Chains Stiffness Effect on the Vertical Segregation of Mixed Polymer Brushes in Selective Solvent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Method
2.1. Model
2.2. Self-Consistent Field Method
3. Results and Discussion
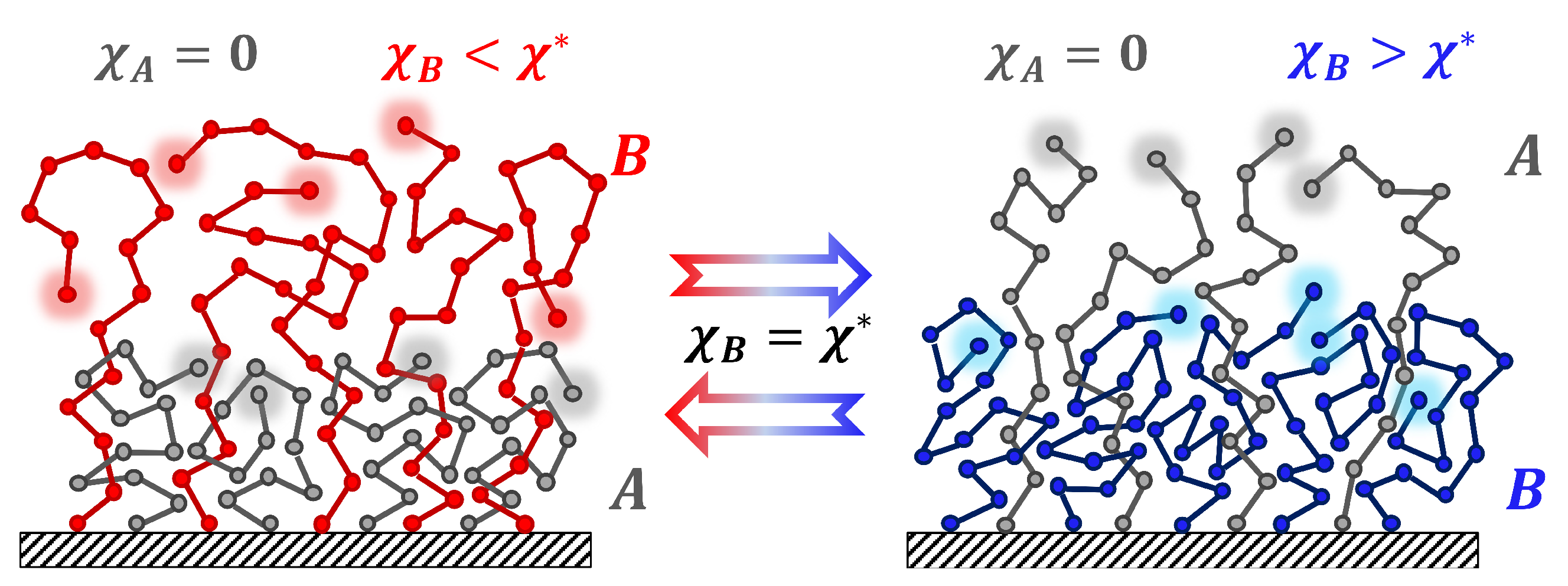
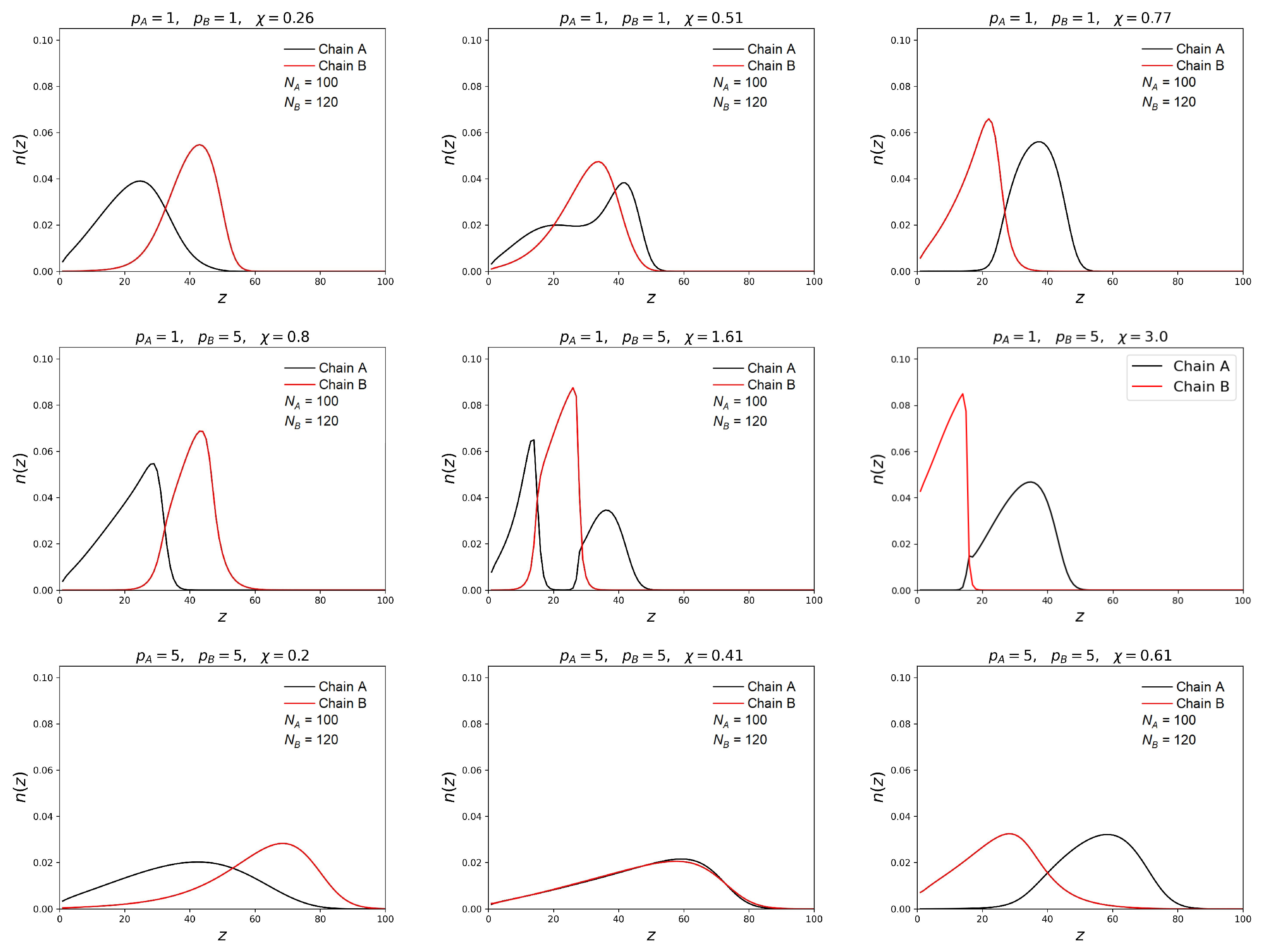
3.1. Profiles of the Polymer Volume Fractions and Free Ends Distributions
3.2. Dependence of the Transition Point on the Brush Characteristics
3.3. Steepness of the Transition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LCST | The lower critical solution temperature |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| PAA | Poly(acrylic acid) |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PNIPAAm | Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| SCF (method) | The self-consistent field (method) |
| SF-SCF (method) | The Scheutjens–Fleer self-consistent field (method) |
| SPC | Smart polymer coatings |
References
- Giussi, J.M.; Cortez, M.L.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Recent developments in flame retardant polymeric coatings. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C. Surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization for applications in sensors, non-biofouling surfaces and adsorbents. Polym. J. 2016, 48, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ferris, R.; Zhang, J.; Ducker, R.; Zauscher, S. Stimulus-responsive polymer brushes on surfaces: Transduction mechanisms and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jamali, S.; Liu, Q.; Maia, J.; Baek, J.B.; Jiang, N.; Xu, M.; Dai, L. Conformational transitions of polymer brushes for reversibly switching graphene transistors. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 7434–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Jung, J. Polymer brush: A promising grafting approach to scaffolds for tissue engineering. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Feng, C.; Hu, J.; Shi, P.; Gu, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Spin-casting polymer brush films for simuli-responsive and anti-fouling surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6685–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Truong, V.K.; Woo, S.Y.; Dickey, M.D.; Hsiao, L.; Genzer, J. Counterpropagating gradients of antibacterial and antifouling polymer brushes. Biomacromolecules 2021, 23, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmyn, A.R.; Teunissen, L.W.; Fritz, P.; van Lagen, B.; Smulders, M.M.J.; Zuilhof, H. Diblock and random antifouling bioactive polymer brushes on gold surfaces by visible-light-induced polymerization (SI-PET-RAFT) in water. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirin, L.; Galuschko, A.; Kreer, T.; Johner, A.; Baschnagel, J.; Binder, K. Polymerbrush lubrication in the limit of strong compression. Eur. Phys. J. E 2010, 33, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Ghasemi, A.; Zangabad, P.; Rahighi, R.; Barsi, S.; Mirshekari, H.; Amiri, M.; Pishabad, Z.; Aslani, A.; Bozorgomid, M. Smart micro/nanoparticles in stimulusresponsive drug/gene delivery systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1457–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dou, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J. Bioresponsive drug delivery systems for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. J. Control Release 2020, 327, 641–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfhaid, L.H.K. Recent advance in functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles with stimuli-responsive polymer brush for controlled drug delivery. Soft Mater. 