Fabrication and Assessment of Orodispersible Tablets Loaded with Cubosomes for the Improved Anticancer Activity of Simvastatin against the MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of SIM-Loaded Cubosomes
2.2.2. Characterisation of SIM-Loaded Cubosomes
- Determination of Entrapment Efficiency percentage (EE%)
- Vesicle Size Distribution and Zeta Potential analysis.
- In Vitro Release
- Qn: cumulative percentage of SIM released
- Cn: concentration of SIM in the dissolution medium at the nth sample
- Vr: volume of dissolution medium
- Vs: volume of sample
- : the summation of the concentrations measured formerly
2.2.3. Characterisation of the Selected SIM-Loaded Cubosomal Formula
- X-ray Diffraction Analysis
- Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
- The Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra of SIM, PF-127, mannitol and SIM-loaded cubosome were obtained by an FTIR Perkin Elmer spectrophotometer (Spectrum BX, USA). Firstly, an accurate weight of each sample was mixed with potassium bromide (spectroscopic grade) then compressed into disks with a hydraulic press. The scan was performed from 4000 to 600 cm−1. The results were investigated by Perkin Elmer software (Spectrum V5.3.1, Milford, MA, USA).
- Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
- To assess the morphological characteristics of the selected formula, a transmission electron microscope (TEM; JEOL JEM-1010, Tokyo, Japan) was utilized. Firstly, the sample was sonicated for 1 min and suitably diluted then one drop from the formula was put on a carbon-coated copper grid. After that, phosphotungstic acid was added to stain the sample. Finally, the sample was allowed to be dried in the air for 5 min and image was taken at a magnification power of 10,000×. The apparatus was operated at 80 KV.
2.2.4. Manufacture of Directly Compressed Oral Disintegrating Tablets Containing the Selected Cubosomal Formula
2.2.5. Characterization of SIM Cubosomes-Loaded ODTs
- Weight Variation
- Tablets’ Hardness
- Friability
- In Vitro Tablet Disintegration
- In Vitro Dissolution Analysis
2.2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Analysis
- Cell Culture
- MTT Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Entrapment Efficiency Percentage (EE%)
3.2. Vesicle Size Distribution and Zeta Potential Analysis
3.3. In Vitro Release
3.4. Characterisation of the Selected SIM-Loaded Cubosomal Formula
3.4.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.4.2. FTIR Analysis
3.4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.5. Evaluation of ODTs Containing SIM Cubosomes
3.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rezvanian, M.; Mohd Amin, M.C.I.; Ng, S.F. Development and physicochemical characterization of alginate composite film loaded with simvastatin as a potential wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heba, F.S.; Rasha, M.K.; Heba, A.A.; Hanan, O.F.; Randa, M.Z. Fabrication and Appraisal of Simvastatin via Tailored Niosomal Nanovesicles for Transdermal Delivery Enhancement: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran, G.; Salvamani, S.; Ahmad, S.A.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Pattiram, P.D.; Shukor, M.Y. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity and phytocomponent investigation of Basella alba leaf extract as a treatment for hypercholesterolemia. Drug Des. Devel. 2015, 9, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fazio, S. The role of statin therapy in primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. US Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, B.; Nicola, F.; Lorenzo, A.; Rodolfo, P.; Corsini, A. Pleiotropic effects of statin in atherosclerosis and diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, B72–B78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, J.; Yu, Z. Pleiotropic use of statins as non-lipid-lowering drugs. