3.1. Phase 1—Print Calibrations
With FFF, preliminary calibration is crucial so that adequate melt conditions can be set at the nozzle and proper bed adhesion can be achieved for a given printer–filament combination. Nozzle temperatures were first calibrated for each filament using temperature towers, as shown in
Figure 3. These towers print sections at a specified temperature that bridge from one side to the other, increasing in temperature as it moves vertically from section to section away from the build plate. Feature resolution (e.g., from the inscribed temperature markings), bridging capability, and stringing were all qualitatively assessed to identify build quality at each temperature. The optimal temperature for each filament was identified as the lowest temperature that maintains feature resolutions, enables proper bridging, and contains minimal stringing.
Table 1 contains the optimal nozzle temperatures for all nine filaments. The White filaments for each brand appear to have optimal temperatures less than or equal to the Black and Green filaments. This may be due to differences in the rheological behavior of the highly pigmented filaments when molten, as well as differences in processing history, which affect melt flow during extrusion through the nozzle [
42,
48]. Across each filament color, SUNLU typically has the highest optimal nozzle temperature, followed by OVERTURE and then HATCHBOX. While the disparities in temperature here are not drastic, these again may be due to slight differences in compositions, molecular weights, etc., from being manufactured by different companies, thus likely affecting the rheological behavior at higher temperatures and, thus, the ideal extrusion temperature through the nozzle. Interestingly, these nozzle temperatures are all at the upper end of the recommended values from the manufacturers, which are 190–220 °C for OVERTURE, 200–230 °C for SUNLU, and 180–210 °C for HATCHBOX. While small differences are highlighted in
Table 1 across brand and color, these results demonstrate that proper steps need to be taken to calibrate nozzle temperatures across filaments on a given printer, as no single temperature can be guaranteed as optimal for a given material type.
After proper nozzle temperatures were selected, Phase 1 tensile specimens were printed in the “Standard”, “Unheated”, “80 °C”, and “Glass” conditions specified in
Section 3.2, measured for geometry, and tested under uniaxial tension. After ranking the measurement data and calculating the
and
values using Equations (1) and (2), the scores for each filament are reported in
Table 2. Across filament brands and colors, the “Standard” and “Glass” conditions typically produced the best (or lowest)
value. These parameter sets both had heated print beds at 60 °C, while the “Unheated” and “80 °C” parameter sets had bed temperatures at 25 and 80 °C, respectively. As previously mentioned, the literature findings have demonstrated that, while bed heating is not necessary for PLA, slightly elevated temperatures at or above the T
g are ideal to produce prints with proper bed adhesion and minimal distortion upon printing; for PLA, these temperatures often range from 60 to 80 °C, which align with manufacturer recommendations. Between the “Standard” and “Glass” conditions, bed surface preparation with tape versus glass did not seem to make a notable difference on geometrical accuracy. Aligning with the reported literature, the “Unheated” and “80 °C” conditions resulted in the worst dimensional control from part distortion or part drooping, respectively. Part distortion may originate from thermal gradients imposed between the print bed and extruded material from the hot end, while part drooping is likely due to excessive softening of printed layers from higher bed temperatures above the T
g [
28].
