Hook Fabric Electroencephalography Electrode for Brain Activity Measurement without Shaving the Head
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
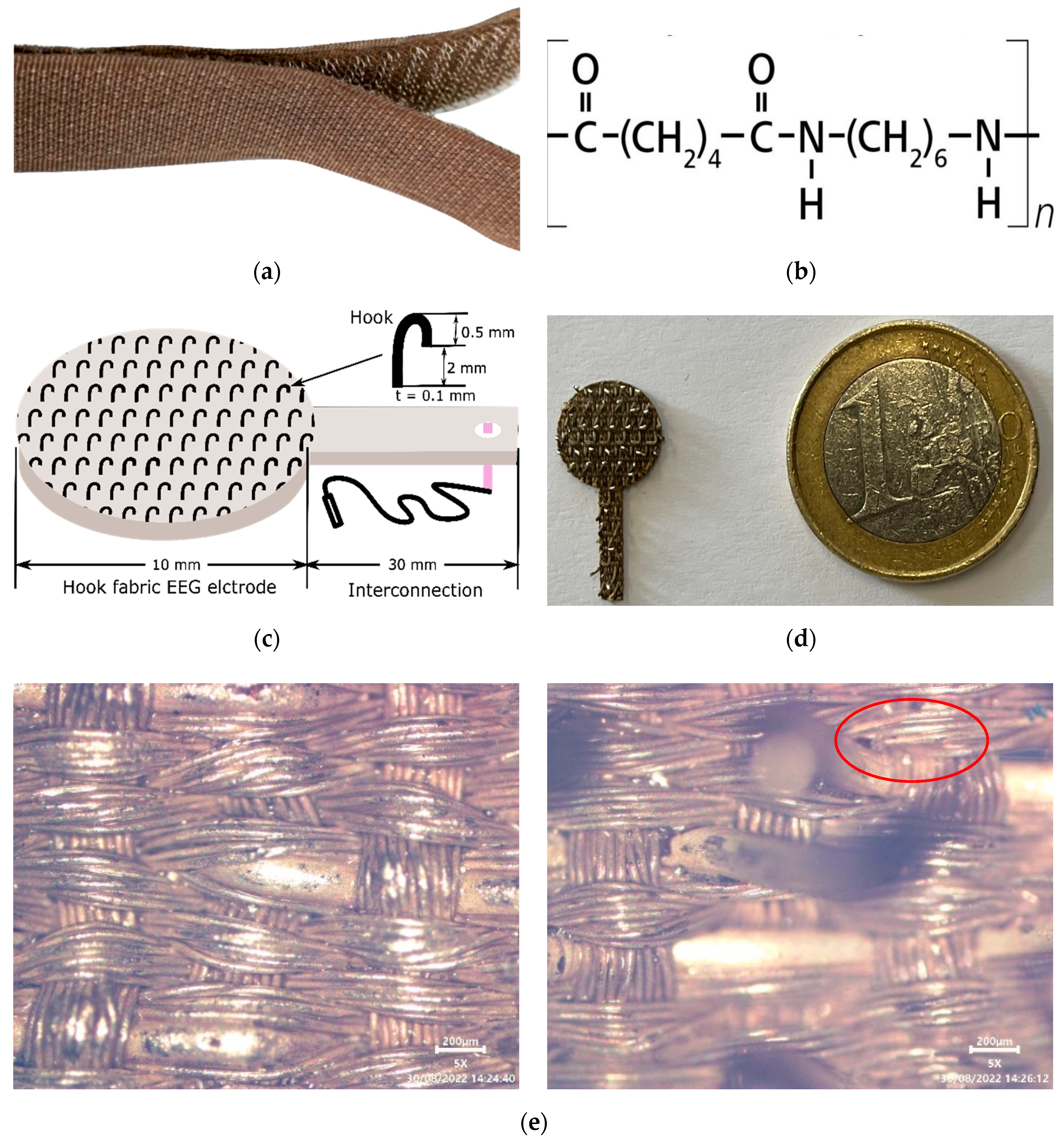
2.1. Textile-Based Electrode (Textrode) Design
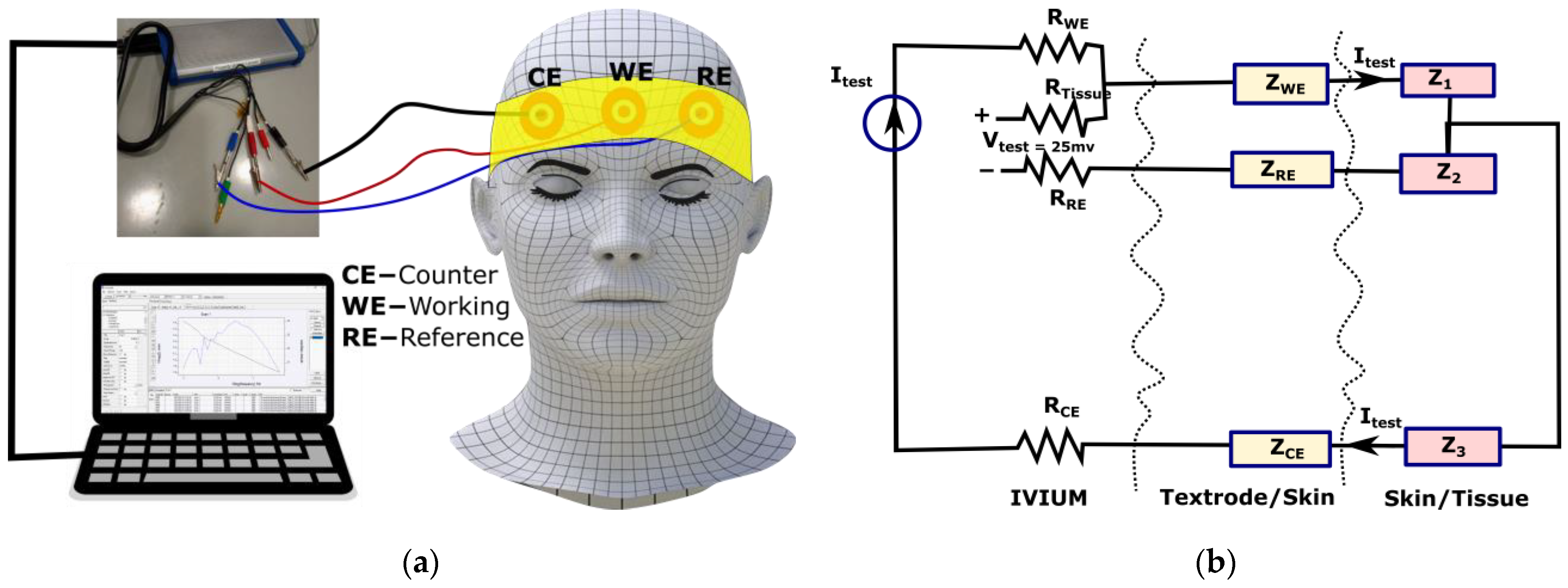
2.2. Skin-to-Electrode Impedance Measurement
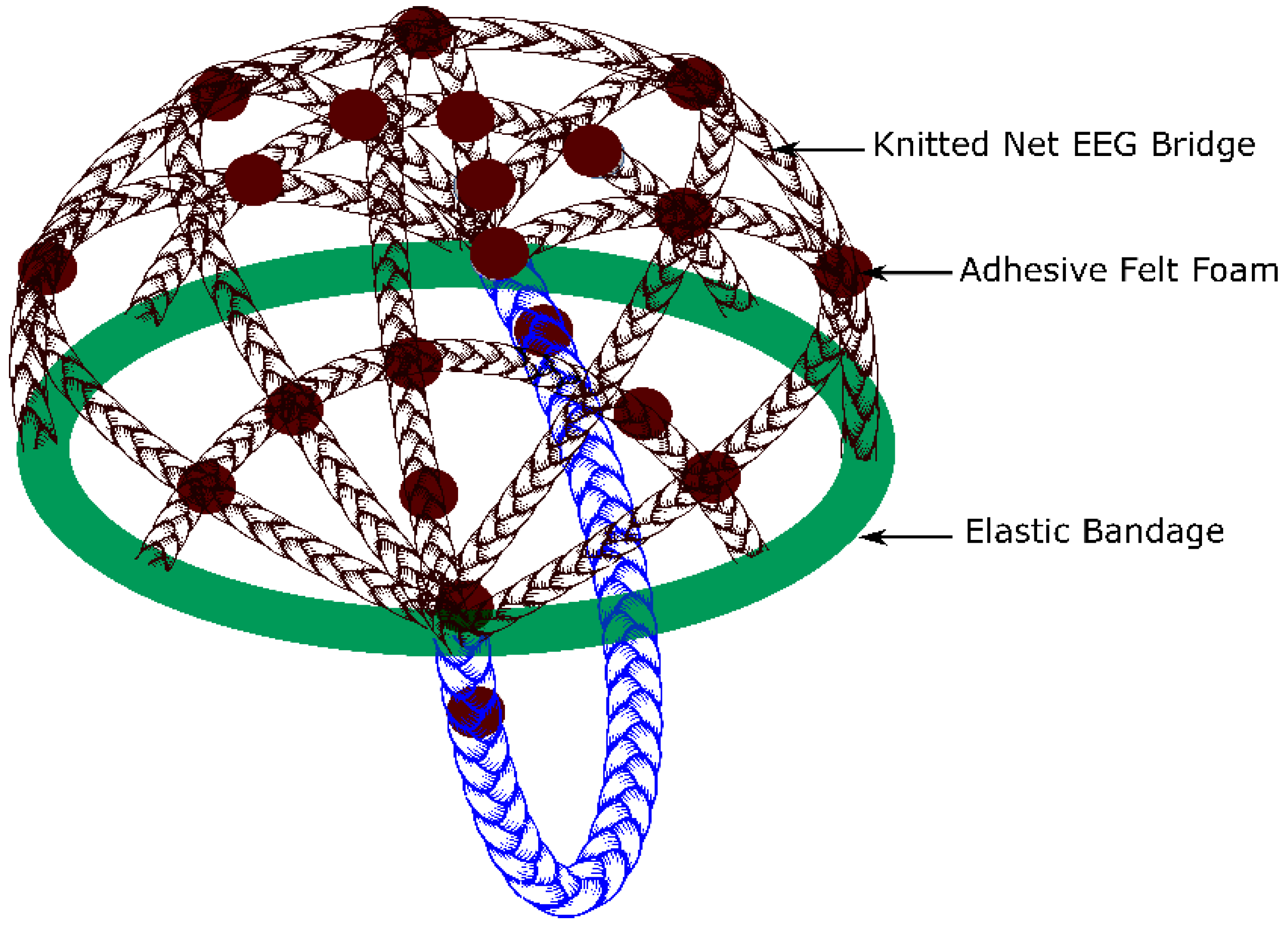
2.3. Knitted Net EEG Electrode Bridge
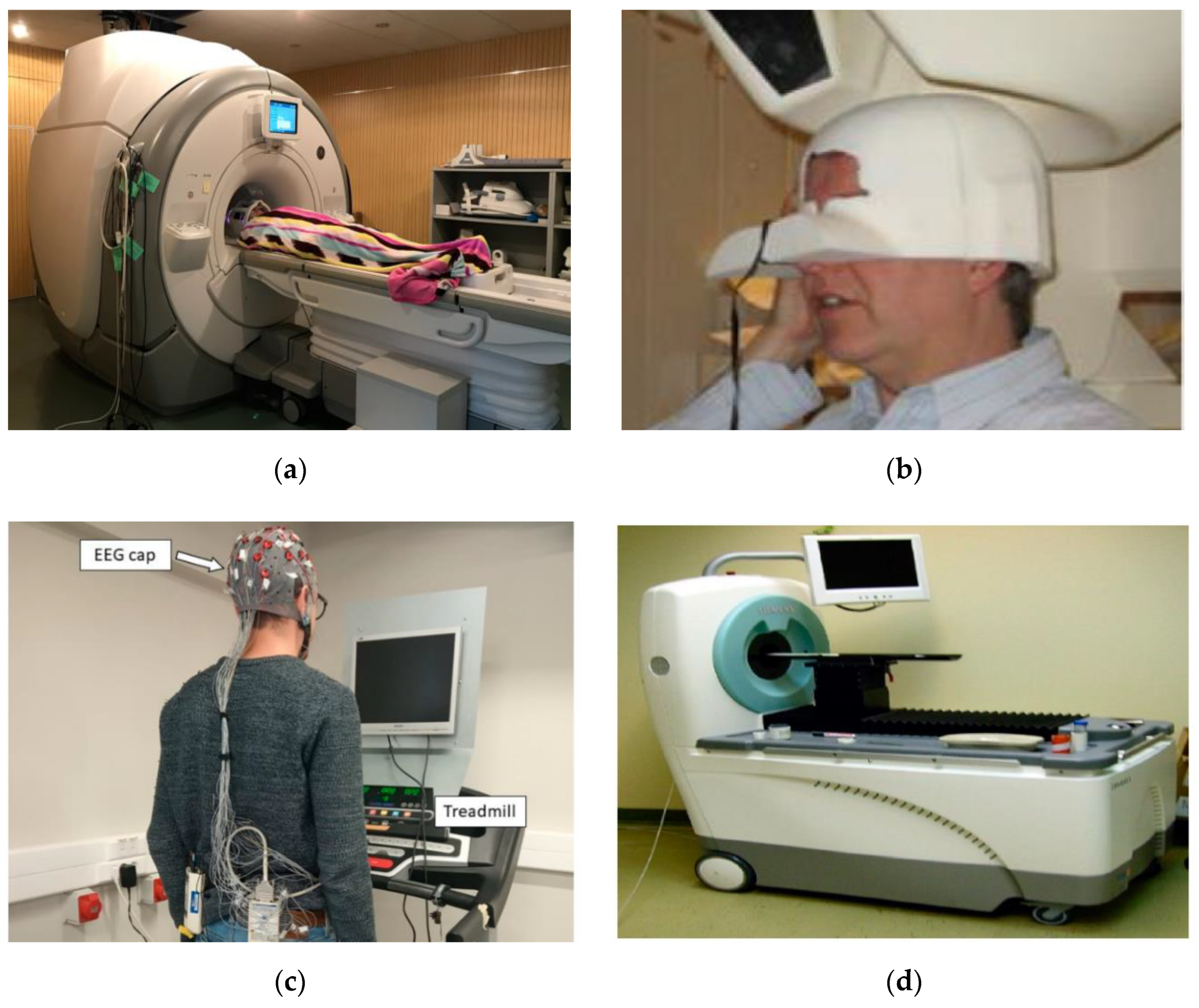
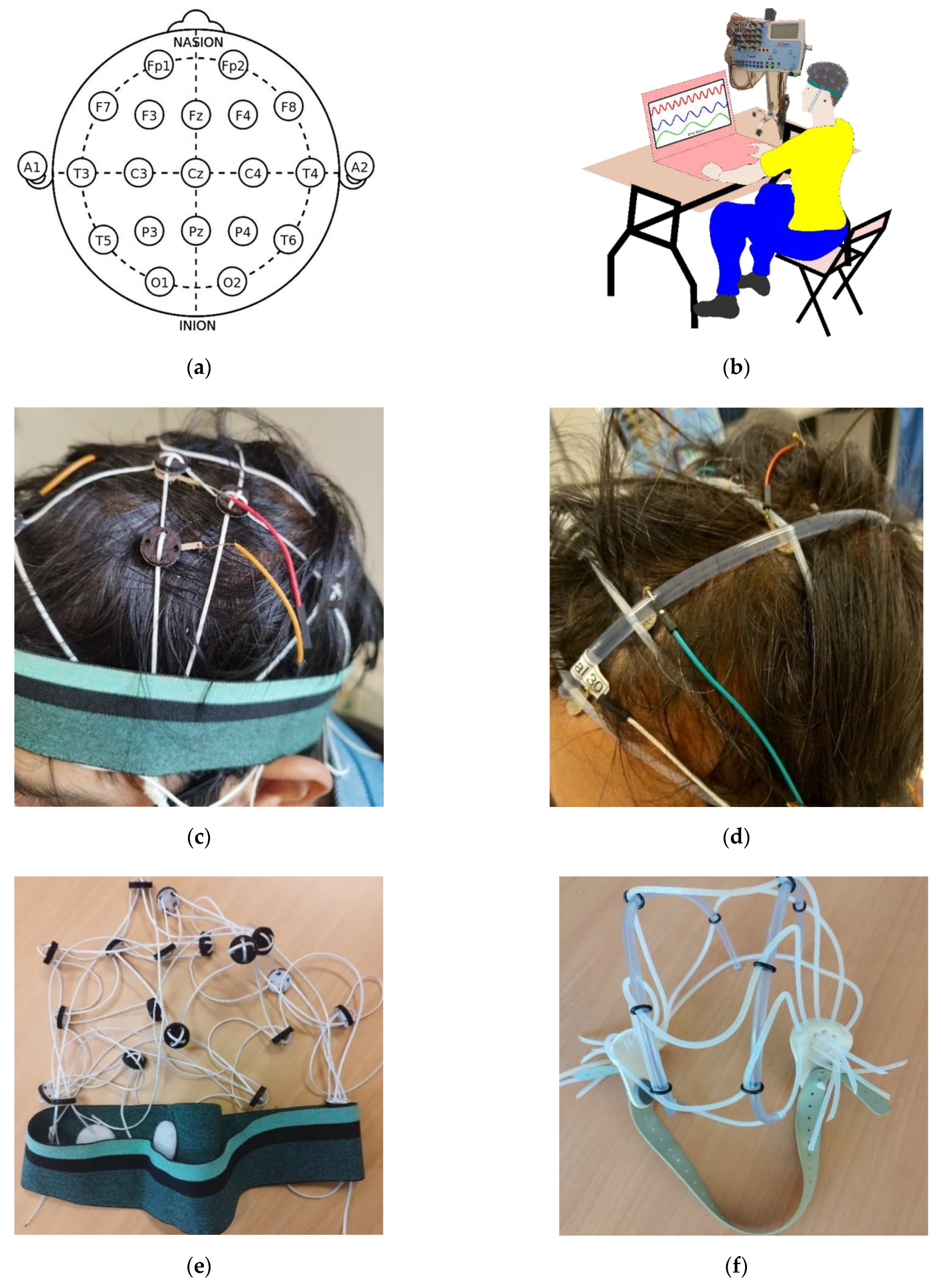
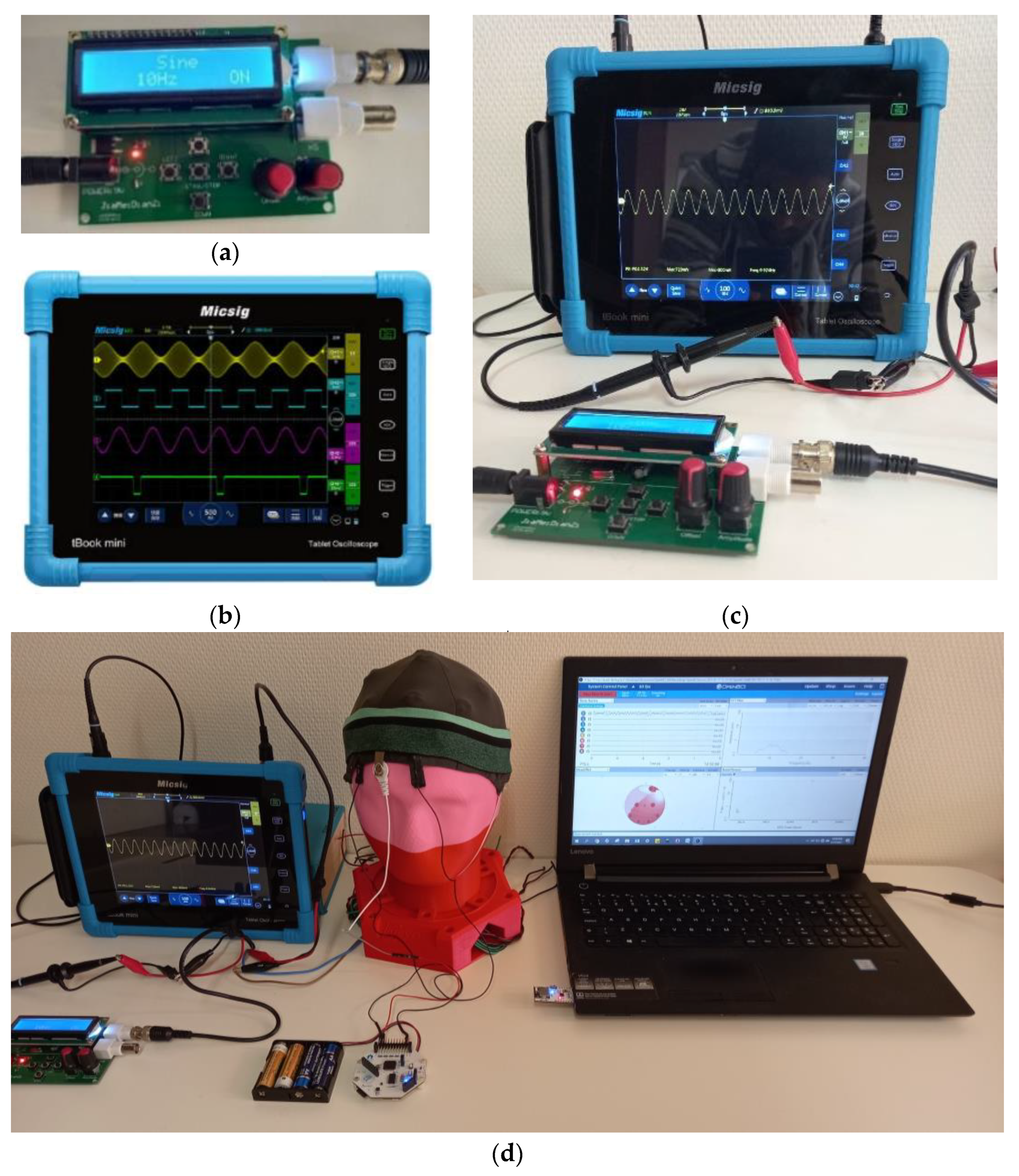
2.4. EEG Measurement
2.5. ITC, ERSP and PSD Analysis
2.6. Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Performance of the Knitted Net Bridge EEG Cap
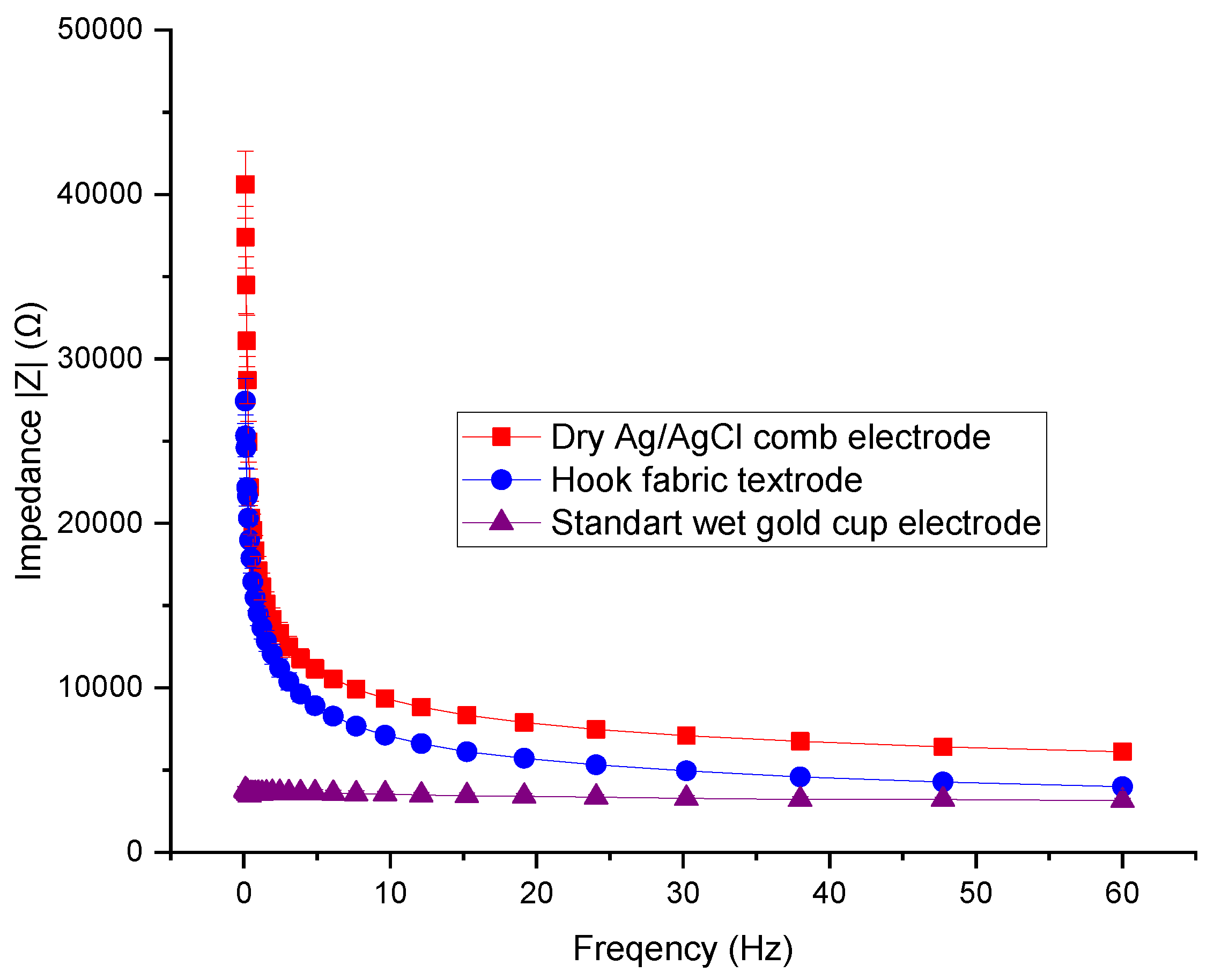
3.2. Skin-to-Electrode Contact Impedance Comparison
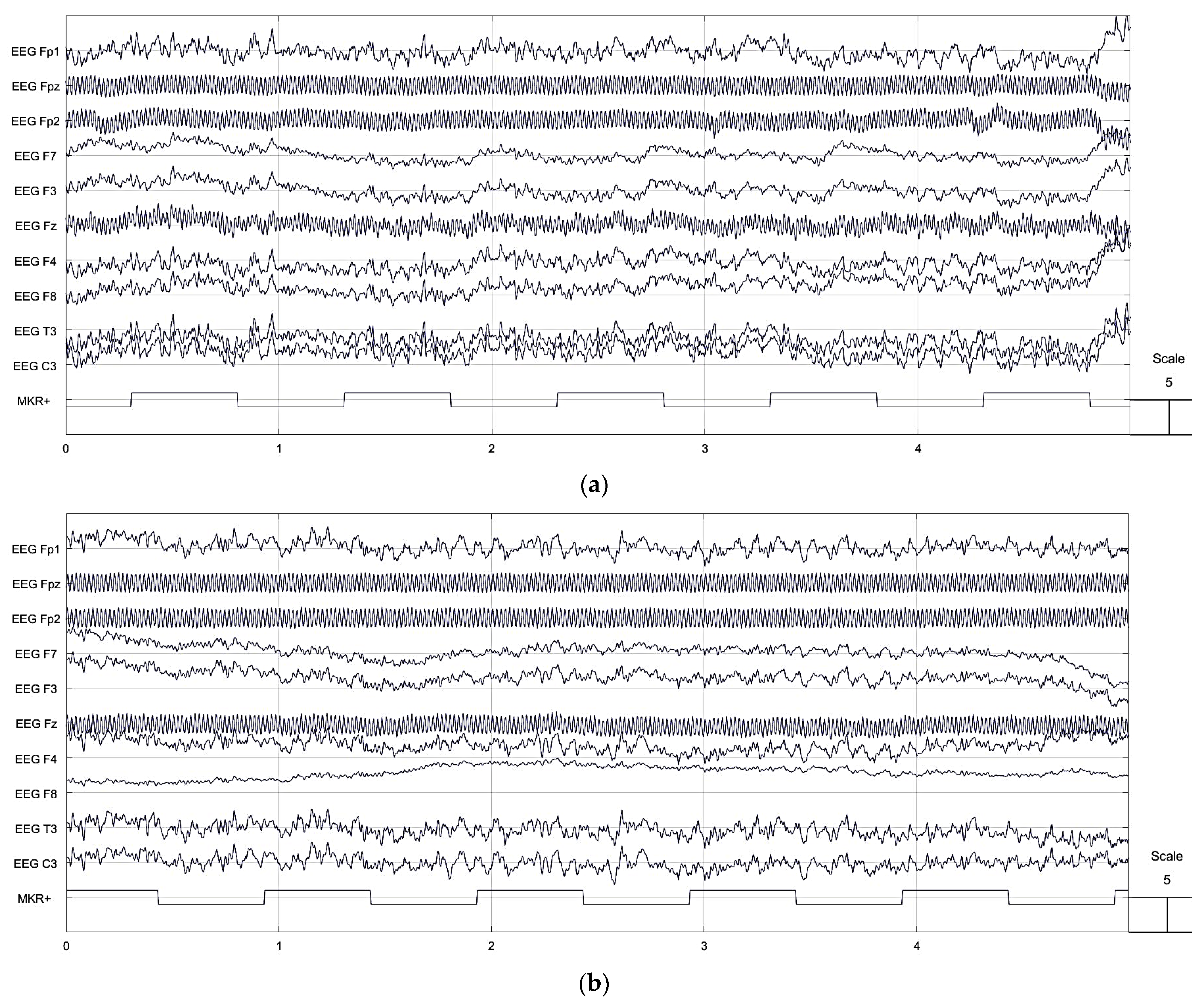
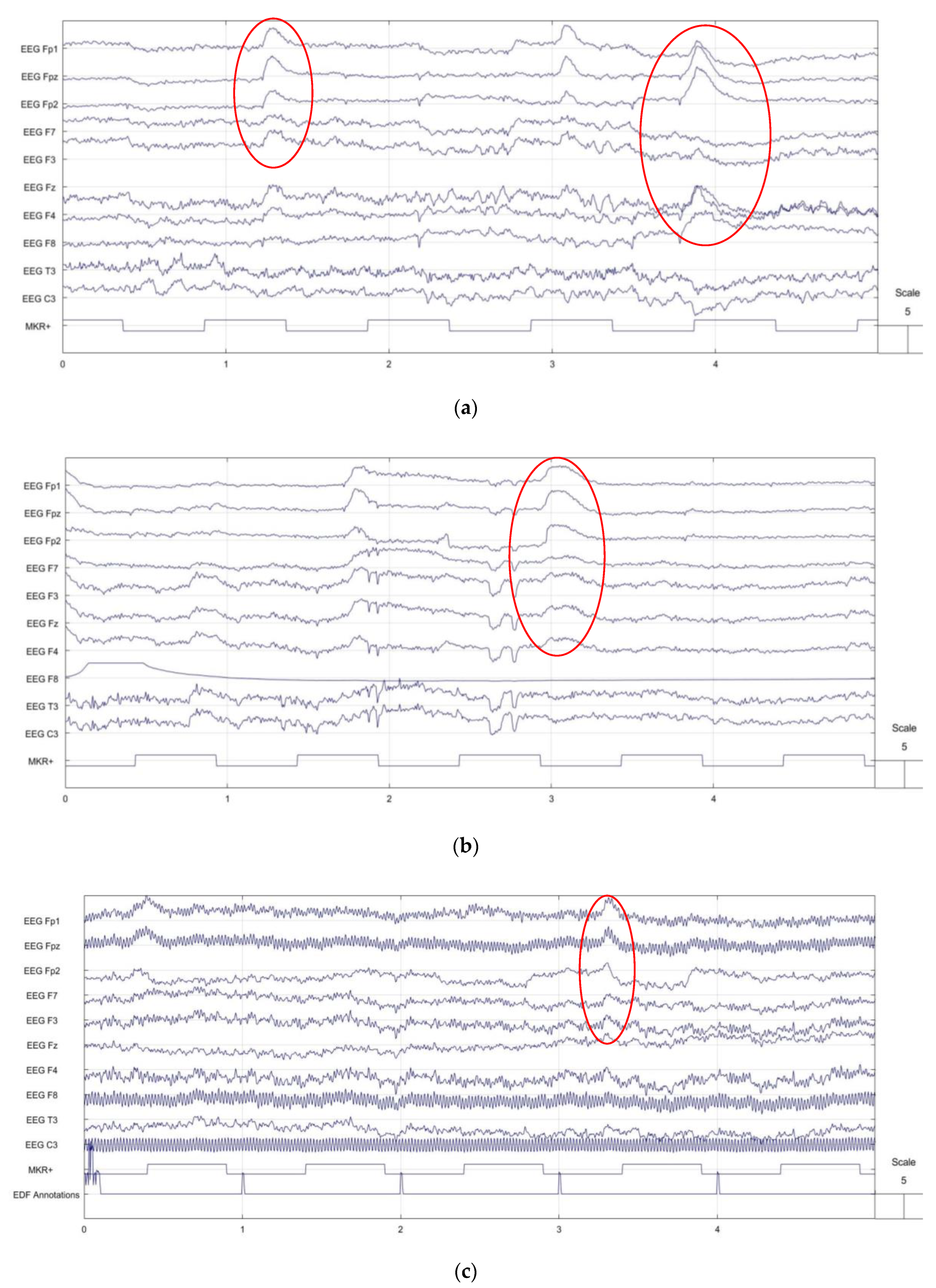
3.3. EEG Signal Comparison
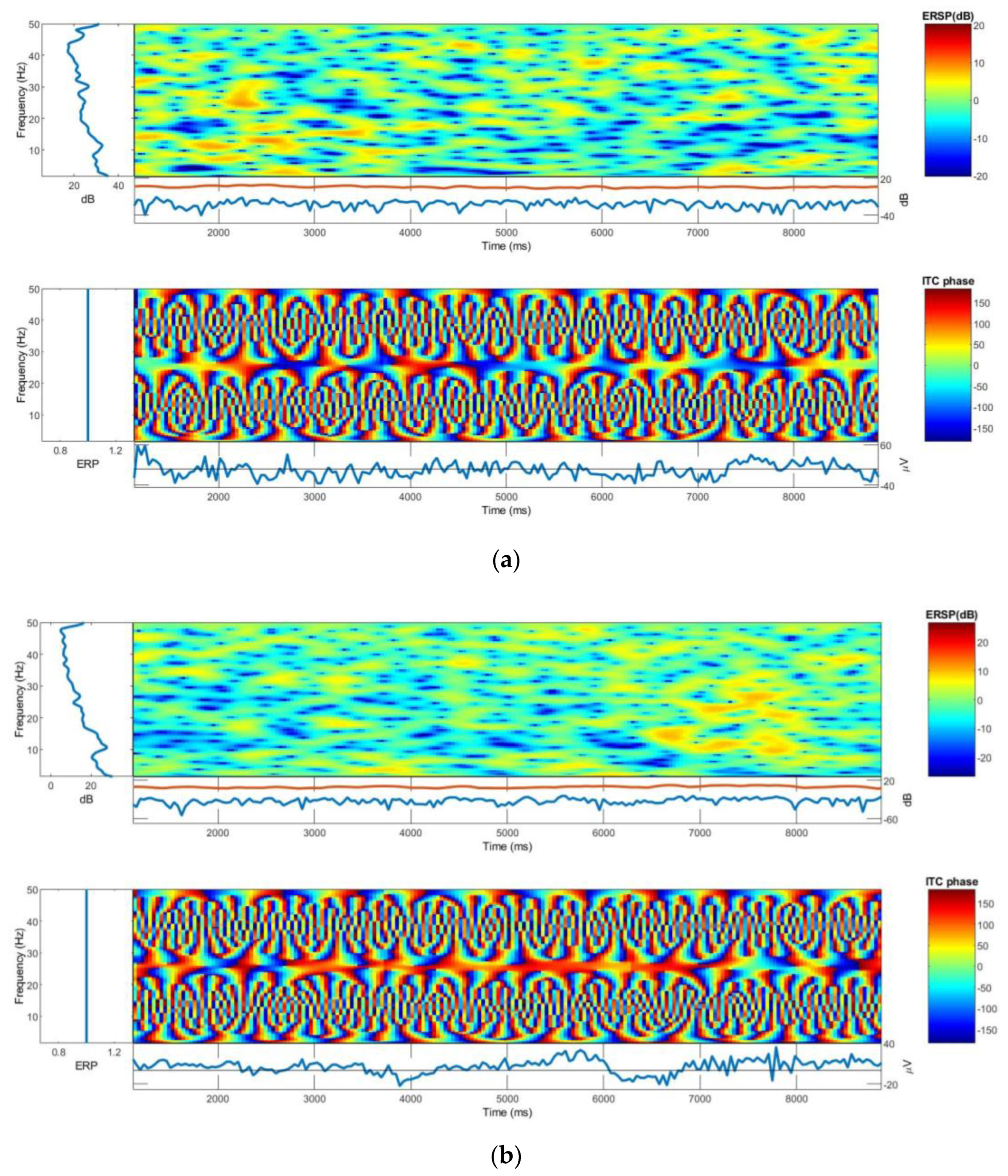
3.4. ITC, ERSP and PSD Analysis
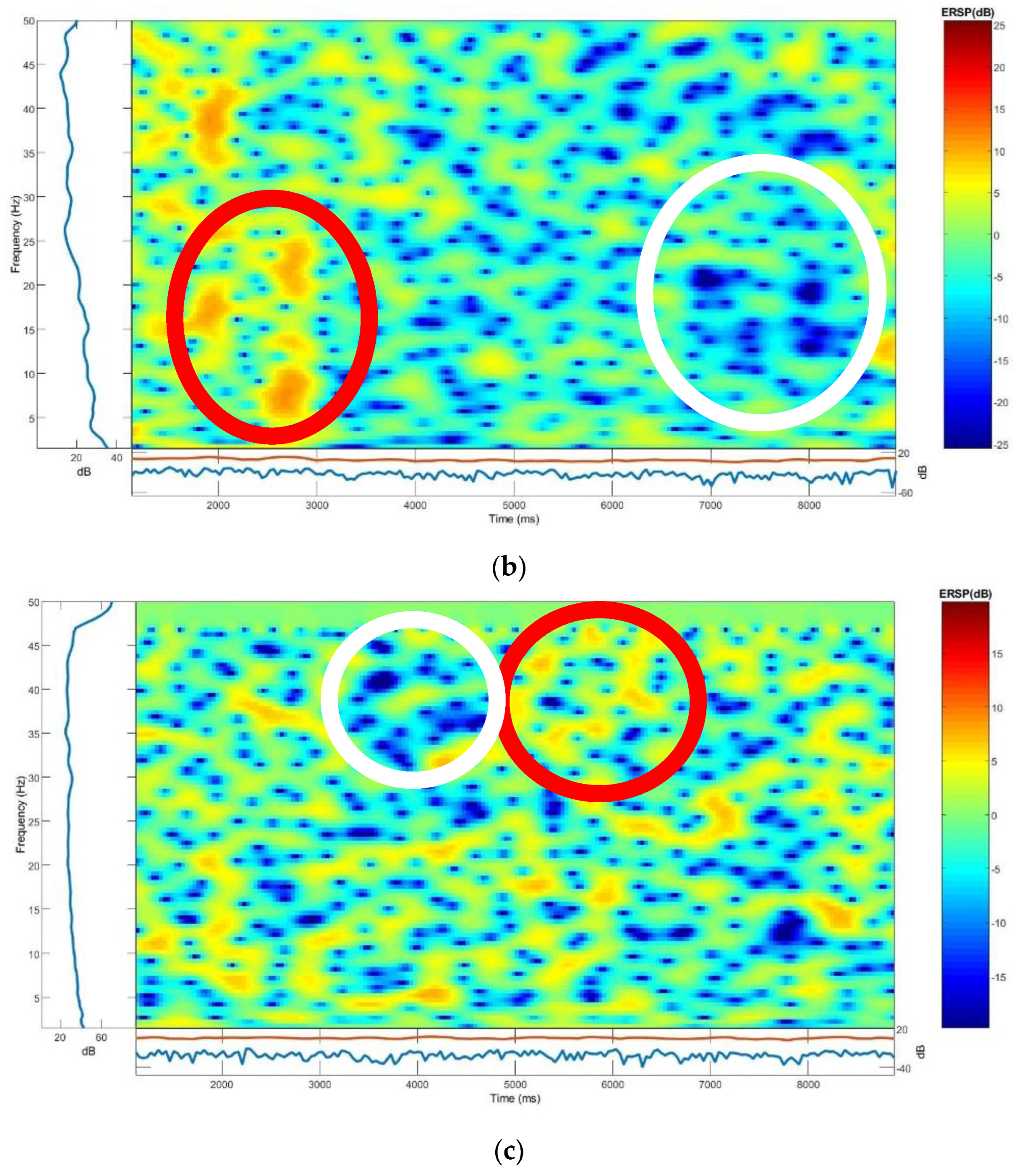
3.4.1. ERSP
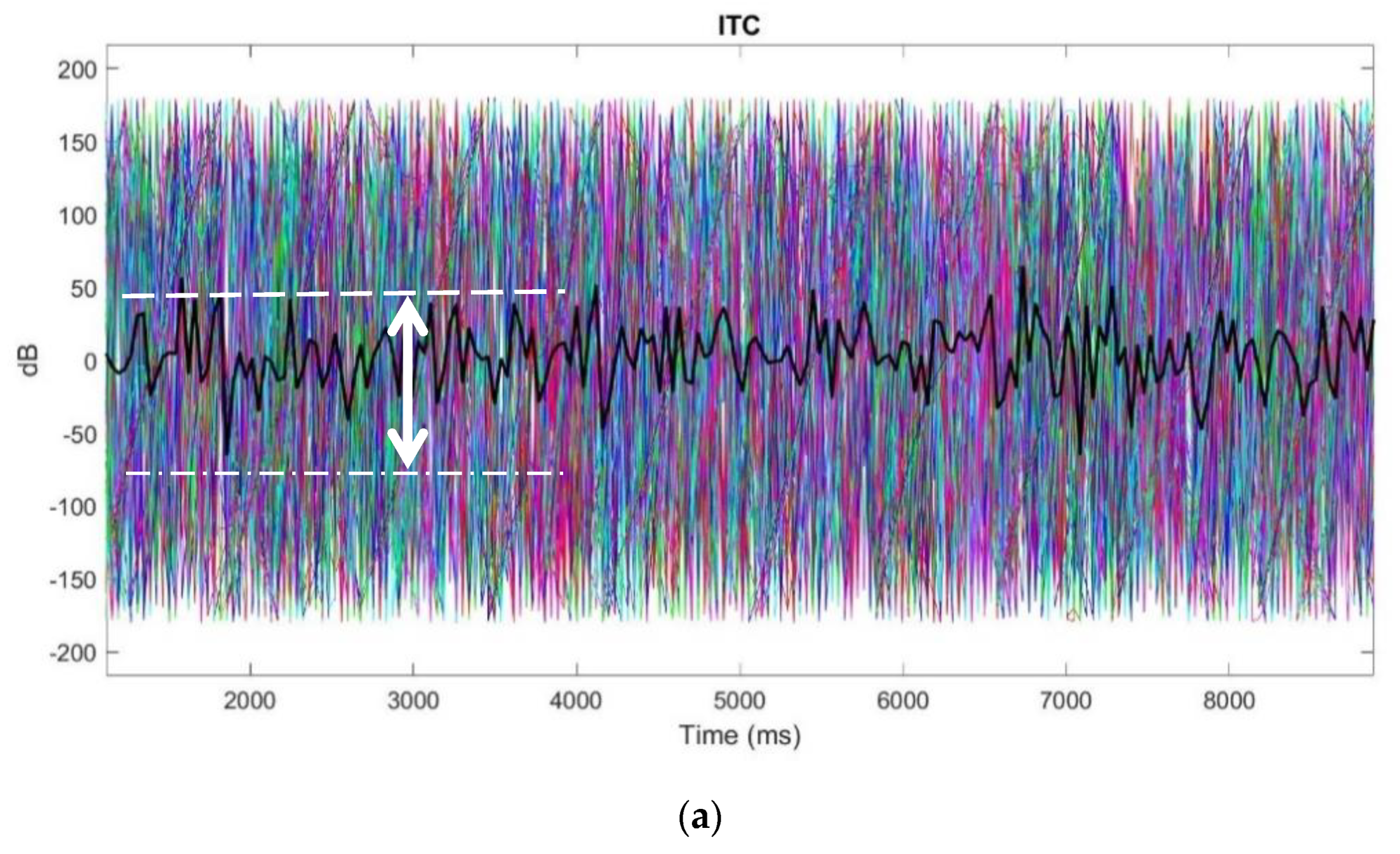
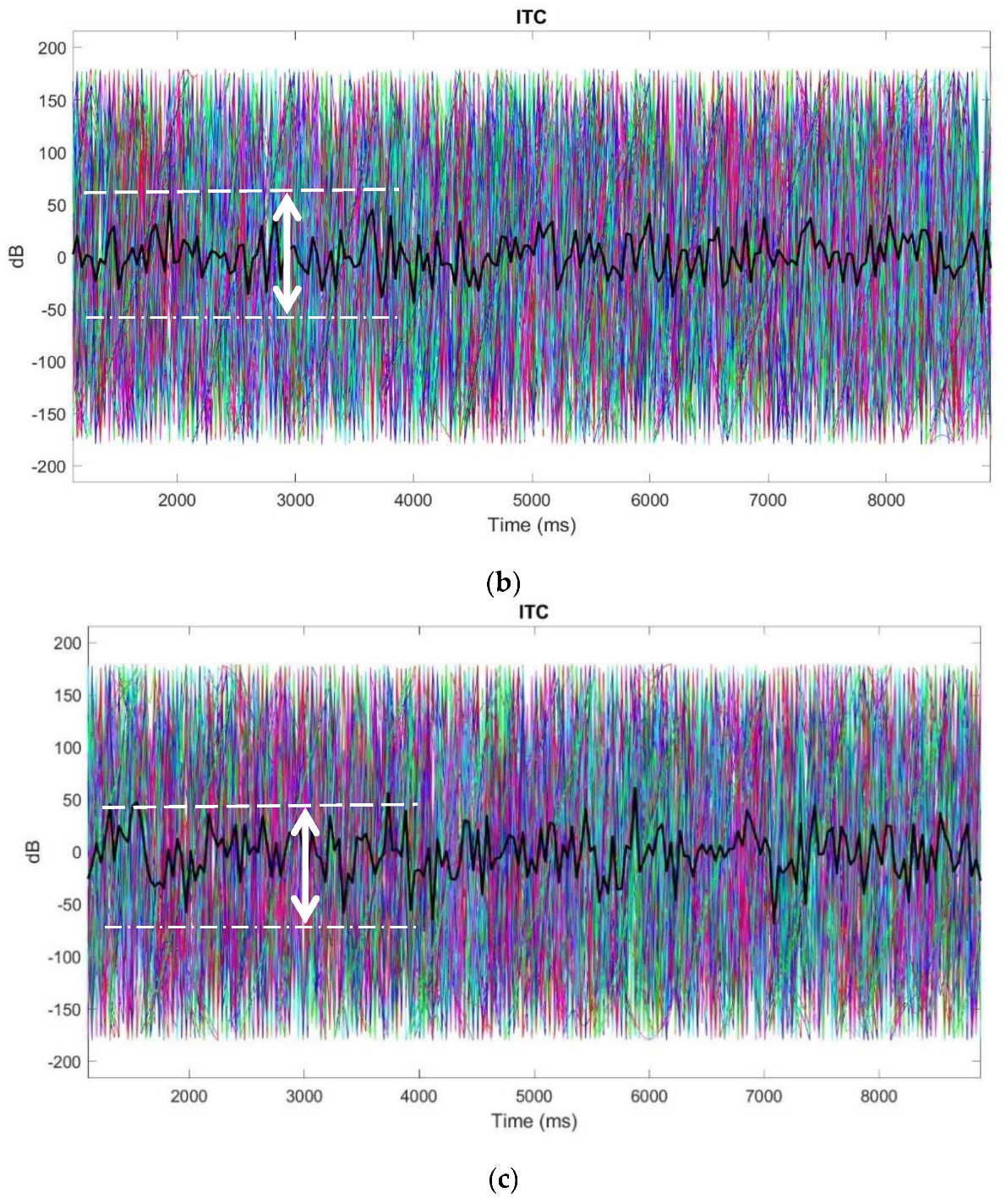
3.4.2. ITC
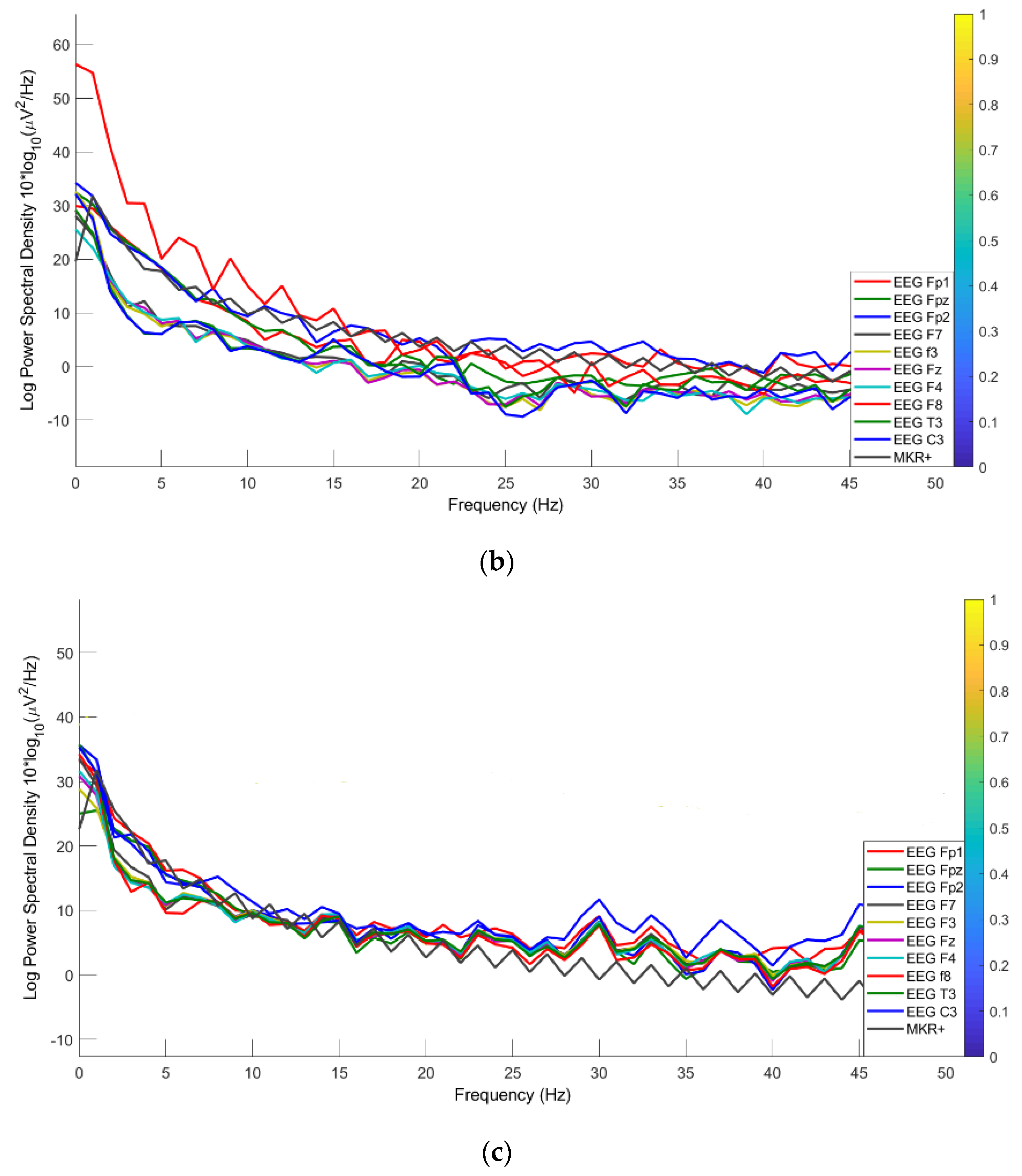
3.4.3. PSD
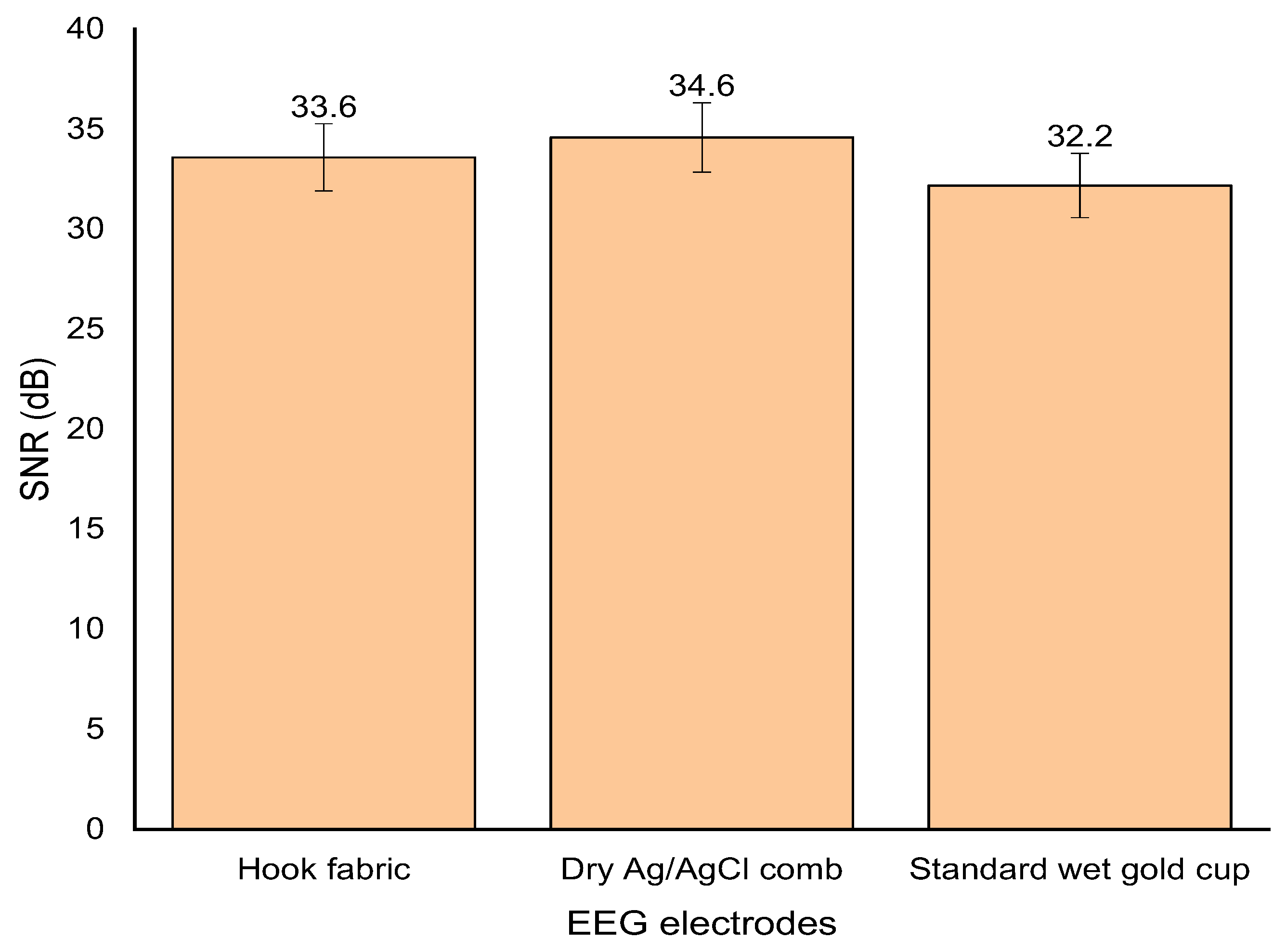
3.5. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
3.6. Effects of Size and Bending on Signal-to-Noise Ratio