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusewicz, L.; Meissner, J.; Toporkiewicz, M.; Sikorski, A.F. The effect of statins on cancer cells–review. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4889–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Nordestgaard, B.; Bojesen, S. Statin use and reduced cancer-related mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Aragaki, A.K.; Tang, J.Y.; Kurian, A.W.; Manson, J.E.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Simon, M.; Desai, P.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Liu, S. Statin use and all-cancer survival: Prospective results from the Women’s Health Initiative. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Z.; Liang, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, W. Effects of statins on cancer mortality and progression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 95 cohorts including 1,111,407 individuals. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majidi, A.; Na, R.; Jordan, S.J.; De, F.A.; Webb, P.M. Statin use and survival following a diagnosis of ovarian cancer: A prospective observational study. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.R.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Chen, K.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Shih, W.T. Statin use improves overall survival of patients with gastric cancer after surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy in Taiwan: A nationwide matched cohort study. Cancers 2020, 12, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, C.; Sagar, S. Enhancing the bioavailability of simvastatin using microemulsion drug delivery system. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 5, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, D.S.; Nasr, M.; Mostafa, M. Bioavailability and hypocholesterolemic effect of proniosomal simvastatin for transdermal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 344–351. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, R.; Larsen, S.W.; Yaghmur, A. Citrem-phosphatidylcholine nano-self-assemblies: Solubilization of bupivacaine and its role in triggering colloidal transition from vesicles to cubosomes and hexosomes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 15142–15150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghmur, A.; Tran, B.V.; Moghimi, S.M. Non-lamellar liquid crystalline nanocarriers for thymoquinone encapsulation. Molecules 2020, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakotoarisoa, M.; Angelov, B.; Garamus, V.M.; Angelova, A. Curcumin-and fish oil-loaded spongosome and cubosome nanoparticles with neuroprotective potential against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in differentiated human SH-SY5Y cells. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Abd el Basset, S.R. Endocytic pathways of optimized resveratrol cubosomes capturing into human hepatoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, M.; Elsayed, I.; Aboelwafa, A.A.; Elshafeey, A.H. A novel concept of overcoming the skin barrier using augmented liquid nanocrystals: Box-Behnken optimization, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.; Aboelwafa, A.A.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Elsayed, I. Central composite optimization of ocular mucoadhesive cubosomes for enhanced bioavailability and controlled delivery of voriconazole. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Hamidi, M. Cubosomes: Remarkable drug delivery potential. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, P.D.; Mertins, O.; Angelov, B.; Angelova, A. Cubosomal lipid nanoassemblies with pH-sensitive shells created by biopolymer complexes: A synchrotron SAXS study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakaskar, R.R. General overview of lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles, dendrimers, micelles, liposomes, spongosomes and cubosomes. J. Drug Targ. 2018, 26, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Tian, D.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Tian, M. Theranostic combinatorial drug-loaded coated cubosomes for enhanced targeting and efficacy against cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swarnakar, N.K.; Thanki, K.; Jain, S. Bicontinuous cubic liquid crystalline nanoparticles for oral delivery of doxorubicin: Implications on bioavailability, therapeutic efficacy, and cardiotoxicity. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1219–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Garg, A.; Verma, A. Nano lipid based carriers for lymphatic voyage of anti-cancer drugs: An insight into the in-vitro, ex-vivo, in-situ and in-vivo study models. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, P.; Giram, P.; Bhole, R.P.; Chang, H.-I.; Raut, S.Y. Nanocarriers based oral lymphatic drug targeting: Strategic bioavailability enhancement approaches. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hadj Ayed, O.; Lassoued, M.A.; Sfar, S. Quality-by-Design Approach Development, Characterization, and In Vitro Release Mechanism Elucidation of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Quetiapine Fumarate Oral Delivery. J. Pharm. Innov. 2021, 17, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radbeh, Z.; Asefi, N.; Hamishehkar, H.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Pezeshki, A. Novel carriers ensuring enhanced anti-cancer activity of Cornus mas (cornelian cherry) bioactive compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Pan, H.; Liu, Y. Glycyrrhetinic acid modified MOFs for the treatment of liver cancer. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 325602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.; Nasr, M.; Saad, A.S.; Mourad, A.A.; Gobba, N.A.; Shata, A.; Hafez, A.-M.; Elsergany, R.N.; Elagamy, H.I.; El-Ahwany, E. Albendazole-loaded cubosomes interrupt the ERK1/2-HIF-1α-p300/CREB axis in mice intoxicated with diethylnitrosamine: A new paradigm in drug repurposing for the inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, M.M.; Sarieddine, R.; Alwattar, J.K.; Chouaib, R.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Anticancer activity of thymoquinone cubic phase nanoparticles against human breast cancer: Formulation, cytotoxicity and subcellular localization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, V.; Janakiraman, K.; Krishnaswami, V.; Natesan, S.; Kandasamy, R. pH responsive delivery of lumefantrine with calcium phosphate nanoparticles loaded lipidic cubosomes for the site specific treatment of lung cancer. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2019, 224, 104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cytryniak, A.; Nazaruk, E.; Bilewicz, R.; Górzyńska, E.; Żelechowska-Matysiak, K.; Walczak, R.; Mames, A.; Bilewicz, A.; Majkowska-Pilip, A. Lipidic cubic-phase nanoparticles (cubosomes) loaded with doxorubicin and labeled with 177Lu as a potential tool for combined chemo and internal radiotherapy for cancers. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Eblovi, N.; Rasi, S.; Drechsler, M.; Di Gregorio, G.M.; Menegatti, E.; Cortesi, R. Lipid-based supramolecular systems for topical application: A preformulatory study. AAPS PharmSci 2003, 5, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, K.; Poorva, J.; Sourabh, J.; Richa, J.; Saurabh, B.; Aakanchha, J. Topical delivery of erythromycin through cubosomes for acne. Pharma. Nanotech. 2018, 6, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Randa, M.Z.; Mohammed, F.A.; Manal, A.A.; Shaikah, F.A.; Vidya, D.S.; Alanood, S.A.; Basmah, N.A.; Rehab, M.Y.; Ossama, M.S. Brain Targeting of Quetiapine Fumarate via Intranasal Delivery of Loaded Lipospheres: Fabrication, In-Vitro Evaluation, Optimization, and In-Vivo Assessment. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1083. [Google Scholar]
