Phenol–Furfural Resin/Graphite/Ag-Based Electrically Conductive Adhesive Composites from Waste Bagasse with Enhanced Thermo-Electric Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Furfural Extraction from Bagasse
2.3. Synthesis of Phenol-Furfural Resin
2.4. Graphite Powder
2.5. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.6. Preparation of Composites and Nanocomposites
2.6.1. Preparation of Graphite–Resin Composites
2.6.2. Preparation of Ag-Resin Nanocomposite
2.6.3. Preparation of Graphite-Ag-Resin Nanocomposite
3. Analysis Techniques
4. Results and Discussion
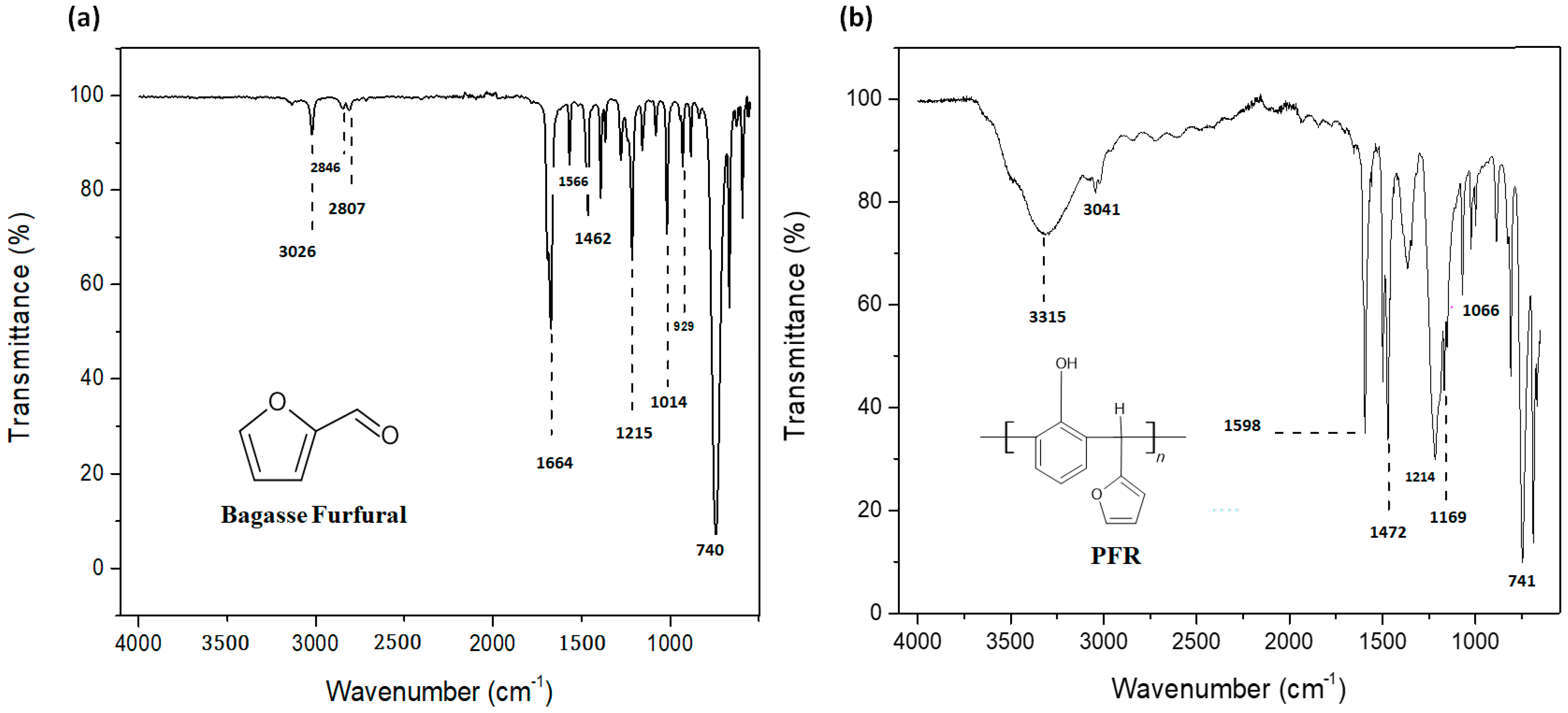
4.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
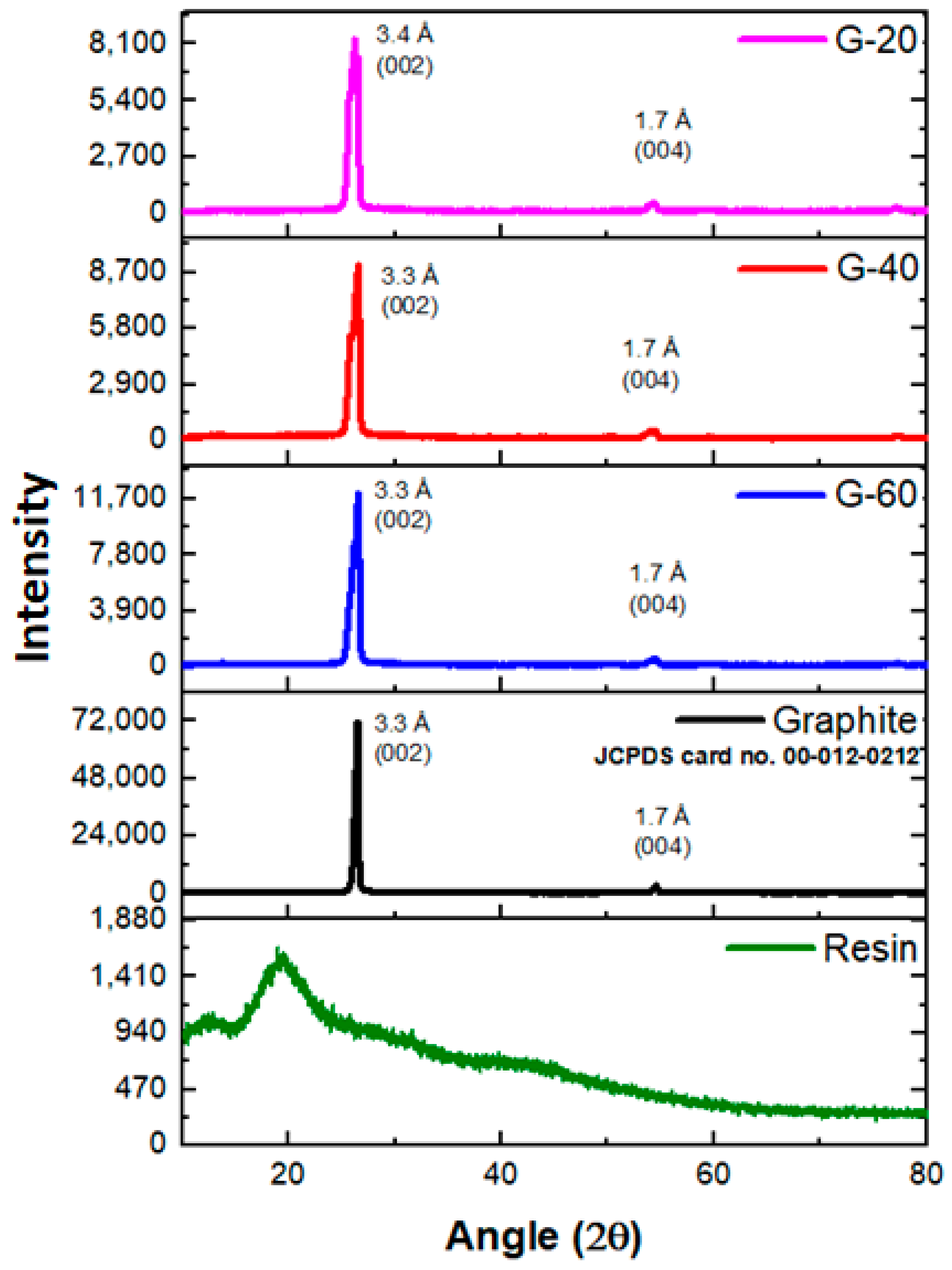
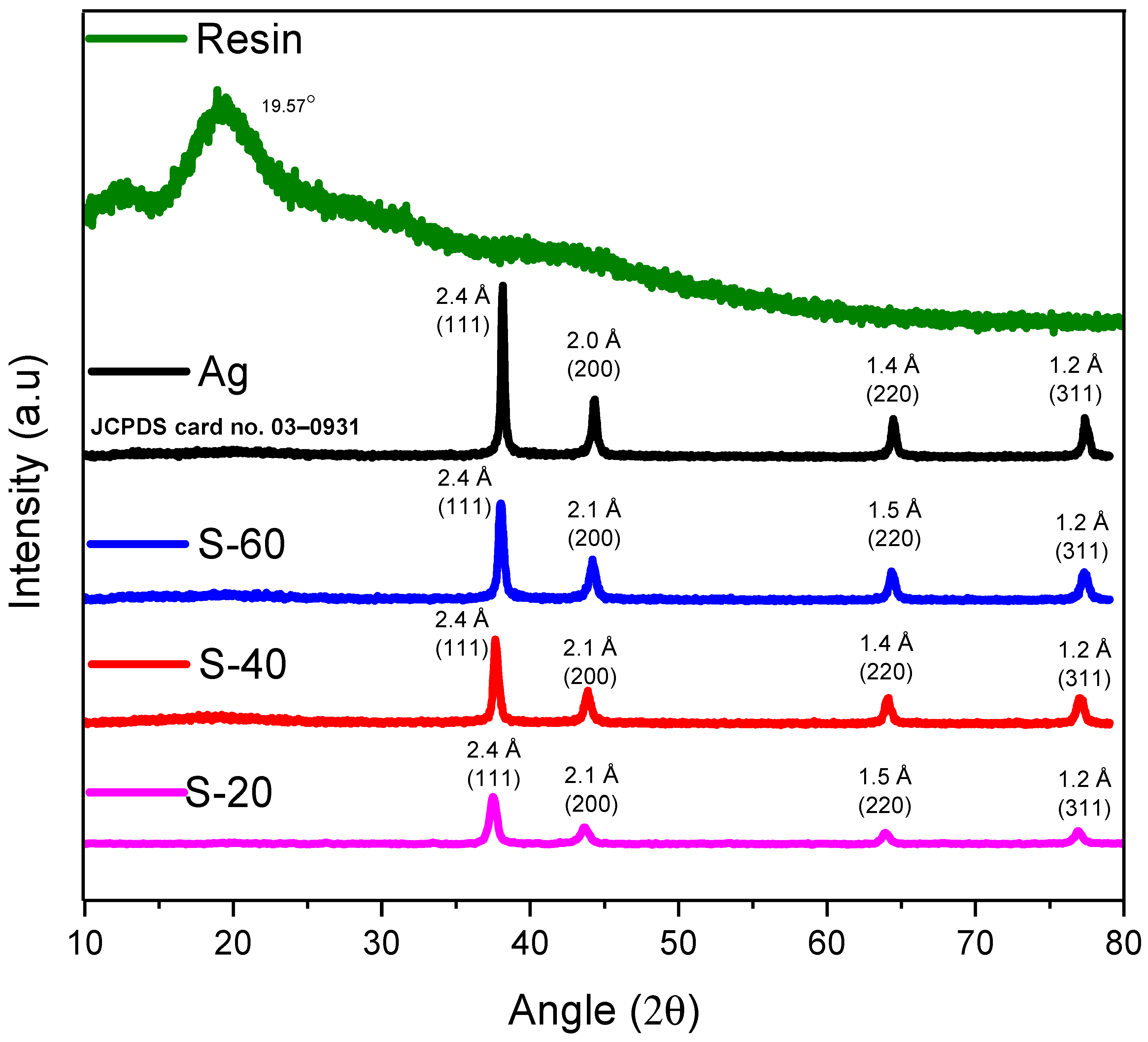
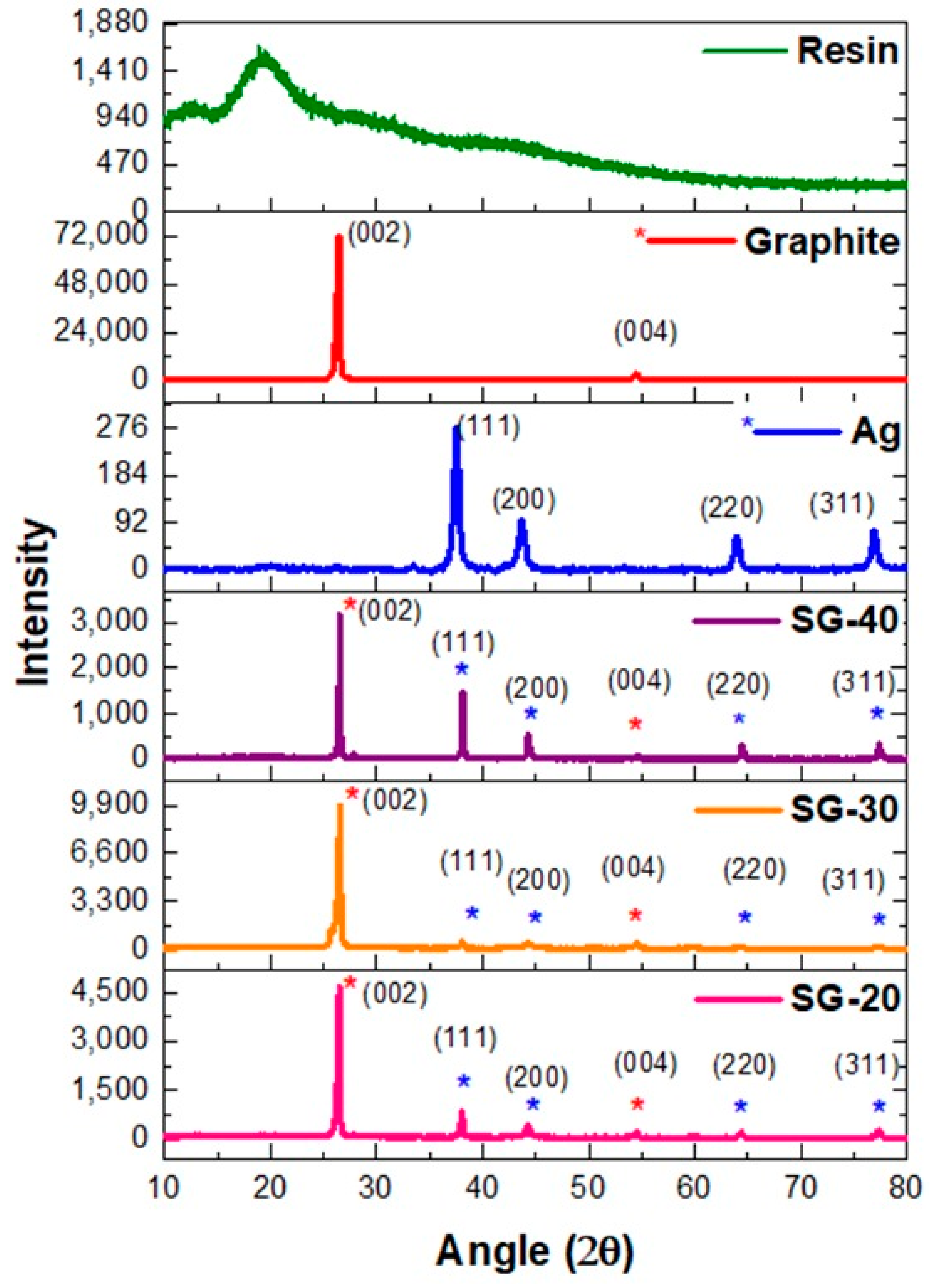
4.2. X-ray Diffractometry (XRD)
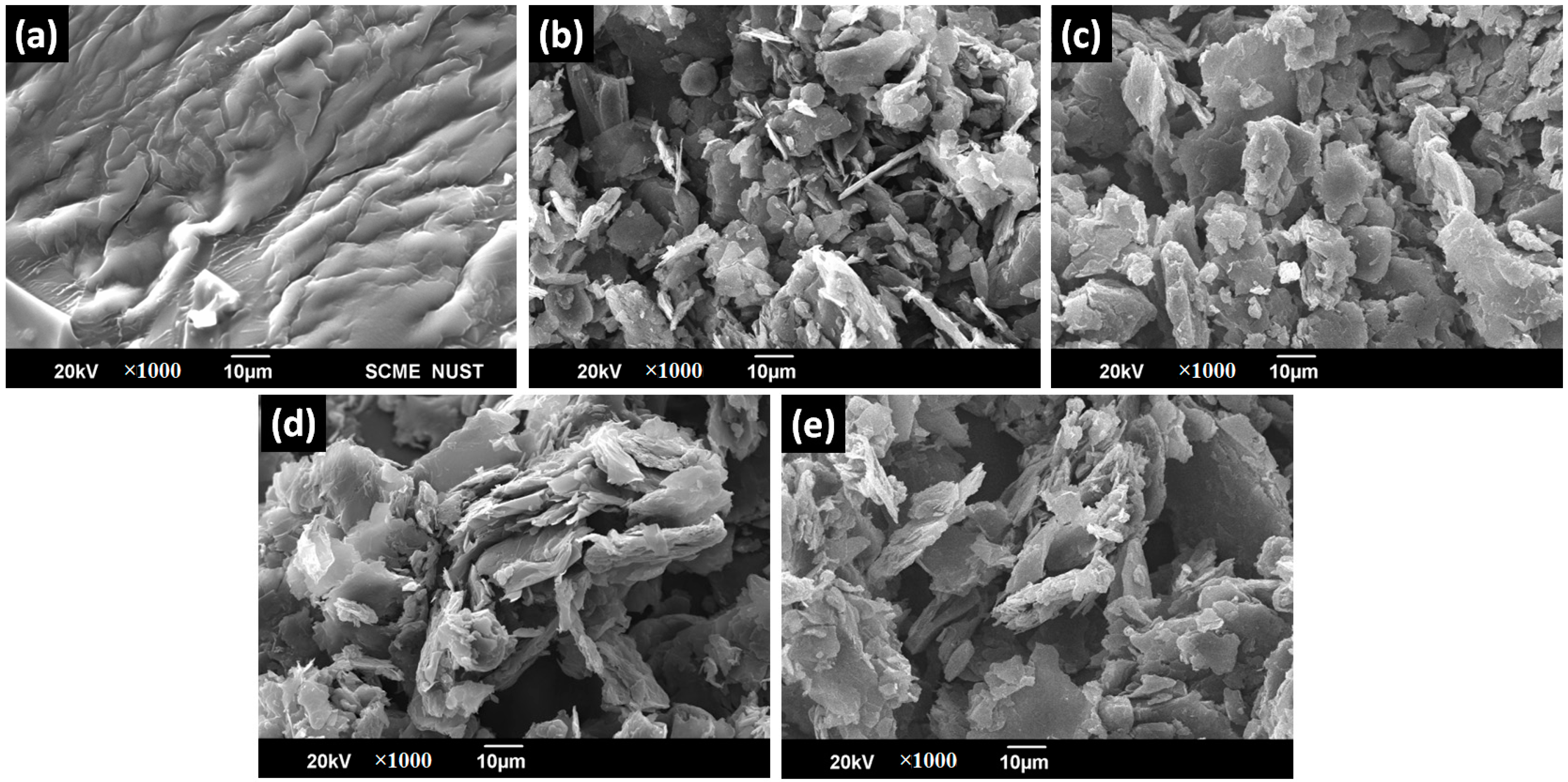
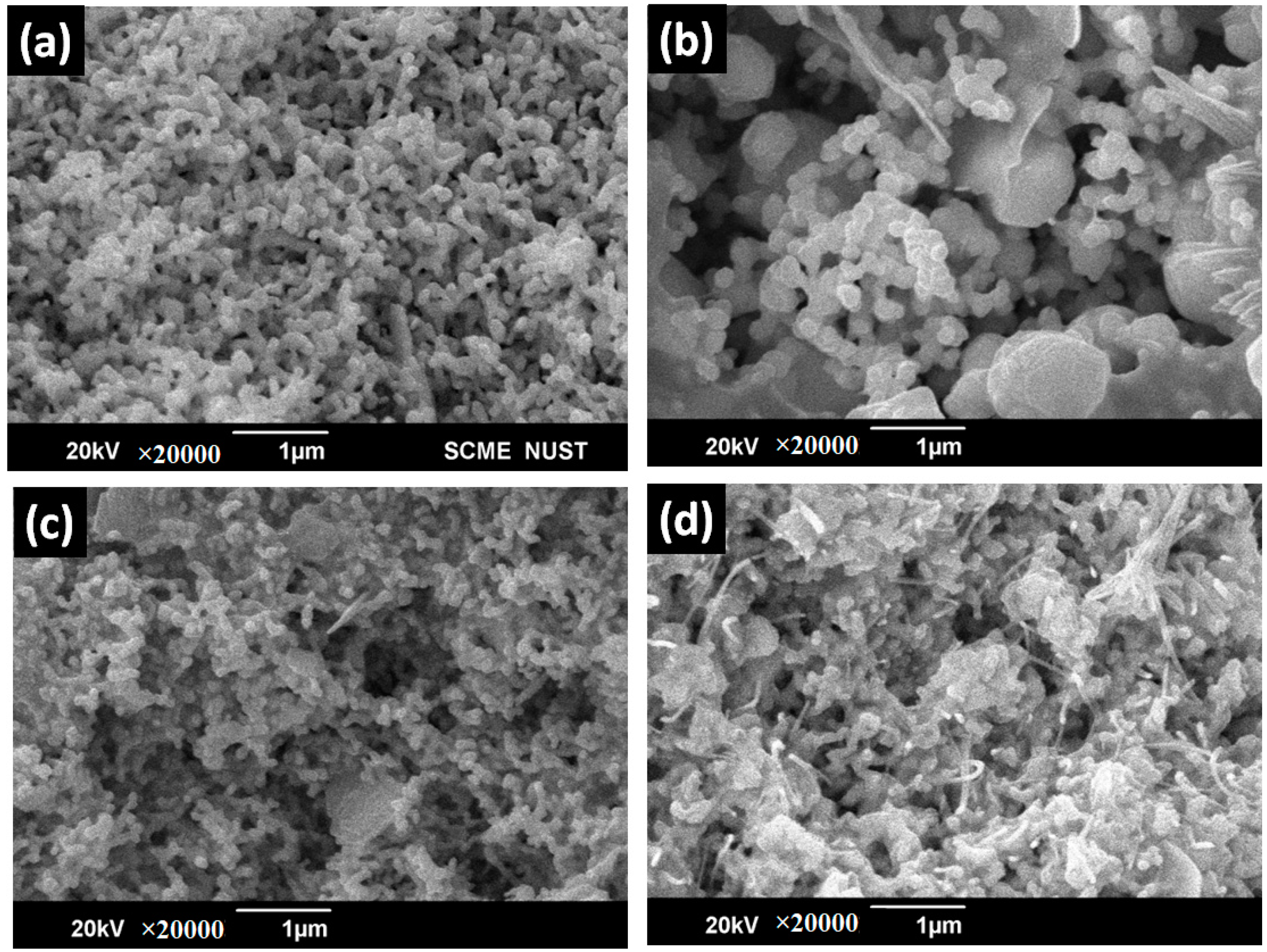
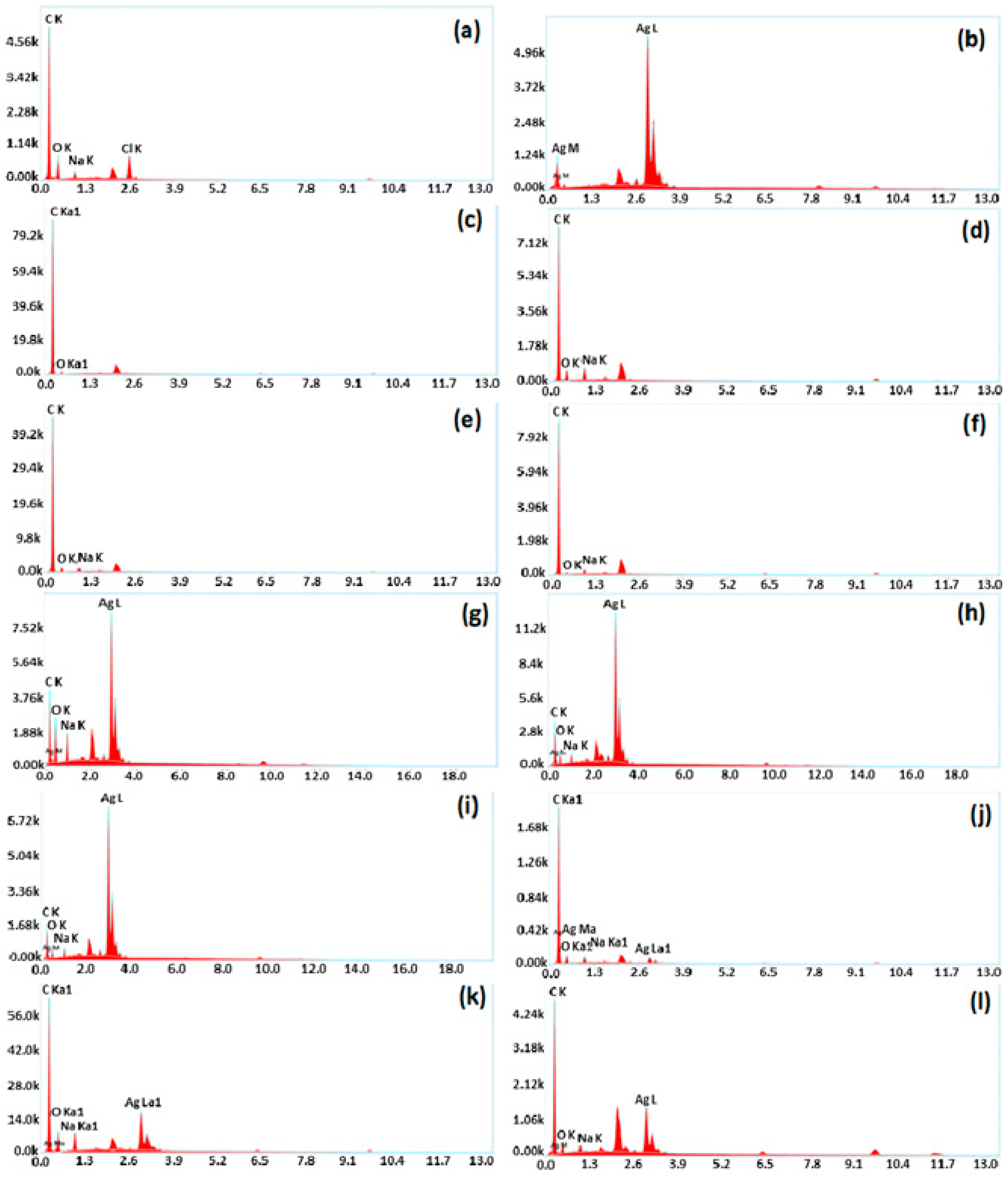
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
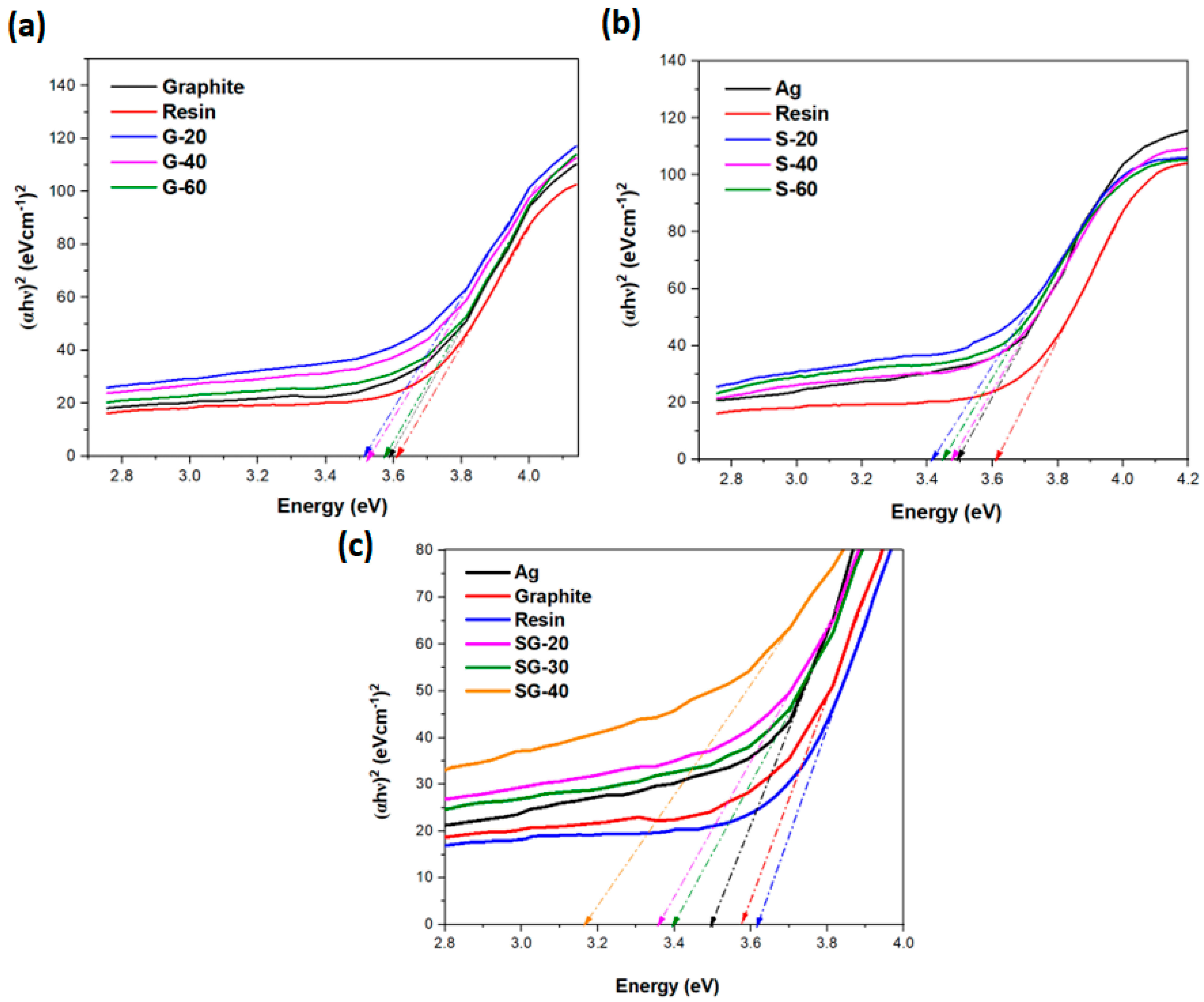
4.5. UV-DRS
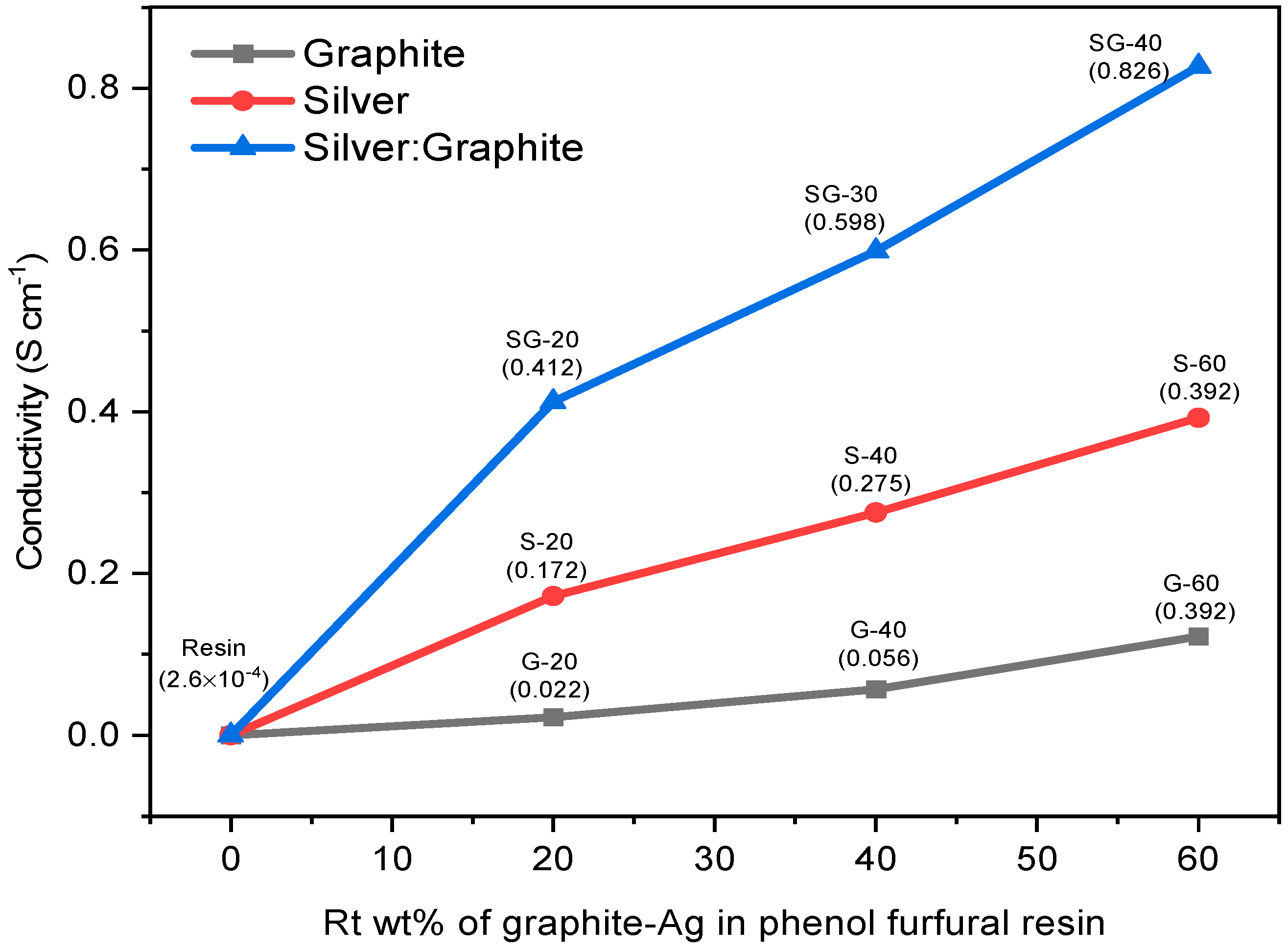
4.6. Four Probe Technique
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: Chemistry, catalysts, and engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, G.W.; Chheda, J.N.; Barrett, C.J.; Dumesic, J.A. Production of liquid alkanes by aqueous-phase processing of biomass-derived carbohydrates. Science 2005, 308, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tondi, G.; Schnabel, T. Bio-based polymers for engineered green materials. Polymers 2020, 12, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Heo, Y.