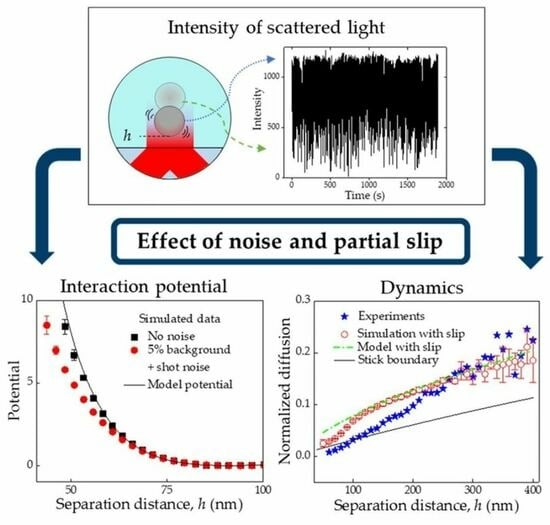
Analysing Sources of Error in Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (TIRM) Experiments and Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Interaction Potential Measurements by TIRM
2.1.1. Theoretical Background
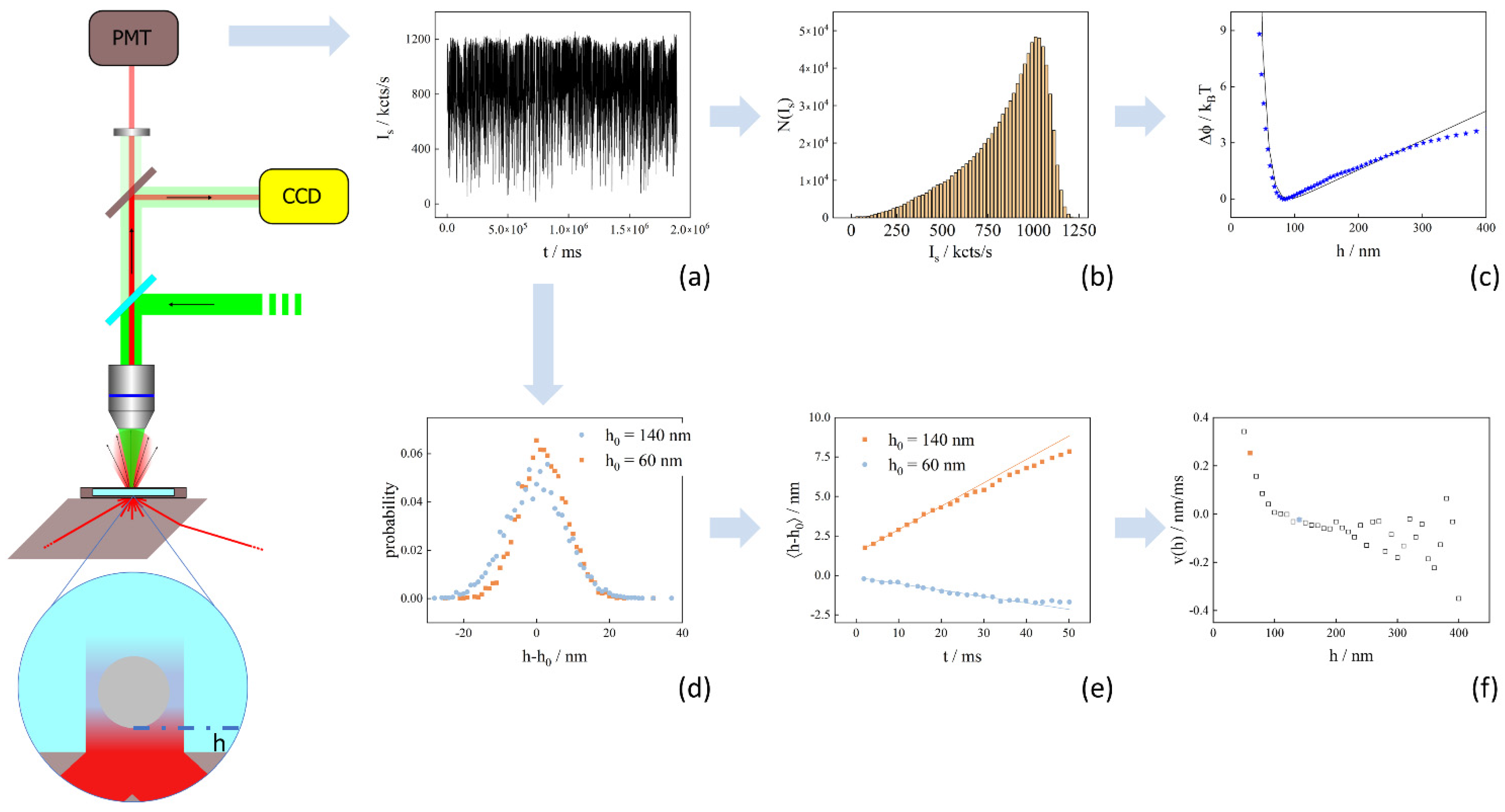
2.1.2. Sample Preparation and TIRM Setup
2.2. Dynamic Properties Measured by TIRM
2.3. Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Static Information from TIRM Intensity Traces
3.1.1. Experimental Potential Profiles
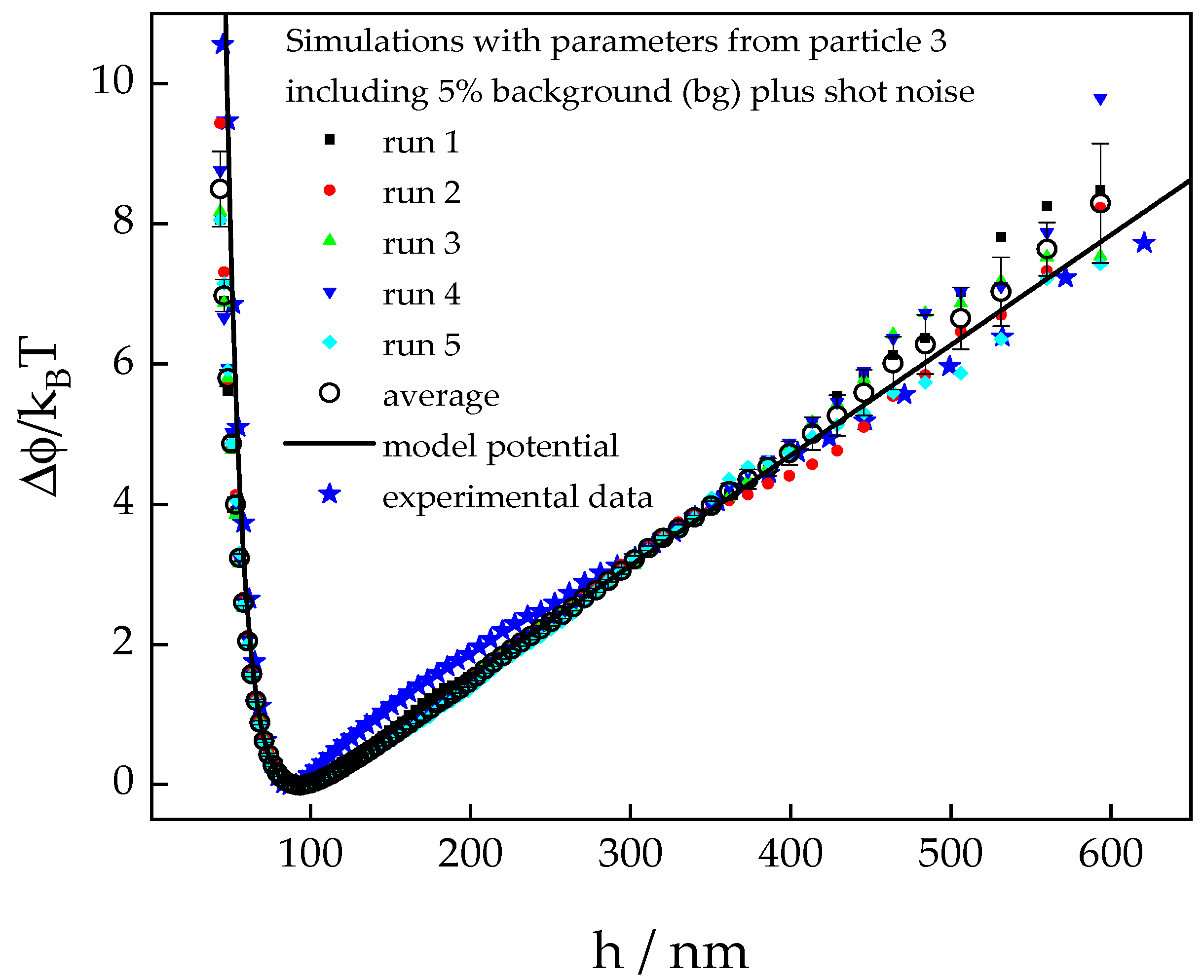
3.1.2. Simulated Potential Profiles
3.2. Dynamic Information from TIRM
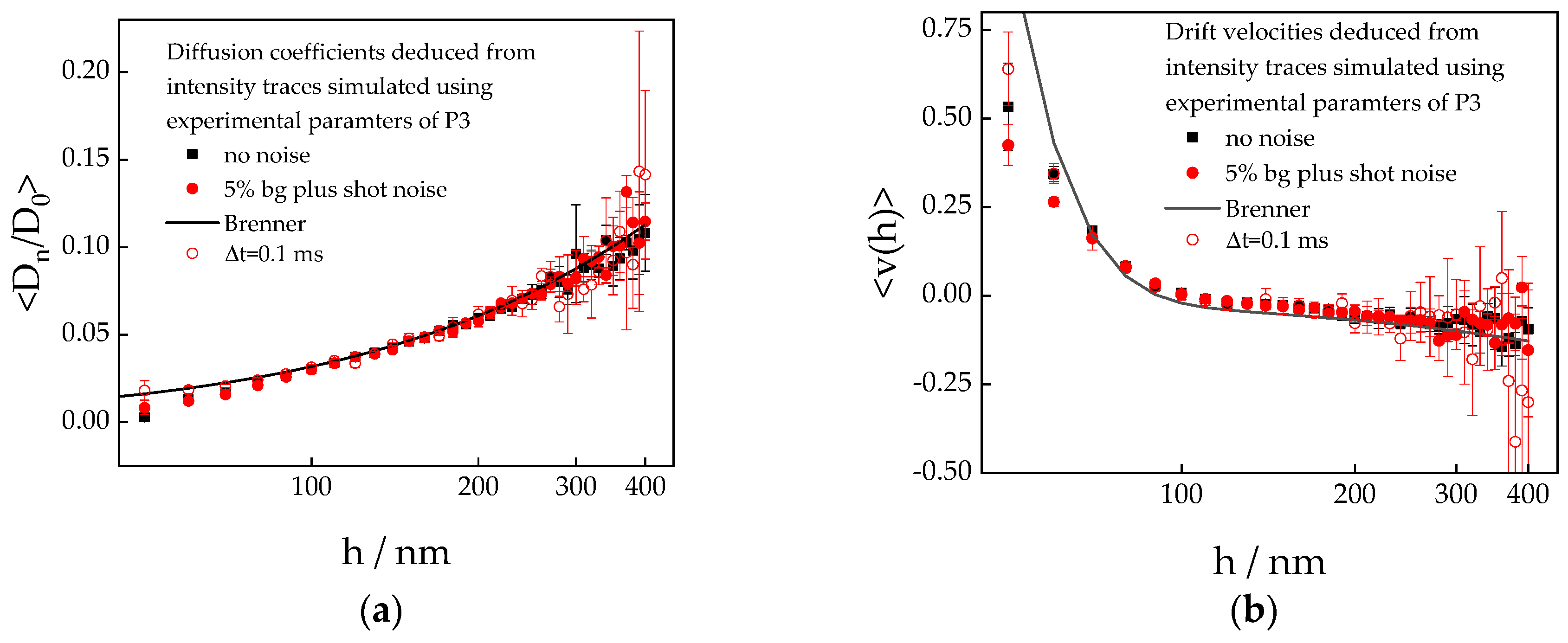
3.2.1. Simulated Diffusion and Velocity Data
3.2.2. Experimental Dynamic Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; ISBN 0-12-375181-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaker, H.C. The London—Van der Waals attraction between spherical particles. Physica 1937, 4, 1058–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W. Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1947, 51, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwey, E.; Overbeek, J.; van Nes, K. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids: The Interaction of Sol Particles Having an Electric Double Layer; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Verwey, E.J.W.; Overbeek, J.T.G. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 9780486409290. [Google Scholar]
- Asakura, S.; Oosawa, F. On Interaction between 2 Bodies Immersed in a Solution of Macromolecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1954, 22, 1255–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, S.; Oosawa, F. Interaction between Particles Suspended in Solutions of Macromolecules. J. Polym. Sci. 1958, 33, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschol, M.; Rosenberger, F. Liquid–liquid phase separation in supersaturated lysozyme solutions and associated precipitate formation/crystallization. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolde, P.R.T.; Frenkel, D. Enhancement of protein crystal nucleation by critical density fluctuations. Science 1997, 277, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, G.B. Cataract as a Protein Condensation Disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 1997, 38, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Stradner, A.; Schurtenberger, P. Potential and limits of a colloid approach to protein solutions. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchell, D.; Song, W.; Daigle, H. Effect of interparticle forces on the stability and droplet diameter of Pickering emulsions stabilized by PEG-coated silica nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 626, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Ren, C.L.; Emelko, M.B. Concurrent Modeling of Hydrodynamics and Interaction Forces Improves Particle Deposition Predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4401–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, H. The slow motion of a sphere through a viscous fluid towards a plane surface. