The Cellular Structure and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Nano-CaCO3/Ethylene-propylene-diene-monomer Composites Prepared by an In-Mold-Decoration/Microcellular-Injection-Molding Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
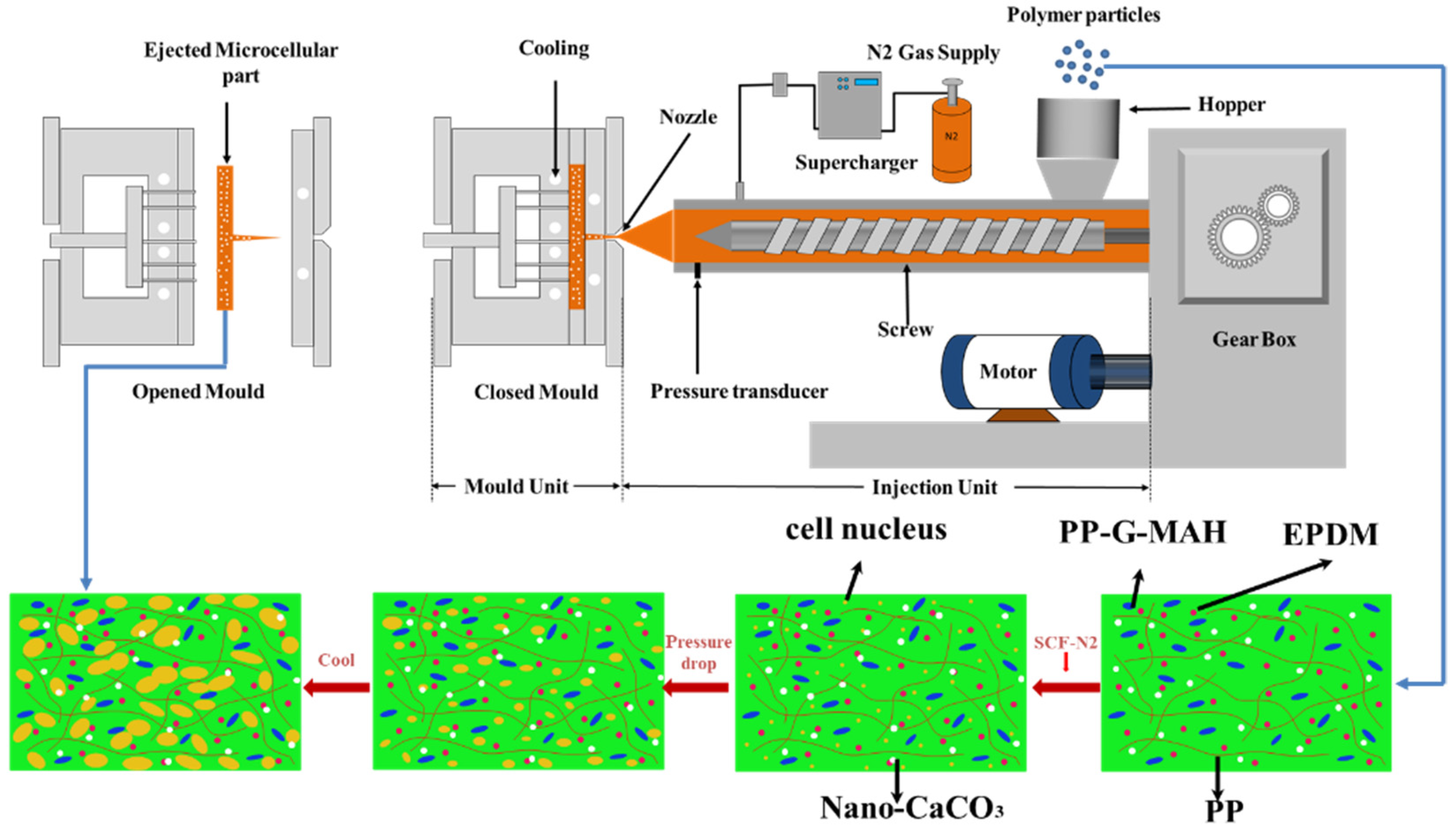
2.2. IMD/MIM Process
2.3. Material Characterization and Testing
2.3.1. Rheological Behavior
2.3.2. Crystallization Behavior
