Palladium Nanoparticle-Loaded Mesostructural Natural Woods for Efficient Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of PNNW Membranes
2.3. Water Flux Test
2.4. Dye Degradation Property Test
3. Characterization
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Preparation of Pd Nanoparticle-Loaded Wood Membranes and Degradation Mechanism
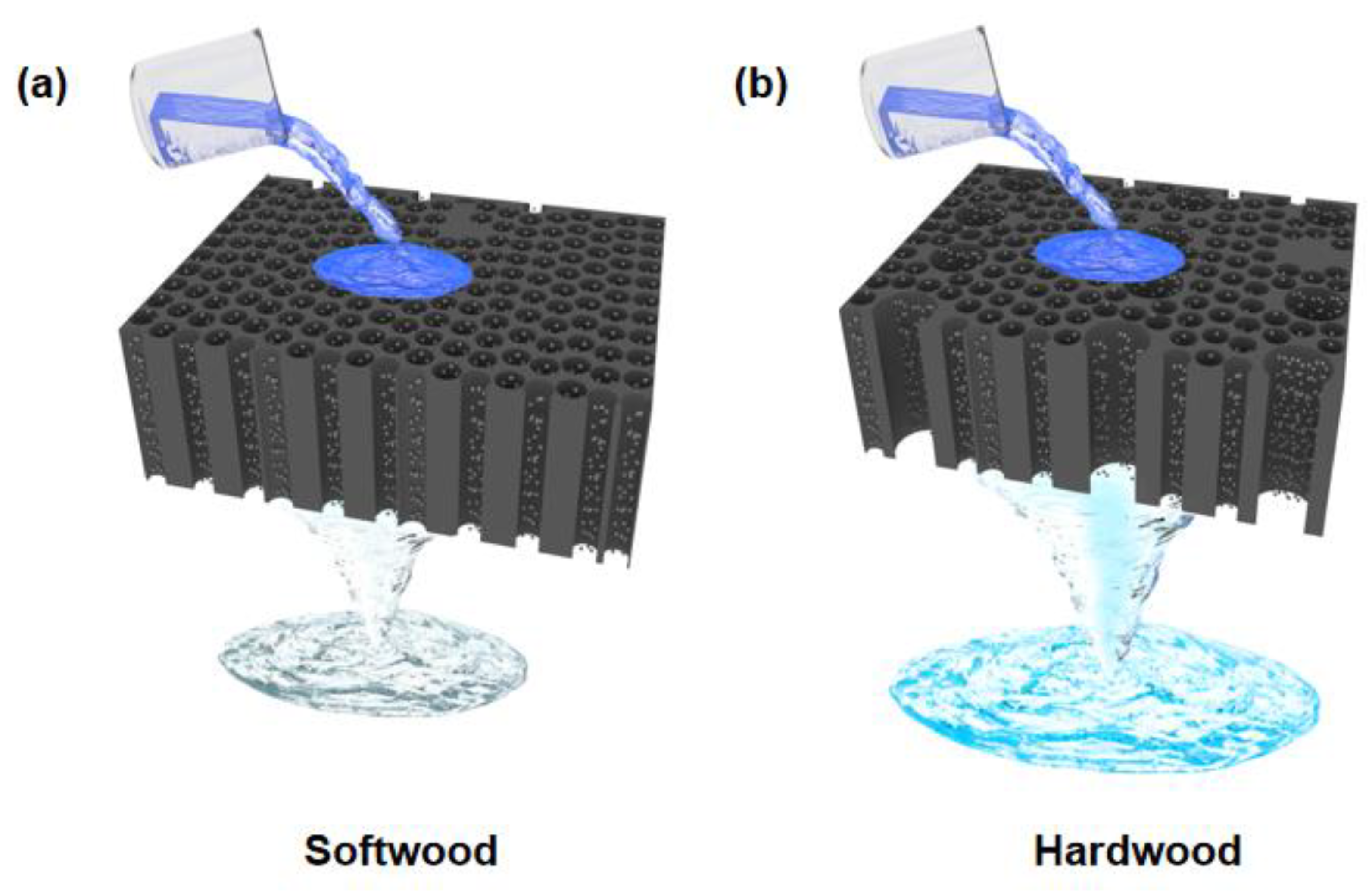
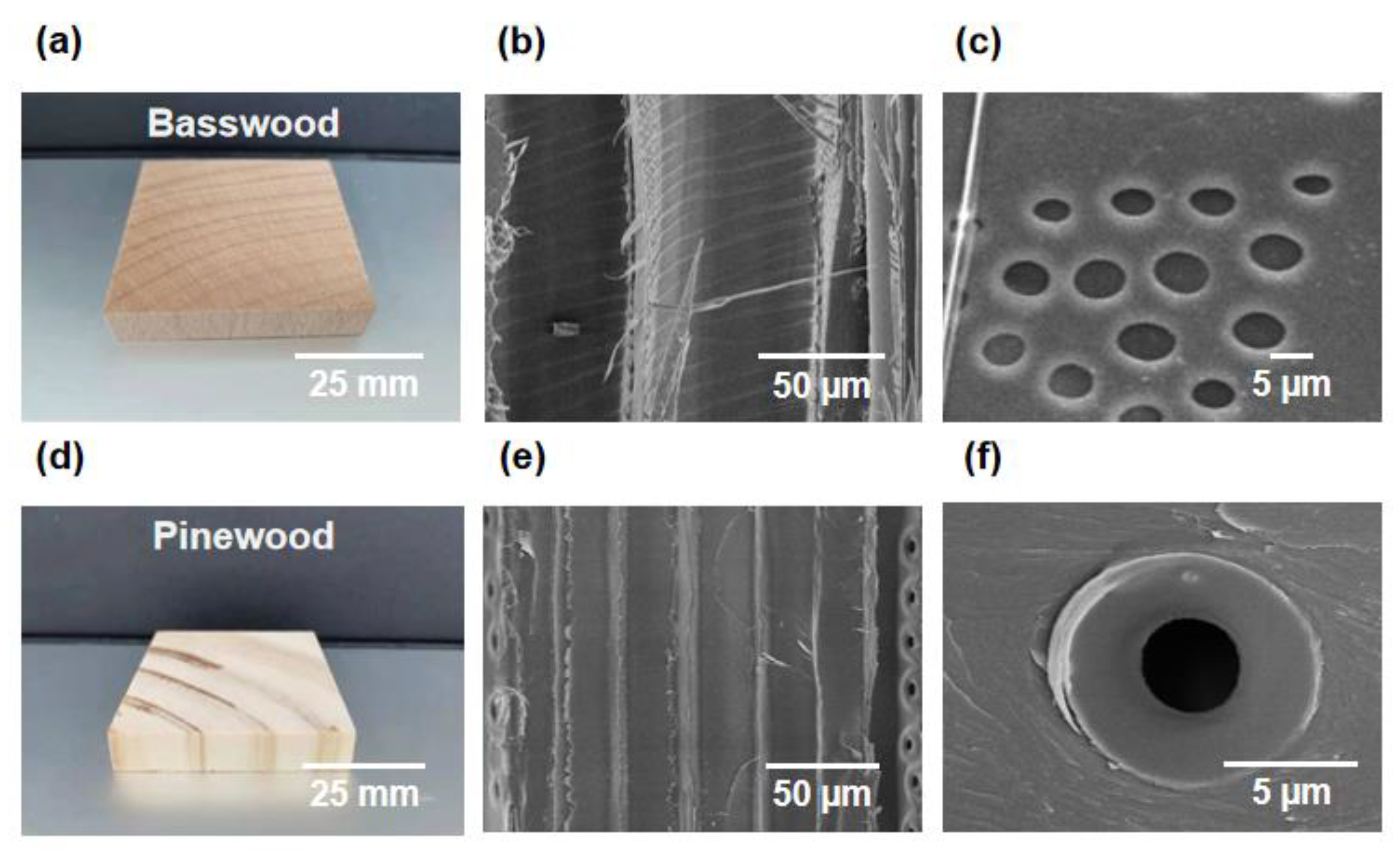
4.2. Microstructures of Natural Woods
4.3. Degradation Property of PNNW Membranes for Single Organic Pollutant
4.4. Degradation Property of PNNW Membranes for Mixed Organic Pollutant
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grant, S.B.; Saphores, J.D.; Feldman, D.L.; Hamilton, A.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Cook, P.L.M.; Stewardson, M.; Sanders, B.F.; Levin, L.A.; Ambrose, R.F.; et al. Taking the "waste" out of "wastewater" for human water security and ecosystem sustainability. Science 2012, 337, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Huo, J.Z.; Zheng, X.J. Wastewater: China’s next water source. Science 2021, 374, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.J.; Umble, A.K. Recover wastewater resources locally. Nature 2016, 529, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersan, G.; Apul, O.G.; Perreault, F.; Karanfil, T. Adsorption of organic contaminants by graphene nanosheets: A review. Water Res. 2017, 126, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Flora, J.R.V.; Park, Y.G.; Badawy, M.; Saleh, H.; Yoon, Y. Removal of natural organic matter from potential drinking water sources by combined coagulation and adsorption using carbon nanomaterials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sheng, G.P.; Lu, Y.Z.; Zeng, R.J.; Yu, H.Q. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater treatment plant effluent by coagulation. Water Res. 2017, 111, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benidris, E.; Ghezzar, M.R.; Ma, A.; Ouddane, B.; Addou, A. Water purification by a new hybrid plasma-sensitization-coagulation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 178, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.T.; Chen, Y.L.; Nie, J.X.; Ma, L.M.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.G. Pilot-scale study on catalytic ozonation of bio-treated dyeing and finishing wastewater using recycled waste iron shavings as a catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, Y.H.; Li, X.Y.; Xia, Q.B.; Wu, J.L.; Li, Y.W.; Xiao, J.; Li, Z. Adsorptive and photocatalytic removal of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in water by metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Asadollahzadeh, M.; Shirazian, S. Molecular separation in liquid phase: Development of mechanistic model in membrane separation of organic compounds. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 262, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.J.; Qin, Z.; Huang, W.W.; Cao, S.F.; Kaplan, D.L.; Buehler, M.J. Design and function of biomimetic multilayer water purification membranes. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.X.; Yuan, J.Y.; Cheng, J.P.; Han, B.H. Synthesis of porous polymer/tissue paper hybrid membranes for switchable oil/water separation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Chen, C.J.; Kuang, Y.D.; Fu, K.; Wang, Y.L.; Yao, Y.G.; Kronthal, S.; Hitz, E.; Song, J.W.; Xu, F.J.; et al. From wood to textiles: Top-down assembly of aligned cellulose nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Jiang, F.; Hu, P.; Kuang, Y.D.; He, S.M.; Li, T.; Chen, C.J.; Murphy, A.; Yang, C.P.; Yao, Y.G.; et al. Anisotropic, mesoporous microfluidic frameworks with scalable, aligned cellulose nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7362–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Li, T.; Chen, C.J.; Dai, J.Q.; Kierzewski, I.M.; Song, J.W.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, C.P.; Wang, C.W.; Hu, L.B. Scalable, anisotropic transparent paper directly from wood for light management in solar cells. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Yao, Y.G.; Jiang, F.; Kuang, Y.D.; Pastel, G.; Xie, H.; Yang, B.; et al. Rich mesostructures derived from natural woods for solar steam generation. Joule 2017, 1, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Hu, F.Q.; Gan, M.X.; Xie, Y.M.; Feng, Q.H. Facile one-step fabrication of all cellulose composites with unique optical performance from wood and bamboo pulp. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisaki, Y.; Koga, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakata, M.; Tsuji, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Kurita, T.; Nogi, M.; Shimidzu, N. Transparent nanopaper-based flexible organic thin-film transistor array. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Li, Y.J.; Song, J.W.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Hitz, E.; Jia, C.; Gong, A.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.Y.; et al. Highly flexible and efficient solar steam generation device. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, L.V.; Muthoka, R.M.; Panicker, P.S.; Agumba, D.O.; Pham, H.D.; Kim, J. All-biobased transparent-wood: A new approach and its environmental-friendly packaging application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 118012. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Wang, X.Q. Highly compressible wood sponges with a spring-like lamellar structure as effective and reusable oil absorbents. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10365–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, W.B.; Xiao, Z.F.