Properties and Structure of Thermoplastic Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyamide Sea-Island Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Thermoplastic Modification of PVA
2.3. Spinning of Sea-Island Pre-Oriented Yarn
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
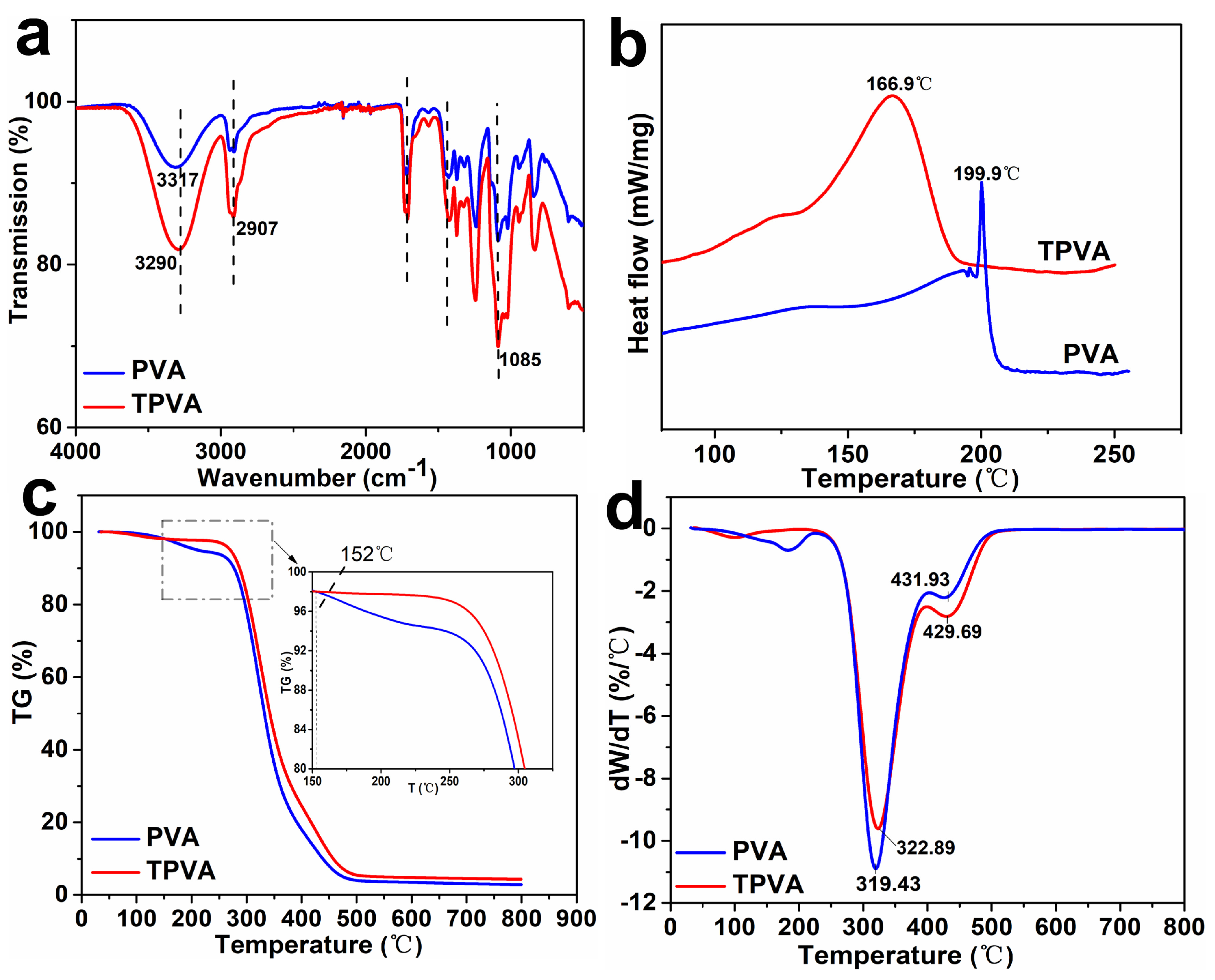
3.1. Chemical Structure and Thermal Behavior of TPVA
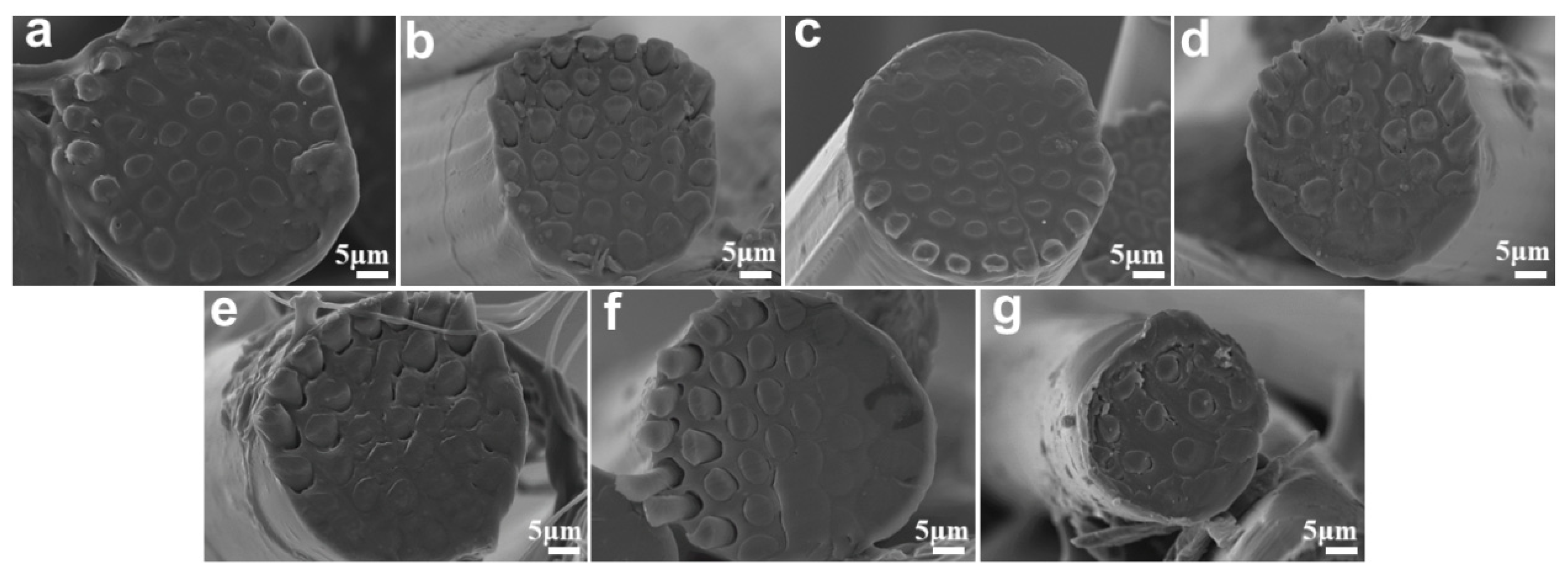
3.2. Effect of Sea-Island Ratio and Spinning Speed on Microstructure
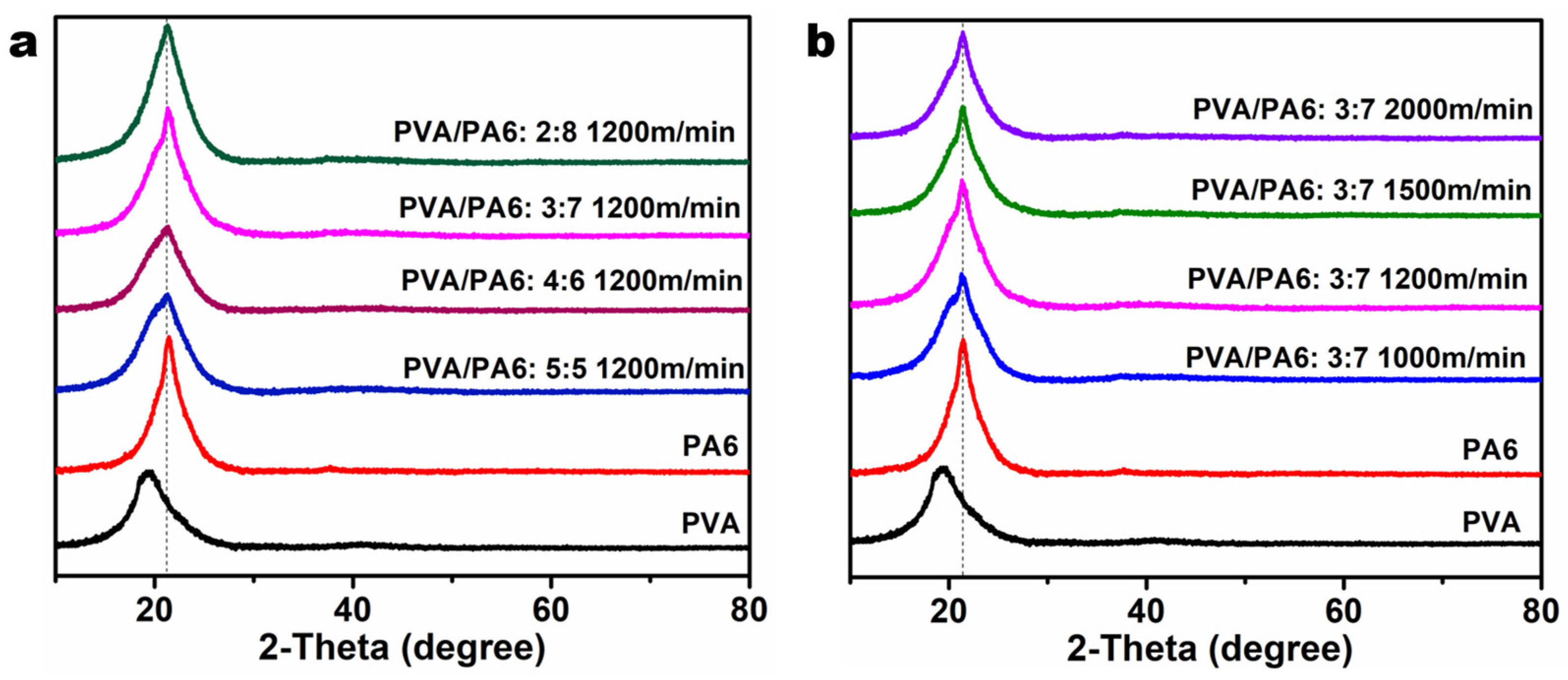
3.3. XRD Analysis of Sea-Island Fiber
3.4. Thermal Analysis of Sea-Island Fibers
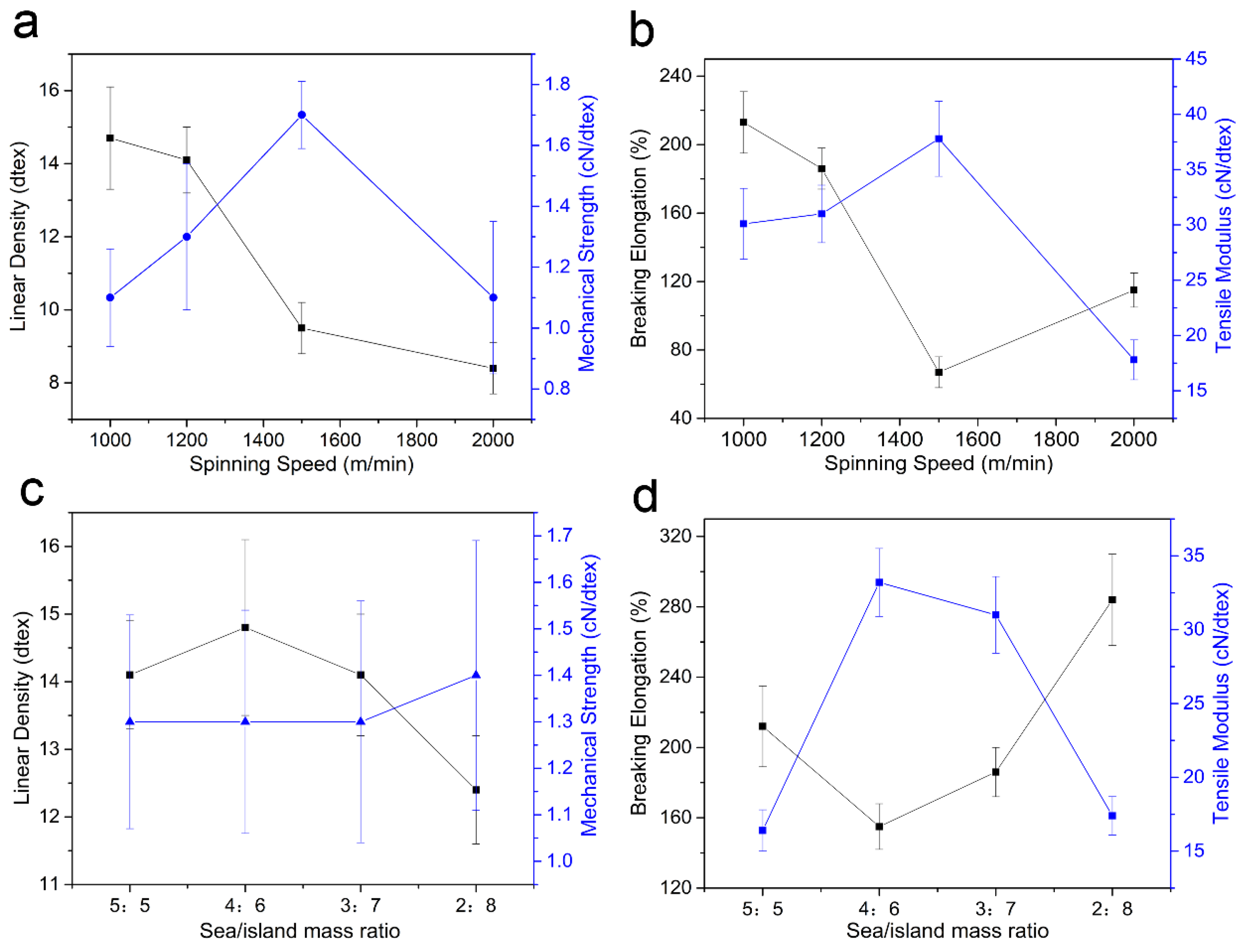
3.5. Mechanical Properties of Sea-Island Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, G.; Wan, K.; Kong, H.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, G. Recent advance in biomass membranes: Fabrication, functional regulation, and antimicrobial applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 305, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehaqui, H.; Qi, Z.; Berglund, L.A. High-porosity aerogels of high specific surface area prepared from nano-fibrillated cellulose (NFC). Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, B.; Qian, Y.; Xu, P.; Qi, J. Micro/nano microfiber synthetic leather base with different nanofiber diameters. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 50, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, Y.; Gu, T.; Bao, L.; Otani, Y.; Seto, T. Performance of nanofiber/microfiber hybrid air filter prepared by wet paper processing. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Sun, G.; Yan, K. Disinfectant Performance of a Chlorine Regenerable Antibacterial Microfiber Fabric as a Reusable Wiper. Materials 2019, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, K.; Fujii, K.; Ohkoshi, Y.; Gotoh, Y.; Nagura, M.; Numata, M.; Kamiyama, M. Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Nanofibers Made by Sea-Island-Type Conjugated Melt Spinning and Laser-Heated Flow Drawing. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Du, S.; Xiao, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chang, Y.; Cui, S. Application of foam dyeing technology on ultra-fine polyamide filament fabrics with acid dye. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 4808–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, S.; Ding, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, H. High strength and high breaking load of single electrospun polyimide microfiber from water soluble precursor. Mater. Lett. 2017, 201, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-C.; Chang, S.-S.; Liang, N.-Y. Fabrication and characterization of antistatic fiber with segmented pie structure. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, M. Melt-spun microbial poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) fibers with enhanced toughness: Synergistic effect of heterogeneous nucleation, long-chain branching and drawing process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, E.; Cayla, A.; Rault, F.; Gonthier, A.; Campagne, C.; Devaux, E. Effect of Viscosity Ratio of Two Immiscible Polymers on Morphology in Bicomponent Melt Spinning Fibers. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2016, 37, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M. Studies on melt spinning of sea-island fibers. II. Dynamics of melt spinning of polypropylene/polystyrene blend fibers. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, E.; Cayla, A.; Rault, F.; Gonthier, A.; LeBlan, T.; Campagne, C.; Devaux, E. Influence of Rheological and Thermal Properties of Polymers During Melt Spinning on Bicomponent Fiber Morphology. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, C.W.; Lee, J.J. Weight Reduction of Sea-island-type PTT/PET Conjugate Fiber and Dyeing of Polytrimethylene Terephthalate Flock Microfibers. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.M.