Compression Property of TPEE-3D Fibrous Material and Its Application in Mattress Structural Layer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Combination of Mattress
2.2. Measurement and Evaluation
2.2.1. Testing of Material Properties
- (1)
- Quasi-static compression
- (2)
- Indentation property of the material
- Indentation hardness: the corresponding force after maintaining for the 30 s when the sample was indented to 40% of its thickness.
- Compressive deflection coefficient: Sf = F65/F25, is the ratio of the force at 65% and 25% indentation in compression.
2.2.2. Testing of Mattress Firmness
- (1)
- Total firmness of the mattress
- Hardness value: the average of the slopes of the load–deflection curves at 210 N, 275 N, and 340 N, as shown in Equation (3) [33], the unit is N/mm.
- Firmness rating: a number (1 decimal) from 1 to 10 characterizes the degree of firmness of the mattress, from firm to soft, as calculated in Equations (4) and (5) [33].
- (2)
- Multilevel firmness of the mattress
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Compression Properties of the Materials
3.1.1. TPEE-3D Fibrous Material
3.1.2. Comparison of the Properties between T3DF and Other Materials
3.2. TPEE-3D Fibrous Material for Mattress Padding Layers
3.2.1. Effect of the T3DF Padding Layer on Mattress Firmness
3.2.2. Comparison of Mattress Firmness between T3DF and Other Padding Materials
3.3. TPEE-3D Fibrous Material for Mattress Core Layers
3.3.1. Effect of the T3DF Core Layer on Mattress Firmness
3.3.2. Comparison of Mattress Firmness between T3DF and Other Core Materials
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- T3DF had good energy absorption capacity, broad indentation hardness range, and higher Sf value, making it an appropriate material for a mattress that can serve both as padding and core layers.
- (2)
- As a padding layer, T3DF’s thickness and density had a significant impact on of the mattress. Using a thick and low-density T3DF proved to be a fitting option for enhancing the comfort of the mattress surface.
- (3)
- As a core layer, T3DF’s thickness and density had a notable impact on of the mattress, while their interaction effected the significantly. A thin T3DF core layer could achieve a softer surface and a firmer bottom of the mattress.
- (4)
- T3DF thickness was the main factor affecting mattress firmness, and the impact of thickness was related to its structural layer. For different structural layers, T3DF thickness should be selected reasonably based on the firmness requirements of the mattress.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwiatkowska, M.; Kowalczyk, I.; Rozwadowski, Z.; Piesowicz, E.; Szymczyk, A. Hytrel-like Copolymers Based on Furan Polyester: The Effect of Poly (Butylene Furanoate) Segment on Microstructure and Mechanical/Elastic Performance. Molecules 2023, 28, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Wu, D.; Xie, W.; Wang, Z.; Peng, S. Thermoplastic polyester elastomer composites containing two types of filler particles with different dimensions: Structure design and mechanical property control. Compos. Struct. 2018, 197, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslaniec, Z.; Pietkiewicz, D. Synthesis and Characteristics of Polyester-Based Thermoplastic Elastomers: Chemical Aspects: Sections 6–7. In Handbook of Thermoplastic Polyesters: Homopolymers, Copolymers, Blends, and Composites; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 629–658. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.; Kim, Y.; Yu, W.R.; Lee, J.U. Exfoliated graphene/thermoplastic elastomer nanocomposites with improved wear properties for 3D printing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 189, 107912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Chen, K.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Pan, Z.J. Facile and large-scale fabrication of self-crimping elastic fibers for large strain sensors. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yu, Z.; Yang, L.; Wen, S.; Zhang, Z.X. Development of thermoplastic polyether ester elastomer microcellular foam with high resilience: Effect of chain extension on foaming behavior and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Xin, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, R. Novel poly (vinylidene fluoride)/thermoplastic polyester elastomer composite membrane prepared by the electrospinning of nanofibers onto a dense membrane substrate for protective textiles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J. The relationship between sleep quality and mattress types. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting; SAGE Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 46, pp. 745–749. [Google Scholar]
- Huysmans, T.; Haex, B.; De Wilde, T.; Van Audekercke, R.; Vander Sloten, J.; Van der Perre, G. A 3D active shape model for the evaluation of the alignment of the spine during sleeping. Gait Posture 2006, 24, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.L.; Feng, Q.; Wong, M.S.; Ng, S.F.; Yummy, Y.M. Study of main and cross-over effects on pressure relief among body mass index (BMI), body position and supporting material properties. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 51, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Yu, C.; Li, H.; Li, M. Effects of mattress firmness on infant body pressure distribution. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2021, 83, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.L.; Jmal, H.; Dupuis, R.; Aubry, E. Visco-hyperelastic constitutive model for modeling the quasi-static behavior of polyurethane foam in large deformation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmal, H.; Dupuis, R.; Aubry, E. Quasi-static behavior identification of polyurethane foam using a memory integer model and the difference-forces method. J. Cell. Plast. 2011, 47, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardzewski, J. New construction of mattress springs. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, B.H.; Moghaddam, M.; Estrada, C.A. Mattress Coil Spring Fatigue and Weight-Bearing Support: Comparison of Weight-Bearing and Non–Weight-Bearing Springs. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2022, 45, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, N.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Effect of fiber surface treatment on structure, moisture absorption and mechanical properties of luffa sponge fiber bundles. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, Z.; Weng, B.; Dai, L.; Wu, S.; Su, N. Compression properties of two novel natural luffa mattress filling materials. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, F.Z.; Chua, M.C.H.; Lim, P.Y.; Yeow, C.H. Effects of mattress material on body pressure profiles in different sleeping postures. J. Chiropr. Med. 2017, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, B.H.; Boolani, A.; Dunklee, G.; Shepardson, A.; Acharya, H. Effect of prescribed sleep surfaces on back pain and sleep quality in patients diagnosed with low back and shoulder pain. Appl. Ergon. 2010, 42, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Wang, S.T.; Lin, P.C.; Liu, C.L.; Chao, Y.F.C. Effects of using a high-density foam pad versus a viscoelastic polymer pad on the incidence of pressure ulcer development during spinal surgery. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2011, 13, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-Y.; Wang, M.-J. Better combination of thickness and hardness of mattress topper for supine sleeping posture: A physiological measurements evaluation. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2020, 78, 102979. [Google Scholar]