The “Standard” and “80 °C” conditions generally produced the specimens with the best mechanical properties across all filament types. There was no apparent pattern by which conditions produced the worst mechanical properties, but it was least frequently observed with the “Standard” condition. With FFF specimens, uniaxial tensile properties are severely affected by interlayer defects and voids, particularly those driven by poor layer adhesion [
9,
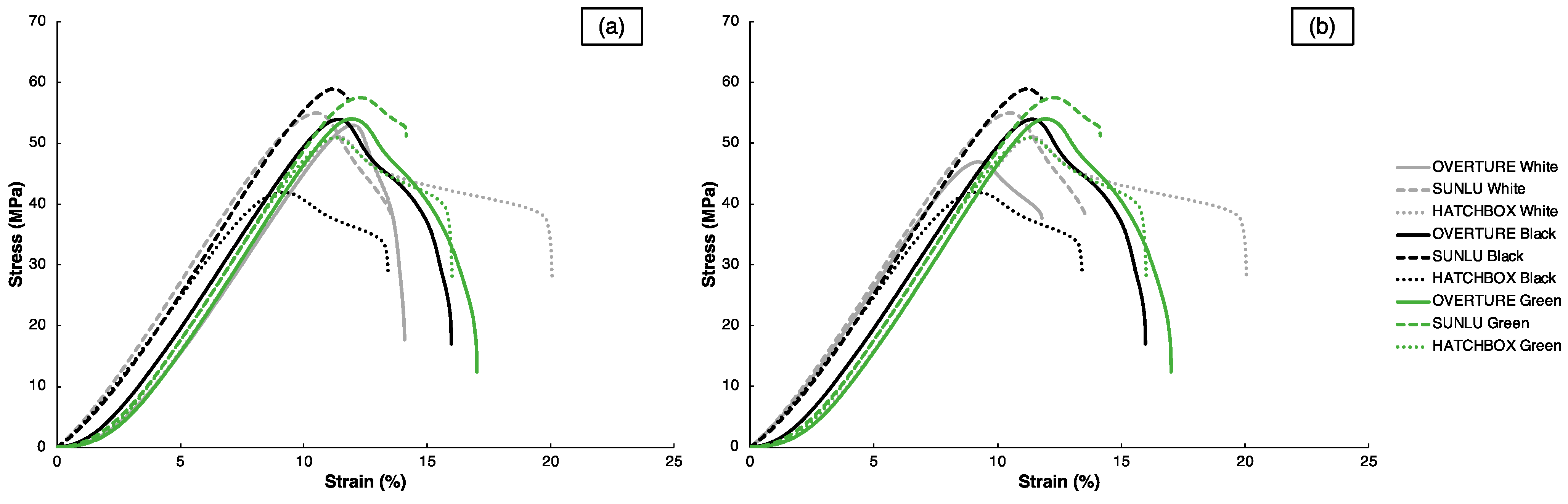
63]. With the assistance from the painter’s tape and higher bed temperatures in the “Standard” and “80 °C” conditions, bed adhesion and subsequent layer adhesion were likely enhanced compared to the other two conditions. The engineering stress–strain curves for the representative samples with the best mechanical properties, as determined by
, are shown in
Figure 4a, alongside the curves for the representative samples within the optimal parameter sets for each filament, as determined by the
values, in
Figure 4b; the
values will be reported shortly after. It is worth noting that since many of the samples with the best mechanical properties are also those with the optimal parameter sets, several curves are identical in both
Figure 4a,b. In both sets of curves in
Figure 4, all filaments have similar
values around 600 MPa, regardless of brand or color. However, significant disparities in
and
exist between filament types, mainly based upon brand. Within each filament color, the SUNLU specimens consistently demonstrate higher
values; however, the SUNLU specimens also exhibit minimal plasticity after reaching their
and have smaller
values compared to the OVERTURE and HATCHBOX samples. This tradeoff of strength and ductility is commonly seen in polymer samples, regardless of whether they are processed through FFF or other 3DP processes [
64,
65,
66]. These differences in tensile properties highlight the diverse behavior that 3D-printed specimens can display by changing filament manufacturer and color, emphasizing further that filament-to-filament variations exist and that 3DP users must take this into account when fabricating components.
Weighing both the dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties through Phase 1 testing, the optimal parameter sets for each filament were determined using the
scores in
Table 3. Apart from the HATCHBOX Green filament, the optimal parameter sets for all other filaments were either “Standard” or “80 °C”; the worst parameter sets were scattered depending on filament type, but the “Unheated” condition was most frequent. It appears that these results were mostly driven by mechanical properties, where the “Standard” and “80 °C” bed conditions likely improved the first layer adhesion and subsequent interlayer bonding, thus enhancing mechanical performance to a point where the significance of dimensional accuracy was outweighed compared to other print conditions. However, in several samples, such as the OVERTURE White and SUNLU White samples, specimen geometry was the dominating factor that determined the optimal parameter set.
The Phase 1 calibrations for the PLA filaments, varying in brand and color, demonstrate that customized printer settings must be made for a specific filament. As filaments vary in processing histories, degree of pigmentation, molecular weights, etc., their response to a given set of printer conditions will likely vary, even if they are categorized as the same material type. Thermal effects on a print’s geometrical accuracy and mechanical properties must be considered during filament calibration steps. With the optimal Phase 1 parameter sets noted as
Table 3’s scores for each filament type, further parameter optimization can be completed with adjustments of “slicer” settings, such as infill density and infill pattern, in Phase 2.