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, J.E.; Ko, J.W.; Kim, I.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Ko, S.I.; Jung, D.H.; Lee, S.G. Alkaline Hydrolysis and Dyeing Characteristics of Sea-Island-Type Ultramicrofibers of PET Tricot Fabrics with Black Disperse Dye. Polymers 2020, 12, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ding, H.; Qi, G.; Li, C.; Xu, P.; Zheng, T.; Zhu, X.; Kenny, J.M.; Puglia, D.; Ma, P. Highly transparent PVA/nanolignin composite films with excellent UV shielding, antibacterial and antioxidant performance. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 162, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMerlis, C.; Schoneker, D. Review of the oral toxicity of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Nath, V.K.; Thomas, J.; Augustine, A.; Kalarikkal, N.; Moustafa, A.; Thomas, S. Electrospun polyvinyl alcohol membranes incorporated with green synthesized silver nanoparticles for wound dressing applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, T.-H.; Lin, C.-A. Elongational flow properties of thermoplastic polyvinyl alcohol/polypropylene from the melt spinning method. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Han, S.S. PVA-based hydrogels for tissue engineering: A review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 66, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Costa-Júnior, E.; Pereira, M.M.; Mansur, H.S. Properties and biocompatibility of chitosan films modified by blending with PVA and chemically crosslinked. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gamal, S.; Sayed, A.E. Physical properties of the organic polymeric blend (PVA/PAM) modified with MgO nanofillers. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 2831–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiba, Z.K.; Mohamed, M.B.; Ahmed, S. Exploring the physical properties of PVA/PEG polymeric material upon doping with nano gadolinium oxide. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Donkai, N.; Miyamoto, T. Preparation and thermal properties of thermoplastic poly(vinyl alcohol) complexes with boronic acids. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1998, 36, 3045–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Shi, S.; Nie, M.; Wang, Q. Freeze-Drying-Promoted Effect of Sorbitol Plasticization for Melt Processing of Poly(vinyl alcohol). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 16005–16012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, J.W.; Zou, L.M.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Y.V. Plasticizing effect of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide content on poly(vinyl alcohol). Polym. Int. 2023, 72, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamidi, A.; Kapourani, A.; Christodoulou, E.; Klonos, P.A.; Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Kyritsis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Barmpalexis, P. Low Molecular Weight Oligomers of Poly(alkylene succinate) Polyesters as Plasticizers in Poly(vinyl alcohol) Based Pharmaceutical Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, R.; Sun, X.; Li, F.; Shen, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xie, D.; Chen, J. Preparation and properties of PBAT/PLA composites modified by PVA and cellulose nanocrystals. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zou, L.; He, J. The preparation and characterization of plasticized PVA fibres by a novel Glycerol/Pseudo Ionic Liquids system with melt spinning method. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, N.; Wang, Q. Crystallization behavior of melt-spun poly(vinyl alcohol) fibers during drawing process. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 17, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.A.; Brünig, H.; Hinüber, C.; Heinrich, G. Melt Spinning of Biodegradable Nanofibrillary Structures from Poly(lactic acid) and Poly(vinyl alcohol) Blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 299, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhamani, S.; Prasad, M.; Sankar, K.U. DSC and FTIR studies on Gellan and Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) blend films. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Yang, T.; Peng, L.; Yi, D. Acrylamide modified poly (vinyl alcohol): Crystalline and enhanced water solubility. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 86598–86605. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.C.; Lin, S.D.; Li, L. Effects of water on drawability, structure, and mechanical properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) melt-spun fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, Y.-K.; Ai, F.-F.; Fan, J.; Xia, Z.-P.; Liu, Y. Hierarchical Porous Polyamide 6 by Solution Foaming: Synthesis, Characterization and Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, B.; Wei, W.; Gu, Q.; Chen, P. Properties and structure of polylactide/poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PLA/PHBV) blend fibers. Polymer 2015, 68, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavian, S.; Fatemi, A. Tensile behavior and modeling of short fiber-reinforced polymer composites including temperature and strain rate effects. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2016, 30, 1414–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | 101 (°) | 200 (°) | D101 (Å) | D200 (Å) | Lc101 (Å) | Lc200 (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA–1200 m/min | 19.4 | – | 0.3 | – | 1.5 | – |
| PA6–1200 m/min | – | 21.4 | – | 0.5 | – | 1.4 |
| PVA/PA6 2:8–1200 m/min | – | 21.2 | – | 0.5 | – | 1.1 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–1200 m/min | 20.4 | 21.3 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| PVA/PA6 4:6–1200 m/min | 20 | 21.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| PVA/PA6 5:5–1200 m/min | 19.5 | 21.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 1 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–1000 m/min | 20.1 | 21.5 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–1500 m/min | 20.5 | 21.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–2000 m/min | 19.9 | 21.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1.2 |