3.7. Sustainability Concerns
4. Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, H. Corticomuscular Coherence and Its Applications: A Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Lv, M.; Chen, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L. How Does Approaching a Lead Vehicle and Monitoring Request Affect Drivers’ Takeover Performance? A Simulated Driving Study with Functional MRI. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvira, M.; Iáñez, E.; Quiles, V.; Ortiz, M.; Azorín, J.M. Pseudo-Online BMI Based on EEG to Detect the Appearance of Sudden Obstacles during Walking. Sensors 2019, 19, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troebinger, L.; Anninos, P.; Barnes, G. Neuromagnetic Effects of Pico-Tesla Stimulation. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggemann, J.; Gross, A.; Pate, S. Non-Intrusive Visualization of Optically Inaccessible Flow Fields Utilizing Positron Emission Tomography. Aerospace 2020, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; French, I.T.; Liang, W.-K.; Lo, Y.-S.; Wang, Y.-R.; Cheng, M.-L.; Huang, N.E.; Wu, H.-C.; Lim, S.-N.; Chen, C.-M.; et al. Evaluating the Different Stages of Parkinson’s Disease Using Electroencephalography with Holo-Hilbert Spectral Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 832637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, L.; Lumley, H.; Shaw, L.; Francis, R.; Price, C.I. Surface Electroencephalography (EEG) during the Acute Phase of Stroke to Assist with Diagnosis and Prediction of Prognosis: A Scoping Review. BMC Emerg. Med. 2022, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhu, S.; Shu, X. State of the Art of Non-Invasive Electrode Materials for Brain–Computer Interface. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzad, R.; Behzad, A. The Role of EEG in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Sleep Disorders. J. Behav. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, D.; Shang, A.; Abdel-Baki, S.; Suzuki, W.; Fenton, A.A. Cognitive Behavior Classification from Scalp EEG Signals. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. The Status of Textile-Based Dry EEG Electrodes. Autex Res. J. 2021, 21, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.J.; Deiss, S.R.; Cauwenberghs, G. A Low-Noise, Non-Contact EEG/ECG Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 November 2007; pp. 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, Y.G.; Park, K.S. Conductive Polymer Foam Surface Improves the Performance of a Capacitive EEG Electrode. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.; Maier, C.; Jung, T.-P.