Biological and Physicochemical Analysis of Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
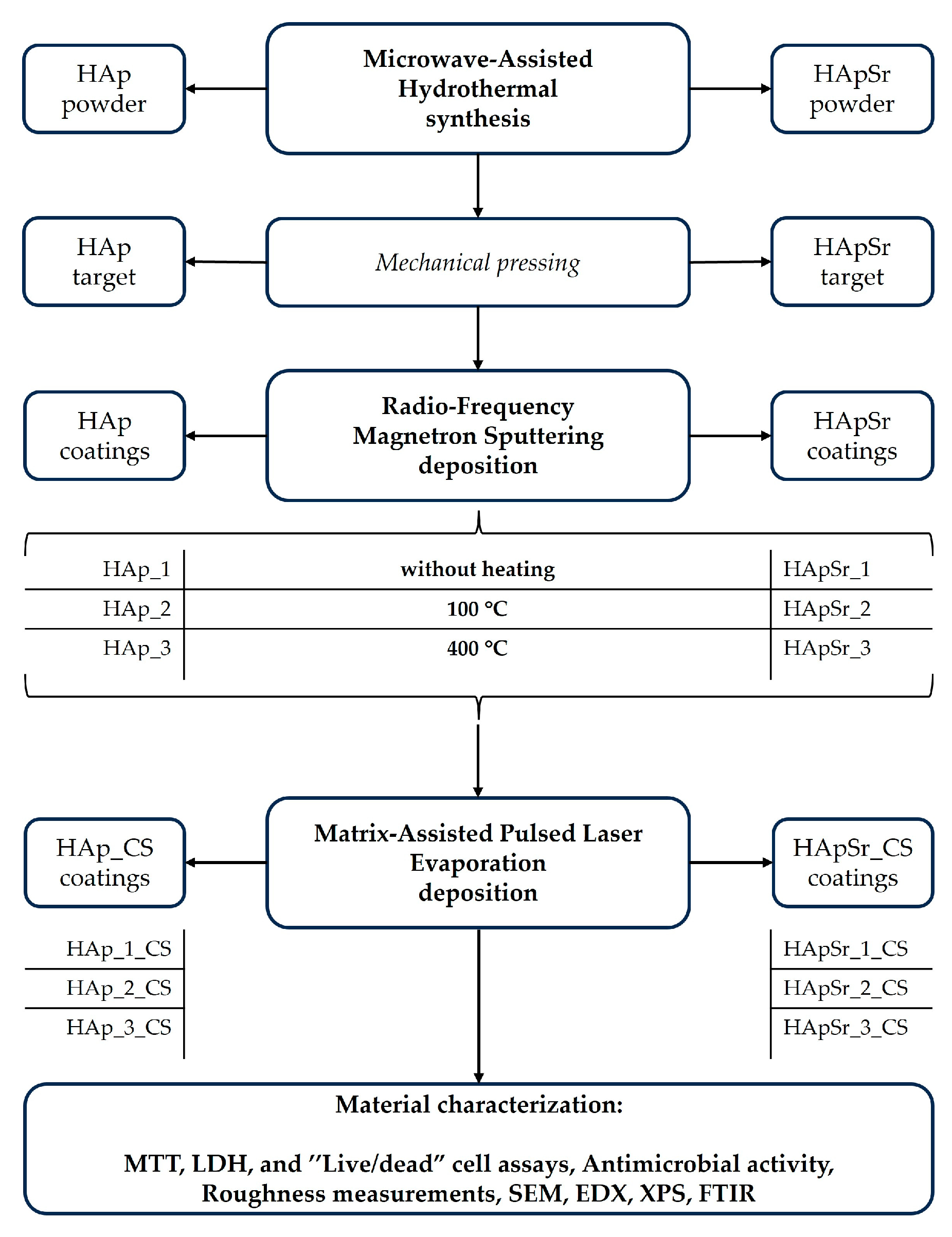
2.2. Synthesis Technique
Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis
2.3. Deposition Techniques
2.3.1. Radio-Frequency Magnetron Sputtering Deposition
2.3.2. Matrix-Assisted Pulsed Laser Evaporation Deposition
2.4. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
3.1. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
3.1.1. Hydroxyapatite and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings
3.1.2. Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Coatings
| XPS Peaks | Binding Energy (eV) | XPS Peak Assignment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAp_1_CS (eV) | HAp_2_CS (eV) | HAp_3_CS (eV) | HApSr_1_CS (eV) | HApSr_2_CS (eV) | HApSr_3_CS (eV) | ||
| Ca 2p1/2 | 350.5 | 350.5 | 350.5 | 350.6 | 350.6 | 350.5 | Ca-Ca; Ca-OH; Ca-O in HAp [20,54] |
| Ca 2p3/2 | 347 | 347 | 347 | 347.1 | 347.1 | 347 | Ca-Ca; Ca-OH; Ca-O in HAp [20,54] |
| O 1s | 532.4 | 532.4 | 532.5 | 532.5 | 532.5 | 532.4 | Polysaccharide [18,59] backbone of chitosan |
| 530.6 | 530.6 | 530.7 | 530.7 | 530.6 | 530.6 | O-Ca in HAp and CaCO3/amide of acetylated functions [20,54]/[59] | |
| C 1s | 288.5 | 288.8 | 288.7 | 288.6 | 288.6 | 288.5 | O-C=O/CO32− [52] |
| 287.4 | 287.6 | 287.5 | 287.5 | 287.4 | 287.4 | N–C=O/C=O [59,60,61]/[52] | |
| 286 | 286 | 286 | 286 | 286 | 286 | C-OH; C-O-C/C-N [52]/[59,60,61] | |
| 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | C-C; C-H [52,57,58] | |
| N1s | 400.4 | 400.5 | 400.5 | 400.6 | 400.6 | 400.7 | C–NH–C=O [63] |
| 399.3 | 399.3 | 399.4 | 399.4 | 399.4 | 399.4 | C-NH2 [63] | |
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
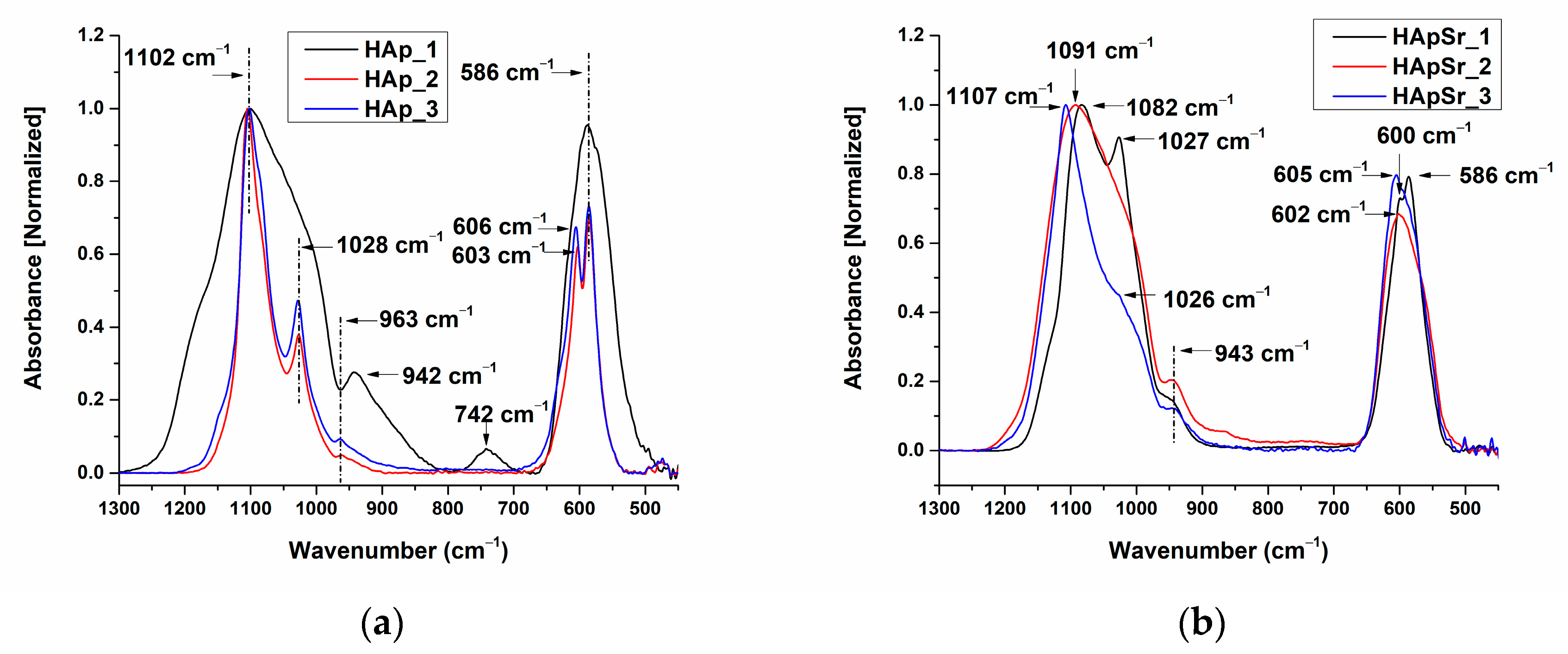
3.2.1. FTIR Spectra of Hydroxyapatite and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Powders
3.2.2. FTIR Spectra of Hydroxyapatite and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings
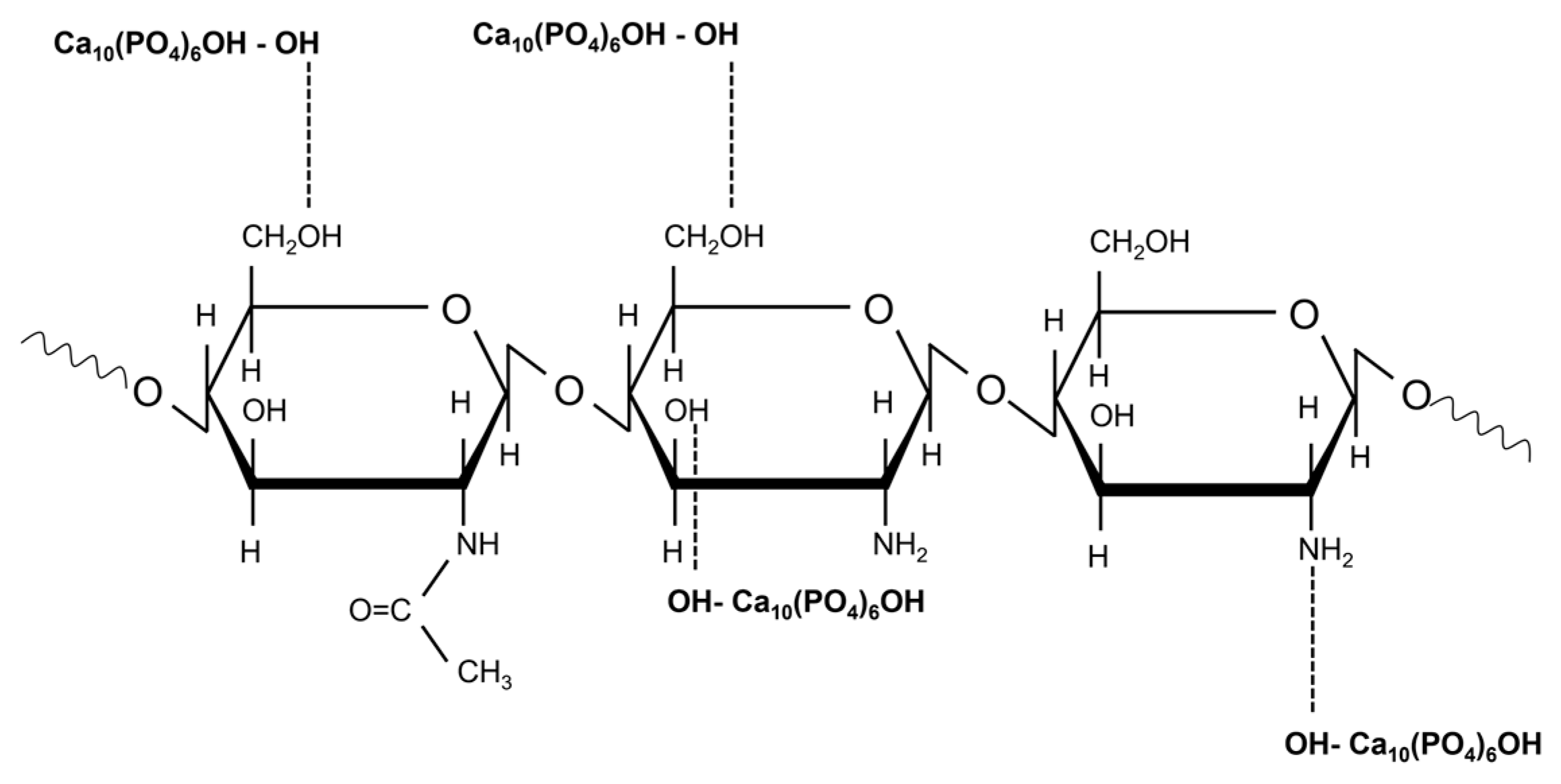
3.2.3. FTIR Spectra of Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Coatings
FTIR Spectra of HAp_CS Samples
FTIR Spectra of HApSr_CS Samples
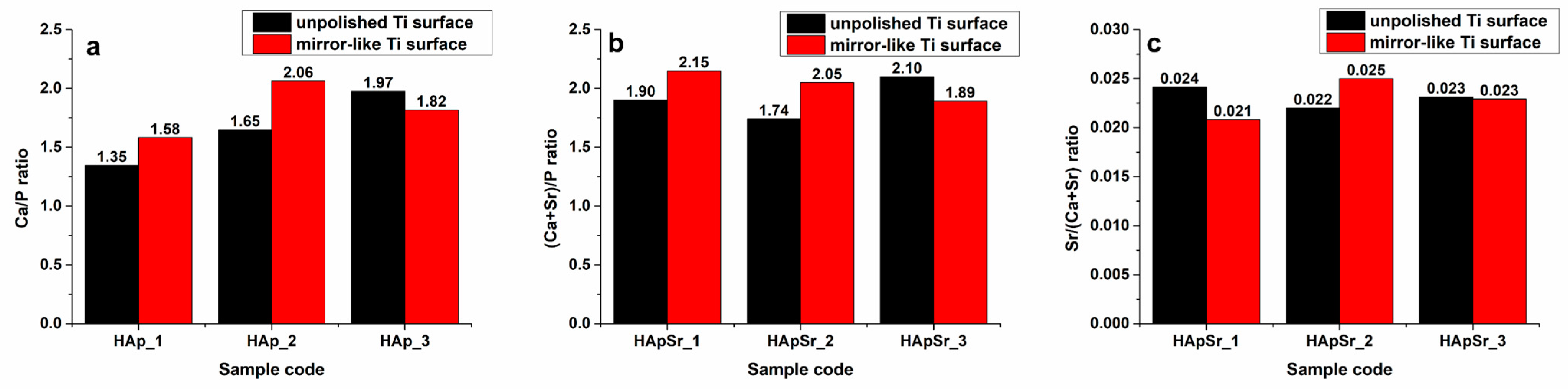
3.3. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
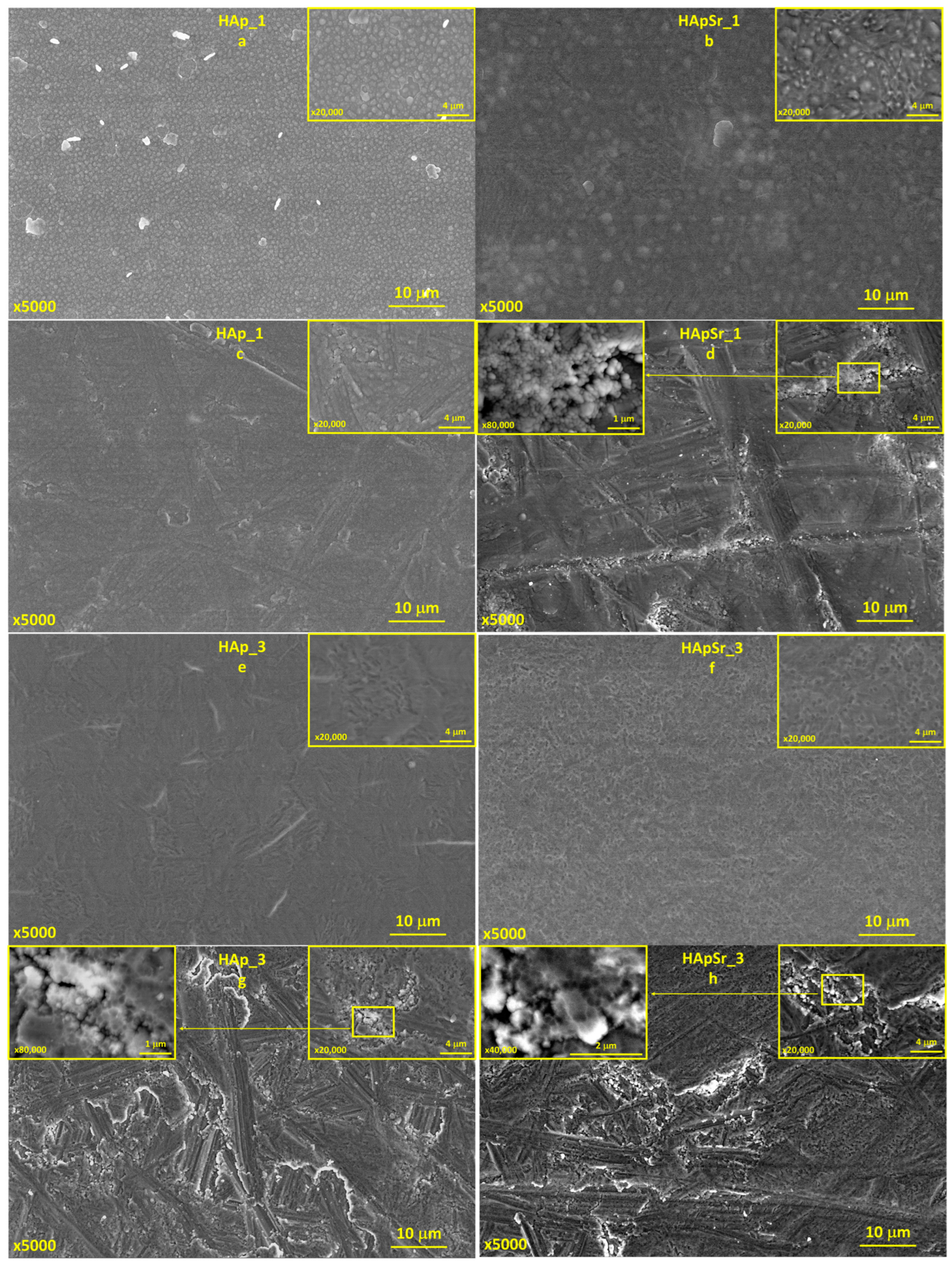
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscpoy
3.4.1. Hydroxyapatite and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings
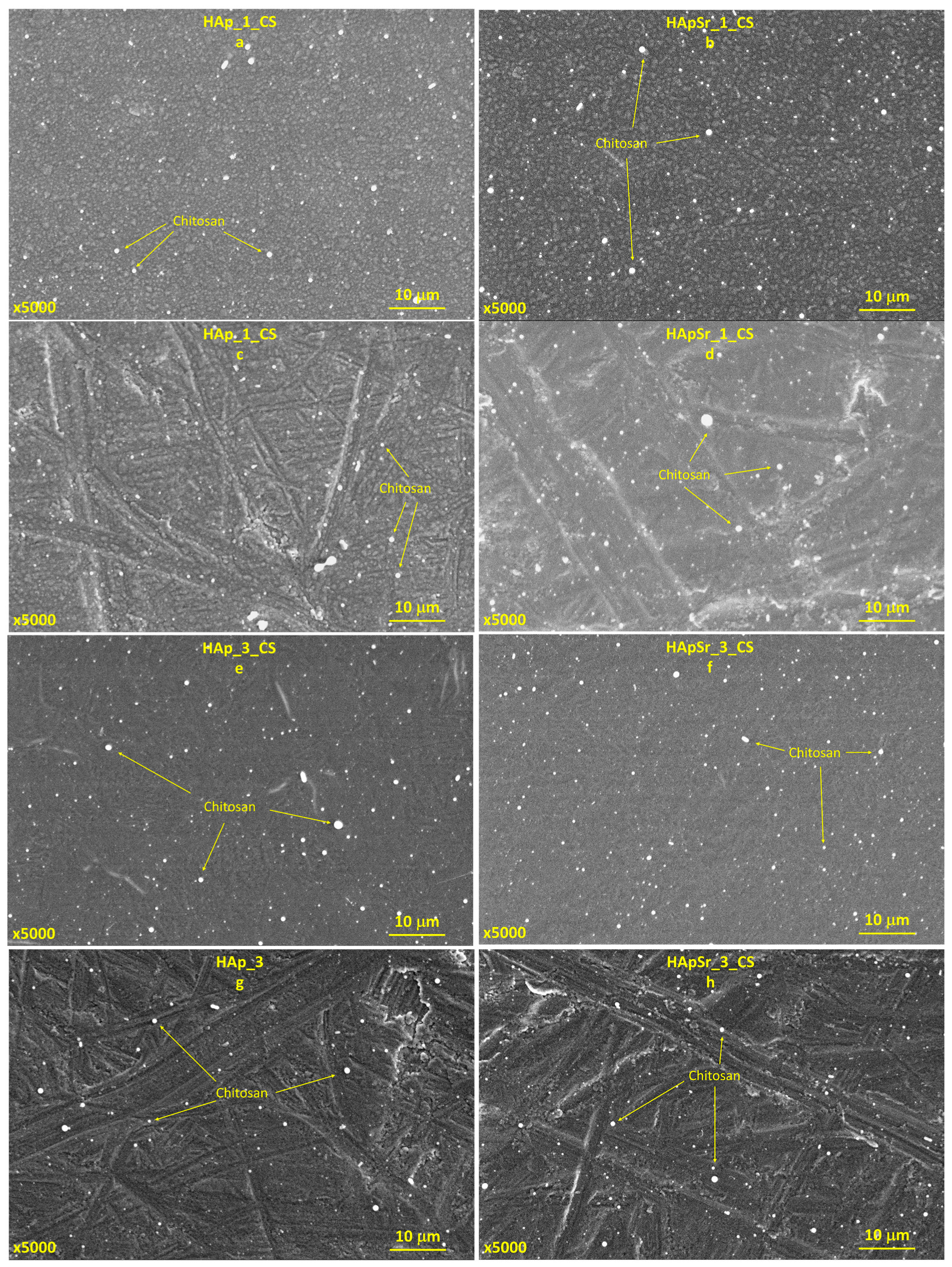
3.4.2. Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Coatings
3.5. Roughness Measurements
3.6. Biological Assays
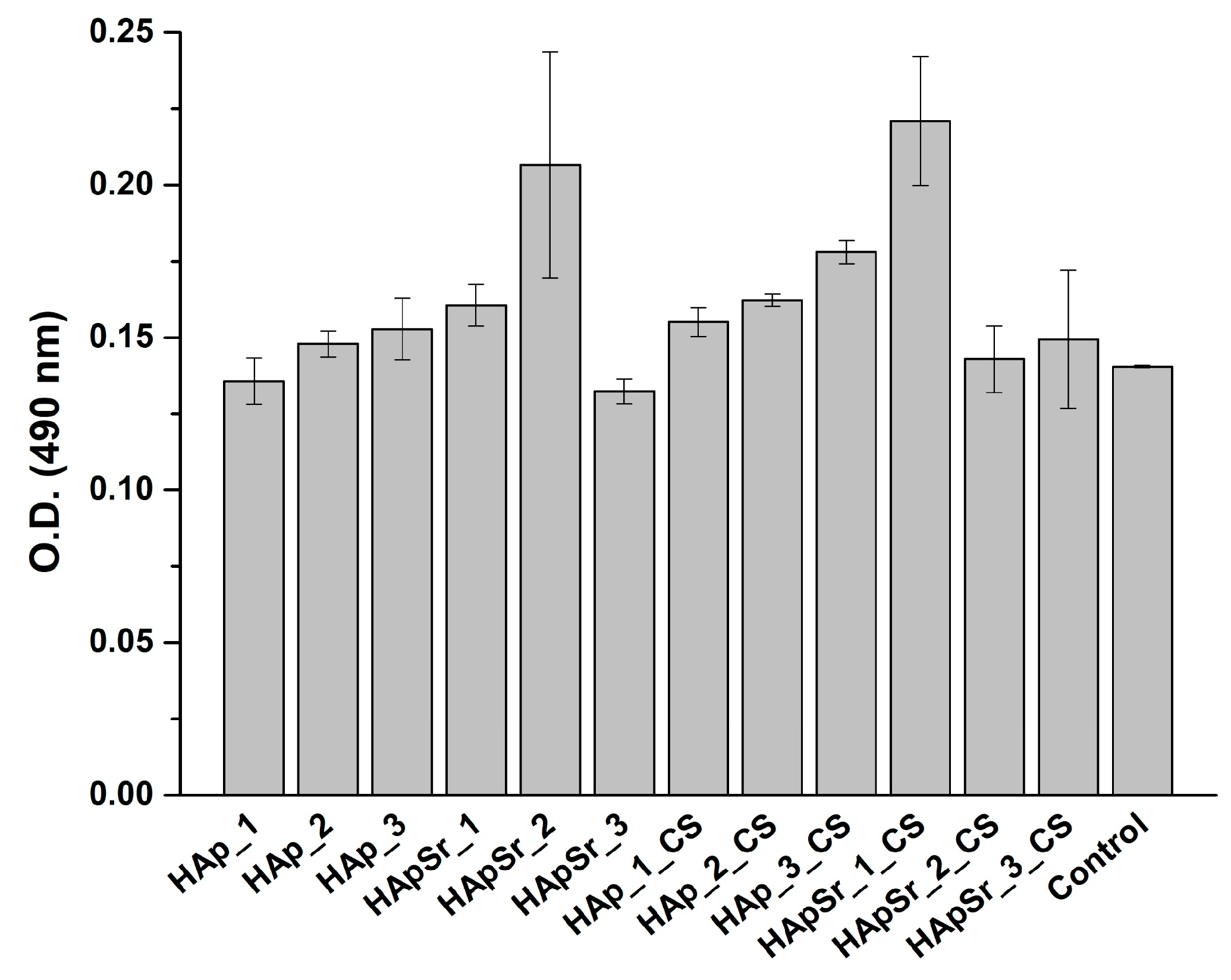
3.6.1. MTT Assay
3.6.2. LDH Assay
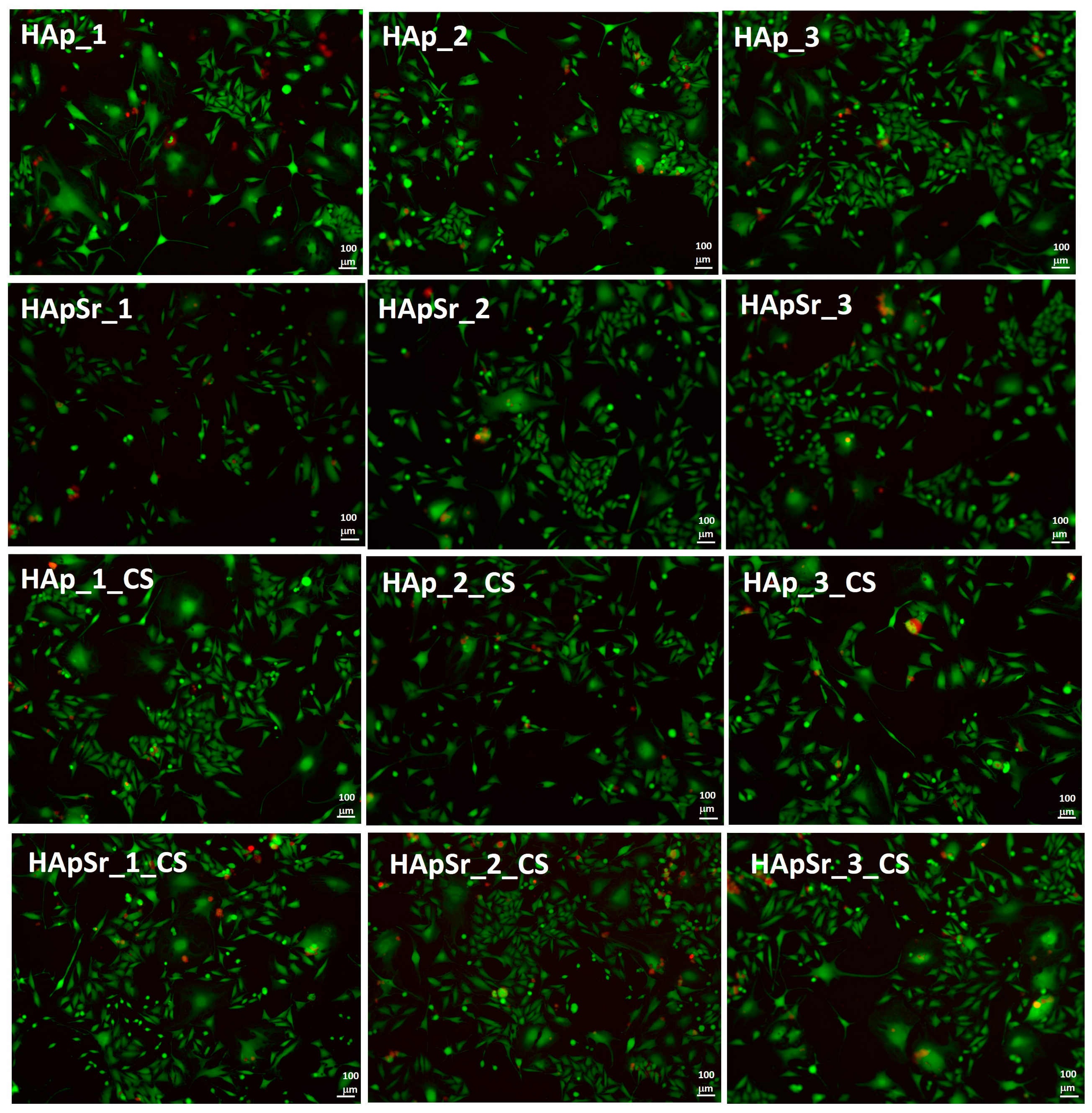
3.6.3. Live/Dead Assay
3.6.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berzina-Cimdina, L.; Borodajenko, N. Research of Calcium Phosphates Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. In Infrared Spectroscopy—Materials Science, Engineering and Technology; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Deng, H.; Liu, X.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y. Double Network Composite Scaffolds Based on Oxidized Dextran/Gelatin Hydrogel and Magnesium Calcium Phosphate Cement. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 677, 132307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monmaturapoj, N.; Uanlee, T.; Nampuksa, K.; Kasiwat, A.; Makornpan, C. Preparation and Properties of Porous Biphasic Calcium Phosphate/Bioactive Glass Composite Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Xie, D.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Z. Sintering Densification Mechanism and Mechanical Properties of the 3D-Printed High-Melting-Point-Difference Magnesium Oxide/Calcium Phosphate Composite Bio-Ceramic Scaffold. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 144, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-J.; Park, S.-S.; Tripathi, G.; Lee, B.-T. Injectable Demineralized Bone Matrix Particles and Their Hydrogel Bone Grafts Loaded with β-Tricalcium Phosphate Powder and Granules: A Comparative Study. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Wojasi’nski, M.W.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kopeckopec, K.; Ciach, T. Controlled Formation of Highly Porous Polylactic Acid-Calcium Phosphate Granules with Defined Structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2022, 144, 213195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshid, S.; Ebrahimian-Hosseinabadi, M.; Rafienia, M. Electrophoretic Deposition of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate/Graphene Nanocomposite Coatings on Ti6Al4V Substrate for Biomedical Applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 892, 162150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Liang, C.; Li, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lian, J.; Ren, L. Double-Layer Calcium Phosphate Sandwiched Siloxane Composite Coating to Enhance Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of Magnesium Alloys for Bone Tissue Engineering. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 177, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furko, M.; Detsch, R.; Tolnai, I.; Balázsi, K.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Balázsi, C. Biomimetic Mineralized Amorphous Carbonated Calcium Phosphate-Polycaprolactone Bioadhesive Composites as Potential Coatings on Implant Materials. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 18565–18576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Valverde, N.; López-Valverde, A.; Aragoneses, J.M.; De Sousa, B.M.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Ramírez, J.M. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of Calcium-Phosphate Coating on the Osseointegration of Titanium Implants. Materials 2021, 14, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniac, I.V. Handbook of Bioceramics and Biocomposites; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9783319124605. [Google Scholar]
- Filip, D.G.; Surdu, V.A.; Paduraru, A.V.; Andronescu, E. Current Development in Biomaterials—Hydroxyapatite and Bioglass for Applications in Biomedical Field: A Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, A.; Žužić, A.; Ivanišević, I.; Kamboj, N.; Ivanković, H. Ionic Substituted Hydroxyapatite for Bone Regeneration Applications: A Review. Open Ceram. 