| Sample | Tm (°C) a | ΔH (J/g) | X (%) | Tc (°C) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA–1200 m/min | 295.6 | 17.6 | 10.4 | – |
| PA6–1200 m/min | 231.8 | 26.7 | 14.1 | 187.2 |
| PVA/PA6 2:8–1200 m/min | 230.8 | 17.8 | 9.6 | 182.3 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–1200 m/min | 230.3 | 22.1 | 12.1 | 180.4 |
| PVA/PA6 4:6–1200 m/min | 230.1 | 26.3 | 14.3 | 180.6 |
| PVA/PA6 5:5–1200 m/min | 227.5 | 15.6 | 9.3 | 173.3 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–1000 m/min | 229.4 | 18.1 | 9.9 | 179.7 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–1500 m/min | 230.5 | 22.8 | 12.4 | 180.3 |
| PVA/PA6 3:7–2000 m/min | 230.6 | 25.6 | 14 | 181.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Qian, X. Properties and Structure of Thermoplastic Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyamide Sea-Island Fibers. Polymers 2023, 15, 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092071
Song B, Cao Y, Wang L, Shen Y, Qian X. Properties and Structure of Thermoplastic Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyamide Sea-Island Fibers. Polymers. 2023; 15(9):2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092071
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Bing, Yang Cao, Liang Wang, Yake Shen, and Xiaoming Qian. 2023. "Properties and Structure of Thermoplastic Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyamide Sea-Island Fibers" Polymers 15, no. 9: 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092071
APA StyleSong, B., Cao, Y., Wang, L., Shen, Y., & Qian, X. (2023). Properties and Structure of Thermoplastic Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyamide Sea-Island Fibers. Polymers, 15(9), 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092071





