric mucus. Gut 1972, 13, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, Z.; Chasan, B.; Bansil, R.; Turner, B.S.; Bhaskar, K.R.; Afdhal, N.H. Atomic force microscopy reveals aggregation of gastric mucin at low pH. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3458–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cone, R.; Wirtz, D.; Hanes, J. Altering Mucus Rheology to “Solidify” Human Mucus at the Nanoscale. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Sun, A.; Chen, C.S.; Mintz, A.J.; Chin, W.C. Nicotine alters mucin rheological properties. Am. J.-Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L149–L157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coggon, D.; Taylor, A.N. Coal mining and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A review of the evidence. Thorax 1998, 53, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahy, J.V.; Dickey, B.F. Airway mucus function and dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.M.; Duran-Robles, E.; Goshia, T.; Mesina, M.; Garcia, C.; Young, J.; Sibal, A.; Chiu, M.H.; Chin, W.C. CeO2 nanoparticles attenuate airway mucus secretion induced by TiO2 nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, J.C. Pathophysiology of airflow limitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randell, S.H.; Boucher, R.C. Effective mucus clearance is essential for respiratory health. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.Y.; Vazquez, C.I.; Shiu, R.F.; Garcia, A.K.; Le, C.; Patel, P.; Sadqi, M.; Chin, W.C. Effects of Rock Dust Particles on Airway Mucus Viscosity. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansil, R.; Stanley, E.; LaMont, J.T. Mucin biophysics. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1995, 57, 635–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J.P.; Turner, B.S.; Afdhal, N.H.; Ewoldt, R.H.; McKinley, G.H.; Bansil, R.; Erramilli, S. Rheology of Gastric Mucin Exhibits a pH-Dependent Sol-Gel Transition. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joyner, K.; Song, D.; Hawkins, R.F.; Silcott, R.D.; Duncan, G.A. Designing viscoelastic mucin-based hydrogels. bioRxiv 2019, 656801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meldrum, O.W.; Yakubov, G.E.; Bonilla, M.R.; Deshmukh, O.; McGuckin, M.A.; Gidley, M.J. Mucin gel assembly is controlled by a collective action of non-mucin proteins, disulfide bridges, Ca2+-mediated links, and hydrogen bonding. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Authimoolam, S.P.; Vasilakes, A.L.; Shah, N.M.; Puleo, D.A.; Dziubla, T.D. Synthetic Oral Mucin Mimic from Polymer Micelle Networks. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3099–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wirtz, D.; Hanes, J. Micro- and macrorheology of mucus. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghannam, M.T.; Esmail, M.N. Rheological properties of carboxymethyl cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 64, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchabane, A.; Bekkour, K. Rheological properties of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2008, 286, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğrul, H.; Arslan, N. Production of carboxymethyl cellulose from sugar beet pulp cellulose and rheological behaviour of carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 54, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Mason, T.G. Rotational Diffusion Microrheology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 018304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrs, L.; Bartlett, P. One-and two-point micro-rheology of viscoelastic media. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, S251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, J.C.; Hoffman, B.D. Multiple-Particle Tracking and Two-Point Microrheology in Cells. Methods Cell Biol. 2007, 83, 141–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mason, T.G.; Ganesan, K.; Zanten, J.H.V.; Wirtz, D.; Kuo, S.C. Particle Tracking Microrheology of Complex Fluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 3282–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gisler, T.; Weitz, D.A. Tracer microrheology in complex fluids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 3, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittes, F.; Schnurr, B.; Olmsted, P.D.; MacKintosh, F.C.; Schmidt, C.F. Microscopic Viscoelasticity: Shear Moduli of Soft Materials Determined from Thermal Fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 3286–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patteson, A.E.; Gopinath, A.; Purohit, P.K.; Arratia, P.E. Particle diffusion in active fluids is non-monotonic in size. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partridge, J.D.; Ariel, G.; Schvartz, O.; Harshey, R.M.; Be’er, A. The 3D architecture of a bacterial swarm has implications for antibiotic tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patteson, A.E.; Gopinath, A.; Goulian, M.; Arratia, P.E. Running and tumbling with E. coli in polymeric solutions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patteson, A.E.; Gopinath, A.; Arratia, P.E. Active colloids in complex fluids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 21, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Arratia, P.E.; Patteson, A.E.; Gopinath, A. Quenching active swarms: Effects of light exposure on collective motility in swarming Serratia marcescens. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20180960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patteson, A.E.; Gopinath, A.; Arratia, P.E. The propagation of active-passive interfaces in bacterial swarms. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, B.; Gopinath, A.; Yang, J.; Gollub, J.P.; Arratia, P.E. Flagellar Kinematics and Swimming of Algal Cells in Viscoelastic Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, A.; Gopinath, A.; Deshpande, V. Continuum-based computational models for cell and nuclear mechanics. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 2007, 2, 1169–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, C.; Thornton, D.J. Mucins: The frontline defence of the lung. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Button, B.; Anderson, W.H.; Boucher, R.C. Mucus Hyperconcentration as a Unifying Aspect of the Chronic Bronchitic Phenotype. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13 (Suppl. 2), S156–S162. [Google Scholar]
- Crocker, J.C.; Grier, D.G. Methods of Digital Video Microscopy for Colloidal Studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 179, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Zerubia, J.; Olivo-Marin, J.C. Gaussian approximations of fluorescence microscope point-spread function models. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.C. Random Walks in Biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, T.G. Estimating the viscoelastic moduli of complex fluids using the generalized Stokes–Einstein equation. Rheol. Acta 2000, 39, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-González, M. One- and Two-Point Particle Tracking Microrheology of Complex Viscoelastic Fluids. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Celli, J.; Gregor, B.; Turner, B.; Afdhal, N.H.; Bansil, R.; Erramilli, S. Viscoelastic Properties and Dynamics of Porcine Gastric Mucin. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Monitoring and Sampling Approaches to Assess Underground Coal Mine Dust Exposures; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Verdugo, P.; Deyrup-Olsen, I.; Aitken, M.; Villalon, M.; Johnson, D. Molecular mechanism of mucin secretion: I. The role of intragranular charge shielding. J. Dent. Res. 1987, 66, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Baviskar, P.; Webster, R.; Webby, R. The interaction between respiratory pathogens and mucus. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lieleg, O.; Vladescu, I.; Ribbeck, K. Characterization of Particle Translocation through Mucin Hydrogels. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, G.W.; Ridley, C.; Collins, R.; Roseman, A.; Ford, R.; Thornton, D.J. The MUC5B mucin polymer is dominated by repeating structural motifs and its topology is regulated by calcium and pH. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mani, M.; Gopinath, A.; Mahadevan, L. How Things Get Stuck: Kinetics, Elastohydrodynamics, and Soft Adhesion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 226104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gopinath, A.; Mahadevan, L. Elastohydrodynamics of wet bristles, carpets and brushes. Proc. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 467, 1665–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, P.; Tamayo, J.; Shiu, R.-F.; Chin, W.-C.; Gopinath, A. Size-Dependent Diffusion and Dispersion of Particles in Mucin. Polymers 2023, 15, 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153241
Kumar P, Tamayo J, Shiu R-F, Chin W-C, Gopinath A. Size-Dependent Diffusion and Dispersion of Particles in Mucin. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153241
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Parveen, Joshua Tamayo, Ruei-Feng Shiu, Wei-Chun Chin, and Arvind Gopinath. 2023. "Size-Dependent Diffusion and Dispersion of Particles in Mucin" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153241
APA StyleKumar, P., Tamayo, J., Shiu, R.-F., Chin, W.-C., & Gopinath, A. (2023). Size-Dependent Diffusion and Dispersion of Particles in Mucin. Polymers, 15(15), 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153241