3.2. Phase 2—“Slicer” Adjustments
After the nozzle temperature and bed conditions are calibrated for a given filament on an FFF printer, processing parameter adjustments can be manipulated in a “slicer” software to produce customized parts with varying properties. For prototyping applications, the two commonly varied parameters are infill density and infill pattern. Infill density is typically adjusted to less than 100% to produce lightweight components, while also saving time and money by using less filament and completing prints in a shorter timeframe. Infill pattern can be customized to provide differing degrees of structural support to a component, particularly if it is utilized in a semi-functional manner where the integrity of mechanical behavior matters.
In Phase 2, three infill densities—10%, 50%, and 100%—and three infill patterns—Lines, Triangles, and Gyroid—were explored using the Phase 1 optimal parameter sets to observe how mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy changed with processing parameter selection. Similar to Phase I, after tensile testing, the dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties of the samples in each print condition for each filament were ranked, which
and
values are reported in
Table 4 after being calculated using Equations (1) and (4), respectively. No apparent trends are observed with the
values as the infill density or pattern is changed. Any standout values here are likely determined by print-to-print variations, as the prints for each filament using different parameter sets were completed on different days.
While infill settings do not appear to greatly influence print geometry, mechanical properties vary significantly, particularly with infill density. The 100% infill density produced the best tensile properties across all filament types, whereas the 10% infill density typically resulted in the worst properties. Consistent with the literature findings, as infill density is decreased, the void space within the printed samples increases; as these void spaces are often defined by sharp, faceted boundaries, the increased number of stress concentrations leads to lower strength values and worse ductility [
22,
67]. Interestingly, the worst parameter set for mechanical properties uses the Lines pattern at 10% infill density in all filaments except the HATCHBOX Green, which uses the Triangles pattern at 50% infill density. The angular void spaces created using the sub-100% infill density in these two parameter sets are contrasted by the rounded void spaces produced using the Gyroid infill pattern at all sub-100% infill densities, which reduce the number of stress concentrations and make crack nucleation and propagation more difficult. As such, higher
values are seen in nearly all filaments for the Gyroid infills compared to the Lines and Triangles infills at each respective sub-100% infill density. The disparities in infill pattern configurations are visualized using the “slicer” outputs in
Figure 2. Future work should include fractography analysis to confirm the influence of stress concentrations on specimen failure mechanisms derived from infill pattern.
While the sub-100% infill density specimens exhibit inferior strength and ductility compared to their 100% infill density counterparts, one must consider the property variation normalized with specimen mass. As lightweight components are often printed at lower infill densities, a calculation of
, for instance, is warranted for each filament at each parameter set. The average
values for the OVERTURE, SUNLU, and HATCHBOX filaments, which are segmented by filament color, infill pattern, and infill density, are plotted in
Figure 5a–c, respectively. For every set of prints with a given filament type, filament color, and infill pattern, the 50% infill density appears to produce the worst
ratio. There are minimal differences between the values for the 10% and the 100% infill density specimens, yet the
values for the 10% infill density specimens usually are higher than the 100% infill density specimens. This indicates that there is a tradeoff when choosing a lower infill density to create semi-functional prints. If users desire higher strength values, they may choose a higher infill density; however, if specimen mass must be considered, caution should be taken to select an appropriate infill density that yields the greatest return on investment. In the case of
values, infill pattern and filament color do not appear to make a significant difference. The filament brand, however, appears to influence these values, with lower values corresponding to the 10%, 50%, and 100% infill density samples made using the HATCHBOX filament—at 7.29 ± 0.22 MPa/g, 6.09 ± 0.24 MPa/g, and 6.97 ± 0.37 MPa/g, respectively— across infill patterns and filament colors compared to the OVERTURE filament—at 7.92 ± 0.32 MPa/g, 6.67 ± 0.26 MPa/g, and 7.64 ± 0.34 MPa/g, respectively—and the SUNLU filament—at 8.36 ± 0.21 MPa/g, 6.87 ± 0.27 MPa/g, and 8.14 ± 0.41 MPa/g, respectively. These results demonstrate that 3DP users must consider filament brand in combination with print infill density to maximize
values for a given part build.
Combining the scores from
Table 4 using Equation (3), the
scores were calculated and reported in
Table 5. It is quite evident that mechanical properties are again dominating the selection of optimal parameter sets, as indicated by the lowest
values, where the 100% infill density samples far outperform all other infill densities to such a significant degree that dimensional accuracy plays a minimal role. Infill pattern does not have a consistent effect on the optimal parameter set as identical infills are produced for all patterns at 100% density, as depicted by
Figure 2 in
Section 3.2. The worst parameter sets in Phase 2, as indicated by the highest
values in
Table 5, typically correspond to 10% infill density and either Lines or Triangles as an infill pattern. These parameters are, again, likely driven by the inferior mechanical performance from the higher degree of stress concentrations associated with an increased void space. Using the optimal and worst-case Phase 2 parameter sets indicated by
Table 5, the effects of filament thermal characteristics and post-processing were investigated in Phase 3 as a means of improving mechanical performance.
