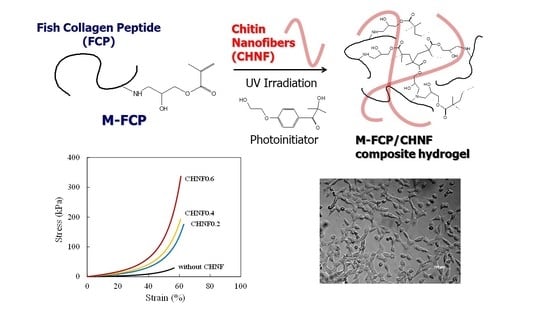
Photocrosslinked Fish Collagen Peptide/Chitin Nanofiber Composite Hydrogels from Marine Resources: Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and an In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Methacrylate-Modified Fish Collagen Peptide (M-FCP)
2.3. Preparation of M-FCP/CHNF Composite Hydrogel by Photoirradiation
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Methacrylate-Modified Collagen Peptide (M-FCP)
3.2. Preparation of M-FCP/CHNF Composite Hydrogels by Photocrosslinking
3.3. Mechanical Properties of M-FCP/CHNF Composite Hydrogels
3.4. Cell Proliferation on M-FCP/CHNF Composite Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, J.L.; Asche, F.; Garlock, T. Globalization and commoditization: The transformation of the seafood market. J. Commod. Mark. 2018, 12, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Mendis, E. Bioactive compounds from marine processing byproducts-A review. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.T.; Byun, H.G.; Nam, K.S.; Joo, D.S.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and characterization of antioxidative peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of Alaska pollack skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) skin. Process Biochem. 2001, 36, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Fan, H.; Chalamaiah, M.; Wu, J. Preparation of low-molecular-weight, collagen hydrolysates (peptides): Current progress, challenges, and future perspectives. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimura, S.; Nagata, H.; Uemura, Y.; Fahmi, A.; Shigematsu, T.; Kida, K. Development of an effective process for utilization of collagen from livestock and fish waste. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Kiyose, C.; Higuchi, T.; Uchida, N.; Suzuki, H. Effect of collagen hydrolysates from salmon and trout skins on the lipid profile in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10477–10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Maehata, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Kusubata, M.; Hattori, S.; Tanaka, K.; Miyamoto, C.; Yoshino, F.; Yoshida, A.; Wada-Takahashi, S.; et al. Direct assessments of the antioxidant effects of the novel collagen peptide on reactive oxygen species using electron spin resonance spectroscopy. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 116, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Composite electrospun nanomembranes of fish scale collagen peptides/chito-oligosaccharides: Antibacterial properties and potential for wound dressing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Hu, W.; Han, X.; Fan, L.; Tao, S. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan/collagen peptide/oxidized konjac composite hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Kong, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M. Gastric acid-response chitosan/alginate/tilapia collagen peptide composite hydrogel: Protection effects on alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Q.-Q.; Hu, Z.; Lin, Z.-P.; Quan, W.-Y.; Deng, Y.-F.; Li, S.-D.; Li, P.-W.; Chen, Y. Chitosan hydrogel in combination with marine peptides from tilapia for burns healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, A.; Osaki, T.; Matahira, Y.; Tsuka, T.; Imagawa, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Minami, S. Correlation of Plasma Amino Acid Concentrations and Chondroprotective Effects of Glucosamine and Fish Collagen Peptide on the Development of Osteoarthritis. J. Vet.-Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, J. Hydrolyzed tilapia fish collagen induces osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 065020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, O.; Reich, C.; Wenisch, S.; Hild, A.; Burg-Roderfeld, M.; Siebert, H.-C.; Arnhold, S. Hydrolyzed fish collagen induced chondrogenic differentiation of equine adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 134, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, D.Q.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, B.L.; Gao, L.Z. A Novel Gelatin-carbon Nanotubes Hybrid Hydrogel. Macromol. Biosci. 2003, 3, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelli, R.; Del Buffa, S.; Tempesti, P.; Bonini, M.; Ridi, F.; Baglioni, P. Enhanced formation of hydroxyapatites in gelatin/imogolite macroporous hydrogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadat-Shojai, M.; Khorasani, M.-T.; Jamshidi, A. 3-Dimensional cell-laden nano-hydroxyapatite/protein hydrogels for bone regeneration applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-F.; Lee, S.-C. Effect of hydrotalcite on the swelling and mechanical behaviors for the hybrid nanocomposite hydrogels based on gelatin and hydrotalcite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Ueda, H.; Tabata, Y. Fabrication and Biocompatibility of Collagen Sponge Reinforced with Poly(glycolic acid) Fiber. Tissue Eng. 2003, 9, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.; Foston, M.; Ragauskas, A.J. Improving the mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin hydrogels cross-linked by cellulose nanowhiskers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Teng, A.; Liu, A. Mechanical reinforcement of gelatin hydrogel with nanofiber cellulose as a function of percolation concentration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Tamura, A.; Arisaka, Y.; Seo, J.H.; Yui, N. Mechanically reinforced gelatin hydrogels by introducing slidable supramolecular cross-linkers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, A.; Kakugo, A.; Gong, J.P.; Osada, Y.; Takai, M.; Erata, T.; Kawano, S. High Mechanical Strength Double-Network Hydrogel with Bacterial Cellulose. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. Physically Crosslinked Biocompatible Silk-Fibroin-Based Hydrogels with High Mechanical Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K. Pullulan dialdehyde crosslinked gelatin hydrogels with high strength for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, T.; Iyoda, T. Egg white-based strong hydrogel via ordered protein condensation. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, e460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Govender, P.P.; Mamo, M.A.; Tamulevicius, S.; Thakur, V.K. Recent progress in gelatin hydrogel nanocomposites for water purification and beyond. Vacuum 2017, 146, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, N.; Hayashi, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Sakiyama, A.; Nakano, A.; Shibata, M. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Photo-Crosslinked Fish Gelatin/Imogolite Nanofiber Composite Hydrogel. Materials 2012, 5, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Mori, M.; Teramoto, N.; Iisaka, M.; Suzuki, N.; Noto, M.; Kaimoto, Y.; Kakimoto, M.; Yamada, M.; Shiratsuchi, E.; et al. Preparation of Photocrosslinked Fish Elastin Polypeptide/Microfibrillated Cellulose Composite Gels with Elastic Properties for Biomaterial Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.M.; Lee, S.W.; Lim, J.N.; You, Y.; Lee, T.S.; Kang, P.H.; Park, W.H. Chitin and chitosan nanofibers: Electrospinning of chitin and deacetylation of chitin nanofibers. Polymer (Guildf) 2004, 45, 7137–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-P.; Feng, X.-Q.; Gao, H. Ultrasonic technique for extracting nanofibers from nature materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 073112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifuku, S.; Nogi, M.; Abe, K.; Yoshioka, M.; Morimoto, M.; Saimoto, H.; Yano, H. Preparation of chitin nanofibers with a uniform width as α-chitin from crab shells. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaberria, A.M.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Diaz, R.H.; Labidi, J. Processing of α-chitin nanofibers by dynamic high pressure homogenization: Characterization and antifungal activity against A. niger. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Cooper, A.; Kapetanovic, A.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Rolandi, M. A facile bottom-up route to self-assembled biogenic chitin nanofibers. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 5298–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchessault, R.H.; Morehead, F.F.; Walter, N.M. Liquid Crystal Systems from Fibrillar Polysaccharides. Nature 1959, 184, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Chitin nanocrystals prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of α-chitin. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadokawa, J.; Takegawa, A.; Mine, S.; Prasad, K. Preparation of chitin nanowhiskers using an ionic liquid and their composite materials with poly(vinyl alcohol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifuku, S.; Saimoto, H. Chitin nanofibers: Preparations, modifications, and applications. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3308–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q. Emerging chitin and chitosan nanofibrous materials for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9477–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, P.; Kazemzadeh-Narbat, M.; Rosenzweig, R.; Zhang, X.; Khademhosseini, A.; Annabi, N.; Rolandi, M. Ultrastrong and flexible hybrid hydrogels based on solution self-assembly of chitin nanofibers in gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA). J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2539–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, D.; Yano, H.; Abe, K. Insect Cuticle-Mimetic Hydrogels with High Mechanical Properties Achieved via the Combination of Chitin Nanofiber and Gelatin. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 5571–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L. Enhanced mechanical properties and gelling ability of gelatin hydrogels reinforced with chitin whiskers. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Peh, G.S.L.; Ang, H.P.; Lwin, N.; Adnan, K.; Mehta, J.; Tan, W.; Yim, E. Sequentially-crosslinked bioactive hydrogels as nano-patterned substrates with customizable stiffness and degradation for corneal tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kooten, T.G.; Spijker, H.T.; Busscher, H.J. Plasma-treated polystyrene surfaces: Model surfaces for studying cell-biomaterial interactions. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, P. A rapid quantitation of cell attachment and spreading based on digital image analysis: Application for cell affinity and compatibility assessment of synthetic polymers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zund, G.; Ye, Q.