Facile Synthesis of Catechol-Containing Polyacrylamide Copolymers: Synergistic Effects of Amine, Amide and Catechol Residues in Mussel-Inspired Adhesives
Abstract
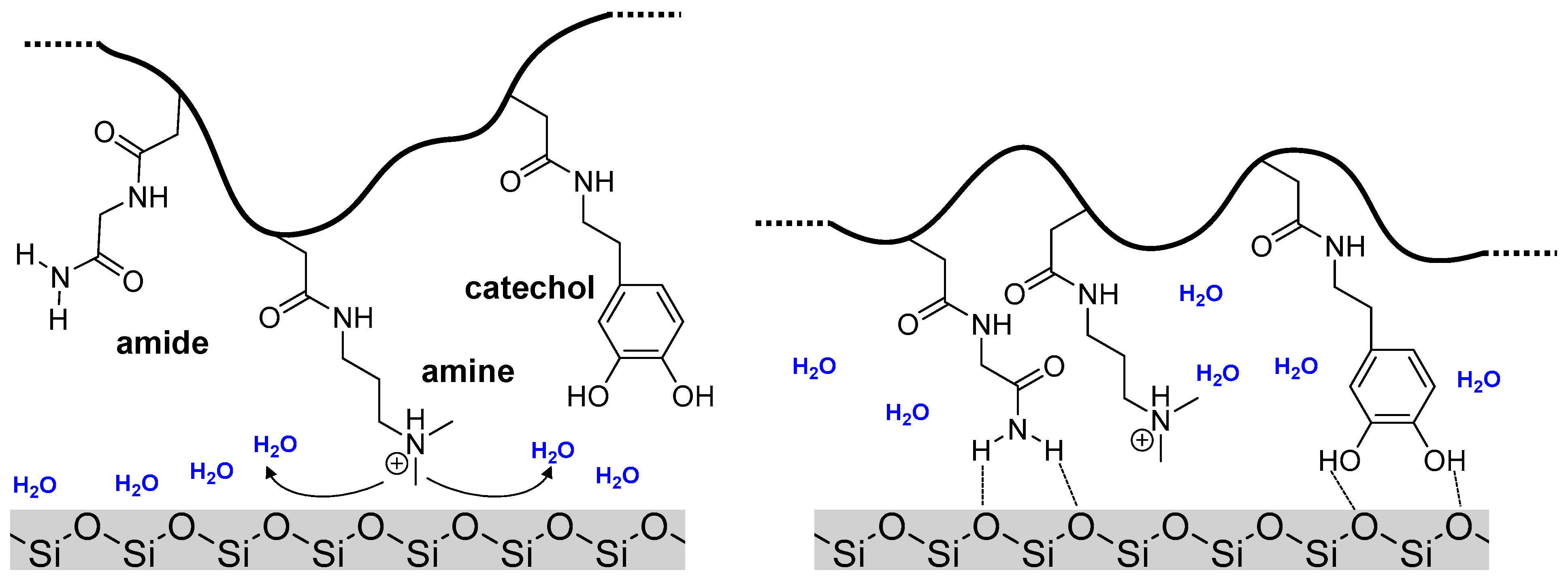
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 1H NMR
2.2. Size Exclusion Chromatography-Multi-Angle Light Scattering (H2O-SEC-MALS)
2.3. Dimethylacetamide-Size Exclusion Chromatography (DMAc-SEC)
2.4. Freeze-Drying
2.5. High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.6. Elllipsometry
2.7. Quartz Crystal Microbalance Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
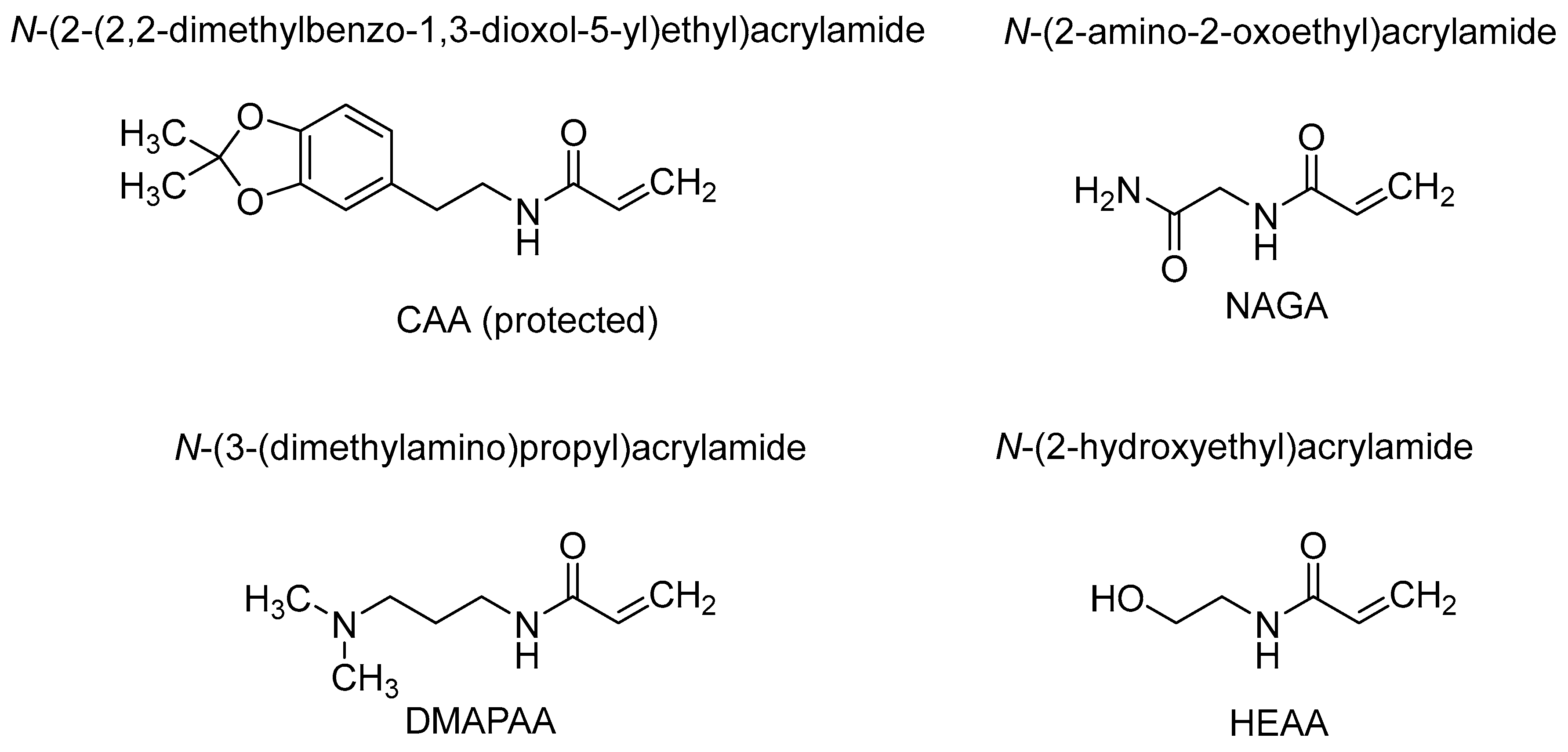
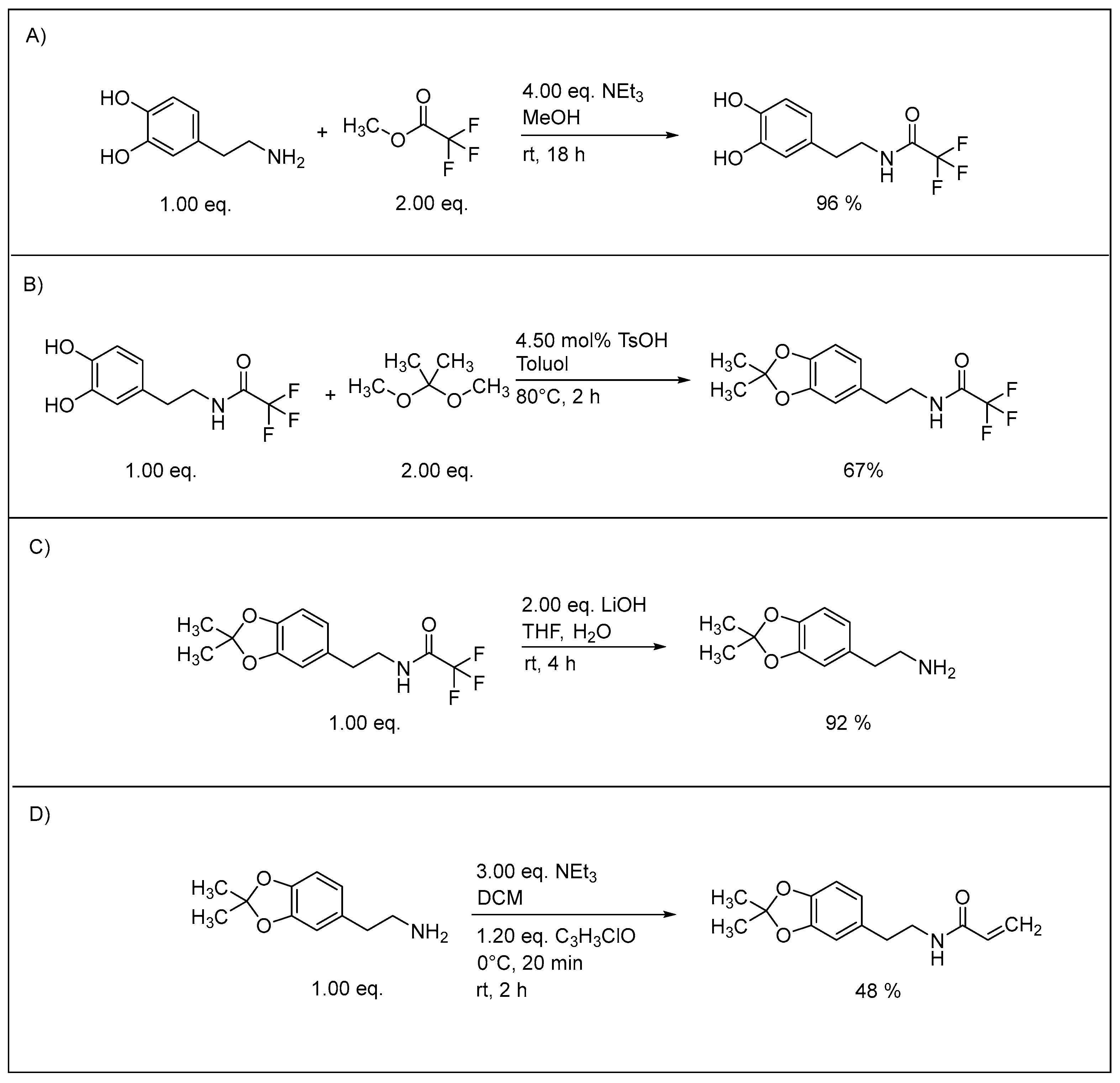
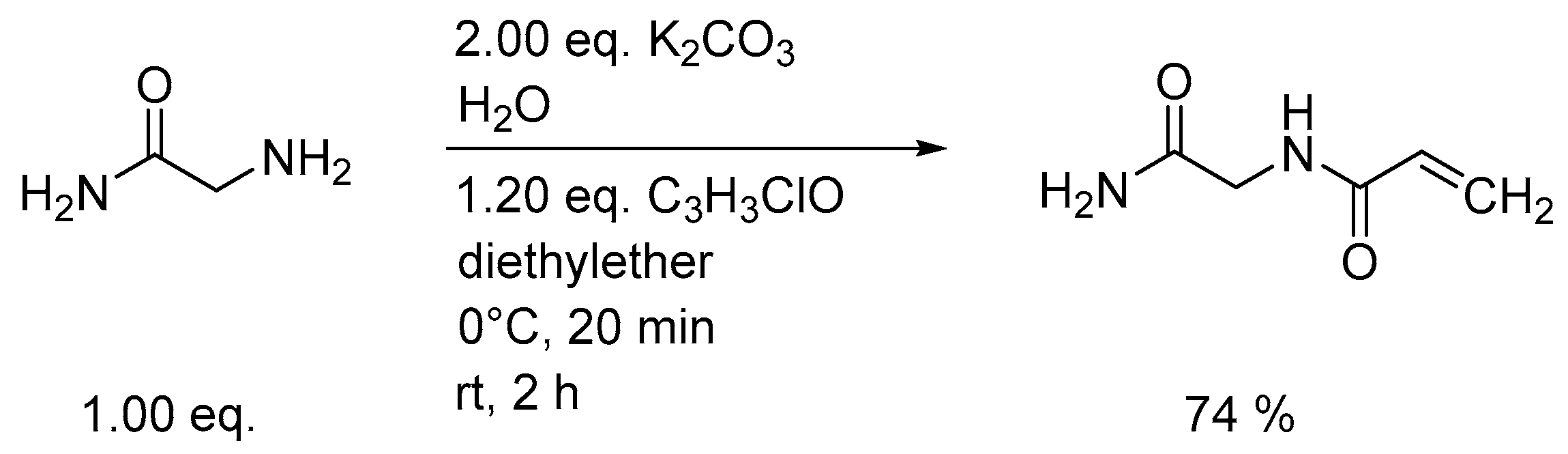
3.1. Synthesis of Monomers
3.2. Polymer Synthesis
3.3. Acetonide Deprotection
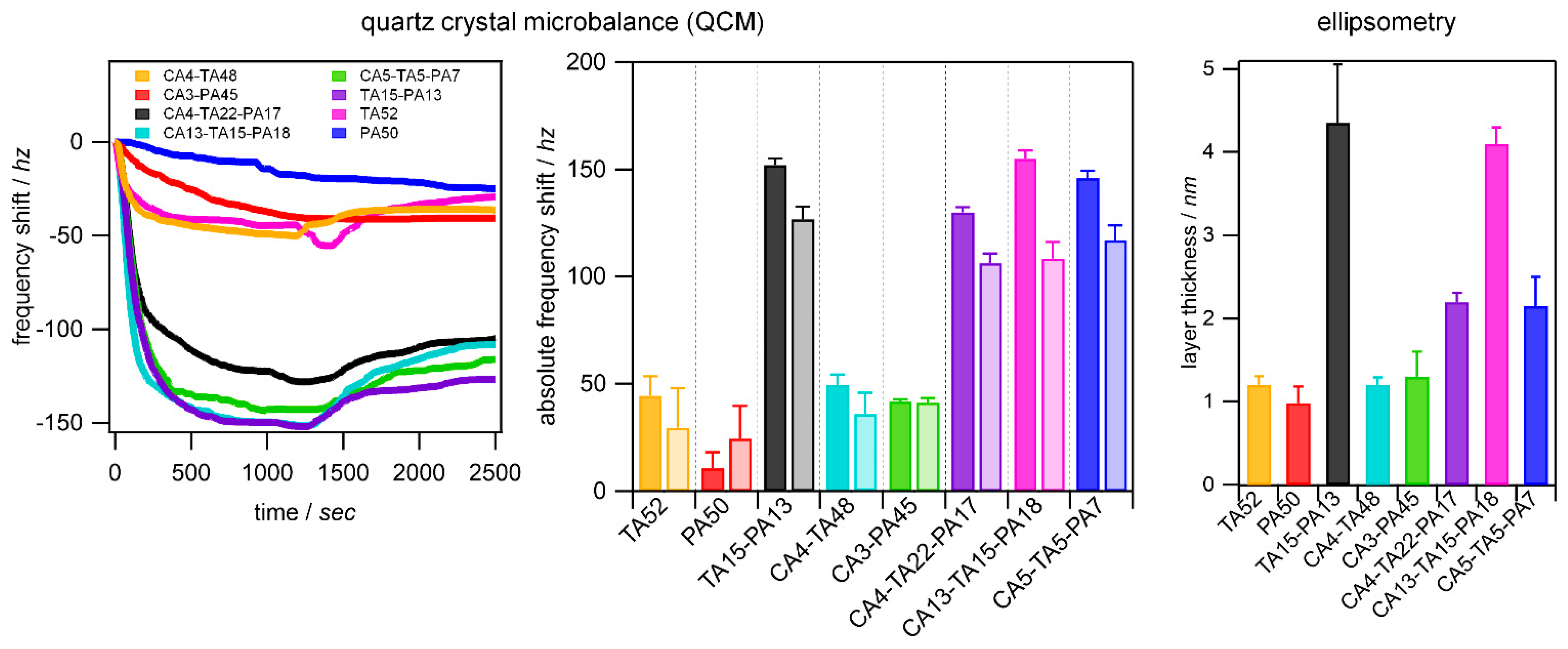
3.4. Adsorption to Quartz Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Israelachvili, J.; Wennerström, H. Role of hydration and water structure in biological and colloidal interactions. Nature 1996, 379, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, C.; Gao, L.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y. Hidden complexity of synergistic roles of Dopa and lysine for strong wet adhesion. Mat. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 2664–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, A.H.; van Hees, I.A.; Yang, J.; Kamperman, M. Bioinspired Underwater Adhesives by Using the Supramolecular Toolbox. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H. Mussel adhesion—Essential footwork. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. Mussel-Inspired Adhesives and Coatings. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2011, 41, 99–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Scherer, N.F.; Messersmith, P.B. Single-molecule mechanics of mussel adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12999–13003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Hwang, J.; Deming, T.J. Role of l-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine in Mussel Adhesive Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5825–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Danner, E.; Waite, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Zeng, H.; Hwang, D.S. Adhesion of mussel foot proteins to different substrate surfaces. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, G.D.; Stow, P.R.; Lewis, R.B.; Andresen Eguiluz, R.C.; Valois, E.; Kristiansen, K.; Butler, A.; Israelachvili, J.N. Impact of Molecular Architecture and Adsorption Density on Adhesion of Mussel-Inspired Surface Primers with Catechol-Cation Synergy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18673–18681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tahir, M.N.; Kappl, M.; Tremel, W.; Metz, N.; Barz, M.; Theato, P.; Butt, H.-J. Influence of Binding-Site Density in Wet Bioadhesion. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3872–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, M.V.; Maier, G.P.; Dobbs, H.A.; Higdon, N.J.; Waite, J.H.; Butler, A.; Israelachvili, J.N. Defining the Catechol-Cation Synergy for Enhanced Wet Adhesion to Mineral Surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9013–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, G.P.; Rapp, M.V.; Waite, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Butler, A. Adaptive synergy between catechol and lysine promotes wet adhesion by surface salt displacement. Science 2015, 349, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Xia, L.; Wang, L.; Qin, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y. Single-molecule study of the synergistic effects of positive charges and Dopa for wet adhesion. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4416–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kord Forooshani, P.; Lee, B.P. Recent approaches in designing bioadhesive materials inspired by mussel adhesive protein. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, W.Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, H.Z.; Ouyang, Q.Q.; Zhang, D.Y.; Li, S.D.; Li, P.W.; Yang, Z.M. Mussel-Inspired Catechol-Functionalized Hydrogels and Their Medical Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, J.L.; Zeng, H.B.; Yu, J. Recent progress in synthesis and application of mussel-inspired adhesives. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, B.H.; Zhou, Y.S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M.; Wang, Z.K. Mussel-inspired hydrogels: From design principles to promising applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3605–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.X.; Sun, Z.M.; Zhu, X.W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, T.F.; Cholewinski, A.; Yang, F.; Zhao, B.X.; Pinnaratip, R.; et al. Catechol-functionalized hydrogels: Biomimetic design, adhesion mechanism, and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 433–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, N.R.; Chen, Y.; Hosseini, V.; Wang, W.Y.; Nasiri, R.; Mahmoodi, M.; Yalcintas, E.P.; Haghniaz, R.; Mecwan, M.M.; Karamikamkar, S.; et al. Recent developments in mussel-inspired materials for biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 6653–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.Y.; Liu, W.G. Recent advances in wet adhesives: Adhesion mechanism, design principle and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 116, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.L.; Gong, J.P. Bioinspired Underwater Adhesives. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Z.B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.W. Stimuli-responsive polydopamine-based smart materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8319–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Zhang, P.; Peng, Q.; Cui, J.; Hao, J.; Zeng, H. Principles of Cation−π Interactions for Engineering Mussel-Inspired Functional Materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkar, A.R.; Kelley, J.D.; Pinnaratip, R.; Lee, B.P. Effect of Ionic Functional Groups on the Oxidation State and Interfacial Binding Property of Catechol-Based Adhesive. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Lee, D.W.; Ahn, B.K.; Seo, S.; Kaufman, Y.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. Underwater contact adhesion and microarchitecture in polyelectrolyte complexes actuated by solvent exchange. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogsgaard, M.; Behrens, M.A.; Pedersen, J.S.; Birkedal, H. Self-Healing Mussel-Inspired Multi-pH-Responsive Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Lee, Y.; Kong, W.H.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G.; Lee, H. Catechol-Functionalized Chitosan/Pluronic Hydrogels for Tissue Adhesives and Hemostatic Materials. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxer, S.; Portmann, C.; Tosatti, S.; Gademann, K.; Zürcher, S.; Textor, M. Surface Assembly of Catechol-Functionalized Poly(l-lysine)-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) Copolymer on Titanium Exploiting Combined Electrostatically Driven Self-Organization and Biomimetic Strong Adhesion. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.D.; Wilker, J.J. Underwater Bonding with Charged Polymer Mimics of Marine Mussel Adhesive Proteins. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 5085–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, H. A mussel-inspired catecholic ABA triblock copolymer exhibits better antifouling properties compared to a diblock copolymer. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 4622–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.K.; Das, S.; Linstadt, R.; Kaufman, Y.; Martinez-Rodriguez, N.R.; Mirshafian, R.; Kesselman, E.; Talmon, Y.; Lipshutz, B.H.; Israelachvili, J.N.; et al. High-performance mussel-inspired adhesives of reduced complexity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Oh, D.X.; Kim, S.; Seo, J.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Masic, A.; Han, D.K.; Cha, H.J. Mussel-Mimetic Protein-Based Adhesive Hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Achazi, K.; Liebe, H.; Schulz, A.; Noeske, P.L.M.; Grunwald, I.; Haag, R. Mussel-Inspired Dendritic Polymers as Universal Multifunctional Coatings. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11650–11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, S.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xu, J.R. Underwater bonding strength of marine mussel-inspired polymers containing DOPA-like units with amino groups. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8919–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, A.B.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, H.X.; Ghaemi, S.; Ishihara, K.; Liu, Y.; Narain, R. Rapid Mussel-Inspired Surface Zwitteration for Enhanced Antifouling and Antibacterial Properties. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Y.; Huang, B.X.; Wang, Q.H.; Wu, W.L.; Coates, P.; Sefat, F.; Lu, C.H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.M. A Mussel-Inspired Antibacterial Hydrogel with High Cell Affinity, Toughness, Self-Healing, and Recycling Properties for Wound Healing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Waite, J.H. Proteins in Load-Bearing Junctions: The Histidine-Rich Metal-Binding Protein of Mussel Byssus. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 14223–14231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Waite, J.H. Linking adhesive and structural proteins in the attachment plaque of Mytilus californianus. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26150–26158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepecki, L.M.; Hansen, K.M.; Waite, J.H. Characterization of a Cystine-Rich Polyphenolic Protein Family from the Blue Mussel Mytilus edulis L. Biol. Bull. 1992, 183, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papov, V.V.; Diamond, T.V.; Biemann, K.; Waite, J.H. Hydroxyarginine-containing Polyphenolic Proteins in the Adhesive Plaques of the Marine Mussel Mytilus edulis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 20183–20192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Gourdon, D.; Sun, C.; Holten-Andersen, N.; Anderson, T.H.; Waite, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N. Adhesion mechanisms of the mussel foot proteins mfp-1 and mfp-3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3782–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.; Strzelczyk, A.K.; Wedler, N.; Kropf, C.; Schmidt, S.; Hartmann, L. Sequence-defined positioning of amine and amide residues to control catechol driven wet adhesion. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 9919–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payra, D.; Naito, M.; Fujii, Y.; Yamada, N.L.; Hiromoto, S.; Singh, A. Bioinspired adhesive polymer coatings for efficient and versatile corrosion resistance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 15977–15984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Keijsers, J.; van Heek, M.; Stuiver, A.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Kamperman, M. The effect of molecular composition and crosslinking on adhesion of a bio-inspired adhesive. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3121–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Penas, A.; Biswas, C.S.; Liang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.P.; Stadler, F.J. Effect of Hydrophobic Interactions on Lower Critical Solution Temperature for Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-dopamine Methacrylamide) Copolymers. Polymers 2019, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.H.; Li, L.