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry and Noncontact EEG Sensors for Mobile Brain–Computer Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2012, 20, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, S. Non-Contact EEG Active Multielectrode Hardware Design; Flinders University: Adelaide, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.M.; Cauwenberghs, G. Wireless Non-Contact EEG/ECG Electrodes for Body Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Body Sensor Networks, Singapore, 7–9 June 2010; pp. 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Gordo, M.; Sanchez-Morillo, D.; Valle, F. Dry EEG Electrodes. Sensors 2014, 14, 12847–12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, P.; Raedt, R.; Carrette, E.; Schaubroeck, D.; Vanfleteren, J.; Cardon, L. A 3D Printed Dry Electrode for ECG/EEG Recording. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2012, 174, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofhede, J.; Seoane, F.; Thordstein, M. Soft Textile Electrodes for EEG Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine, Corfu, Greece, 3–5 November 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Audette, W.E.; Bieszczad, J.; Allen, L.V.; Diamond, S.G.; Kynor, D.B. Design and Demonstration of a Head Phantom for Testing of Electroencephalography (EEG) Equipment; Creare, Inc.: Hanover, NH, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.J.; Deiss, S.R.; Jung, T.-P.; Cauwenberghs, G. A Brain-Machine Interface Using Dry-Contact, Low-Noise EEG Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 May 2008; pp. 1986–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, A.; Perera, P.; Sarsenbayeva, Z.; McEwan, A.; De Silva, A.C.; Withana, A. Fully 3D-Printed Dry EEG Electrodes. Sensors 2023, 23, 5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, A.; Collu, R.; Spanu, A.; Fraschini, M.; Barbaro, M.; Cosseddu, P. Wearable System Based on Ultra-Thin Parylene C Tattoo Electrodes for EEG Recording. Sensors 2023, 23, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. A Dry EEG Textrode from a PEDOT:PSS/PDMS-Coated Cotton Fabric for Brain Activity Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 20 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. Dry Electroencephalography Textrode for Brain Activity Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22077–22085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.M.; Mattila, H.; Janka, M.; Virkki, J. Impedance Evaluation of Textile Electrodes for EEG Measurements. Text. Res. J. 2023, 93, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Van Langenhove, L. Development