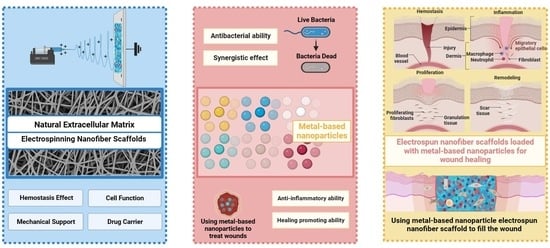
Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds Loaded with Metal-Based Nanoparticles for Wound Healing
Abstract
Share and Cite
Dang, Z.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhao, P. Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds Loaded with Metal-Based Nanoparticles for Wound Healing. Polymers 2024, 16, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010024
Dang Z, Ma X, Yang Z, Wen X, Zhao P. Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds Loaded with Metal-Based Nanoparticles for Wound Healing. Polymers. 2024; 16(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Zheng, Xuemei Ma, Zihao Yang, Xiaohu Wen, and Pengxiang Zhao. 2024. "Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds Loaded with Metal-Based Nanoparticles for Wound Healing" Polymers 16, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010024
APA StyleDang, Z., Ma, X., Yang, Z., Wen, X., & Zhao, P. (2024). Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds Loaded with Metal-Based Nanoparticles for Wound Healing. Polymers, 16(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010024