3.3. Phase 3—Thermal Analysis and Post-Processing
Annealing, as a post-processing treatment, was investigated with all nine PLA filaments for the optimal and worst-case parameter sets identified in Phase 2 to observe how part geometry and tensile properties vary in ideal and non-ideal print scenarios. Before selecting the annealing conditions, the thermal characteristics of all PLA filaments must first be considered so that proper treatment times and temperatures might be selected.
The DSC curves in
Figure 6 reveal the thermophysical transitions upon heating and cooling for all nine filaments, where the normalized heat flow (in W/g) is plotted against temperature (in °C) for the filaments in the as-fabricated state upon heating for DSC Run #1 in
Figure 6a, in the normalized state upon heating for DSC Run #2 in
Figure 6b, and upon cooling between Runs #1 and #2 in
Figure 6c. Specific values extracted from the DSC heating curves in
Figure 6a,b are reported in
Table 6. The data from the as-fabricated state are useful to describe the effects of processing history, typically from filament production, on the thermal behavior of the PLA filaments, which resembles the condition of the filament prior to melting in FFF. On the other hand, the data from the normalized state—which are generated upon melting after heating the as-fabricated filament in
Figure 6a—are useful to describe the thermal behavior of PLA independent of its fabrication method, which may better describe the nature of the material after melting in FFF. In
Figure 6a, three distinct transitions are observed: (1) glass transition, (2) cold crystallization, and (3) melting. Similar glass transitions are observed for all filaments, with an average T
g at 64.67 ± 1.27 °C, which is typical for PLA, as indicated by an exaggerated endothermic peak upon heating in
Figure 6a. This endothermic peak at the glass transition is indicative of residual stresses from prior thermal processing—in this case, filament fabrication—which are relieved due to molecular relaxation upon heating [
68]. Another by-product of residual stresses is the shifting of the T
g values when compared to the stress-free polymer; this will be compared shortly to the stress-free PLA in the normalized state in
Figure 6b. Similar melting behavior across all filaments is also seen, with an average T
m of 165.41 ± 5.56 °C, as indicated by the endothermic peak expected for semi-crystalline PLA. The melting peaks appear to vary over a much larger range compared to the glass transition, with the lowest peak temperatures for the OVERTURE filaments and the highest peak temperatures for the SUNLU filaments. The same pattern is seen with the
values, as indicated by the area under the curve in
Figure 6a upon melting, where
represents the energy released during the melting of crystalline regions in a polymer. It is important to note that the T
g and T
m values for the nine filaments considered are related to the recommended FFF print bed and nozzle temperatures for PLA, respectively. Specifically, the T
g and T
m values here are slightly lower than the ideal bed and nozzle temperatures, indicating that slightly higher values are ideal for FFF than the peak temperatures observed through DSC. If known, 3DP users can make more informed processing parameter selection using thermal characterization data to achieve successful filament melting and part production.
Cold crystallization behavior is far more variable in the filaments compared to the glass transition and melting behaviors, as observed in the exothermic peaks between the T
g and T
m in
Figure 6 and the respective values in
Table 6. Where applicable, the average peak cold crystallization temperature (T
cc) value across all filaments is 97.77 ± 12.38 °C, which is consistent for the HATCHBOX filaments (94.95 ± 2.2 °C) and relatively spread out for the SUNLU filaments (100.58 ± 18.82 °C), ranging from 85.30 °C (SUNLU Black) to 131.61 °C (SUNLU White); no OVERTURE filaments exhibit cold crystallization tendencies, as indicated by “N/A” in
Table 6. Thermal history and additive content are major factors influencing cold crystallization behaviors, given the reliance of crystallization kinetics upon the nucleation sites present in the original filament melt [
47,
69]. Given the previously observed differences between the as-fabricated filaments, it is not surprising to see this variation. The disparities in cold crystallization across the filament types are echoed by the variations in
, mainly by brand, as seen in
Table 6. Crystallinity values, as calculated by Equation (5), range from 6.62% (SUNLU Green) to 26.25% (OVERTURE Green) from Run #1. Typically, this spread in
would be justified by observing the baseline shift at the glass transition, which is reflected by the ∆C
p values, as reported in
Table 6. Given that glass transition only applies to the amorphous regions of a polymer, smaller ∆C
p values—and, therefore, a less pronounced glass transition—are observed if the amorphous content is lower, thus indicating a higher
[
70]. However, from the Run #1 data in
Table 6, this trend is not clear. This is likely due to the fact that the residual stress state of the as-fabricated PLA filaments is high from thermomechanical processing during filament production, which has been reported to skew DSC data without normalization [
68,
71]. While studying cold crystallization and
is interesting from an academic perspective, this is less relevant in a practical 3DP scenario, as the PLA filaments will be melted anyway in their as-fabricated state through the heated nozzle. As such, these trends are most relevant to observe with the Run #2 data after normalization, which most closely resemble the characteristics of the printed component.