2021, 6, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Strontium Functionalized in Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Prominent Role in Osteoimmunomodulation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 928799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmenev, R.A. A Review of Plasma-Assisted Methods for Calcium Phosphate-Based Coatings Fabrication. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2035–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.O.; Mello, A.; Farina, M.; Rossi, A.M.; Rossi, A.L. Nanoscale Analysis of Calcium Phosphate Films Obtained by RF Magnetron Sputtering during the Initial Stages of Deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 279, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmenev, R.; Vladescu, A.; Surmeneva, M.; Ivanova, A.; Braic, M.; Grubova, I.; Cotrut, C.M. Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputter Deposition as a Tool for Surface Modification of Medical Implants. In Modern Technologies for Creating the Thin-Film Systems and Coatings; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3004-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zarif, M.E.; Yehia-Alexe, S.A.; Bita, B.; Negut, I.; Locovei, C.; Groza, A. Calcium Phosphates–Chitosan Composite Layers Obtained by Combining Radio-Frequency Magnetron Sputtering and Matrix-Assisted Pulsed Laser Evaporation Techniques. Polymers 2022, 14, 5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.Z.; Chen, C.Z.; Yu, H.J.; Zhang, S.J. The Effect of Process Conditions on the Properties of Bioactive Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering. Vacuum 2008, 83, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.O.; Mello, A.; Sendão, H.; Costa, L.T.; Rossi, A.L.; Ospina, R.O.; Borghi, F.F.; Silva Filho, J.G.; Rossi, A.M. Growth of Crystalline Hydroxyapatite Thin Films at Room Temperature by Tuning the Energy of the RF-Magnetron Sputtering Plasma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9435–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.R.; O’Kane, C.; Meenan, B.J. Control of Calcium Phosphate Thin Film Stoichiometry Using Multi-Target Sputter Deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 233, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozelskaya, A.I.; Kulkova, S.E.; Fedotkin, A.Y.; Bolbasov, E.N.; Zhukov, Y.M.; Stipniece, L.; Bakulin, A.V.; Useinov, A.S.; Shesterikov, E.V.; Locs, J.; et al. Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering of Sr- and Mg-Substituted β-Tricalcium Phosphate: Analysis of the Physicochemical Properties and Deposition Rate of Coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 509, 144763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, K.; Hoshino, T.; Aoki, H.; Masuzawa, T. Phase Composition of Sputtered Film from a Mixture Target of Hydroxyapatite and Strontium-Apatite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.; Salma-Ancane, K.; Stipniece, L.; Meenan, B.J.; Boyd, A.R. The Deposition of Strontium and Zinc Co-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, A.R.; Rutledge, L.; Randolph, L.D.; Meenan, B.J. Strontium-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Coatings Deposited via a Co-Deposition Sputter Technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, A.R.; Rutledge, L.; Randolph, L.D.; Mutreja, I.; Meenan, B.J. The Deposition of