2.3.3. Microstructure
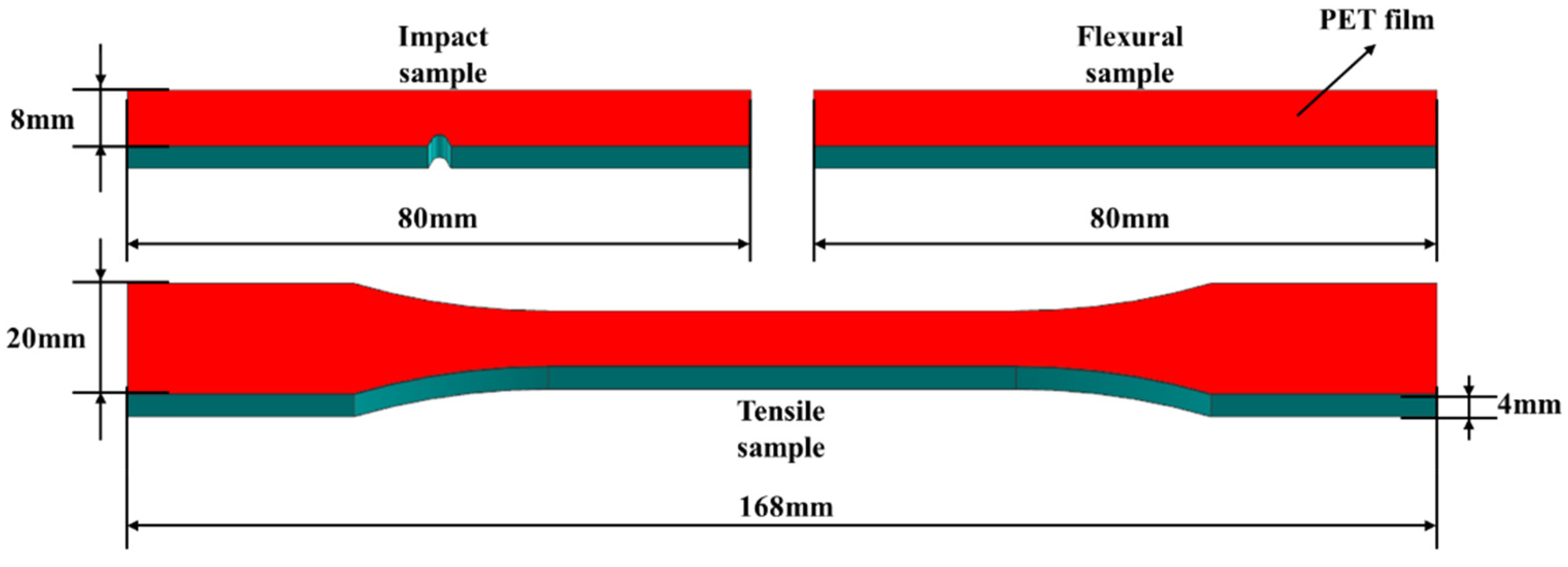
2.3.4. Mechanical Performance Test
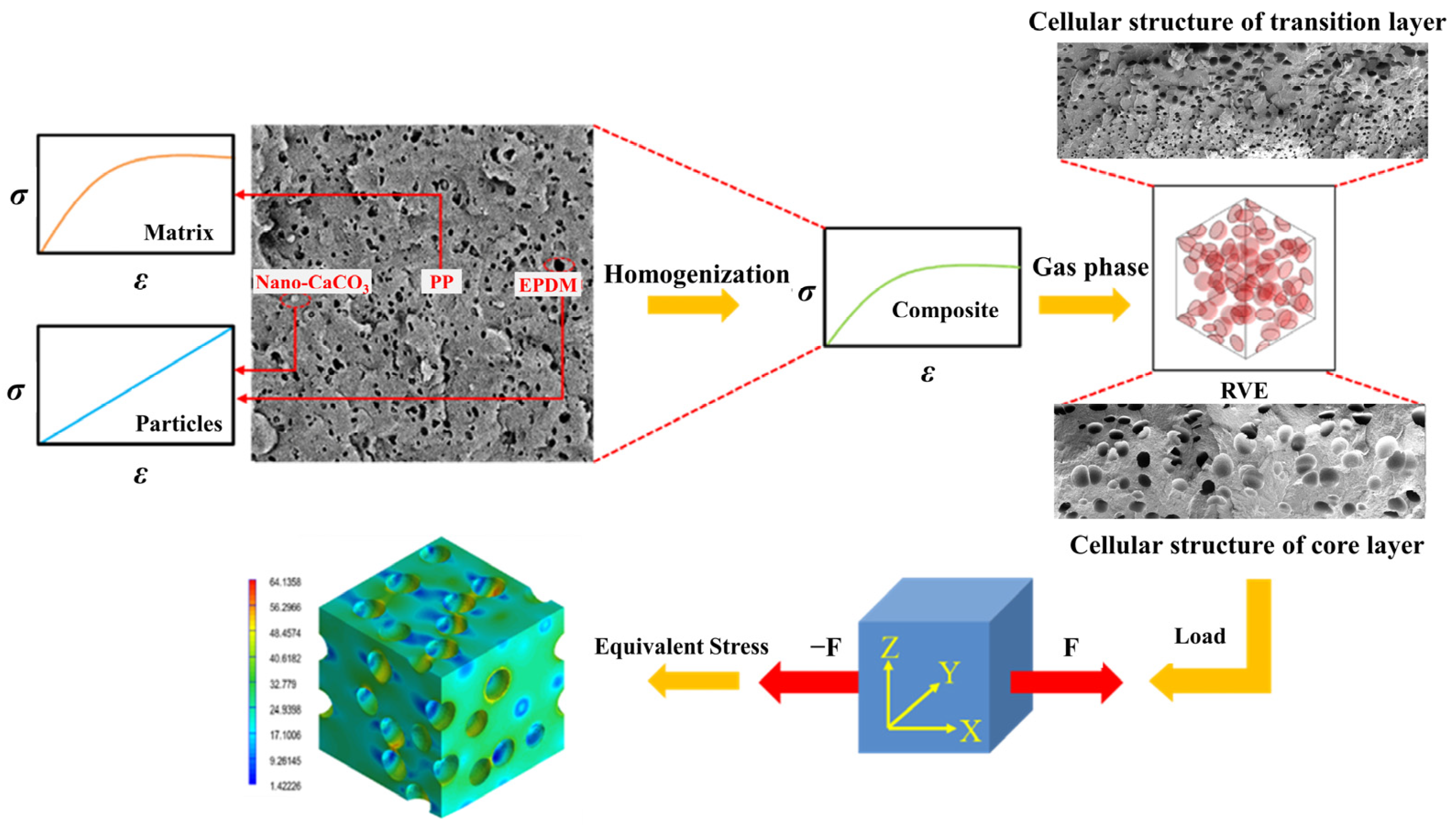
2.4. The Construction of RVE and Analysis Process
- (1)
- PP composites were considered to suit an elastic–plastic model, which meant that the curves of tensile stress and strain conformed to Hooke’s law.
- (2)
- The core-layer bubbles were spherical, and the transition-layer bubbles were ellipsoid.