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Shi, X.C.; Yeh, J.M.; Zhang, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Conducting Copolymer with Aniline Tetramer as Intelligent Biological Adhesive for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, K.; Meyer, W. Synthesis and Characterization of Catechol-Containing Polyacrylamides with Adhesive Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilfiker, J.N.; Stadermann, M.; Sun, J.; Tiwald, T.; Hale, J.S.; Miller, P.E.; Aracne-Ruddle, C. Determining thickness and refractive index from free-standing ultra-thin polymer films with spectroscopic ellipsometry. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 421, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, B.-H.; Messersmith, P.B. Acetonide protection of dopamine for the synthesis of highly pure N-docosahexaenoyldopamine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 2403–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.; Steffens, R.C.; Paul, T.J.; Hartmann, L. Catechol-functionalized sequence-defined glycomacromolecules as covalent inhibitors of bacterial adhesion. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 6091–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckigt, J.; Antonchick, A.P.; Wu, F.; Waldmann, H. The Pictet–Spengler Reaction in Nature and in Organic Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8538–8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Kamperman, M. Jack of all trades: Versatile catechol crosslinking mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8271–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatzel, S.; Badi, N.; Päch, M.; Laschewsky, A.; Lutz, J.-F. Well-defined synthetic polymers with a protein-like gelation behavior in water. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4517–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemnitz, C.R.; Loewen, M.J. “Amide Resonance” Correlates with a Breadth of C−N Rotation Barriers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2521–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Final Polymer | Monomer Reaction Ratio [%] | Monomer Incorporation [%] a | n | Đ | Yield | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Sample Code) | CAA | TA | PA | HY | CAA | TA | PA | HY | [kDa] | [%] | |
