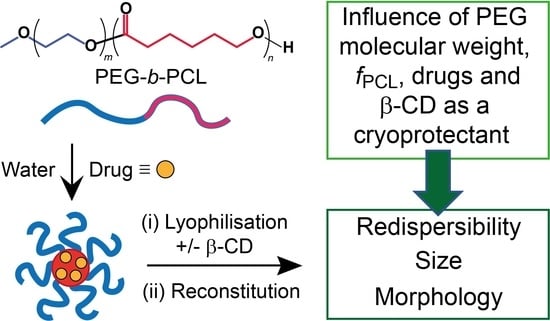
Influence of Lyophilization and Cryoprotection on the Stability and Morphology of Drug-Loaded Poly(ethylene glycol-b-ε-caprolactone) Micelles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Synthesis of PEGx-b-PCLy Copolymers
2.3.2. Determination of CAC
2.3.3. Preparation of Blank and Drug-Loaded Micelle Solutions
2.3.4. Lyophilization and Reconstitution of Micelles
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Critical Aggregation Concentration of PEG-b-PCL Copolymers
3.2. Effects of Lyophilization and Reconstitution on Blank Micelles
3.3. Effects of Lyophilization and Reconstitution on Drug-Loaded Micelles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, J.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Polymeric micelles drug delivery system in oncology. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperkar, K.; Patel, D.; Atanase, L.I.; Bahadur, P. Amphiphilic Block Copolymers: Their Structures, and Self-Assembly to Polymeric Micelles and Polymersomes as Drug Delivery Vehicles. Polymers 2022, 14, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.; Satpathy, S.; Shenoy, A.K.; Bush, J.A.; Kazi, M.; Hussain, M.D. Formulation and evaluation of mixed polymeric micelles of quercetin for treatment of breast, ovarian, and multidrug resistant cancers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2869–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Fessi, H. Investigation of nanocapsules stabilization by amorphous excipients during freeze-drying and storage. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.; Hu, L.; Liu, H.; Pan, H.-C. Effect of freeze-drying process on the physical stability and properties of Voriconazole complex system. Dry. Technol. 2018, 36, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretton, M.A.; Chiappetta, D.A.; Sosnik, A. Cryoprotection–lyophilization and physical stabilization of rifampicin-loaded flower-like polymeric micelles. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Stainmesse, S.; Fessi, H. Freeze-drying of nanoparticles: Formulation, process and storage considerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1688–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.L.; Li, X.R.; Yang, K.W.; Liu, Y. Amphotericin B-loaded poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactide) micelles: Preparation, freeze-drying, and in vitro release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.; Mehnert, W. Freeze-drying of drug-free and drug-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN). Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 157, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.; van Colen, G.; Sander, B.; Golas, M.M.; Uezguen, S.; Weigandt, M.; Goepferich, A. Drug loading of polymeric micelles. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, C.; Como, C.; Gurny, R.; Möller, M. Investigations on the lyophilisation of MPEG–hexPLA micelle based pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, K.; Tian, B.; Han, J.; Feng, D. Preparation of protein-loaded PEG-PLA micelles and the effects of ultrasonication on particle size. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossen, P.; Witzigmann, D.; Sieber, S.; Huwyler, J. PEG-PCL-based nanomedicines: A biodegradable drug delivery system and its application. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y. Physical stability and lyophilization of poly (ε-caprolactone)-b-poly (ethyleneglycol)-b-Poly (ε-caprolactone) micelles. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2006, 6, 3032–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. The eradication of breast cancer and cancer stem cells using octreotide modified paclitaxel active targeting micelles and salinomycin passive targeting micelles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulahoum, H.; Ghorbanizamani, F.; Bayir, E.; Timur, S.; Zihnioglu, F. A polyplex human saliva peptide histatin 5-grafted methoxy PEG-b-polycaprolactone polymersome for intelligent stimuli-oriented doxorubicin delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, Z.; Winoto, W.; Shen, Y.; Radosz, M. Block Copolymer Micelles Formed in Supercritical Fluid Can Become Water-Dispensable Nanoparticles: Poly(ethylene glycol)−block-Poly(ϵ-caprolactone) in Trifluoromethane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungkham, H.; Swatdipakdi, N.; Theerasilp, M.; Karnkla, S.; Chittchang, M.; Ploypradith, P.; Nasongkla, N. PEG-b-PCL and PEG-b-PLA polymeric micelles as nanocarrieres for lamellarin N delivery. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 3245–3248. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, A.; Olbrich, C.; Krause, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Kissel, T. Polymeric micelles for parenteral delivery of Sagopilone: Physicochemical characterization, novel formulation approaches and their toxicity assessment in vitro as well as in vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressing, M.E.; Jiskoot, W.; Talsma, H.; van Ingen, C.W.; Beuvery, E.C.; Crommelin, D.J. The influence of sucrose, dextran, and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as lyoprotectants for a freeze-dried mouse IgG 2a monoclonal antibody (MN12). Pharm. Res. 1992, 9, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-Y.; Min, S.-G.; You, S.-K.; Choi, M.-J.; Hong, G.-P.; Chun, J.