Polymer Blends Based on 1-Hexadecyl-3-methyl Imidazolium 1,3-Dimethyl 5-Sulfoisophthalate Ionic Liquid: Thermo-Mechanical, Surface Morphology and Antibacterial Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
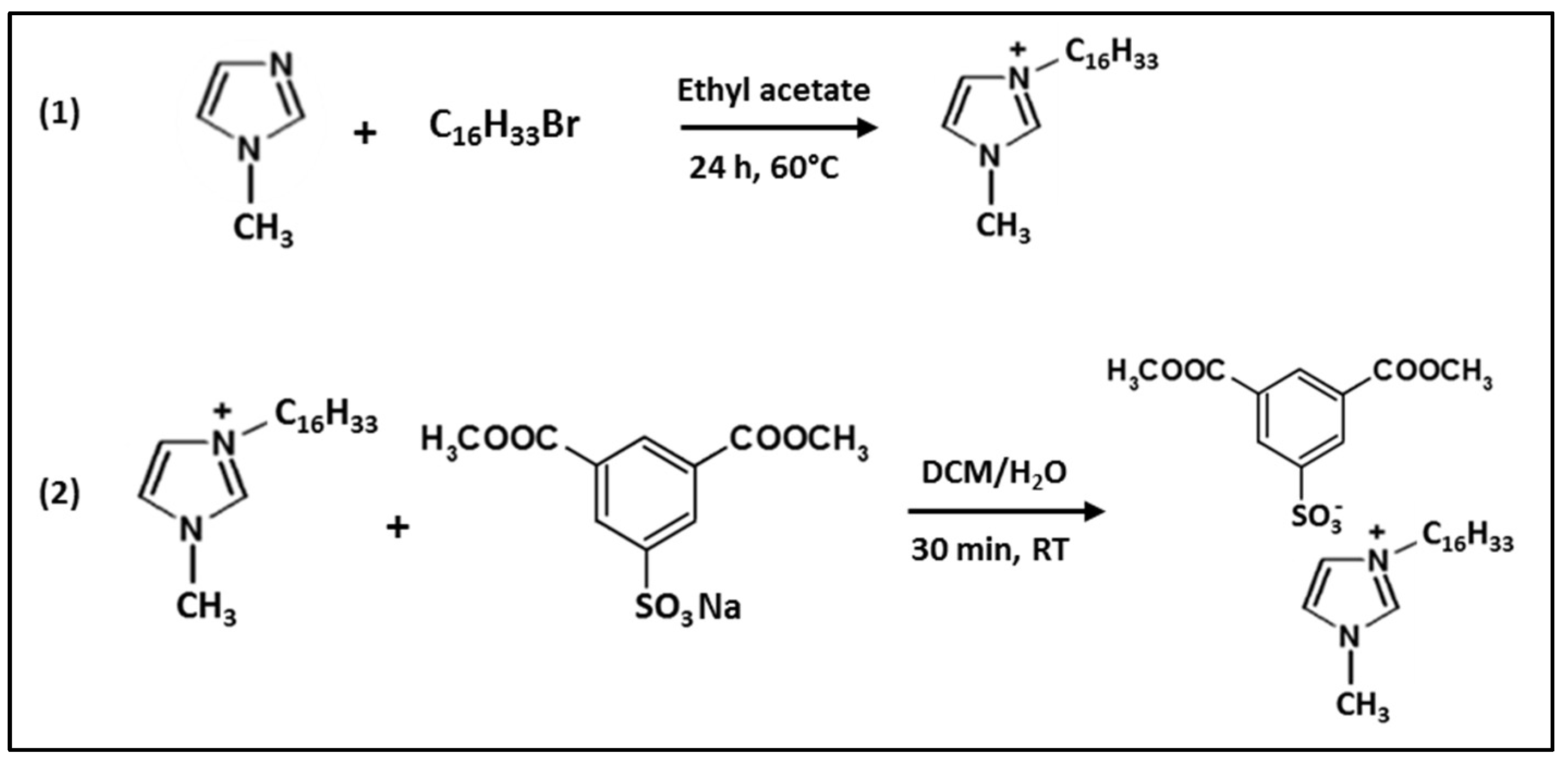
2.2. HdmimDMSIP Synthesis
2.3. Blends and Films Preparation
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.4.3. Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (Py-GC/MS)
2.4.4. Mechanical Properties
2.4.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.6. Contact Angle (CA)
2.4.7. IL Release from the Film Blends
2.4.8. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.4.9. Antibacterial Screening
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of HdmimBr and HdmimDMSIP ILs
3.2. Blend Film Preparation
3.3. Thermal Analysis
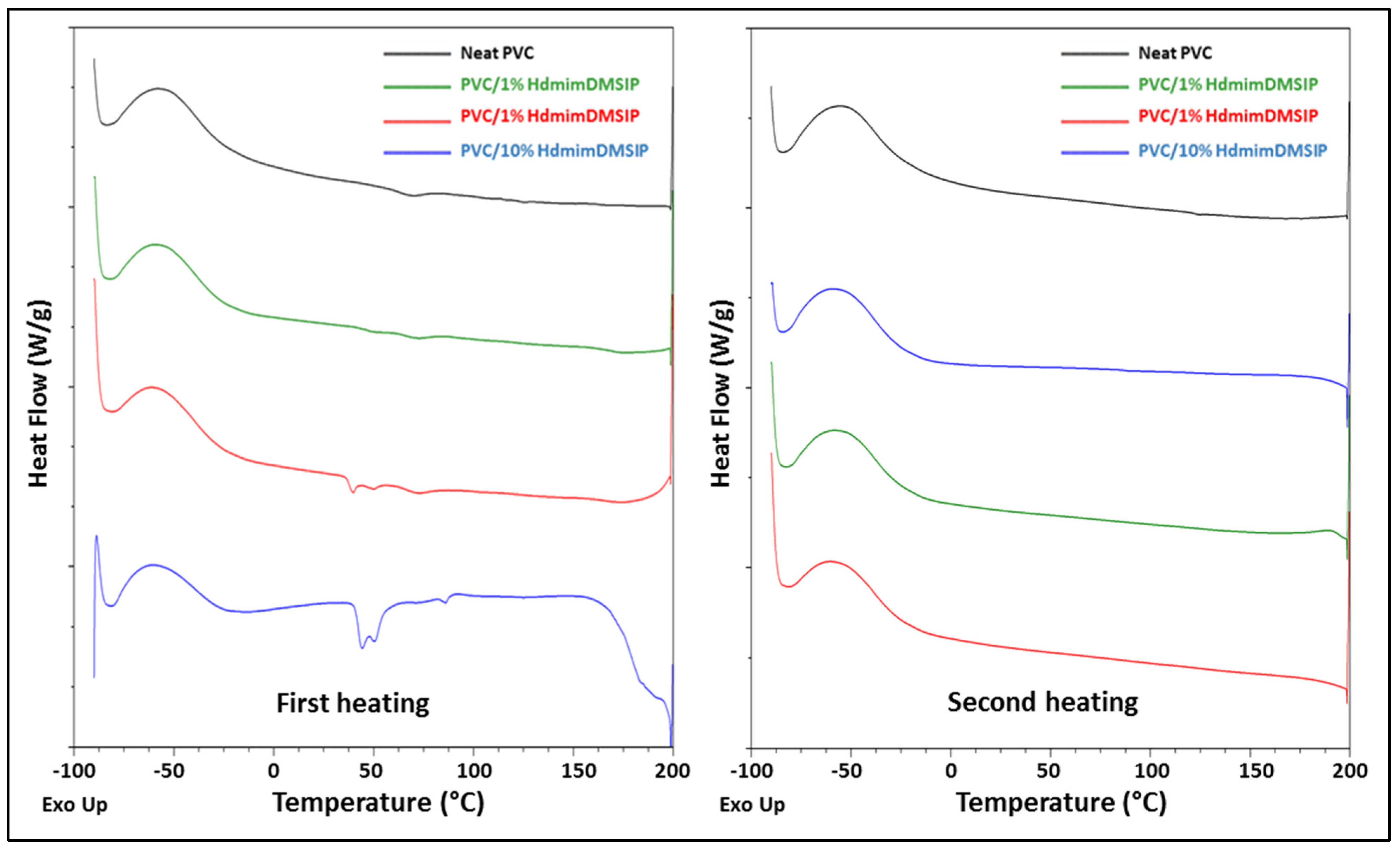
3.3.1. DSC
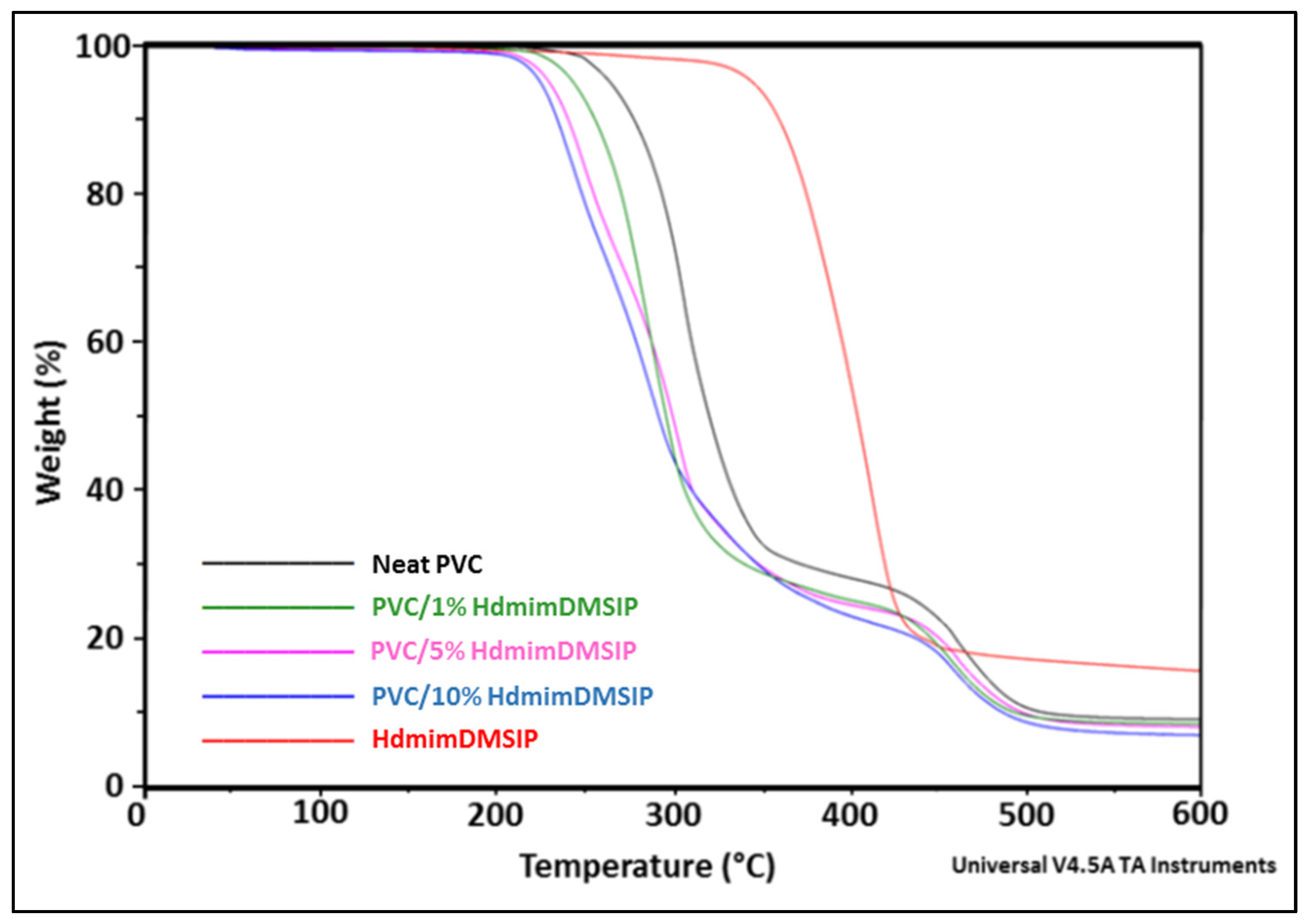
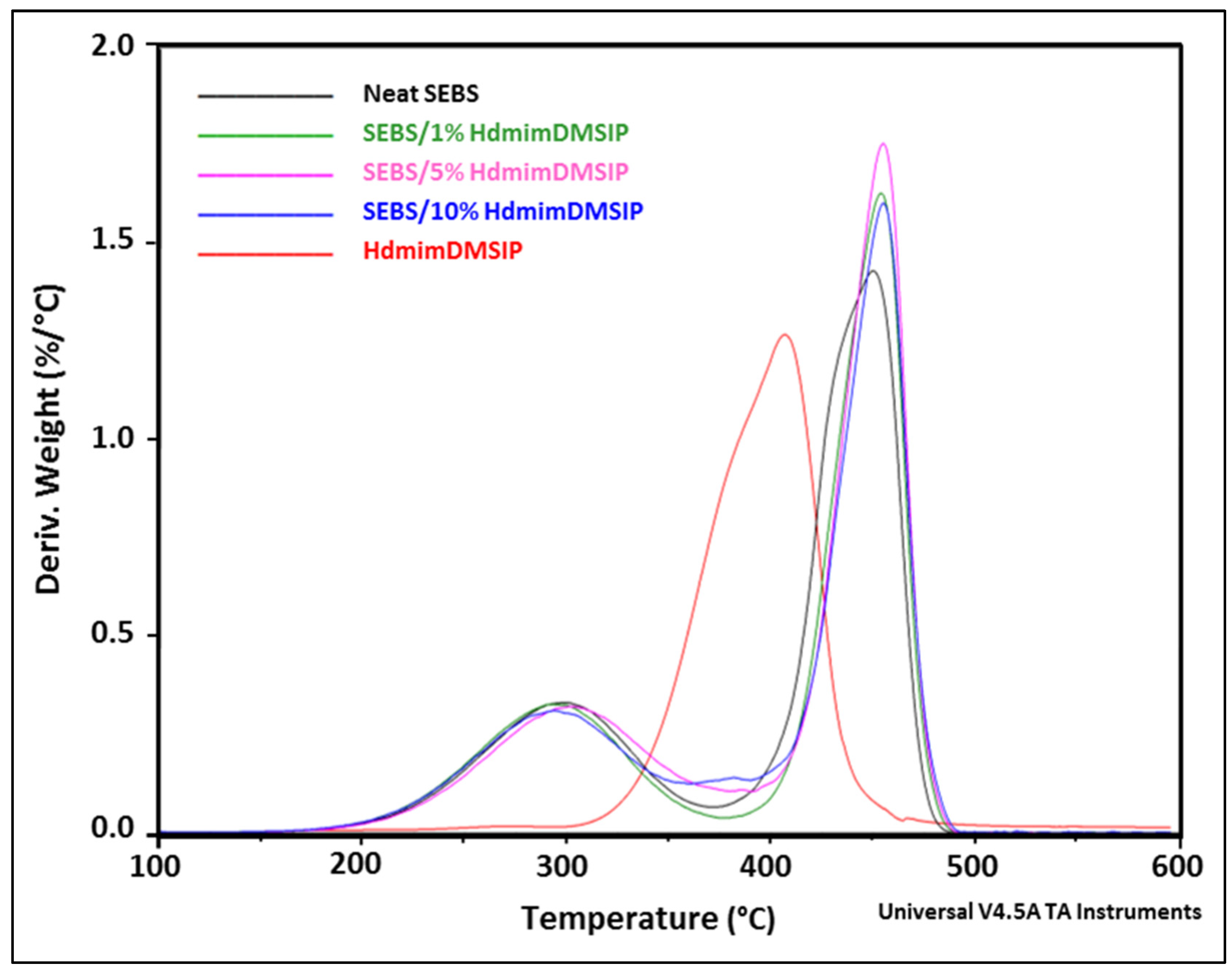
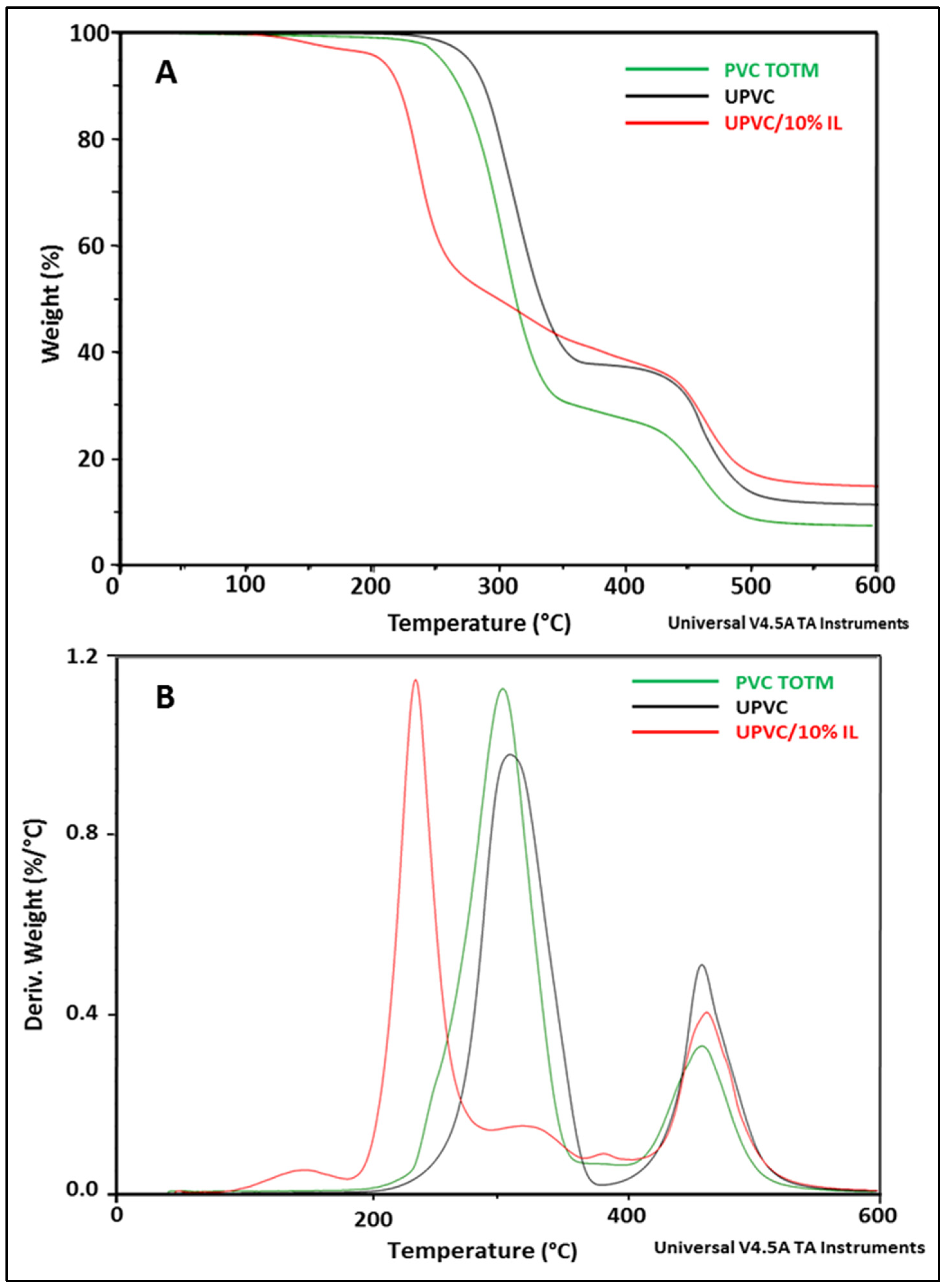
3.3.2. TGA
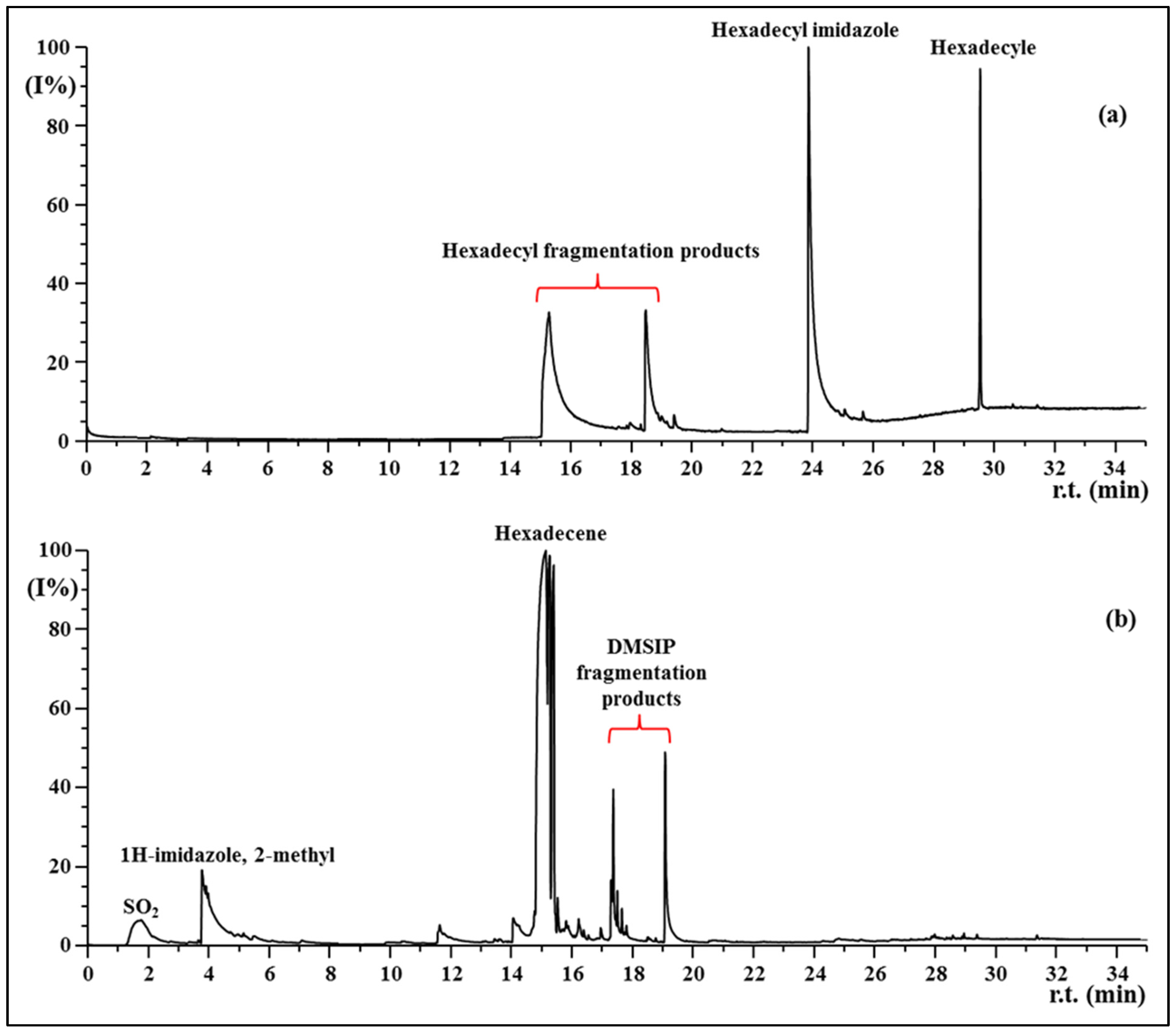
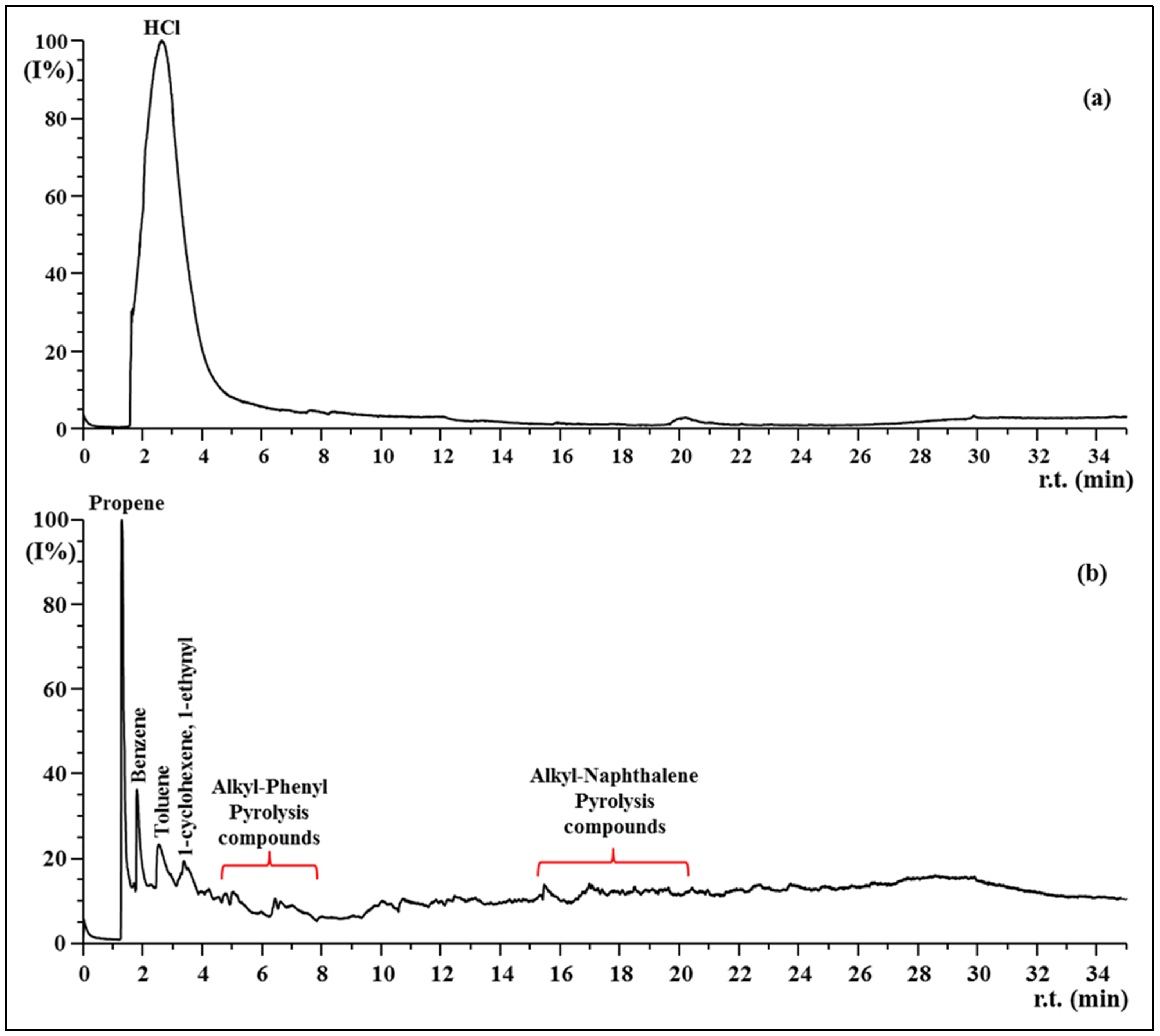
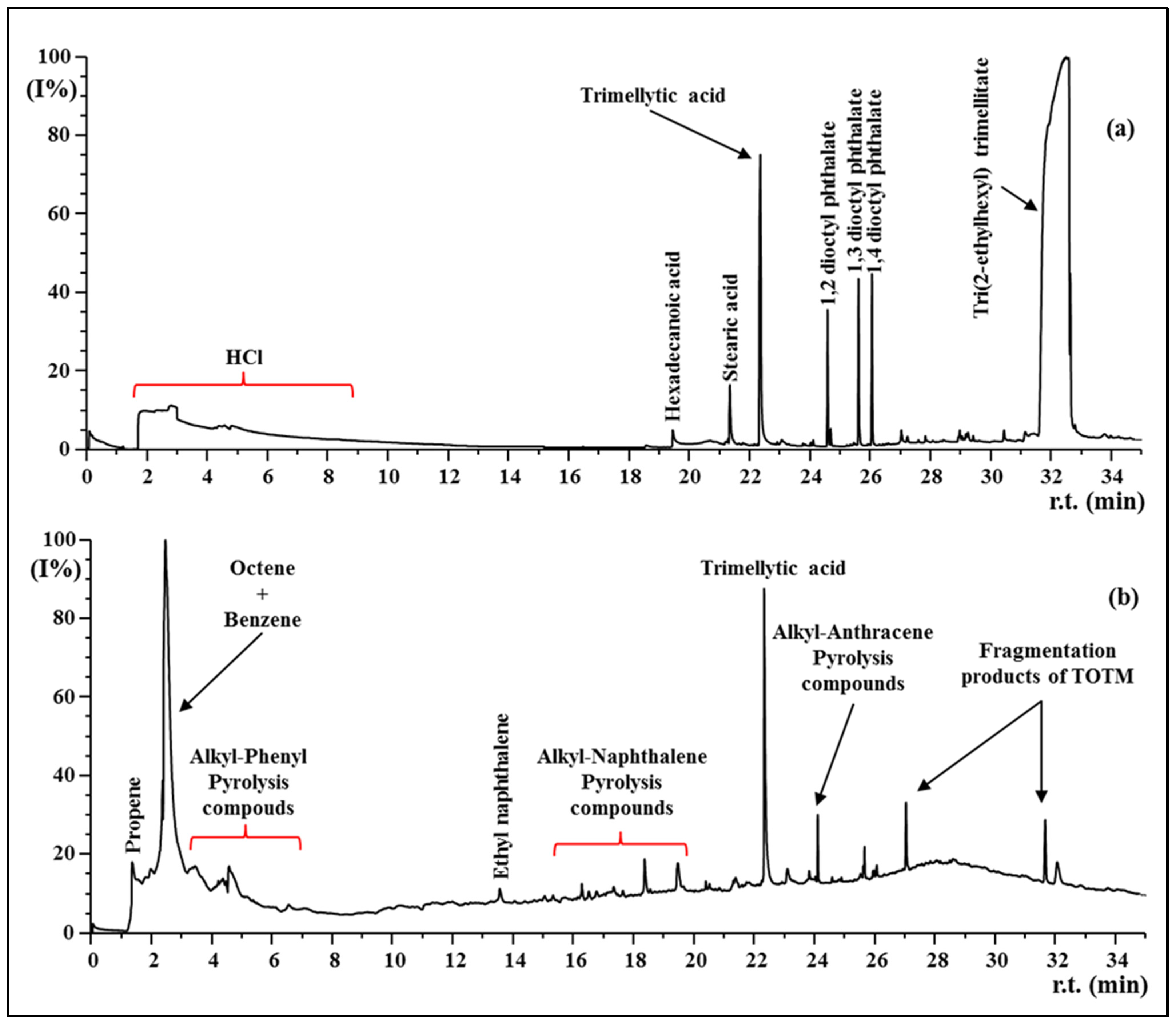
3.4. Py-GC MS
3.5. Mechanical Properties
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy SEM
3.7. Contact Angle
3.8. IL Release
3.9. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allegranzi, B.; Nejad, S.B.; Combescure, C.; Wilco, G.; Attar, H.; Donaldson, L.; Pippet, D. Burden of endemic health-care-associated infection in developing countries: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2011, 377, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Guidos, R.; Gilbert, D.; Bradley, J.; Boucher, H.W.; Sheld, W.M.; Bartlett, J.G.; Edwards, J., Jr. The Epidemic of Antibiotic-Resistant Infections: A Call to Action for the Medical Community from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvey, M.R.; Simor, A.E. Antimicrobial resistance in hospitals: How concerned should we be? CMAJ 2009, 180, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frieri, M.; Kumar, K.; Boutin, A. Antibiotic resistance the global threat. J. Infect. Public Health 2017, 10, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Ullah, S.; Ahmad, I.; Qureshi, A.K.; Balkhairf, K.S.; Rehman, M.A. Green