Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Blended with Chitosan: A Potential Single-Use Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning of CS and PET
2.3. Electrospinning of Blended Polymers
2.4. Solubility Test
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
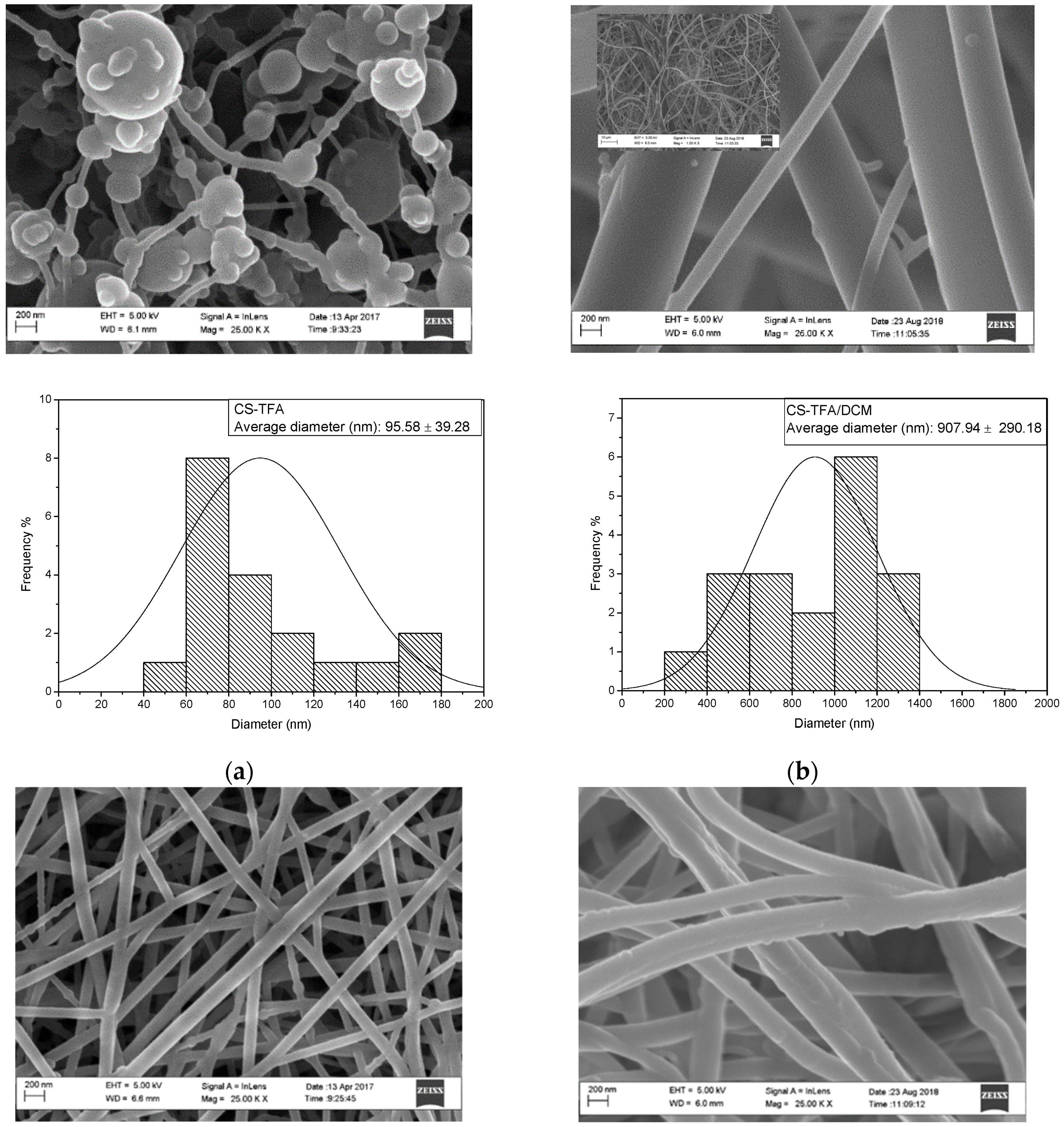
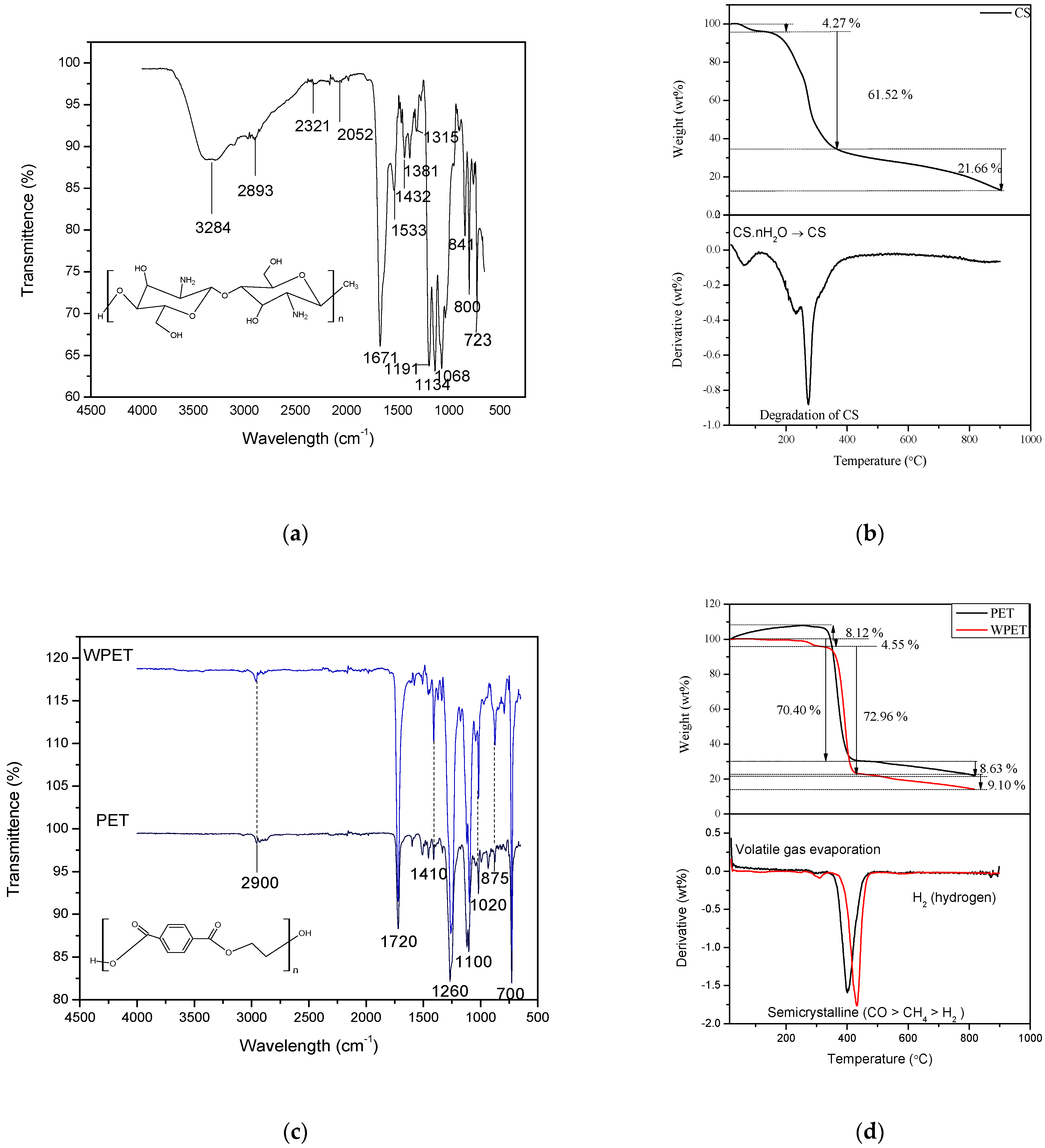
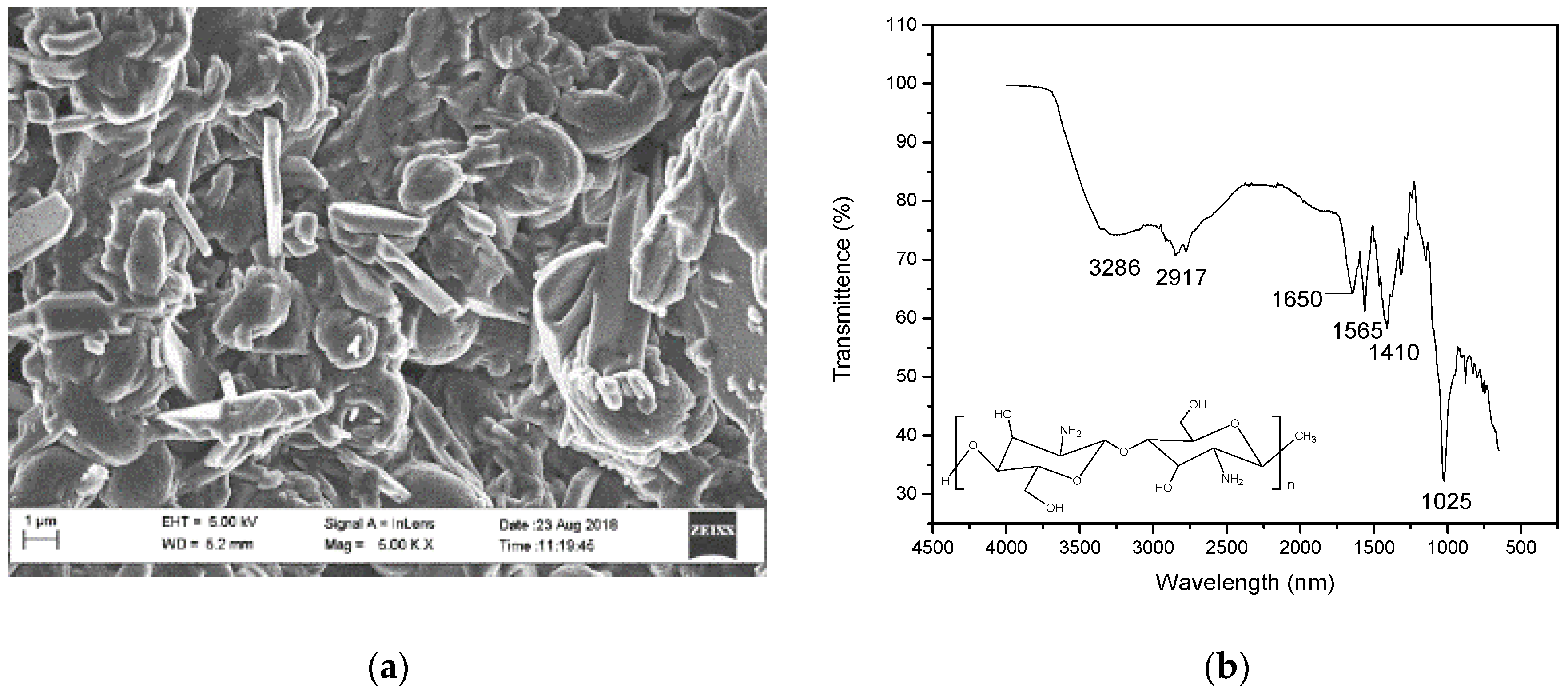
3.1. Characterization of Electrospun CS, PET, WPET, CS-PET, and CS-WPET Nanofibers
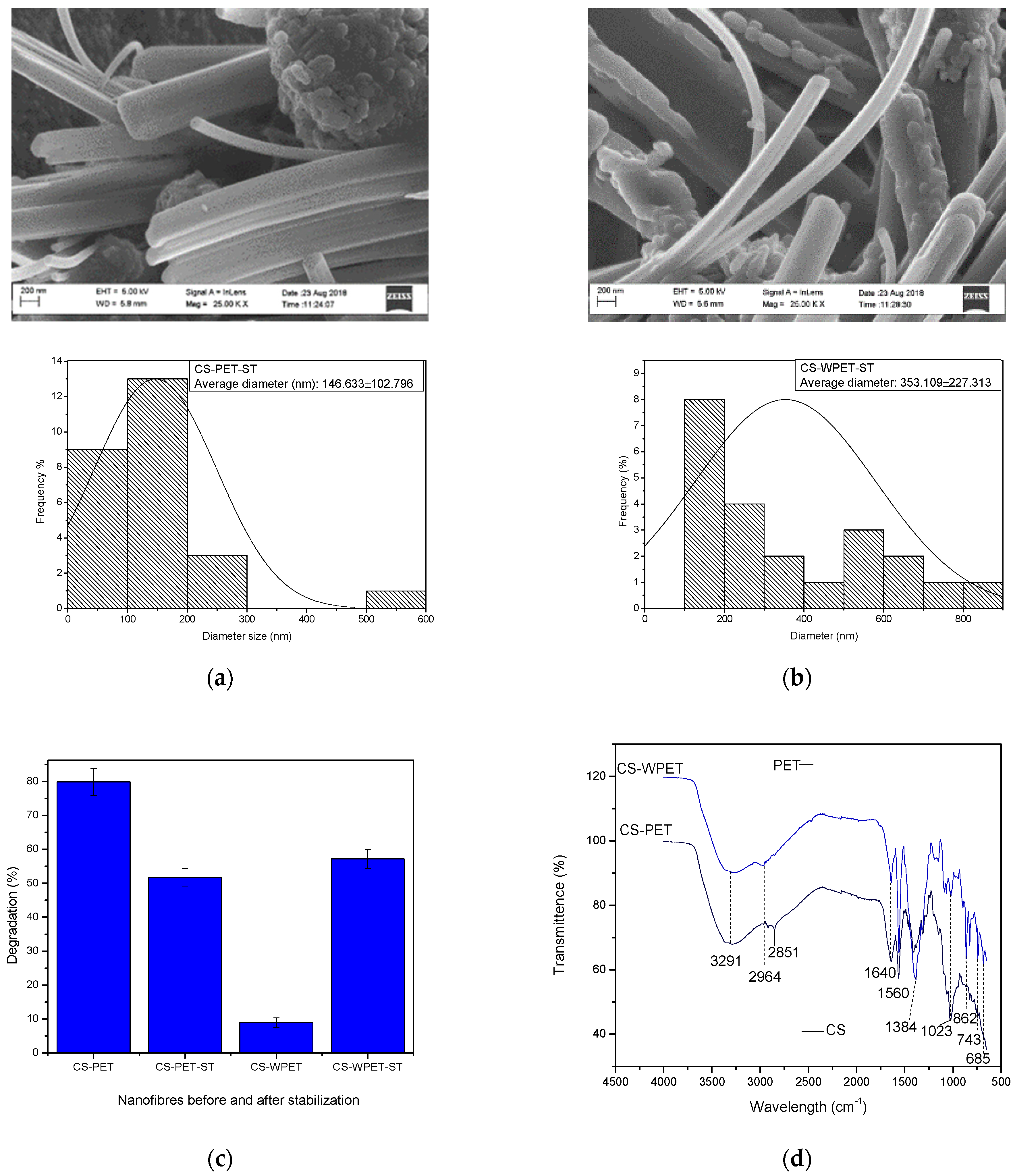
3.2. Nanofibers Solubility
- 10 mL of 3 M of NaOH solution in methanol;
- K2CO3 solution and ethanol solvent for 120 min.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Letcher, M. Introduction to Plastic Waste and Recycling. Plastic Waste and Recycling; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourshed, M.; Masud, M.H.; Rashid, F.; Joardder, M.U.H. Towards the effective plastic waste management in Bangladesh: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27021–27046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briain, O.Ό.; Mendes, A.R.; McCarron, S.; Healy, M.G.; Morrison, L. The role of wet wipes and sanitary towels as a source of white microplastic fibres in the marine environment. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, M. London’s fatbergs and effective infrastructuring. Soc. Stud. Sci. 2020, 50, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.L. Causes, Effects and Solutions of Operational Problems in Wastewater Systems due to Nonwoven Wet Wipes. Ph.D. Thesis, Berlin Institute of Technology, Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal, A.; Singh, S.K. Removal of heavy metals by nanoadsorbents: A review. J. Environ. Biotechnol. Res. 2017, 6, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Queen, H. Electrospinning Chitosan-based Nanofibres for Biomedical Applications. Text. Eng. 2006, 7, 2742–2750. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Li, Z.H. Preparations, properties and applications of chitosan-based nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenares, J.C.; Varma, R.S.; Lisowski, P. Sustainable hybrid photocatalysts: Titania immobilized on carbon materials derived from renewable and biodegradable resources. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5736–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereao, O.K.; Bode-Aluko, C.; Ndayambaje, G.; Fatoba, O.; Petrik, L.F. Electrospinning: Polymer Nanofibre Adsorbent Applications for Metal Ion Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Cha, D.; Kim, H.; Nishida, A.; Yamamoto, H. Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Minato, K.I.; Kumagai, G.; Hayashi, S.; Yamamoto, H. Chitosan nanofibre. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3291–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Gámiz-González, M.A.; Botelho, G.; Vidaurre, A.; Gomez Ribelles, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Sencadas, V. Effect of neutralization and cross-linking on the thermal degradation of chitosan electrospun membranes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 117, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totito, T.C.; Laatikainen, K.; Pereao, O.; Bode-Aluko, C.; Petrik, L. Adsorptive recovery of Cu2+ from aqueous solution by PET or WPET nanofibres modified with SiAMPy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbs, A.; Porter, D.W.; Mercer, R.; Castranova, V.; Sargent, L.; Sriram, K. Nanoparticulates. In Haschek and Rousseaux’s Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1373–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L. A Novel Eco-Friendly Vanadium Precipitation Method by Hydrothermal Hydrogen Reduction Technology. Minerals 2017, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espíndola-González, A.; Martínez-Hernández, A.L.; Fernández-Escobar, F.; Castaño, V.M.; Brostow, W.; Datashvili, T.; Velasco-Santos, C. Natural-Synthetic