-Y. Effect of β-cyclodextrin on physical properties of nanocapsules manufactured by emulsion–diffusion method. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Chae, S.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Kweon, J.K.; Cho, C.S.; Jang, M.K.; Nah, J.W. Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of amphiphilic block copolymer self-aggregates formed by poly (ethylene glycol)-block-poly (ϵ-caprolactone). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 3520–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, N.M.; Mudie, S.T.; Hawley, A.M.; Cookson, D.J.; Mertens, H.D.; Cowieson, N.; Samardzic-Boban, V. A low-background-intensity focusing small-angle X-ray scattering undulator beamline. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, K.S.; Clulow, A.J.; Krasowska, M.; Gillam, T.; Miklavcic, S.J.; Williamson, N.H.; Blencowe, A. Interrogating the relationship between the microstructure of amphiphilic poly(ethylene glycol-b-caprolactone) copolymers and their colloidal assemblies using non-interfering techniques. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilavsky, J.; Jemian, P.R. Irena: Tool suite for modeling and analysis of small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Lin, H.; Jiang, S.; Han, L.; Hou, S.; Lin, S.; Cheng, Z.; Bian, W.; Zhang, X. Enhanced oral bioavailability and bioefficacy of phloretin using mixed polymeric modified self-nanoemulsions. Food Sci. Nutri. 2020, 8, 3545–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetko, I.V.; Tanchuk, V.Y. Application of associative neural networks for prediction of lipophilicity in ALOGPS 2.1 program. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Geissman, T.A.; Edwards, J.D. Gossypol, a Pigment of Cottonseed. Chem. Rev. 1960, 60, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushko, V.; Thaler, M.; Karp, C. Pyrene fluorescence fine structure as a polarity probe of hydrophobic regions: Behavior in model solvents. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1981, 210, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.C.; Winnik, M.A. The Py scale of solvent polarities. Solvent effects on the vibronic fine structure of pyrene fluorescence and empirical correlations with ET and Y values. Photochem. Photobiol. 1982, 35, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satturwar, P.; Eddine, M.N.; Ravenelle, F.; Leroux, J.C. pH-responsive polymeric micelles of poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(alkyl(meth)acrylate-co-methacrylic acid): Influence of the copolymer composition on self-assembling properties and release of candesartan cilexetil. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumanis, K.P.; Holdich, R.G.; Georgiadou, S. Synthesis and micellization of a pH-sensitive diblock copolymer for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, A.L.; Nikles, S.M.; Nikles, J.A.; Brazel, C.S.; Nikles, D.E. Polymer micelles with crystalline cores for thermally triggered release. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10653–10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, A.M.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Kenney, M.E.; Oleinick, N.L.; Gupta, A.S. Delivery of the photosensitizer Pc 4 in PEG–PCL micelles for in vitro PDT studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2386–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Jundi, A.; Buwalda, S.; Bethry, A.; Hunger, S.; Coudane, J.; Bakkour, Y.; Nottelet, B. Double-hydrophilic block copolymers based on functional poly (ε-caprolactone) s for pH-dependent controlled drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2019, 21, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, X.; Rao, W.; Ai, F.; Zhao, F.; Men, K.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Huang, M. Preparation, characterization and application of star-shaped PCL/PEG micelles for the delivery of doxorubicin in the treatment of colon cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; He, B.; Li, S. Arginine modified polymeric micelles as a novel drug delivery system with enhanced endocytosis efficiency. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Zhu, W.; Shen, Z. Synthesis, isothermal crystallization and micellization of mPEG–PCL diblock copolymers catalyzed by yttrium complex. Polymer 2007, 48, 6791–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M.L.; Won, C.-Y.; Malick, A.W.; Kwon, G.S. In vitro release of the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin from poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(ε-caprolactone) micelles. J. Control. Release 2006, 110, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.B.; Gong, C.Y.; Huang, M.J.; Wang, J.W.; Pan, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, G.Z.; Gou, M.L.; Wang, K.; Tu, M.J.; et al. Thermoreversible gel-sol behavior of biodegradable PCL-PEG-PCL triblock copolymer in aqueous solutions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.J.; Joo, M.K.; Choi, B.G.; Park, M.H.; Hamley, I.W.; Jeong, B. Multiple Sol-Gel Transitions of PEG-PCL-PEG Triblock Copolymer Aqueous Solution. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 2064–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Joo, M.K.