biocides, a promising technology: Current and future applications to industry and industrial processes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 94, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuguerra, S.; Caccamo, L.; Mancuso, M.; Arena, R.; Rappazzo, A.C.; Genovese, L.; Santulli, A.; Messina, C.M.; Maricchiolo, G. The antioxidant power of horseradish, Armoracia rusticana, underlies antimicrobial and antiradical effects, exerted in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 34, 1567–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, M.; Catalfamo, M.; Laganà, P.; Rappazzo, A.C.; Raymo, V.; Zampino, D.C.; Zaccone, R. Screening of antimicrobial activity of citrus essential oils against pathogenic bacteria and Candida strains. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2019, 34, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demberelnyamba, D.; Kim, K.-S.; Choi, S.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.-J.; Yoo, I.-D. Synthesis and antimicrobial properties of imidazolium and pyrrolidinonium salts. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.B.; Long, T.E. Imidazole- and imidazolium-containing polymers for biology and material science applications. Polymer 2010, 51, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampino, D.; Ferreri, T.; Puglisi, C.; Carbone, D.; Mancuso, M.; Zaccone, R.; Scaffaro, R.; Fiaccabrino, A. PVC silver zeolite composites with antimicrobial properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 6734–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, G.; Bernardo, P.; Carroccio, S.; Ussia, M.; Restuccia, C.; Parafati, L.; Calarco, A.; Zampino, D. Heterogenized Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in Pebax®Rnew. Thermal, Gas Transport and Antimicrobial Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampino, D.; Mancuso, M.; Zaccone, R.; Ferreri, T.; Borzacchiello, A.; Zeppetelli, S.; Dattilo, S.; Ussia, M.; Ferreri, L.; Carbone, D.C.; et al. Thermo-mechanical, antimicrobial and biocompatible properties of PVC blends based on imidazolium ionic liquids. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 122, 111920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.C.; Dai, M.; Ahmed, S.; Hao, H.