| TA52 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 52 | 0 | 48 | 23.5 | 1.97 | 91 |
| PA50 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 50.33 | 1.36 | 39 |
| TA15-PA13 | 0 | 15 | 15 | 70 | 0 | 15 | 13 | 72 | 69.9 | 1.74 | 93 |
| CAA4-TA48 | 5 | 45 | 0 | 50 | 4 | 48 | 0 | 48 | 21.9 | 2.61 | 98 |
| CAA3-PA45 | 5 | 0 | 45 | 50 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 52 | 23.4 | 1.92 | 45 |
| CAA5-TA5-PA7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 85 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 83 | 63.1 | 1.87 | 98 |
| CAA4-TA22-PA17 | 5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 50 | 4 | 22 | 17 | 57 | 64.4 | 1.73 | 94 |
| CAA13-TA15-PA18 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 55 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 54 | 50.9 | 1.12 | 91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonda, L.; Müller, J.; Fischer, L.; Löwe, M.; Kedrov, A.; Schmidt, S.; Hartmann, L. Facile Synthesis of Catechol-Containing Polyacrylamide Copolymers: Synergistic Effects of Amine, Amide and Catechol Residues in Mussel-Inspired Adhesives. Polymers 2023, 15, 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183663
Bonda L, Müller J, Fischer L, Löwe M, Kedrov A, Schmidt S, Hartmann L. Facile Synthesis of Catechol-Containing Polyacrylamide Copolymers: Synergistic Effects of Amine, Amide and Catechol Residues in Mussel-Inspired Adhesives. Polymers. 2023; 15(18):3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183663
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonda, Lorand, Janita Müller, Lukas Fischer, Maryna Löwe, Alexej Kedrov, Stephan Schmidt, and Laura Hartmann. 2023. "Facile Synthesis of Catechol-Containing Polyacrylamide Copolymers: Synergistic Effects of Amine, Amide and Catechol Residues in Mussel-Inspired Adhesives" Polymers 15, no. 18: 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183663
APA StyleBonda, L., Müller, J., Fischer, L., Löwe, M., Kedrov, A., Schmidt, S., & Hartmann, L. (2023). Facile Synthesis of Catechol-Containing Polyacrylamide Copolymers: Synergistic Effects of Amine, Amide and Catechol Residues in Mussel-Inspired Adhesives. Polymers, 15(18), 3663. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183663