- (3)
- The uniaxial peak strain ε11 = 0.03 was used for model loading.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Behavior
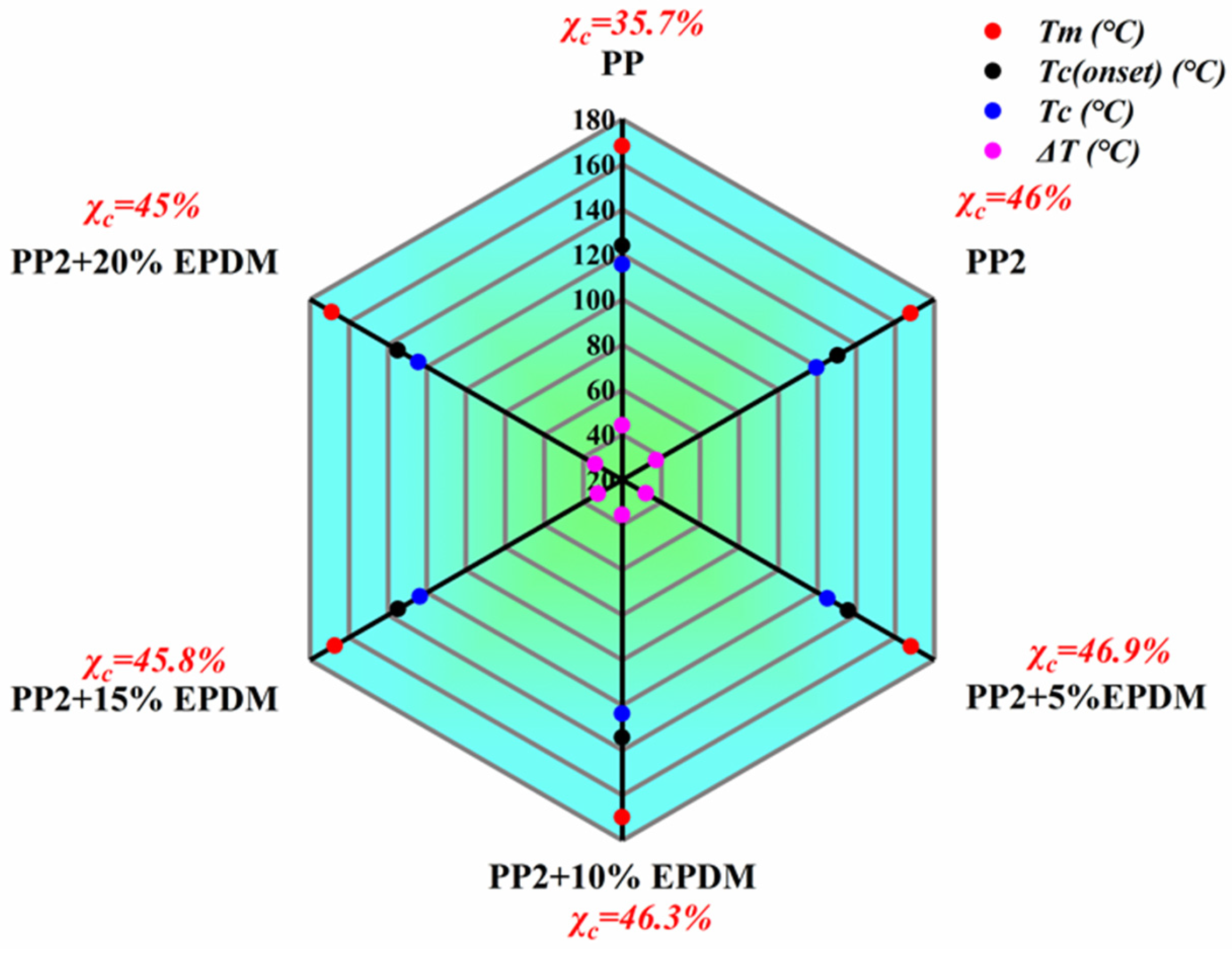
3.2. Thermal Analysis
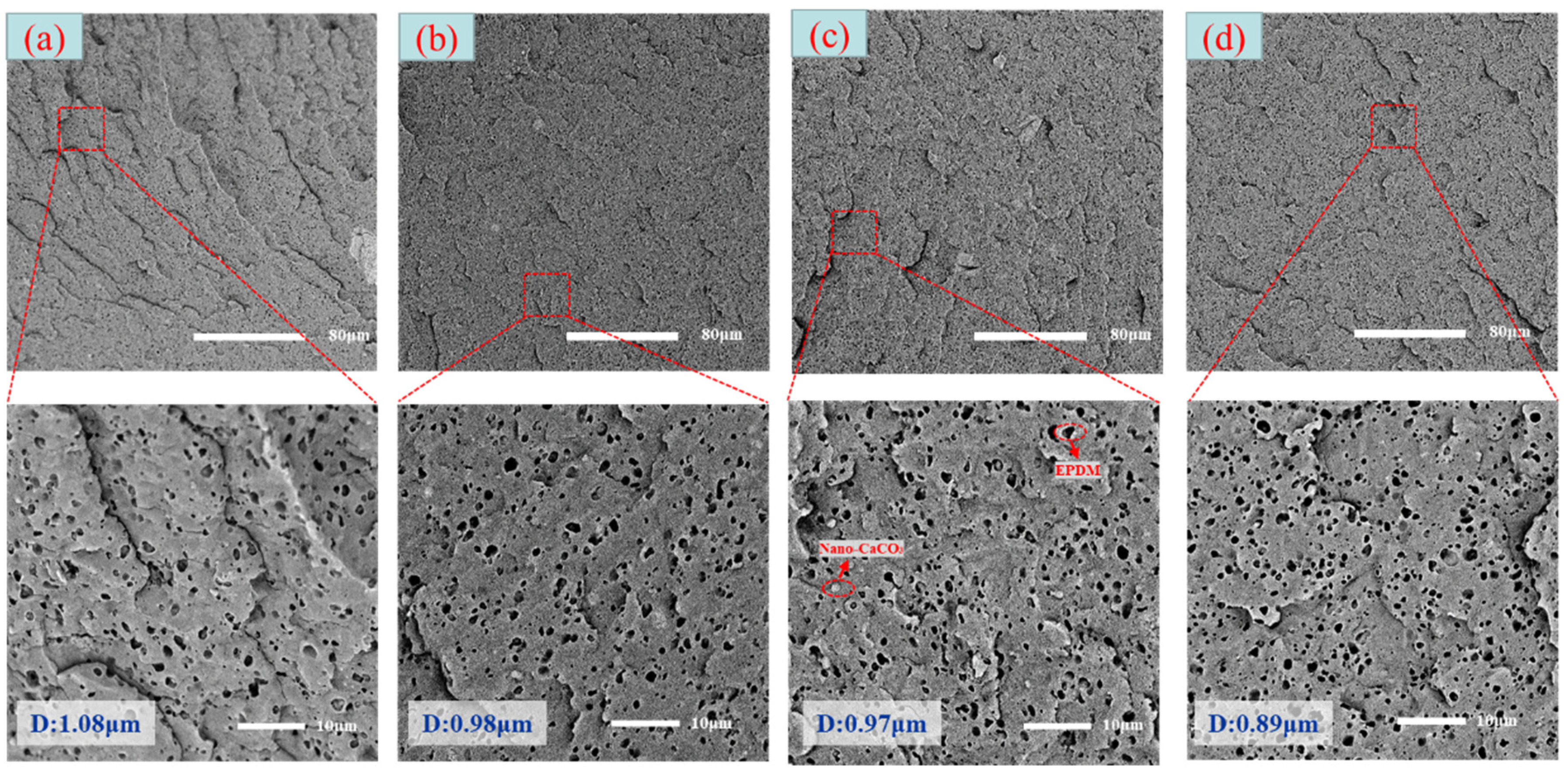
3.3. Distribution of Elastomer Particles
3.4. Microcellular Structure
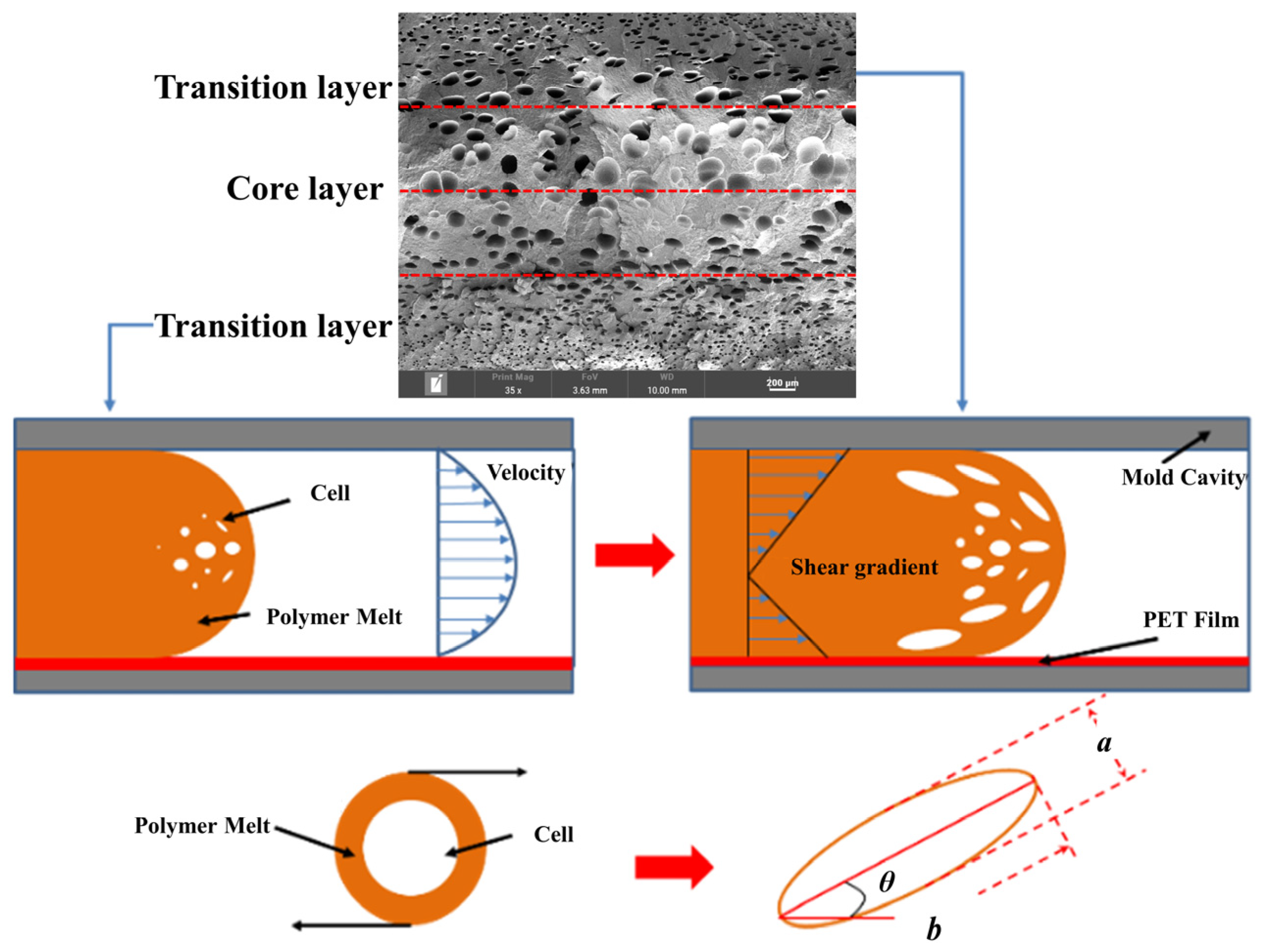
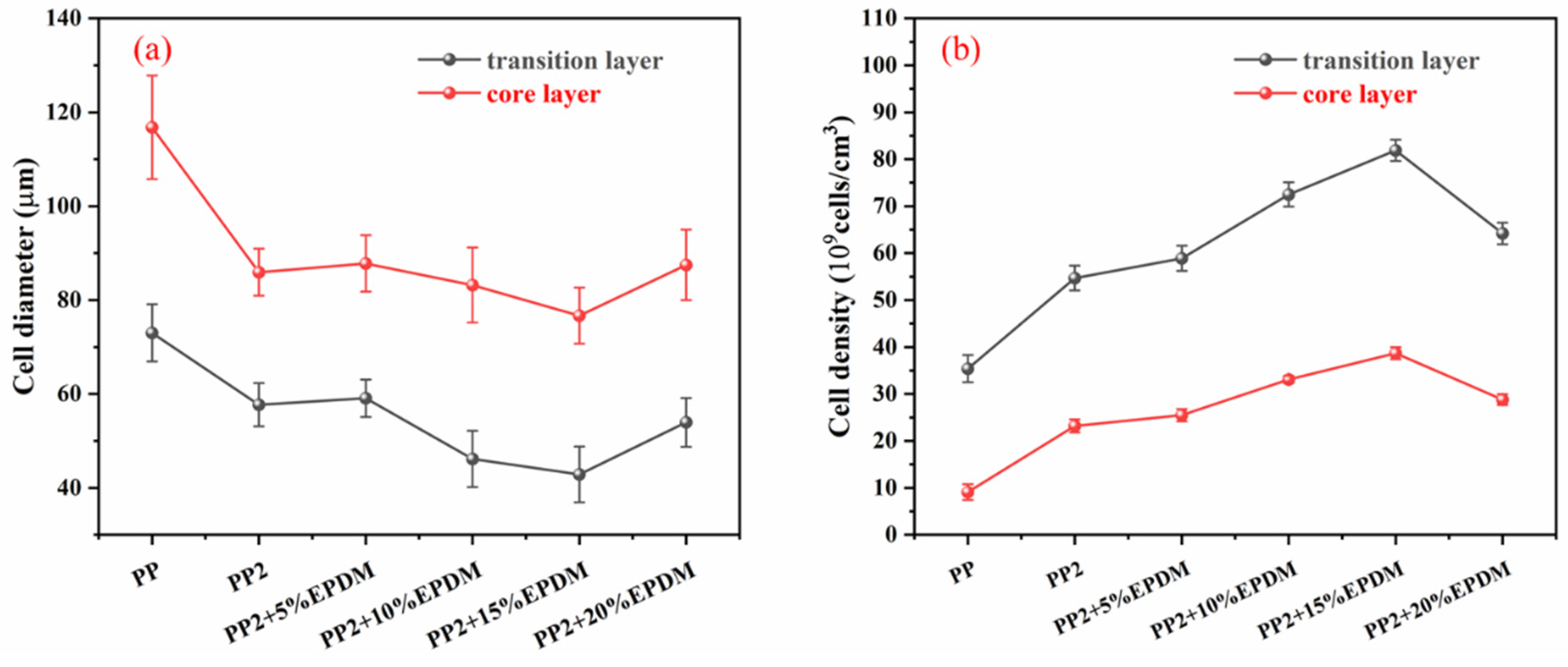
3.4.1. The Microcellular Structure Perpendicular to the Melt-Flow Direction
3.4.2. The Microcellular Structure Parallel to the Melt-Flow Direction
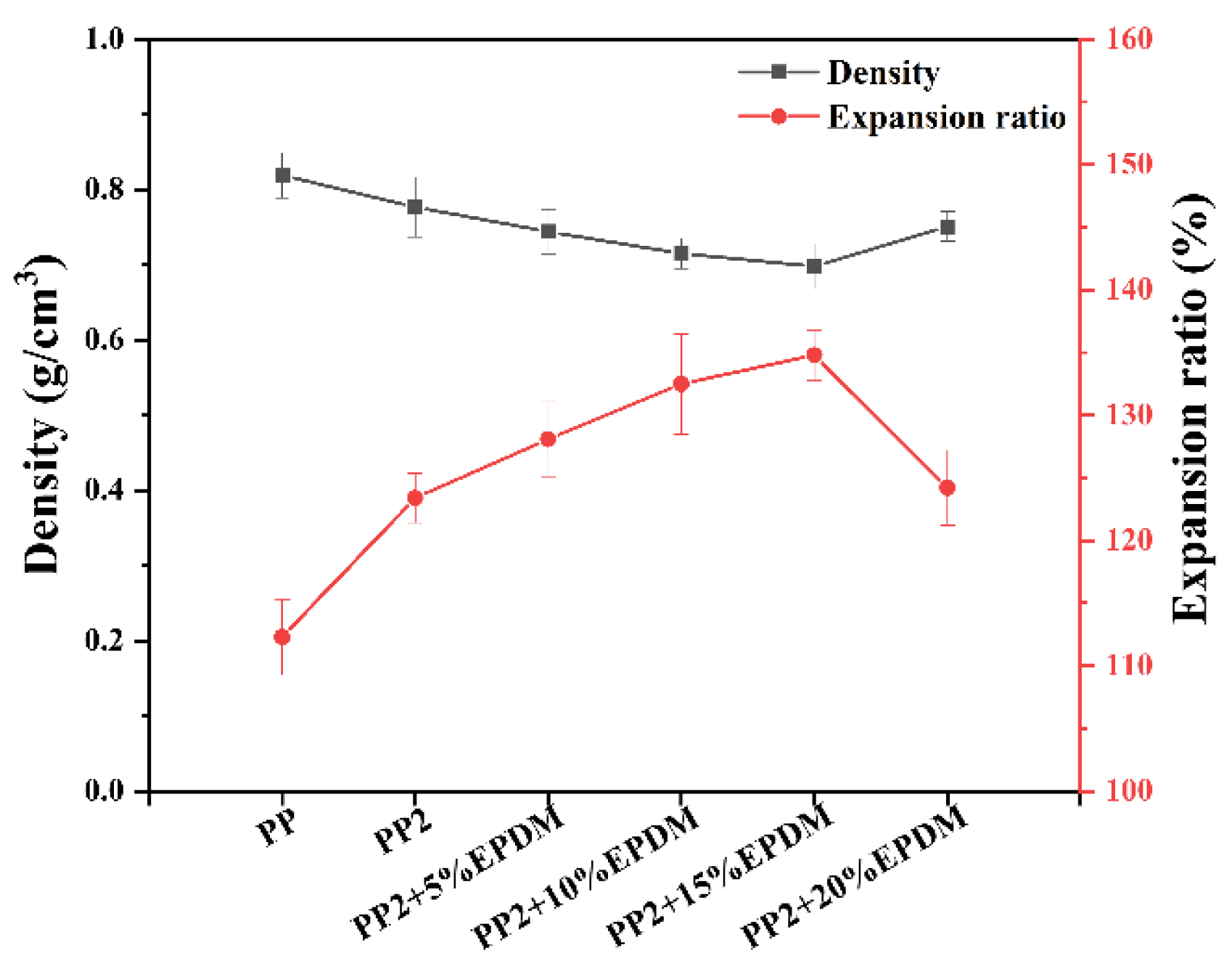
3.4.3. Density and Expansion Ratio
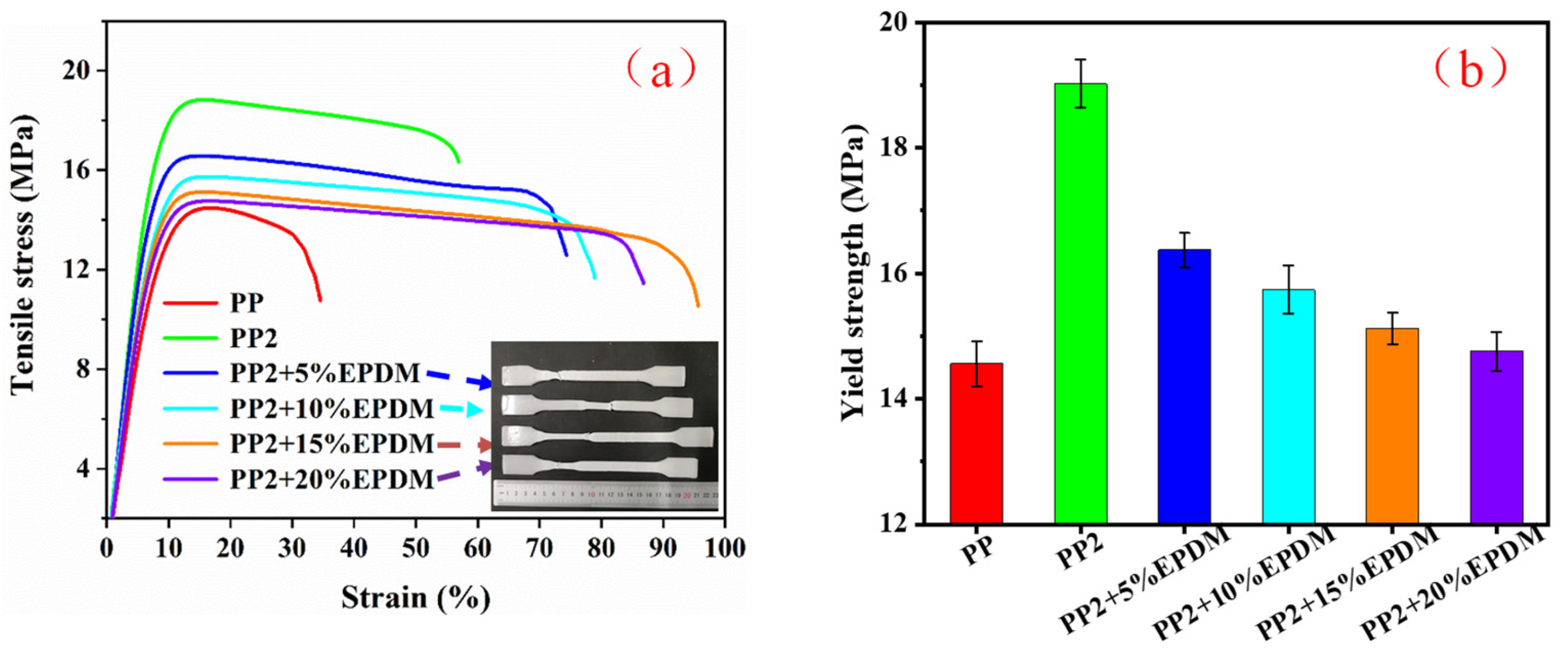
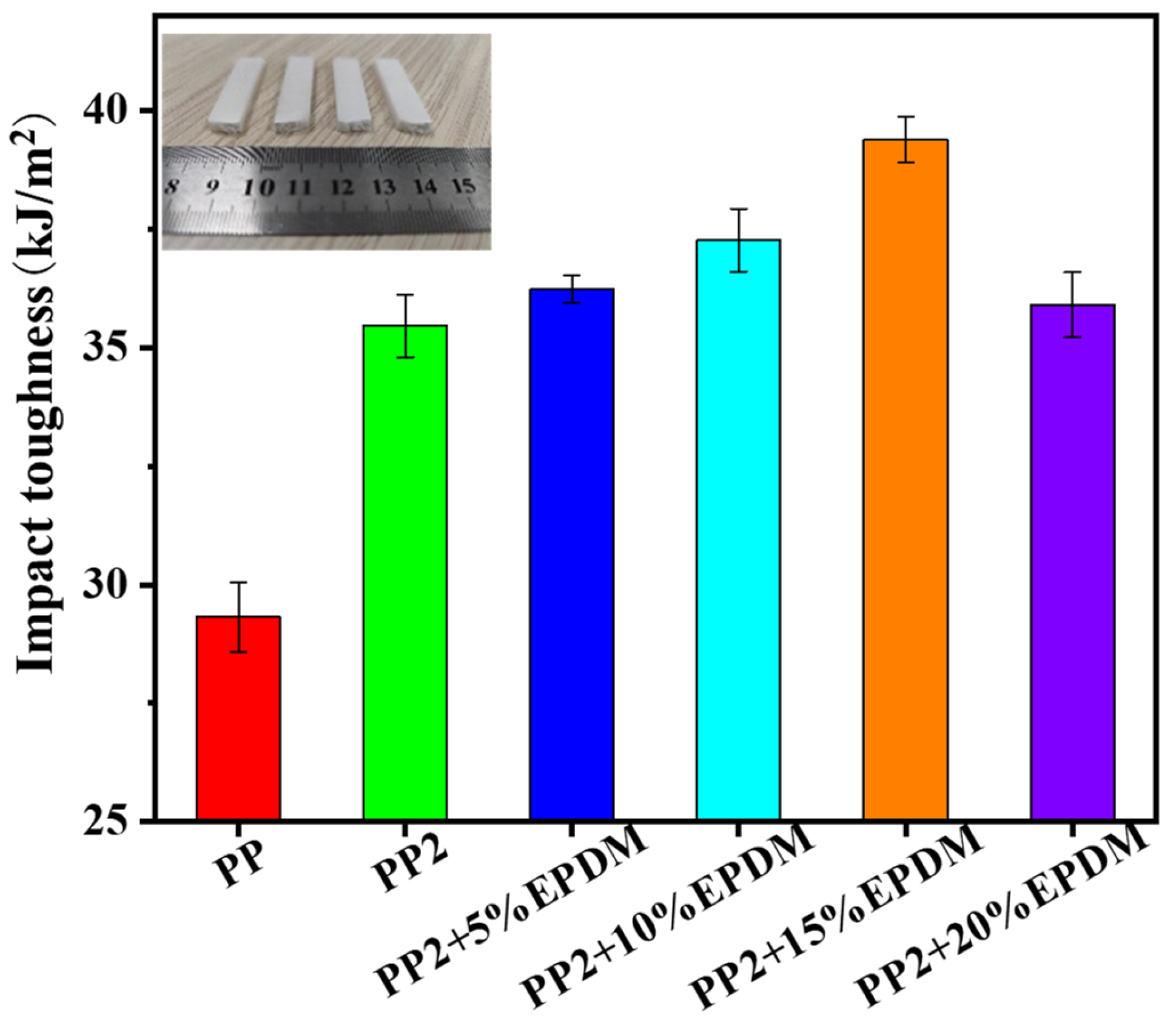
3.5. Mechanical Properties
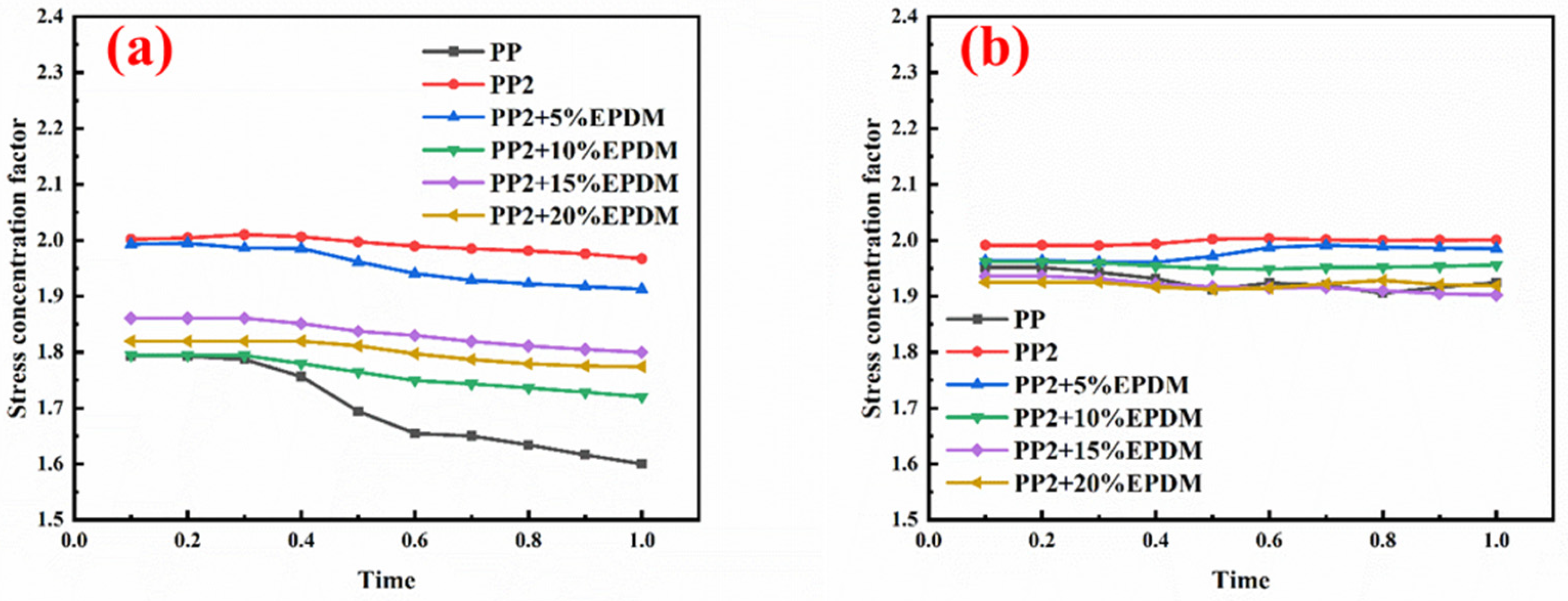
3.6. Multi-Scale Simulation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, V.; Suh, N.P. A process for making microcellular thermoplastic parts. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 30, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, C.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Gracia, I.; de Lucas, A.; Garcia, M.T. Reduction of the carbon footprint through polystyrene recycling: Economical evaluation. Process Saf. Environ. 2016, 101, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Dong, B.B.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, M.X.; Xiao, M.J. Injection-molded lightweight and high electrical conductivity composites with microcellular structure and hybrid fillers. Cell Polym. 