Strontium-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Ivanova, A.A.; Epple, M.; Pichugin, V.F.; Surmeneva, M.A. Physical Principles of Radio-Frequency Magnetron Sputter Deposition of Calcium-Phosphate-Based Coating with Tailored Properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 413, 127098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pana, I.; Braic, V.; Vladescu, A.; Ion, R.; Parau, A.C.; Zoita, N.C.; Dinu, M.; Kiss, A.E.; Cimpean, A.; Braic, M. SiC- and Ag-SiC-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings Grown Using Magnetron Sputtering on Ti Alloy for Biomedical Application. Coatings 2022, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Victor, R.; da Cunha Santos, A.M.; de Sousa, B.V.; de Araújo Neves, G.; de Lima Santana, L.N.; Menezes, R.R. A Review on Chitosan’s Uses as Biomaterial: Tissue Engineering, Drug Delivery Systems and Cancer Treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K. Chitosan Composites for Bone Tissue Engineering—An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2252–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piqué, A. Deposition of Polymers and Biomaterials Using the Matrix-Assisted Pulsed Laser Evaporation (MAPLE) Process. Pulsed Laser Depos. Thin Film. Appl. Growth Funct. Mater. 2006, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavlu, A.P.; Dinca, V.; Filipescu, M.; Dinescu, M. Matrix-Assisted Pulsed Laser Evaporation of Organic Thin Films: Applications in Biology and Chemical Sensors. In Laser Ablation–From Fundamentals to Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, A.; Antunović, M.; Teruel-Biosca, L.; Ferrer, G.G.; Babić, S.; Urlić, I.; Ivanković, M.; Ivanković, H. Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Substituted Calcium Phosphate/Chitosan Composite Scaffold. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, M.J.L.; dos Santos, B.F.F.; Tavares, A.A.; Maciel, M.A.; de Medeiros Lucena, B.; Fook, M.V.L.; de Silva, S.M.L. The Impact of the Ionic Cross-Linking Mode on the Physical and In Vitro Dexamethasone Release Properties of Chitosan/Hydroxyapatite Beads. Molecules 2019, 24, 4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, Q. Preparation of Chitosan/Nano Hydroxyapatite Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Microspheres for Bone Repair. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Huang, S.W.; Kao, I.F.; Yen, S.K. The Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/Calcium Phosphate Composite Microspheres for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xianmiao, C.; Yubao, L.; Yi, Z.; Li, Z.; Jidong, L.; Huanan, W. Properties and in Vitro Biological Evaluation of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Membranes for Bone Guided Regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.H.; Yao, L.; Xue, R.; Sun, J.; Song, R. In-Situ Mineralization of Chitosan/Calcium Phosphate Composite and the Effect of Solvent on the Structure. Front. Mater. Sci. 2011, 5, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreghici, D.B.; Butoi, B.; Predoi, D.; Iconaru, S.L.; Stoican, O.; Groza, A. Chitosan–Hydroxyapatite Composite Layers Generated in Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering Discharge: From Plasma to Structural and Morphological Analysis