Several distinct differences can be observed in the nine PLA filaments after normalization from Run #2 DSC data in
Figure 6b and
Table 6. A tight spread is still observed in the T
g values, averaging 54.39 ± 1.78 °C. These values are shifted approximately 10 °C to lower temperatures compared to Run #1; additionally, the severe endothermic peak during the glass transition from Run #1 is not observed; instead, there is a gradual baseline shift that is expected during the glass transition. This is logical given that residual stress alleviation is typically accompanied by lowered T
g values and an absence of endothermic peaks during the glass transition when analyzed through DSC, as previously mentioned. Similar T
m values are observed from Run #2 data compared to Run #1, with the characteristic endothermic peak at several degrees lower than Run #1, and an average of 161.50 ± 3.26 °C. For most filaments, the
values appear to increase for the second run; the exceptions here are the OVERTURE White and SUNLU White filaments. This is characteristic of increased crystallinity typically observed in normalized filaments. The cold crystallization behavior is equally as variable in Run #2 compared to Run #1, with several filaments exhibiting crystallization that was not observed in Run #1 and several filaments not showing crystallization that was observed in Run #1. The T
cc values average to be 103.69 ± 16.94 °C in Run #2, when applicable, with values ranging from 85.42 °C (SUNLU Black) to 127.53 °C (SUNLU White). Even with normalization from the first melt, cold crystallization relies heavily on molecular weight, stereochemistry, etc., so it is not surprising to see these variations repeated in Run #2. The
values also fluctuate, ranging from 0.94% (OVERTURE White) to 58.49% (SUNLU Green). In this case, however, crystallinity does not rely upon the original manufacturing method but, instead, varies with the cold crystallization behavior, which is derived from how the PLA filaments have responded to the cooling step after melting in Run #1. Interestingly, all filaments that exhibit a cold crystallization peak upon heating in Run #2 do not exhibit an appreciable exothermic crystallization peak upon cooling between Runs #1 and #2, as shown in
Figure 6c. This is likely due to each filament’s tendency to nucleate crystals in the melt upon cooling at the specified cooling rate (10 °C/min), which is influenced by factors such as polymer composition and molecular weight [
72].
The DSC data analysis from
Figure 6 and
Table 6 highlights distinct thermal behaviors for the nine PLA filaments, which are reliant upon thermal history and molecular differences induced by manufacturing. The trends in thermophysical tendencies upon heating and cooling revealed from the DSC analysis are useful in a 3DP environment, as thermal cycles are often encountered that fluctuate between a solid state and a molten state, which rely upon the filaments’ thermal characteristics. The Run #1 heating data, particularly the T
g and T
m, are indicative of the filament going into the FFF printer and can inform the selection of proper print bed and nozzle temperatures, respectively, to achieve adequate melting and bonding during extrusion. The Run #2 data, on the other hand, are more indicative of what can be expected in the printed component, as they take into account a normalization step from melting. However, the cooling rates and thermal cycles involved with FFF are not accounted for in the cooling rates between Runs #1 and #2, nor the heating rates in Run #2; thus, variations are expected to occur between practical FFF processing and the ideal DSC environment. With an understanding of the thermal characteristics of the as-fabricated and normalized PLA filaments, a proper annealing treatment can be selected. Recommended annealing conditions for PLA vary depending on part geometry, but samples are typically processed between the T
g and T
m to provide enough energy to kickstart crystallization without creating dimensional instabilities. For FFF-printed PLA specimens, annealing times vary quite substantially in the literature from as little as 5 min to as long as 2 h [
55,
73,
74]. In this study, an annealing temperature of 75 °C was chosen, which is just above the normalized filaments’ average T
g value. Annealing was performed for 15 min after the samples reached 75 °C, which is on the lower end of the processing times observed in the literature. A shorter annealing period was explored in hopes of minimizing part distortion, given that the specimens were not fixtured in a mold during annealing and were, therefore, more susceptible to geometrical changes with longer treatment times.