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z. Antimicrobial Drugs in Fighting against Antimicrobial Resistence. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, L.; Consoli, G.M.L.; Clarizia, G.; Zampino, D.C.; Nostro, A.; Granata, G.; Ginestra, G.; Giuffrida, M.L.; Zimbone, S.; Bernardo, P. A Novel Material based on an Antibacterial Choline-Calixarene Nanoassembly Embedded in Thin Films. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 20685–20701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, B.F. Antimicrobial Ionic Liquids. In Ionic Liquids: Applications and Perspectives; Alexander, K., Ed.; InTech: Sydney, Australia, 2011; Volume 26, pp. 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Kumari, M.; Khan, A.B. Recent advances in the applications of ionic liquids in protein stability and activity: A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 3701–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.; Spulak, M.; Garcia, M.T.; Gathergood, N. Antimicrobial toxicity studies of ionic liquids leading to a ‘hit’ MRSA selective antibacterial imidazolium salt. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, Q.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Mao, H.; Wang, B.; Yan, F. Structure-Antibacterial Activity Relationships of Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Monomers, Poly(ionic liquids) and Poly(ionic liquid) Membranes: Effect of Alkyl Chain Length and Cations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12684–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Khastgir, D.; Bhowmick, A.K. Phase Modification of SEBS Block Copolymer by Different Additives and Its Effect on Morphology, Mechanical and Dynamic Mechanical Properties. J. App. Polym. Sci. 1998, 67, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livi, S.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gérard, J.-F.; Pham, T.N. Polymers and Ionic Liquids: A Successful Wedding. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.P.; Rahman, M.; Brazel, C.S. Application of ionic liquids as low-volatility plasticizers for PMMA. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Brazel, C.S. Ionic liquids: New generation stable plasticizers for poly(vinyl chloride). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 96, 3371–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.X.; Wang, S. Study on ionic liquid [bmim]PF6 and [hmim]PF6 as plasticizer for PVC paste resin. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugatti, V.; Viscusi, G.; Di Bartolomeo, A.; Iemmo, L.; Zampino, D.C.; Vittoria, V.; Gorrasi, G. Ionic Liquid as Dispersing Agent of LDH-Carbon Nanotubes into a Biodegradable Vinyl Alcohol Polymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.I.; Rodriguez, H.; Mirjafari, A. Dual functional ionic liquids as plasticisers and antimicrobial agents for medical polymer. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, M.; Berti, C.; Binassi, E.; Fiorini, F.; Sullalti, S.; Acquasanta, F.; Vannini, M.; Di Gioia, D.; Aloisio, I. Imidazolium poly (butylene terephthalate) ionomers with long-term antimicrobial activity. Polymer 2012, 53, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalsky, K.F.; Lyoshina, L.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Tarasyuk, O.; Bulko, O.; Lobok, S. Antimicrobial Properties and Thermal Stability of Polycarbonate Modified with 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Ionic Liquids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Hu, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Xiong, Y. Functional poly(ethylene terephthalate) materials prepared by condensation copolymerization with ionic liquids. Polym. Bull. 2013, 70, 3031–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredelake, C.P.; Crosthwaite, J.M.; Hert, D.G.; Aki, S.N.V.K.; Brennecke, J.F. Thermophysical Properties of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, E.; Calvar, N.; Domínguez, Á. Ionic Liquids—Current State of Art; Scott, H., Ed.; InTech Open Science: Sydney, Australia, 2015; Volume 8, pp. 199–228. ISBN 978-953-51-2122-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, V.F.; Junior, E.C.; Simões, D.N.; Pittol, M.; Tomacheski, D.; Compomanes Santana, R.M. Use of Copper Microparticles in SEBS/PP Compounds. Part 1: Effects on Morphology, Thermal, Physical, Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20180304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.L.; LeCompte, K.; Hargens, L.; McEwen, A.B. Thermal properties of imidazolium ionic liquids. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 357–358, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.H.; Gilman, J.W.; Nyden, N.; Harris, R.H.; Sutto, T.E.; Callahan, J.; Trulove, P.C.; DeLong, H.C.; Fox, D.M. Thermal degradation studies of alkylimidazolium salts and their application in nanocomposites. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 409, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; De Vos, N.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaudo, G.; Puglisi, C. Evolution of Aromatics in the thermal degradation of poly(vinyl chloride): A mechanistic study. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1991, 33, 229–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, H.; Ishimura, S.; Kumai, M. Thermal Decomposition Behaviors of Imidazolium-type Ionic Liquids Studied by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.; Thomas, D.; Vijayalakshmi, K.P.; George, B.K. Mechanistic outlook on thermal degradation of 1,3-dialkyl imidazolium ionic liquids and organoclays. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 9421–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, N.; Girard, M.; Wilde, A.; Bruhn, T.; Kappenstein, O.; Vieth, B.; Hutzier, C.; Luch, A. Thermal stability of polymer additives: Comparison of decomposition models including oxidative pyrolysis. J. Vinyl. Addit. Technol. 2019, 25, E12–E27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistrali, F.; Pironi, A. Styrenic block copolymers. In Developments in Rubber Technology; Whelan, A., Lee, K.S., Eds.; Applied Science: London, UK, 1982; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, O.S.; Broadbelt, L.J. Recovery of high-valued products from styrene-based polymers through coprocessing: Experiments and mechanistic modelling. Catal. Today 1998, 40, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, T.M.; Woo, O.S.; Broadbelt, L.J. Detailed mechanistic modelling of polymer degradation: Application to polystyrene. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supryanto, S.; Ylitervo, P.; Richards, T. Gaseous products from primary reaction of plastic pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.W.; Broadbelt, L.J. Tertiary resource recovery from waste polymers via pyrolysis: Neat and binary mixture reactions of polypropylene and polystyrene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 4716–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.S.; Edge, M.; Wilkinson, A.; Liauw, C.M.; Mourelatou, D.; Barrio, J.; MartõÂnez-Zaporta, M.A. Degradation and stabilisation of styrene-ethylene-butadiene-styrene (SEBS) block copolymer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 71, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, K.; Kovářík, T.; Muzaffar, A.; Basheer Ahamed, M.; Khadheer Pasha, S.K. Mechanical analysis of polymers. In Polymer Science and Innovative Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 117–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, C.A.; Galán, C.; Fatou, J.G.; Parellada, M.D.; Barrio, J.A. Thermal and mechanical properties of poly(styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) triblock copolymers. Polymer 1997, 38, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, T.T.; Bruckard, W.J.; Koh, P.T.L.; Nguyen, A.V. A review of factors that affect contact angle and implications for flotation practice. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2009, 150, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, L.; Chau, P.K.W.; Earle, M.J.; Gilea, M.A.; Gilmore, B.F.; Gorman, S.P.; McCann, M.T.; Seddon, K.R. Antibiofilm activities of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Visser, A.E.; Reichert, W.M.; Willauer, H.D.; Broker, G.A.; Rogers, R.D. Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem. 2001, 3, 3156–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Xu, R.; Dai, P.; Wu, Y. Novel hybrid copolymer by incorporating POSS into hard segments of thermoplastic elastomer SEBS via click coupling reaction. Polymer 2013, 54, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, H. Surface Modification and Characterization of SEBS Films Obtained by In Situ and Ex Situ Oxidization with Potassium Permanganate. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 2262–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Lu, Y.; Li, N.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Q.; Bai, H.; Xie, Z. Hyperbranch-Crosslinked S-SEBS Block Copolymer Membranes for Desalination by Pervaporation. Membranes 2020, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, O.F.; Castro, R.; Gutierrez, M.; Valenzuela, D.G.; Santos, L.; Ramirez, D.; Guzman, L. Novel alkylimidazolium ionic liquids as an Antibacterial Alternative to Pathogens of the Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Molecules 2018, 23, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodyna, D.; Bardeau, J.-F.; Metelytsia, L.; Riabov, S.; Kobrina, L.; Laptiy, S.; Kalashnikova, L.; Parkhomenko, V.; Tarasyuk, O.; Rogalsky, S. Efficient antimicrobial activity and reduced toxicity of 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquid/b-cyclodextrin complex. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Christiansen, B.; Gebel, J.; Goroncy-Bermes, P.; Hartemann, P.; Heeg, P.; Ilschner, C.; Kramer, A.; Larsone, E.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: What is so special about multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria? GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, L.K.; Weinstein, R.A. The epidemiology of Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae: The impact and evolution of a global menace. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




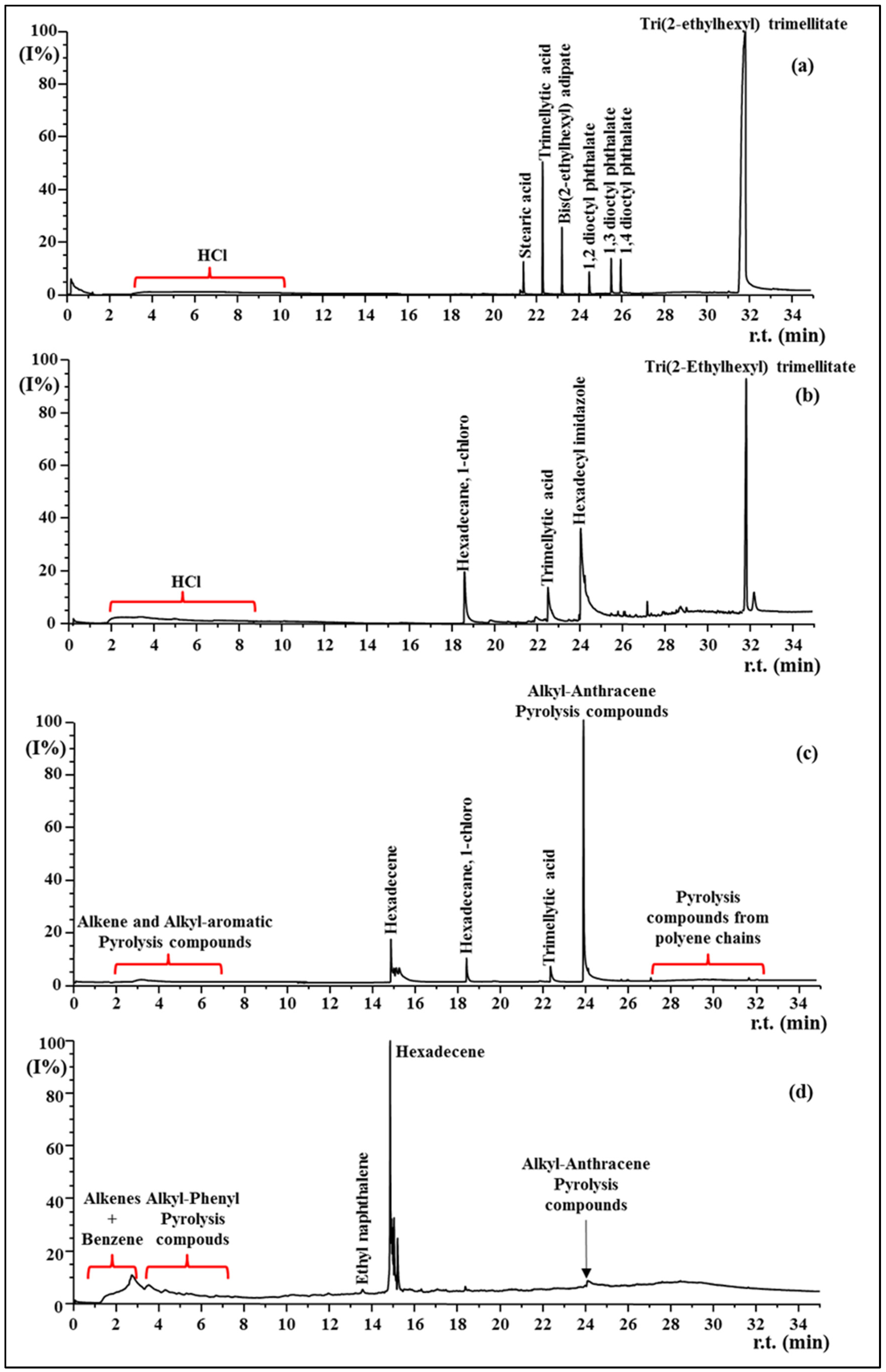

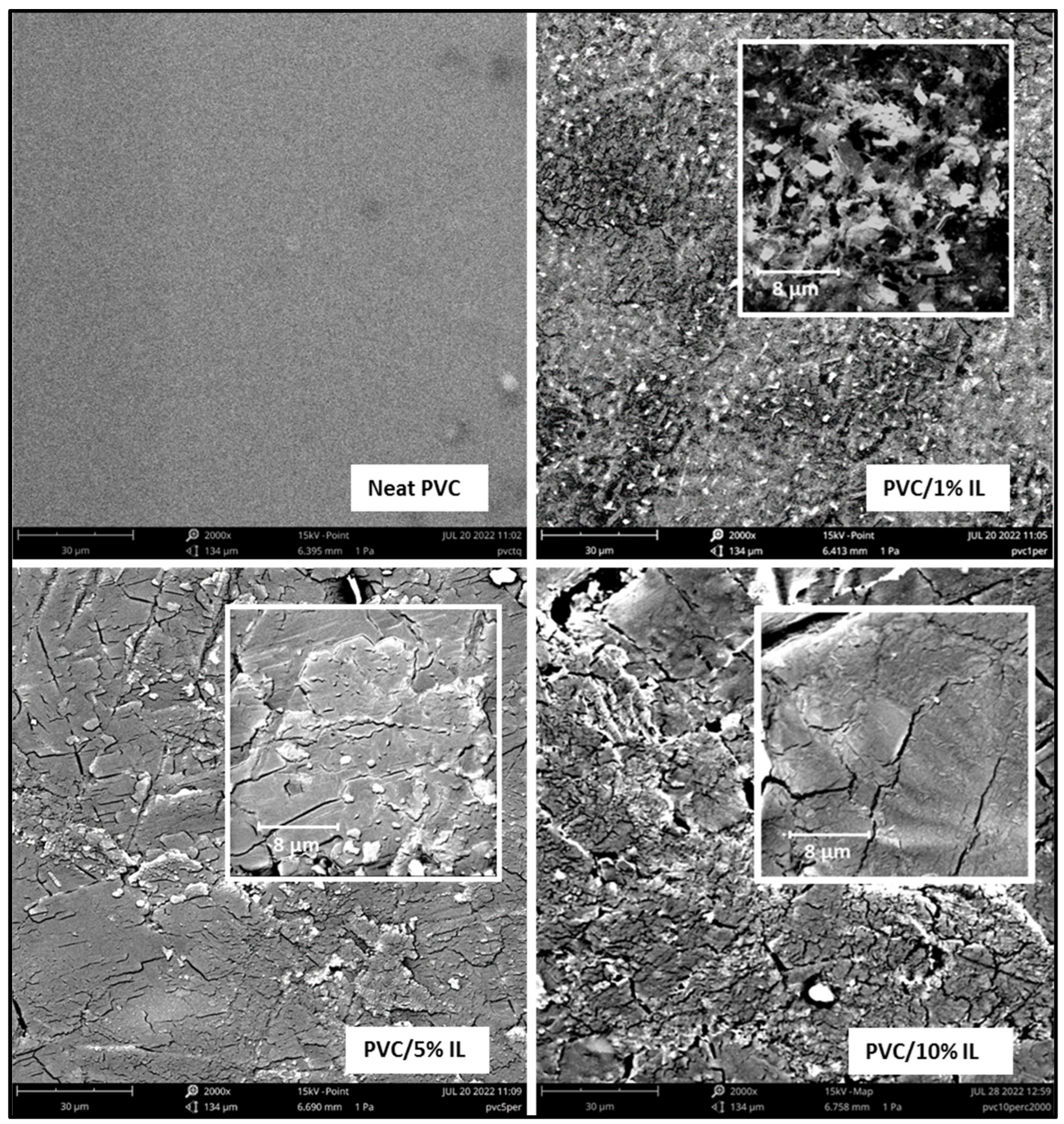
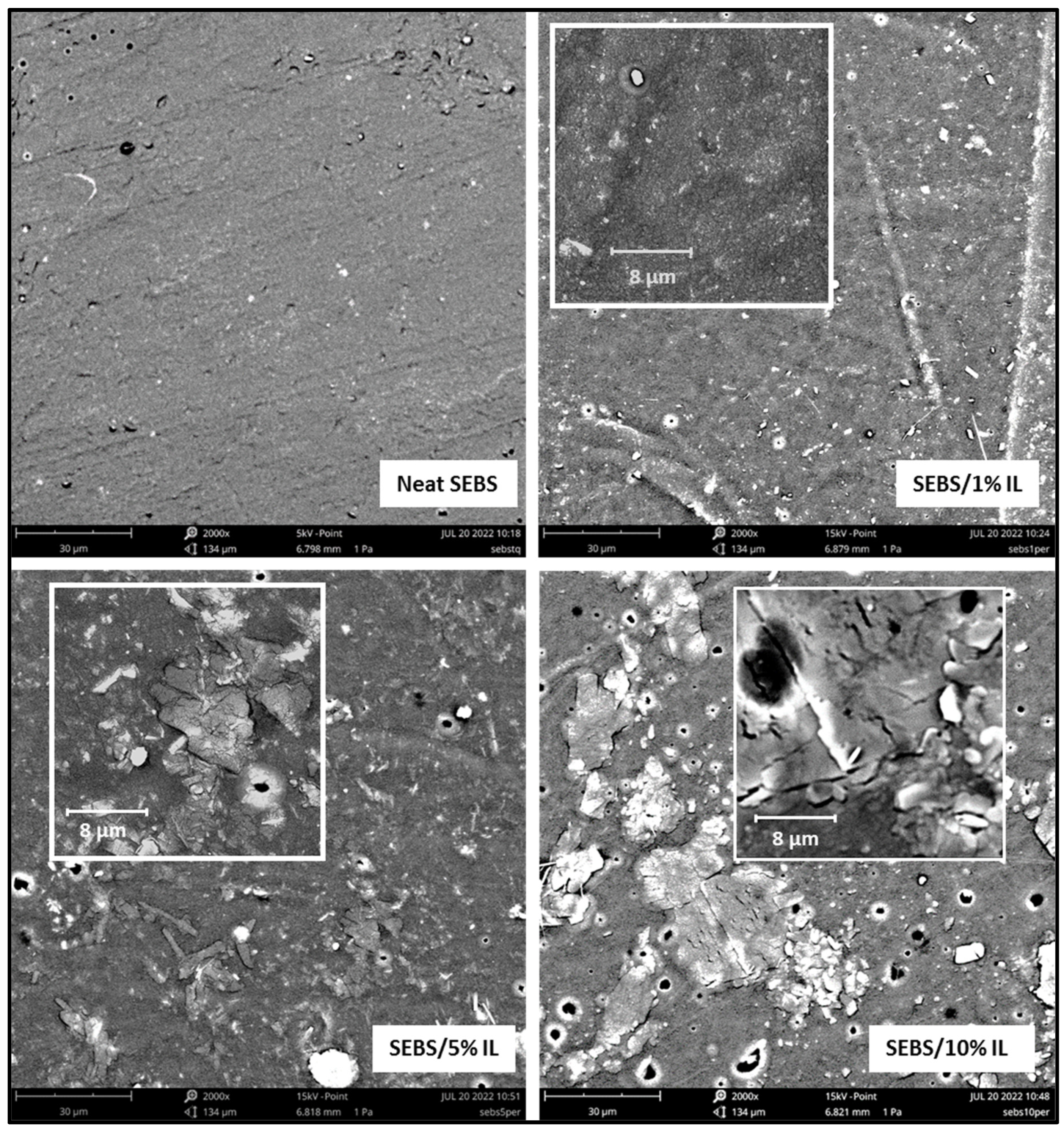
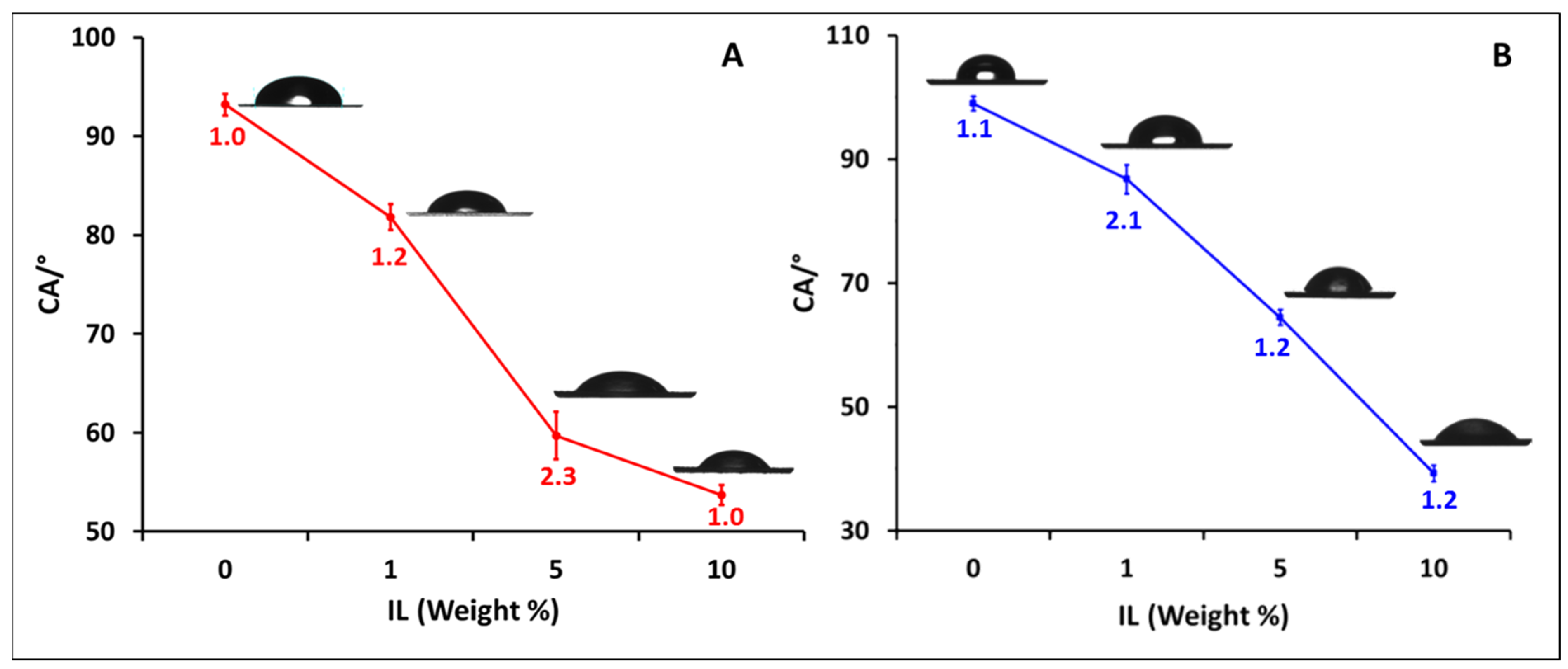

| Samples | E, Young’s Modulus [Mpa] | σ, Tensile Stress [Mpa] | ε, Strain at Break [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | 12.00 ± 0.781 | 13.68 ± 0.33 | 264.70 ± 14.7 |
| PVC/1% IL | 9.81 ± 0.667 *** | 13.00 ± 0.39 | 289.60 ± 16.6 |
| PVC/5% IL | 7.39 ± 0.199 **** | 10.36 ± 1.58 *** | 294.90 ± 38.8 |
| PVC/10% IL | 7.19 ± 0.361 **** | 10.16 ± 1.05 *** | 317.70 ± 44.2 |
| SEBS | 24.60 ± 1.270 | 20.73 ± 0.39 | 1287.90 ± 26 |
| SEBS/1% IL | 23.20 ± 2.150 | 20.04 ± 0.40 | 1139.60 ± 49 *** |
| SEBS/5% IL | 22.40 ± 2.000 *** | 19.84 ± 0.67 | 1120.00 ± 22 *** |