of Layers. Polymers 2020, 12, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Mao, M.; Li, J.; Wei, T.; Sun, H. Chitosan/Hydroxyapatite Composite Coatings on Porous Ti6Al4V Titanium Implants: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2020, 50, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, Z.; Kalantar, M.; Soriente, A.; Fasolino, I.; Kharaziha, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Raucci, M.G. In-Situ Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan/Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite Coatings to Improve the Bioactive Properties of Ti6Al4V Substrates. Materials 2020, 13, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xia, X.; Guo, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Wang, H. Biological and Antibacterial Properties of the Micro-Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Coating on Titanium. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanca, C.; Patella, B.; Capuana, E.; Lopresti, F.; Brucato, V.; Carfì Pavia, F.; La Carrubba, V.; Inguanta, R. Behavior of Calcium Phosphate–Chitosan–Collagen Composite Coating on AISI 304 for Orthopedic Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarif, M.E.; Bita, B.; Yehia-Alexe, S.A.; Negut, I.; Groza, A. Spectral Analysis of Strontium-Doped Calcium Phosphate/Chitosan Composite Films. Polymers 2023, 15, 4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, A.; Stan, G.E.; Ristoscu, C.; Popescu-Pelin, G.; Sopronyi, M.; Besleaga, C.; Luculescu, C.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Hussien, M.D.; Marsan, O.; et al. Combinatorial MAPLE Deposition of Antimicrobial Orthopedic Maps Fabricated from Chitosan and Biomimetic Apatite Powders. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadajkar, A.S.; Ahn, C.; Nguyen, K.T.; Zhu, Q.; Komabayashi, T. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Four Vital Pulp Therapy Materials on L929 Fibroblasts. ISRN Dent. 2014, 2014, 191068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, K.; Sabbagh Alvani, A.A. First-Principles Study on Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite as a Biocompatible Filler for Photo-Cured Dental Composites. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 56, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Feki, H.; Savariault, J.M.; Ben Salah, A. Structure Refinements by the Rietveld Method of Partially Substituted Hydroxyapatite: Ca9Na0.5(PO4)4.5(CO3)1.5(OH)2. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 287, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, J.; Dourado, E.R.; Eon, J.G.; Ellis, D.E.; Gonzalez, G.; Rossi, A.M. The Structure of Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassarre, F.; Altomare, A.; Mesto, E.; Lacalamita, M.; Dida, B.; Mele, A.; Bauer, E.M.; Puzone, M.; Tempesta, E.; Capelli, D.; et al. Structural Characterization of Low-Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite Obtained by Solid-State Synthesis. Crystals 2023, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Reference Pages: Spin Orbit Splitting. Available online: https://www.xpsfitting.com/2012/08/spin-orbit-splitting.html (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Biesinger, M.C. Accessing the Robustness of Adventitious Carbon for Charge Referencing (Correction) Purposes in XPS Analysis: Insights from a Multi-User Facility Data Review. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 597, 153681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komai, S.; Hirano, M.; Ohtsu, N. Spectral Analysis of Sr 3d XPS Spectrum in Sr-Containing Hydroxyapatite. Surf. Interface Anal. 2020, 52, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Surmenev, R.A.; Tyurin, A.I.; Mukhametkaliyev, T.M.; Teresov, A.D.; Koval, N.N.; Pirozhkova, T.S.; Shuvarin, I.A.; Oehr, C. Comparative Study of the Radio-Frequency Magnetron Sputter Deposited CaP Films Fabricated onto Acid-Etched or Pulsed Electron Beam-Treated Titanium. Thin Solid Films 2014, 571, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.C.; Borghi, F.F.; Ospina, R.O.; López, E.O.; Borges, F.O.; Mello, A. Nd:YAG (532 Nm) Pulsed Laser Deposition Produces Crystalline Hydroxyapatite Thin Coatings at Room Temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 329, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jian, Y.; Li, R.; Dai, X.; Wu, W.; Zhong, J.; Chen, C. Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Performance Study of Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite Coatings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 270, 124752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V. X-ray Photoelectron and Ion Scattering Spectroscopic Surface Analyses of Amorphous and Crystalline Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles with Different Chemical Histories. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 5531–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Elkhooly, T.; Reicha, F. The Effect of Different Solvents for Chitosan Solubilization on The Crystal Growth of in Situ Prepared Hydroxyapatite. Egypt. J. Phys. 2017, 45, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maachou, H.; Genet, M.J.; Aliouche, D.; Dupont-Gillain, C.C.; Rouxhet, P.G. XPS Analysis of Chitosan-Hydroxyapatite Biomaterials: From Elements to Compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Elgammal, W.E.; Hashem, A.H.; Mohamed, A.E.; Awad, M.A.; Hassan, S.M. Development of a Chitosan Derivative Bearing the Thiadiazole Moiety and Evaluation of Its Antifungal and Larvicidal Efficacy. Polym. Bull. 2023, 81, 1303–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Fouda, A.; Elgammal, W.E.; Eid, A.M.; Elsenety, M.M.; Mohamed, A.E.; Hassan, S.M. New Thiadiazole Modified Chitosan Derivative to Control the Growth of Human Pathogenic Microbes and Cancer Cell Lines. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gengenbach, T.R.; Major, G.H.; Linford, M.R.; Easton, C.D. Practical Guides for X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS): Interpreting the Carbon 1s Spectrum. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 2021, 39, 013204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, P.P.; Feng, H.F.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W.Q. Fabrication of Biocompatible and Mechanically Reinforced Graphene Oxide-Chitosan Nanocomposite Films. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandecandelaere, N.; Rey, C.; Drouet, C. Biomimetic Apatite-Based Biomaterials: On the Critical Impact of Synthesis and Post-Synthesis Parameters. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2593–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.K.; Leoni, M.; Maniglio, D.; Migliaresi, C. Hydroxyapatite Nanorods: Soft-Template Synthesis, Characterization and Preliminary in Vitro Tests. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 28, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-López, J.M.; Iafisco, M.; Rodríguez, I.; Tampieri, A.; Prat, M.; Gómez-Morales, J. Crystallization of Bioinspired Citrate-Functionalized Nanoapatite with Tailored Carbonate Content. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3491–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, Y.; Farlay, D.; Delmas, P.D.; Meunier, P.J.; Boivin, G. Time Sequence of Secondary Mineralization and Microhardness in Cortical and Cancellous Bone from Ewes. Bone 2010, 46, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, C.; Renugopalakrishnan, V.; Collins, B.; Glimcher, M.J. Calcified Tissue International Laboratory Investigations Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Study of the Carbonate Ions in Bone Mineral During Aging. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1991, 49, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Structural Characterisation of Apatite-Like Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Uskoković, V. Visualizing Different Crystalline States during the Infrared Imaging of Calcium Phosphates. Vib. Spectrosc. 2020, 108, 103045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluduma, L. Production and Characterization of Oxyhydroxyapatites. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 762, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Szatkowski, T.; Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Zdarta, J.; Szwarc-Rzepka, K.; Paukszta, D.; Wysokowski, M.; Ehrlich, H.; Jesionowski, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composites. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2015, 51, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pighinelli, L.; Kucharska, M. Chitosan-Hydroxyapatite Composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Evdokimov, K.E.; Pichugin, V.F.; Peitsch, T.; Epple, M. The Influence of the Deposition Parameters on the Properties of an Rf-Magnetron-Deposited Nanostructured Calcium Phosphate Coating and a Possible Growth Mechanism. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2010, 205, 3600–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravathy, P.; Kumar, T.S.S. Bioactivity Enhancement by Sr Doped Zn-Ca-P Coatings on Biomedical Magnesium Alloy. J. Magnes. Alloy 2019, 7, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Huang, W.L.; Hung, T.C.; Wen, T.C. Hydroxyapatite Formation with the Interface of Chitin and Chitosan. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 118, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Hu, C.C.; Tseng, Y.Y.; Sakthivel, R.; Fan, K.S.; Wang, A.N.; Wang, Y.M.; Chung, R.J. Study on Strontium Doped Tricalcium Silicate Synthesized through Sol-Gel Process. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidak, Z.; Marie, P.J. Strontium Signaling: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications in Osteoporosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’ Sullivan, C.; O’ Neill, L.; O’ Leary, N.D.; O’ Gara, J.P.; Crean, A.M.; Ryan, K.B. Osteointegration, Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity of Orthopaedic Titanium Surfaces Coated with Silver and Strontium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Using a Novel Blasting Process. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| XPS Peaks | Binding Energy (eV) | XPS Peak Assignment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAp_1 | HAp_2 | HAp_3 | HApSr_1 | HApSr_2 | HApSr_3 | ||
| Ca 2p1/2 | 350.6 | 350.5 | 350.5 | 350.3 | 350.7 | 350.5 | Ca-Ca; Ca-OH; Ca-O in HAp [20,54,55] |
| 351.5 | 351.4 | 351.2 | 351.1 | 351.3 | 351.2 | Ca-O in a calcium phosphate phase [20] | |
| Ca 2p3/2 | 347.1 | 347 | 347 | 346.8 | 347.2 | 347 | Ca-Ca; Ca-OH; Ca-O in HAp [20,54,55,56] |
| 348 | 347.9 | 347.7 | 347.6 | 347.8 | 347.7 | Ca-O in a calcium phosphate phase [20] | |
| P 2p1/2 | 134 | 133.9 | 133.8 | 133.8 | 134.1 | 133.9 | P-O in PO4 of Hap [20,54,55] |
| P 2p3/2 | 133.2 | 133.1 | 132.9 | 132.9 | 133.3 | 133 | P-O in PO4 of Hap [20,54,55] |
| O 1s | 532.2 | 532.4 | 532.5 | 532.3 | 532.5 | 532.7 | HPO42− [18] |
| 531.3 | 531.5 | 531.3 | 531.1 | 531.3 | 531.3 | O-P, O-H, and O-C in PO43−, OH− and CO32− [20] | |
| 530.7 | 530.8 | 530.7 | 530.5 | 530.6 | 530.6 | O-Ca in Hap and CaCO3 [20,54] | |
| C 1s | 288.6 | 288.4 | 288.5 | 288.5 | 288.6 | 288.4 | O-C=O/CO32− [52] |
| 287.4 | 287.4 | 287.4 | 287.4 | 287.4 | 287.4 | C=O [52] | |
| 286 | 286 | 286 | 286 | 286.1 | 286.1 | C-OH/C-O-C [52] | |
| 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | 284.6 | C-C/C-H [52,57,58] | |
| Sample Code | Ra (nm) Optically Polished/Unpolished |
|---|---|
| HApSr_1 | 27/541 |
| HApSr_2 | 32/360 |
| HApSr_3 | 47/384 |
| HApSr_1_CS | 27/381 |
| HApSr_2_CS | 38/403 |
| HApSr_3_CS | 49/376 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarif, M.E.; Bita, B.; Yehia-Alexe, S.A.; Negut, I.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Andronescu, E.; Groza, A. Biological and Physicochemical Analysis of Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite Layers. Polymers 2024, 16, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131922
Zarif ME, Bita B, Yehia-Alexe SA, Negut I, Gradisteanu Pircalabioru G, Andronescu E, Groza A. Biological and Physicochemical Analysis of Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite Layers. Polymers. 2024; 16(13):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131922
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarif, Maria Elena, Bogdan Bita, Sasa Alexandra Yehia-Alexe, Irina Negut, Gratiela Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, Ecaterina Andronescu, and Andreea Groza. 2024. "Biological and Physicochemical Analysis of Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite Layers" Polymers 16, no. 13: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131922
APA StyleZarif, M. E., Bita, B., Yehia-Alexe, S. A., Negut, I., Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G., Andronescu, E., & Groza, A. (2024). Biological and Physicochemical Analysis of Sr-Doped Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite Layers. Polymers, 16(13), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131922