2022, 20, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurds, L.; Lauko, J.; Rowan, A.E.; Amiralian, N. Tailored nanocellulose-grafted polymer brush applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 17173–17188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Gautrot, J.E. Responsive polymer brush design and emerging applications for nanotheranostics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2000953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Kikuchi, A.; Akiyama, Y.; Kanazawa, H.; Okano, T. Protein separations via thermally responsive ionic block copolymer brush layers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 26254–26263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, G.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xin, Q.; Han, S. Protein fractionation of pH-responsive brush-modified ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer membranes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, G.F.D.; Kyriakidou, M.; Adali, Z.; Xiong, K.; Hailes, R.L.N.; Dahlin, A. Electrically switchable polymer brushes for protein capture and release in biological environments. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.L.; Merlitz, H.; Sommer, J.; Wu, C. Microphase Separation of Mixed Binary Polymer Brushes at Different Temperatures. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 7194–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczykowa, M.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. Conducting Polymers, Hydrogels and Their Composites: Preparation, Properties and Bioapplications. Polymers 2019, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakharchenko, A.; Guz, N.; Laradji, A.; Katz, E.; Minko, S. Magnetic field remotely controlled selective biocatalysis. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratek-Skicki, A.; Eloy, P.; Morga, M.; Dupont-Gillain, C. Reversible Protein Adsorption on Mixed PEO/PAA Polymer Brushes: Role of Ionic Strength and PEO Content. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3037–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ye, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Graphene functionalized with azo polymer brushes: Surface-initiated polymerization and photoresponsive properties. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, F.; Theato, P. Temperature- and light-responsive smart polymer materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7468–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolatkhah, A.; Wilson, L. Magnetite/Polymer Brush Nanocomposites with Switchable Uptake Behavior Toward Methylene Blue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5595–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Asami, N.; Uragami, T. A reversibly antigen- responsive hydrogel. Nature 1999, 399, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Katti, P.S.; Gu, Z. Enzyme-responsive nanomaterials for controlled drug delivery. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12273–12286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspoor, S.; Agbolaghi, S.; Nazari, M.; Abbasi, F. Conventional and rare-patched rod/coil matrix-dispersed patternings on single crystals affected by Rigidity, amorphism and crystallinity of brushes. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 94, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspoor, S.; Agbolaghi, S.; Abbasi, F. Chemical and physical effects of processing environment on simultaneous single crystallization of biodegradable poly(ϵ-caprolactone) and poly(l-lactide) brushes and poly(ethylene glycol) substrate. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 103, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspoor, S.; Agbolaghi, S.; Mahmoudi, M.; Jahanbani, Y.; Abbasi, F.; Sarvari, R. Effect of miscibility on migration of third component in star-like co-continuous and disperse-within-disperse mixed brushes. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minko, S.; Müller, M.; Usov, D.; Scholl, A.; Froeck, C.; Stamm, M. Lateral versus Perpendicular Segregation in Mixed Polymer Brushes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 035502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minko, S.; Luzinov, I.; Luchnikov, V.; Müller, M.; Patil, S.; Stamm, M. Bidisperse Mixed Brushes: Synthesis and Study of Segregation in Selective Solvent. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7268–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Charpota, N.; Mei, H.; Terlier, T.; Pietrzak, D.; Stein, G.E.; Verduzco, R. Impact of Processing Effects on Surface Segregation of Bottlebrush Polymer Additives. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 8909–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Laws, T.S.; Mahalik, J.P.; Li, J.; Mah, A.H.; Terlier, T.; Bonnesen, P.; Uhrig, D.; Kumar, R.; Stein, G.E.; et al. Entropy and enthalpy mediated segregation of bottlebrush copolymers to interfaces. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 8910–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalik, J.P.; Sumpter, B.G.; Kumar, R. Vertical phase segregation induced by dipolar interactions in planar polymer brushes. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 7096–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Pester, C.W. Mixed Polymer Brushes for “Smart” Surfaces. Polymers 2020, 12, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estillore, N.; Advincula, R. Stimuli-responsive binary mixed polymer brushes and free-standing films by LbL-SIP. Langmuir 2011, 27, 5997–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, G.; Siband, E.; Gallas, B.; Cousin, F.; Hourdet, D.; Tran, Y. Responsive Adsorption of N-Isopropylacrylamide Based Copolymers on Polymer Brushes. R Polym. 2020, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Léonforte, F.; Müller, M. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Mixed Brushes: A Computer Simulation Study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12450–12462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, I.; Merlitz, H.; Rosenthal, A.; Uhlmann, P.; Sommer, J.U. Design of binary polymer brushes with tuneable functionality. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 7237–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Agbolaghi, S.; Mozaffari, Z.; Abbaspoor, S.; Massoumi, B.; Sarvari, R.; Hosseinzadeh, N. Star-like Poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide) and Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Copolymers Self-Arranged in Newfound Single Crystals and Associated Novel Class of Polymer Brush Regimes with V-Type Tethers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Jia, Y.; He, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Temperature-Controlled Reversible Exposure and Hiding of Antimicrobial Peptides on an Implant for Killing Bacteria at Room Temperature and Improving Biocompatibility in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35830–35837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkert, S.; Bittrich, E.; Kuntzsch, M.; Müller, M.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Bellmann, C.; Uhlmann, P.; Stamm, M. Protein Resistance of PNIPAAm Brushes: Application to Switchable Protein Adsorption. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M. Phase diagram of a mixed polymer brush. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 030802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, S.; Kopyshev, A.; Donges, J.; Yang, H.K.; Rühe, J. Domain Memory of Mixed Polymer Brushes. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4660–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, S.; Kopyshev, A.; Donges, J.; Rühe, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, B.; Müller, M. Memory of surface patterns in mixed polymer brushes: Simulation and experiment. Langmuir ACS J. Surfaces Colloids 2007, 23, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlitz, H.; He, G.L.; Wu, C.X.; Sommer, J.U. Nanoscale Brushes: How to Build a Smart Surface Coating. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 115702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Vos, W.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; de Keizer, A.; Kleijn, J.; Stuart, M.A.C. Adsorption of Anionic Surfactants in a Nonionic Polymer Brush: Experiments, Comparison with Mean-Field Theory, and Implications for Brush-Particle Interaction. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9252–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.; Milchev, A.; Binder, K. Polymer brushes in solvents of variable quality: Molecular dynamics simulations using explicit solvent. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 084905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, D.; Merlitz, H.; Sommer, J.U. A new numerical approach to dense polymer brushes and surface instabilities. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 044903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, D.; Sommer, J.U. Binary and Bidisperse Polymer Brushes: Coexisting Surface States. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12496–12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Müller, M. Microphase Separation of Diblock Copolymer Brushes in Selective Solvents: Single-Chain-in-Mean-Field Simulations and Integral Geometry Analysis. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2251–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbolaghi, S.; Abbaspoor, S.; Abbasi, F. A comprehensive review on polymer single crystals—From fundamental concepts to applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 22–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkilic, N.