2019, 38, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, B.; Wittmann, J.C.; Lovinger, A.J. Structure and morphology of poly(propylenes): A molecular analysis. Polymer 1996, 37, 4979–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xie, P.; Yang, H.; Dang, K.; Xu, Y.; Sain, M.; Yang, W. A review of thermoplastic polymer foams for functional applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 11579–11604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, A.; Mighri, F.; Ajji, A.; Rodrigue, D. Current issues and challenges in polypropylene foaming: A review. Cell. Polym. 2015, 34, 299–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J. Polypropylene: Structure, Blends and Composites—Composites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Chapter 3; pp. 50–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachtanapun, P.; Selke, S.; Matuana, L.M. Relationship between cell morphology and impact strength of microcellular foamed high-density polyethylene/polypropylene blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Pascual, S.; Saiz-Arroyo, C.; Vuluga, Z.; Corobea, M.C.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A. Foams with Enhanced Ductility and Impact Behavior Based on Polypropylene Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.J.; He, B.; Guo, W.; Hua, L.; Yang, Q. Effects of Nano-CaCO3 Content on the Crystallization, Mechanical Properties, and Cell Structure of PP Nanocomposites in Microcellular Injection Molding. Polymers 2018, 10, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.X.; Wang, J.K. Improving polypropylene microcellular foaming through blending and the addition of nano-calcium carbonate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 106, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hikima, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Ohshima, M. Fabrication of lightweight microcellular foams in injection-molded polypropylene using the synergy of long-chain branches and crystal nucleating agents. Polymer 2017, 128, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Zhao, G.Q.; Dong, G.W.; Mu, Y.; Park, C.B. Lightweight and strong microcellular injection molded PP/talc nanocomposite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, H. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) modifier to develop bimodal cell structure in polypropylene/TPUmicrocellular foam in presence of supercritical CO2. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2020, 27, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanporean, C.G.; Vuluga, Z.; Radovici, C.; Panaitescu, D.M.; Iorga, M.; Christiansen, J.D.; Mosca, A. Polypropylene/organoclay/SEBS nanocomposites with toughness-stiffness properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6573–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharsia, R.; Gupta, N.; Jerro, H.D. Investigation of flexural strength properties of rubber and nanoclay reinforced hybrid syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 417, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayah, I.N.; Mariatti, M.; Ismail, H.; Kamarol, M. Evaluation of PP/EPDM nanocomposites filled with SiO2, TiO2 and ZnO nanofillers as thermoplastic elastomeric insulators. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2015, 44, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Gu, J.; Le, C.; Ding, Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, P. Preparation and Properties of Microcellular PP/EPDM/Talc Composite Materials. Plastics 2014, 43, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoreishy, M.H.R.; Naderi, G.; Pahlavan, M. An investigation into the thermal transport properties of PP/EPDM/clay nanocomposites using a new combined experimental/numerical method. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2016, 45, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknall, C.B.; Clayton, D.; Keast, W.E. Rubber-toughening of plastics: Part 2 Creep mechanisms in HIPS/PPO blends. J. Mater. Sci. 1972, 7, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y. Experimental and numerical study of the elastic properties of PMI foams. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2688–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus-Michalska, M. Prediction of Elastic Properties of Polyurethane-Infiltrated Carbon Foams. Mech. Control. 2012, 31, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Microcellular Injection Molding; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Li, H.; Guo, W.; Wu, M.; Zeng, F. Effect of olefin block copolymer on the toughness of microcellular polypropylene composite. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 9, 035301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, W.; Meng, Z.; Wei, W.; Hua, L.; Yang, Q. Effect of POE on mechanical properties and cellular structure of PP/Nano-CaCO3 composites in IMD/MIM process. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 095308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei, M.; Shaayegan, V.; Wang, C.; Costa, F.; Han, S.; Park, C.B.; Bussmann, M. Numerical analysis of the effect of the local variation of viscosity on bubble growth and deformation in polymer foaming. J. Rheol. 2019, 63, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoguz, Y.; Pesetskii, S.; Makarenko, O. Polyamide 6 and polyamide 66 blends with functionalized polyolefins: Effect of phenomenal increase in viscosity and melt strength of polyamide 66-based materials. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 3095–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Materials | Density (g/cm3) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 0.92 | 1350 | 0.4 |