- Randa, M.Z.; Munerah, M.A.; Manal, A.A.; Lara, A.E.; Vidya, D.S.; Alanood, S.A.; Rehab, M.Y.; Mayada, S. Central Composite Optimization of Glycerosomes for the Enhanced Oral Bioavailability and Brain Delivery of Quetiapine Fumarate. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 940. [Google Scholar]
- Azza, A.; Matloub, A.; Mona, M.A.; Alaa, H.S.; Maha, Z.R.; Hanan, F.A.; Ghada, I.F. Cubic liquid crystalline nanoparticles containing a polysaccharide from Ulva fasciata with potent antihyperlipidaemic activity. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, B.A.; Sayed, S.; Elsayed, G.M. Enhanced transdermal delivery of ondansetron using nanovesicular systems: Fabrication, characterization, optimization and ex-vivo permeation study-Box-Cox transformation practical example. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 115, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadel, A.; Areej, H.A. Nanostructured liquid crystalline formulation as a remarkable new drug delivery system of anti-epileptic drugs for treating children patients. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 790–800. [Google Scholar]
- Qushawy, M.; Nasr, A.; Abd-Alhaseeb, M.; Swidan, S. Design, optimization and characterization of a transfersomal gel using miconazole nitrate for the treatment of candida skin infections. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, V.; Swarnakar, N.K.; Mishra, P.R.; Verma, A.; Kaul, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Jain, N.K. Paclitaxel loaded PEGylated gleceryl monooleate based nanoparticulate carriers in chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7206–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Pan, H.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Pan, W.; Yuan, Y. The potential use of novel chitosan-coated deformable liposomes in an ocular drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, S.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Kamel, A.O. Etodolac transdermal cubosomes for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Ex vivo permeation and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies. Drug Delv. 2017, 24, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samia, M.O.; Aliaa, I.; Kariman, D.H.; Sara, H.D. Formulation and Evaluation of Cubosomes as Skin Retentive System for Topical Delivery of Clotrimazole. J. Adv. Pharm. Res. 2019, 3, 68–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xinsheng, P.; Yanfang, Z.; Ke, H.; Lingzhen, Q.; Linghui, D.; Ge, L.; Xin, P.; Chuanbin, W. Characterization of cubosomes as a targeted and sustained transdermal delivery system for capsaicin. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 4209–4218. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.I. Tenoxicam-Kollicoat IR® Binary Systems: Physicochemical and Biological Evaluation. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2014, 71, 647–659. [Google Scholar]
- Md, S.; Abdullah, S.T.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bani-Jaber, A.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Karim, S.; Shahzad, N.; Gabr, G.A.; Alamoudi, A.J.; Rizg, W.Y. Ambroxol hydrochloride loaded gastro-retentive nanosuspension gels potentiate anticancer activity in lung cancer (A549) cells. Gels 2021, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, R.M.; Alfadhel, M.M.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alsaqr, A.; Al-Kharashi, L.A.; Anwer, M.K. Formulation of Chitosan-Coated Brigatinib Nanospanlastics: Optimization, Characterization, Stability Assessment and In-Vitro Cytotoxicity Activity against H-1975 Cell Lines. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