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; de Vos, W.M. Responsive polymer brushes for controlled nanoparticle exposure. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17871–17878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleer, G.J.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Scheutjens, J.M.H.M.; Cosgrove, T.; Vincent, B. Polymers at Interfaces; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1993; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Amoskov, V.; Birshtein, T.; Pryamitsyn, V. Theory of Polymer Brushes of Liquid-Crystalline Polymers. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7240–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leermakers, F.; Scheutjens, J.; Gaylord, R. Modelling the amorphous phase of a melt crystallized, semicrystalline polymer: Segment distribution, chain stiffness, and deformation. Polymer 1984, 25, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, C.; Leermakers, F.; Fleer, G. Adsorption of Semiflexible Polymers. Macromolecules 1995, 29, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, C.; Leermakers, F.; Fleer, G. Chain stiffness and bond correlations in polymer brushes. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 8214–8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, I.V.; Amoskov, V.M.; Darinskii, A.A.; Birshtein, T.M. The Structure of Dipolar Polymer Brushes and Their Interaction in the Melt. Impact of Chain Stiffness. Polymers 2020, 12, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutjens, J.; Fleer, G. Statistical theory of the adsorption of interacting chain molecules. 1. Partition function, segment density distribution, and adsorption isotherms. J. Phys. Chem. 1979, 83, 1619–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, W.; Kuhn, H. Rigidity of chain molecules and its determination from viscosity and flow birefringence in dilute solutions. J. Colloid Sci. 1948, 3, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailov, I. Software for SCF Simulations of the Binary Brushes in the Selective Solvent. Available online: https://github.com/IvanMikhailovIMCRAS/Flex_2_2.git (accessed on 7 December 2022).





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lukiev, I.V.; Mogelnitskaya, Y.A.; Mikhailov, I.V.; Darinskii, A.A. Chains Stiffness Effect on the Vertical Segregation of Mixed Polymer Brushes in Selective Solvent. Polymers 2023, 15, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030644
Lukiev IV, Mogelnitskaya YA, Mikhailov IV, Darinskii AA. Chains Stiffness Effect on the Vertical Segregation of Mixed Polymer Brushes in Selective Solvent. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030644
Chicago/Turabian StyleLukiev, Ivan V., Yana A. Mogelnitskaya, Ivan V. Mikhailov, and Anatoly A. Darinskii. 2023. "Chains Stiffness Effect on the Vertical Segregation of Mixed Polymer Brushes in Selective Solvent" Polymers 15, no. 3: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030644
APA StyleLukiev, I. V., Mogelnitskaya, Y. A., Mikhailov, I. V., & Darinskii, A. A. (2023). Chains Stiffness Effect on the Vertical Segregation of Mixed Polymer Brushes in Selective Solvent. Polymers, 15(3), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030644