| SEBS/10% IL | 21.20 ± 1.320 *** | 18.26 ± 1.00 **** | 1111.10 ± 30 *** |
| Sample | S. epidermidis Halos (mm) ± SD a | E. coli Halos (mm) ± SD a |
|---|---|---|
| Neat PVC | NI | NI |
| PVC/1% HdmimDMSIP | 3.7 ± 1.2 *** | NI |
| PVC/5% HdmimDMSIP | 5.3 ± 2.1 **** | 2.0 ± 1.4 |
| PVC/10% HdmimDMSIP | 5.7 ± 1.2 **** | 2.0 ± 1.0 |
| Neat SEBS | NI | NI |
| SEBS/1% HdmimDMSIP | 2.0 ± 0.1 *** | NI |
| SEBS/5% HdmimDMSIP | 4.5 ± 0.7 **** | 2.0 ± 0.1 *** |
| SEBS/10% HdmimDMSIP | 8.0 ± 0.1 **** | 3.0 ± 0.1 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zampino, D.C.; Samperi, F.; Mancuso, M.; Ferreri, T.; Ferreri, L.; Dattilo, S.; Mirabella, E.F.; Carbone, D.C.; Recca, G.; Scamporrino, A.A.; et al. Polymer Blends Based on 1-Hexadecyl-3-methyl Imidazolium 1,3-Dimethyl 5-Sulfoisophthalate Ionic Liquid: Thermo-Mechanical, Surface Morphology and Antibacterial Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15040970
Zampino DC, Samperi F, Mancuso M, Ferreri T, Ferreri L, Dattilo S, Mirabella EF, Carbone DC, Recca G, Scamporrino AA, et al. Polymer Blends Based on 1-Hexadecyl-3-methyl Imidazolium 1,3-Dimethyl 5-Sulfoisophthalate Ionic Liquid: Thermo-Mechanical, Surface Morphology and Antibacterial Properties. Polymers. 2023; 15(4):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15040970
Chicago/Turabian StyleZampino, Daniela C., Filippo Samperi, Monique Mancuso, Tiziana Ferreri, Loredana Ferreri, Sandro Dattilo, Emanuele F. Mirabella, Domenico C. Carbone, Giuseppe Recca, Andrea A. Scamporrino, and et al. 2023. "Polymer Blends Based on 1-Hexadecyl-3-methyl Imidazolium 1,3-Dimethyl 5-Sulfoisophthalate Ionic Liquid: Thermo-Mechanical, Surface Morphology and Antibacterial Properties" Polymers 15, no. 4: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15040970
APA StyleZampino, D. C., Samperi, F., Mancuso, M., Ferreri, T., Ferreri, L., Dattilo, S., Mirabella, E. F., Carbone, D. C., Recca, G., Scamporrino, A. A., Novello, E., & Puglisi, C. (2023). Polymer Blends Based on 1-Hexadecyl-3-methyl Imidazolium 1,3-Dimethyl 5-Sulfoisophthalate Ionic Liquid: Thermo-Mechanical, Surface Morphology and Antibacterial Properties. Polymers, 15(4), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15040970