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1961, 16, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.J.; Cox, R.G.; Brenner, H. Slow viscous motion of a sphere parallel to a plane wall—2 Couette flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1967, 22, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Tandon, R.K.; White, L.R. Measurement of Forces between 2 Mica Surfaces in Aqueous Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Solutions. Nature 1979, 277, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, M.; Vanicek, J.; Zäch, M. The extended surface forces apparatus. II. Precision temperature control. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 3556–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, M. The extended surface forces apparatus. Part I. Fast spectral correlation interferometry. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker, W.A.; Senden, T.J.; Pashley, R.M. Direct Measurement of Colloidal Forces Using an Atomic Force Microscope. Nature 1991, 353, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witko, T.; Baster, Z.; Rajfur, Z.; Sofińska, K.; Barbasz, J. Increasing AFM colloidal probe accuracy by optical tweezers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.H.; Yu, J.; Rice, S.A. Direct measurements of constrained Brownian motion of an isolated sphere between two walls. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 3909–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, S.L.; Keyser, U.F.; Pagliara, S. Local characterization of hindered Brownian motion by using digital video microscopy and 3D particle tracking. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 23708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zong, Y.; Zhao, K. The Curvature Effect on the Diffusion of Single Brownian Squares on a Cylindrical Surface in the Presence of Depletion Attractions. Langmuir 2021, 37, 9264–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.H.; OSTROWSKY, N.; Sornette, D. Brownian Dynamis Close to a Wall studied by Photon-Correlation Spectroscopy from an Evanescent Wave. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoda, M.; Sakai, K.; Takagi, K. Measurement of anisotropic Brownian motion near an interface by evanescent light-scattering spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 58, 6275–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, P.; Dhont, J.K.G.; Lang, P.R. Anisotropy of Brownian motion caused only by hydrodynamic interaction with a wall. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2006, 74, 21402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, V.N.; Petekidis, G.; Swan, J.W.; Brady, J.F. Dynamics of concentrated hard-sphere colloids near a wall. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 68302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.A.; Lisicki, M.; Cichocki, B.; Dhont, J.K.G.; Lang, P.R. Rotational diffusion of spherical colloids close to a wall. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 98305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieve, D.C. Measurement of colloidal forces with TIRM. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 82, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bike, S.G. Measuring colloidal forces using evanescent wave scattering. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, M.A.; Prieve, D.C. Direct measurement of retarded van der Waals attraction. Langmuir 1999, 15, 7925–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudhardt, D.; Bechinger, C.; Leiderer, P. Direct measurement of depletion potentials in mixtures of colloids and nonionic polymers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechinger, C.; Rudhardt, D.; Leiderer, P.; Roth, R.; Dietrich, S. Understanding depletion forces beyond entropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 3960–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleshchanok, D.; Tuinier, R.; Lang, P.R. Depletion interaction mediated by a polydisperse polymer studied with total internal reflection microscopy. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9121–9128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- July, C.; Lang, P.R. Depletion Interactions Effected by Different Variants of fd Virus. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18647–18651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sio, S.; Lang, P.R. Depletion Interaction Mediated by fd-Virus: On the Limit of Low Density and Derjaguin Approximation. Z. Phys. Chemie-Int. J. Res. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 229, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleshchanok, D.; Lang, P.R. Steric repulsion by adsorbed polymer layers studied with total internal reflection microscopy. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4332–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertlein, C.; Helden, L.; Gambassi, A.; Dietrich, S.; Bechinger, C. Direct measurement of critical Casimir forces. Nature 2008, 451, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helden, L.; Knippenberg, T.; Tian, L.; Archambault, A.; Ginot, F.; Bechinger, C. Critical Casimir interactions of colloids in micellar critical solutions. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 2737–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gong, X.; Ngai, T. Measurements of long-range interactions between protein-functionalized surfaces by total internal reflection microscopy. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3101–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merminod, S.; Edison, J.R.; Fang, H.; Hagan, M.F.; Rogers, W.B. Avidity and surface mobility in multivalent ligand-receptor binding. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 12602–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumai’an, E.; Zhang, L.; Bevan, M.A. Blood Protein Exclusion from Polymer Brushes. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doicu, A.; Vasilyeva, A.A.; Efremenko, D.S.; Wirth, C.L.; Wriedt, T. A light scattering model for total internal reflection microscopy of geometrically anisotropic particles. J. Mod. Opt. 2019, 66, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wirth, C.L. Anisotropic colloidal particles near boundaries. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 131, 150903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; Domínguez-Medina, S.; Yan, J.; Efremenko, D.S.; Vasilyeva, A.A.; Doicu, A.; Wriedt, T.; Wirth, C.L. Developing Scattering Morphology Resolved Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (SMR-TIRM) for Orientation Detection of Colloidal Ellipsoids. Langmuir 2020, 36, 13041–13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Ngai, T. Total internal reflection microscopy: A powerful tool for exploring interactions and dynamics near interfaces. Soft Matter 2023, 19, 4611–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FREJ, N.A.; Prieve, D.C. Hindered Diffusion of a Single Sphere Very Near a Wall in a Nonuniform Force-Field. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 7552–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, M.A.; Prieve, D.C. Hindered diffusion of colloidal particles very near to a wall: Revisited. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADAMCZYK, Z.; ADAMCZYK, M.; van de Ven, T. Resistance coefficient of a solid sphere approaching plane and curved boundaries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 96, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Helden, L.; Brettschneider, T.; Wehr, J.; Bechinger, C. Influence of noise on force measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 170602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, T.; Volpe, G.; Helden, L.; Wehr, J.; Bechinger, C. Force measurement in the presence of Brownian noise: Equilibrium-distribution method versus drift method. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2011, 83, 41113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sio, S.; July, C.; Dhont, J.K.G.; Lang, P.R. Near wall dynamics of a spherical particle in crowded suspensions of colloidal rods—Dynamic information from TIRM revisited. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 9232–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, P.; Kleshchanok, D.; Lang, P.R. Interaction potential and near wall dynamics of spherical colloids in suspensions of rod-like fd-virus. Eur. Phys. J. E 2008, 26, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholl, D.S.; Fenwick, M.K.; Atman, E.; Prieve, D.C. Brownian dynamics simulation of the motion of a rigid sphere in a viscous fluid very near a wall. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 9268–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Pine, D.J. Effect of photon counting shot noise on total internal reflection microscopy. Soft Matter 2021, 18, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Marbach, S.; Zheng, J.A.; Holmes-Cerfon, M.; Pine, D.J. Comprehensive view of microscopic interactions between DNA-coated colloids. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derjaguin, B. Untersuchungen über die Reibung und Adhäsion, IV. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1934, 69, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetama, R.J.; Walz, J.Y. A new approach for analyzing particle motion near an interface using total internal reflection microscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetama, R.J.; Walz, J.Y. Investigation of short-time particle dynamics near an interface in the presence of nonadsorbed macro-ions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8318–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, D.J.; Onishi, Y. Calculation of the resistance and mobility functions for two unequal rigid spheres in low-Reynolds-number flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1984, 139, 261–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, B.; Jones, R.B. Image representation of a spherical particle near a hard wall. Phys. A 1998, 258, 273–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiel-Jeżewska, M.L.; Wajnryb, E. Motion of a particle with stick-slip boundary conditions towards a flat interface: Hard wall or free surface. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermak, D.L.; Buckholz, H. Numerical integration of the Langevin equation: Monte Carlo simulation. J. Comput. Phys. 1980, 35, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Particle No. | κ−1/nm | Fg/fN | hmin/nm | B/kBT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12.41 | 57 | 102.2 | 655 |
| 2 | 10.4 | 61 | 68.5 | 115 |
| 3 | 10.2 | 64 | 91 | 1167 |
| 4 | 9.7 | 57 | 66 | 165 |
| 5 | 11.3 | 54 | 124 | 8780 |
| 6 | 9.1 | 52 | 86 | 1555 |
| Slip Parameter ζ | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/12 | 1/4 | 3.5749 | −6.2238 | 10.7 |
| 0.12 | 1/4 | 2.20 | −2.6414 | 4.55 |
| 1/3 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 0.708214 | 0.033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivera-Morán, J.A.; Lang, P.R. Analysing Sources of Error in Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (TIRM) Experiments and Data Analysis. Polymers 2023, 15, 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214208
Rivera-Morán JA, Lang PR. Analysing Sources of Error in Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (TIRM) Experiments and Data Analysis. Polymers. 2023; 15(21):4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214208
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivera-Morán, J. Alejandro, and Peter R. Lang. 2023. "Analysing Sources of Error in Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (TIRM) Experiments and Data Analysis" Polymers 15, no. 21: 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214208
APA StyleRivera-Morán, J. A., & Lang, P. R. (2023). Analysing Sources of Error in Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (TIRM) Experiments and Data Analysis. Polymers, 15(21), 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214208