hybrid polymers developed via electrospinning: The effect of PET in chitosan/starch system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnals, G.L.; DeBarr, J.A.; Rostam-Abadi, M.; Lizzio, A.A.; Brady, T.A. Application of Thermal Analysis Techniques in Activated Carbon Production. Prepr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Fuel Chem. 1996, 41, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Biazar, E.; Ahmadian, M.; Saeed Heidari, K.; Gazmeh, A.; Mohammadi, S.-F.; Lashay, A.; Hashemi, H. Electro-spun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) mat as a keratoprosthesis skirt and its cellular study. Fibres Polym. 2017, 18, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Sánchez, M.A.; Chinchillas -Chinchillas, M.J.; Gaxiola, A.; Alvarado-Beltrán, C.G.; Hurtado-Macías, A.; Orozco-Carmona, V.M.; Almaral-Sánchez, J.L.; Sepúlveda-Guzmán, S.; Castro-Beltrán, A. The Use of Recycled PET for the Synthesis of New Mechanically Improved PVP Composite Nanofibres. Polymers 2022, 14, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, M.; Fornari, R.; de Voogt, P.; Franz, R. Migration of oligomers from PET: Determination of diffusion coefficients and comparison of experimental versus modelled migration. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLachlan, N.J.; Dubovi, E.J. Fenner’s Veterinary Virology; Elsevier B.V: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 5, pp. 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, G.T.; Sanzana, J.; Mei, L.H.I. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan-PHB Blends. Bol. Soc. Chil. Quím. 2002, 47, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yu, S. Solid-film sampling method for the determination of protein secondary structure by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4459–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumirska, J.; Czerwicka, M.; Kaczyński, Z.; Bychowska, A.; Brzozowski, K.; Thöming, J.; Stepnowski, P. Application of Spectroscopic Methods for Structural Analysis of Chitin and Chitosan. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1567–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnaveni, B.; Ragunathan, R. Extraction and characterization of chitin and chitosan from F.Solani CBNR BKRR, synthesis of their bionanocomposites and study of their productive application. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Wang, F.Y.; Mao, C.F.; Liao, W.T.; Hsieh, C.D. Studies of chitosan: II. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/gelatin ternary blend films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Britto, D.; Campana-Filho, S.P. Kinetics of the thermal degradation of chitosan. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 465, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, J.; Liu, F.; Majeed, H.; Zhong, F. Characterization of tara gum ediblefilms incorporated with bulk chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler-Borowska, M.; Chełminiak, D.; Kaczmarek, H.; Kaczmarek-Kędziera, A. Effect of side substituents on thermal stability of the modified chitosan and its nanocomposites with magnetite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 124, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Hefian, E.A.; Nasef, M.M.; Yahaya, A.H. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/Agar Blended Films: Part 2. Thermal, Mechanical, and Surface Properties. J. Chem. 2012, 9, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Strain, I.N.; Wu, Q.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Olsson, R.T.; Andersson, R.L. Electrospinning of recycled PET to generate tough mesomorphic fibre membranes for smoke filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín, D.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Rodríguez, M.; García, M.A.; Faccini, M. Aminated Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) nanofibres for the selective removal of Pb(II) from polluted water. Materials 2017, 10, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Ke, H.; Zhang, T.; Dong, J.; Qiao, H.; Wang, H.; Fong, H. Preparation, Morphology and Properties of Electrospun Lauric Acid/PET Form-Stable Phase Change Ultrafine Composite Fibres. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2011, 19, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, P. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) A Beginner’s Guide; PerkinElmer: Waltham, MA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Tiwari, P. Thermal degradation study of waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) under inert and oxidative environments. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 679, 178340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Şimşek, M.; Aldemir, S.D.; Kazaroǧlu, N.M.; Gumuşderelioǧlu, M. Honey-based PET or PET/chitosan fibrous wound dressings: Effect of honey on electrospinning process. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, E.; Prabu, K. Isolation and FTIR spectroscopy characterization of chitin from local sources. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar]
- Shirsat, N.D.; Momin, P.S.A.; Bandekar, A.A.; Sayed, U. Synthesis of Water Soluble Chitosan from Marine Waste and Its Application in Wet Wipes Formulations. Asian J. Res. Chem. 2012, 5, 4169. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, S.; Park, S. Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibres and their applications to the adsorption of Cu (II) and Pb (II) ions from an aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, C.