| EPDM | 0.82 | 6 | 0.49 |
| nano-CaCO3 | 2.83 | 10,000 | 0.31 |
| Sets | The Core Layer | The Transition Layer |
|---|---|---|
| PP | 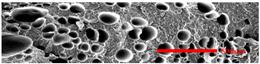 | 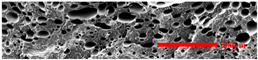 |
| PP2 | 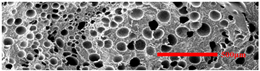 |  |
| PP2 + 5% EPDM |  |  |
| PP2 + 10% EPDM | 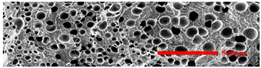 | 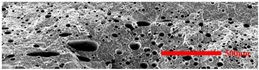 |
| PP2 + 15% EPDM | 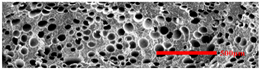 | 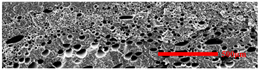 |
| PP2 + 20% EPDM | 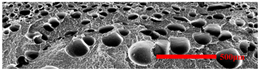 | 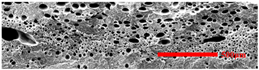 |
| Sets | The Core Layer | The Transition Layer |
|---|---|---|
| PP | 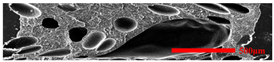 |  |
| PP2 | 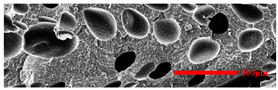 | 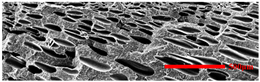 |
| PP2 + 5% EPDM |  |  |
| PP2 + 10% EPDM |  |  |
| PP2 + 15% EPDM |  | 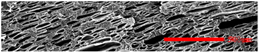 |
| PP2 + 20% EPDM | 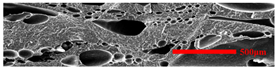 |  |
| Sets | The Core Layer | The Transition Layer |
|---|---|---|
| PP | 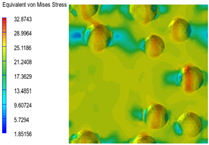 | 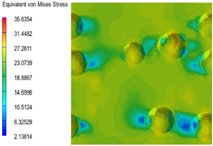 |
| PP2 | 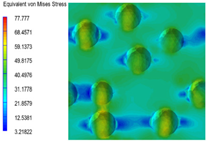 |  |
| PP2 + 5% EPDM | 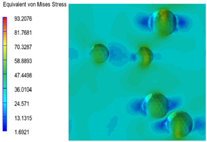 |  |
| PP2 + 10% EPDM |  |  |
| PP2 + 15% EPDM |  |  |
| PP2 + 20% EPDM | 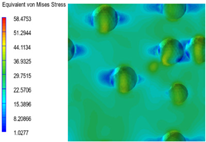 | 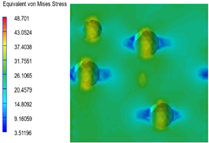 |
| Sets | The Core Layer | The Transition Layer |
|---|---|---|
| PP | 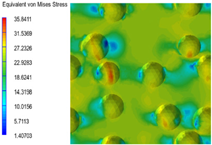 |  |
| PP2 | 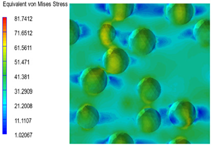 |  |