-J.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J. Recent advances in organic thermoelectric materials: Principle mechanisms and emerging carbon-based green energy materials. Polymers 2019, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, T.; Wang, B.; Jia, Z.; Wu, H.; Lan, D.; Huang, Z.; Feng, A.; Ma, M.; Wu, G. A review of metal oxide-related microwave absorbing materials from the dimension and morphology perspective. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 10961–10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xu, B.; Ma, M.; Feng, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G. Electrostatic self-assembly synthesis of ZnFe2O4 quantum dots (ZnFe2O4@C) and electromagnetic microwave absorption. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 179, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.; Safronov, A.; Terzian, T.; Volodina, N.; Beketov, I.; Lezama, L.; Prieto, L.M. Fe45Ni55 magnetic nanoparticles obtained by electric explosion of wire for the development of functional composites. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2015, 6, 3800104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scordo, G.; Bertana, V.; Scaltrito, L.; Ferrero, S.; Cocuzza, M.; Marasso, S.L.; Romano, S.; Sesana, R.; Catania, F.; Pirri, C.F. A novel highly electrically conductive composite resin for stereolithography. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Boyd, G.; Strickland, R. Adhesive properties of furfural-modified phenol-formaldehyde resins as oriented strandboard binders. Holzforschung 1994, 48, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.H. Resin forming reactions of furfural and phenol. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 2673–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A.; Pasch, H.; Simon, C.; Rode, K. Structure of resorcinol, phenol, and furan resins by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and 13C NMR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A.; Orovan, E.; Cameron, F. The development of weather-and boil-proof phenol-resorcinol-furfural cold-setting adhesives. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 1984, 42, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-M.; Guo, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhang, K.; Yuen, M.M.; Fu, X.-Z.; Yu, S.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. One-step preparation of silver hexagonal microsheets as electrically conductive adhesive fillers for printed electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13685–13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vittoria, V.; Vertuccio, L.; Naddeo, C.; Russo, S.; De Vivo, B.; Lamberti, P.; Spinelli, G.; Tucci, V. Development of epoxy mixtures for application in aeronautics and aerospace. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15474–15488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, I.; Krupa, I. Electro-conductive resins filled with graphite for casting applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.E.; Moura, D.; Hilliou, L.; Krause, B.; Pötschke, P.; Figueiredo, H.; Alves, R.; Lepleux, E.; Pacheco, L.; Paiva, M.C. Mixed carbon nanomaterial/epoxy resin for electrically conductive adhesives. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Mustapha, M. Electrical conductivity of silver conductive ink synthesized using chemical reduction method. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2267, 020034. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-X.; Du, Z.-X.; Bai, R.-F. Crystal structure of aqua-bis (5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O) zinc (II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn. Z. Krist. New Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-X.; Du, Z.-X.; Wang, J.; Feng, X. Two mononuclear zinc (II) complexes constructed by two types of phenoxyacetic acid ligands: Syntheses, crystal structures and fluorescence properties. Z. Nat. B 2019, 74, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Ma, M.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, G. Fabrication of NiFe2O4@carbon fiber coated with phytic acid-doped polyaniline composite and its application as an electromagnetic wave absorber. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25932–25941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Du, Z.-X. A binuclear cadmium (II) cluster based on π⋯π stacking and halogen⋯halogen interactions: Synthesis, crystal analysis and fluorescent properties. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Du, Z.-X.; Feng, X. A new binuclear NiII complex with tetrafluorophthalate and 2, 2′-bipyridine ligands: Synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties. Z. Nat. B 2019, 74, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suherman, H.; Mahyoedin, Y.; Septe, E.; Rizade, R. Properties of graphite/epoxy composites: The in-plane conductivity, tensile strength and Shore hardness. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2019, 6, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakate, S.; Mathur, R.; Kakati, B.; Dhami, T.L. Properties of graphite-composite bipolar plate prepared by compression molding technique for PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 4537–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Itkis, M.E.; Bekyarova, E.; Haddon, R.C. Effect of single-walled carbon nanotube purity on the thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 133102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, L. Design and Synthesis of Functional Silane-Based Silicone Resin and Application in Low-Temperature Curing Silver Conductive Inks. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, G.; Lin, T.; He, P. The mixture of silver nanowires and nanosilver-coated copper micronflakes for electrically conductive adhesives to achieve high electrical conductivity with low percolation threshold. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Hou, T.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, G. Preparation and characterization of epoxy resin filled with Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets with excellent electric conductivity. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Qi, X.; Yang, M.; Cao, Y.; Lin, T.; He, P.; Paik, K.-W. A study on the resistivity and mechanical properties of modified nano-Ag coated Cu particles in electrically conductive adhesives. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 9171–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, R.A.; Khare, N.G.; Cole, D.P.; Karna, S.P.; Srivastava, A.K. Green synthesis of a silver nanoparticle–graphene oxide composite and its application for As (III) detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14432–14440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.Z.; Mahmood, A.; Hussain Shah, S.T. Phenol-Furfural Resin/Montmorillonite Based High-Pressure Green Composite from Renewable Feedstock (Saccharum munja) with Improved Thermo-Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawy, H.R.; Nada, A.A.; Baraka, A.; Elsayed, M.A. Novel synthesis of bimetallic Ag-Cu nanocatalysts for rapid oxidative and reductive degradation of anionic and cationic dyes. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, B.; Bai, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and application of functionalized ionic liquids as solvent to corn stalk for phenolic resin modification. e-Polymers 2015, 15, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agasti, N.; Kaushik, N. One pot synthesis of crystalline silver nanoparticles. Am. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rew, Y.; Baranikumar, A.; Tamashausky, A.V.; El-Tawil, S.; Park, P. Electrical and mechanical properties of asphaltic composites containing carbon based fillers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, D.; Kenny, J.; Manfredi, L.; Vázquez, A. Influence of the chemical composition on the thermal degradation and fire resistance of resol type phenolic resins. Mater. Eng. 2001, 12, 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- George, P.; Chowdhury, P. Complex dielectric transformation of UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra for estimating optical band-gap energies and materials classification. Analyst 2019, 144, 3005–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Kumar, R.; Goutam, S.; Sagar, S.S. Sunlight irradiation induced synthesis of silver nanoparticles using glycolipid bio-surfactant and exploring the antibacterial activity. J. Bioeng. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 6, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


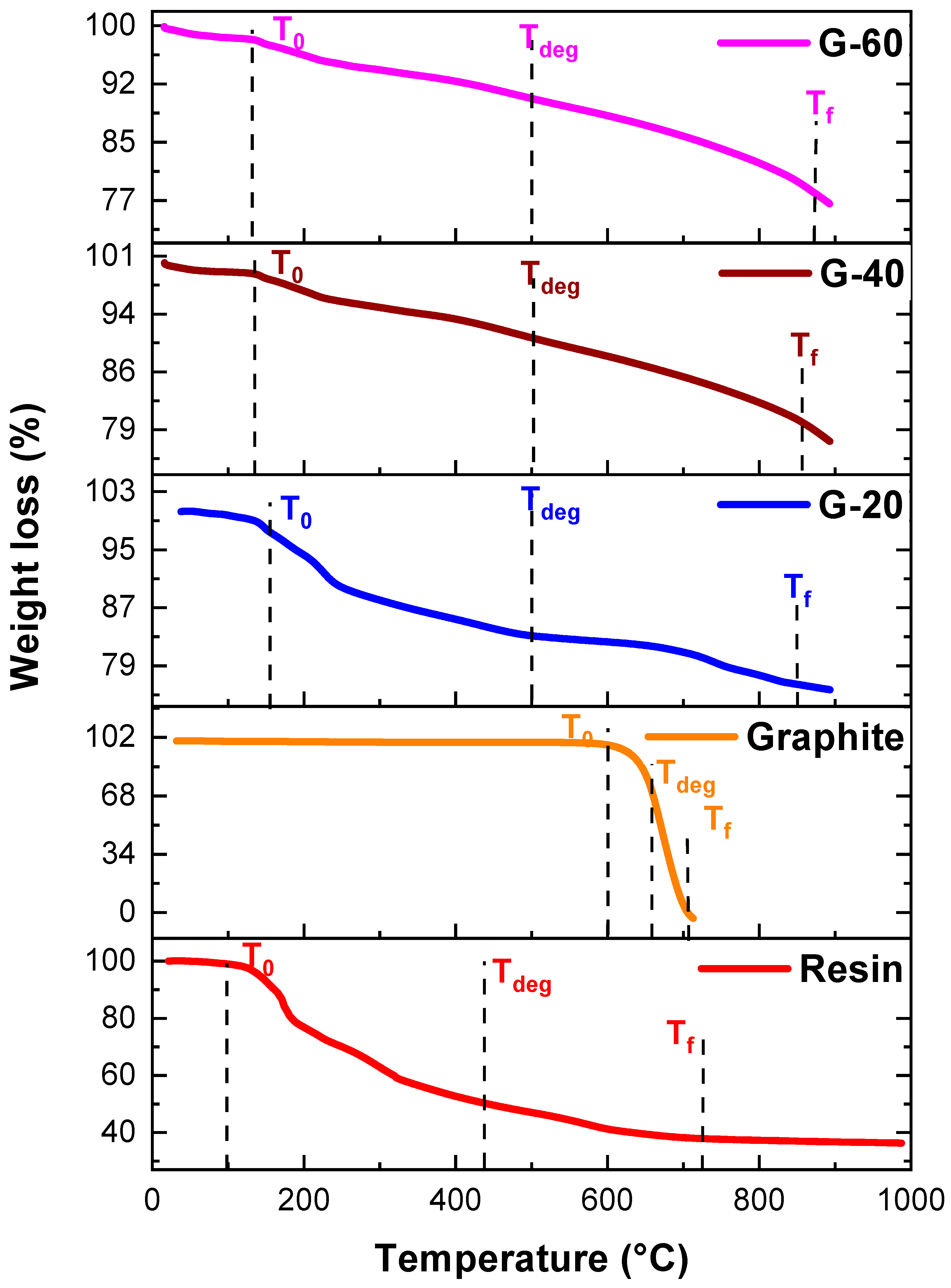
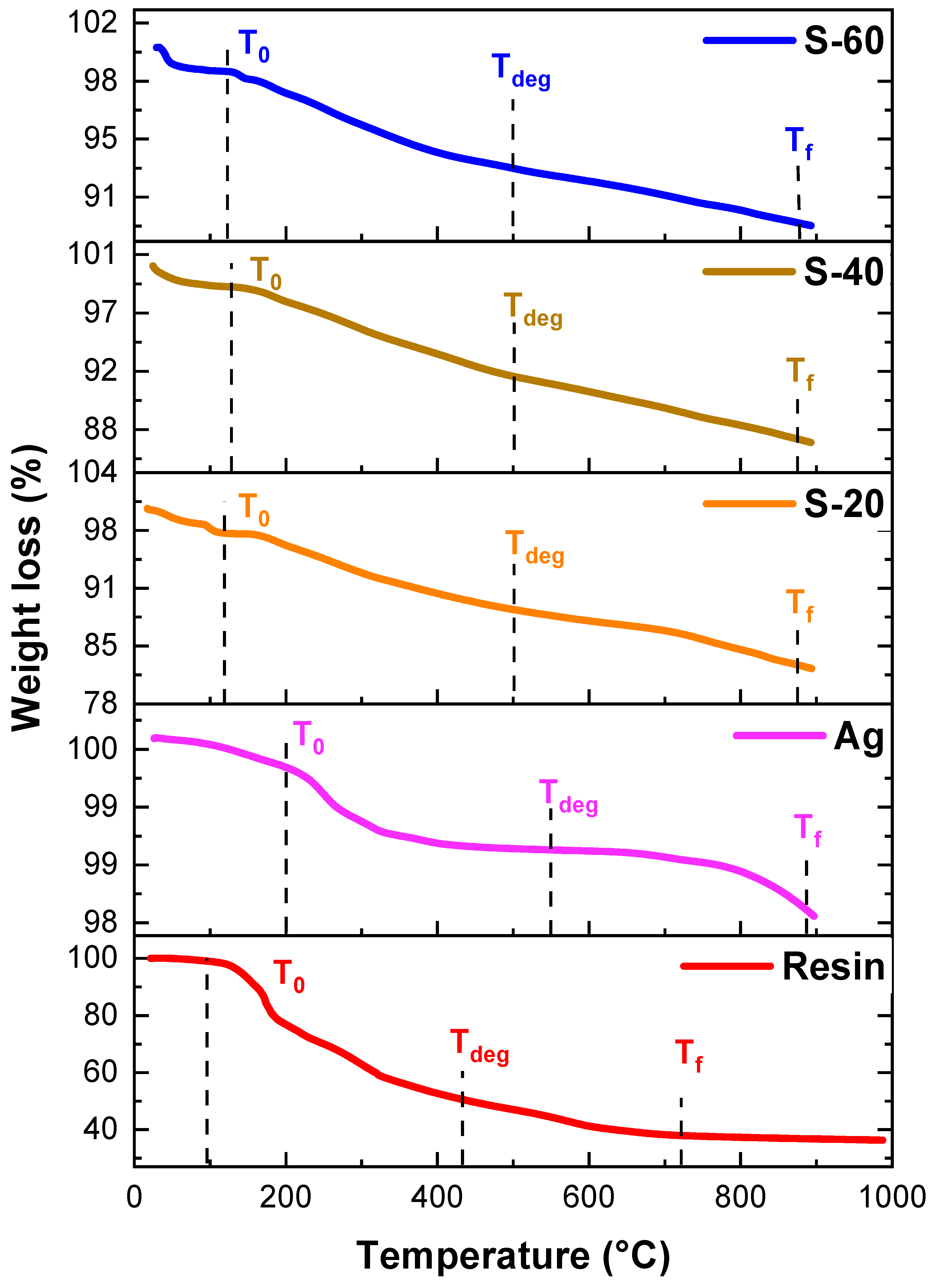
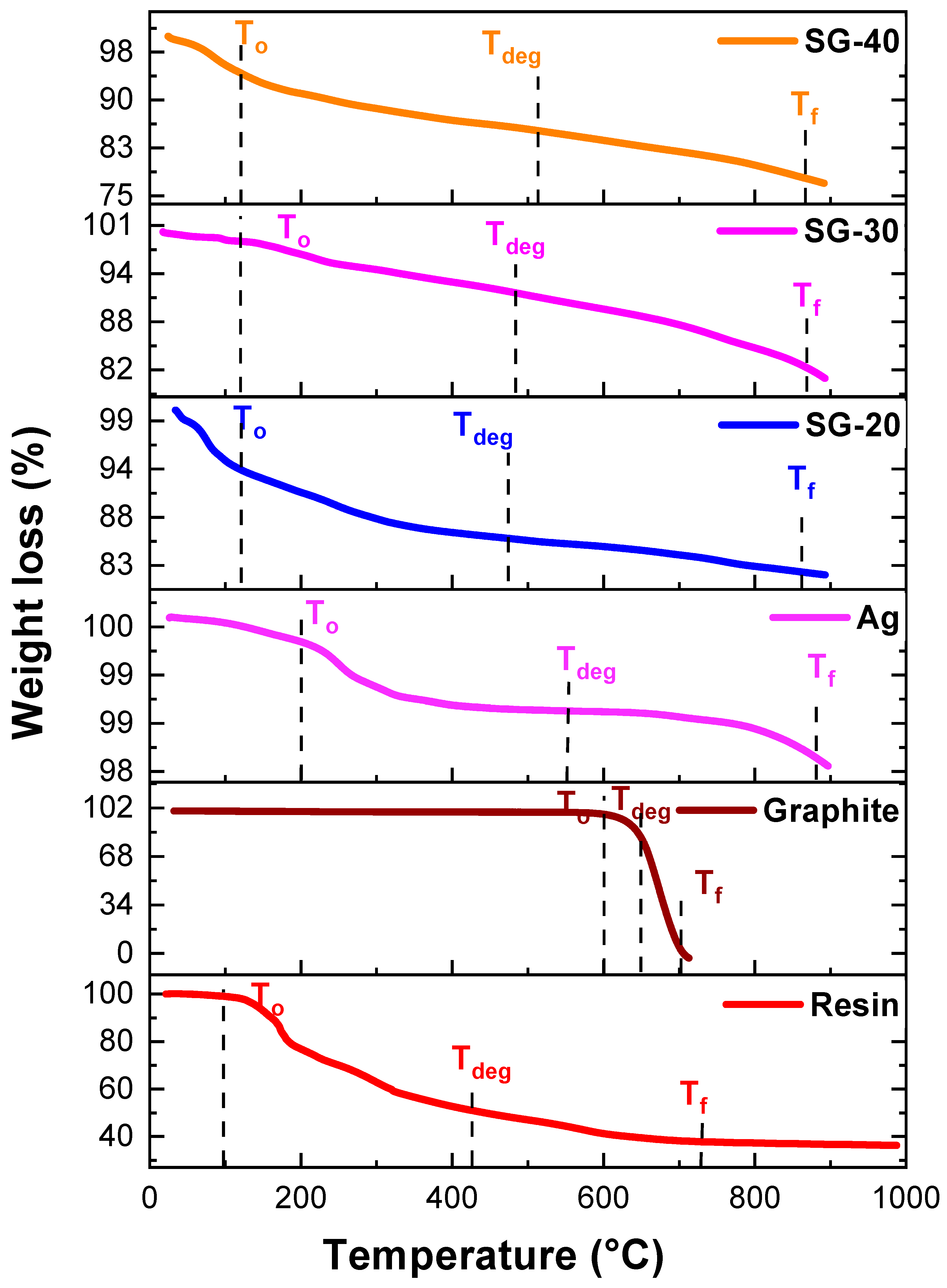
| Pure Resin and Nanocomposites | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | Tdeg | Tf | |
| Bagasse resin | 96 | 438 | 727 |
| Ag | 200 | 545 | 883 |
