Design and Fabrication of Polymer Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Insole Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
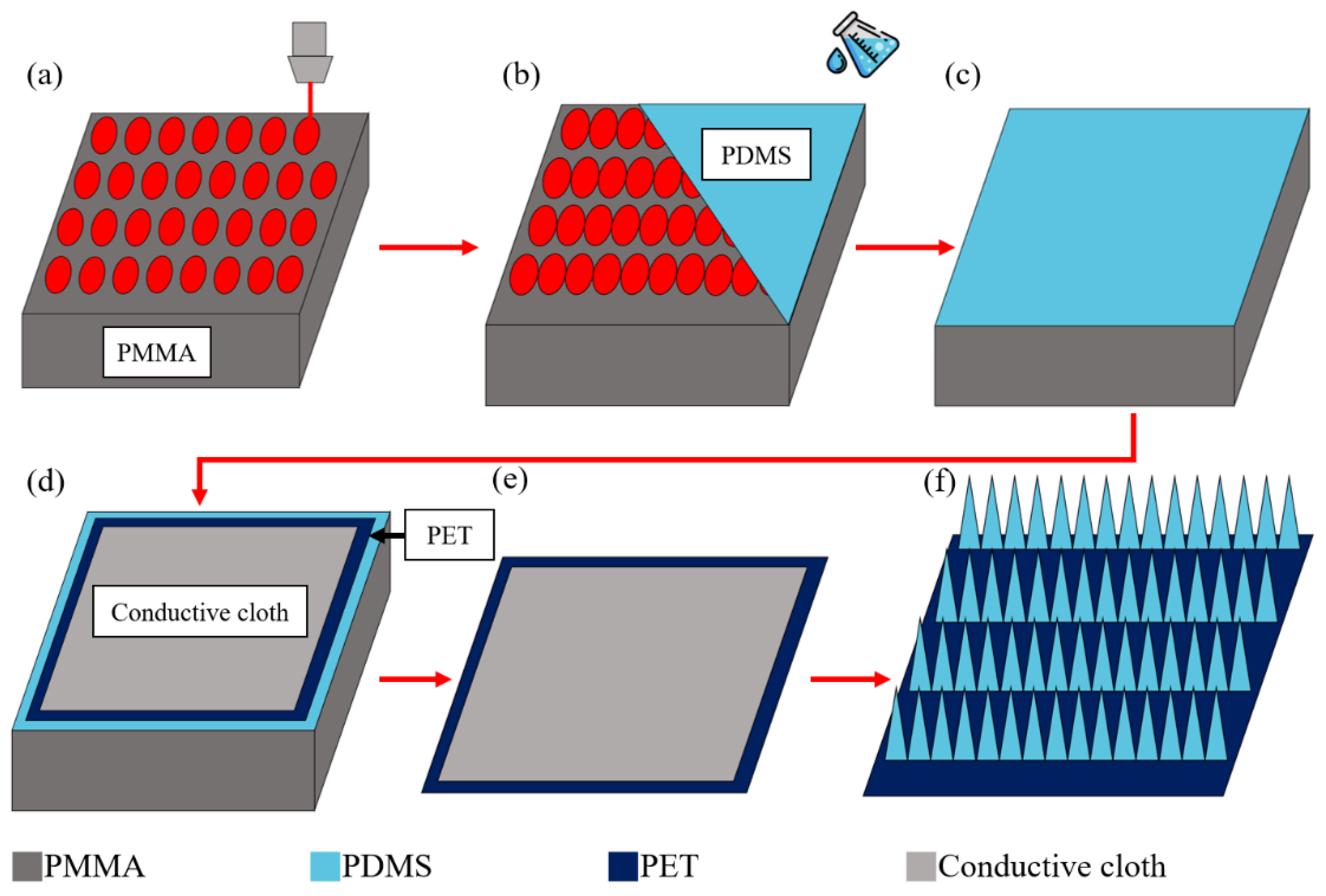
2.1. The Material Selection and Fabrication of PDMS-TENGs
2.2. Experiment and Measurement of MN-PDMS-TENG
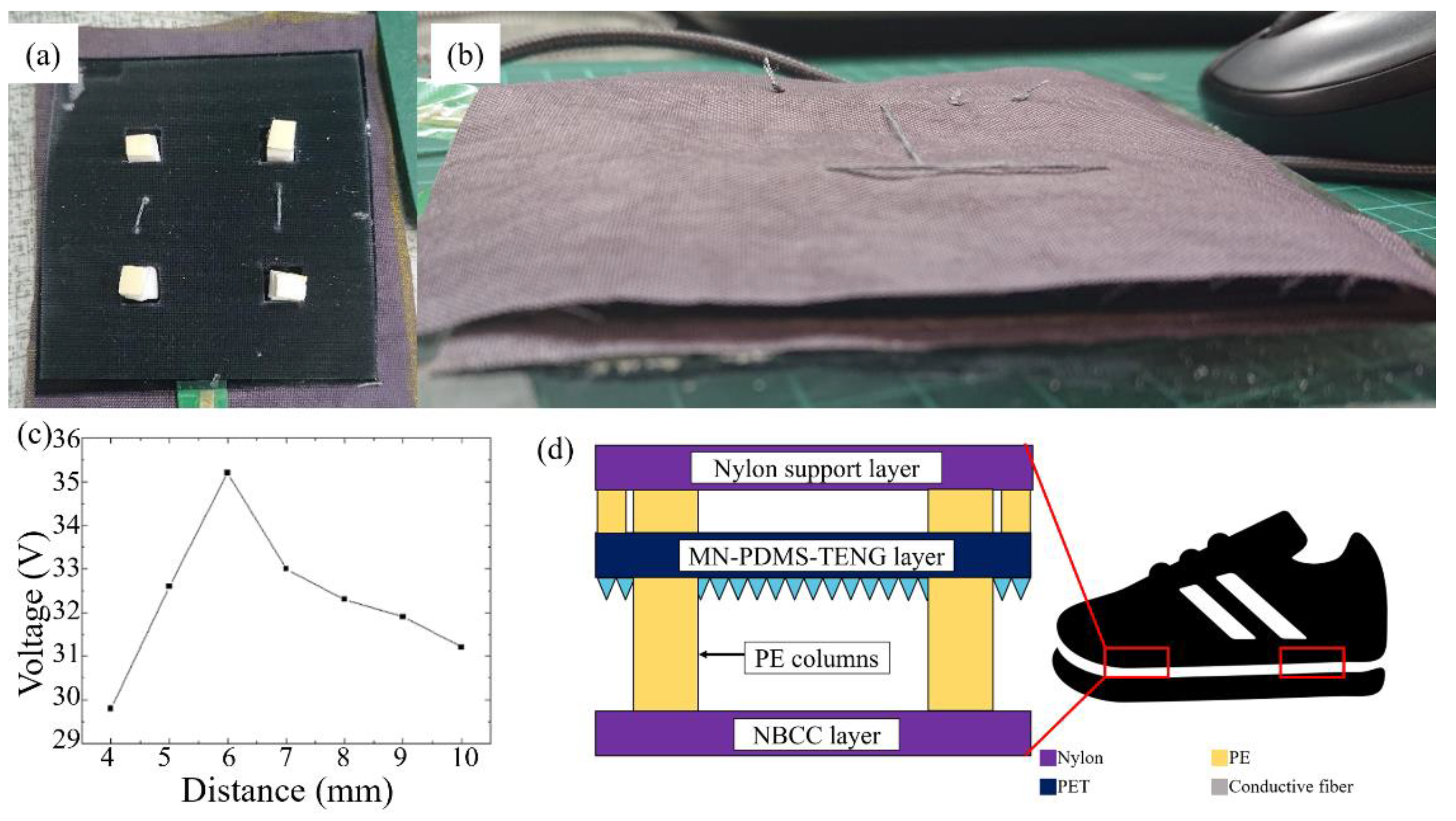
2.3. The Experiment and Measurement of PDMS-TENG and PDMS-TENG Insole
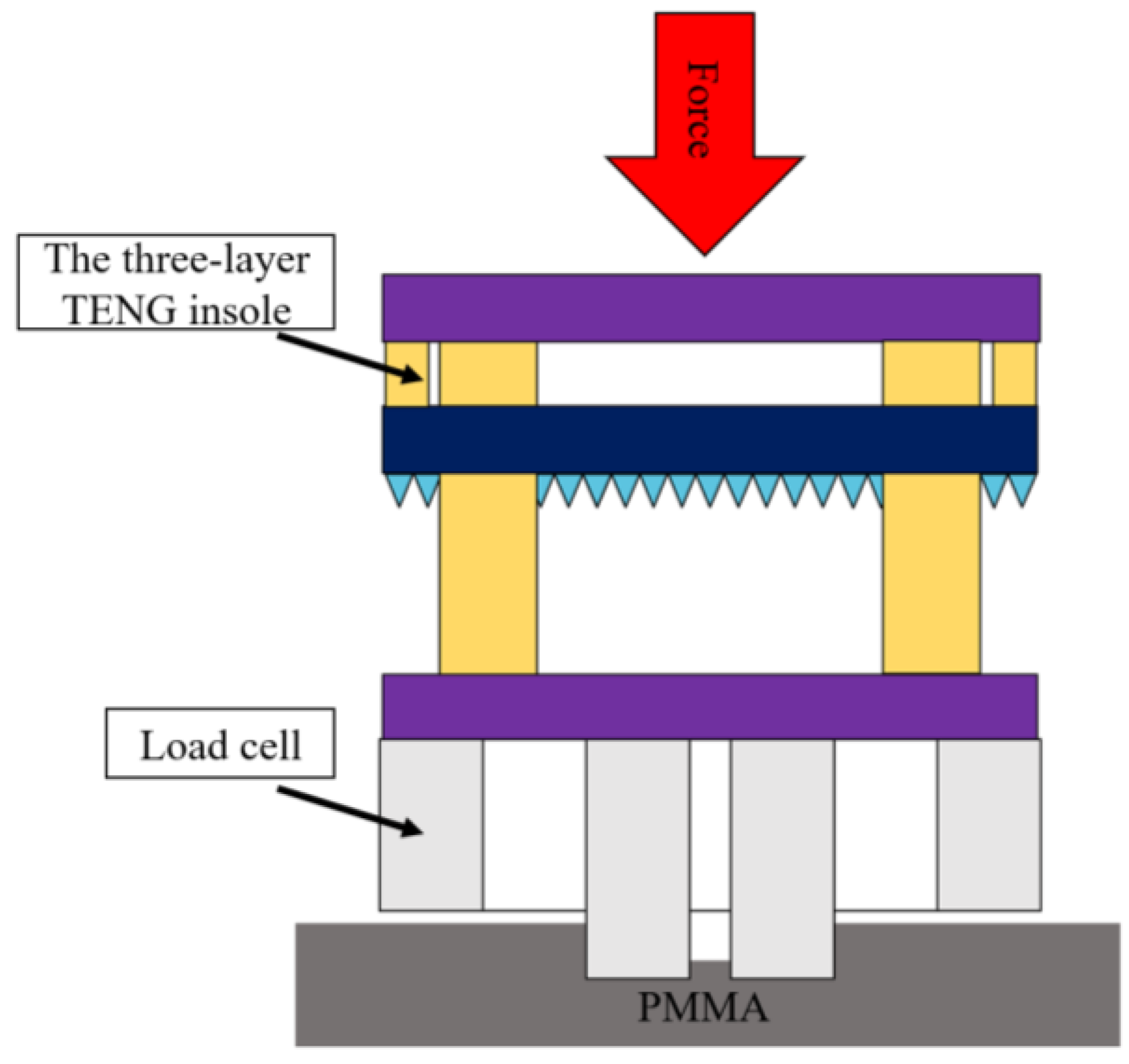
2.4. The Design and Process of the Three-Layer TENG Insole
3. Results and Discussion
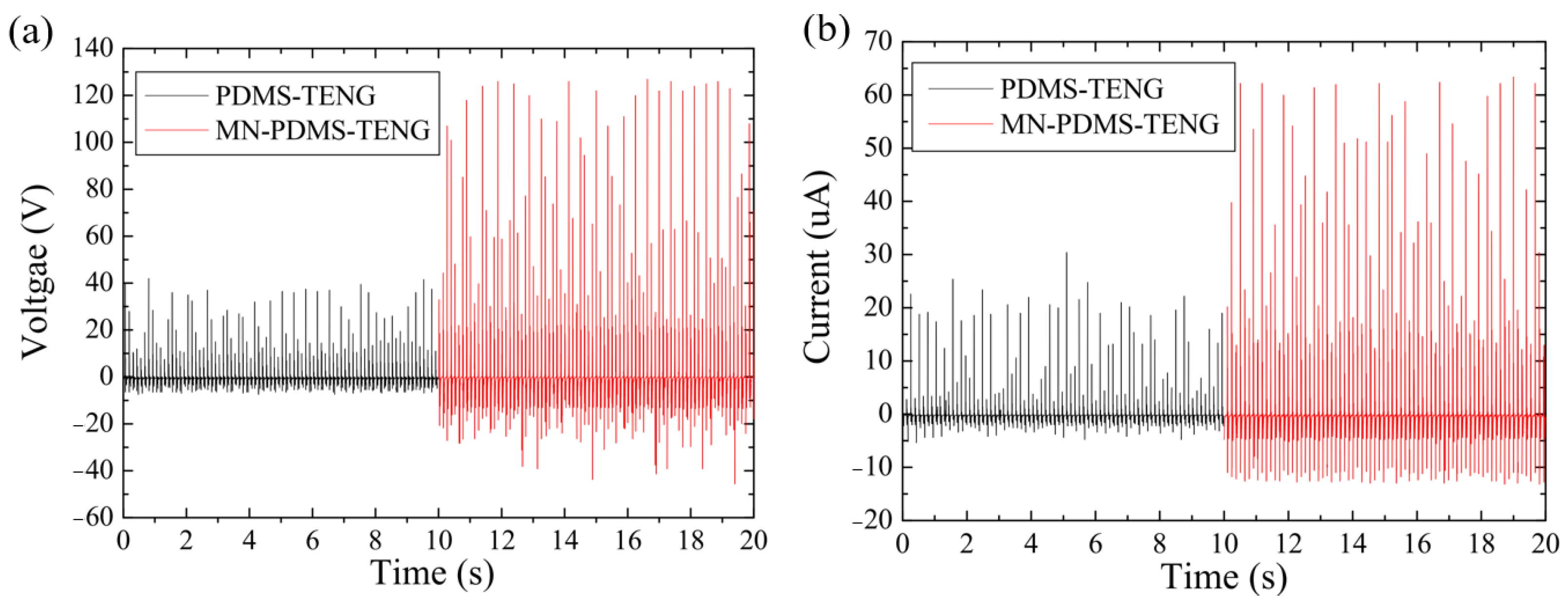
3.1. The Electric Output Performance of MN-PDMS-TENG
3.2. The Electric Output Performance of the Three-Layer TENG Insole
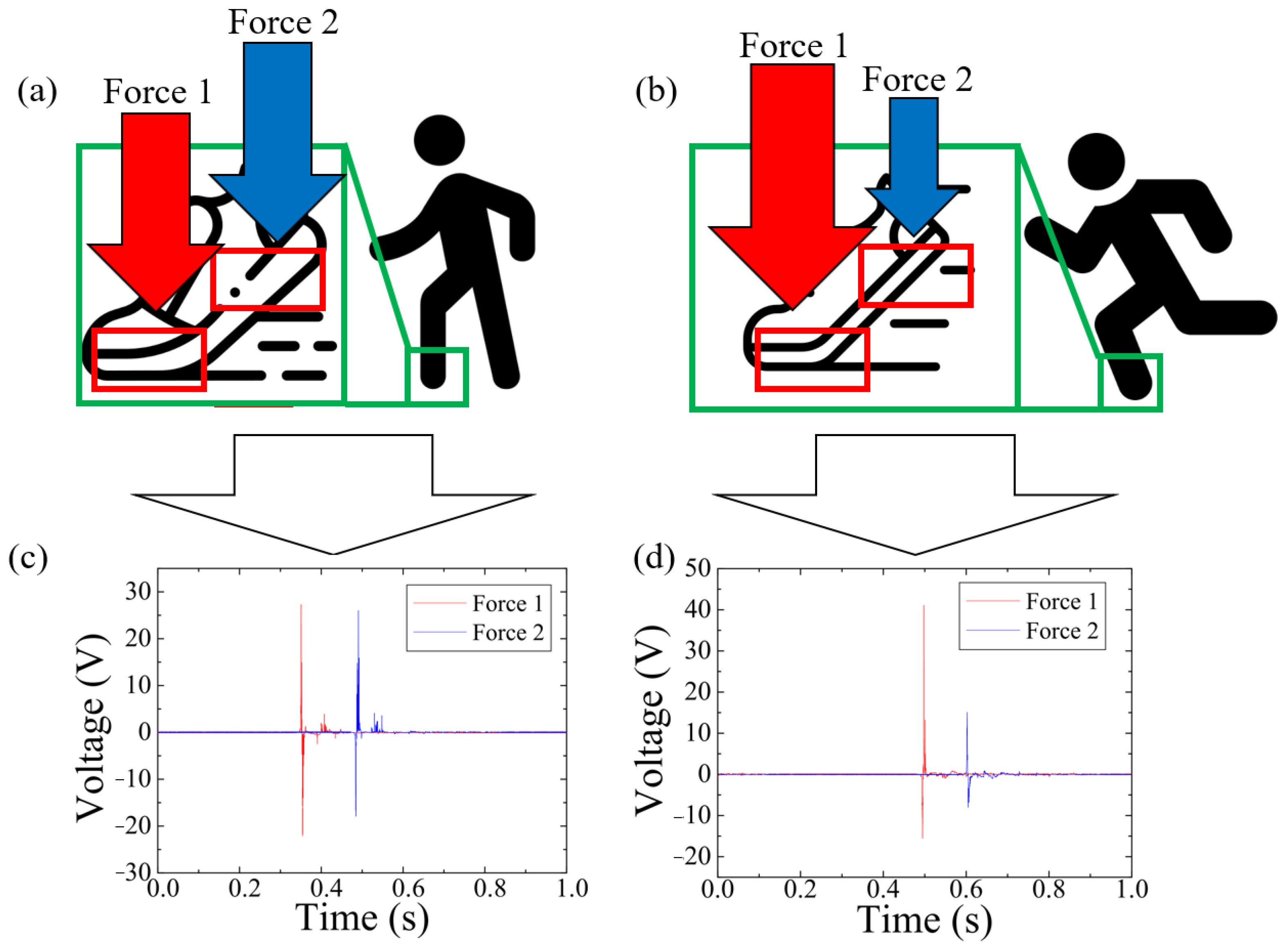
3.3. Human Walking and Running Force Detection
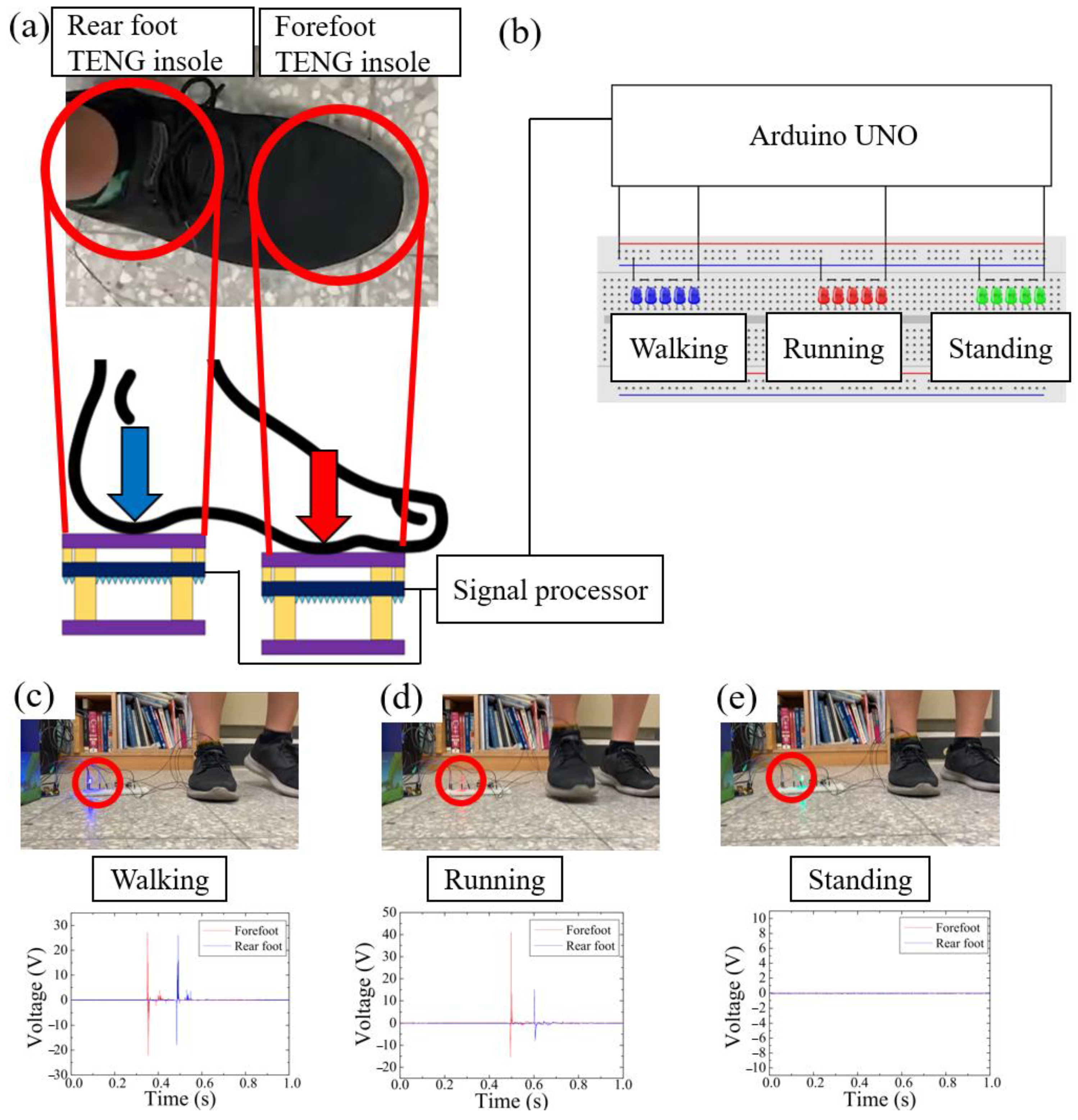
3.4. Human Stepping State Sensing System with the Three-Layer TENG Insole
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology for self-powered systems and as active mechanical and chemical sensors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9533–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.L. A dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerator for wind energy harvesting and self-powered wind speed monitoring. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6244–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, T.; Wu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, D. Triboelectric nanogenerator with a seesaw structure for harvesting ocean energy. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nazar, A.; Wang, J.; Xia, K.; Wang, D.; Ji, X.; Jiao, P. Rolling Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerators (RS-TENG) under Low-Frequency Ocean Wave Action. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Peng, W.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.; Zi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. All-elastomer-based triboelectric nanogenerator as a keyboard cover to harvest typing energy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7973–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Xie, Y.; Long, J.; Zhao, P.; Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Dong, S. A self-power-transmission and non-contact-reception keyboard based on a novel resonant triboelectric nanogenerator (R-TENG). Nano Energy 2018, 50, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lai, C.L.; Xu, B.; So, M.Y.; Li, Z. Fabric-rebound triboelectric nanogenerators with loops and layered structures for energy harvesting and intelligent wireless monitoring of human motions. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Human walking-driven wearable all-fiber triboelectric nanogenerator containing electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric nanofibers. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Raj, N.P.; Kim, S.J. Materials beyond conventional triboelectric series for fabrication and applications of triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybridized electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerator for scavenging biomechanical energy for sustainably powering wearable electronics. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3521–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appamato, I.; Bunriw, W.; Harnchana, V.; Siriwong, C.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Thongbai, P.; Chanthad, C.; Chompoosor, A.; Ruangchai, S.; Prada, T.; et al. Engineering Triboelectric Charge in Natural Rubber–Ag Nanocomposite for Enhancing Electrical Output of a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 15, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, R.; Huang, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, H. Copper particles-PTFE tube based triboelectric nanogenerator for wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Sun, S.; Jiang, D.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Advances in triboelectric nanogenerator powered electrowetting-on-dielectric devices: Mechanism, structures, and applications. Mater. Today 2022, 58, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Cao, Y.; Qu, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, W.; Pu, X.; Li, Z. Hybrid nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting, motion state detection, and pulse sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijoy, K.V.; John, H.; Saji, K.J. Self-powered ultra-sensitive millijoule impact sensor using room temperature cured PDMS based triboelectric nanogenerator. Microelectron. Eng. 2022, 251, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Shin, J.; Yoon, J.; Lim, K.H.; Sim, G.D.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, J. Three-dimensional skin-type triboelectric nanogenerator for detection of two-axis robotic-arm collision. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, V.L.; Chung, C.K. A Facile Method and Novel Mechanism Using Microneedle-Structured PDMS for Triboelectric Generator Applications. Small 2017, 13, 1700373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, V.L.; Chung, C.K. Harvesting mechanical energy, storage, and lighting using a novel PDMS based triboelectric generator with inclined wall arrays and micro-topping structure. Appl. Energy 2018, 213, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Tao, B.; Yin, Z.; Wu, H. Multidimensional force sensors based on triboelectric nanogenerators for electronic skin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56320–56328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.; Xu, Y.; Cochran, P.; Gadegaard, N.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Dahiya, R. Origin of the contact force-dependent response of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, T. Self-powered flow sensing for automobile based on triboelectric nanogenerator with magnetic field modulation mechanism. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munirathinam, P.; Chandrasekhar, A. Self-Powered Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Security Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Dai, X.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, L.B. Self-powered high-resolution smart insole system for plantar pressure mapping. BMEMat 2023, 1, e12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Lan, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hossain, G.; Grabher, G.; Sun, J. A stretchable and helically structured fiber nanogenerator for multifunctional electronic textiles. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Power-generating shoe insole based on triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered consumer electronics. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, T.K.; Lo, Y.L. Fiber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Mechanical Energy Harvesting and Its Application to a Human-Machine Interface. Sensors 2022, 22, 9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Ren, L.; Xue, H.; Li, B.; Niu, S.; Ren, L. Reconfigurable Fiber Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Defect Detection. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 7721–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, M.; Qiu, Q.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Multilayered fiber-based triboelectric nanogenerator with high performance for biomechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, L.; Wen, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Wei, A.; Sun, X. Coaxial triboelectric nanogenerator and supercapacitor fiber-based self-charging power fabric. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42356–42362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Xu, B.; Gao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. Breathable fabric-based triboelectric nanogenerators with open-porous architected polydimethylsiloxane coating for wearable applications. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.C.; Guo, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A triboelectric nanogenerator-based smart insole for multifunctional gait monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material | Voc | Isc | Power | LEDs | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMPA-cotton | 85.4 V | 2.32 μA | 348.5 μW/m | 30 | [27] |
| Cu-CNT-Silicone | 140 V | 7.5 µA m–1 | 5.5 µW | X | [28] |
| CA-PES-PS+C-PS | 115.2 V | 9.21 μA, | X | 60 | [29] |
| H3PO4/PVA-silicone-carbon fiber-silicone | 42.9 V | 0.51 μA | ∼1.12 μW | 1 | [11] |
| PET-MN-PDMS-Al | 73.6 V | 36.00 μA | 1.296 mW 0.264 W/m2 | 90 | Previous work [25] |
| PET-MN-PDMS-Al | 129.2 V | 64.00 μA | 4.10 mW 1.14 W/m2 | 120 | This research |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-J.; Chung, C.-K. Design and Fabrication of Polymer Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Insole Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204035
Huang Y-J, Chung C-K. Design and Fabrication of Polymer Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Insole Applications. Polymers. 2023; 15(20):4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204035
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, You-Jun, and Chen-Kuei Chung. 2023. "Design and Fabrication of Polymer Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Insole Applications" Polymers 15, no. 20: 4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204035
APA StyleHuang, Y.-J., & Chung, C.-K. (2023). Design and Fabrication of Polymer Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Insole Applications. Polymers, 15(20), 4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204035