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, W.K.; Sohn, Y.S.; Jeong, B. Gelation behavior of poly (ethylene glycol) and polycaprolactone triblock and multiblock copolymer aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4873–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suys, E.J.; Warren, D.B.; Pham, A.C.; Nowell, C.J.; Clulow, A.J.; Benameur, H.; Porter, C.J.; Pouton, C.W.; Chalmers, D.K. A nonionic polyethylene oxide (PEO) surfactant model: Experimental and molecular dynamics studies of Kolliphor EL. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgleish, D.G.; Spagnuolo, P.A.; Goff, H.D. A possible structure of the casein micelle based on high-resolution field-emission scanning electron microscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, H.; Blum, S.A. Single-Micelle and Single-Zinc-Particle Imaging Provides Insights into the Physical Processes Underpinning Organozinc Reactions in Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capacchione, C.; Della Sala, P.; Quaratesi, I.; Bruno, I.; Pauciulo, A.; Bartiromo, A.R.; Iannece, P.; Neri, P.; Talotta, C.; Gliubizzi, R.; et al. Poly(Ethylene Glycol)/β-Cyclodextrin Pseudorotaxane Complexes as Sustainable Dispersing and Retarding Materials in a Cement-Based Mortar. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 12250–12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhu, J.-l.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Li, J. Thermoresponsive supramolecular micellar drug delivery system based on star-linear pseudo-block polymer consisting of β-cyclodextrin-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and adamantyl-poly(ethylene glycol). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, T.; He, H.; Gou, J.; Tang, X. Improved Core Viscosity Achieved by PDLLA10kCo-Incorporation Promoted Drug Loading and Stability of mPEG2k-b-PDLLA2.4k Micelles. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Song, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J. Nonviral DNA Delivery System with Supramolecular PEGylation Formed by Host–Guest Pseudo-Block Copolymers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5057–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yang, Z.; Fu, X.; Yung, B.C.; Yang, J.; Mao, Z.; Shao, L.; Hua, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Polyrotaxane-based supramolecular theranostics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyers-Montoya, E.; García-Casillas, P.; Vargas-Requena, C.; Escobedo-González, R.; Martel-Estrada, S.A.; Martínez-Pérez, C.A. Polycaprolactone/Amino-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Prepared by an Electrospinning Technique. Polymers 2016, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Ormond, B.R.; Gupta, B.S.; Tonelli, A.E. Efficient wound odor removal by β-cyclodextrin functionalized poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varan, C.; Wickström, H.; Sandler, N.; Aktaş, Y.; Bilensoy, E. Inkjet printing of antiviral PCL nanoparticles and anticancer cyclodextrin inclusion complexes on bioadhesive film for cervical administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Memon, A.H.; Liang, H. Molecular model and in vitro antioxidant activity of a water-soluble and stable phloretin/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-H.; Wu, L.-M.; Ma, X.-Y. Study on structure and characterization of inclusion complex of gossypol/beta cyclodextrin. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 61, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, I.; Terada, N.; Hashida, S.; Sakurai, K.; Sato, T.; Shiraishi, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Masunaga, H.; Ogawa, H.; Ito, K. Encapsulation of a hydrophobic drug into a polymer-micelle core explored with synchrotron SAXS. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7544–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.; Trench, D.; Putnam, J.; Stenzel, M.H.; Lord, M.S. Curcumin-loading-dependent stability of PEGMEMA-based micelles affects endocytosis and exocytosis in colon carcinoma cells. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretton, M.A.; Glisoni, R.J.; Chiappetta, D.A.; Sosnik, A. Molecular implications in the nanoencapsulation of the anti-tuberculosis drug rifampicin within flower-like polymeric micelles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, M.S.; Faisal, K.S.; Clulow, A.J.; Albrecht, H.; Krasowska, M.; Blencowe, A. Influence of Lyophilization and Cryoprotection on the Stability and Morphology of Drug-Loaded Poly(ethylene glycol-b-ε-caprolactone) Micelles. Polymers 2023, 15, 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081974
Hussain MS, Faisal KS, Clulow AJ, Albrecht H, Krasowska M, Blencowe A. Influence of Lyophilization and Cryoprotection on the Stability and Morphology of Drug-Loaded Poly(ethylene glycol-b-ε-caprolactone) Micelles. Polymers. 2023; 15(8):1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081974
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Md. Saddam, Khandokar Sadique Faisal, Andrew J. Clulow, Hugo Albrecht, Marta Krasowska, and Anton Blencowe. 2023. "Influence of Lyophilization and Cryoprotection on the Stability and Morphology of Drug-Loaded Poly(ethylene glycol-b-ε-caprolactone) Micelles" Polymers 15, no. 8: 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081974
APA StyleHussain, M. S., Faisal, K. S., Clulow, A. J., Albrecht, H., Krasowska, M., & Blencowe, A. (2023). Influence of Lyophilization and Cryoprotection on the Stability and Morphology of Drug-Loaded Poly(ethylene glycol-b-ε-caprolactone) Micelles. Polymers, 15(8), 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15081974