- Nagamachi, M.; Ishihara, S.; Nakamura, M.; Morishima, K. Development of a pressure-ulcer-preventing mattress based on ergonomics and Kansei engineering. Geronechnol. Int. J. Fundam. Asp. Technol. Serve Ageing Soc. 2013, 11, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamachi, M. Kansei engineering: A new ergonomic consumer-oriented technology for product development. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 1995, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Ishihara, K.; Nagamachi, M. Finite element estimation of pressure distribution inside the trunk on a mattress. Int. J. Autom. Smart Technol 2015, 5, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, S.; Yagi, T.; Ozone, M.; Matsumura, M.; Sekiguchi, H.; Ganeko, M.; Uchida, S.; Nishino, S. High rebound mattress toppers facilitate core body temperature drop and enhance deep sleep in the initial phase of nocturnal sleep. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmal, H.; Ju, M.L.; Dupuis, R.; Aubry, E. Generalization of the memory integer model for the analysis of the quasi-static behaviour of polyurethane foams. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 4651–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Czubernat, K.; Jin, S.Y.; Altenhof, W.; Maeva, E.; Seviaryna, I.; Bandyopadhyay-Ghosh, S.; Sain, M.; Gu, R. Mechanical response of hard bio-based PU foams under cyclic quasi-static compressive loading conditions. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 59, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, H.; Li, X. A novel method for comfort assessment in a supine sleep position using three-dimensional scanning technology. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2018, 67, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.M.; Magkiriadis, I.; Harrigan, J.J. Compressive strain at the onset of densification of cellular solids. J. Cell. Plast. 2006, 42, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, J.S. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) geofoam: An introduction to material behavior. Geotext. Geomembr. 1994, 13, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltz, J.; Gruenbaum, G. Evaluation of cushioning properties of plastic foams from compressive measurements. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1981, 21, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E 2439:2008; Flexible Cellular Polymeric Materials—Determination of Hardness (Indentation Technique). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- 23769:2021; Furniture—Beds and Mattresses—Test Methods for the Determination of Functional Characteristics and Assessment Criteria. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Wong, D.W.C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tan, Q.; Chen, T.L.W.; Zhang, M. Sleeping mattress determinants and evaluation: A biomechanical review and critique. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe, S.; Ryan, M.; McShane, G.; Theobald, P. Energy absorbing characteristics of additively manufactured TPE cellular structures. InImpact J. Innov. Impact 2016, 8, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.T.; Xing, M.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.Y.; Fu, C.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.H. Nitrogen/phosphorus synergistic flame retardant-filled flexible polyurethane foams: Microstructure, compressive stress, sound absorption, and combustion resistance. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21192–21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, S.; Wang, Q.; Tanaka, Y.; Kagawa, Y. Compressive mechanical properties of closed-cell aluminum foam–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 64, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Weng, B.; Wu, S.; Chen, T.; Chen, Y. Effect of chemical treatments on the properties of high-density Luffa mattress filling materials. Materials 2019, 12, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarfato, P.; Di Maio, L.; Incarnato, L. Structure and physical-mechanical properties related to comfort of flexible polyurethane foams for mattress and effects of artificial weathering. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 109, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, L. Determination of pressure indices to characterize the pressure-relief property of spacer fabric based on a pressure pad system. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Shi, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yue, H.; Ni, Z.; Sha, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of mattress bedding layer structure on pressure relief performance and subjective lying comfort. J. Tissue Viability 2023, 32, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquirol Caussa, J.; Palmero Cantariño, C.; Bayo Tallón, V.; Cos Morera, M.À.; Escalera, S.; Sánchez, D.; Sánchez Padilla, M.; Serrano Domínguez, N.; Relats Vilageliu, M. Automatic RBG-depth-pressure anthropometric analysis and individualised sleep solution prescription. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2017, 41, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, A.; Ohno, N.; Miyati, T.; Okuwa, M.; Nakatani, T.; Sanada, H.; Sugama, J. Investigation of effects of urethane foam mattress hardness on skin and soft tissue deformation in the prone position using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Tissue Viability 2019, 28, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
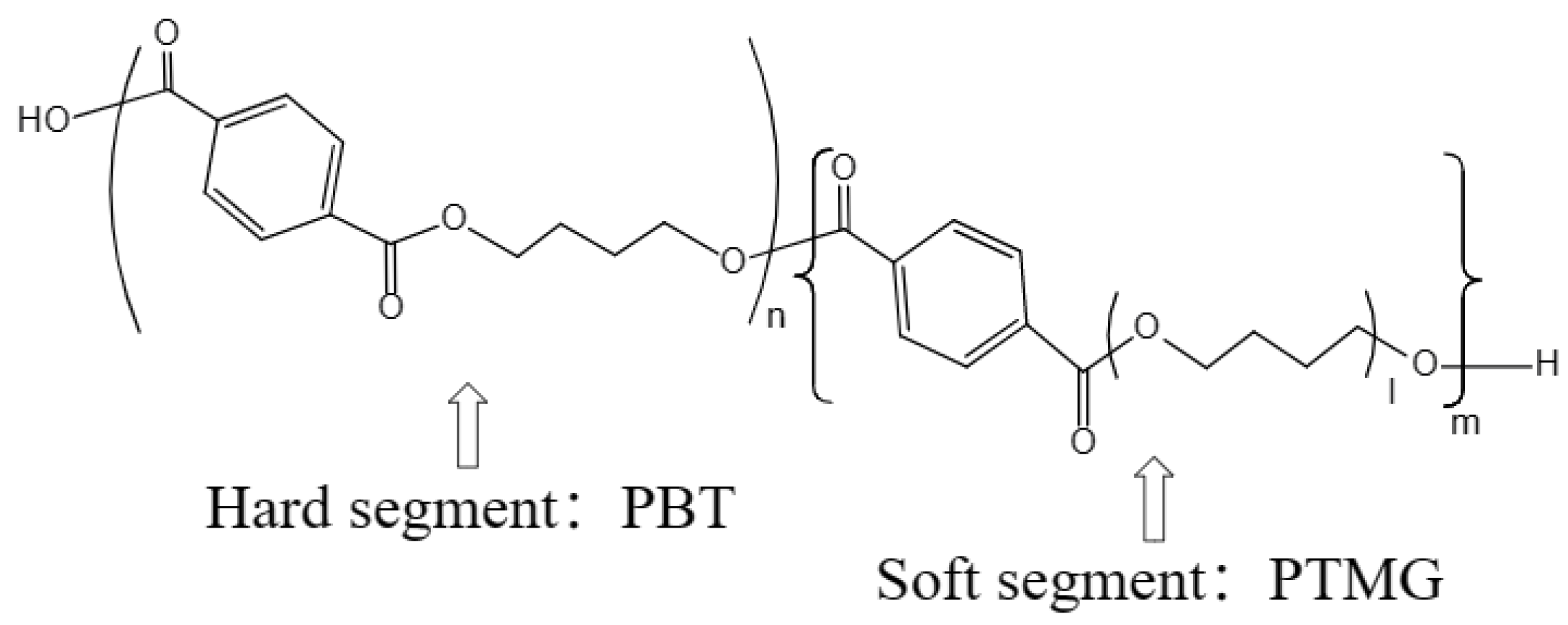
















| Material | Density (kg·m−3) | Other Parameters | Thickness (mm) | Mattress Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPEE-3D fibrous material (T3DF) | 45\55\65\75 | - | 20 | Padding layer |
| 40 | Padding layer/Core layer | |||
| 60 | Core layer | |||
| 80 | Core layer | |||
| Latex foam (LF) | 25 | 80% latex content | 40 | Padding layer |
| Polyurethane foam (PU) | 25 | - | 40 | Padding layer |
| Pocketed spring (PS) | - | 2.0 60 6 1 | 80 | Core layer |
| 2.1 60 6 |
| Density/kg·m−3 | 25% IFD 1/N | 40% IFD/N | 65% IFD/N | Sf 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 81.8 ± 8.8 3 | 127 ± 12 | 359 ± 35 | 4.4 ± 0.6 |
| 55 | 89.3 ± 8.2 | 131 ± 11 | 334 ± 24 | 3.7 ± 0.3 |
| 65 | 119 ± 14 | 182 ± 20 | 361 ± 28 | 3.0 ± 0.2 |
| 75 | 218 ± 15 | 334 ± 33 | 611 ± 82 | 2.8 ± 0.3 |
| Material | 25% IFD/N | 40% IFD/N | 65% IFD/N | Sf |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PU | 132 ± 11 | 155 ± 13 a 1 | 320 ± 27 | 2.4 ± 0.2 b |
| LF | 69.3 ± 6.5 | 134 ± 11 b | 386 ± 30 | 5.6 ± 0.7 a |
| T3DF 45 | 81.8 ± 8.8 | 127 ± 12 b | 359 ± 35 | 4.4 ± 0.6 a |
| Source | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 16.222 | <0.001 |
| Thickness | 30.583 | <0.001 |
| Density × Thickness | 1.446 | 0.148 |
| Density | Thickness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Hardness value | 6.592 | <0.001 | 8.061 | <0.001 |
| Firmness rating | 7.125 | <0.001 | 8.410 | <0.001 |
| 9.834 1 | <0.001 | 14.849 | 0.001 | |
| 1.865 | 0.155 | 1.274 | 0.267 | |
| 9.354 | <0.001 | 9.044 | 0.005 | |
| Source | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 22.220 | <0.001 |
| Thickness | 208.981 | <0.001 |
| Density × Thickness | 7.543 | <0.001 |
| Density | Thickness | Density × Thickness | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Hardness value | 3.117 | 0.024 | 165.874 | <0.001 | 1.948 | 0.319 |
| Firmness rating | 8.460 | <0.001 | 120.692 | <0.001 | 2.156 | 0.076 |
| 8.241 | 0.037 | 262.161 | 0.007 | 0.829 | 0.554 | |
| 3.065 | <0.001 | 5.568 | <0.001 | 15.625 | <0.001 | |
| 24.824 1 | <0.001 | 483.464 | <0.001 | 3.860 | 0.003 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, J.-J.; Shen, L.-M. Compression Property of TPEE-3D Fibrous Material and Its Application in Mattress Structural Layer. Polymers 2023, 15, 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183681
Fang J-J, Shen L-M. Compression Property of TPEE-3D Fibrous Material and Its Application in Mattress Structural Layer. Polymers. 2023; 15(18):3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183681
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Jiao-Jiao, and Li-Ming Shen. 2023. "Compression Property of TPEE-3D Fibrous Material and Its Application in Mattress Structural Layer" Polymers 15, no. 18: 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183681
APA StyleFang, J.-J., & Shen, L.-M. (2023). Compression Property of TPEE-3D Fibrous Material and Its Application in Mattress Structural Layer. Polymers, 15(18), 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183681