Before identifying mechanical property changes with annealing, the effects of post-processing on specimen dimensions should be discussed.
Table 7 highlights the percent differences in tensile specimen geometry, according to
Figure 2 labeling, between the as-printed and annealed conditions for each filament using both the optimal and worst-case Phase 3 parameter sets. For nearly all specimens, the specimen size decreases in the XY-plane and increases in the Z-direction after annealing; specifically, dimensions A through E typically decrease, while dimension F increases. Dimensional changes are not uncommon in polymer annealing and are typically associated with residual stress relief and crystallization [
51,
75]. Large percent changes, however, were observed in several samples—as high as 6.57%—which is undesirable for prints that require tight tolerances. Specimen fixturing, such as in a mold, or different annealing conditions may be required to mitigate the effect of dimensional changes during post-processing.
Changes in mechanical properties after post-processing were also tracked, and the percent differences in key tensile properties between the annealed and as-printed conditions for each filament for both the optimal and worst-case parameter sets are reported in
Table 8. There appears to be substantial variation in the magnitude of mechanical property changes after post-processing for each filament brand, color, and parameter set. The values of
change most consistently, with the values being nearly all lower in the annealed state compared to the as-printed state. These results are not ideal for an annealed condition, as increases in strength, and sometimes ductility, are expected with proper thermal processing. All other variations in stiffness, strength, and ductility metrics, which seemingly scatter across filament types, are likely associated with a non-optimized set of treatment conditions for the different filaments, further indicating the need for material-specific post-processing optimization to improve part properties.
The variable mechanical property changes with annealing are reflected by similar trends in the printed specimens’ thermal characteristics, as seen in the DSC curves of both the as-printed and annealed samples using the optimal and worst-case parameter sets in
Figure 7, and the changes in T
g, T
cc, and T
m after annealing for both parameter sets in
Table 9; the tabulated DSC data used to calculate the values in
Table 9 are reported in
Spreadsheet S9 (“Printed Specimen DSC Tabulated Values”) as Supplementary Materials. Minimal differences can be seen between the curves of the as-printed specimens from the optimal and worst-case parameter sets in
Figure 7a,b; however, larger differences are notable between the curves of the samples in the annealed condition in
Figure 7c,d. This could be justified based upon the thermal gradients imparted to the samples during annealing for a specific parameter set, given that the samples from the worst-case parameter sets had less than 100% infill density, whereas the samples from the optimal parameter sets all had 100% infill density. With a higher void space content and a lower mass in a given sample for the worst-case printed samples, heat-transfer kinetics occur more rapidly during annealing and may cause different thermophysical transitions in the printed specimens. This is reflected in the different residual stress states, variable
values, and changes in peak characteristics in the annealed specimens from the worst-case parameter sets versus the optimal parameter sets.
Comparing the as-printed and annealed samples from the optimal parameter sets in
Figure 7a,c, respectively, and from the worst-case parameter sets in
Figure 7b,d, respectively, large deviations in peak positions are observed.
Table 9 highlights the extent of these changes, most notably with an average decrease in T
g and T
m for nearly all samples upon annealing. This is reflected by the marginally smoother glass transitions and more pronounced melting peaks in the associated regions of
Figure 7c,d. The T
cc values vary more substantially, though, for all samples after post-processing, either increasing or decreasing depending on the sample. This is evident through the changes in peak positions on the DSC curves in
Figure 7c,d. The decreases in the T
g and T
m are characteristic of residual stress relief, which is expected upon annealing. However, the variation in T
cc, as well as the
values in
Table 9, demonstrates differing degrees of efficacy of the annealing treatment, depending on the sample. Specifically, annealing is expected to increase the degree of crystallinity in the semi-crystalline polymer by providing enough energy to create short- or long-range order; yet, in the samples considered herein, some specimens decrease
substantially after annealing. This indicates non-ideal annealing conditions at 75 °C and 15 min for certain filaments, whether it be non-ideal temperature or time, while these conditions are satisfactory for other filaments. Additional optimization of post-processing conditions per filament type and processing parameter set would be necessary to achieve ideal annealing, further indicating how differing filaments require specific optimization steps in 3DP, even if they belong to the same material type and are printed in similar geometries.