of a Flex and Stretchy Conductive Cotton Fabric Via Flat Screen Printing of PEDOT:PSS/PDMS Conductive Polymer Composite. Sensors 2020, 20, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, G.; Bifulco, P.; Cesarelli, M.; McEwan, A.; Nikpour, A.; Jin, C.; Gunawardana, U.; Sreenivasan, N.; Wabnitz, A.; Hamilton, T. Fully Open-Access Passive Dry Electrodes BIOADC: Open-Electroencephalography (EEG) Re-Invented. Sensors 2019, 19, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. Validating Poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) Polystyrene Sulfonate-Based Textile Electroencephalography Electrodes by a Textile-Based Head Phantom. Polymers 2021, 13, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B. Development of Dry EEG Textrodes for Brain Activity Monitoring. Ph.D. Dissertation, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-H.; de Beeck, M.; Vanderheyden, L.; Carrette, E.; Mihajlović, V.; Vanstreels, K.; Grundlehner, B.; Gadeyne, S.; Boon, P.; Van Hoof, C. Soft, Comfortable Polymer Dry Electrodes for High Quality ECG and EEG Recording. Sensors 2014, 14, 23758–23780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micromed Group Brain Quick® Clinical EEG Line. Available online: https://micromedgroup.com/en/brain-quick-clinical-eeg-line/ (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Wolfram Droh GmbH EEG Caps Type Schwarzer. Available online: https://www.ternimed.de/epages/62826360.sf/en_GB/?ObjectPath=/Shops/62826360/Products/TER-510198/SubProducts/510198-1 (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- Florida Reserach Institute Disposable/Reusable Dry EEG Electrode. Available online: https://fri-fl-shop.com/products/new-longer-5mm-spike-disposable-reusable-dry-eeg-electrode-tde-210?pr_prod_strat=copurchase&pr_rec_id=d440f28f3&pr_rec_pid=6710085845045&pr_ref_pid=6710083321909&pr_seq=uniform (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L. Temporal and Spatial Features of Single-Trial EEG for Brain-Computer Interface. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2007, 2007, 037695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash-Kille, A.; Sharma, A. Inter-Trial Coherence as a Marker of Cortical Phase Synchrony in Children with Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder Fitted with Hearing Aids and Cochlear Implants. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinker, S.T.; Crake, C.; Ives, J.R.; Bubrick, E.J.; McDannold, N.J. Scalp Sensor for Simultaneous Acoustic Emission Detection and Electroencephalography during Transcranial Ultrasound. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 155017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J. Insight into the Contact Impedance between the Electrode and the Skin Surface for Electrophysical Recordings. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 13906–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. Hook Fabric Electroencephalography Electrode for Brain Activity Measurement without Shaving the Head. Polymers 2023, 15, 3673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183673
Tseghai GB, Malengier B, Fante KA, Van Langenhove L. Hook Fabric Electroencephalography Electrode for Brain Activity Measurement without Shaving the Head. Polymers. 2023; 15(18):3673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183673
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseghai, Granch Berhe, Benny Malengier, Kinde Anlay Fante, and Lieva Van Langenhove. 2023. "Hook Fabric Electroencephalography Electrode for Brain Activity Measurement without Shaving the Head" Polymers 15, no. 18: 3673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183673
APA StyleTseghai, G. B., Malengier, B., Fante, K. A., & Van Langenhove, L. (2023). Hook Fabric Electroencephalography Electrode for Brain Activity Measurement without Shaving the Head. Polymers, 15(18), 3673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183673