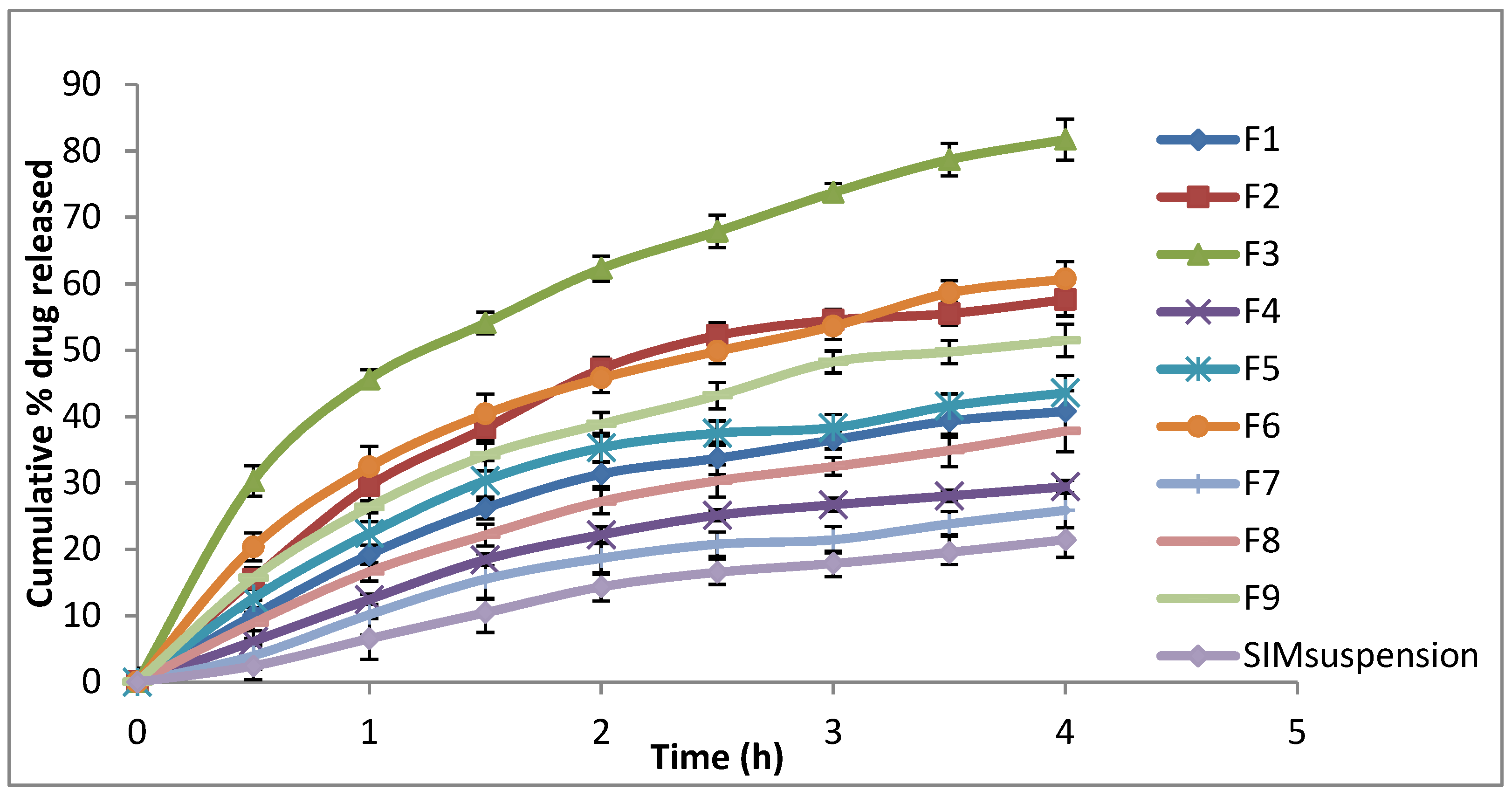





| Formulation | Dispersed Phase (5% of Total Dispersion Weight) | Stabiliser | EE% | Particle Size (nm ± SD) | PDI (±SD) | Zeta Potential (mV ± SD) | % Drug Released | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % GMO | % Pluronic F127 | % PVA | ||||||
| F1 | 97.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 33.52 ± 1.55 | 188.3 ± 4.32 | 0.355 ± 0.03 | −55.5 ± 0.17 | 40.78 ± 1.23 |
| F2 | 95 | 5 | 0 | 51.20 ± 1.11 | 311.2 ± 10.13 | 0.600 ± 0.01 | −51.0 ± 0.85 | 57.60 ± 2.45 |
| F3 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 61.87 ± 1.46 | 316.6 ± 11.26 | 0.677 ± 0.02 | −46.0 ± 0.61 | 81.71 ± 3.12 |
| F4 | 95 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 40.05 ± 1.46 | 197.3 ± 4.98 | 0.369 ± 0.01 | −57.9 ± 0. 11 | 29.42 ± 2.35 |
| F5 | 92.5 | 5 | 2.5 | 57.41 ± 1.29 | 199.9 ± 3.88 | 0.352 ± 0.01 | −54.6 ± 0. 15 | 43.57 ± 2.87 |
| F6 | 87.5 | 10 | 2.5 | 70.39 ± 1.75 | 194.1 ± 3.01 | 0.292 ± 0.04 | −47.6 ± 0. 15 | 60.71 ± 1.89 |
| F7 | 92.5 | 2.5 | 5 | 49.71 ± 1.69 | 187.4 ± 3.56 | 0.349 ± 0.02 | −56.3 ± 0. 55 | 25.88 ± 3.45 |
| F8 | 90 | 5 | 5 | 65.09 ± 1.97 | 217.3 ± 5.23 | 0.401 ± 0.01 | −53.5 ± 0. 25 | 37.80 ± 2.54 |
| F9 | 85 | 10 | 5 | 80.80 ± 1.35 | 181.9 ± 3.64 | 0.352 ± 0.01 | −47.7 ± 0. 78 | 51.45 ± 2.84 |
| Formula | Zero-Order | First-Order | Higuchi Diffusion Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Slope | R2 | Slope | R2 | Slope | |
| F1 | 0.9193 | −9.814 | 0.9538 | −0.0563 | 0.9863 | −21.912 |
| F2 | 0.8767 | −13.814 | 0.9308 | −0.0939 | 0.9737 | −31.3812 |
| F3 | 0.8751 | −17.883 | 0.9864 | −0.1723 | 0.9946 | −41.0951 |
| F4 | 0.9161 | −7.29 | 0.9364 | −0.0381 | 0.9717 | −16.1828 |
| F5 | 0.8683 | −9.9166 | 0.9122 | −0.0583 | 0.9801 | −22.709 |
| F6 | 0.8892 | −13.549 | 0.9599 | −0.0948 | 0.9950 | −30.8936 |
| F7 | 0.9330 | −6.36 | 0.9494 | −0.0322 | 0.9645 | −13.9382 |
| F8 | 0.9355 | −8.96 | 0.9632 | −0.0497 | 0.9859 | −19.8257 |
| F9 | 0.8984 | −12.003 | 0.9496 | −0.0764 | 0.9909 | −27.1718 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaki, R.M.; El Sayeh Abou El Ela, A.; Almurshedi, A.S.; Aldosari, B.N.; Aldossari, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.A. Fabrication and Assessment of Orodispersible Tablets Loaded with Cubosomes for the Improved Anticancer Activity of Simvastatin against the MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Polymers 2023, 15, 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071774
Zaki RM, El Sayeh Abou El Ela A, Almurshedi AS, Aldosari BN, Aldossari AA, Ibrahim MA. Fabrication and Assessment of Orodispersible Tablets Loaded with Cubosomes for the Improved Anticancer Activity of Simvastatin against the MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071774
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaki, Randa Mohammed, Amal El Sayeh Abou El Ela, Alanood S. Almurshedi, Basmah Nasser Aldosari, Abdullah A. Aldossari, and Mohamed A. Ibrahim. 2023. "Fabrication and Assessment of Orodispersible Tablets Loaded with Cubosomes for the Improved Anticancer Activity of Simvastatin against the MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071774
APA StyleZaki, R. M., El Sayeh Abou El Ela, A., Almurshedi, A. S., Aldosari, B. N., Aldossari, A. A., & Ibrahim, M. A. (2023). Fabrication and Assessment of Orodispersible Tablets Loaded with Cubosomes for the Improved Anticancer Activity of Simvastatin against the MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Polymers, 15(7), 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071774