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, H.G.; Wang, Y.G.; Xie, Y.J. Wood-based mesoporous filter decorated with silver nanoparticles for water purification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5134–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.J.; Gong, A.S.; Zhu, M.W.; Chen, G.; Lacey, S.D.; Jiang, F.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, Y.B.; Dai, J.Q.; Yao, Y.G.; et al. Mesoporous, three-dimensional wood membrane decorated with nanoparticles for highly efficient water treatment. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirbas, I.; Cifci, A. An effective and fast solution for classification of wood species: A deep transfer learning approach. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 69, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Zhao, P. Study on simultaneous classification of hardwood and softwood species based on spectral and image characteristics. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, K.; Barwicki, J.; Rzodkiewicz, W.; Dawidowski, M. Evaluation of mechanical and energetic properties of the forest residues shredded chips during briquetting process. Energies 2021, 14, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, B.; Wan, C.; Wang, K. The effect of different moderate thermal modification durations on the wood properties of american alder. Materials 2022, 15, 8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.M.; Chen, C.J.; Kuang, Y.D.; Mi, R.Y.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Kong, W.Q.; Gan, W.T.; Xie, H.; Hitz, E.; et al. Nature-inspired salt resistant bimodal porous solar evaporator for efficient and stable water desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.D.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, G.; Pei, Y.; Pastel, G.; Jia, C.; Song, J.W.; Mi, R.Y.; Yang, B.; Das, S.; et al. Bioinspired solar-heated carbon absorbent for efficient cleanup of highly viscous crude oil. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Jia, C.; Xiang, H.; Zhu, M. Palladium Nanoparticle-Loaded Mesostructural Natural Woods for Efficient Water Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030658
Wang Z, Jia C, Xiang H, Zhu M. Palladium Nanoparticle-Loaded Mesostructural Natural Woods for Efficient Water Treatment. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030658
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zirun, Chao Jia, Hengxue Xiang, and Meifang Zhu. 2023. "Palladium Nanoparticle-Loaded Mesostructural Natural Woods for Efficient Water Treatment" Polymers 15, no. 3: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030658
APA StyleWang, Z., Jia, C., Xiang, H., & Zhu, M. (2023). Palladium Nanoparticle-Loaded Mesostructural Natural Woods for Efficient Water Treatment. Polymers, 15(3), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030658