| PP2 + 5% EPDM | 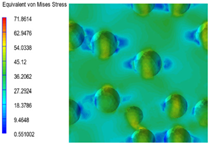 |  |
| PP2 + 10% EPDM | 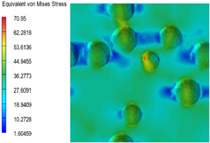 |  |
| PP2 + 15% EPDM |  | 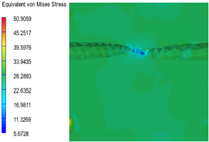 |
| PP2 + 20% EPDM |  | 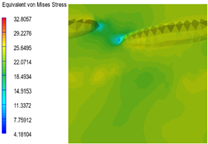 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Mao, H.; Guo, W. The Cellular Structure and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Nano-CaCO3/Ethylene-propylene-diene-monomer Composites Prepared by an In-Mold-Decoration/Microcellular-Injection-Molding Process. Polymers 2023, 15, 3604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173604
Zeng F, Liu X, Chen Y, Li H, Mao H, Guo W. The Cellular Structure and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Nano-CaCO3/Ethylene-propylene-diene-monomer Composites Prepared by an In-Mold-Decoration/Microcellular-Injection-Molding Process. Polymers. 2023; 15(17):3604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173604
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Fankun, Xiaorui Liu, Yingxian Chen, Hao Li, Huajie Mao, and Wei Guo. 2023. "The Cellular Structure and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Nano-CaCO3/Ethylene-propylene-diene-monomer Composites Prepared by an In-Mold-Decoration/Microcellular-Injection-Molding Process" Polymers 15, no. 17: 3604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173604
APA StyleZeng, F., Liu, X., Chen, Y., Li, H., Mao, H., & Guo, W. (2023). The Cellular Structure and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Nano-CaCO3/Ethylene-propylene-diene-monomer Composites Prepared by an In-Mold-Decoration/Microcellular-Injection-Molding Process. Polymers, 15(17), 3604. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173604