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Schoeberlein, A.; Schmid, A.C.; Grunenfelder, J.; Vogt, P.; Turina, M. Tissue engineering in cardiovascular surgery: MTT, a rapid and reliable quantitative method to assess the optimal human cell seeding on polymeric meshes. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 1999, 15, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, H.K.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.M.; Oh, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Chung, C.P.; Choi, S.C.; Park, W.H.; Min, B.M. Electrospinning of chitin nanofibers: Degradation behavior and cellular response to normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3934–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Azuma, K.; Izawa, H.; Morimoto, M.; Ochi, K.; Osaki, T.; Ito, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Saimoto, H.; Ifuku, S. Preparation and biocompatibility of a chitin nanofiber/gelatin composite film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1882–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Hatakeyama, M.; Kitaoka, T. Combination of Polysaccharide Nanofibers Derived from Cellulose and Chitin Promotes the Adhesion, Migration and Proliferation of Mouse Fibroblast Cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ezazi, N.Z.; Liu, L.; Ajdary, R.; Xiang, W.; Borghei, M.; Santos, H.A.; Rojas, O.J. Microfibers synthesized by wet-spinning of chitin nanomaterials: Mechanical, structural and cell proliferation properties. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 29450–29459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Zheng, H.; Du, Y.; Xiang, W.; Deng, H. Applications of chitin and chitosan nanofibers in bone regenerative engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquet, D.; Felsenfeld, D.P.; Sheetz, M.P. Extracellular matrix rigidity causes strengthening of integrin-cytoskeleton linkages. Cell 1997, 88, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, T.; Georges, P.C.; Flanagan, L.A.; Marg, B.; Ortiz, M.; Funaki, K.; Zahir, N.; Ming, W.; Weaver, V.; Janmey, P.A. Effects of substrate stiffness on cell morphology, cytoskeletal structure, and adhesion. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2005, 60, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipanayi, E.; Mudera, V.; Brown, R.A. Close dependence of fibroblast proliferation on collagen scaffold matrix stiffness. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2009, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.M.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning of silk fibroin nanofibers and its effect on the adhesion and spreading of normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Hosseinkhani, H.; Hosseinkhani, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Estrada, G.G.; Kobayashi, H. Quantitative analysis of cell adhesion on aligned micro- and nanofibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 84A, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-D.; Huang, C.-F.; Hsu, S. Composites of waterborne polyurethane and cellulose nanofibers for 3D printing and bioapplications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Water | M-FCP | 0.96% CHNF Dispersion | Irgacure 2959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-FCP15 | 8.45 g | 1.50 g (15%) | - | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
| M-FCP15/CHNF0.2 | 6.37 g | 1.50 g (15%) | 2.08 g (0.2%) | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
| M-FCP15/CHNF0.4 | 4.28 g | 1.50 g (15%) | 4.17 g (0.4%) | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
| M-FCP15/CHNF0.6 | 2.20 g | 1.50 g (15%) | 6.25 g (0.6%) | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
| M-FCP20 | 7.95 g | 2.00 g (20%) | - | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
| M-FCP20/CHNF0.2 | 5.87 g | 2.00 g (20%) | 2.08 g (0.2%) | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
| M-FCP20/CHNF0.4 | 3.75 g | 2.00 g (20%) | 4.17 g (0.4%) | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
| M-FCP20/CHNF0.6 | 1.70 g | 2.00 g (20%) | 6.25 g (0.6%) | 0.05 g (0.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yano, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shibata, M.; Ifuku, S.; Teramoto, N. Photocrosslinked Fish Collagen Peptide/Chitin Nanofiber Composite Hydrogels from Marine Resources: Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and an In Vitro Study. Polymers 2023, 15, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030682
Yano S, Yamaguchi K, Shibata M, Ifuku S, Teramoto N. Photocrosslinked Fish Collagen Peptide/Chitin Nanofiber Composite Hydrogels from Marine Resources: Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and an In Vitro Study. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030682
Chicago/Turabian StyleYano, Shinya, Kei Yamaguchi, Mitsuhiro Shibata, Shinsuke Ifuku, and Naozumi Teramoto. 2023. "Photocrosslinked Fish Collagen Peptide/Chitin Nanofiber Composite Hydrogels from Marine Resources: Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and an In Vitro Study" Polymers 15, no. 3: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030682
APA StyleYano, S., Yamaguchi, K., Shibata, M., Ifuku, S., & Teramoto, N. (2023). Photocrosslinked Fish Collagen Peptide/Chitin Nanofiber Composite Hydrogels from Marine Resources: Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and an In Vitro Study. Polymers, 15(3), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030682