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, C.H.I. Fabrication of sonicated chitosan nanofibre mat with enlarged porosity for use as hemostatic materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suwannamek, N.; Srikulkit, K. Properties of Binary and Ternary Composites of Polypropylene Containing Soybean Oil-g-Chitosan and Hydrophobic Phosphonated Silica Properties of Binary and Ternary Composites of Polypropylene Containing Soybean Oil-g-Chitosan and Hydrophobic Phosphonated. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2015, 25, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.A.A.; Haider, S.; Al-Masry, W.A.; Al-Zeghaye, Y. Fabrication of chitosan nanofibres membrane and its treatment. Coll. Eng. King Saud Univ. 2013, 1–4. Available online: www.jeaconf.org/UploadedFiles/.../a2a3a6d5-6810-4b3e-93a0-09140c4740c4.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2019).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Totito, T.C.; Laatikainen, K.; Bode-Aluko, C.; Pereao, O.; Petrik, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Blended with Chitosan: A Potential Single-Use Material. Polymers 2023, 15, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020442
Totito TC, Laatikainen K, Bode-Aluko C, Pereao O, Petrik L. Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Blended with Chitosan: A Potential Single-Use Material. Polymers. 2023; 15(2):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020442
Chicago/Turabian StyleTotito, Thandiwe Crystal, Katri Laatikainen, Chris Bode-Aluko, Omoniyi Pereao, and Leslie Petrik. 2023. "Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Blended with Chitosan: A Potential Single-Use Material" Polymers 15, no. 2: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020442
APA StyleTotito, T. C., Laatikainen, K., Bode-Aluko, C., Pereao, O., & Petrik, L. (2023). Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Blended with Chitosan: A Potential Single-Use Material. Polymers, 15(2), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020442