| Graphite | 600 | 658 | 705 |
| G-20 | 154 | 499 | 847 |
| G-40 | 133 | 500 | 855 |
| G-60 | 130 | 499 | 874 |
| S-20 | 117 | 499 | 874 |
| S-40 | 127 | 500 | 871 |
| S-60 | 122 | 500 | 876 |
| SG-20 | 120 | 474 | 860 |
| SG-30 | 120 | 484 | 866 |
| SG-40 | 120 | 512 | 865 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zehra, S.M.; Bibi, M.; Mahmood, A.; Khattak, A.; Asad, M.Z.; Zehra, S.H. Phenol–Furfural Resin/Graphite/Ag-Based Electrically Conductive Adhesive Composites from Waste Bagasse with Enhanced Thermo-Electric Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153283
Zehra SM, Bibi M, Mahmood A, Khattak A, Asad MZ, Zehra SH. Phenol–Furfural Resin/Graphite/Ag-Based Electrically Conductive Adhesive Composites from Waste Bagasse with Enhanced Thermo-Electric Properties. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153283
Chicago/Turabian StyleZehra, Syeda Mahnoor, Maryam Bibi, Azhar Mahmood, Abraiz Khattak, Muhammad Zeeshan Asad, and Syeda Hijab Zehra. 2023. "Phenol–Furfural Resin/Graphite/Ag-Based Electrically Conductive Adhesive Composites from Waste Bagasse with Enhanced Thermo-Electric Properties" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153283
APA StyleZehra, S. M., Bibi, M., Mahmood, A., Khattak, A., Asad, M. Z., & Zehra, S. H. (2023). Phenol–Furfural Resin/Graphite/Ag-Based Electrically Conductive Adhesive Composites from Waste Bagasse with Enhanced Thermo-Electric Properties. Polymers, 15(15), 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153283








